Exhibition dates: 2nd July 2010 – 3rd February, 2011
Curator: Douglas Eklund, Associate Curator in the Department of Photographs
Many thankx to The Metropolitan Museum of Art for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
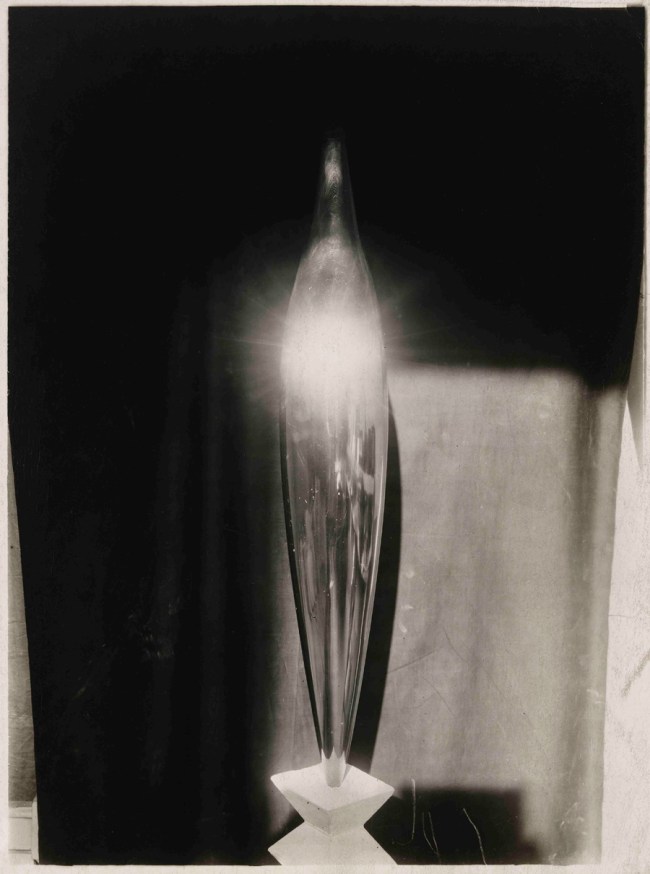
Richard Long (British, b. 1945)
County Cork, Ireland
1967
Gelatin silver print
76.2 x 101.6 cm (30 x 40 in.)
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, Purchase, Vital Projects Fund Inc. Gift, through Joyce and Robert Menschel, 2010
© Richard Long
Long was a key figure in recasting sculpture in two directions: inward toward the gestures of bodies in space and outward toward the creation of ephemeral works made directly in the landscape. A student of the sculptor Anthony Caro at Saint Martins College of Art, Long was well versed in the reductive quality of geometric abstraction but sought to make the form of his works even more elegantly simple and wedded to life. He would go for solitary walks in the English countryside, and at a particular place he would create elemental forms such as a line, an x shape, or a circle by walking over the ground to leave a temporary imprint. A photograph such as County Cork, Ireland – in which the shape seems to hover in the image like a flying saucer – is thus an imprint of an imprint; the form of the work is derived from the holistic relationship between the concept (idea), the action of the body (figure), and the site of his gesture (ground). It is also informed by an astute understanding of the profound links between British culture and the landscape, from prehistoric hill figures through nineteenth-century theories of the Picturesque.
Wall text from the exhibition
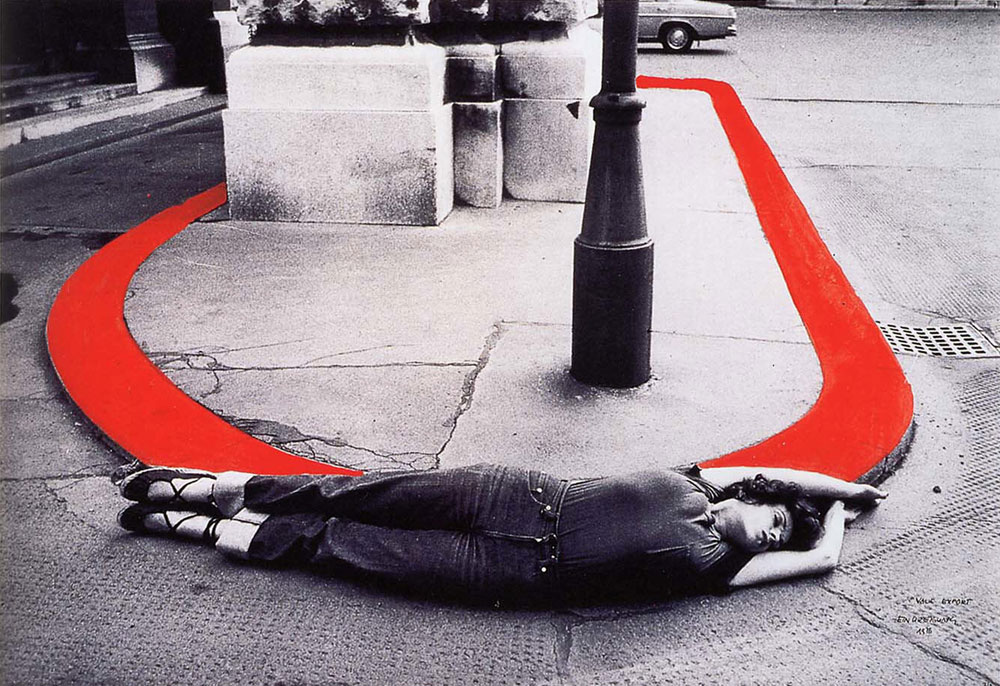
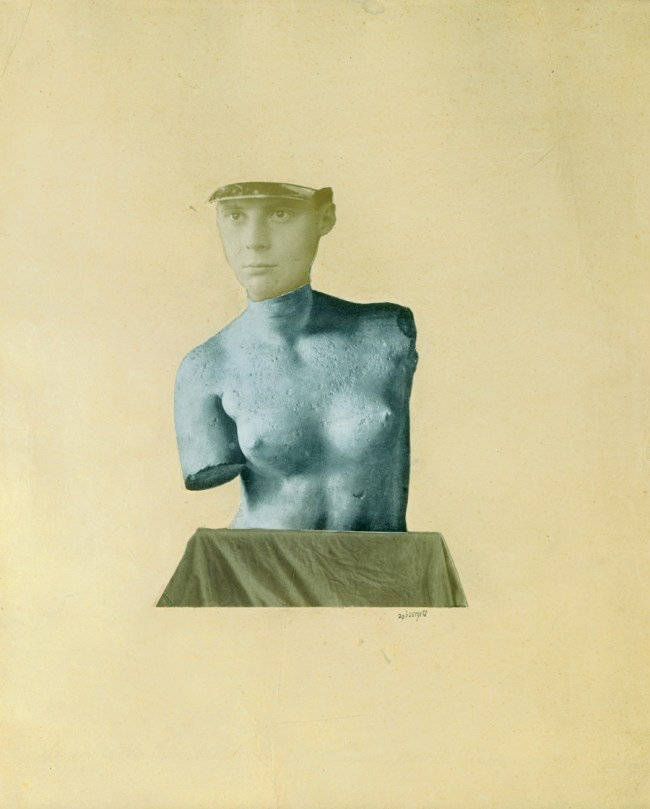
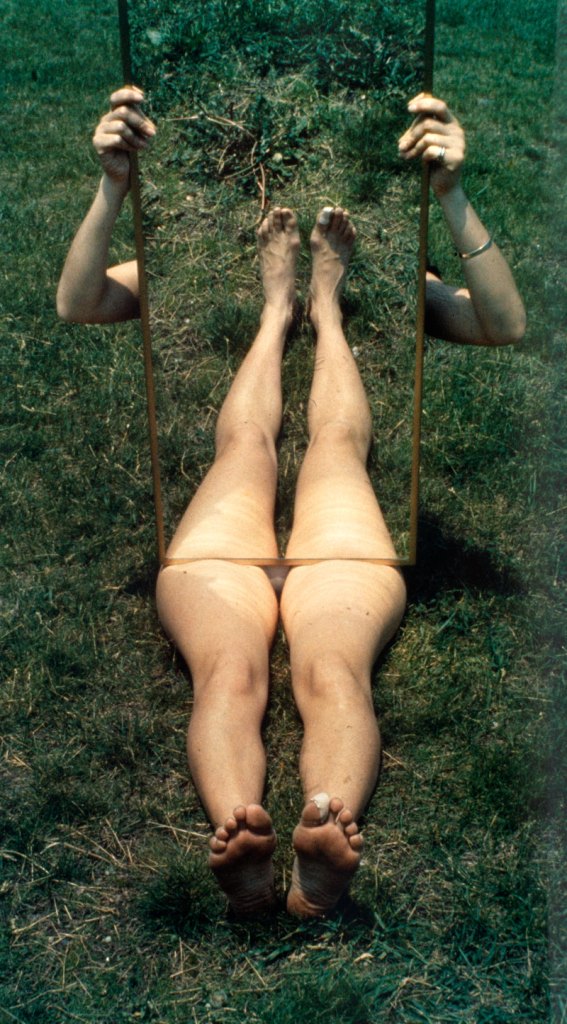
VALIE EXPORT (Austrian, b. 1940)
Encirclement
1976
Gelatin silver print
40.8 x 61cm (16 1/16 x 24 in.)
Promised Gift of Thea Westreich and Ethan Wagner
© VALIE EXPORT, Courtesy Charim Gallery Vienna
In her series Body Configurations, the artist had herself or female colleagues photographed in local streets, stairwells, and alleyways, contorting their bodies to mimic the harsh geometries of the city. Influenced not only by the Actionists but also by the human sculpture of Robert Morris, Export complicates the coolly inhuman systems of Minimalism by reintroducing the human body into abstraction, an intimate yet public gesture that effortlessly transmutes the personal into the political.
Wall text from the exhibition
![Felix Gonzalez-Torres (American born Cuba, 1957–1996) '[No Title]' 1985 from the exhibition 'Between Here and There: Passages in Contemporary Photography' at The Metropolitan Museum of Art Felix Gonzalez-Torres (American born Cuba, 1957–1996) '[No Title]' 1985 from the exhibition 'Between Here and There: Passages in Contemporary Photography' at The Metropolitan Museum of Art](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/02/felix-gonzalez-torres-no-title-1985.jpg?w=284)
Felix Gonzalez-Torres (American born Cuba, 1957–1996)
[No Title]
1985
Instant black-and-white print
7.2 x 6.9cm (2 13/16 x 2 11/16 in.)
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York
Purchase, Anonymous Gift, 1997
© The Felix Gonzalez-Torres Foundation, Courtesy of Andrea Rosen Gallery, New York
Gonzalez-Torres first came to prominence in the early 1990s with his interactive site-specific installations of candy stacks and printed paper. These “antimonuments” parody the coldness and rigor of Minimalist sculpture while actively encouraging participation by the audience. This early work conveys the sense of exile that the artist felt in America after fleeing his native Cuba. It can also suggest a Romantic conception of the soul yearning for the Infinite (represented by the sea) despite the hemming-in of the razor-thin barbed wire that blocks our passage. On the back of this photograph, the artist collaged a printed fragment, possibly from a magazine advertisement, showing cut-off portions of the words “THE BO[?]” and “ANYMORE.” Although made, signed, and dated by the photographer, Gonzalez-Torres thought of works such as this as lying outside his core oeuvre.
Text from The Metropolitan Museum of Art website
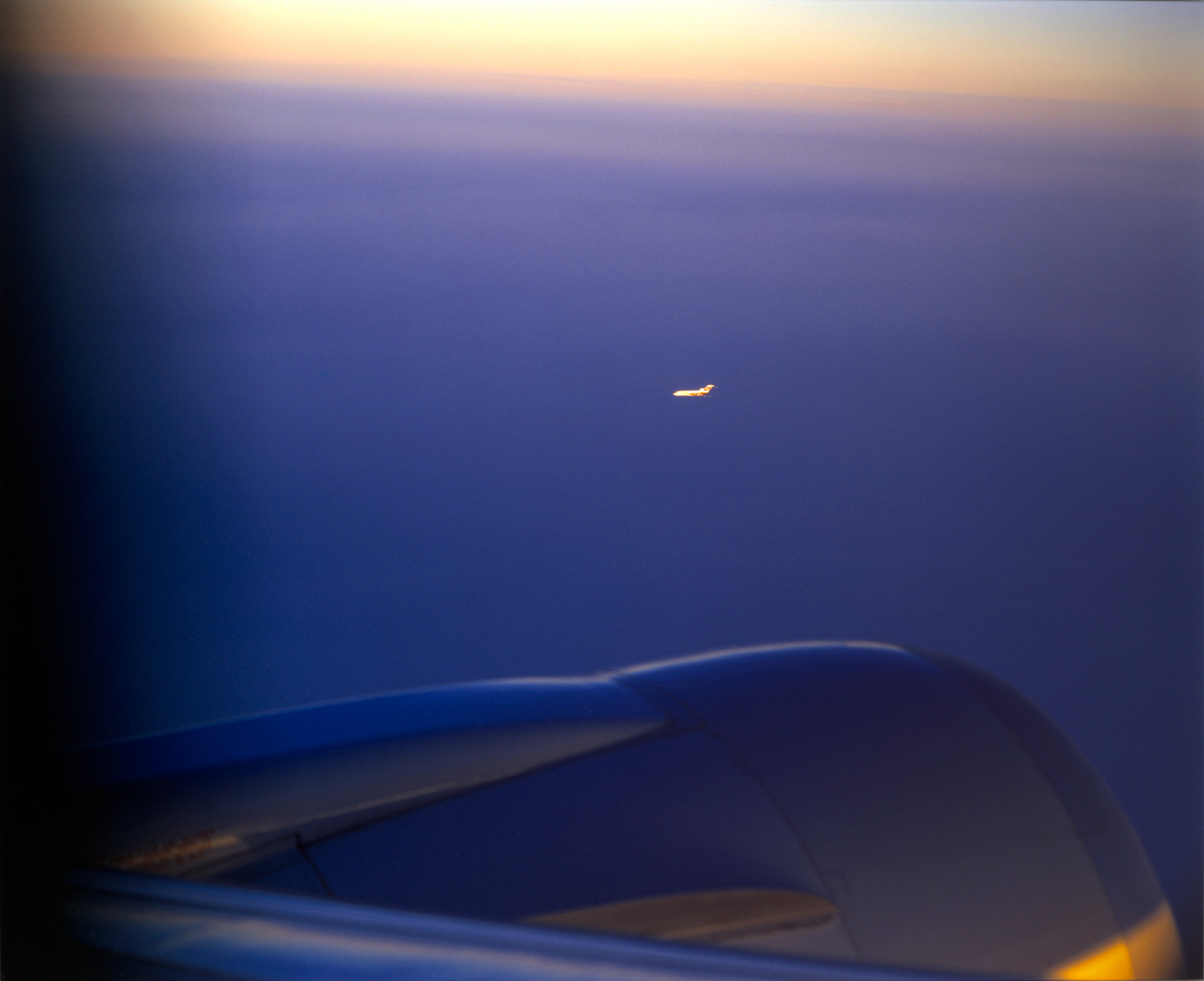
Doug Aitken (American, b. 1968)
Passenger
1997
Chromogenic print
100.5 x 122cm (39 9/16 x 48 1/16 in.)
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, Purchase, Alfred Stieglitz Society Gifts, 2004
© Doug Aitken
Aitken is best known for multiscreen video installations exploring the ways in which perception and consciousness are transformed by our global, technology-driven existence. Passenger belongs to a group of still photographs made in 1997 showing planes in flight, most of which focus on the faint traceries of takeoffs and landings over desolate airport landscapes. In its emphasis on luminosity and atmosphere, this example reveals Aitken’s debt to older California artists such as James Turrell and Robert Irwin. It is also unabashedly sensual: Aitken’s high production values – reminiscent of Technicolor cinematography and glossy advertising – refer directly to the media images that unavoidably condition our responses to the world.
There is something of the sublime in Aitken’s photograph, however, in that it describes the limits of the visible while flooding the eye with colour. Starting from an experience familiar to all air travellers of “two ships passing” in the ether, the artist proposes a more complex statement about the way we perceive reality – namely, that the one thing that we cannot see is ourselves seeing and thus that our understanding of the world is always partial and incomplete.
Wall text from the exhibition
Themes of dislocation and displacement in contemporary photography will be explored in The Metropolitan Museum of Art’s forthcoming exhibition in the Joyce and Robert Menschel Hall for Modern Photography. Drawn almost entirely from the Museum’s collection, Between Here and There: Passages in Contemporary Photography on view July 2, 2010 through February 13, 2011, will feature 22 artists whose photographic works convey a sense of a rootless or unfixed existence.
In the 1960s and 1970s, photography was often embraced by artists who had abandoned conventional art media and who were more interested in creating a work of art that took place over a period of time, in a serial progression, or in a fleeting gesture. The individual painting or sculpture was deemed insufficient to represent the fragmented experience that characterises the modern world; thus artists showed how a work of art could take the form of a walk (Richard Long), a 20-foot-long book (Ed Ruscha), or a series of postcards outlining the precise time that the artist got up each day (On Kawara). Since the 1980s, however, the more conventional practice of creating a carefully executed, singular photograph has regained prominence in contemporary art. Works by Rineke Dijkstra, Thomas Struth, and Weng Fen embody a belief in photography’s traditional powers of description, while reflecting feelings of dislocation in our newly global society.
The exhibition also will include works by: Vito Acconci, Doug Aitken, Darren Almond, Lothar Baumgarten, Matthew Buckingham, VALIE EXPORT, Felix Gonzalez-Torres, Svetlana Kopystiansky, Bruce Nauman, Dennis Oppenheim, Allen Ruppersberg, Fazal Sheikh, Erin Shirreff, Robert Smithson, Anne Turyn, and Jeff Wall.
The first half of the exhibition shows how artists in 1960s and 1970s, working in the context of Minimal and Conceptual art, were drawn to photography for its differences from traditional art media: it was low-tech, easily reproducible, and not considered a valuable art object. Photography was also enlisted to document ephemeral works of art. Bruce Nauman and Vito Acconci, for instance, created performances that focused on the actions and movements of their bodies in space, and captured these works in photographs and videos.
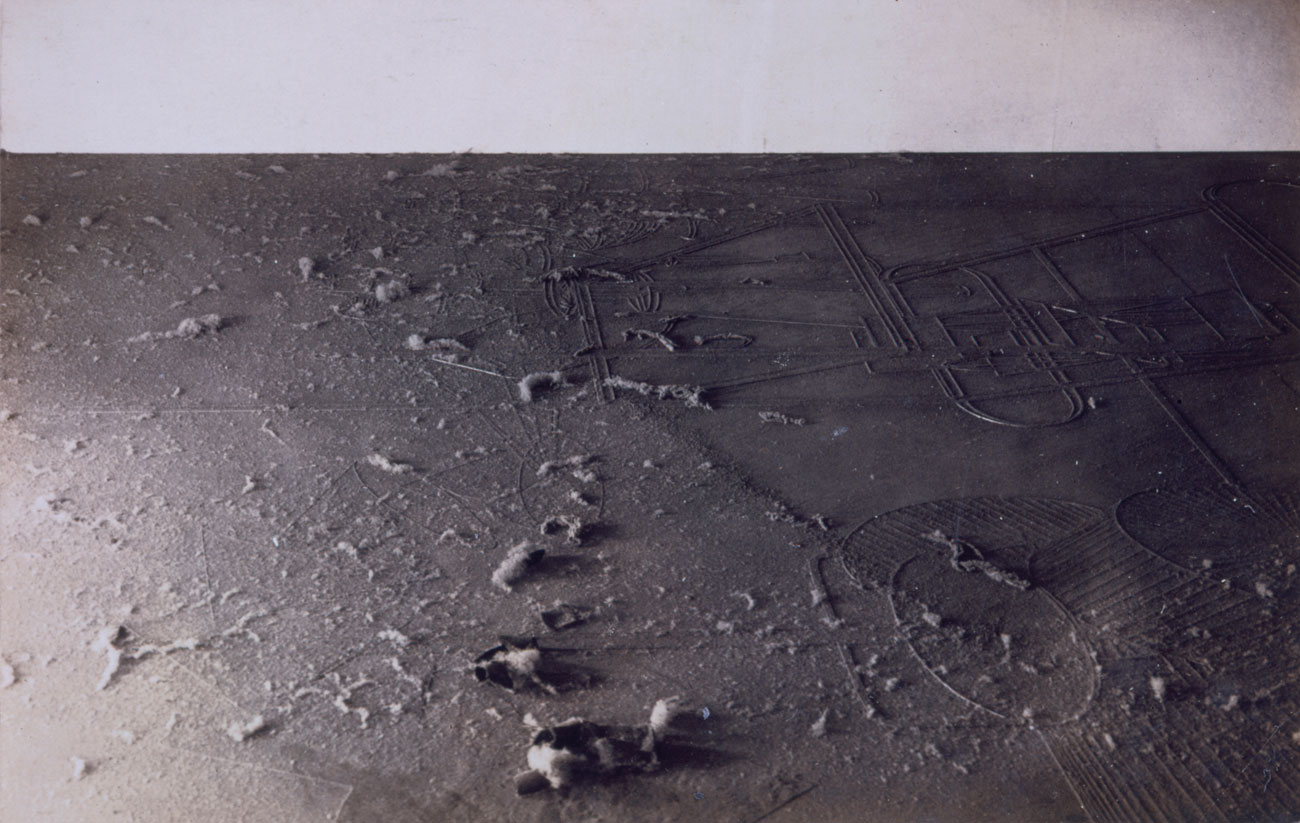
Other artists, such as Robert Smithson, chose to work directly in the landscape – often in distant or inaccessible locations – and their “Earthworks” could generally be seen only through photographs. Smithson is best known for his landmark Spiral Jetty (1970) in the Great Salt Lake, Utah. For an early experiment in his Mirror Displacements series of photographs, Smithson placed small mirrors into snow drifts on the roof of his apartment building. Through dizzying shifts in scale, the artist’s 1969 study transforms a corner of his Manhattan roof into an Alpine landscape.
A student of Anthony Caro, British artist Richard Long was well versed in the reductive quality of geometric abstraction, but sought to make his works even more simple and wedded to life. He would go for solitary walks in the countryside, and at a particular place he would create elemental forms such as a line, X, or circle by walking over the ground to leave a temporary imprint. Long’s photograph County Cork, Ireland (1967) – in which a circle seems to hover over the grass like a flying saucer – is thus an imprint of an imprint, creating a holistic relationship between the concept, the action of the body, and the site of his gesture.
For her series Body Configurations, the Austrian artist VALIE EXPORT had herself and female colleagues photographed in local streets, as they contorted their bodies to mimic the harsh geometries of the city. Encirclement (1976) shows a woman lying in the street, her body elongated and arched to follow the bright red curve the sidewalk. The photograph reintroduces the human body into abstraction in an intimate yet public gesture.
Beginning in the 1980s, there was a renewed interest in photography’s historical genres and recommitment to technical skill and visual fidelity, as seen in Rineke Dijkstra’s portraits. Geopolitical displacement and cultural migration are referenced in one of Dijkstra’s most important bodies of work to date: her photographs of a Bosnian refugee girl, Almerisa. Between Here and There will feature four portraits of Almerisa that Dijkstra made between 1994 and 2000, beginning at an asylum seekers’ center in the Netherlands. Eight photographs from this series of 11 works were acquired recently by the Museum.
In both photographs and films, Doug Aitken explores the ways in which perception is transformed by our global, technology-driven existence. Aitken’s photograph Passenger (1997), taken from the window of an airplane in flight, shows another plane flying in parallel in the remote distance, illuminated by the sun setting on a slanted horizon. Aitken references sensations of being adrift in mid-air and of “two ships passing” – paths that do not quite connect, despite their proximity to each other.
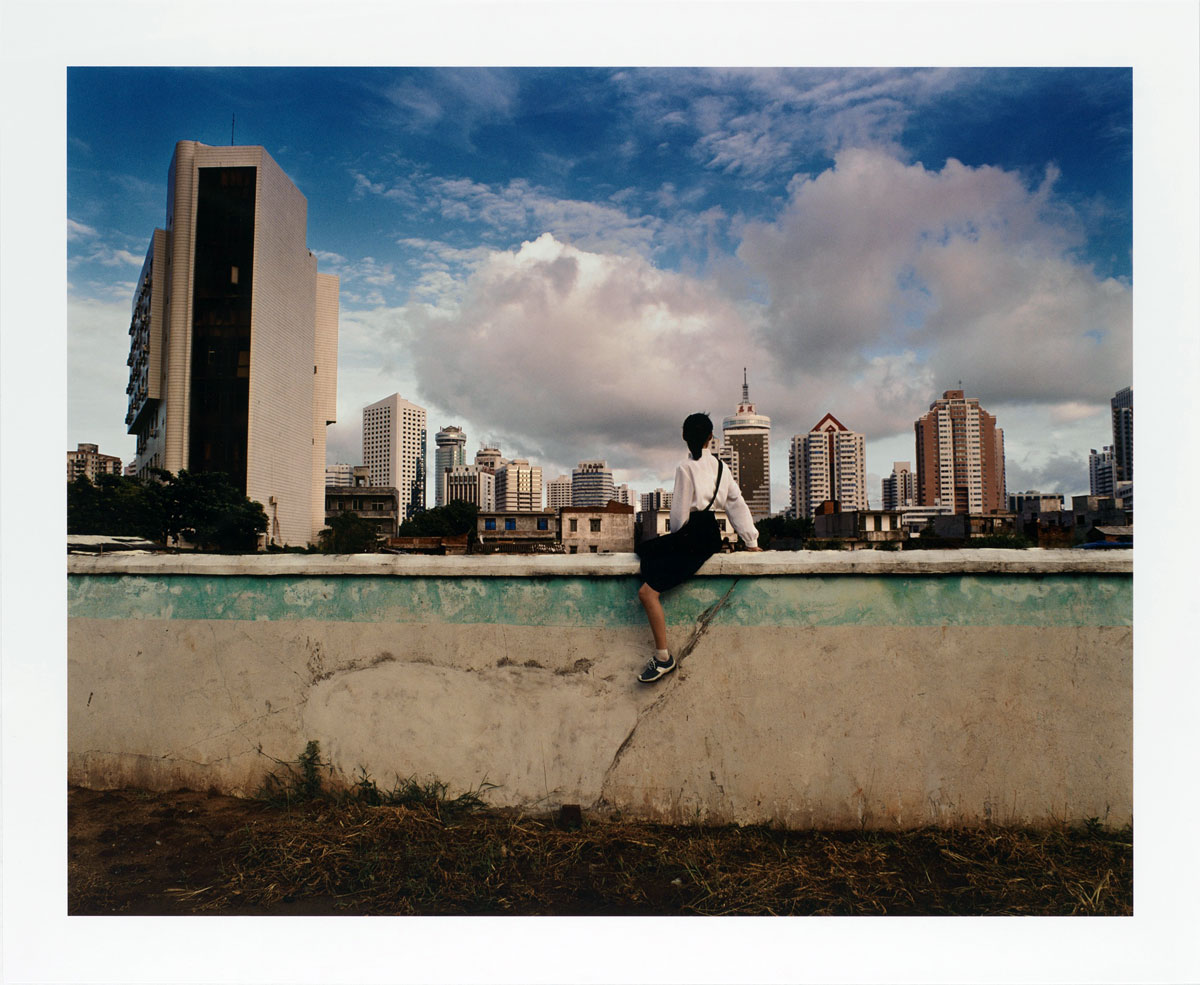
Chinese artist Weng Fen explores a young generation poised at a transitional moment between China’s traditional rural society and a quickly burgeoning urbanism. Bird’s Eye View: Haikou V (2002) shows a woman – perhaps an outsider or a new arrival to the city – perched on an old wall, looking toward the new skyscrapers on the horizon, but not fully occupying the space of the past or the future. This work is part of a group of recent gifts and promised gifts of contemporary Chinese photographs to the Museum.
The exhibition comes full circle with a recently acquired video by Erin Shirreff. Roden Crater (2009) takes as its subject artist James Turrell’s legendarily inaccessible and still unfinished celestial observatory carved out of a 400,000-year-old extinct volcano. Shirreff’s mesmerising fixed-camera view of the distant “Earthwork” shows an improbable succession of slow-moving climactic and light effects on the crater, creating a haunting meditation on the never-ending quest for resolution in life and in art.
Between Here and There: Passages in Contemporary Photography is organised by Douglas Eklund, Associate Curator in the Department of Photographs.”
Text from The Metropolitan Museum of Art website
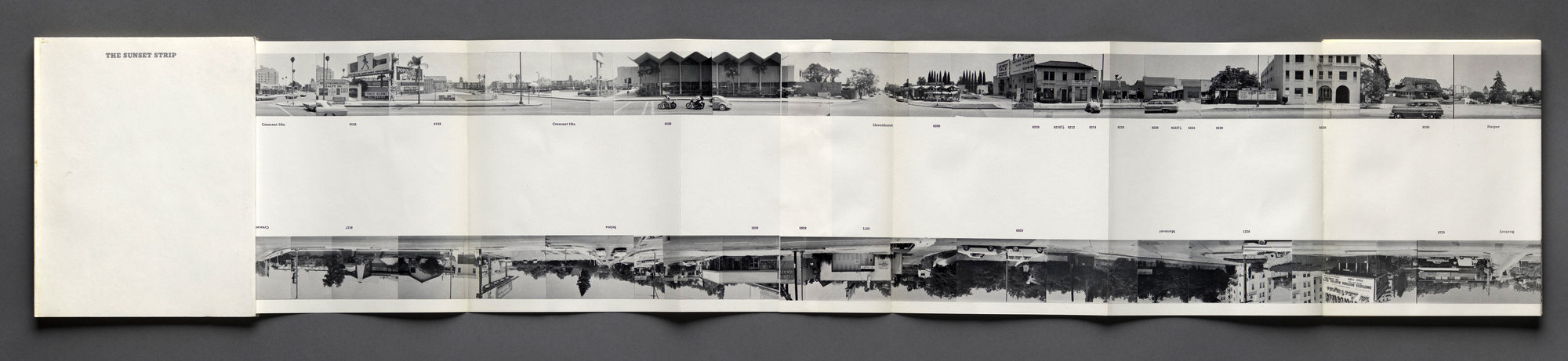

Ed Ruscha (American, b. 1937)
Every Building on the Sunset Strip
1966
Artist book, offset printed
Each page: 7 x 5 1/2 inches (17.8 x 14cm)
Overall: 7 1/8 x 5 5/8 x 1/2 inches (18.1 x 14.3 x 1.1cm)
© Ed Ruscha
Early in the development of both Minimal and Conceptual art, the linguistic phrase as instruction or directive became paramount: the idea was primary and its execution could be by anyone who followed directions. This paradigm displaced the role of the artist from a kind of benighted savage to cool producer, and no artist commented more sharply on this new “informational” style than the West Coast painter Ed Ruscha, whose Pop-inflected canvases were often of resonant or humorous words such as Flash or Oof rendered in cartoonish yet formally precise typefaces floating on monochromatic backgrounds.
Ruscha’s books are similarly head-scratching fulfillments of their titles. First came Twentysix Gasoline Stations (1962), as blank as an instructional manual and offering a serial Warholian accounting of the most flatfooted-looking snapshots of banal roadside filling stations imaginable. The photographs were not the art, and it was not a luxurious livre d’artiste. Its meaning lay somewhere in the puzzled response of the reader thumbing through it and the circuitous, even futile route that it took through the culture. As Ruscha himself kidded, “My books end up in the trash.” Every Building on the Sunset Strip … is – like a row of bricks placed on the floor by sculptor Carl Andre – a model of “one thing after another” Minimalism as well as a readymade chance arrangement (the strip itself) of the artist’s beloved vernacular architectural eyesores.
Text from The Metropolitan Museum of Art website
Thomas Struth (German, b. 1954)
National Museum of Art, Tokyo
1999
Chromogenic print
179.4 x 276.9cm (70 5/8 x 109 in.)
Purchase, Jennifer and Joseph Duke, Joyce and Robert Menschel, and Anonymous Gifts, Gift of Dr. Mortimer D. Sackler, Theresa Sackler and Family, and Fletcher and Harris Brisbane Dick Funds, 2001
© Thomas Struth
Throughout the 1990s Struth photographed people in museums, cathedrals, and other shrines that function as tourist meccas for the secular religion of art. The subject of this work is half of a Japanese-French exchange of treasures. The Japanese sent their prized eighth-century bodhisattva from Nara to the Louvre, where it was encased in bulletproof glass and displayed in an incongruously ornate Second Empire gallery. Struth’s photograph shows the French contribution, also behind glass, in the hall the Japanese designed to exhibit it.
Quintessentially Gallic, Delacroix’s 1830 painting Liberty Leading the People is a hymn to the supreme rights of the individual, shot through with sex and high drama. The mise-en-scène, however, is an uncanny reflection of late twentieth-century spectacle culture – the movie theatre, where the crowd passively absorbs images on a glowing screen. Yet, Struth is not simply demonstrating the collision between Delacroix’s characters, who rush forward into history, and those who are immobilised in the face of it; he also discerns a respectful distance on the part of the Japanese toward their visitor, an appreciation of difference and cultural specificity that is a key to this artist’s work.
Text from The Metropolitan Museum of Art website
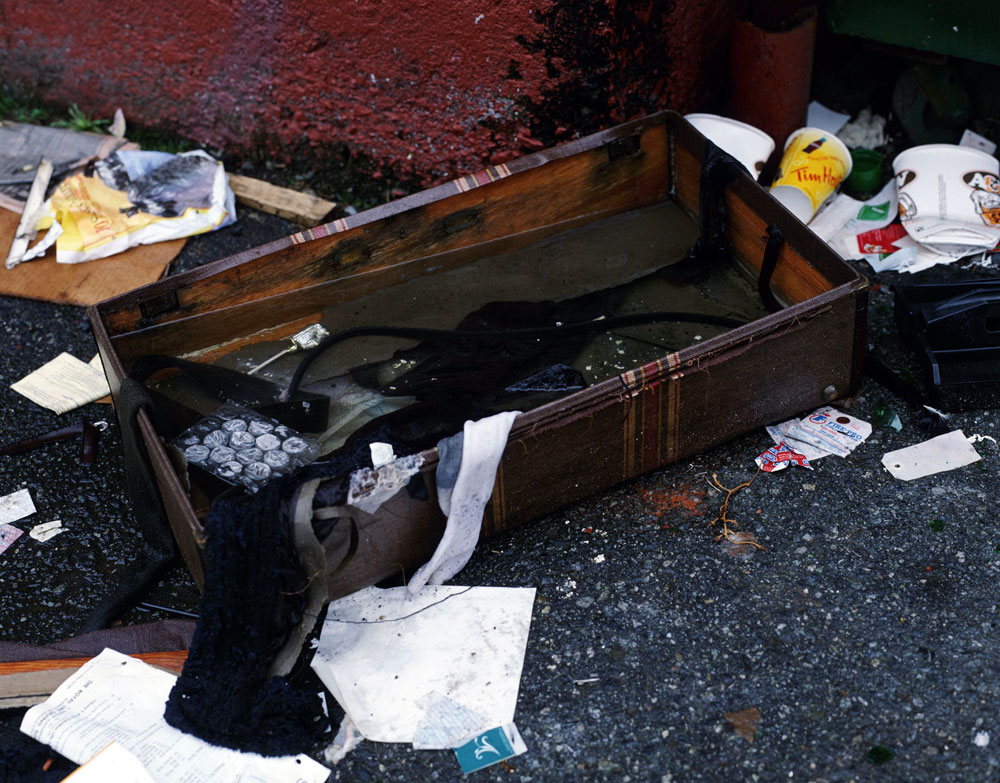
Jeff Wall (Canadian, b. 1946)
Rainfilled Suitcase
2001
Transparency in light box
Collection of Jennifer Saul and Stephen Rich, New York
© Jeff Wall
Wall’s tableaux straddle the worlds of the museum and the street. For the last three decades, the artist has created elaborately staged and meticulously rendered scenes of urban and suburban conflict and disorder that he witnessed firsthand, which were then shown as colour transparencies in light boxes reminiscent of backlit advertising images seen in airports and bus stops. About 2000, Wall also began to make smaller, more elliptical photographs – isolating the kinds of details that previously would have been seen in the background of his larger, more programmatic pictures. This grimy half of an abandoned suitcase filled with old clothes and rain seems paradoxically to be both as obsessively arranged as a still life and as randomly disordered as the average flotsam and jetsam on any down-and-out street corner.
Wall text from the exhibition
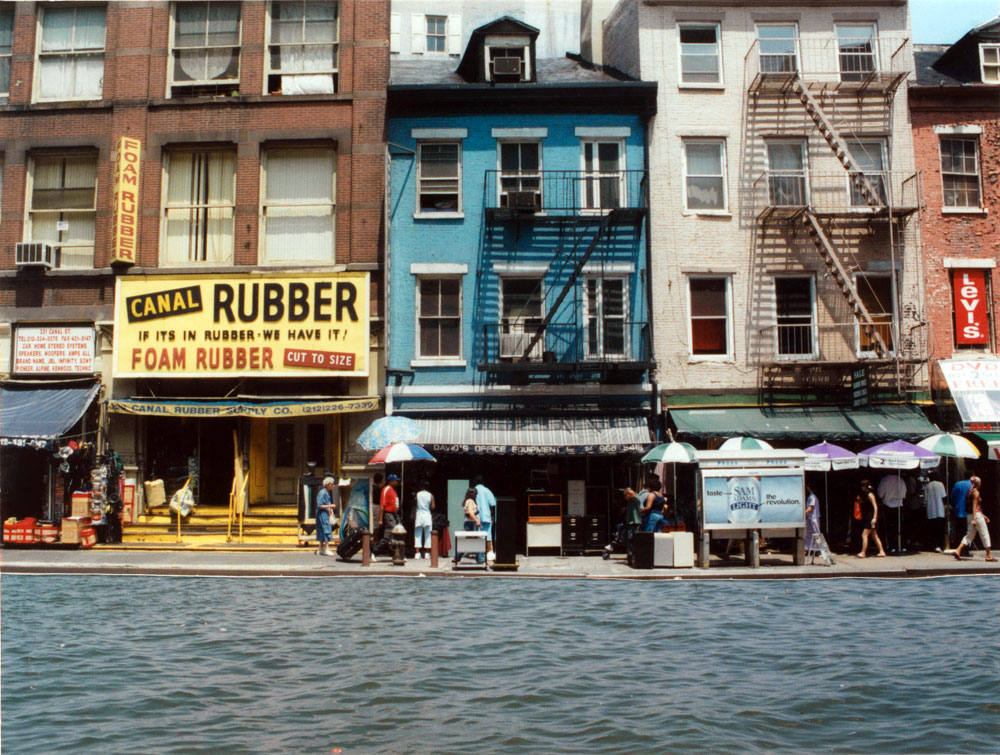
Matthew Buckingham (American, b. 1963)
Canal St. Canal No. 3
2002
Chromogenic prints
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, Purchase, Vital Projects Fund Inc. Gift, through Joyce and
Robert Menschel, 2010
© Matthew Buckingham
This is the maquette for a postcard that the artist created for the group show “Nostalgia.” The postcard was sold in the shops along Canal Street accompanied by the following text beneath the image:
ABOVE: a section of Canal Street as it might look today if a 1791 proposal to build a “Venetian-style” canal connecting the Hudson and East Rivers across Lower Manhattan had been realised. The canal and an accompanying commercial harbour were meant to replace both a small stream which ran along present-day Canal Street, and the so-called Fresh Water or Collect Pond, a befouled 70-acre swamp that one New York newspaper of the day called a “shocking hole.” Instead, real-estate interests prevailed, and the stream was widened only enough to drain the pool so it could be filled in and developed. Many basements of new buildings on the landfill soon flooded, so the stream was further enlarged to increase drainage – making it, in effect, an open sewer. After much complaint about odour, and despite efforts to beautify the waterway with a tree-lined promenade, it was covered over in 1819. Flaws in this re-design kept Canal Street smelling foul for years. It is rumoured that the natural spring which once fed the Fresh Water Pond still flows deep below Canal Street today.*
Wall text from the exhibition
*Luc Sante defines nostalgia as a state of inarticulate contempt for the present combined with a fear of the future.
Weng Fen (Chinese, b. 1961)
Bird’s Eye View: Haikou V
2002
Chromogenic print
50 x 62.7cm (19 11/16 x 24 11/16 in.)
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, Gift of Ellie Warsh, 2009
© Weng Fen
Weng Fen belongs to a generation of Chinese photographers whose principal subject is a China in the throes of physical, social, economic, and political change. His Bird’s Eye View series focuses on the elevated urbanism of cities such as Haikou, Shanghai, and Shenzhen. Many of these photographs feature schoolgirls with their backs to the camera, perched on a wall or precipice, staring at the landscape – adolescent figures on the threshold of personal transition looking out onto a landscape and a culture at a similarly transformational moment.
Wall text from the exhibition
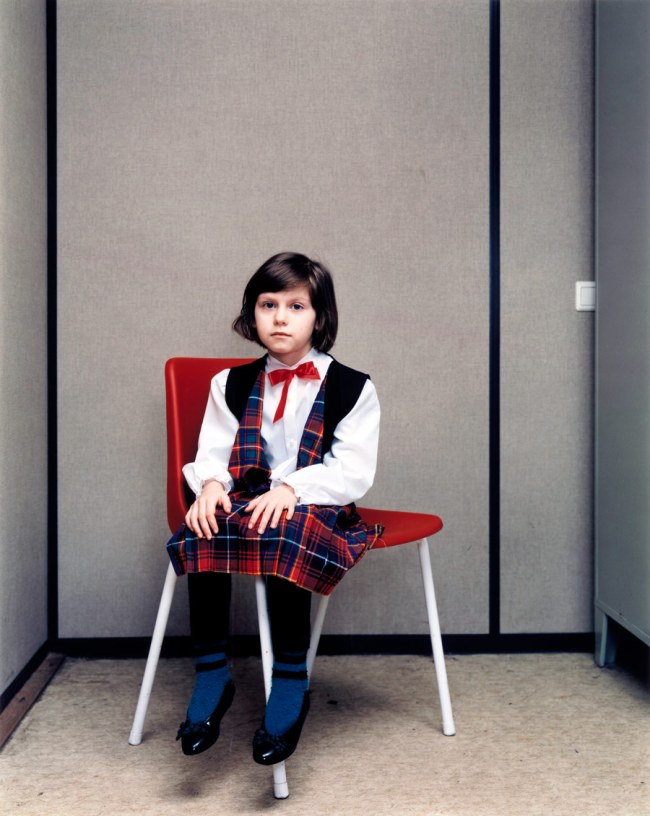

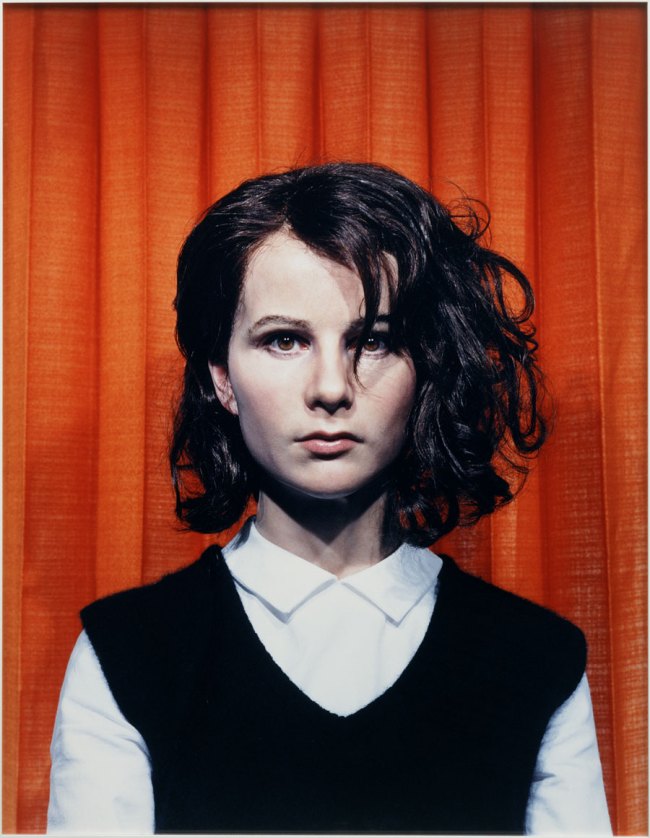
Rineke Dijkstra (Dutch, b. 1959)
Almerisa, Asylum Seekers’ Center, Leiden, The Netherlands, March 14, 1994
1994
Chromogenic print
120 x 100cm (47 1/4 x 39 3/8 in)
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, Gift of Ellen Kern, 2008
© Rineke Dijkstra
Dijkstra is best known for her portraits of teenage beachgoers in Poland, Croatia, the Ukraine, Belgium, England, and America, which convey the poignant intensity of adolescence with startling eloquence. In all her work, she is particularly drawn to subjects in a state of transition – blood-spattered matadors just minutes after bullfights, women cradling their newborns moments after delivery – and renders them with respect, attentiveness, and compassion.
Between 1994 and 2008 Dijkstra made eleven photographs of a Bosnian refugee girl named Almerisa, from her initial processing at an asylum seekers’ center in the Netherlands to her fully Westernised adulthood and motherhood. Here, the imprint of geopolitical displacement is rendered without cant and that of childhood is captured without nostalgia. Like all great portraitists, Dijkstra extracts an elemental, almost mythic quality from the irreducible individuality of her subject – of the eternal radiating from the everyday. This selection is from a recent gift to the Metropolitan of eight of the eleven portraits of Almerisa.
Wall text from the exhibition
The Metropolitan Museum of Art
1000 Fifth Avenue at 82nd Street
New York, New York 10028-0198
Information: 212-535-7710
Opening hours:
Sunday – Tuesday and Thursday: 10am – 5pm
Friday and Saturday: 10am – 9pm
Closed Wednesday


















































![Margaret Bourke-White (American, 1906-1971) '[Iron Mountain, Tennessee]' 1937 from the exhibition 'American Modern: Abbott, Evans, Bourke-White' at the Amon Carter Museum of American Art, Fort Worth, Texas Margaret Bourke-White (American, 1906-1971) '[Iron Mountain, Tennessee]' 1937 from the exhibition 'American Modern: Abbott, Evans, Bourke-White' at the Amon Carter Museum of American Art, Fort Worth, Texas](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/12/margaret-bourke-white-iron-mountain-tennessee-1937.jpg)





![Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975) '[Lunchroom Window, New York City]' 1929 from the exhibition 'American Modern: Abbott, Evans, Bourke-White' at the Amon Carter Museum of American Art, Fort Worth, Texas Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975) '[Lunchroom Window, New York City]' 1929 from the exhibition 'American Modern: Abbott, Evans, Bourke-White' at the Amon Carter Museum of American Art, Fort Worth, Texas](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/12/walker-evans-lunchroom-window-new-york-city-1929.jpg)




![Lewis W. Hine (American, 1874-1940) '[Crowd of Newsies, Including One Girl]' 1910 Lewis W. Hine (American, 1874-1940)
'[Crowd of Newsies, Including One Girl]' 1910](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/11/lewis-hine-crowd-of-newsies.jpg)





















































![Leon Levinstein (American, 1910-1988) 'Untitled [Head of Man with Hat and Cigar]' c. 1960 from the exhibition 'Hipsters, Hustlers, and Handball Players: Leon Levinstein's New York Photographs, 1950-1980' at The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, June - October, 2010 Leon Levinstein (American, 1910-1988) 'Untitled [Head of Man with Hat and Cigar]' c. 1960 from the exhibition 'Hipsters, Hustlers, and Handball Players: Leon Levinstein's New York Photographs, 1950-1980' at The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, June - October, 2010](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/09/leon-levinstein-head-of-man-with-hat-and-cigar.jpg)








![Leon Levinstein (American, 1910-1988) 'Untitled [Beach Scene: Woman Wearing Paper Bag Hat, Coney Island, New York]' 1950s Leon Levinstein (American, 1910-1988) 'Untitled [Beach Scene: Woman Wearing Paper Bag Hat, Coney Island, New York]' 1950s](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/09/leon-levinstein-beach-scene.jpg?w=809)




























You must be logged in to post a comment.