Exhibition dates: 20th December 2011 – 6th May 2012
Anthony Friedkin (American, b. 1949)
Clockwork Malibu
1978
Gelatin silver print
11 15/16 x 18 5/16 in
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
Gift of Sue and Albert Dorskind
© Anthony Friedkin
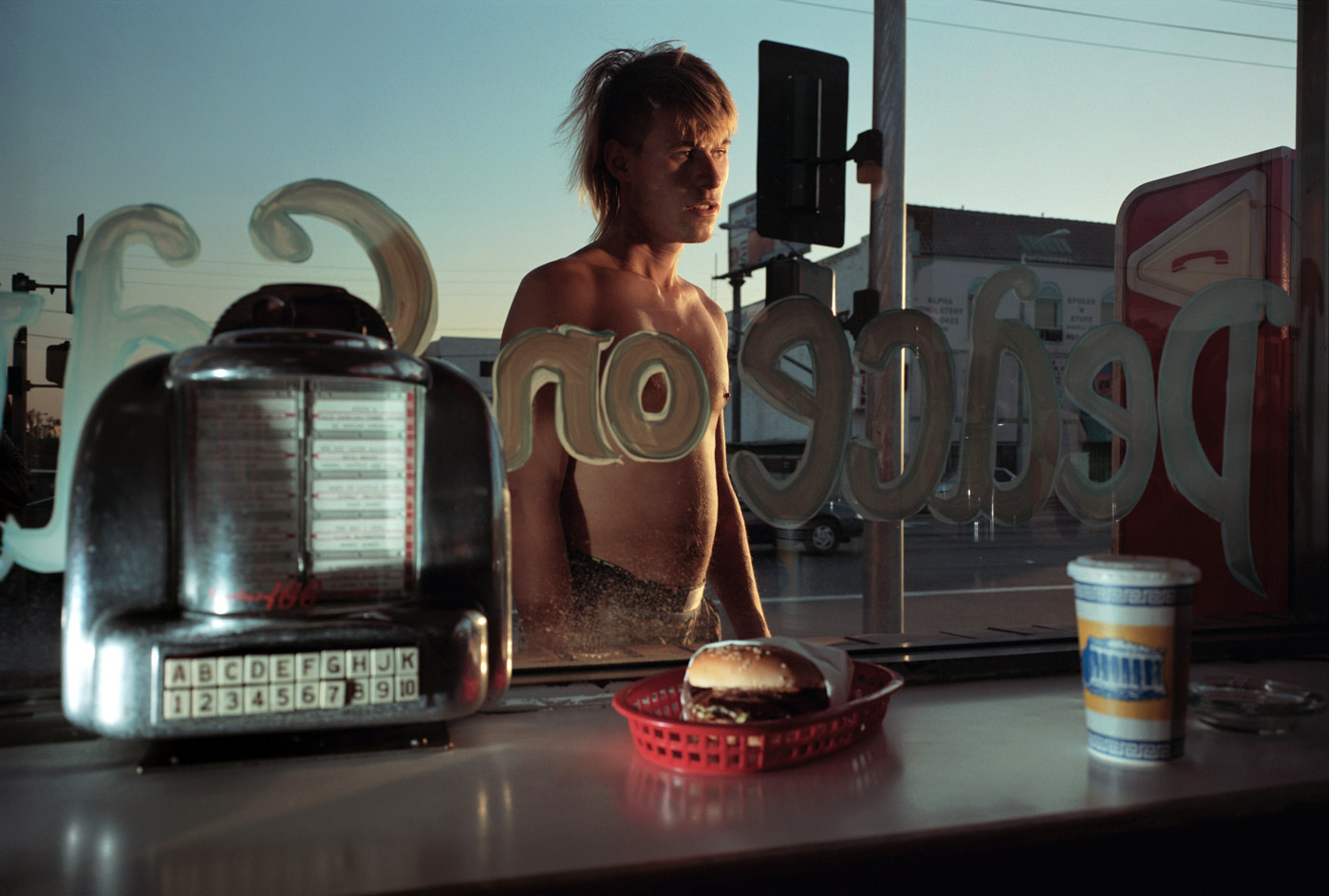
While Anthony Friedkin has documented subjects as diverse as the marginalised gay community of San Francisco, convicts at Folsom Prison, and brothels in New York, it is the Southern California coastline that has remained a recurrent theme throughout his forty-five-year career. The Los Angeles native took up photography about the same time he learned to surf. His images of waves deftly communicate the primordial power and elusive mysteries that he ascribes to the ocean. This photograph of surfer Rick Dano on an early morning drive up the coast conveys a mood of quiet, anticipatory harmony.
Text from Pacific Standard Time at the Getty
I have never particularly liked Los Angeles as a city. There seems to be something unappealing about the place, some energy lurking just beneath the surface that you can’t quite put your finger on. Maybe it is the comparison with the vivacious San Francisco just up the coast, the awful public transport or, more spookily, the lack of people on the street. People never walk anywhere in LA, it’s a car town. When I did walk on the street I felt vulnerable and surveyed with suspicion by people in cars, like a rabbit caught in the headlights.
These photographs confirm this feeling. Unlike the visual acoustics of the architectural photographs of Julius Shulman (photographs that mythologised this urban metropolis and then exported that idealised presence and Californian mid-century design to the rest of the world) these photographs have an unbelievably desolatory nature to them. They seem to be joyless and sorrowful, devoid of warmth, comfort, or hope – as though the human and the city were separated, as if we are separated from a loved one.
The row after row of tinderbox houses, the ubiquitous cars, the sense of emptiness, hopelessness and menace (see Gary Winogrand Los Angeles 1964, below – if looks could kill this would be it, the bandaged broken nose just perfect for the photograph) all paint a picture of despair. Even the supposedly quiet, anticipatory harmony of the photograph of surfer Rick Dano by Anthony Friedkin (1978, below top) is, to me, full of unresolved tension. The mist in the background hanging over the rocks, blocking out the view, the filthy hands and the bandaged little finger of the right hand, the downcast eyes, the impossibly long cigarette handing from his lips and most importantly the empty distance between the figure and the safety of the automobile. The tension in that distance and the downcast eyes says nothing to me of harmony but of isolation, sadness and regret.
Los Angeles is not my favourite city but it is a fascinating place none the less, as these photographs do attest.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the J. Paul Getty Museum for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
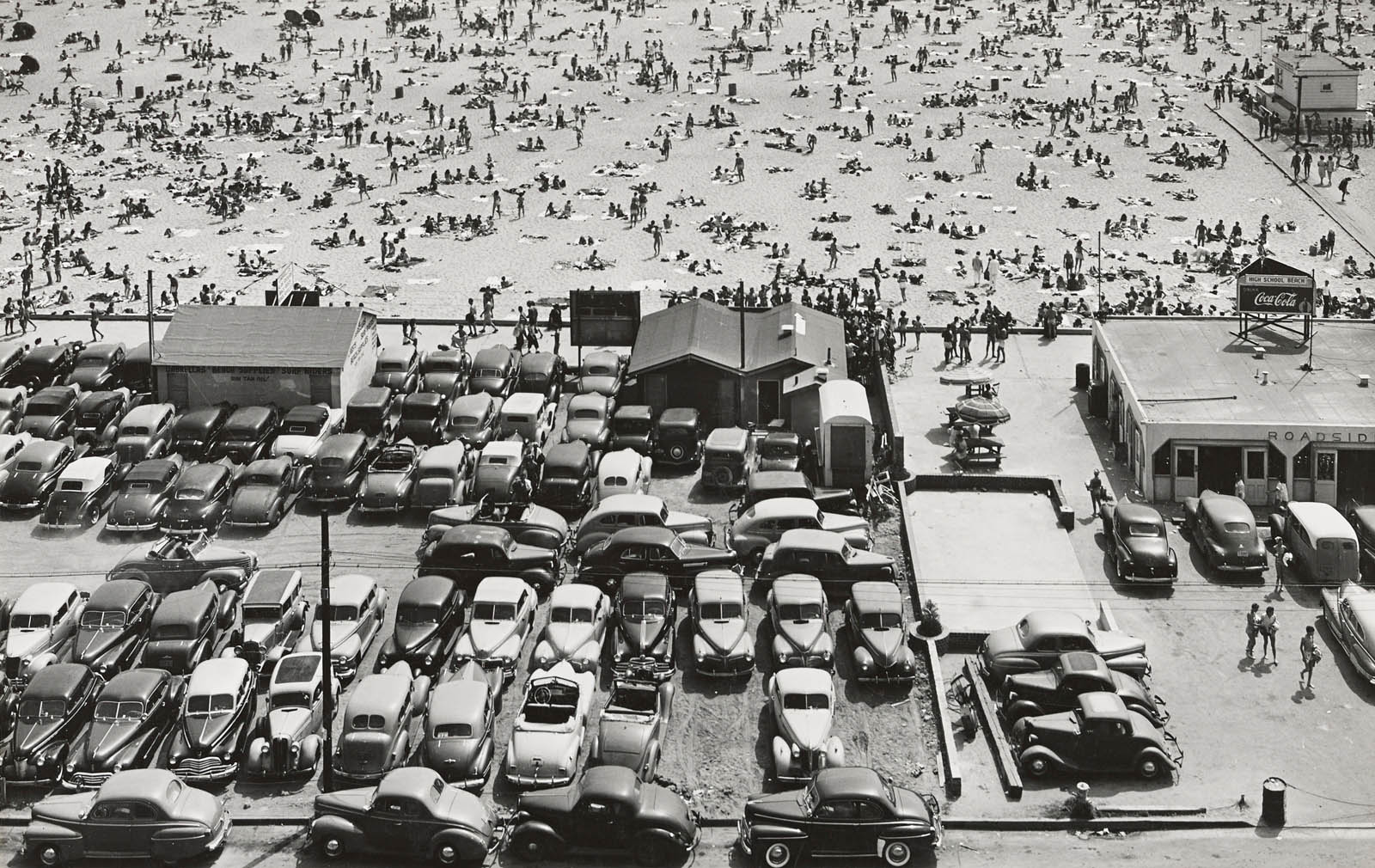
Max Yavno (American, 1911-1985)
High School Beach
1945
Gelatin silver print
22.1 x 34.4cm
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
Gift of Marjorie and Leonard Vernon
© 1988 Centre for Creative Photography, The University of Arizona Foundation
Anthony Hernandez (American, b. 1947)
Automotive Landscapes #5: Los Angeles
1978
Gelatin silver print
11 3/4 x 17 1/8 in
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
Purchased in part with funds provided by the Photographs Council of the J. Paul Getty Museum
© Anthony Hernandez
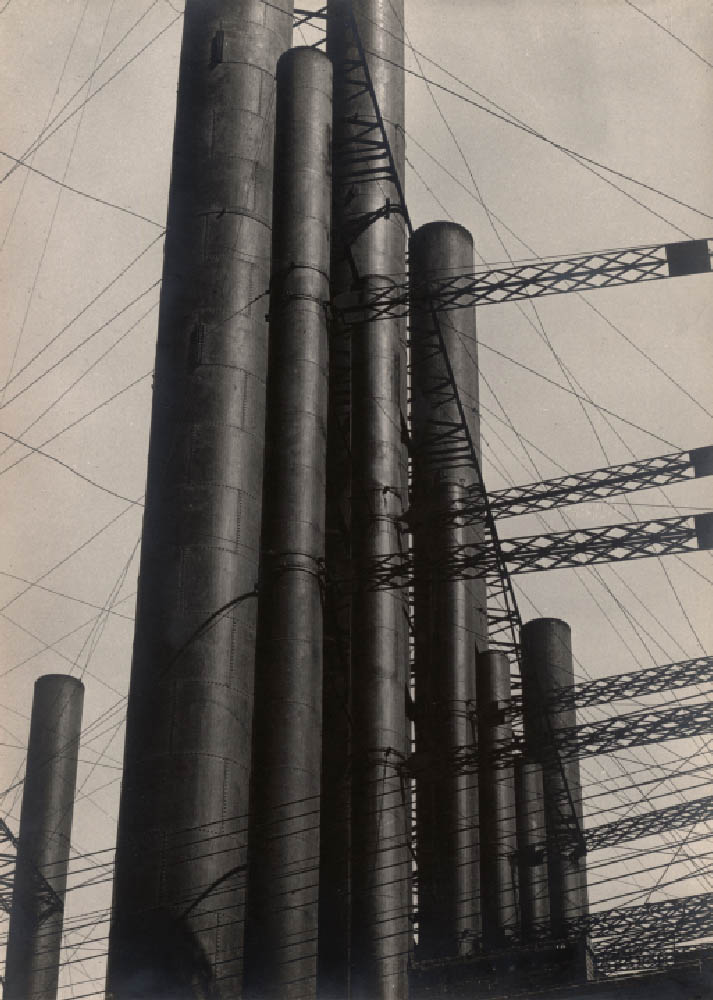
Hernandez started photographing what he refers to as “automotive landscapes” in 1977, using a 35mm camera until he realised that a large-format camera loaded with 5 x 7-inch negative film would provide the detail he desired. Taken from a slightly elevated vantage point, Hernandez’s image of an immobilised truck and its lone mechanic in front of a repair shop presents a sobering view of Los Angeles’s car-dominant culture.
Text from Pacific Standard Time at the Getty
Gary Winogrand (American, 1928-1984)
Los Angeles
1964
Gelatin silver print
9 x 13 7/16 in
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
© 1984 The Estate of Gary Winogrand
This image of a couple seated in a parked convertible in front of a nightclub on Sunset Boulevard simultaneously captures the glamour and seediness associated with Hollywood. Evoking a 1940s or ’50s film noir crime drama, a seeming tough guy and femme fatale continue their heated conversation, apparently oblivious to the traffic around them – and to the photographer observing them. A native of New York City, Winogrand studied painting at Columbia University and photography at the New School for Social Research before doing freelance commercial work. He photographed incessantly, using a 35mm camera to create wide-angled or tilted shots that are densely composed and layered with meaning. More than 2,500 rolls of film remained undeveloped at the time of his death in 1984.
Text from Pacific Standard Time at the Getty
As part of the region-wide Pacific Standard Time: Art in L.A., 1945-1980 initiative, The J. Paul Getty Museum presents In Focus: Los Angeles, 1945-1980, an exhibition of photographs from the permanent collection made by artists whose time in Los Angeles inspired them to create memorable images of the city, on view at the Getty Center from December 20, 2011 – May 6, 2012.
This exhibition features both iconic and relatively unknown work by artists whose careers are defined by their association with Los Angeles, who may have lived in the city for a few influential years, or who might have visited only briefly,” said Virginia Heckert, curator, Department of Photographs, the J. Paul Getty Museum, and curator of the exhibition.
The photographs are loosely grouped around the themes of experimentation, street photography, architectural depictions, and the film and entertainment industry. Works featured in the exhibition are from artists such as Jo Ann Callis, Robert Cumming, Joe Deal, Judy Fiskin, Anthony Friedkin, Robert Heinecken, Anthony Hernandez, Man Ray, Edmund Teske, William Wegman, Garry Winogrand, and Max Yavno. Two of the works in the exhibition by Anthony Hernandez and Henry Wessel Jr. were acquired with funds from the Getty Museum Photographs Council. Drawn from the Museum’s permanent collection, including several recent acquisitions inspired by the Pacific Standard Time initiative, the exhibition offers visitors the opportunity to familiarise themselves with a broad range of approaches to the city of Los Angeles as a subject and to the photographic medium itself.
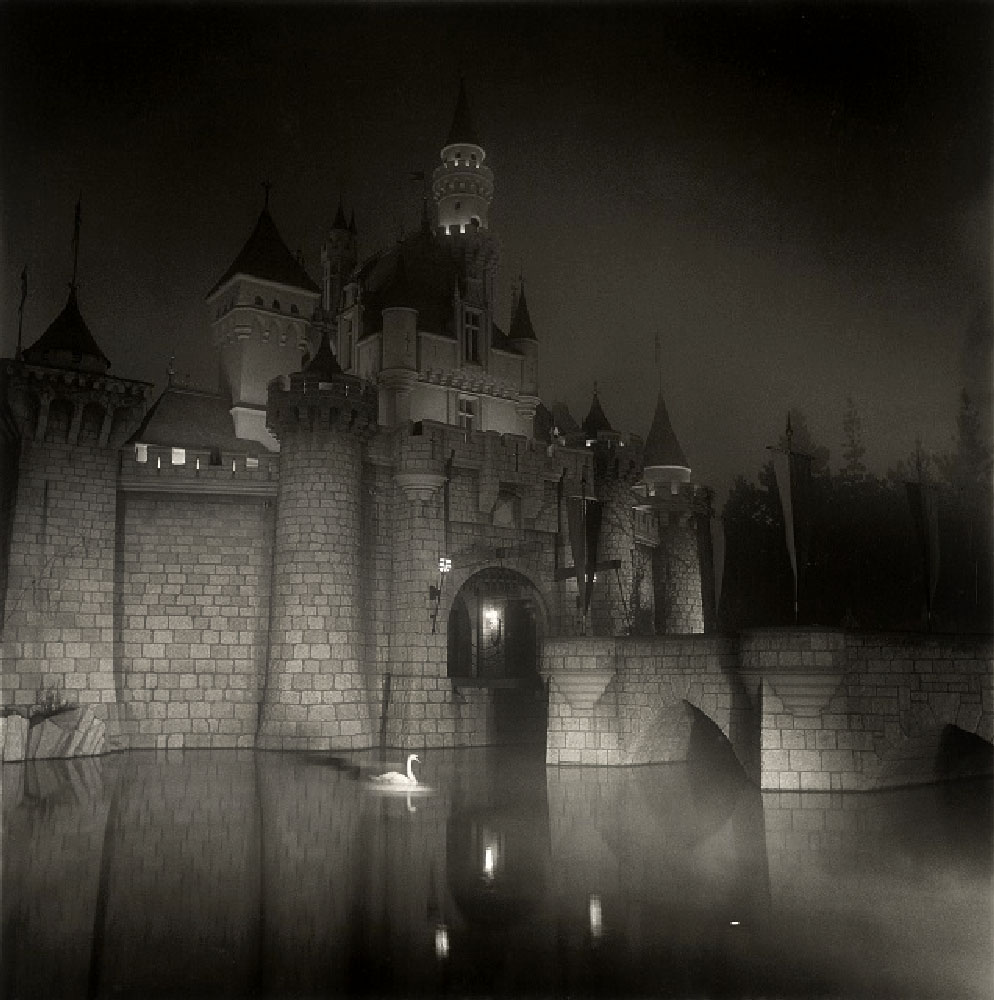
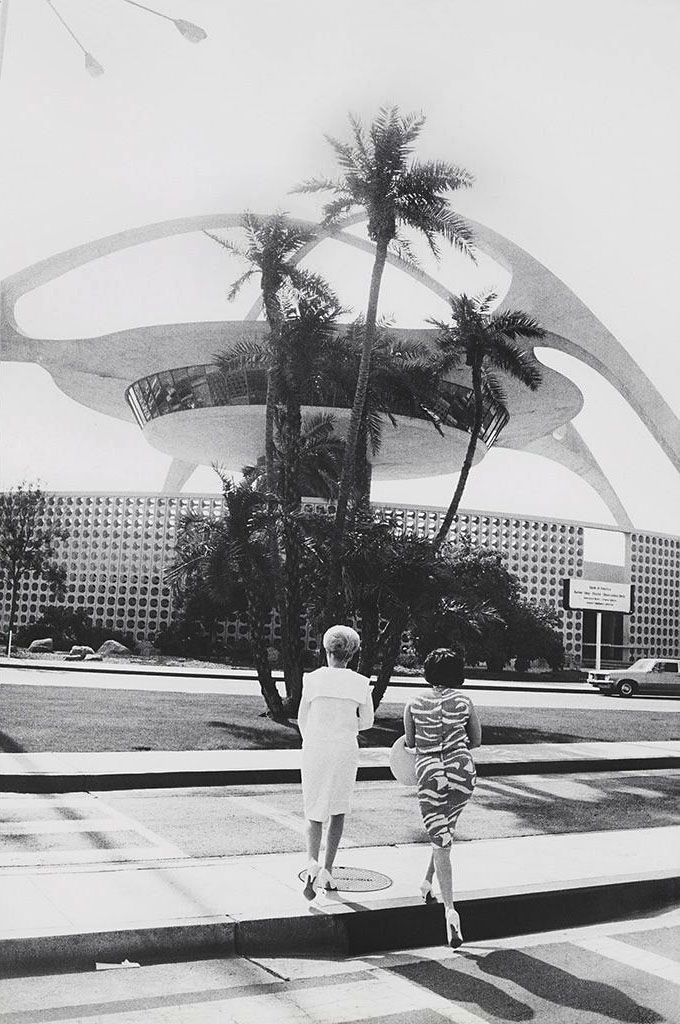
One of the most well-known works in the exhibition is Garry Winogrand’s photograph of two women walking towards the landmark theme building designed by Charles Luckman and William Pereira that has come to symbolise both Los Angeles International Airport and mid-century modern architecture in popular culture. Though a quintessential New Yorker, Winogrand made some of his most memorable photographs in Los Angeles, where he chose to settle in the final years of his life. Also included in the exhibition is Diane Arbus’ dreamily lit photograph of Sleeping Beauty Castle at Disneyland park in Anaheim. Although technically not located in either the city or the county of Los Angeles, Disneyland – and Arbus’ photograph – continues to capture the notion of entertainment and fantasy that has come to be so intrinsically associated with the city.
Other photographers in the In Focus: Los Angeles exhibition who produced the majority of their most creative work in the city include Edmund Teske, with his experimentation in the darkroom and his complex double solarisation process; Robert Heinecken, with images that are equally complex but often incorporate existing printed materials, such as negatives; Anthony Hernandez, whose portraits of Angelenos on the street emphasise the isolation of the individual in an urban environment; and Anthony Friedkin, who combines his passions for surfing and the Southland beaches in his photographs. The inclusion of three photographs from Judy Fiskin’s earliest photographic series, Stucco (1973-1976), provided the impetus for a monographic presentation of the artist’s complete photographic work by Getty Publications. Entitled Some Aesthetic Decisions: The Photographs of Judy Fiskin and featuring an introductory essay by curator Virginia Heckert, the book will be published concurrently with this exhibition.
Press release from the J. Paul Getty Museum website
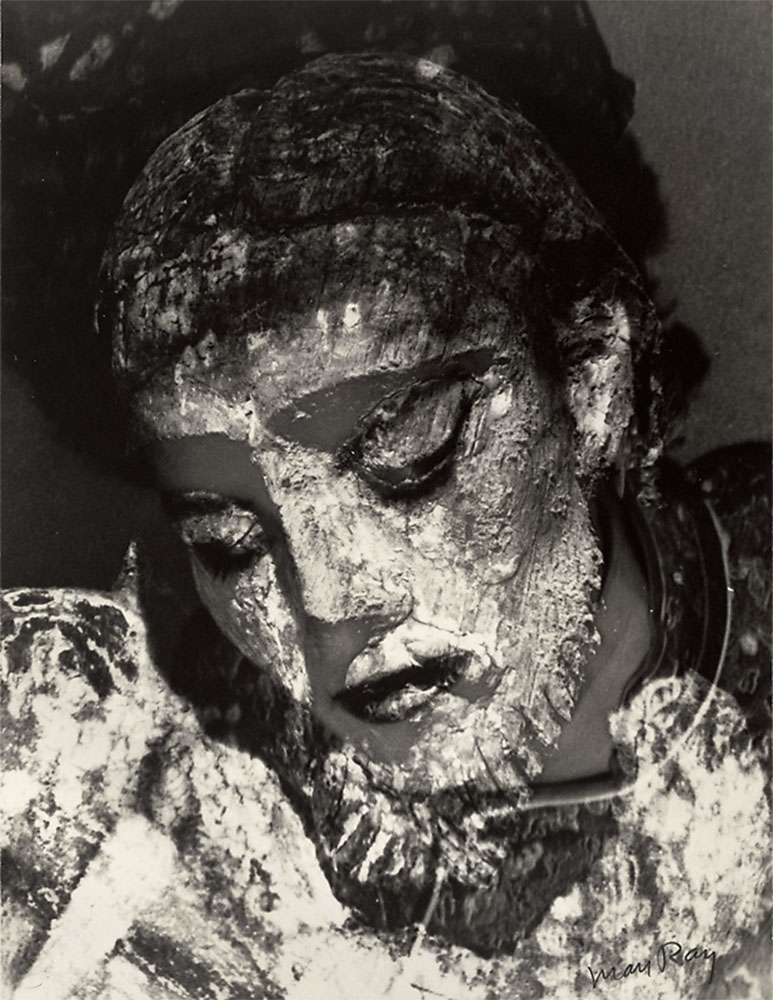
Man Ray (Emmanuel Radnitsky)(American, 1890-1976)
Juliet with Mud Mask
1945
Gelatin silver print
35.6 x 27.1cm
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
© Man Ray Trust
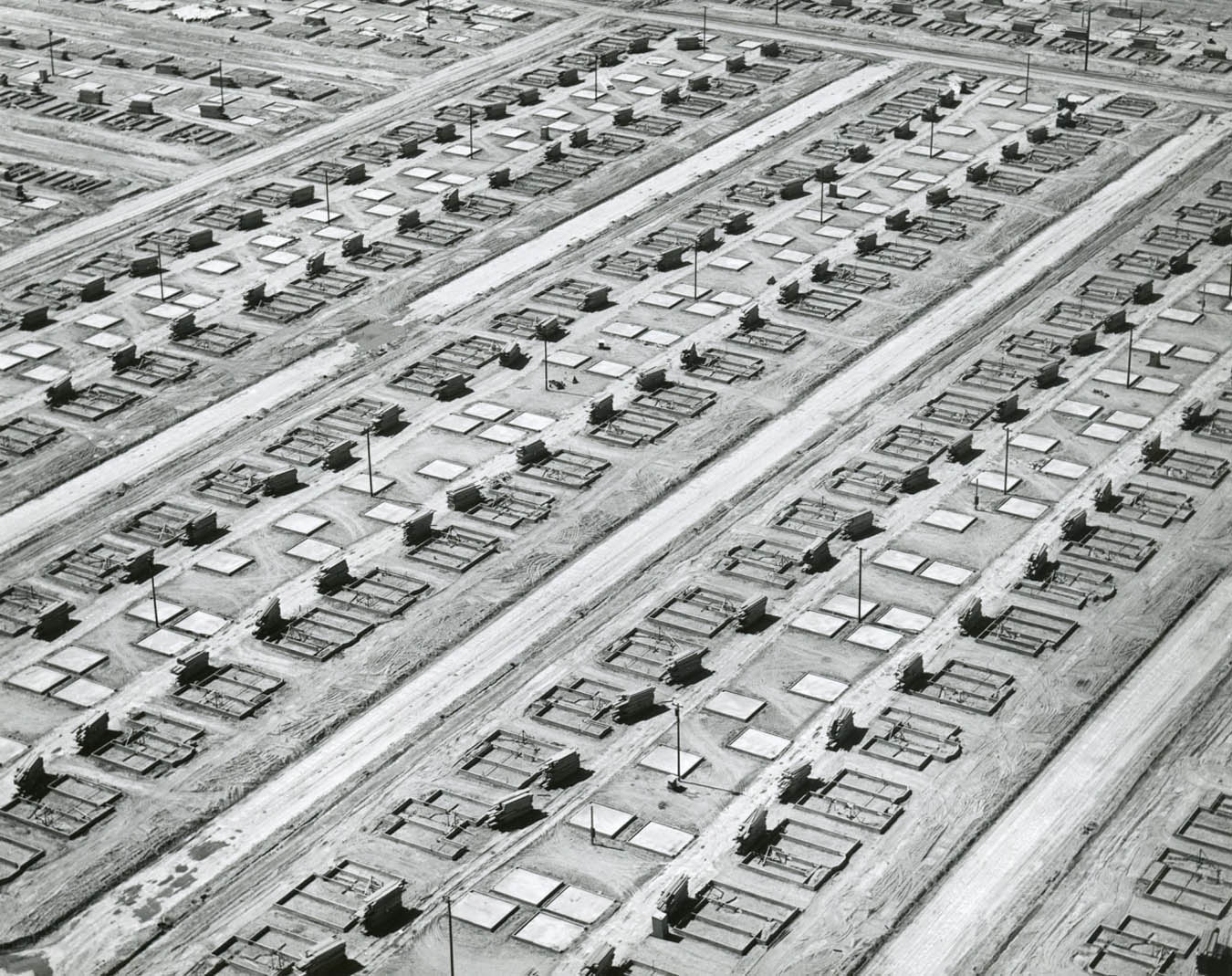
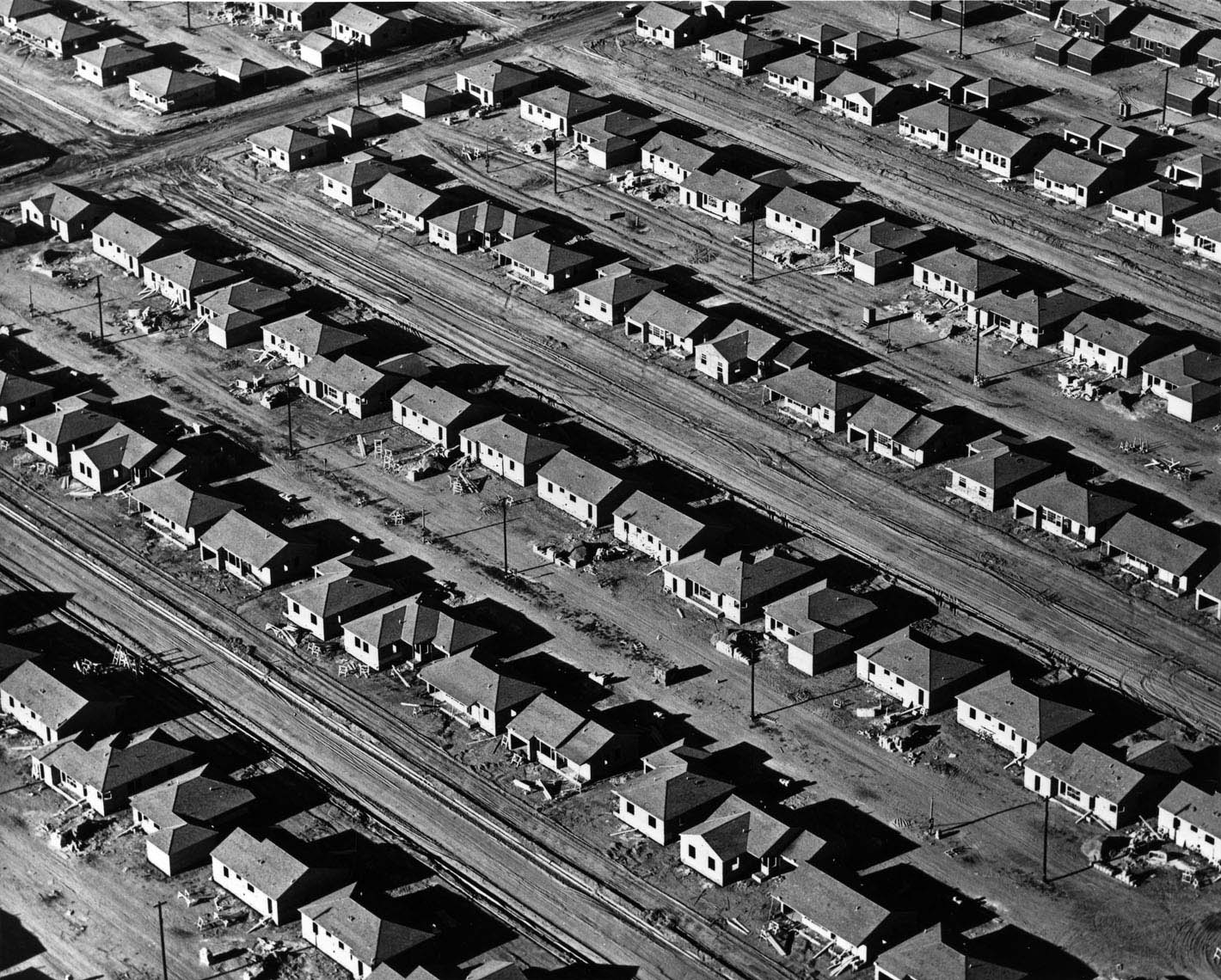
William Garnett (American, 1916-2006)
Foundations and Slabs, Lakewood, California
1950
Gelatin silver print
18.9 x 23.8cm
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
© Estate of William A. Garnett
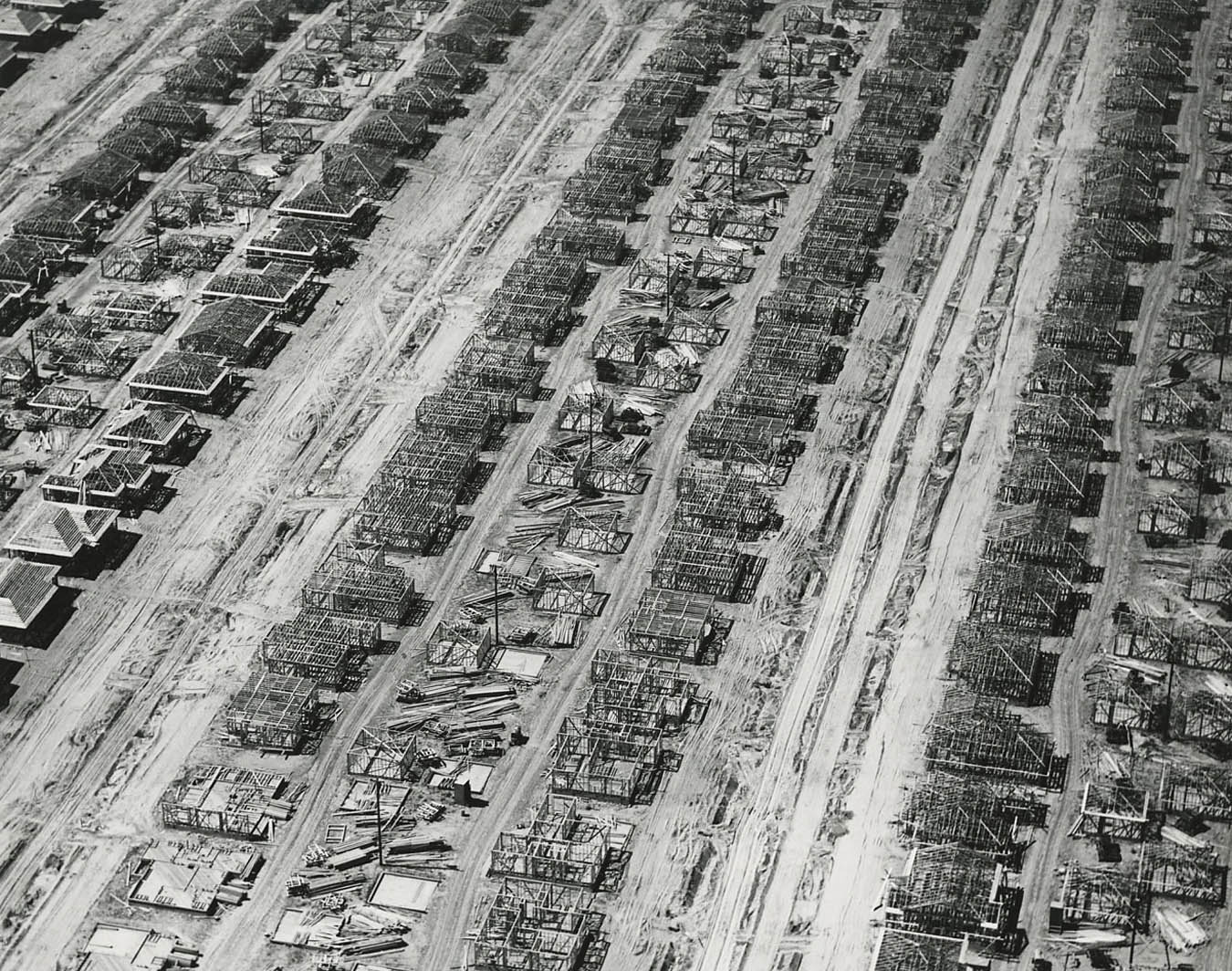
William Garnett (American, 1916-2006)
Framing, Lakewood, California
1950
Gelatin silver print
18.4 x 24.1cm
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
© Estate of William A. Garnett
William Garnett (American, 1916-2006)
Plaster and Roofing, Lakewood, California
1950
Gelatin silver print
18.4 x 24.1cm
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
© Estate of William A. Garnett
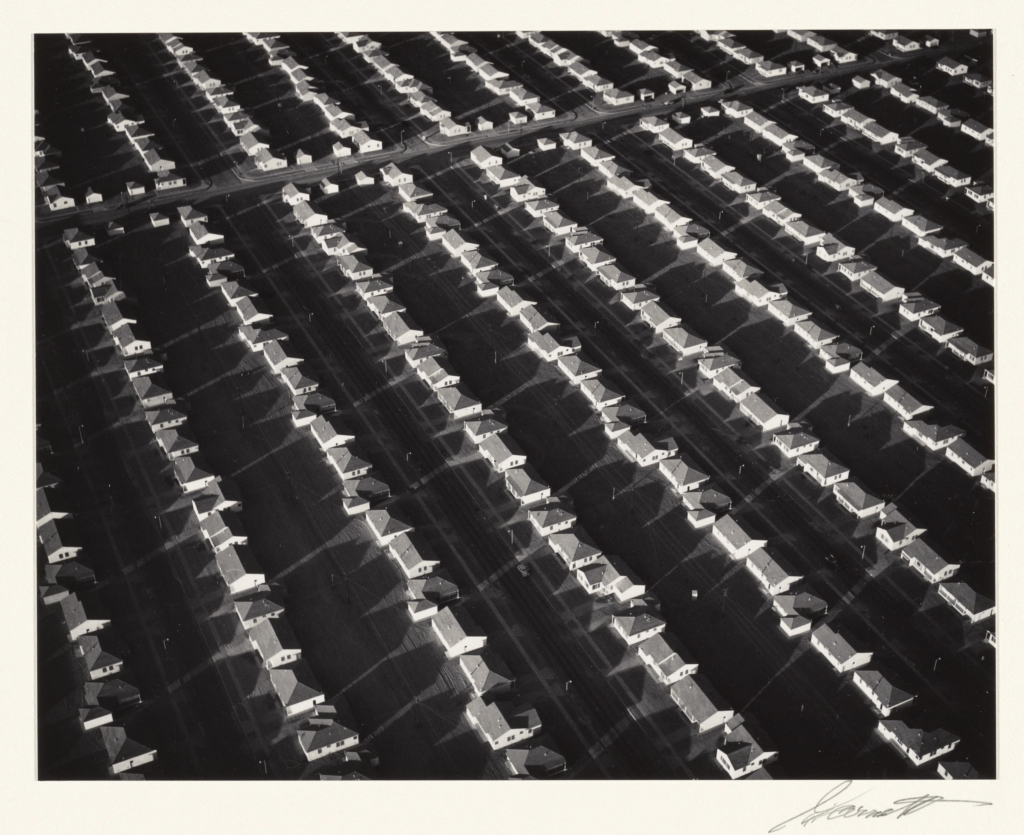
William A. Garnett (American, 1916-2006)
Finished Housing, Lakewood, California
1950
Gelatin silver print
7 3/8 x 9 7/16 in
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
© Estate of William A. Garnett
The reduced scale and regular spacing of shapes lend a toy-like quality to Garnett’s suite of prints depicting construction phases of tract housing in the Los Angeles County suburb of Lakewood. The deep shadows, overall patterning, and dramatic diagonals that slice through each composition introduce a sophisticated sense of design and abstraction. After studying photography at Art Center College of Design and military service during World War II, William Garnett learned to fly so that he could photograph his subjects from his Cessna 170-B airplane. Although he was hired by developers to document the construction of 17,500 affordable single-family residences in Lakewood, the majority of his aerial photographs depict the beauty of America’s landscape.
Text from Pacific Standard Time at the Getty
Diane Arbus (American, 1923-1971)
A Castle in Disneyland
Negative, 1962; print, 1973
Gelatin silver print
24 x 24cm
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
© Estate of Diane Arbus
Grant Mudford (Australian, b. 1944)
Los Angeles (US 257/10a)
Negative, 1976; print, 1980
Gelatin silver print
19 1/4 x 13 1/8 in
© Grant Mudford
After working for ten years as a commercial photographer, Sydney native Grant Mudford received funding from the Australia Council for the Arts, enabling him to travel throughout the United States to pursue personal work. Mudford’s love of architecture – particularly the vernacular, often anonymous structures of urban America – is evident in the photographs he produced. His head-on depictions of the façades of simple commercial buildings are enlivened by signage, the play of light and shade, the placement of doors and windows, or, as in this image, the rich variety of textures.
Text from Pacific Standard Time at the Getty
Joe Deal (American, 1947-2010)
Backyard, Diamond Bar, California
1980
Gelatin silver print
11 3/16 x 11 1/4 in
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
© Joe Deal
Joe Deal rose to prominence in the mid-1970s when work he made as a graduate student at the University of New Mexico was included in the exhibition New Topographics: Photographs of a Man-Altered Landscape (1975). From 1976 to 1989, he taught photography at the University of California, Riverside, where he was instrumental in establishing a photography program and developing the university-affiliated California Museum of Photography. His photographs of Diamond Bar feature backyards of this primarily residential suburb located at the junction of the Pomona and Orange freeways in eastern Los Angeles County. Deal’s implementation of a slightly elevated perspective that eliminates the horizon line and provides a view into neighbouring yards effectively conveys the close quarters of life in a master-planned community.
Text from Pacific Standard Time at the Getty
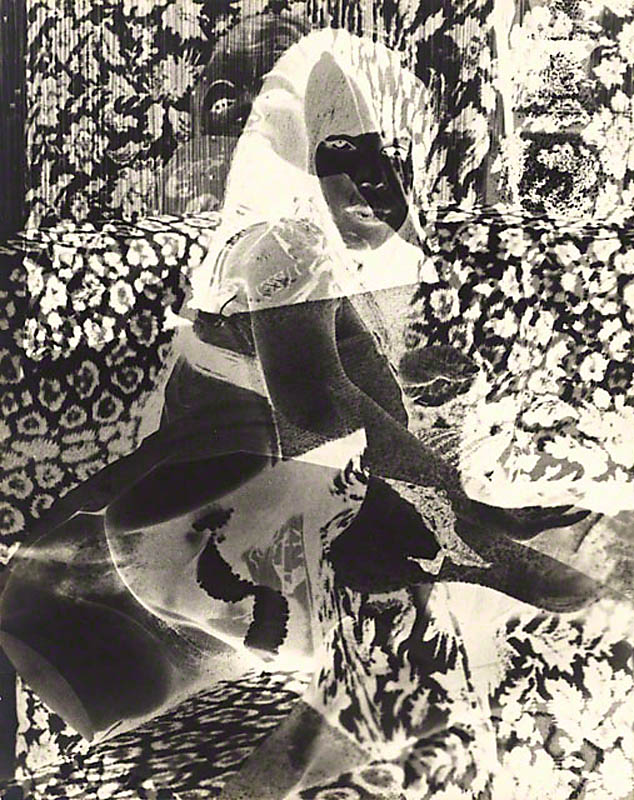
Robert Heineken (American, 1931-2006)
Untitled (Studies #7)
1970
Gelatin silver print
9 15/16 x 7 15/16 in.
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
© The Estate of Robert Heineken
Garry Winogrand (American, 1928-1984)
Los Angeles International Airport
1964
Gelatin silver print
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
© 1984 The Estate of Garry Winogrand
“It is immediately apparent that no city has ever been produced by such an extraordinary mixture of geography, climate, economics, demography, mechanics and culture; nor is it likely that an even remotely similar mixture will ever occur again.” ~ Reyner Banham, Los Angeles: The Architecture of Four Ecologies, 1971
This exhibition features photographs – made between 1945 and 1980 – from the Museum’s collection that represent diverse responses to the city of Los Angeles as a subject and to photography as a medium for documentary and creative expression. It is loosely grouped around the themes of experimental photography, vernacular architecture, car culture, and fantasy and the film industry.
Both iconic and relatively unknown works are included. One of the best known is Garry Winogrand’s image of two women walking towards the Theme Building at L.A. International Airport (see image above). Though a quintessential New Yorker, Winogrand settled in Los Angeles near the end of his life.
Experimental Photography
With its reclining figure set against a patterned background, Robert Heineken’s image recalls the odalisques of French painter Henri Matisse (see image above). To Heineken, however, traditional subjects and techniques were of little interest. He created this camera-less photograph by using a page torn from a magazine as the negative. This allowed light to pass through and merge depictions on both sides of the page into a single image with reversed tones.
In 1963, Heineken founded the photography program at the University of California, Los Angeles. He forged new directions in photography, utilising strategies of manipulation and appropriation to address themes of consumer culture and sexual politics.
Vernacular Architecture
Judy Fiskin’s propensity to backlight her subjects makes it difficult to read the details in the modest examples of vernacular architecture found in Westside neighbourhoods of Los Angeles that she photographed for her Stucco series. Viewers may be inclined to squint against the harsh light of Southern California that Fiskin makes so palpable. Nevertheless, the small scale of her images, contained by the black edges of the negative, encourages close viewing.
After completing graduate studies in art history at UCLA, Fiskin joined the faculty of the California Institute of Arts in 1977.
Car Culture
A native of Los Angeles, following two years of study at East Los Angeles College and two years of service in the U.S. Army, Anthony Hernandez took up photography in earnest around 1970.
For this image, Hernandez preset his 35mm camera so that objects within a specific range would be in focus. Then, while walking the streets of downtown Los Angeles, he swung the camera to his eye for a fraction of a second to capture fellow pedestrians as well as the ambient mood of a city more typically experienced from the driver’s seat (see image below).
Fantasy and the Film Industry
Los Angeles native Anthony Friedkin took up photography about the same time he learned to surf, and was already an accomplished photographer by age 16. He then studied at Art Center College of Design and the University of California, Los Angeles.
Friedkin began working as a still photographer for motion pictures in 1975. His depiction of row after row of film cans might be viewed as a historical document of a medium that has been replaced by new technology (see image below).
Anonymous. “In Focus: Los Angeles, 1945-1980,” on the J. Paul Getty Museum website Nd [Online] Cited 18/10/2024
Anthony Hernandez (American, b. 1947)
Los Angeles #3
1971
Gelatin silver print
7 3/4 x 11 13/16 in
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
Purchased in part with funds provided by the Photographs Council
© Anthony Hernandez
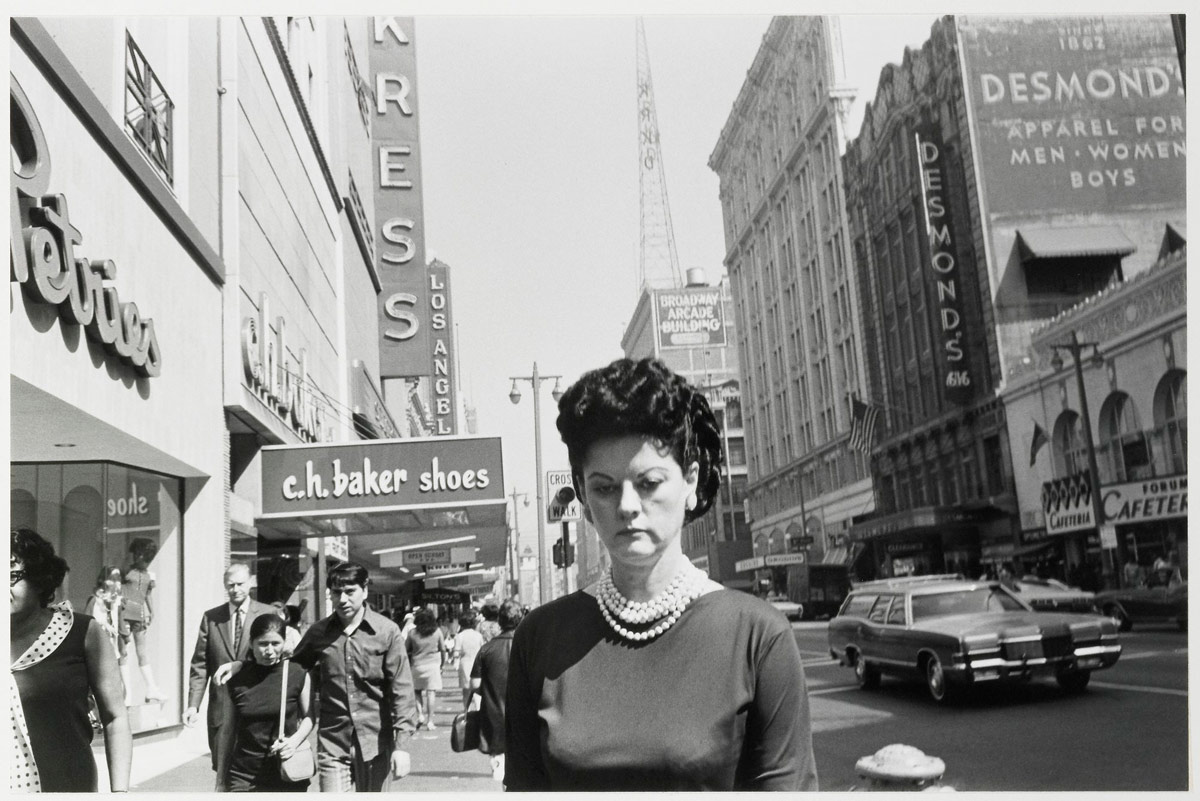
Following two years of study at East Los Angeles College and two years of service in the U.S. Army, Anthony Hernandez took up photography in earnest around 1970. For this image, he preset his 35mm camera so that objects within a specific range would be in focus. Then, while walking the streets of downtown Los Angeles, he swung the camera to his eye for a fraction of a second to capture fellow pedestrians as well as the ambient mood of a city more typically experienced from the driver’s seat. A native of Los Angeles, Hernandez has continued to photograph the city, addressing issues of community, shelter, and survival in his work.
Text from Pacific Standard Time at the Getty
Anthony Friedkin (American, b. 1949)
Film Can Library, Universal Studios
1978
Gelatin silver print
12 x 17 11/16 in
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
Gift of Sue and Albert Dorskind
© Anthony Friedkin
Anthony Friedkin began taking photographs at a young age and had already published his work by the time he was 16. He nonetheless found it important to study photography seriously and did so at Art Center College of Design and the University of California, Los Angeles. Employment as a still photographer for motion pictures beginning in 1975 undoubtedly prepared him to create a portfolio of images of Universal Studios a few years later. His depiction of row after row of film cans might be viewed as a historical document of a medium that has been replaced by new technology. Friedkin’s continued commitment to shooting black-and-white film that he develops and prints in his own darkroom has become increasingly rare.
Text from Pacific Standard Time at the Getty
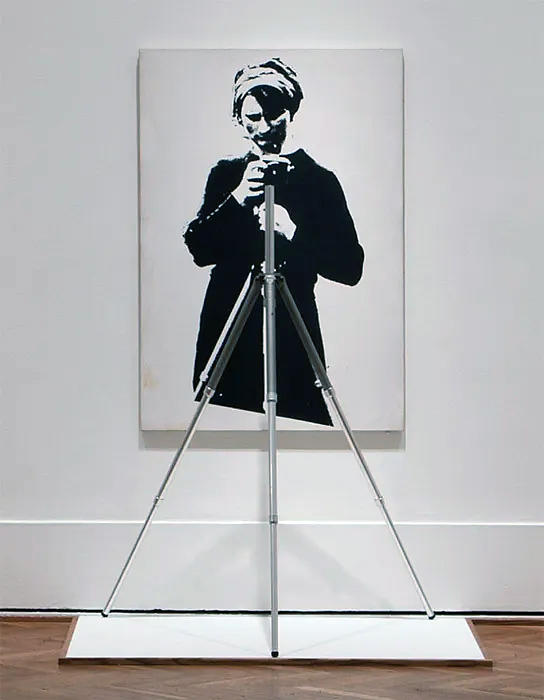
Darryl J. Curran (American, b. 1935)
Cocktails with Heinecken
about 1974
Gelatin silver print
9 1/4 x 14 in
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
Gift of Darryl J. Curran
© Darryl J. Curran
After completing his undergraduate degree in design at the University of California, Los Angeles, Darryl Curran entered the school’s newly established photography program, studying with Robert Heinecken, who is positioned toward the center of this image in a black turtleneck. The repeated printing of two frames is typical of Curran’s approach to the photographic medium and the ease with which he employs techniques and strategies derived from his background in printmaking and design. Another form of “mirroring” occurs in the placement of a Heineken beer bottle opposite Heinecken the artist. Curran founded the Department of Photography at California State University, Fullerton, where he taught from 1967 to 2001.
Text from Pacific Standard Time at the Getty
Henry Wessel Jr. (American, 1942-2018)
Los Angeles
1971
Gelatin silver on Dupont Veragam paper print
7 15/16 x 11 7/8 in
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
Purchased with funds provided by the Photographs Council of the J. Paul Getty Museum
© Henry Wessel
Henry Wessel began taking photographs while majoring in psychology at Pennsylvania State University in the mid-1960s. Travel throughout the United States in subsequent years led him to direct his gaze increasingly to details of human interaction with the natural and man-made environment. Wessel’s move to the West Coast in the early 1970s inspired him to incorporate light and climate into his work. His inclusion in the seminal exhibition New Topographics: Photographs of a Man-Altered Landscape, organised in 1975 by the George Eastman House in Rochester, New York, solidified his reputation as a keen observer of the American topography. In this image, electrical and telephone lines tether a row of modest residences to a single utility pole.
Text from Pacific Standard Time at the Getty
The J. Paul Getty Museum
1200 Getty Center Drive
Los Angeles, California 90049
Opening hours:
Daily 10am – 5pm








































































![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. [Ruins of the Hiroshima Prefectural Commercial Exhibition Hall (A-Bomb Dome)] October 24, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Ruins of the Hiroshima Prefectural Commercial Exhibition Hall (A-Bomb Dome)]' October 24, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/3-hgz-2006_1_33-web.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[View of burned-over area with Hiroshima Kirin Beer Hall at far right]' October 16, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[View of burned-over area with Hiroshima Kirin Beer Hall at far right]' October 16, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/view-of-burned-over-area-with-hiroshima-kirin-beer-hall.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Ruins of Shima Surgical Hospital, Hiroshima]' October 24, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Ruins of Shima Surgical Hospital, Hiroshima]' October 24, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/ruins-of-shima-surgical-hospital.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Group of people near damaged trolley cars, Hiroshima]' October 31, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Group of people near damaged trolley cars, Hiroshima]' October 31, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/group-of-people-near-damaged-trolley-cars.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. [Distorted steel-frame structure of Odamasa Store, Hiroshima] November 20, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Distorted steel-frame structure of Odamasa Store, Hiroshima]' November 20, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/1-hgz-2006_1_68-web.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Reinforced-concrete fire shutter in cast wall of Yasuda Life Insurance Company, Hiroshima branch]' November 15, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Reinforced-concrete fire shutter in cast wall of Yasuda Life Insurance Company, Hiroshima branch]' November 15, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/reinforced-concrete-fire-shutter-in-cast-wall-of-yasuda-life-insurance-company.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. [Ruins of Chugoku Coal Distribution Company or Hiroshima Gas Company] November 8, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Ruins of Chugoku Coal Distribution Company or Hiroshima Gas Company]' November 8, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/7-hgz-035_hiroshima-web.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. [Remains of a school building] November 17, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Remains of a school building]' November 17, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/6-hgz-065_hiroshima-web.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. ["Shadow" of a hand valve wheel on the painted wall of a gas storage tank; radiant heat instantly burned paint where the heat rays were not obstructed, Hiroshima] October 14 - November 26, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '["Shadow" of a hand valve wheel on the painted wall of a gas storage tank; radiant heat instantly burned paint where the heat rays were not obstructed, Hiroshima]' October 14 - November 26, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/4-hgz-2006_1_431-web.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. [Interior of Hiroshima City Hall auditorium with undamaged walls and framing but spalling of plaster and complete destruction of contents by fire] November 1, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Interior of Hiroshima City Hall auditorium with undamaged walls and framing but spalling of plaster and complete destruction of contents by fire]' November 1, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/8-hgz-031_hiroshima-web.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Ruins of Sumitomo Fire Insurance Company, Hiroshima branch]' October 24, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Ruins of Sumitomo Fire Insurance Company, Hiroshima branch]' October 24, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/ruins-of-sumitomo-fire-insurance-company.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. [Rooftop view of atomic destruction, looking southwest, Hiroshima] October 31, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Rooftop view of atomic destruction, looking southwest, Hiroshima]' October 31, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/10-hgz-006_hiroshima-web.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Burned-over landscape north of ground zero in the vicinity of Hiroshima Castle]' October 31, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Burned-over landscape north of ground zero in the vicinity of Hiroshima Castle]' October 31, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/burned-over-landscape-north-of-ground-zero-in-the-vicinity-of-hiroshima-castle.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Interior with heavy spalling of cement plaster by fire in combustiible floor of Yasuda Life Insurance Company, Hiroshima branch]' November 1, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Interior with heavy spalling of cement plaster by fire in combustiible floor of Yasuda Life Insurance Company, Hiroshima branch]' November 1, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/interior-with-heavy-spalling-of-cement-plaster.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Damaged turbo-generator and electrical panel of Chugoku Electric Company, Minami Sendamachi Substation, Hiroshima]' November 18, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Damaged turbo-generator and electrical panel of Chugoku Electric Company, Minami Sendamachi Substation, Hiroshima]' November 18, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/damaged-turbo-generator-and-electrical-panel.jpg)
![United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Steel stairs warped by intense heat from burned book stacks of Asano Library, Hiroshima]' November 15, 1945 United States Strategic Bombing Survey, Physical Damage Division. '[Steel stairs warped by intense heat from burned book stacks of Asano Library, Hiroshima]' November 15, 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/11-hgz-193_hiroshima-web.jpg?w=650&h=790)













































































You must be logged in to post a comment.