Exhibition dates: 17th May – 4th October, 2015
Curators: Roxana Marcoci, Senior Curator, and Sarah Meister, Curator with Drew Sawyer, Beaumont and Nancy Newhall Curatorial Fellow, Department of Photography at MoMA
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Calle California. Vuelta de Rocha. La Boca
1931
Gelatin silver print, printed 1996
7 5/8 × 11 5/16″ (19.4 × 28.7cm)
IVAM, Institut Valencià d’Art Modern
The work of Greta Stern is the better known of these two artists (Ringl + Pit studio and the surreal, psychoanalytic 1950s work), but I find it is the underrated photographs of Horacio Coppola that are the gems in this posting.
It is a bit rough that Richard B. Woodward, commenting on the exhibition on the Collector Daily website (below), observes that with no production after 1938 it “raises suspicions that he was not an artist who sustained himself at a top level.” I beg to differ. Many illuminati have short, explosive and powerful careers before giving the game away, or changing to a different medium or form.
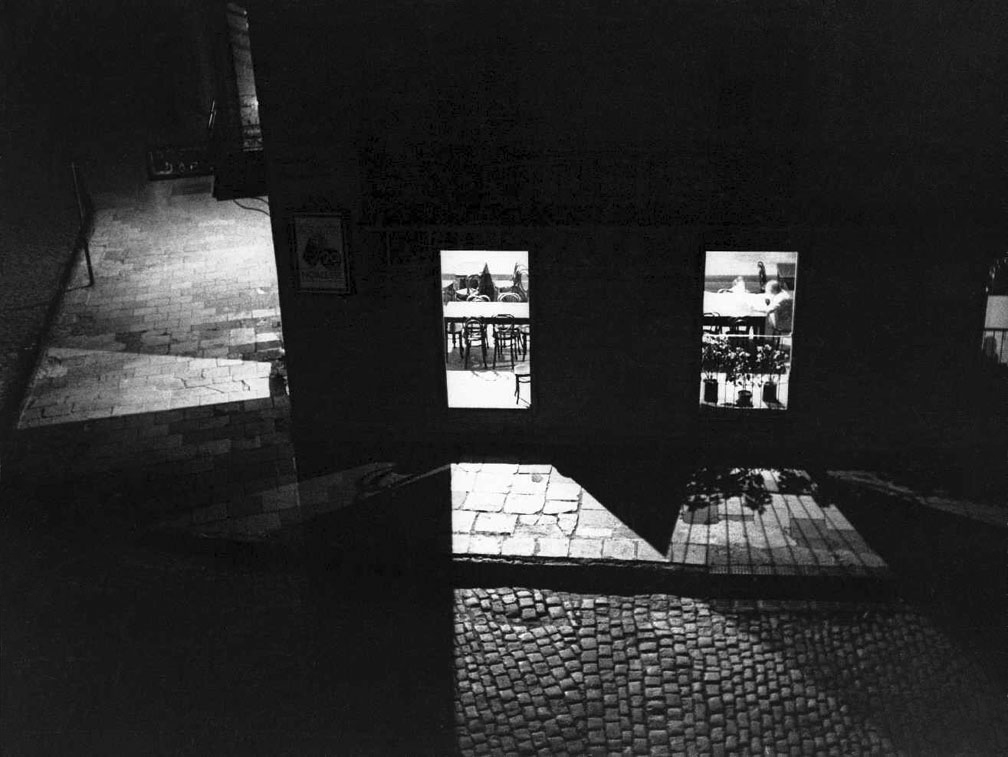
He also observes that, “Coppola failed to channel the nocturnal otherworldliness of the city found in Brassäi and Brandt, only a few of these photos have the haunted quality they achieved,” after the curators of the exhibition, in the catalogue, compare Coppola’s work to those two esteemed individuals. He cites a “sneaky street picture” from 1936 as evidence and instance of an image where Coppola captured a magical moment. I think both curators and critic are missing the point. Coppola is certainly NOT like Brassäi and Brandt in that his photographs at night are not ROMANTIC photographs of the nocturnal fabric of the city. Coppola’s images do NOT possess the kind of magic that Woodward is looking for (that of Brassai’s Paris at Night for example), that he believes should be there, simply because they are of a different order. But that does not make them any less valuable in terms of their insight and energy.
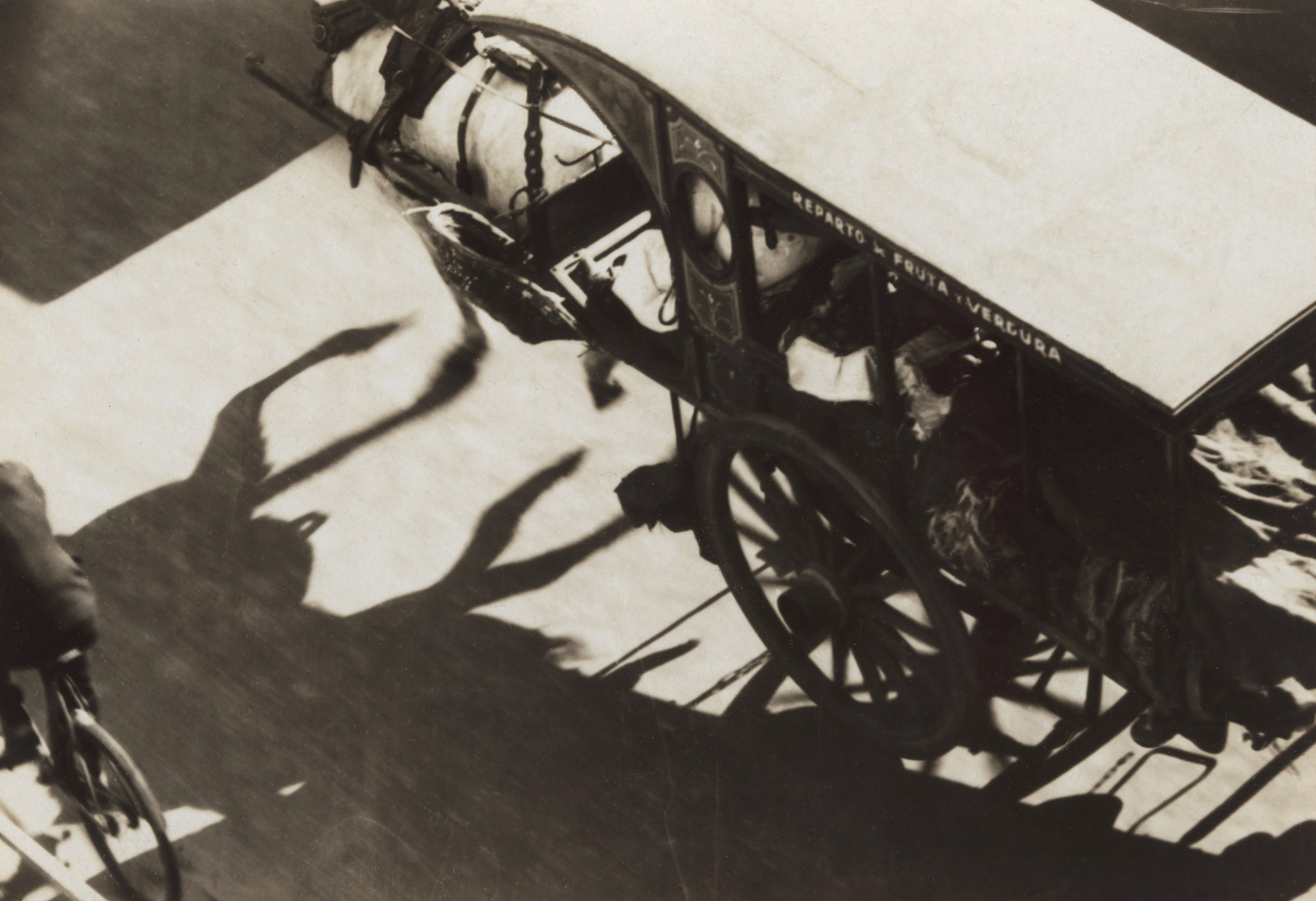
Coppola’s images, steeped in his training at the Bauhaus, are objective, modernist magic. By that I mean they possess a most uncanny use of form, of space and light. Day or night, he places his camera so carefully, in such a controlled and ego-less way, that the precision of his renditions is exquisite. For example, look at Calle Florida (1936, below). What seems an ordinary street, a photograph that anyone could have taken. But no! look again. That perfect rendition of shadow, darkness, movement and the spaces between the figures, The eye is led down the street to the vanishing point and then is released with all that pent up energy in to the V of the sky. Magnificent.
I wish I had more of his photographs to show you, especially his night shots. Coppola wasn’t a Walker Evans or a Paul Strand, certainly not a Kertész, Brassäi or Brandt because he simply was himself, with his own unique signature. He should NEVER be put down for that. I hope this wonderful artist starts to get the recognition he deserves.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Museum of Modern Art for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Buenos Aires
1931
Gelatin silver print
3 1/8 x 4 9/16″ (8 x 11.6cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Vital Projects Fund, Robert B. Menschel
“The catalog contends that Grete Stern and Horacio Coppola created a stunning body of work, but the show argues, in many ways, for two discrete bodies of work. What might have been accomplished instead of trying to insert two lesser known figures into the canon is to highlight what’s really interesting about their lives and careers: that they – and particularly Stern – were migratory and interdisciplinary, harbingers of the kinds of artistic practice we see today in which commerce, parenthood and politics can no longer be elided, and so they become part of the work. The museum could have showcased their work along with that of their friends and compatriots, from Bauhaus to Buenos Aires, from the literary world to the poets, writers, activists and psychoanalysts with whom they interacted and not just as mute players in this narrative. Now that would have been an extraordinary show.”
Martha Schwendener. “‘From Bauhaus to Buenos Aires: Grete Stern and Horacio Coppola,’ a Bicontinental Couple” on the NY Times website, May 28 2015
“Coppola (1906-2012), on the other hand, has no paper trail of distinction. Outside of his native Argentina, where he was an early convert to Modernism in the late 1920s and later an evangelist for the style, his name draws a blank in most art circles. Parr and Badger cite his Buenos Aires, published in 1937, in volume 2 of their photobook history. But not until 2011 were Coppola’s photographs exhibited in New York, and then only in an imported group show titled Light of Modernity in Buenos Aires (1929-1954) at the Nailya Alexander Gallery. Since then, nothing until now…
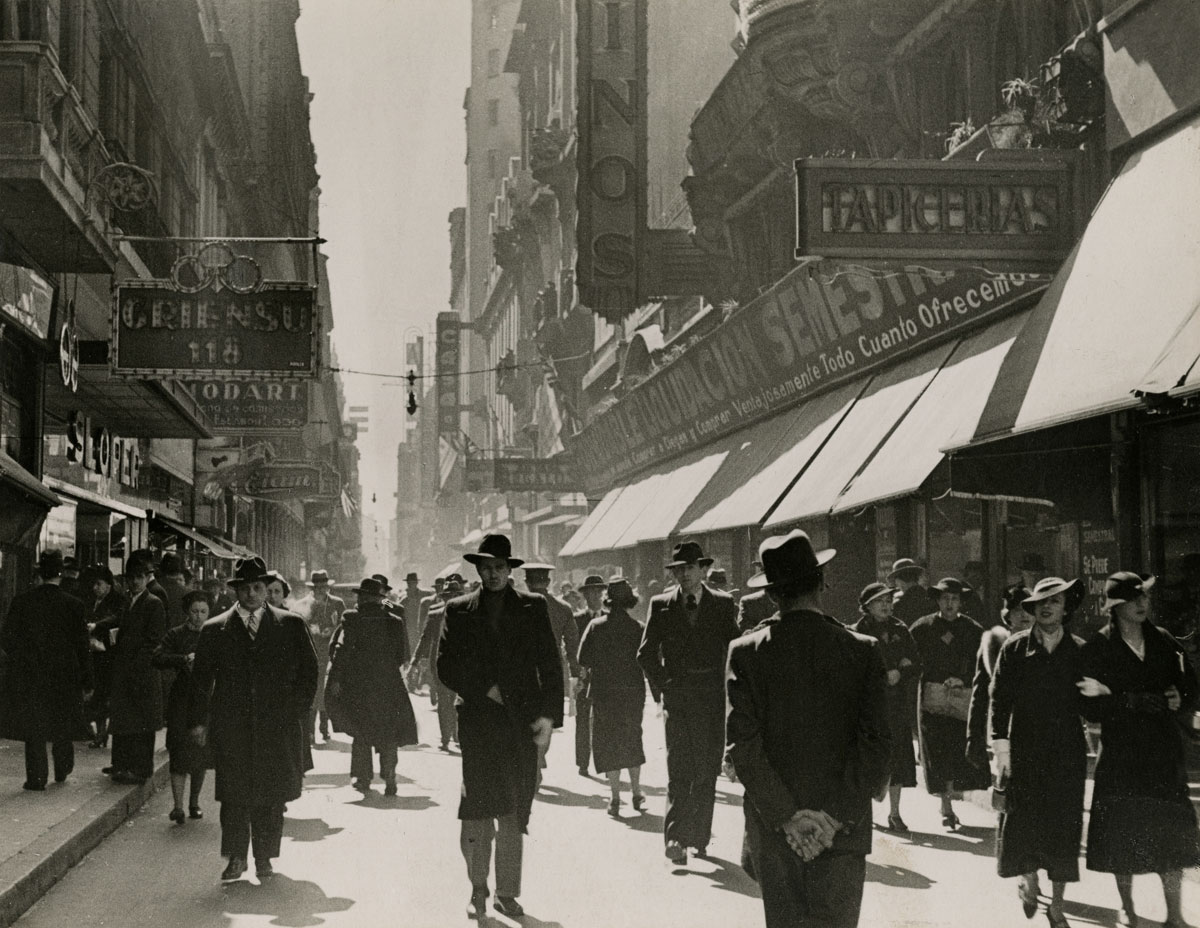
The wall of photographs in the next room, done after 1935 when he returned to Argentina – and the basis of the book Buenos Aires – are meant to present Coppola at the height of his powers. Meister puts these views of the Argentine capital – teeming with urban crowds on the streets or at racetracks, shopping at department stores, walking through illuminated streets at night – on a par with Brassäi’s of Paris and Brandt’s of London.
This is a stretch. Perhaps because the prints are hung salon-style, many of them too low for their details to be read, or, more likely, because Coppola failed to channel the nocturnal otherworldliness of the city found in Brassäi and Brandt, only a few these photos have the haunted quality they achieved. If I knew Buenos Aires and had an interior map of these places in my head, I might change my mind. But a sneaky street picture from 1936 of three passersby looking into the front windows of a bridal shop, which are filled with staged, idealised portraits of marriage bliss, is one of the few instances where Coppola captured a magical moment. The absence of anything he did after 1938 raises suspicions that he was not an artist who sustained himself at a top level.”
Richard B. Woodward. “From Bauhaus to Buenos Aires: Grete Stern and Horacio Coppola @MoMA” on the Collector Daily website June 17, 2015 [Online] Cited 01/10/2015. No longer available online
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Rivadivia between Salguero and Medrano
1931
Gelatin silver print, printed 1996
7 5/8 × 11 5/16″ (19.4 × 28.7cm)
IVAM, Institut Valencià d’Art Modern
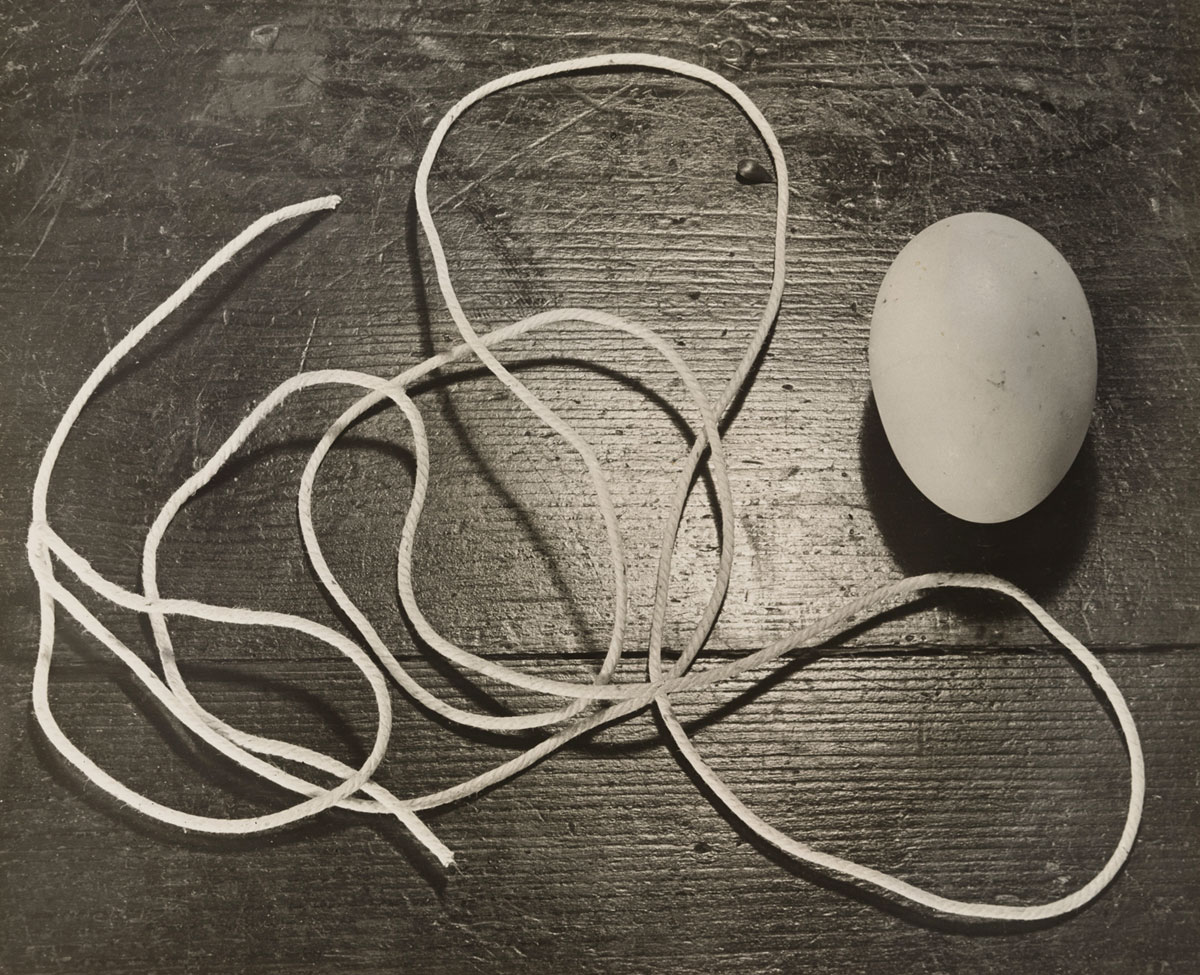
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Still Life with Egg and Twine
1932
Gelatin silver print
8 1/8 x 10 1/8″ (20.7 x 25.7cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection. Acquired through the generosity of Peter Norton
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
London
1934
Gelatin silver print
6 x 7 5/8″ (15.2 x 19.3cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Latin American and Caribbean Fund
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
London
1934
Gelatin silver print
5 11/16 x 7 3/8″ (14.5 x 18.7cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Committee on Photography Fund
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Avenida Diaz Velez al 4800
1936
Gelatin silver print, printed 1952
16 3/4 x 23 1/2″ (42.5 x 59.7cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Agnes Rindge Claflin Fund
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Avenida Diaz Velez al 4800 (detail)
1936
Gelatin silver print, printed 1952
16 3/4 x 23 1/2″ (42.5 x 59.7cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Agnes Rindge Claflin Fund
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Balneario Municipal
1936
Gelatin silver print
8 1/4 x 10 7/16″ (21 x 26.5cm)
Estate of Horacio Coppola; courtesy Galería Jorge Mara – La Ruche, Buenos Aires
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Balneario Municipal (detail)
1936
Gelatin silver print
8 1/4 x 10 7/16″ (21 x 26.5cm)
Estate of Horacio Coppola; courtesy Galería Jorge Mara – La Ruche, Buenos Aires
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Calle Florida
1936
Gelatin silver print
5 11/16 × 7 5/16″ (14.5 × 18.5cm)
Collection Léticia and Stanislas Poniatowski
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Calle Florida (detail)
1936
Gelatin silver print
5 11/16 × 7 5/16″ (14.5 × 18.5cm)
Collection Léticia and Stanislas Poniatowski
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Directorio and J.M. Moreno
1936
Gelatin silver print
6 5/8 × 7 13/16″ (16.8 × 19.8cm)
Museo Nacional Centro de Arte Reina Sofía, Madrid
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Plaza San Martín from Kavanagh
1936
Gelatin silver print
7 5/16 x 10 1/2″ (18.5 x 26.7cm)
Private Collection
From Bauhaus to Buenos Aires: Grete Stern and Horacio Coppola is the first major exhibition of the German-born Grete Stern and the Argentinean Horacio Coppola, two leading figures of avant-garde photography who established themselves on both sides of the Atlantic. In Berlin in 1927, Stern began taking private classes with Walter Peterhans, who was soon to become head of photography at the Bauhaus. A year later, in Peterhans’s studio, she met Ellen (Rosenberg) Auerbach, with whom she opened a pioneering studio specialising in portraiture and advertising. Named after their childhood nicknames, the studio ringl + pit embraced both commercial and avant-garde loyalties, creating proto-feminist works.
In Buenos Aires during the same period, Coppola initiated his photographic experimentations, exploring his surroundings and contributing to the discourse on modernist practices across media in local cultural magazines. In 1929 he founded the Buenos Aires Film Club to introduce the most advanced foreign films to Argentine audiences. His early works show a burgeoning interest in new modes of photographic expression that led him to the Bauhaus in 1932, where he met Stern and they began their joint history.
Following the close of the Bauhaus and the rising threat of the Nazi powers in 1933, Stern and Coppola fled Germany. Stern arrived first in London, where her friends included activists affiliated with leftist circles and where she made her now iconic portraits of German exiles. After traveling through Europe, camera in hand, Coppola joined Stern in London, where he pursued a modernist idiom in his photographs of the fabric of the city, tinged alternately with social concern and surrealist strangeness.
In the summer of 1935, Stern and Coppola embarked for Buenos Aires where they mounted an exhibition in the offices of the avant-garde magazine Sur, announcing the arrival of modern photography in Argentina. The unique character of Buenos Aires was captured in Coppola’s photographic encounters from the city’s centre to its outskirts and in Stern’s numerous portraits of the city’s intelligentsia. The exhibition ends in the early 1950s, with Stern’s forward-thinking Sueños (Dreams), a series of photomontages she contributed to the popular women’s magazine Idilio, portraying women’s dreams with urgency and surreal wit.
The exhibition is accompanied by a major publication edited by Roxana Marcoci and Sarah Meister with a selection of original texts by Stern and Coppola translated into English by Rachel Kaplan. The catalogue will consist of three essays on the artists written by the exhibition curators and scholar Jodi Roberts.
Text from the MoMA website
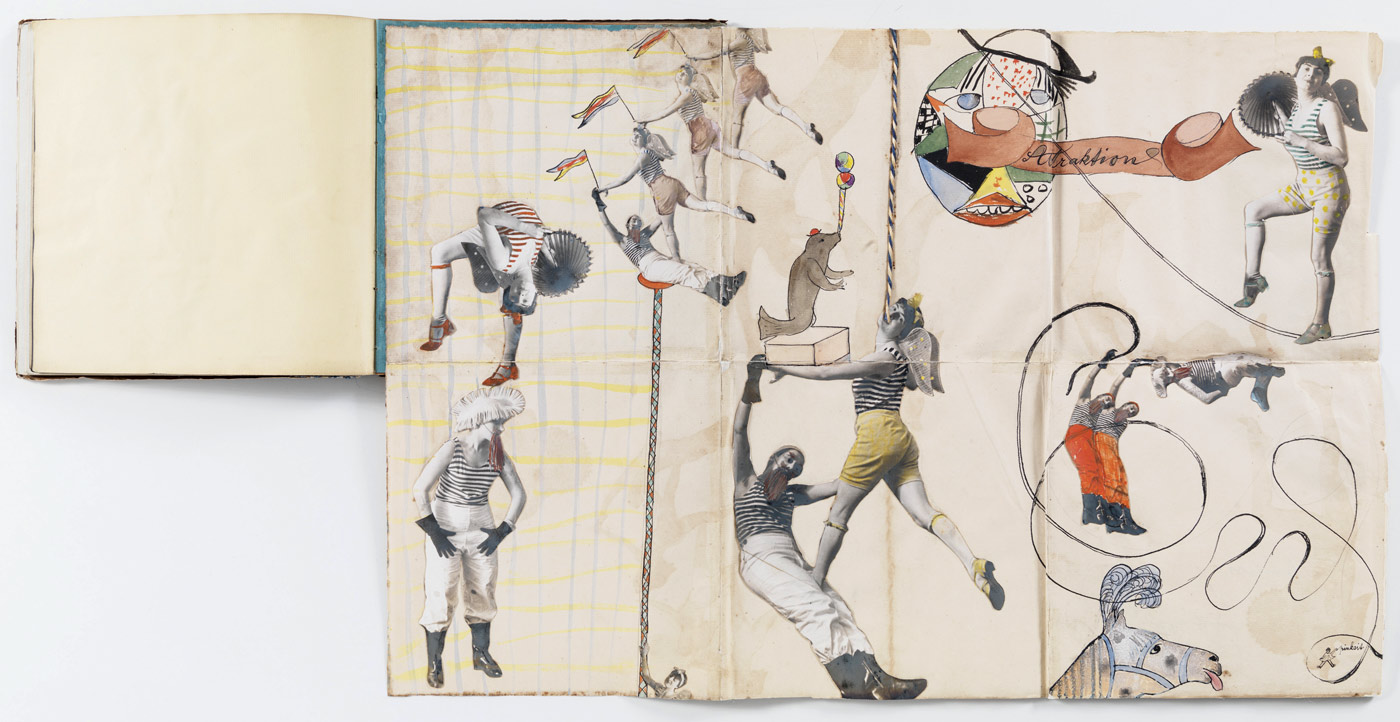
Ringl + Pit (German)
Ringlpitis
1931
Artist book with collage
7 7/8 x 7 7/8″ (20 x 20cm)
Estate of Horacio Coppola, Buenos Aires

Ringl + Pit (German)
Ringlpitis (detail)
1931
Artist book with collage
7 7/8 x 7 7/8″ (20 x 20cm)
Estate of Horacio Coppola, Buenos Aires
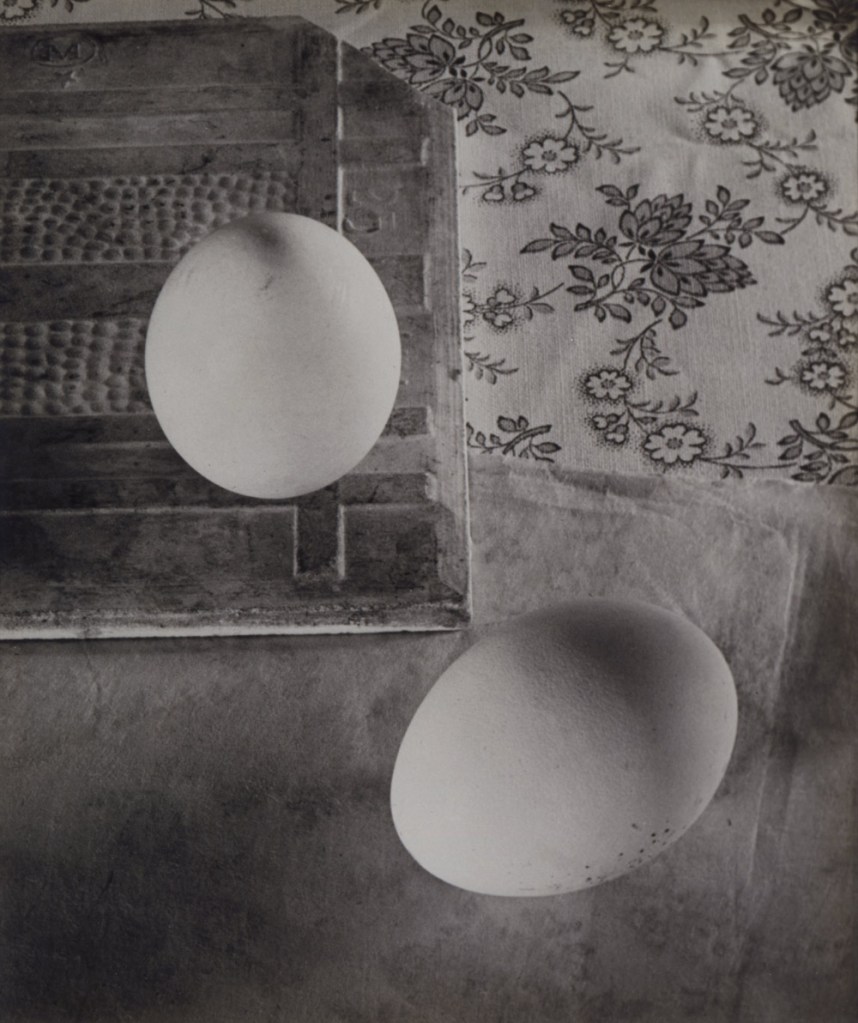

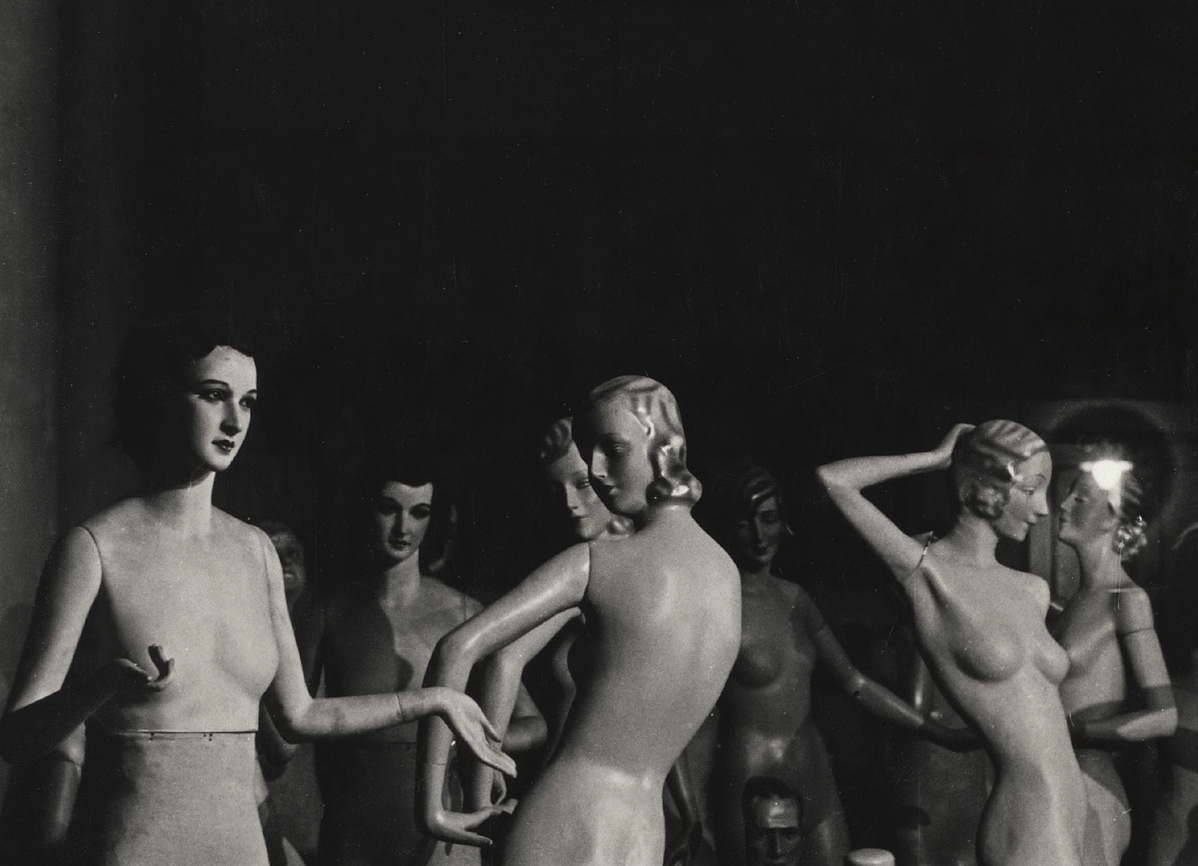
Ringl + Pit (German)
Columbus’ Egg
1930
Gelatin silver print
9 1/4 x 7 7/8″ (23.5 x 20cm)
Collection Helen Kornblum
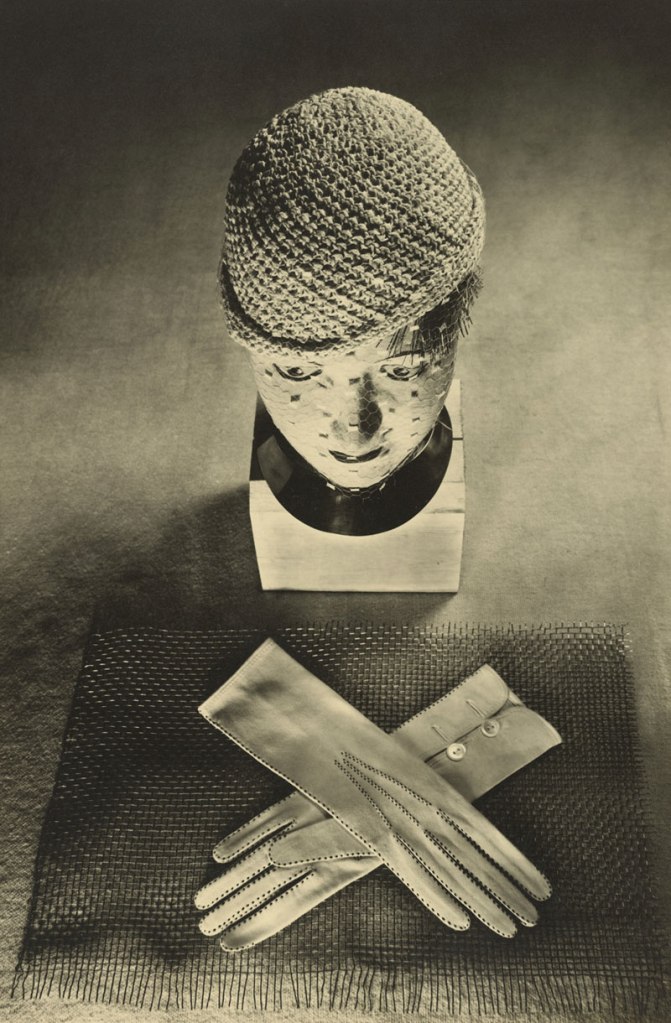

Ringl + Pit (German)
Hat and Gloves
1930
Gelatin silver print
Image: 14 7/8 x 9 3/4″ (37.8 x 24.8cm)
Sheet: 15 11/16 x 10 1/2″ (39.8 x 26.7cm)
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles

Ringl + Pit (German)
Ellen Auerbach
Grete Stern
Soapsuds
1930
Gelatin silver print
7 x 6 1/4″ (17.8 x 15.9cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Acquired through the generosity of Roxann Taylor
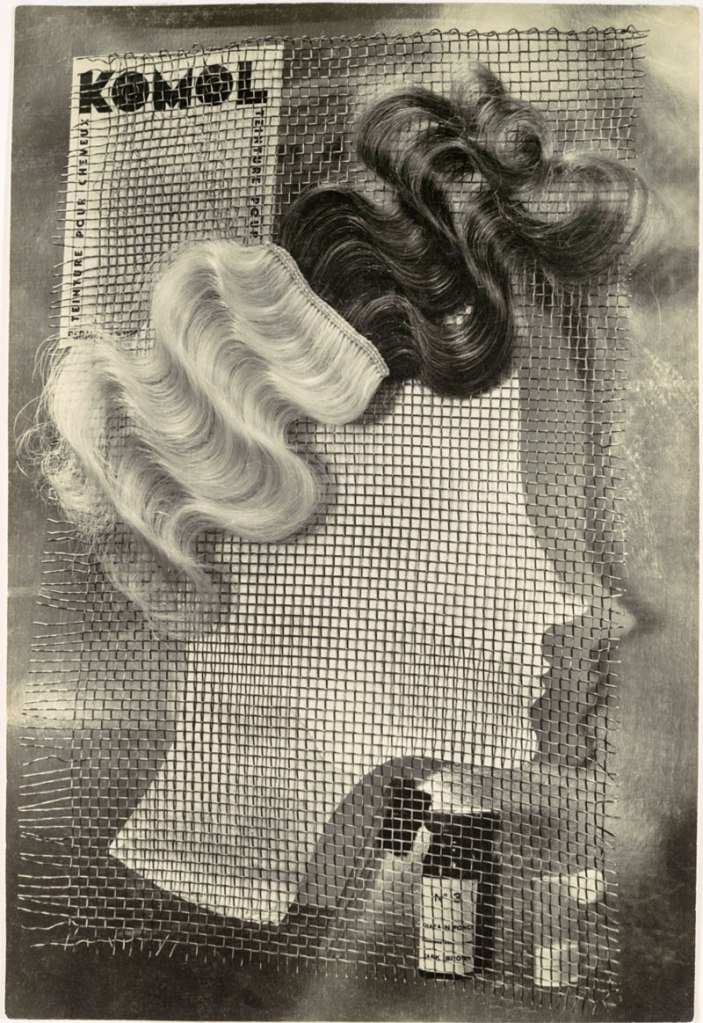

Ringl + Pit (German)
Komol
1931
Gelatin silver print
14 1/8 x 9 5/8″ (35.9 x 24.4cm)
The Metropolitan Museum of Art. Gift of Ford Motor Company and John C. Waddell
Grete Stern (Argentine born Germany, 1904-1999)
Self-Portrait
1943
Gelatin silver print, printed 1958
11 x 8 11/16″ (28 x 22cm)
Estate of Horacio Coppola, Buenos Aires
The Museum of Modern Art has organised the first major exhibition to examine the individual accomplishments and parallel developments of two of the foremost practitioners of avant-garde photography, film, advertising, and graphic design in the first half of the 20th century: Grete Stern (German, 1904-1999) and Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012). From Bauhaus to Buenos Aires: Grete Stern and Horacio Coppola will be on view May 17 through October 4, 2015, and features more than 300 works gathered from museums and private collection across Europe and the Americas – many of which have never before been exhibited in the United States. These include more than 250 vintage photographs and photomontages, 40 works of original typographic design and award-winning advertising materials, 26 photobooks and periodicals, and four experimental 16mm films. From Bauhaus to Buenos Aires is organised by Roxana Marcoci, Senior Curator, and Sarah Meister, Curator; with Drew Sawyer, Beaumont and Nancy Newhall Curatorial Fellow, Department of Photography.
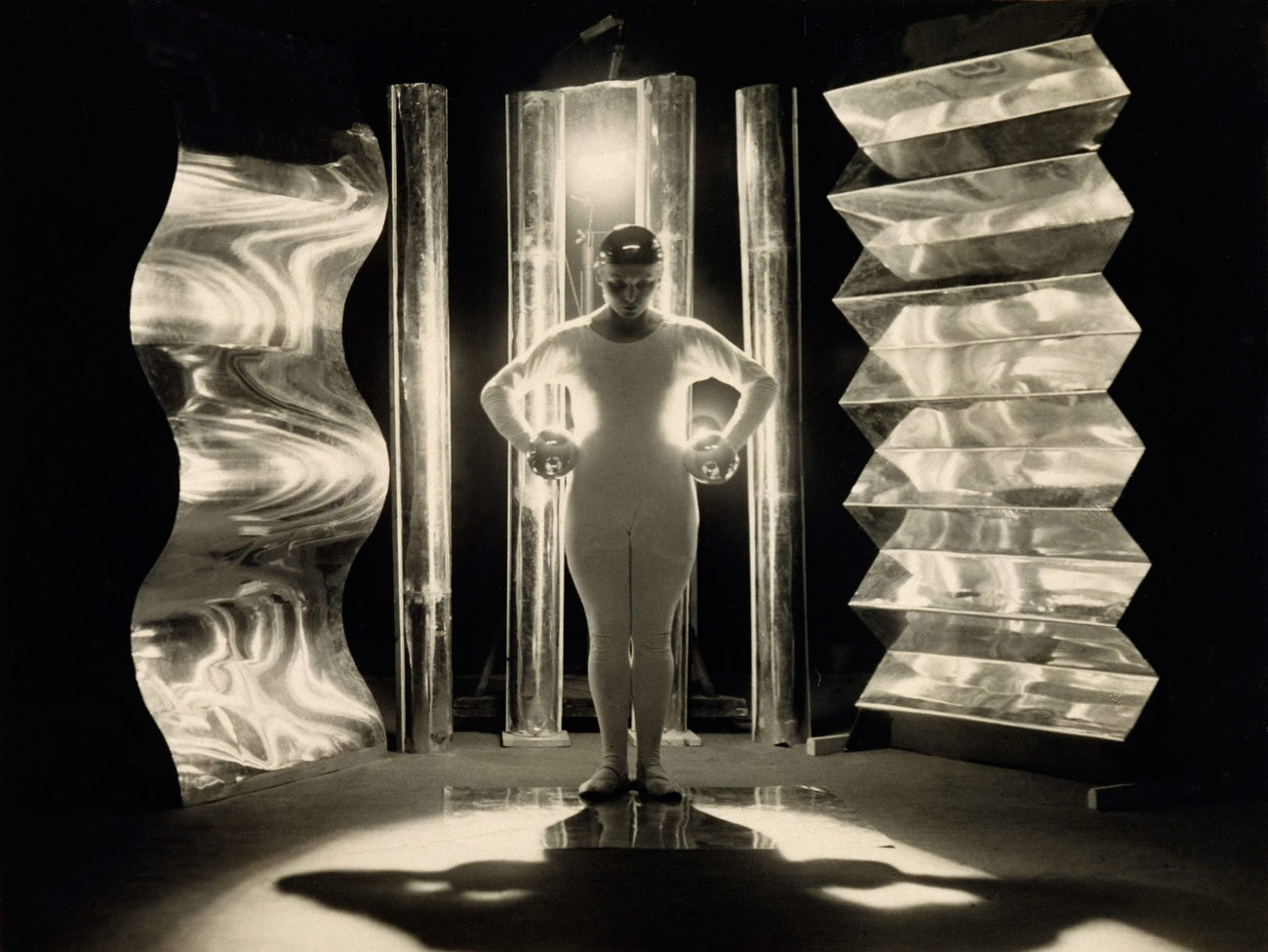
Stern and Coppola were united in their exploration of a modernist idiom, yet despite their relationship as husband and wife (from 1935 to 1943) they pursued this goal along remarkably original paths. Having started their artistic careers within the European avant-garde of the late 1920s and early 1930s, Stern and Coppola produced their major body of works in Argentina, where they thrived amid a vibrant milieu of Argentine and émigré artists and intellectuals. As harbingers of New Vision photography in a country caught up in the throes of forging its own modern identity, their distinctly experimental styles led to their recognition as founders of modern Latin American photography.
The earliest works in the exhibition date from the late 1920s to the early 1930s, when both artists began their initial forays into photography and graphic design. After beginning her studies in Berlin with Walter Peterhans, who became head of photography at the Bauhaus, in 1928 Stern met Ellen (Rosenberg) Auerbach and together they opened the pioneering studio ringl + pit, specialising in portraiture and advertising. Named after their childhood nicknames (Stern was ringl; Auerbach was pit), the studio embraced both commercial and avant-garde loyalties, creating proto-feminist works. The exhibition presents a large number of photographs, graphic design materials, and advertisements by the duo that explored alternative models of the feminine. Defying the conventional style of German advertising photography in this period, ringl + pit emerged as a dissident voice that stirred the interest of critics, artists, and consumers.
Coppola’s first photographs, made in Buenos Aires in the late 1920s, reveal an optical curiosity completely out of sync with prevailing trends in Argentina. Instead of using the camera to accurately render the details of the visible world, Coppola instead explored its potential to complicate traditional understandings of pictorial space. Like Man Ray and László Moholy-Nagy, he was interested in the effects of light, prisms, and glass for their visual and metaphoric potential, and he photographed his native city from unexpected perspectives akin to Germaine Krull’s images of Paris from the same decade. These early works show the burgeoning interest in new modes of photographic expression that led him to the Bauhaus in 1932, where he met Stern.
Following the close of the Bauhaus and the rising threat of the Nazi powers in 1933, Stern and Coppola fled Germany. Stern arrived first in London, where her friends included activists affiliated with leftist circles, and the exhibition presents her now iconic portraits of German exiles, including those of playwright Bertolt Brecht, actress Helene Weigel, Marxist philosopher Karl Korsch, and psychoanalyst Paula Heimann. After traveling and photographing throughout Europe, Coppola joined Stern in London, where his modernist photographs depicting the fabric of the city alternate between social concern and surrealist strangeness.
The exhibition’s third gallery includes films that Coppola produced in Berlin, Paris, and London during these years. The first of these films, Der Traum (The Dream), bears the strongest relationship to Surrealist filmmaking, while his next two films, Un Muelle del Sena (A Quai on the Seine) (1934) and A Sunday on Hampstead Heath (1935), are increasingly ambitious, using the film camera alternately as a still camera and for its unique capacity to pan across a scene and to capture action in urban environments.
In 1935, Stern and Coppola married and embarked for Buenos Aires, where they mounted an exhibition in the offices of the avant-garde magazine Sur, announcing the arrival of modern photography in Argentina. Following the exhibition’s successful critical reception, their home became a hub for artists and intellectuals, both those native to Argentina and the exiles continuously arriving from a war-torn Europe. The fourth gallery in From Bauhaus to Buenos Aires presents Coppola’s photographic encounters from the city’s centre to its outskirts and Stern’s numerous portraits of the city’s intelligentsia.
In 1936, Coppola received a career-defining commission to photograph Buenos Aires for a major publication celebrating the 400th anniversary of the city’s founding. Coppola used the opportunity to construct his own modern vision of the city, one that would incorporate the celebration of the local and his appreciation of the city’s structure inspired by the architect Le Corbusier. Concurrently, Coppola made his final film, The Birth of the Obelisk – an ode to Buenos Aires and its newly constructed monument. The film combines dynamic shots of the city with sequences of carefully constructed stills, demonstrating in six-and-a half minutes a vibrant, confident mix of influences, from Moholy-Nagy and Krull to the Concrete art movement in Argentina to films by Walter Ruttmann, Charles Sheeler, and Paul Strand.
Throughout the 1940s, Stern took incisive portraits of artists and writers, many of whom were aligned with the international antifascist cause and the emergence of an emancipatory feminist consciousness. These included playwright Amparo Alvajar; socialist realist painters Antonio Berni, Gertrudis Chale, and Lino Eneas Spilimbergo; poet Mony Hermelo; and graphic designer Clément Moreau. Among Stern’s numerous other subjects were poet-politician Pablo Neruda, abstract painter Manuel Ángeles Ortiz, and writer Jorge Luis Borges.
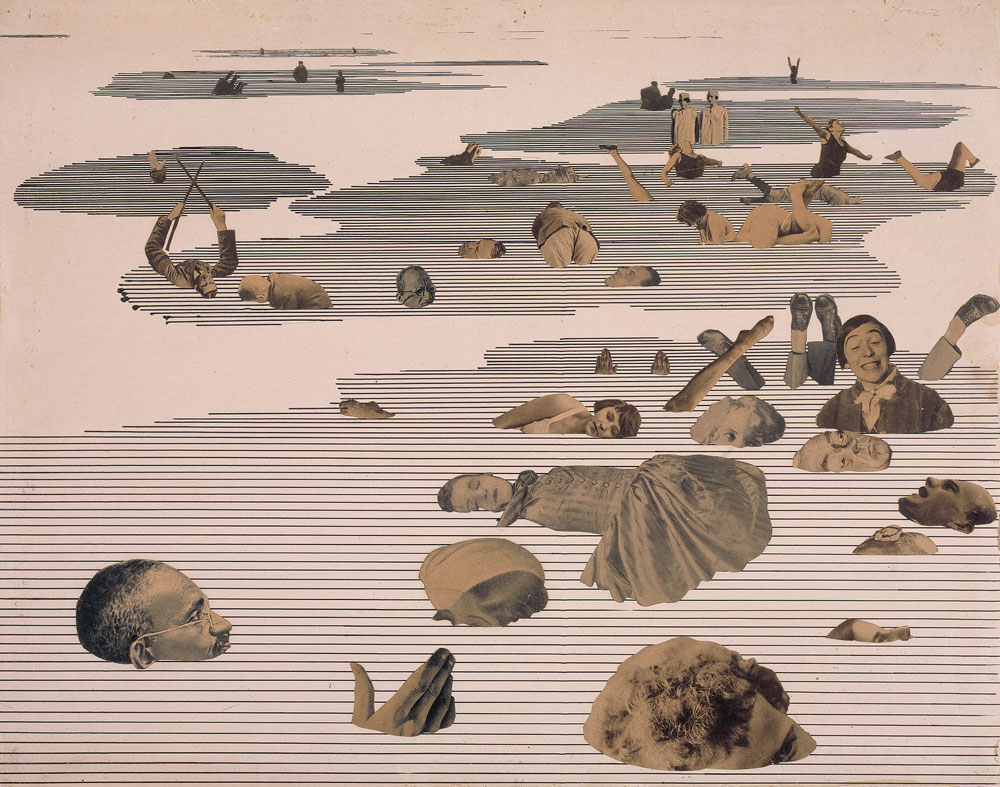
The exhibition concludes in the mid-1950s, at the end of Juan Domingo Perón’s era, with a large presentation of Stern’s Sueños (Dreams), a series of forward-thinking photomontages that she contributed on a weekly basis to the women’s magazine Idilio (Idyll) from 1948 to 1951. In Dream No. 1: Electrical Appliances for the Home, an elegantly dressed woman is converted into a table lamp that waits to be turned on by a male hand, using electricity as a sexual pun to expose feminine objectification. In Dream No. 24: Surprise, a female protagonist hides her face in shock as she confronts a larger-than-life baby doll advancing toward her. Debunking fantasies about women’s lives, Stern plumbed the depths of her own experience as a mother and artist to negotiate the terms between blissful domesticity and entrapment, privacy and exposure, cultural sexism and intellectual rebellion.
Press release from the MoMA website
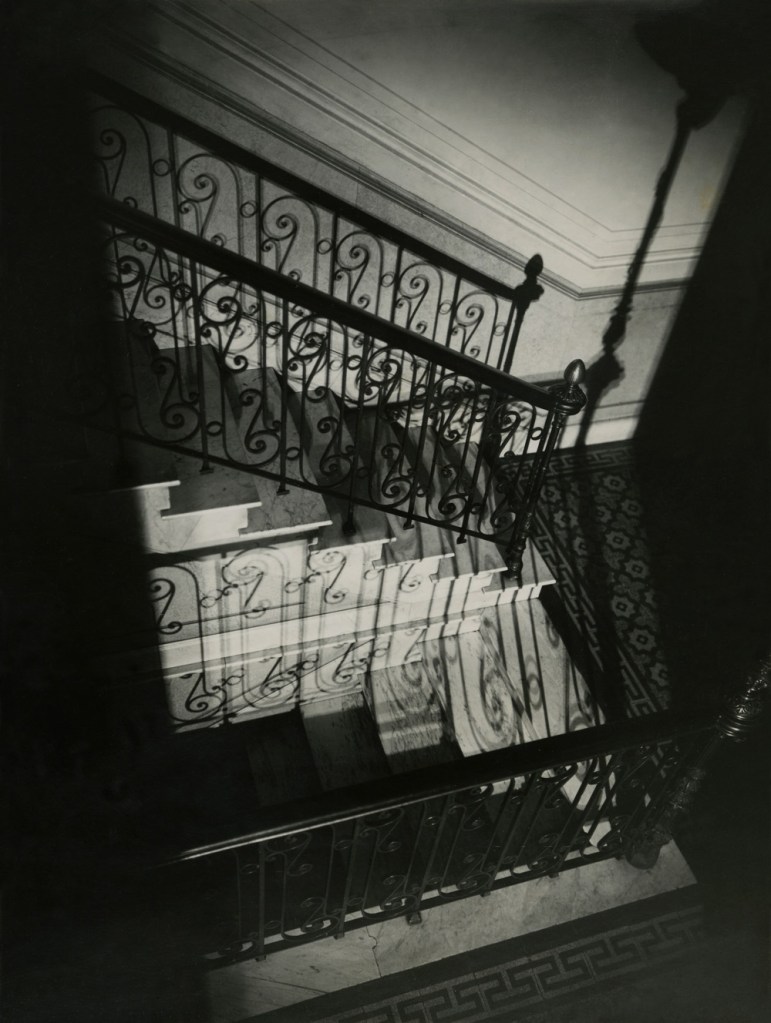

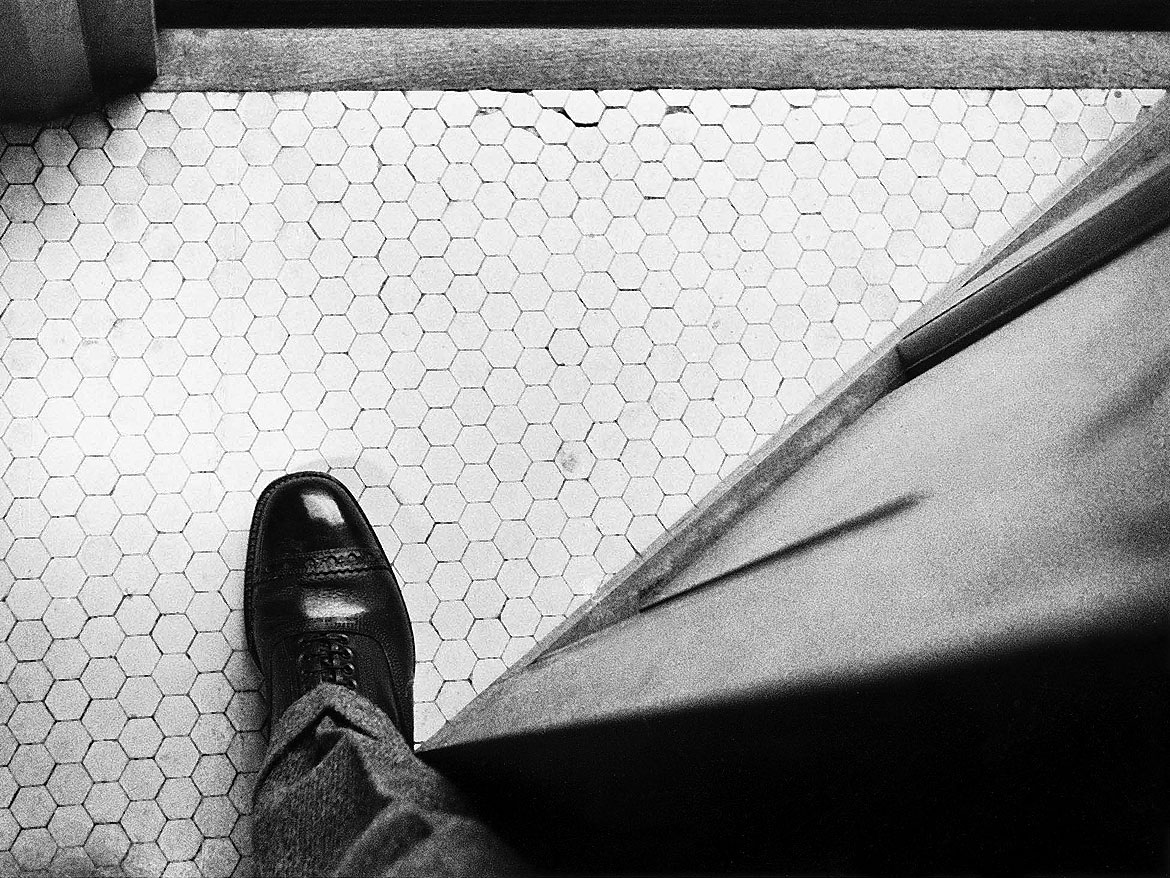
Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Untitled (Staircase at Calle Corrientes)
1928
Gelatin silver print
13 3/4 x 11 3/4″ (34.9 x 29.9cm)
Collection Alexis Fabry, Paris
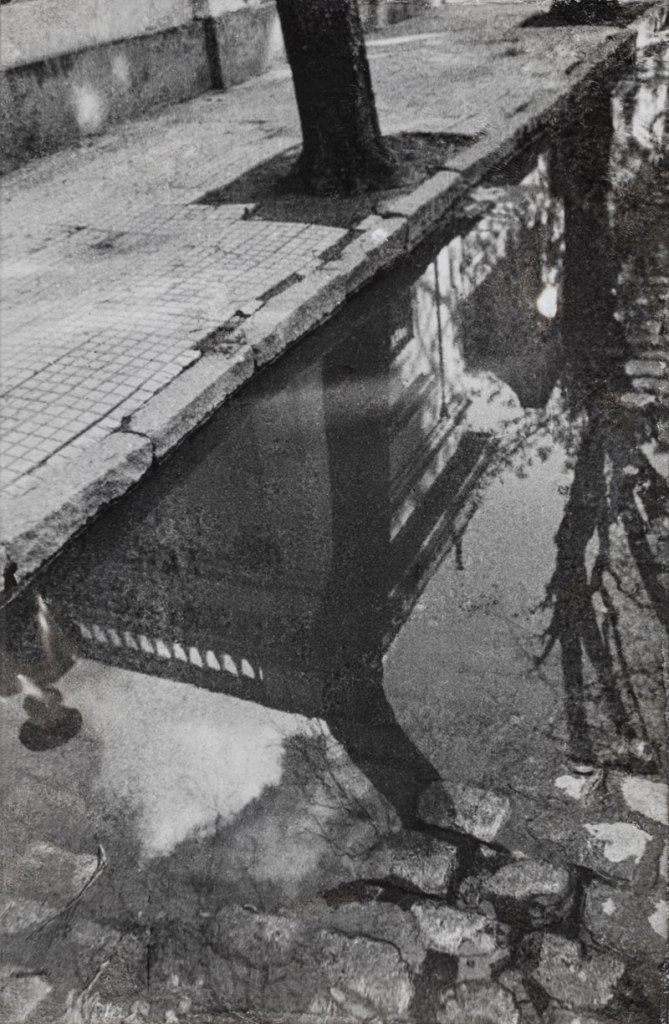

Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
“¡Esto es Buenos Aires!” (Jorge Luis Borges)
“This is Buenos Aires!” (Jorge Luis Borges)
1931
Gelatin silver print
8 11/16 x 5 7/8″ (22 x 15cm)
Estate of Horacio Coppola, Buenos Aires
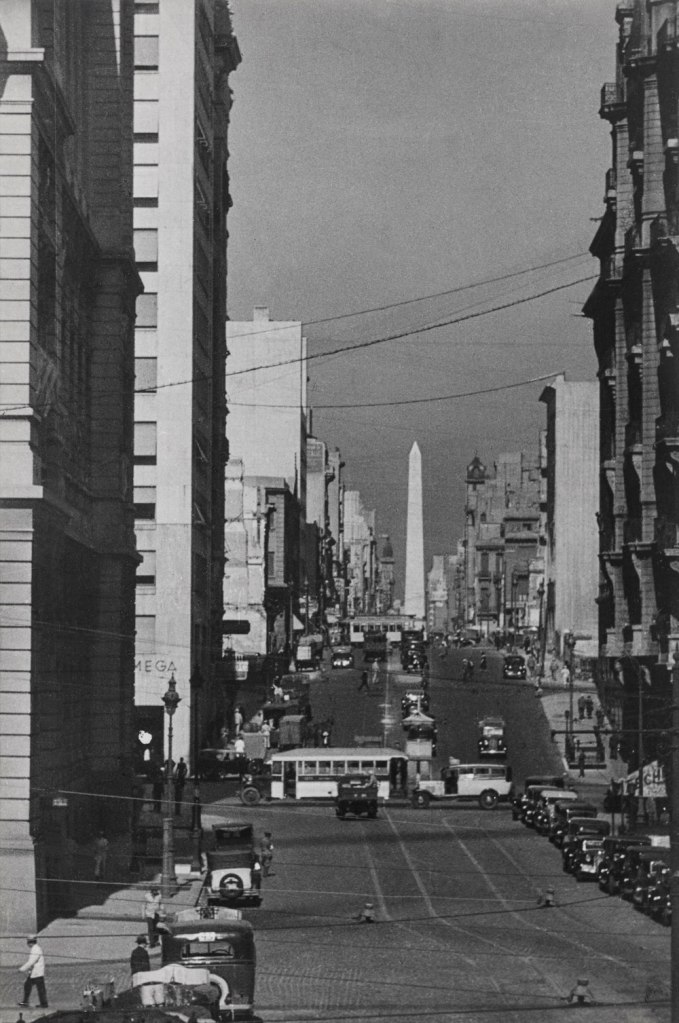

Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Avenida Corrientes towards the West
1936
Gelatin silver print
8 1/16 x 5 5/16″ (20.5 x 13.5cm)
Estate of Horacio Coppola; courtesy Galería Jorge Mara – La Ruche, Buenos Aires

Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Buenos Aires
1936
Gelatin silver print
8 3/16 x 5 15/16″ (20.8 x 15.1cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Latin American and Caribbean Fund

Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Calle Corrientes at the Corner of Reconquista
1936
Gelatin silver print
11 × 7 11/16″ (28 × 19.5cm)
IVAM, Institut Valencià d’Art Modern

Horacio Coppola (Argentine, 1906-2012)
Calle Florida at 8 pm
1936
Gelatin silver print
14 3/4 x 11 7/16″ (37.5 x 29cm)
Eric Franck Fine Art, London
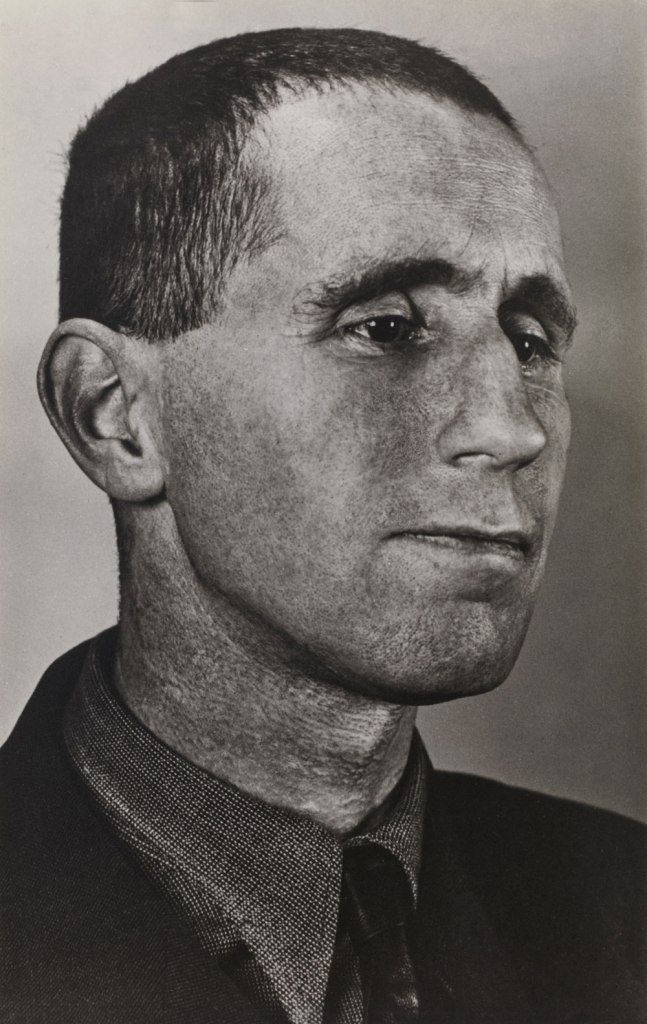

Grete Stern (Argentine born Germany, 1904-1999)
Brecht
1934
Gelatin silver print
10 1/4 x 6 11/16″ (26 x 17cm)
Private Collection, Boston

Grete Stern (Argentine born Germany, 1904-1999)
Gyula Kosice
1945
Gelatin silver print
11 7/16 x 9 1/8″ (29.1 x 23.2cm)
Museum Folkwang, Essen, Germany
Gyula Kosice, born Fernando Fallik (April 26, 1924) in Košice (Slovakia) is a naturalised Argentine sculptor, plastic artist, theoretician and poet, one of the most important figures in kinetic and luminal art and luminance vanguard. He used his natal city name as artist name. He was one of the precursors of abstract and non-figurative art in Latin America.

Grete Stern (Argentine born Germany, 1904-1999)
Jorge Luis Borges
1951
Gelatin silver print
10 13/16 x 8 1/4″ (27.5 x 21cm)
Estate of Horacio Coppola, Buenos Aires
Grete Stern (Argentine born Germany, 1904-1999)
Sueño No. 7: Who Will She Be?
1949
Gelatin silver print
15 1/2 × 19 1/16″ (39.4 × 48.4cm)
Museo Nacional Centro de Arte Reina Sofía, Madrid
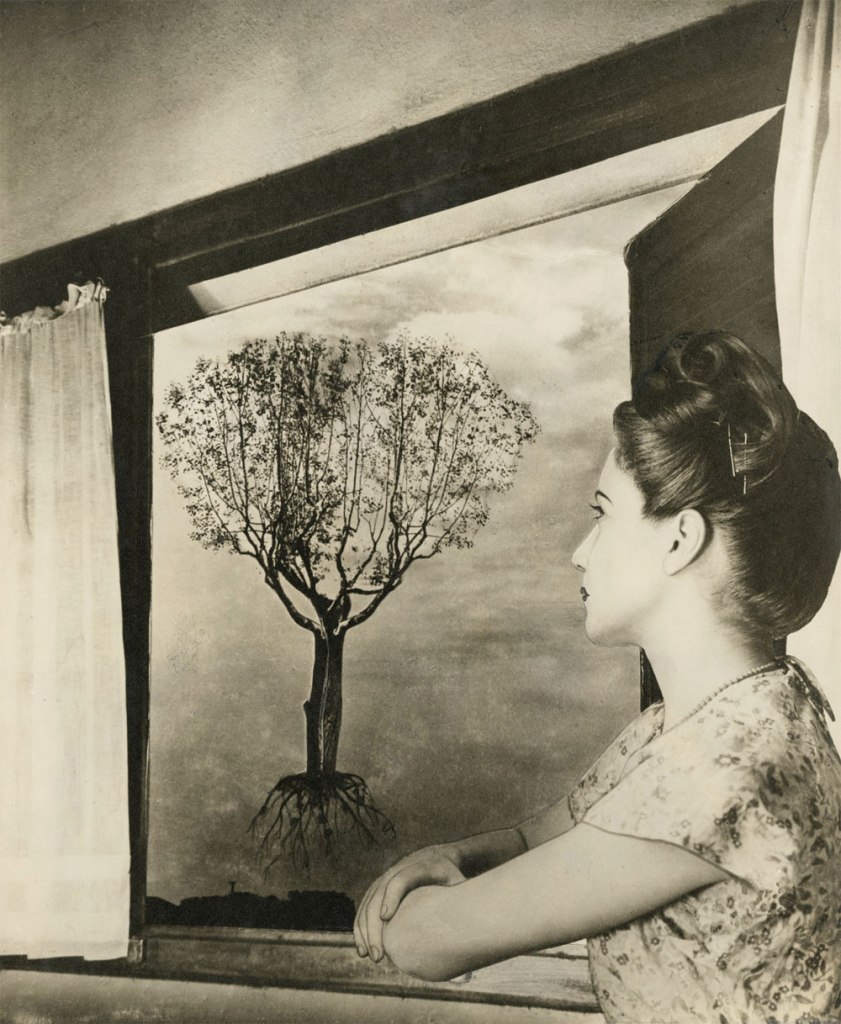

Grete Stern (Argentine born Germany, 1904-1999)
Sueño No. 43: Untitled
1949
Gelatin silver print
17 7/16 × 14 5/16″ (44.3 × 36.3cm)
Collection Léticia and Stanislas Poniatowski
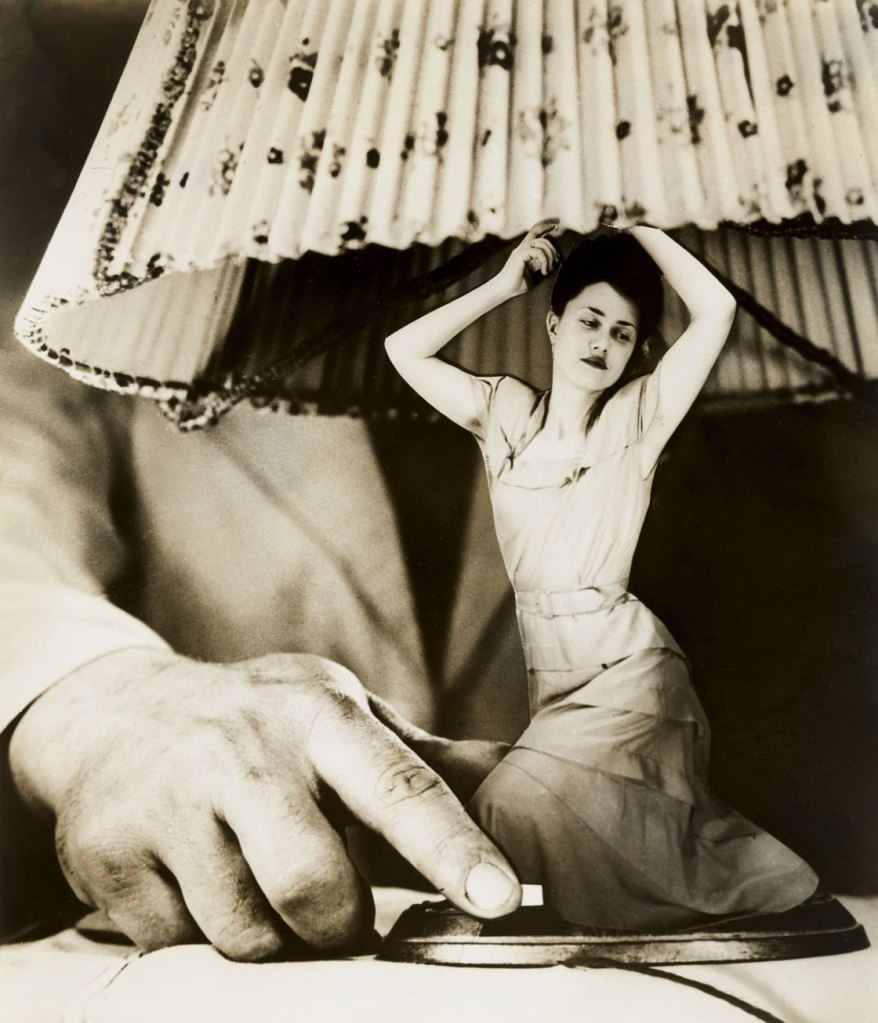

Grete Stern (Argentine born Germany, 1904-1999)
Sueño No. 1: Electrical Appliances for the Home
1949
Gelatin silver print
10 1/2 x 9″ (26.6 x 22.9cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Latin American and Caribbean Fund through gift of Marie-Josée and Henry R. Kravis in honor of Adriana Cisneros de Griffin
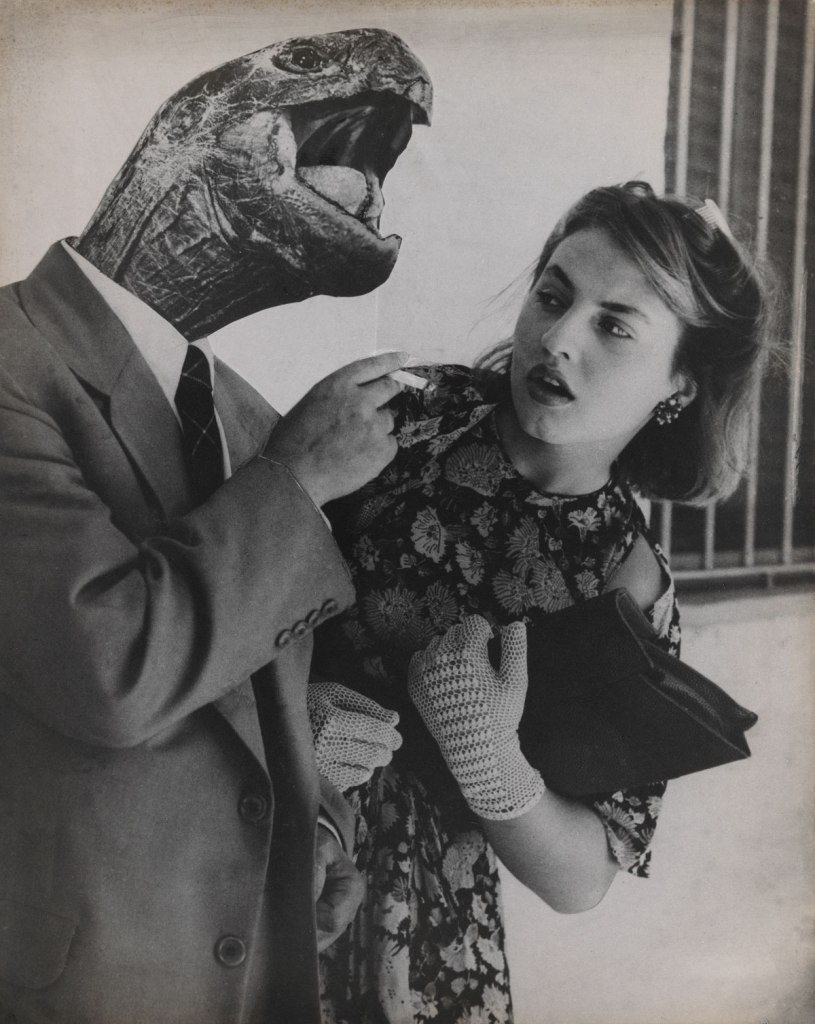

Grete Stern (Argentine born Germany, 1904-1999)
Sueño No. 28: Love without Illusion
1951
Gelatin silver print
19 11/16 × 15 3/4″ (50 × 40cm)
IVAM, Institut Valencià d’ Art Modern
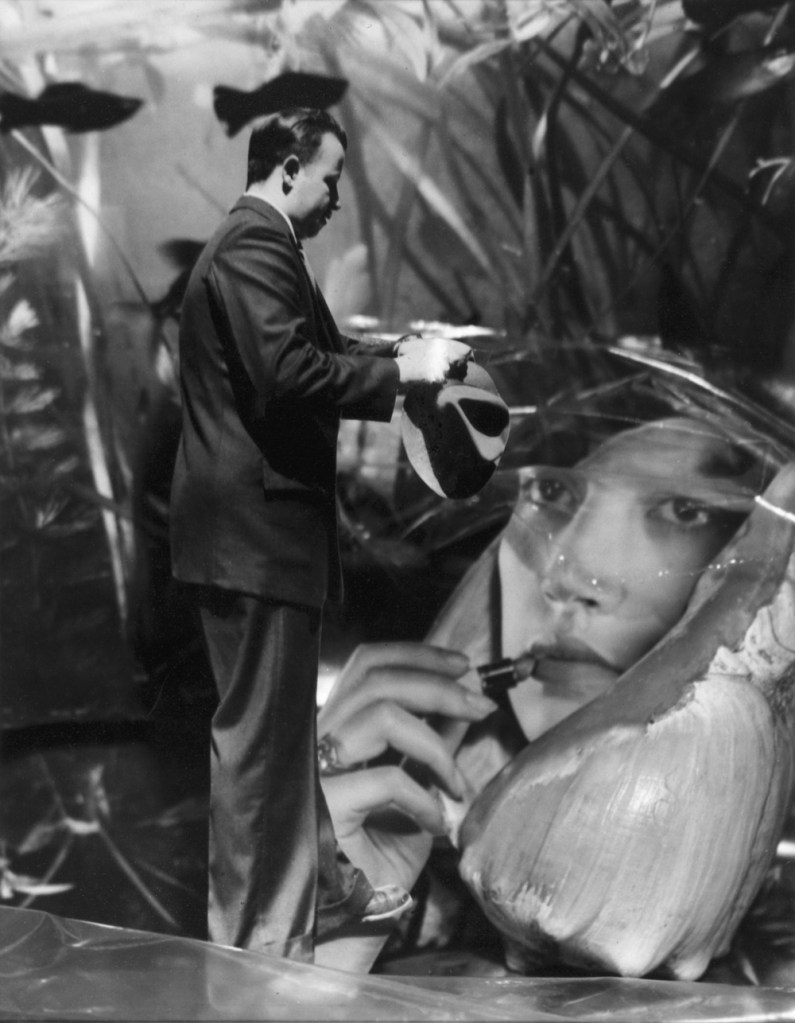

Grete Stern (Argentine born Germany, 1904-1999)
Sueño No. 27: Doesn’t Fade with Water
1951
Gelatin silver print, printed 1990s
11 7/16 x 9 1/16″ (29 x 23cm)
Collection Eduardo F. Costantini, Buenos Aires
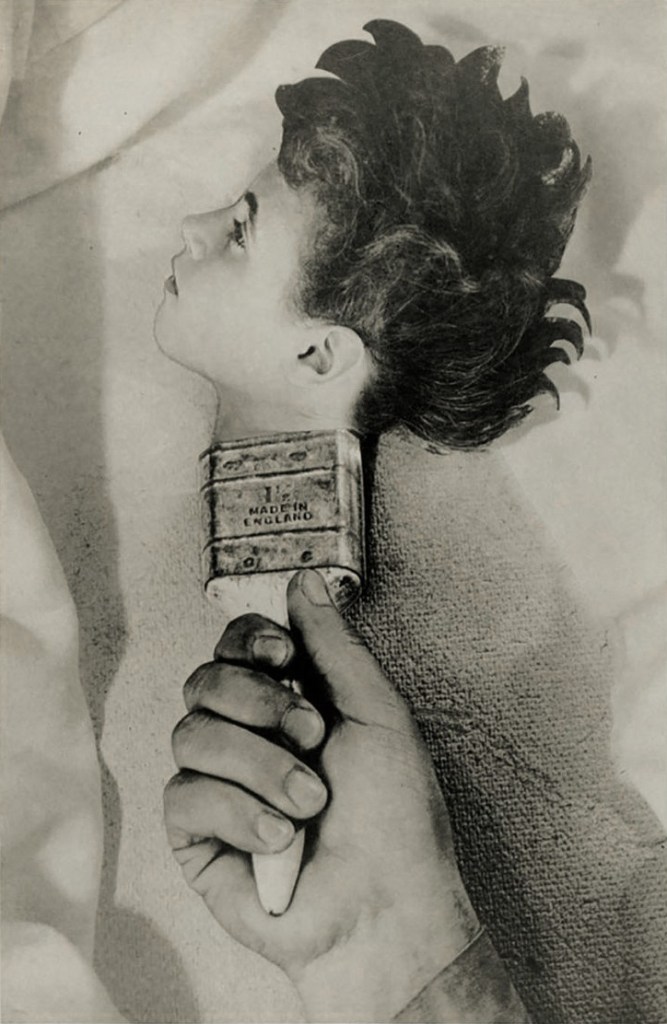
Grete Stern (Argentine born Germany, 1904-1999)
Sueño No. 31: Made in England
1950
Gelatin silver print
19 11/16 × 13 3/16″ (50 × 33.5cm)
IVAM, Institut Valencià d’ Art Modern

Grete Stern (Argentine born Germany, 1904-1999)
D.L.H.
1925
Photocollage
8 7/16 x 6 5/16″ (21.5 x 16cm)
Museum Folkwang, Essen, Germany

Grete Stern (Argentine born Germany, 1904-1999)
Photomontage for Madí, Ramos Mejía, Argentina
1946-1947
Gelatin silver print
23 9/16 x 19 7/16″ (59.8 x 49.4cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Latin American and Caribbean Fund and partial gift of Mauro Herlitzka
“She also photographed members of Madí (from the first two letters of the words “materialismo dialéctico”), who were committed to abstraction as an antidote to the propaganda disseminated by Juan Perón. One of Ms. Stern’s best-known works, on view here, is the “Photomontage for Madí, Ramos Mejia, Argentina” (1946-1947), which she made for the second issue of their journal. For the images, she used the “M” from a neon sign advertising Movado watches and superimposed “Madí” over the obelisk designed by Alberto Prebisch to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Buenos Aires. The obelisk symbolized, for her milieu, abstract geometry.”
Martha Schwendener. “‘From Bauhaus to Buenos Aires: Grete Stern and Horacio Coppola,’ a Bicontinental Couple” on the NY Times website, May 28 2015
The Museum of Modern Art
11 West 53 Street
New York, NY 10019
Phone: (212) 708-9400
Opening hours:
10.30am – 5.30pm
Open seven days a week


















![Lyonel Feininger (American, 1871-1956) 'Untitled [Street Scene, Double Exposure, Halle]' 1929-1930 Lyonel Feininger (American, 1871-1956) 'Untitled [Street Scene, Double Exposure, Halle]' 1929-1930](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/street-scene-double-exposure-halle-1929-1930.jpg)
![Lucia Moholy (British born Czechoslovakia, 1894-1989) 'Untitled [Southern View of Newly Completed Bauhaus, Dessau]' 1926 Lucia Moholy (British born Czechoslovakia, 1894-1989) 'Untitled [Southern View of Newly Completed Bauhaus, Dessau]' 1926](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/lucia-moholy-southern-view-of-newly-completed-bauhaus.jpg)
![Lyonel Feininger (American, 1871-1956) 'Untitled [Train Station, Dessau]' 1928-1929 Lyonel Feininger (American, 1871-1956) 'Untitled [Train Station, Dessau]' 1928-1929](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/gm_326238ex1.jpg)


![Lyonel Feininger (American, 1871-1956) 'Untitled [Night View of Trees and Street Lamp, Burgkühnauer Allee, Dessau]' 1928 Lyonel Feininger (American, 1871-1956) 'Untitled [Night View of Trees and Street Lamp, Burgkühnauer Allee, Dessau]' 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/night-view-of-trees-and-streetlamp-burgkc3bchnauer-allee-dessau-1928.jpg)
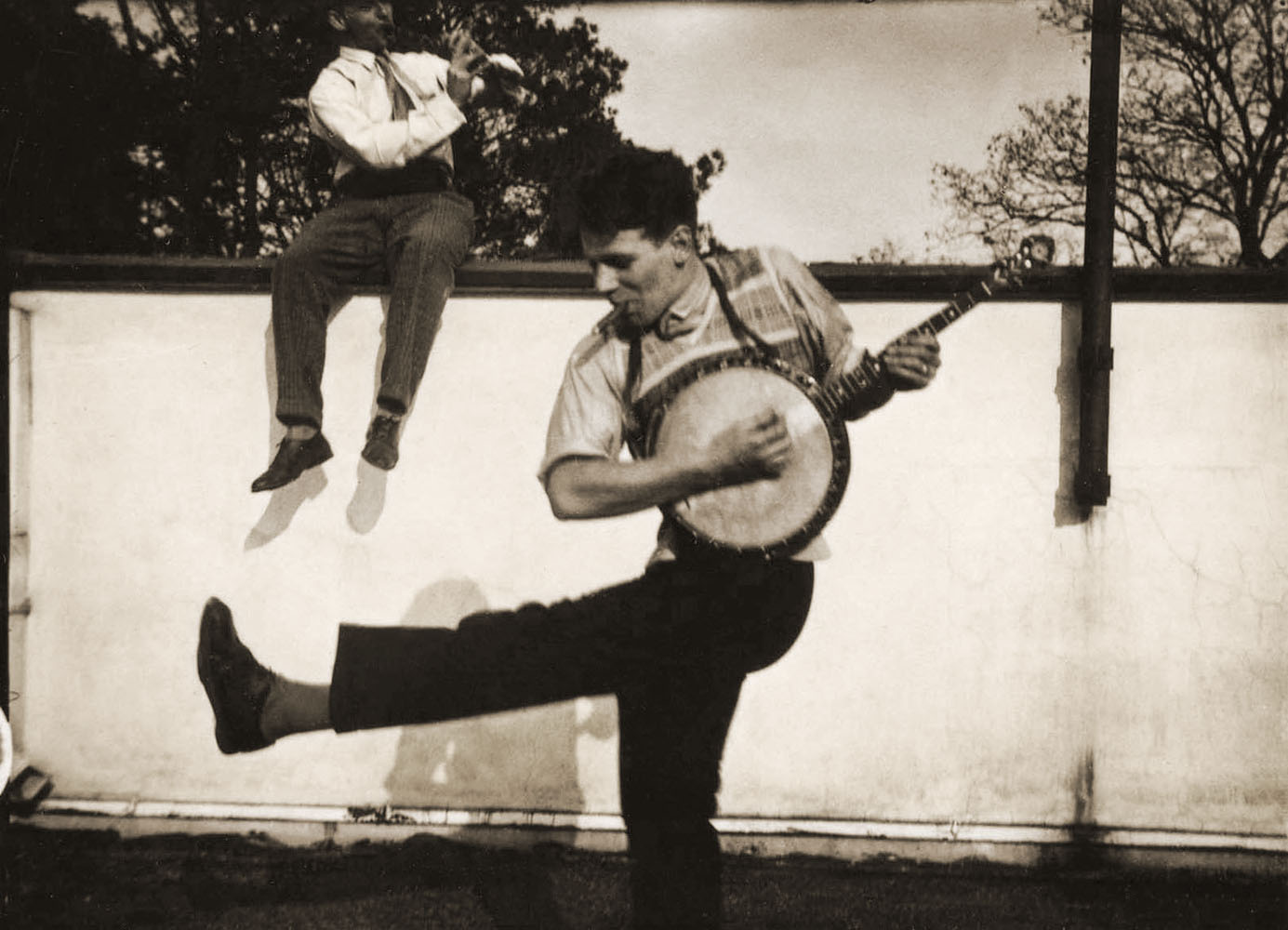
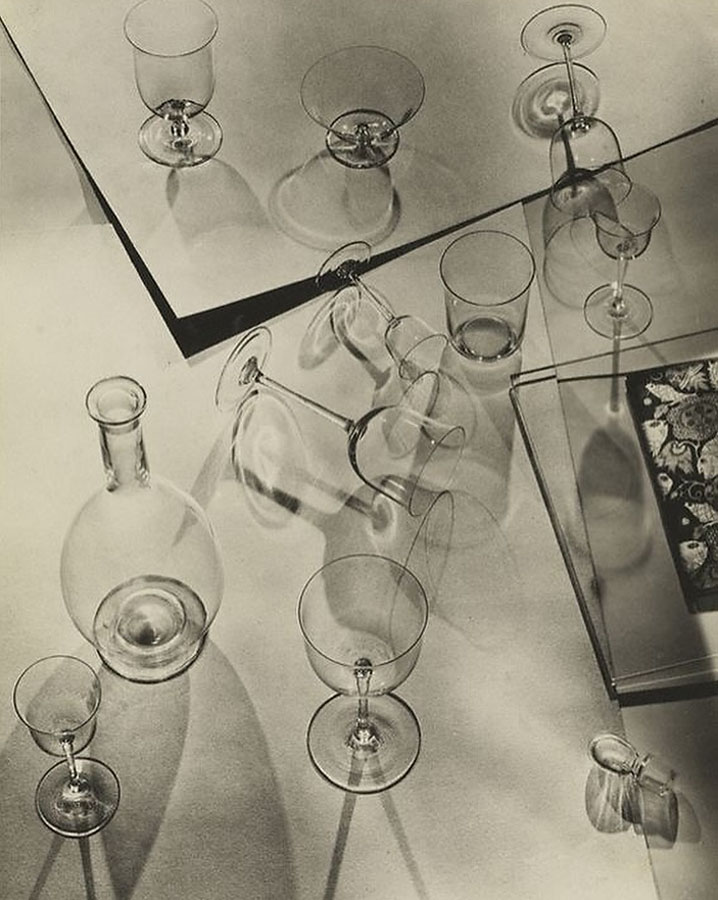
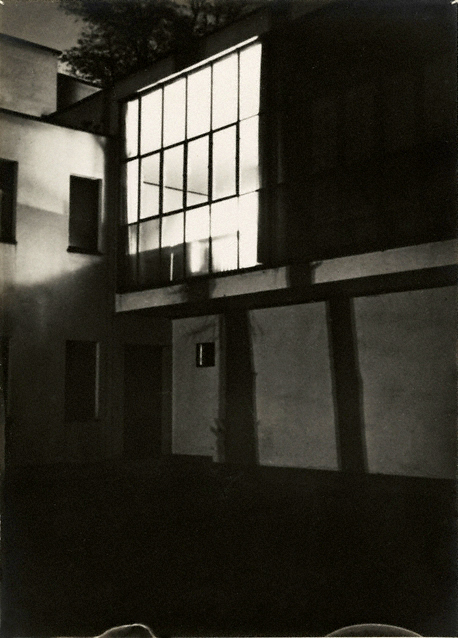









![Irene Bayer-Hecht (American, 1898-1991) 'Untitled [Students on the Shore of the Elbe River, near Dessau]' 1925 Irene Bayer-Hecht (American, 1898-1991) 'Untitled [Students on the Shore of the Elbe River, near Dessau]' 1925](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/irene-bayer-bauhacc88usler-am-strand-der-elbe-bei-dessau-web.jpg)
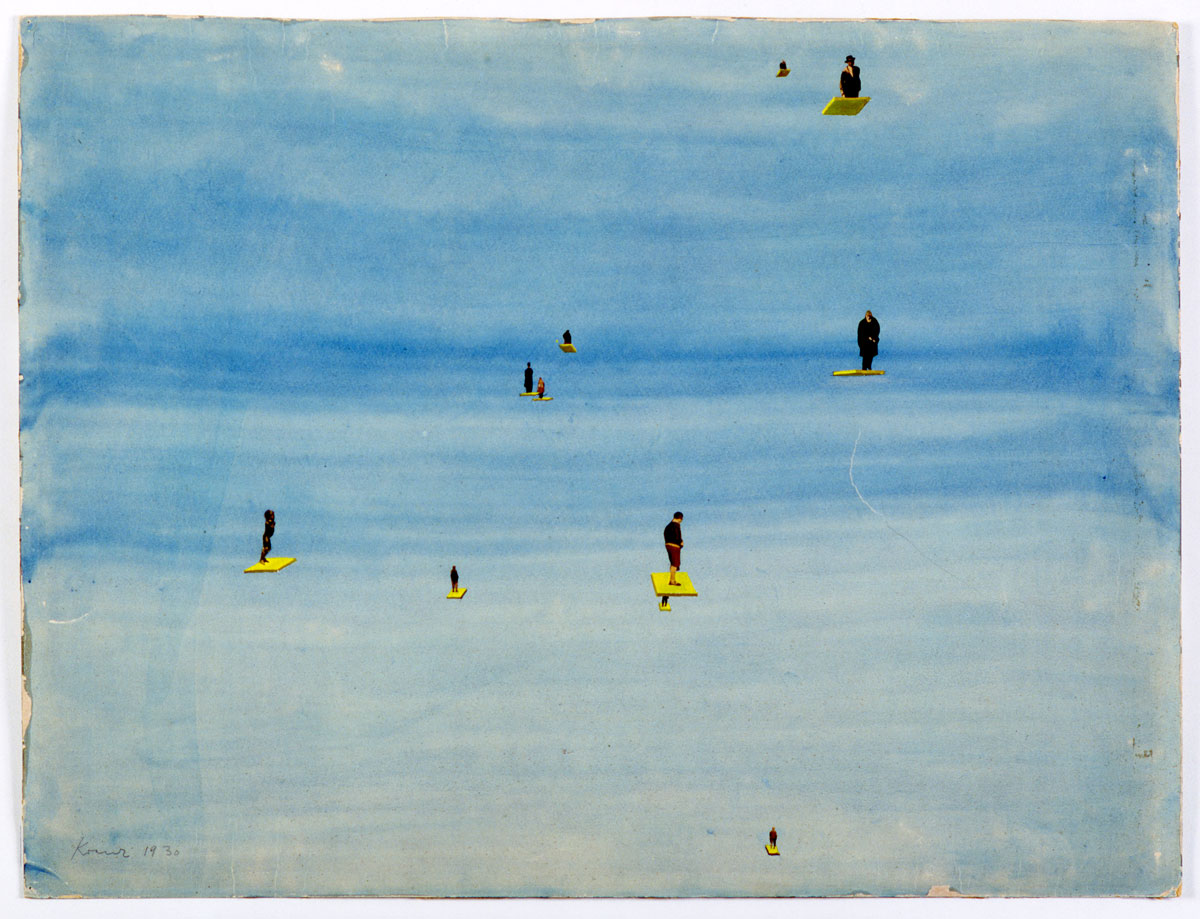









You must be logged in to post a comment.