Exhibition dates: 1st February – 16th April 2011
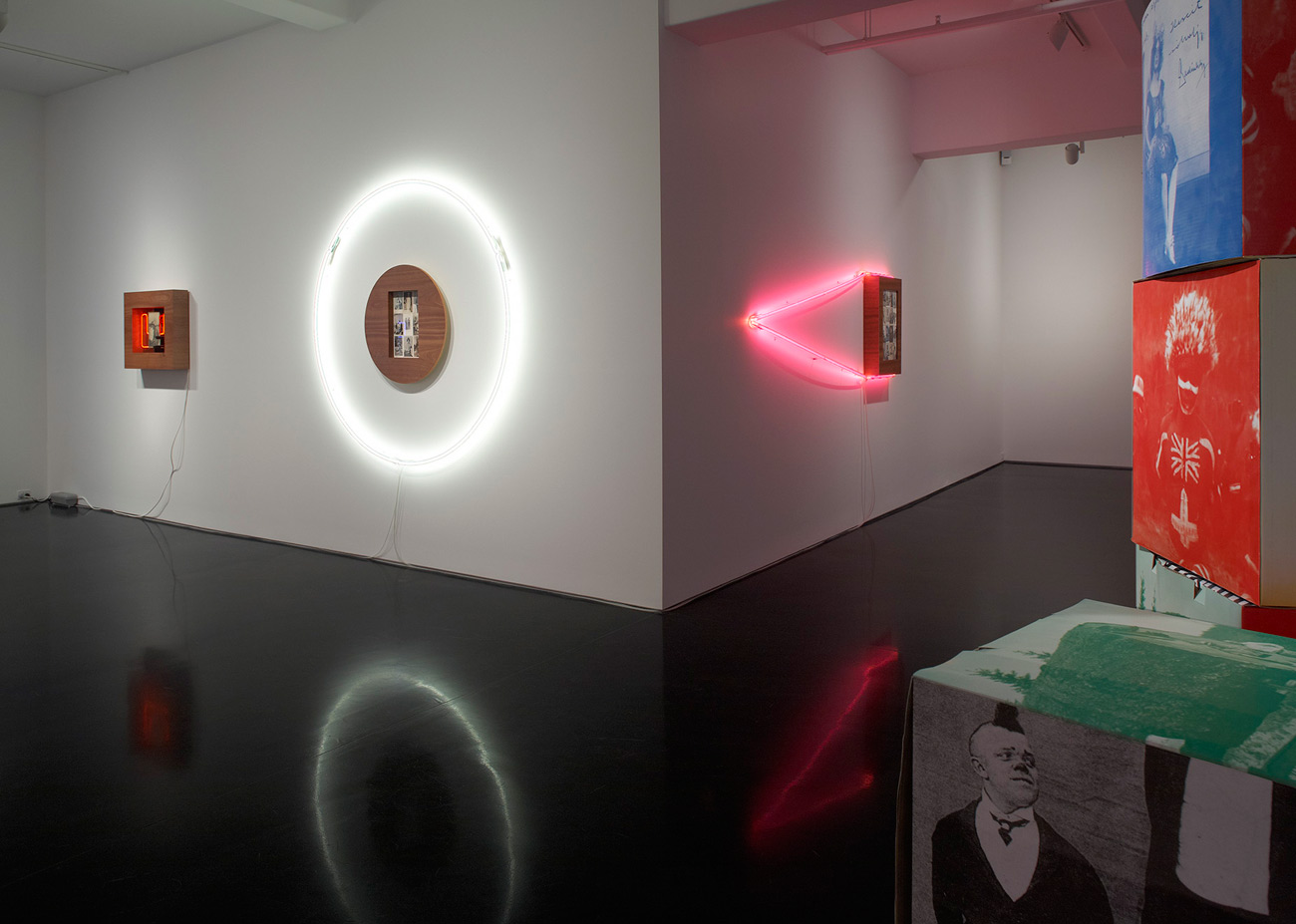
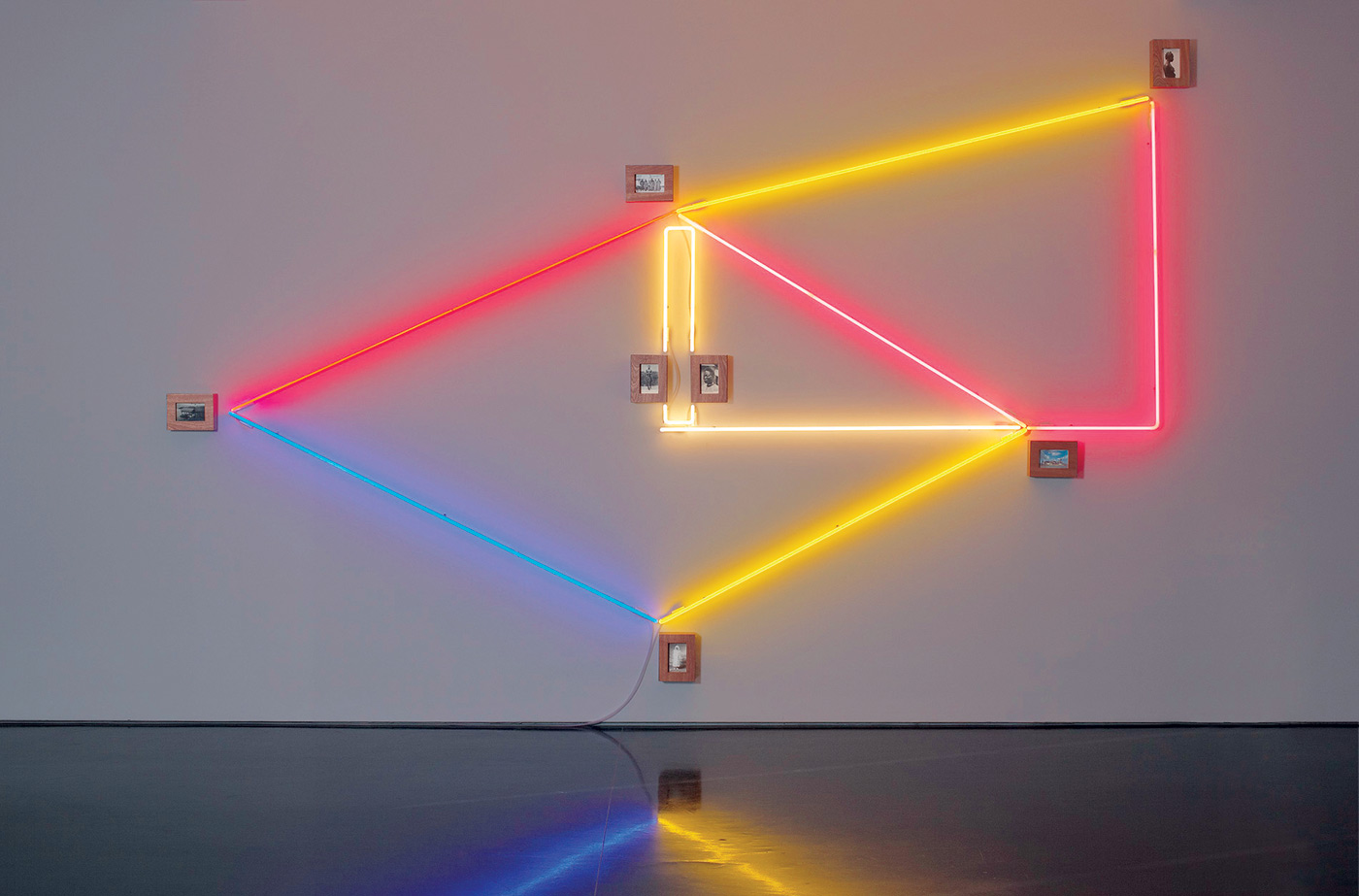
Installation photograph of one of the galleries in the exhibition NETWORKS (cells & silos) at the newly opened Monash University Museum of Art (MUMA) with Nick Mangan’s Colony (2005) in the foreground
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
This is a vibrant and eclectic exhibition at MUMA, one of the best this year in Melbourne. The curator Geraldine Barlow has gathered together some impressive, engaging works that are set off to good effect in the new gallery spaces. I spent a long and happy time wandering around the exhibition and came away visually satiated and intellectually stimulated.
The exhibition “explores the connections between artistic representation of networks; patterns and structures found in nature; and the rapidly evolving field of network science, communications and human relations.” (text from MUMA)
Networks connect – they describe (abstract) connections between people and things. Networks map simple or complex systems and can be real or an abstract representation of those systems. Networks form a nexus, “a sort of concentrated nodal point among a series of chains of markers” that reveals the centralising structure of networks (such as Facebook and Google). Robert Nelson in his review of this exhibition in The Age notes, “Geert Lovink and Ned Rossiter [in their catalogue essay] describe the way networks paradoxically disorganise you, creating a disempowering messy grid of protocols that colonise your headspace … It’s commonplace to celebrate networks because they stimulate excitement about belonging, about extending your reach and joining in. These hopes are as pervasive as the networks themselves. But in structural terms, networks are also insidiously colonising and hierarchical, built on the principle of the rich becoming richer and the poor becoming more dependent.”1
I believe that networks can also be altruistic and non-heirarchical, offering a horizontal consciousness rather than a vertical one: points of view and perspectives on the world that open up these (virtual) spaces to fluidity, mutation, transgression and subversion. Catherine Lumby observes that,
“The contradictory, constantly shifting nature of contemporary information and image flows tends to erode the moral authority of any social order, patriarchal or otherwise. It is this very collapse which has arguably fuelled social revolutions such as feminism and gay and lesbian rights, but which equally disrupts attempts by some to ground them in identity politics.”2
Critical to understanding the construction of these constantly shifting networks in contemporary society are the concepts of weaving and intertexuality. Intertextuality is the concept that texts do not live in isolation, “caught up as they are in a system of references to other books, other texts, other sentences: it is a node within a network… Its unity is variable and relative (Foucault, 1973)“3. In other words the network is decentred and multiple allowing the possibility of transgressive texts or the construction of a work of art through the techniques of assemblage (Deleuze and Guattari) – a form of fluid, associative networking that is now the general condition of art production.4
Infection of the network (by viruses for example) disrupts the pattern/randomness binary and may lead to mutations, ‘differance’ in Derrida’s terminology, spaces that are both fluid and fixed at one and the same time; neither here nor there.
On to (some of) the work.
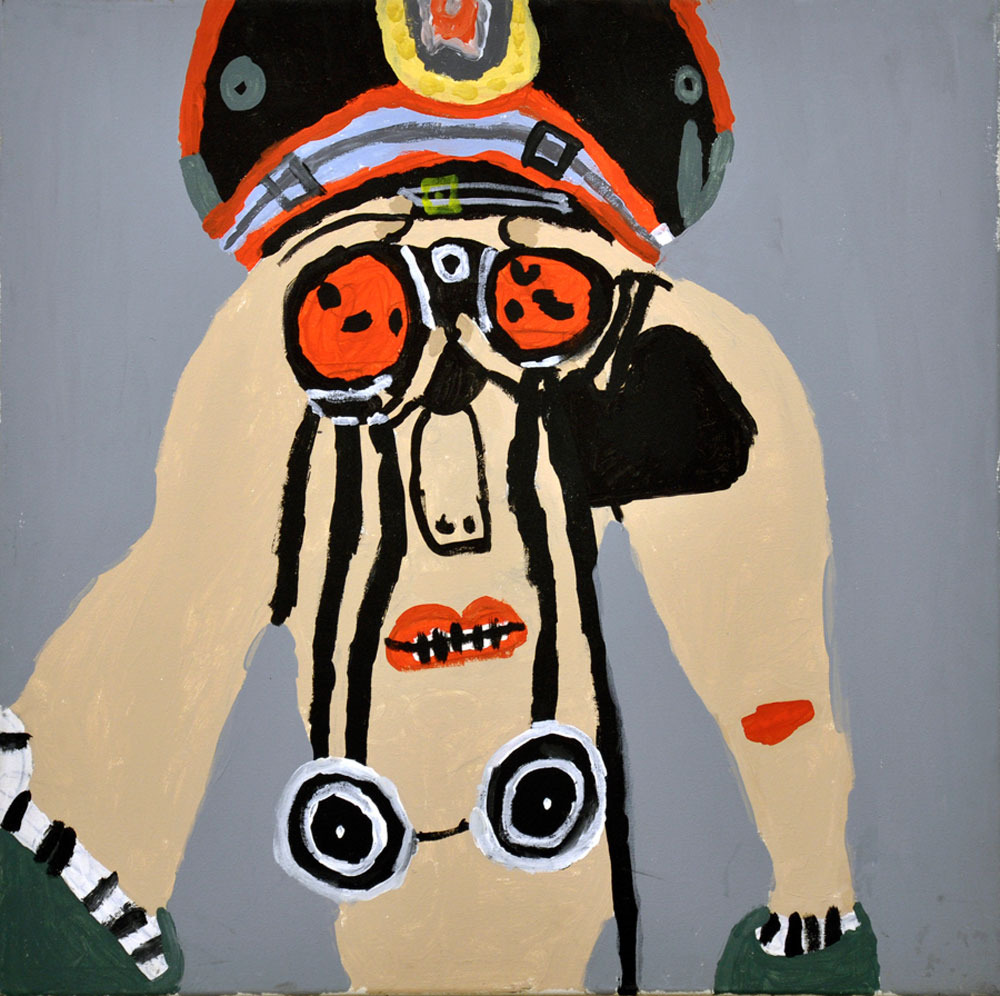
Masato Takasaka’s series of fibre-tipped pen and pencil on paper, Information Superhighway (2006-07), are wonderful, kaleidoscopic works – inventive and fun, full of rhizomic, multi-layered dimensionality. Nick Mangan’s mixed media sculpture Colony (2005, see photograph below) is a spiky, totemic, figurative creature made of axe, shovel and hammer handles and riddled with holes like driftwood that looks like a bizarre, Medieval torture instrument.
Bryan Spiers paintings Shadowmath and New descending (both 2010, see photograph below) are excellent, puzzle-like reinterpretations of delicate, Futuristic movements. As he describes them, “I think of my paintings as puzzles or visual toys. They are images to be manipulated by the viewer; reconfigured, recomposed, expanded upon. Trajectories of change are implied by repeated shapes and graded colour transitions. They describe a continuum to be followed to its logical conclusion outside of the picture plane. This leads to the dissolution of the image, proposing new images yet to be made.”
Heath Bunting’s 3 panel work from The Status project (all 2010) features interrelated data sets that reach a “level of absurdity in attempting to relate radically different but inter-related information.” This mind mapping schematic of connections (coloured connections with labels, markers and legends) based around Bristol, England has some unbelievable entries if you look really closely:
~ A1072 Able to provide natural person date of birth 2010
~ A1073 Able to access the Internet
~ A1003 A terrorist
~ A1047 Providing instruction or training in the use of imaginary firearms such as sticks
~ A1088 Providing training in leopard crawling
Aaron Koblin’s beautiful video Flight patterns (2010) offers a mapping of thousands of plane journeys across the USA over time (based on East Coast time) so that the explosion of their frequency becomes like a fireworks display. Andrew McQualter’s fantastic acrylic paint wall drawings Three propositions, one example (2010-11), painted directly onto the gallery wall show various people, isolated from each other and from the viewer, talking and listening to their iPhones. As Robert Nelson comments, “They’re isolated individuals, all on their own plane, presumably doing social networking or communicating. If you walked past them, they wouldn’t respond because, with heads bowed, they’re absorbed in another reality. Their hands and minds are busy with a reality elsewhere.”
Present but not present, (not) here and there at the same time. This is a critical debate in contemporary culture: do these type of networks lessen our ability to build friendships and connections in the real world or are they just another element in our rhizomic network of associations that help with our interconnectivity: utopian or dystopian or equal measure of both? Does it really matter?
From the UK Kit Wise’s large digital print on aluminium series (including KTM SEA MOW RUH 2010, see below) are effective, offering solarised, negative, brightly coloured collages of seemingly atomised cities (the titles refer to the cities airport abbreviation codes). Mass Ornament (2009) by American artist Natalie Bookchin is one of my favourite works in the exhibition. In a horizontal panel of wall mounted screens play videos of people dancing in their bedroom. Bookchin has gleaned these gems from uploaded personal videos on YouTube – there are handstands, contortions, tap dancing, all manner of performances (some then deleted by the performer) – then collated by the artist and set to a Broadway-type music number. Mesmeric and amazing!
Koji Ryui’s spatial constructions Extended network towards the happy end of the universe (2007-2011, see photograph below) are made of bendy, plastic drinking straws of different colours, encased and moulded into cellular shapes (reminding me of the white of the Melbourne Recital Centre exterior). Trailing off these structures in different colours are airborne-like filaments similar to the plant Old Man’s Beard. “Ryui repeats and arranges these objects in space to create peculiar environments and accidental narratives. In his installations, relationships or spaces between objects are equally as important as the objects themselves.” Wonderful.
Last but not least my favourite work in the exhibition: heart of the air you can hear by Sandra Selig (2011, see photographs below). The photographs do not do the work justice. Made simply from spun polyester, nails and paint this Spirograph-like construction is beautiful in its resonance and colour, captivating in its complexity. Built into a corner of the gallery the work floats at eye level, twists and turns and changes intensity of colour when viewed from different angles. From the front it looks like a spaceship out of Star Wars woven by light!
There are many other excellent works in the exhibition that I have not mentioned. Some of the work disrupts the continual reiteration of norms by weaving a lack of fixity into the network’s existence. Other work visually makes comment on and reinforces the structure of such networks. Whichever it is this is a truly engaging exhibition that no single body, let alone a networked one, should miss.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
1/ Nelson, Robert. “Networks, Cells and Silos” review in The Age newspaper. Melbourne: Fairfax Media, 23/02/2011 [Online] Cited 23/03/2011
2/ Lumby, Catharine. “Nothing Personal: Sex, Gender and Identity in The Media Age,” in Matthews, Jill (ed.,). Sex in Public: Australian Sexual Cultures. St. Leonards: Allen and Unwin, 1997, pp. 14-15
3/ Foucault, Michel cited in Thumlert, Kurt. Intervisuality, Visual Culture, and Education. [Online] Cited 01/04/2011 no longer available online
4/ “To understand the production of art at the end of tradition, which in our lifetime means art at the end of modernism, requires, as the postmodern debate has shown, a careful consideration of the idea of history and the notion of ending. Rather than just thinking ending as the arrival of the finality of a fixed chronological moment, it can also be thought as a slow and indecisive process of internal decomposition that leaves in place numerous deposits of us, in us and with us – all with a considerable and complex afterlife. In this context all figuration is prefigured. This is to say that the design element of the production of a work of art, the compositional, now exists prior to the management of form of, and on, the picture plane. Techniques of assemblage, like montage and collage – which not only juxtaposed different aesthetics but also different historical moments, were the precursors of what is now the general condition of production.”
Fry, Tony. “Art Byting the Dust,” in Hayward, Phillip. Culture, Technology and Creativity in the Late Twentieth Century. London: John Libbey and Company, 1990, pp. 169-170
Many thankx to Monash University Museum of Art for allowing me to publish the text and photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Kerrie Poliness (Australian, b. 1962)
Blue Wall Drawing #1
2007-2011
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Hilarie Mais (British/Australian, b. 1952)
The waiting – anon
1986
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
An interview with the curator: Geraldine Barlow
Where did your interest in networks come from?
I’ve long been fascinated by network maps of human relationships – the graphical representation of something seemingly so complex and multi-layered. The structure of the brain and how this relates to theories of mind is also an area of personal interest. Our society, bodies and relationships are all made up of different kinds of networks, and artists have long been interested in mapping out these structures. I realised some time ago that the visual representation of networks might make for an interesting exhibition, from this point on I collected and ‘tested’ different ideas of what the exhibition might include.
How is this explored in the exhibition?
Human relationships feature in some of the works in the exhibition, but not all. I hope the exhibition offers a wide variety of links between people’s familiar world and daily experiences on the one hand, and more abstract ideas on the other.
There are a number of works from the Monash University Collection included in the exhibition. Can you tell us about these and why you selected them?
The Monash University Collection is a great source of inspiration, it is a wonderful collection, but also, I think any artwork considered closely and over time opens up in surprising ways and offers unexpected insights, working with the works in the collection over a period of years allows me to think about them in a long and slow way.
Dorothy Braund’s work Christ with the disciples listening 1966 was given to the University in 1974. It is a very beautiful formal painting of a series of shaded circles and ellipses. At first glance it is simple and seems to represent a ring of figures, their heads and bodies gathered together. On closer examination it is not so clear where one figure ends and another begins, as a whole the clustered forms seem to operate more like a cell. Historically this cell of men and the ideas attributed to them has had a profound impact, in their day they might have been seen as a kind of terrorist cell.
Through the sensitive composition and balance of abstract form, the artist has created a complex representation of the relationships between people: the ways in which we are both connected to each other, and yet might also circulate ideas in a tight ‘Chinese whispers’ type circle. This work was painted in 1966, long before our current awareness of social and telecommunications networks, but it can still offer us insights in our contemporary world and the way we relate to each other.
How did the new gallery space affect the installation of the exhibition?
The exhibition was slowly forming in my mind, even as Kerstin Thompson’s wonderful gallery space was being designed and built. The gallery has offered a wonderful armature and character for the exhibition to work with, hopefully in the manner of a conversation. Kerstin was been very interested in understand and reflecting the essential structure of the building, not building over what was pre-existing. The exhibition like-wise has an interest in structural models, geometries and patterns – in finding a balance between the regular and the slightly warped. In the central corridor which runs down the spine of the gallery, Thompson has chosen to leave the mechanical services exposed, to allow the essential structure of the building to be a form of ornament. Many of the artists in the exhibition also have an interest in the relationship between structure and ornament.
Sandra Selig (Australian, b. 1972)
heart of the air you can hear
2011
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Sandra Selig (Australian, b. 1972)
heart of the air you can hear (detail)
2011
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Koji Ryui (Australian/Japanese, b. 1976)
Extended network towards the happy end of the universe
2007-2011
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
The connections between artistic representations of networks and the rapidly evolving field of network science are the subject of the latest exhibition at the Monash University Museum of Art (MUMA).
Presenting the work of Australian and international artists, NETWORKS (cells & silos) reflects the organising principles and dynamics of our increasingly networked society, and related patterns found in organic, social and engineered forms.
MUMA’s Senior Curator, Geraldine Barlow conceived and developed the exhibition as a way of continuing the dialogue about the role and effect of different networks in society.
“Art and aesthetics are often treated as very separate enclaves from science, physics and mathematics,” Barlow says. “But art offers us a way to re- contextualise our associations and interactions with the networks around us and look at the effect they have on us. I hope the exhibition will prompt people to think about the networks in their lives and how they mould and shape us.”
A key inspiration for the exhibition was Annamaria Tallas’ documentary, How Kevin Bacon Cured Cancer, which features the work of network scientist Albert-László Barabási.
“The documentary explores the thesis that all networks – both natural and man-made – conform to a similar mathematical formula, with the same patterns emerging over and again,” Barlow said.
The artworks featured in NETWORKS (cells & silos) explore networks as diverse as those found in urban planning and cities, biology, organisations, travel and of course social networks, as well as the dual qualities of hyper-connectedness and isolation that technology has heightened in modern life.
Extending the dialogue about the possibilities of networks is of great interest to MUMA Director, Max Delany, particularly in the university context.
“Within a university we have a vast array of specialist disciplines – science, technology, humanities – all having conversations about how the world is and where we want to be heading,” Delany says. “Often these conversations are held in isolation from each other, but considered together, and from the standpoint of artists, the possibilities of collaborative networks become very exciting.”
This collaboration can be seen in Kerrie Poliness’ work Blue Wall Drawing #1 (2007/2011). Students from Monash University have created the piece, following the formal and conceptual guidelines set out by the artist. Each version of Poliness’ work creates unique patterns and networks as the collaborative team choose how to implement the drawing rules which are structured to allow a different outcome in each space where they are applied.
The exhibition’s accompanying publication contains essays from curator Geraldine Barlow, network and social theorists Geert Lovink and Ned Rossiter, and science documentary filmmaker Annamaria Tallas, all exploring the exhibition’s theme. Digital and hard copies are available on request.
Press release from the Monash University Museum of Art
Bryan Spier (Australian)
Shadowmath and New descending (installation view)
both 2010
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
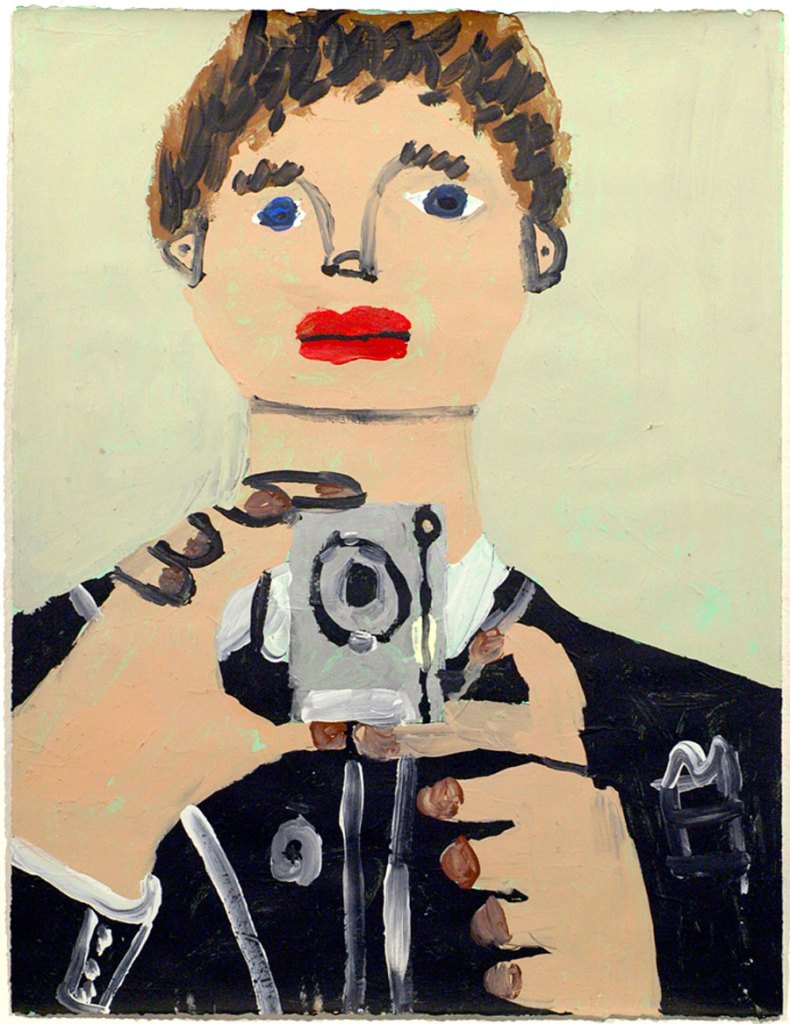
Kit Wise (Australian born England, b. 1975)
KTM SEA MOW RUH
2010
Digital photograph
Monash University Museum of Art (MUMA)
Ground Floor, Building F.
Monash University Caulfield campus
900 Dandenong Road
Caulfield East, VIC 3145
Phone: +61 3 9905 4217
Opening hours:
Tuesday – Friday 10am – 5pm
Saturday 12 – 5pm
Monash University Museum of Art (MUMA) website
LIKE ART BLART ON FACEBOOK
Back to top















































































You must be logged in to post a comment.