Exhibition dates: 18th May – 2nd September 2012
Curator: Pauline Vermare, ICP Curatorial Assistant
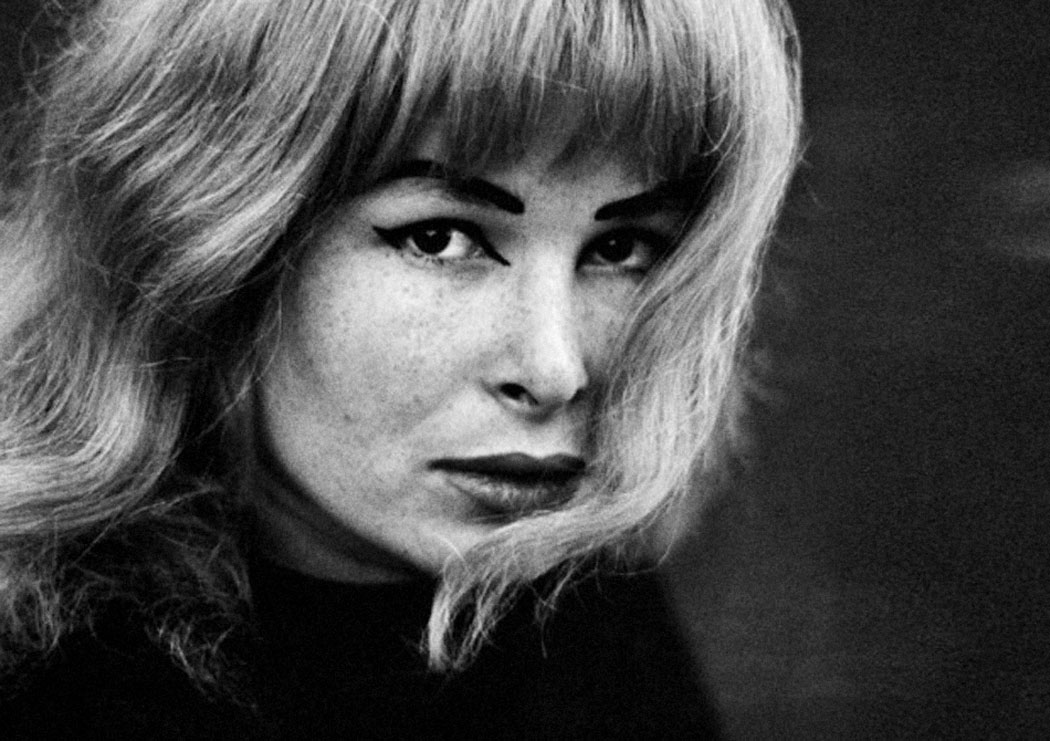
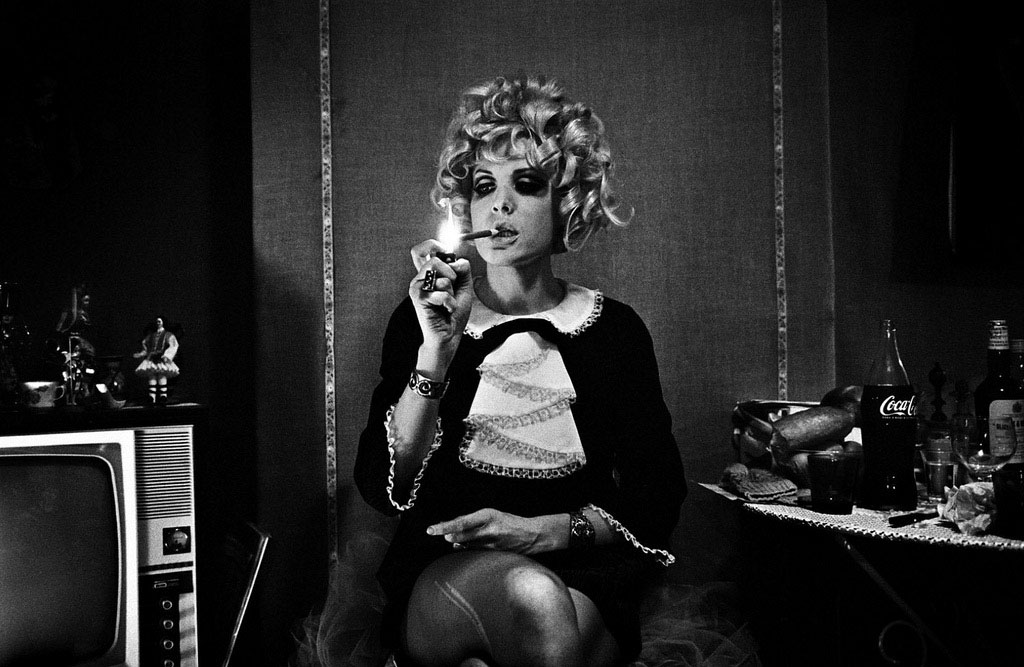
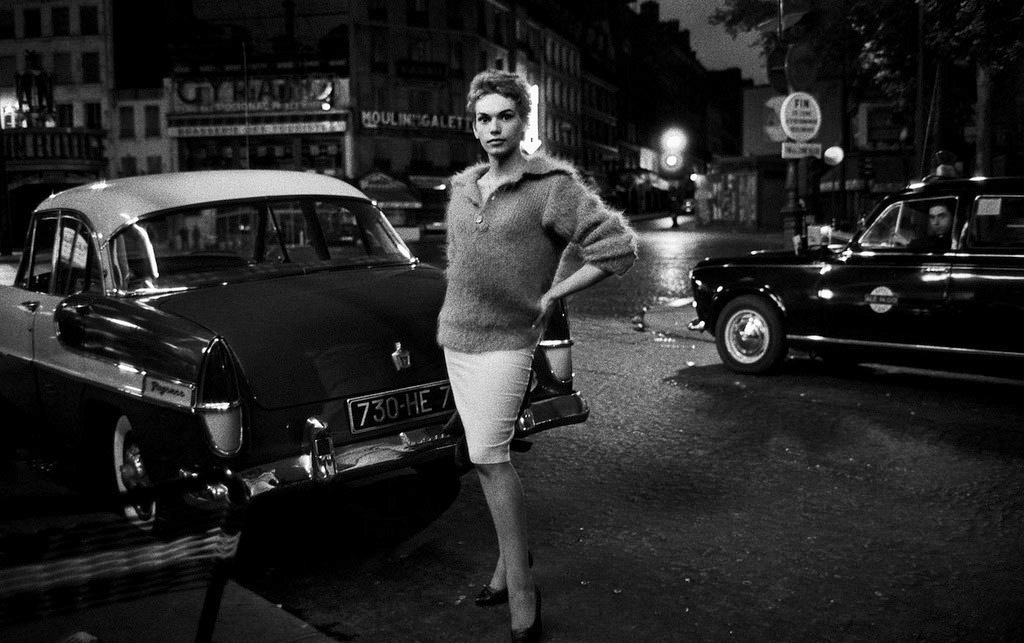
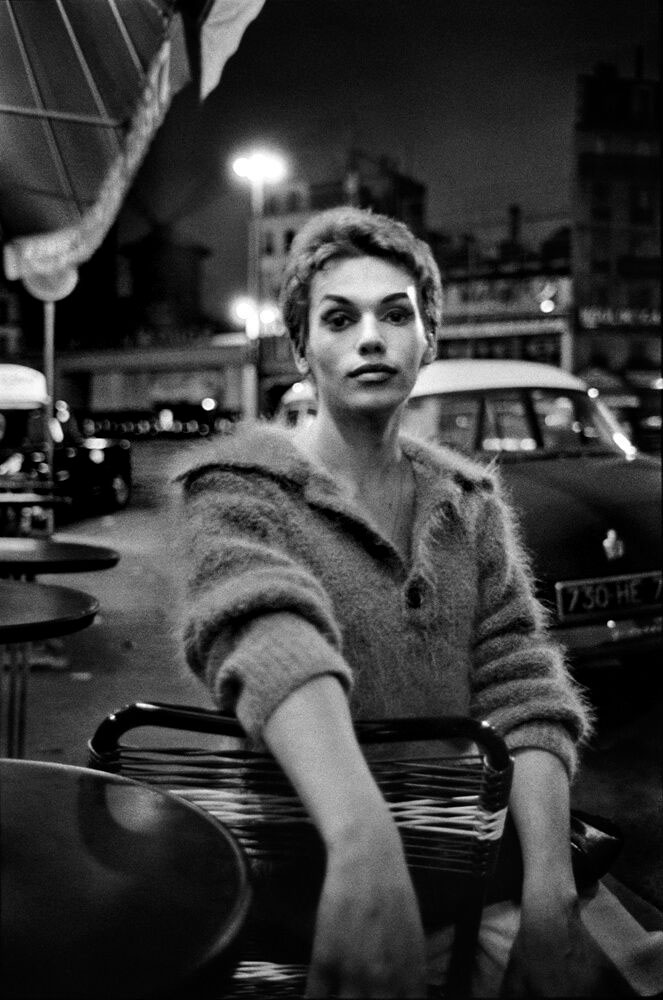
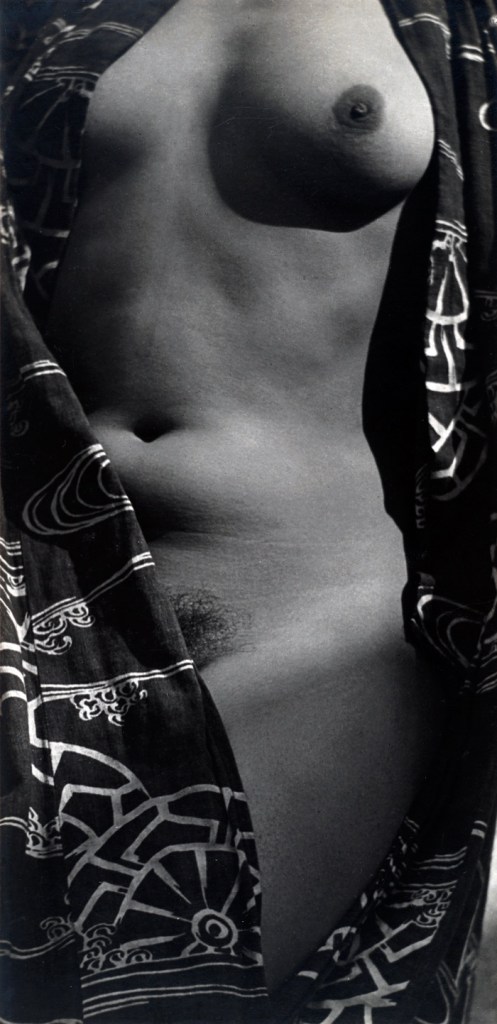
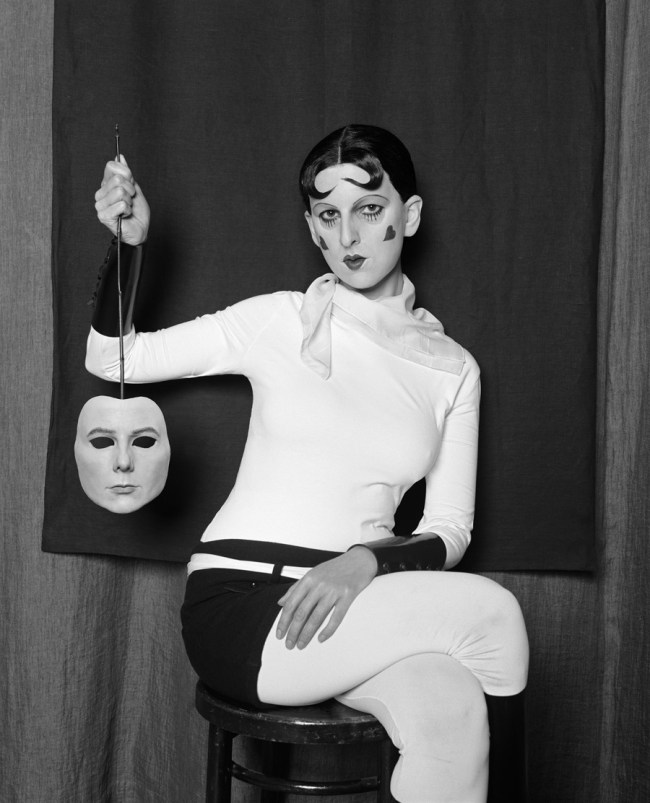
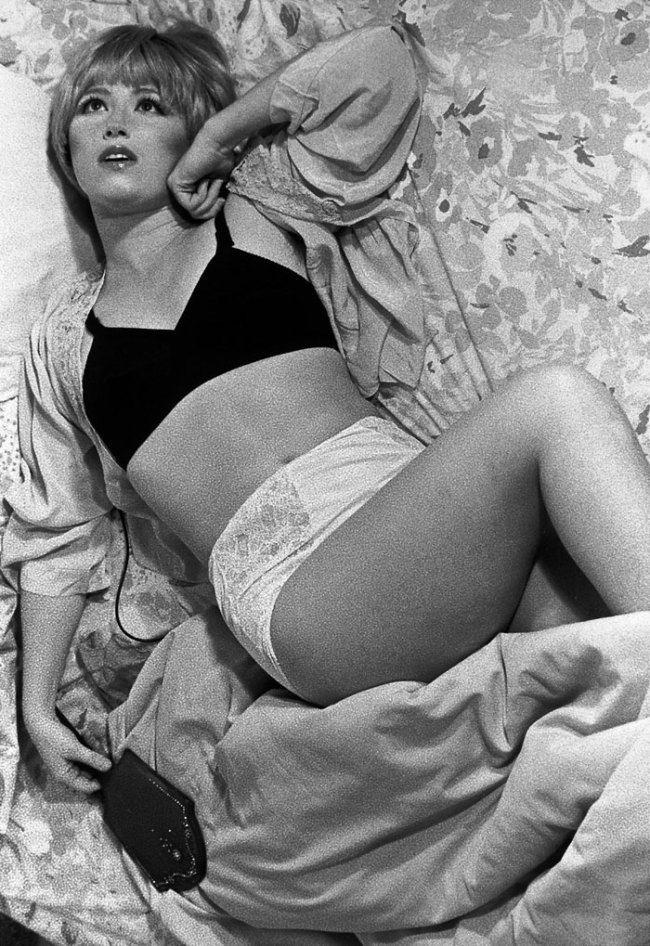
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
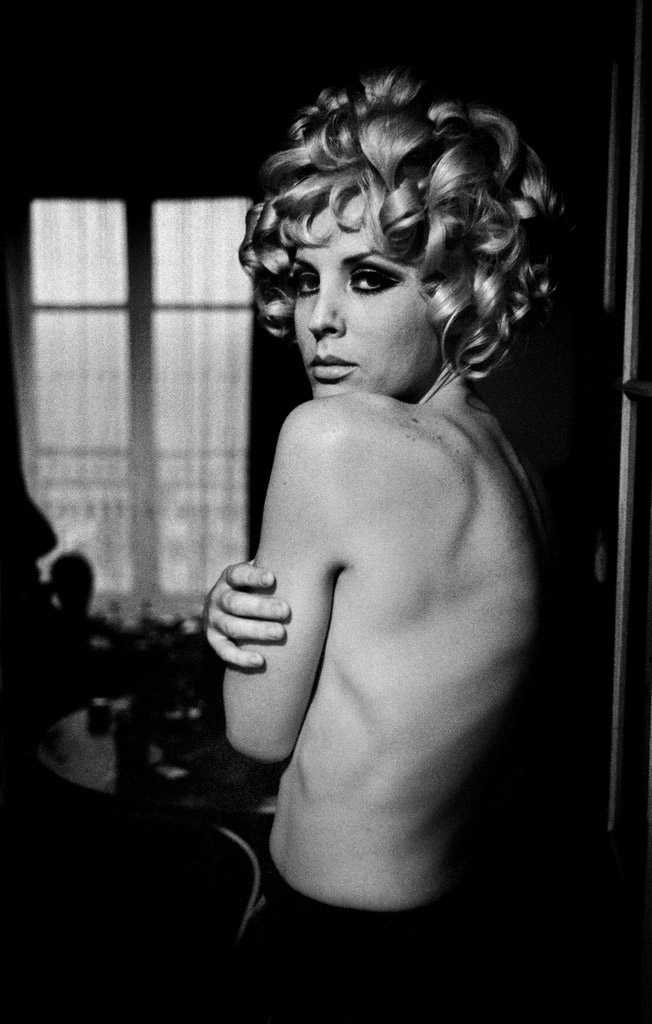
Pepita
1963
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
I am myself
These are stunning photographs; they glow with an inner light and energy. With perfect composition and use of chiaroscuro the artist let’s the women speak for themselves – confident, self assured and happy in the life they are leading. Having come out as a gay man myself in 1975, six short years after the Stonewall Riots in New York, I can attest to how difficult and how much prejudice there was against gay men in the early 1970s. Imagine then, being a transexual living in Paris in the early to mid 1960s and the issues that these woman had to deal with.
And yet there is a joyous quality to these photographs, an intimate relationship between people (not just artist and subject), a sense of fondness, friendship and fraternity. There is an intimacy here that transcends documentation. The last photograph in the posting (Gina, 1963, below) is just this wonderful, happy photograph where you just can’t help smiling yourself. There is a lightness here that is at variance with Brassai’s heavy set Parisian nights, that is more sensitive to the subject than Diane Arbus’ thrusting camera and her depiction of transexuals.
As good as the quote by Strömholm is (below), it is not just the freedom to choose one’s own life and identity, it is the ability to make that choice an informed choice, where you can select from a variety of things, where your preference indicates that your choice is based on one’s values or predilections. Without being informed the decision you may make is not free; if you are uninformed you may be unaware. An informed choice is based upon a clear appreciation and understanding of the facts, implications, and future consequences of any action.
Despite the prejudice and pain these woman would have suffered living an everyday life in the 1960s they have made an informed choice. These are strong, courageous woman and their friend has captured their resolve beautifully.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the International Centre of Photography for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“It was then – and still is – about obtaining the freedom to choose one’s own life and identity.”
“It was because I didn’t understand it myself… as soon as you ask yourself why their lives are the way they are, it becomes difficult not to take pictures.”
“This is a book [Les Amies de Place Blanche] about insecurity. A portrayal of those living a different life in the big city of Paris, of people who endured the roughness of the streets. … This is a book about the quest for self-identity, about the right to live, about the right to own and control one’s own body.”
Christer Strömholm
Christer Strömholm: Les Amies de Place Blanche @ ICP
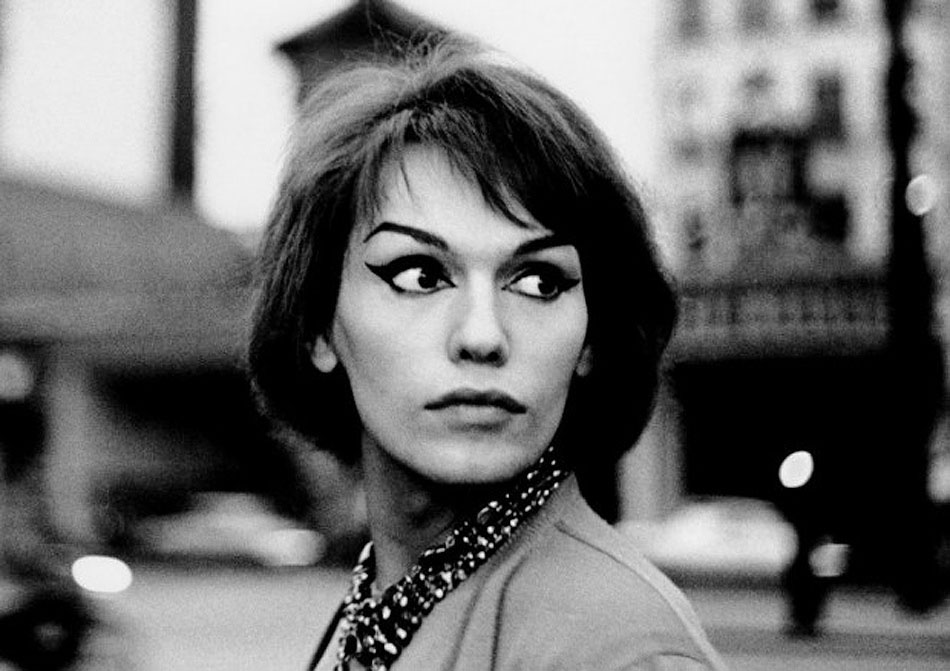
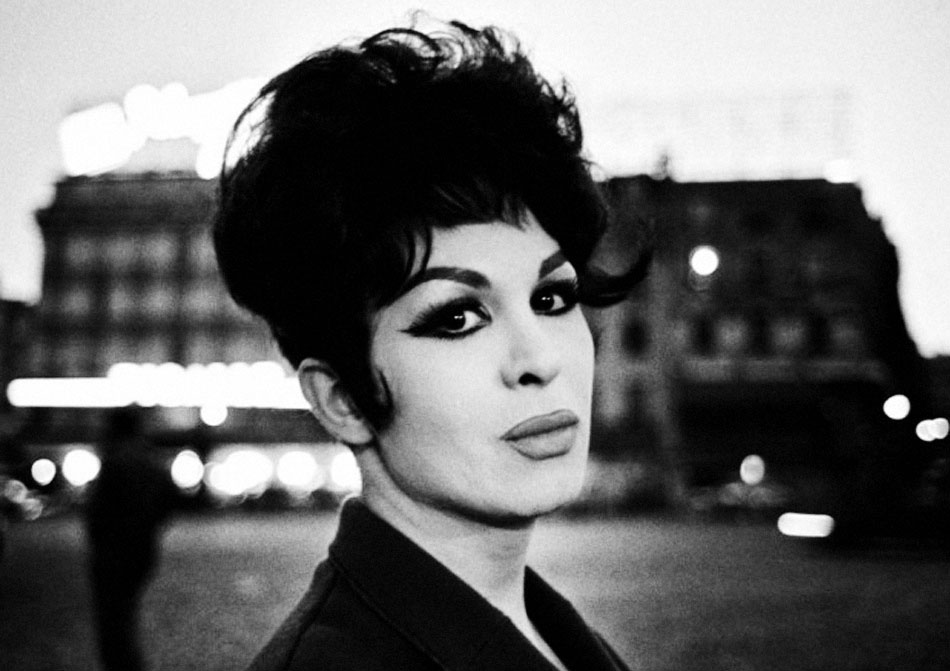
Christer Strömholm (1918-2002) was one of the great photographers of the 20th century, but he is little known outside of his native Sweden. This exhibition presents his most powerful and acclaimed body of work: Les Amies de Place Blanche, a documentation of transsexual “ladies of the night” in Paris in the 1960s. Arriving in Paris in the late 1950s, Strömholm settled in Place Blanche in the heart of the city’s red-light district. There, he befriended and photographed young transsexuals struggling to live as women and to raise money for sex-change operations. Strömholm’s surprisingly intimate portraits and lush Brassaï-like night scenes form a magnificent, dark, and at times quite moving photo album, a vibrant tribute to these girls, the “girlfriends of Place Blanche.” The photographs were first published in Sweden in 1983, and the book quickly sold out, becoming a cult classic; it is being reissued in French and English this year. Strömholm’s photo-essay raises profound issues about sexuality and gender; as he wrote in 1983, “It was then – and still is – about obtaining the freedom to choose one’s own life and identity.” This exhibition, the first presentation of Strömholm’s work in an American museum, is organised by ICP Curatorial Assistant Pauline Vermare
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
At a fun fair, Paris
1954-1955
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
“Lady Leopard” at a fair, Paris
1954-1955
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
“Little Christer”
1955
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Nana, Paris
1959
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Nana, Paris
1959
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Jacky
1959
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Agnès Caprice
1960s
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Agnès Caprice, showgirl of trans cabaret Le Carrousel and frequent subject of photo series Les Amies de La Place Blanche. She later partnered and had a child with an actress and performer of a butch lesbian cabaret. Caprice would pass at a young age due to addiction, after the devastating loss of 7 of her fellow Le Carrousel performers in a 1966 plane crash.
Text from the Genderoutlaws website
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Cobra and Caprice
1961
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Nana
1963
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Carmen, Pigalle, Paris
1962
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Belinda
1967
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Sabrina
1967
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Suzannah, Hôtel Pierrots
1962
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Soraya and Sonia
1962
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Jacky
1961
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Themis
1963
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Giulia and Carol
1964
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Giulia and Carol, Pigalle, Paris
1964
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Sabrina
1967
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Narcissus
1968
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
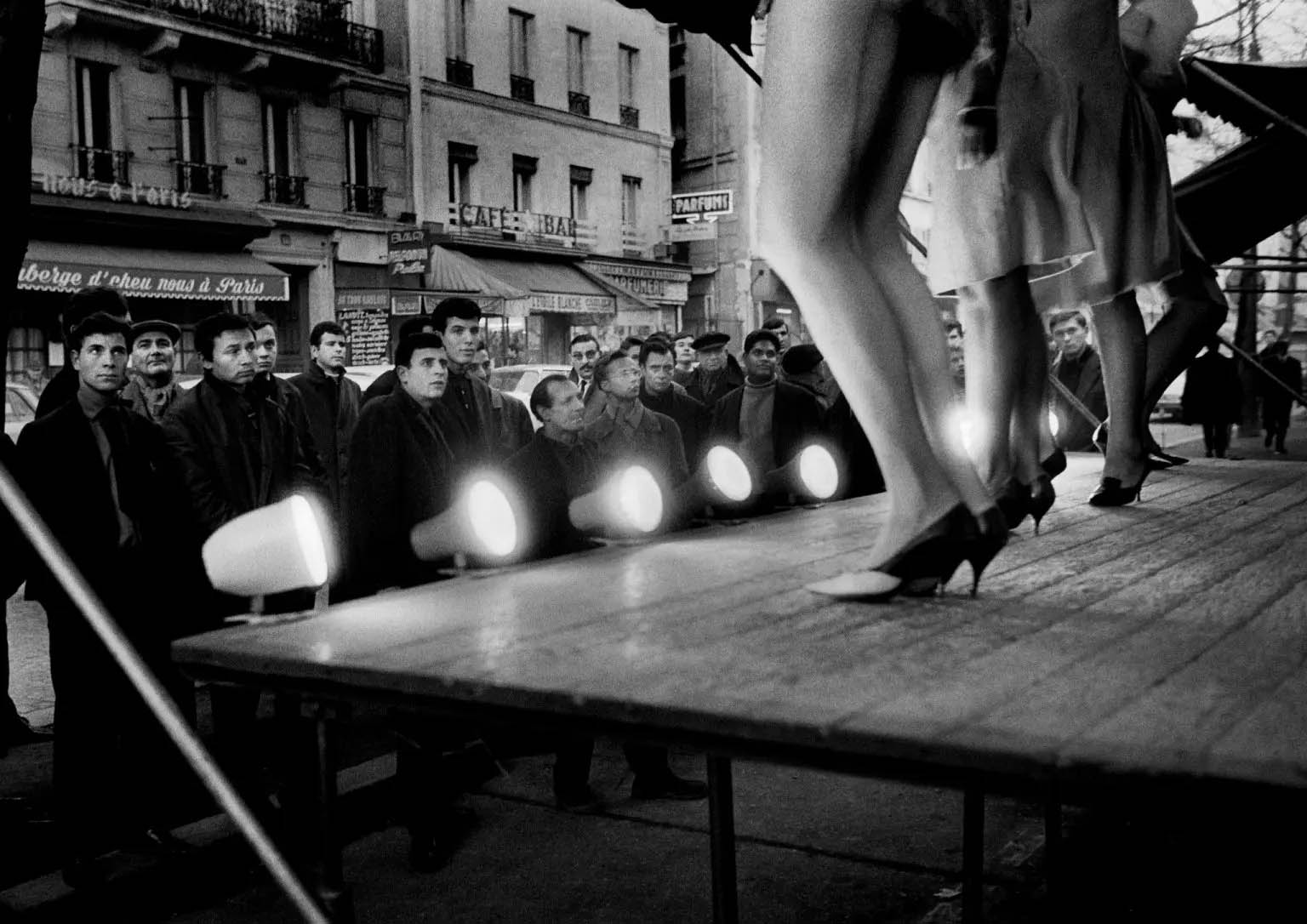
Raising profound issues about identity, sexuality, and gender, Christer Strömholm: Les Amies de Place Blanche, on view at the International Center of Photography (1133 Avenue of the Americas at 43rd Street) May 18 – September 2, 2012, presents 40 photographs, historical publications, and ephemera documenting young transgender males in the heart of Paris’ red-light district in the 1960s.
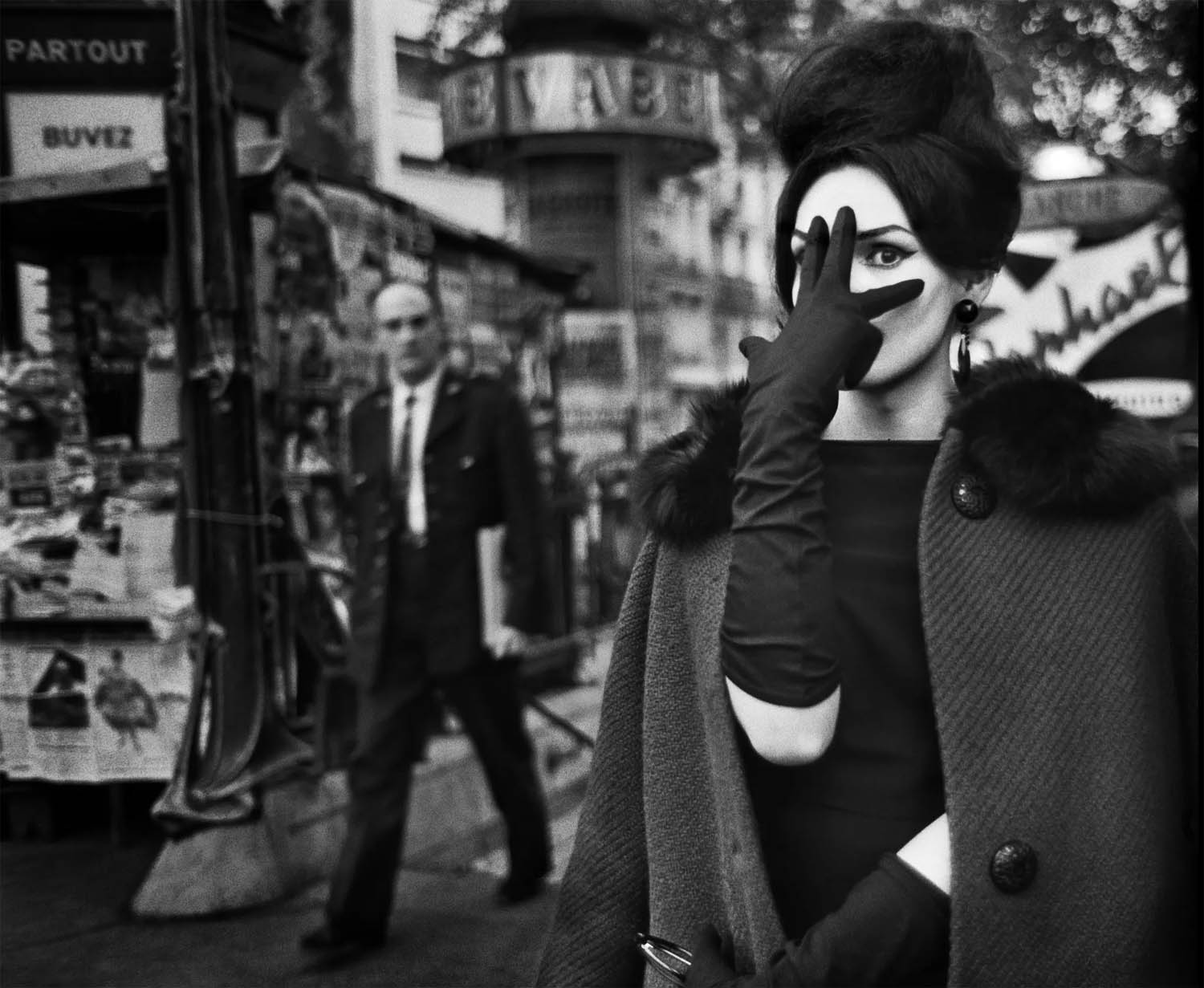
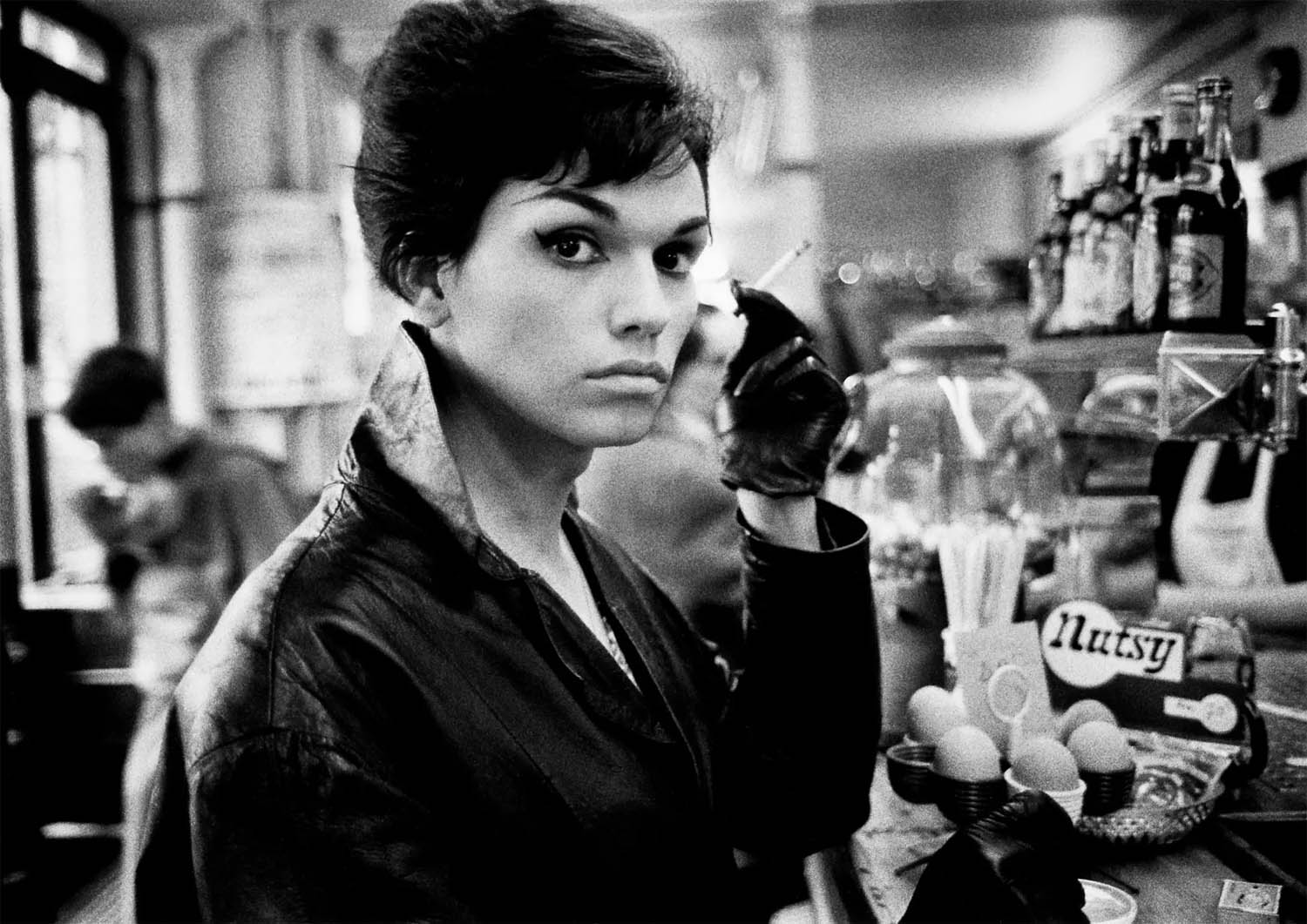
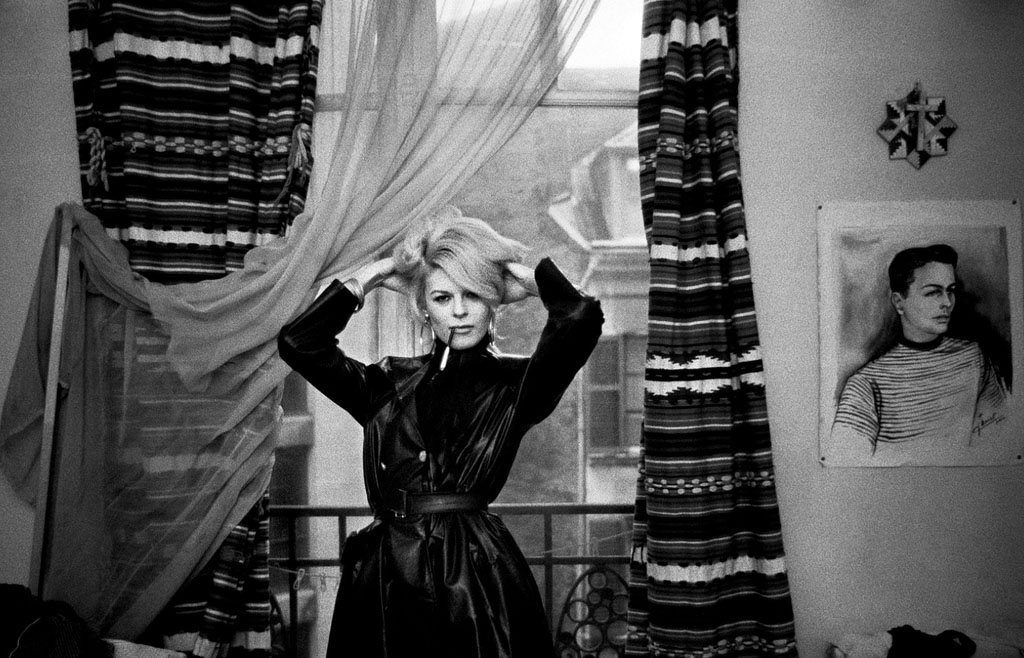
Arriving in Paris in the late 1950s, Christer Strömholm (Stockholm, 1918-2002) settled in Place Blanche, home of the famous Moulin Rouge. There, he befriended and photographed young transsexuals – “ladies of the night” – struggling to live as women and to raise money for sex-change operations. In General Charles de Gaulle’s ultra-conservative France, transvestites were outlaws, regularly abused and arrested by the police for being “men dressed as women outside the period of carnival.” Some of these women had tragic fates. Others, like “Nana” and “Jacky,” eventually fulfilled their destiny and led happy lives as women. Living alongside them for 10 years, Strömholm photographed his subjects in their hotel rooms, in bars, and in the streets of Paris.
“These intimate portraits and Brassaï-like lush night scenes form a magnificent, dark, and moving photo album, a vibrant tribute to these girls,” said ICP Curatorial Assistant Pauline Vermare, who organised the exhibition. These photographs were first published in Sweden in 1983, and the book Vännerna från Place Blanche (“The Girlfriends of Place Blanche”) – which will be reissued this year in French and English – quickly sold out, becoming a cult classic and solidifying Strömholm as one of the great photographers of the 20th century. The work for this exhibition is provided by the Strömholm Estate in Stockholm, the Marvelli Gallery in New York, and from the collection of Alice Zimet.
As Strömholm wrote in 1983: “These are images of people whose lives I shared and whom I think I understood. These are images of women – biologically born as men – that we call ‘transsexuals.’ As for me, I call them ‘my friends of Place Blanche.’ It was then – and still is – about obtaining the freedom to choose one’s own life and identity.”
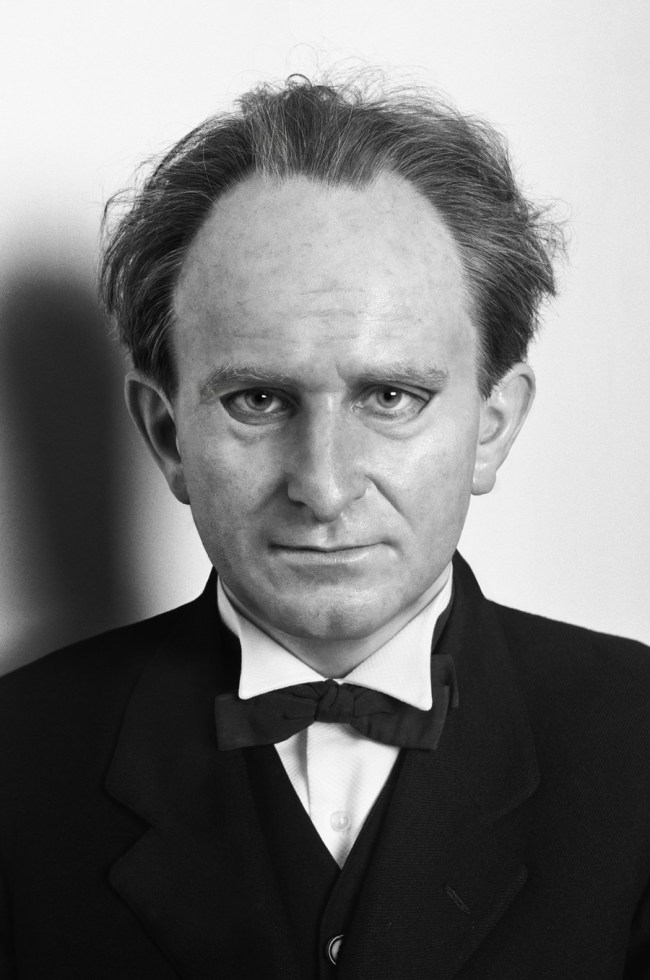
Christer Strömholm is a lesser known artist, but may well be the father figure of Scandinavian photography. A prominent artist and winner of the prestigious Hasselblad Award in 1997, he was also an influential teacher and the mentor to some of today’s leading Swedish photographers including J.H. Engström, Anders Petersen, and Lars Tunbjörk. Highly revered in his native Sweden since the 1980s, he is still little known outside of Europe. This exhibition is the first presentation of Strömholm’s work in an American museum, and features his most powerful and acclaimed body of work.
Press release from the International Centre of Photography website
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Nana with cars
1959
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Nana
1959
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Nana
1959
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Gina and Nana
1960
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Carole and Nana
1960
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
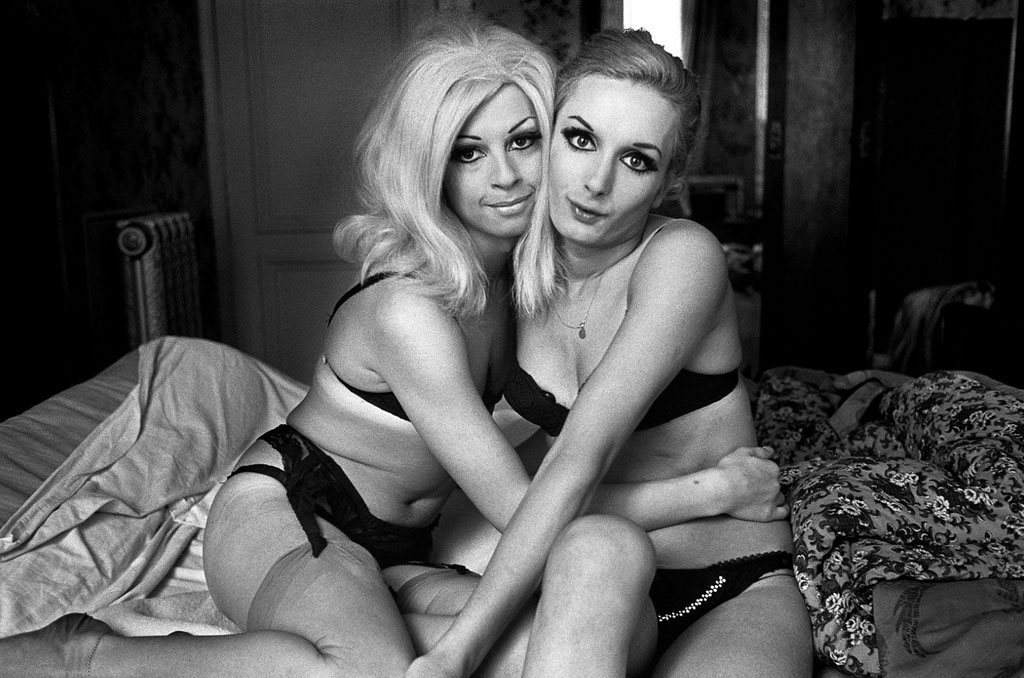
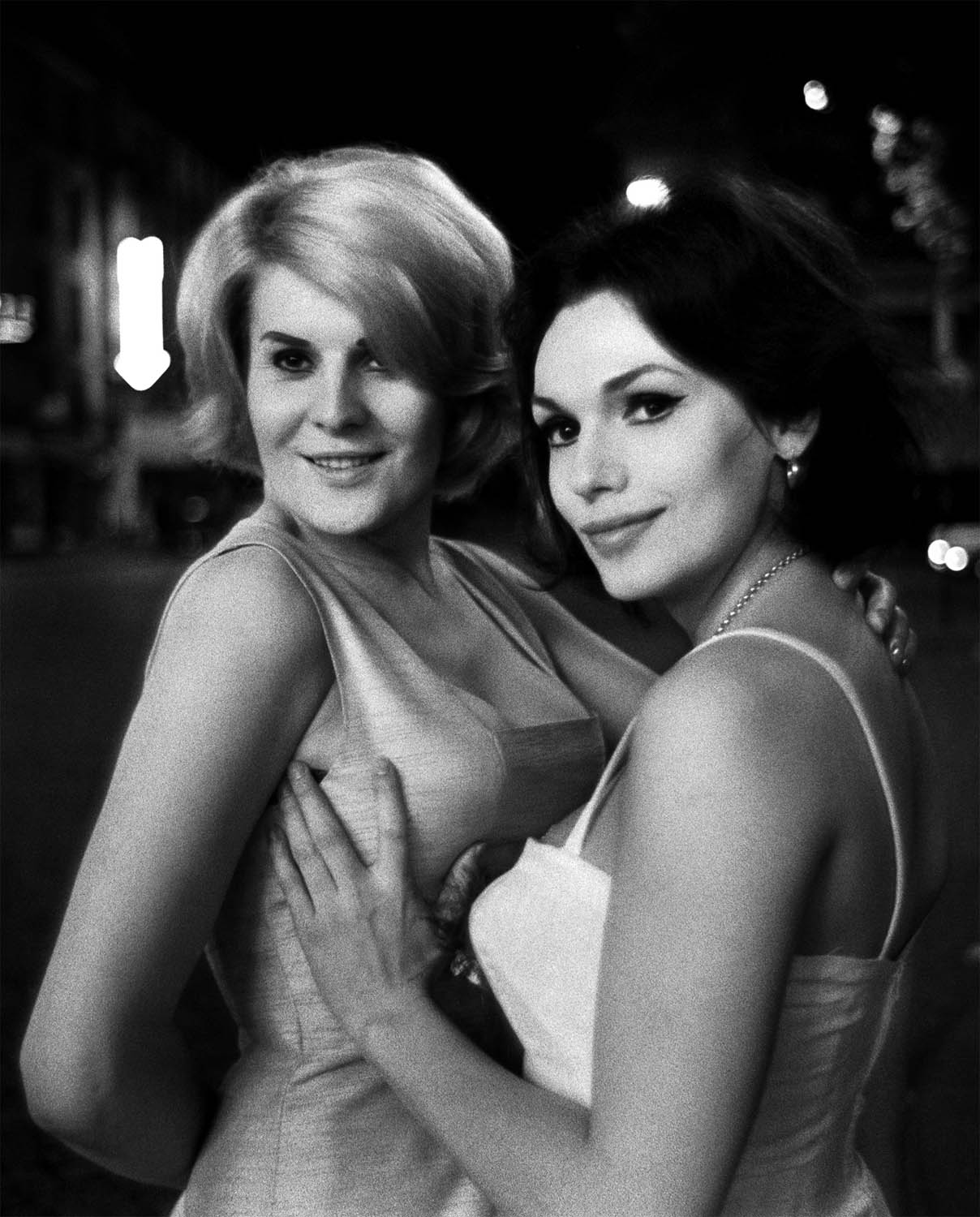
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Suzannah and Sylvia
1962
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Suzannah and Sylvia
1962
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
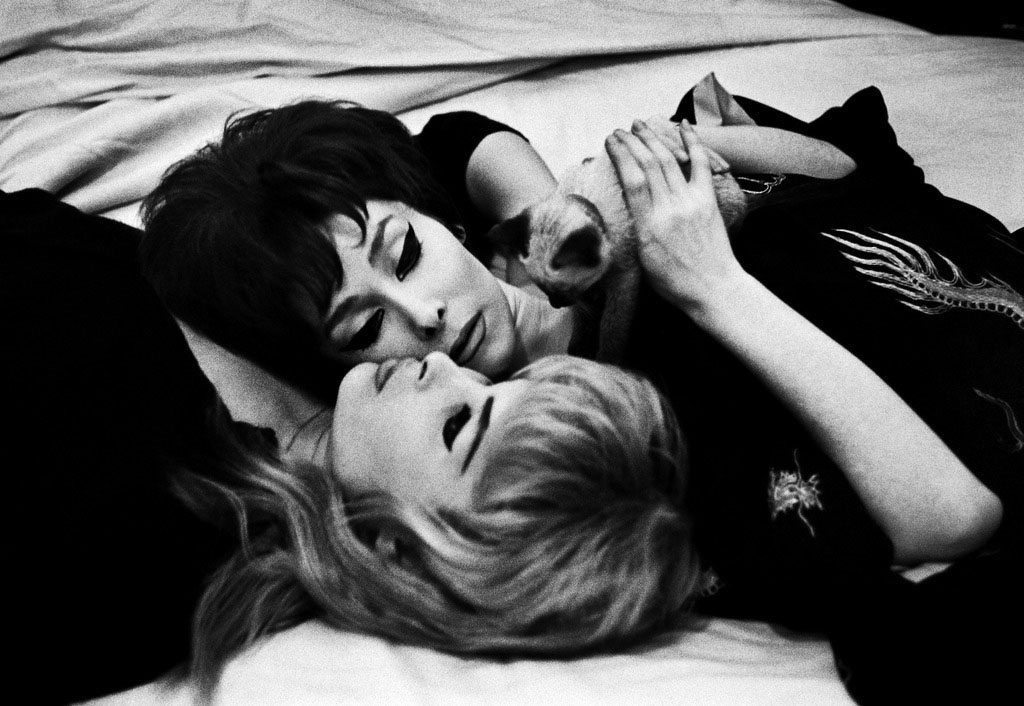
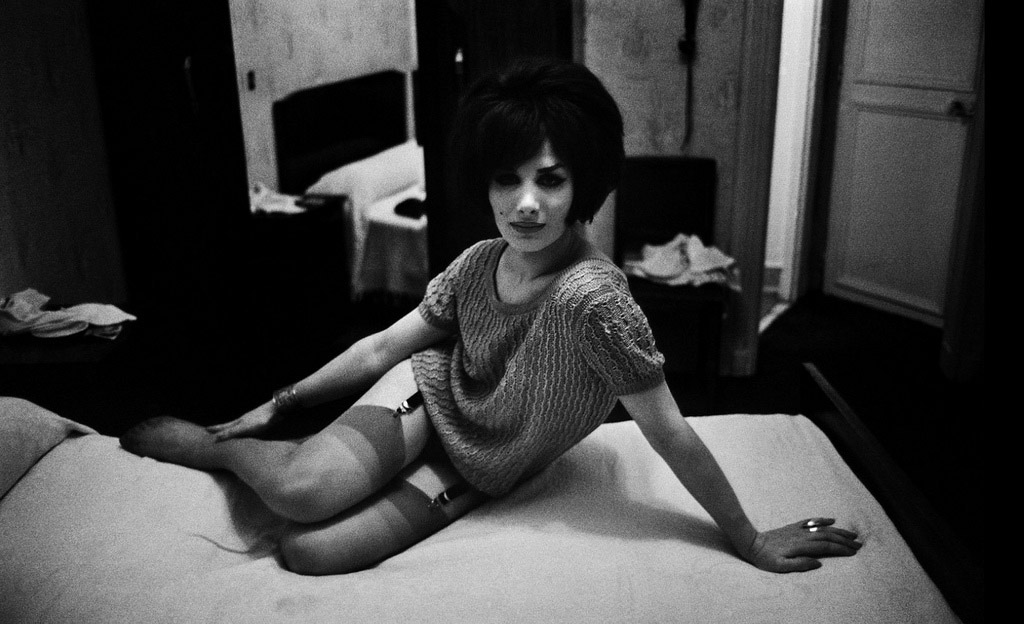
Under the strict Catholic social regime of Charles de Gaulle, transsexuals in Paris at this time were forced to confine their identities to within their hotel rooms, fearing the brutality of the police and imprisonment. Against this political backdrop Strömholm delved into the harsh world of sex work; Strömholm pervades this intimate and world of prostitution and deconstructs the division between private and public. The image of Susannah and Mimosa pictured below provides an insight into their private lives; the playful depiction of the women contrasts heavily with our contextual understanding of the photograph, of the hard life transsexuals endured in Paris. Strömholm reveals a dynamic sense of sorority between Suzanne and Mimosa in this portrait, personal interactions emerge which portrays the women as vibrant characters, a contrast against the grim reality of prostitution in Paris. Strömholm reveals a close bond between the women which goes beyond simplistic definitions of the women solely as exploited sex workers. Whilst Strömholm’s work can be viewed as a social commentary of the transgender women of Paris and the struggles they faced in daily life, there is a rather more emotive and delicate edge to Strömholm’s work which is a stark departure from the work of social documentary photographers.
Anonymous. “Christer Strömholm Exhibition Review: ‘Les Amies de Place Blanche’,” on the Camera History website 23rd January 2013 [Online] Cited 19/09/2024
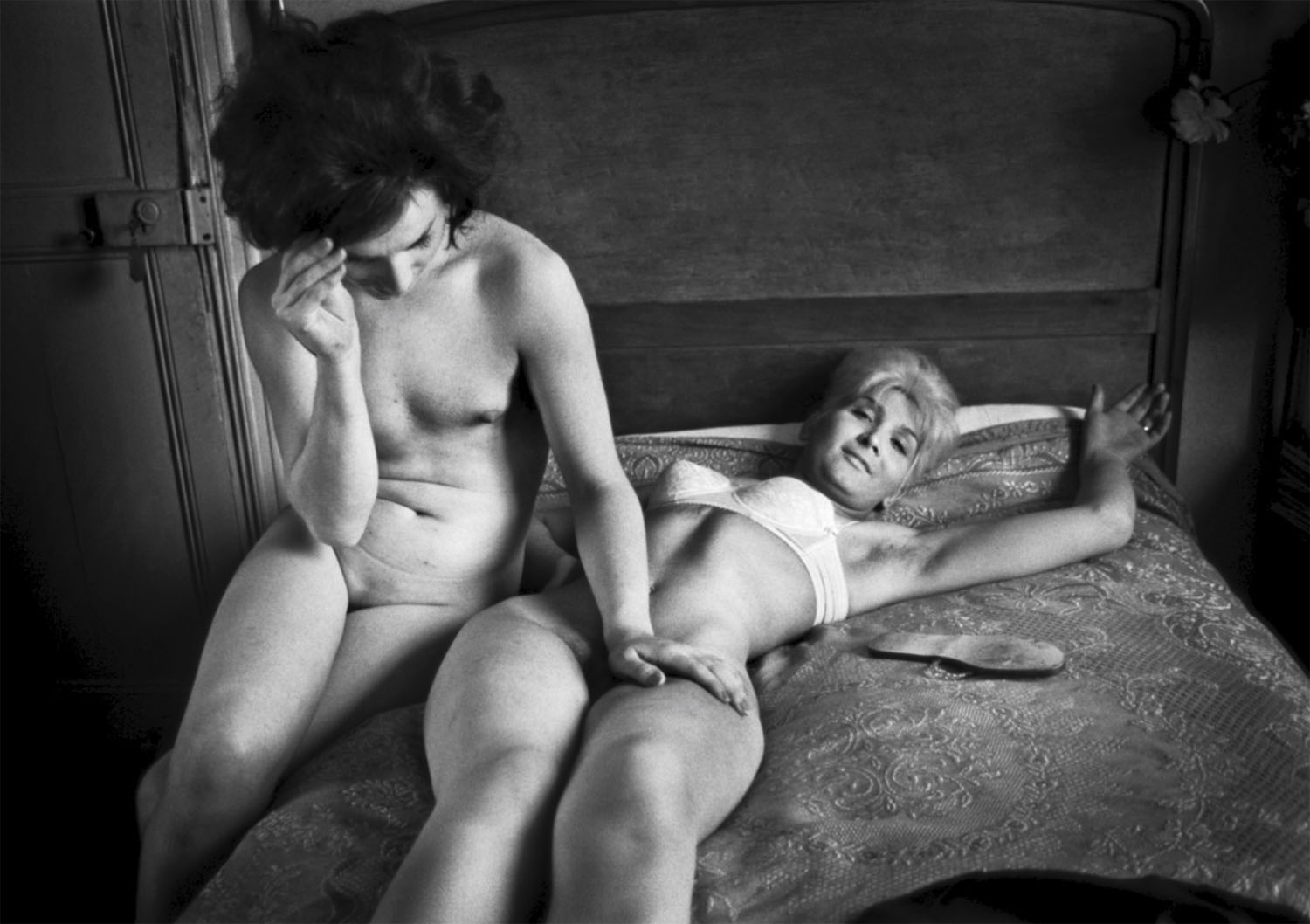
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Sonia, Hôtel Pierrots
1962
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
“This is a book about the quest for self-identity, about the right to live, about the right to own and control one’s body. These are images of people whose lives I shared and whom I think I understood. This is where I arrived in 1959. This is where I settled and started to tell of the life I shared with the transsexuals. They soon became ‘the friends of Place Blanche’. …
After the sun had set, the air cooled down. At the time when shadows stretched, we could catch glimpses of prostitutes walking out of alleys. Big and beautiful women. Some of them exceeded in height their hope-swollen clients. Surrounded by circuses, freaks and snakes, the prostitutes stood there in the buildings’ shadows, keeping a constant eye on the boulevard, the shows and the clients.
Midway through January, when the fairground people set off again, the boulevard went back to normal – the party was over. On the boulevard and in the alleys surrounding place Pigalle and place Blanche, the prostitutes – both male and female, lesbians, transsexuals, transvestites or in other words: the usual group – took back their old spots.
Prostitution was as active as it used to be at the end of the 19th century. Organised prostitution happened all year long. A desperate fight, both to earn the daily bread and, for transsexuals, to see their identitarian dreams come true.
These beautiful ladies dreamt of travelling to Casablanca to undergo surgery. The outcome of a transformation started a long time ago. These women were biologically born as men. They lived here, in the place Blanche neighbourhood. They worked in cabarets, sang, did stripteases. They were outspoken and they answered back immediately to the public, it was a typical Parisian tradition. A cocky and saucy sense of humour.
They earned 60 French francs a day, enough to pay for the food and the hotel room but not enough to afford the 40,000 francs surgery. The streets were their only solution. Some of them had loyal customers, others stood in the same place on the street. Here, prostitution was part of the neighbourhood life. A way to survive.
At the time of the Commune, there already were transvestites on the place Blanche. But it was in the late 50s that the word ‘transsexual’ began to be used. It was also at that time that it became possible for a man to physically become a woman thanks to hormones and surgery. But hormone therapy has also been the cause of tragedies. Often they were denied the help of a doctor. So they had to fend for themselves.
My friends lived together in a world apart, a world of shadows and loneliness, anxiety, hopelessness and alienation. The only thing they demanded was to have the right to be themselves, not to be forced to deny or repress their feelings, to have the right to live their own lives, to be responsible, to be at ease with themselves.
Nothing more. It was then – and still is – about attaining the right to own one’s own life and identity.
Christer Strömholm from his 1983 book Les Amies de Place Blanche
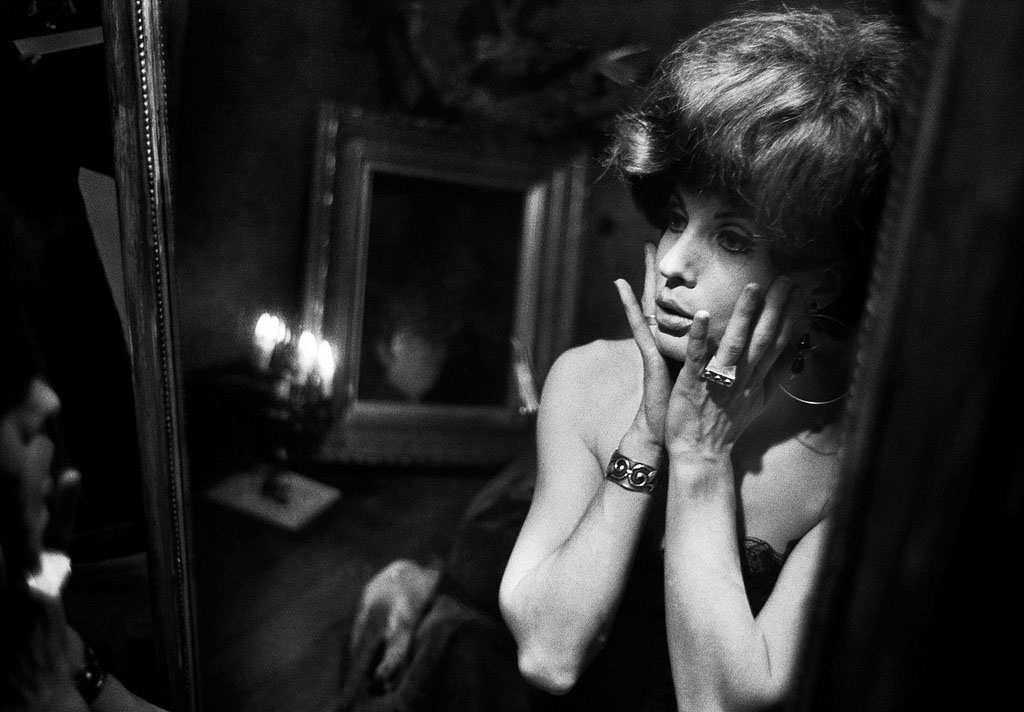
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Sabrina
1967
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
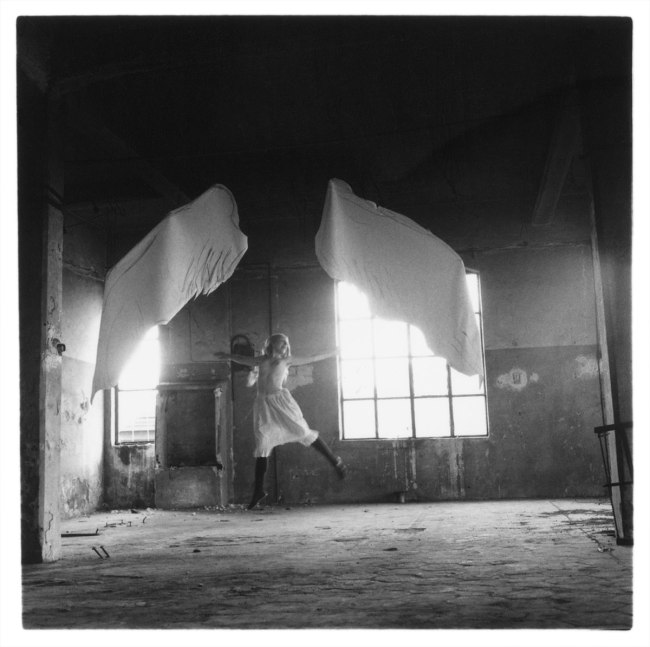
Christer Strömholm (Swedish, 1918-2002)
Gina
1963
Gelatin silver print
© Christer Strömholm/Strömholm Estate
International Center of Photography
1133 Avenue of the Americas at 43rd Street
New York NY 10036
Phone: 212 857 0045
Opening hours:
Wednesday – Monday 11am – 7pm
Closed Tuesdays

















































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.