Exhibition dates: 24th September 2010 – 20th March 2011
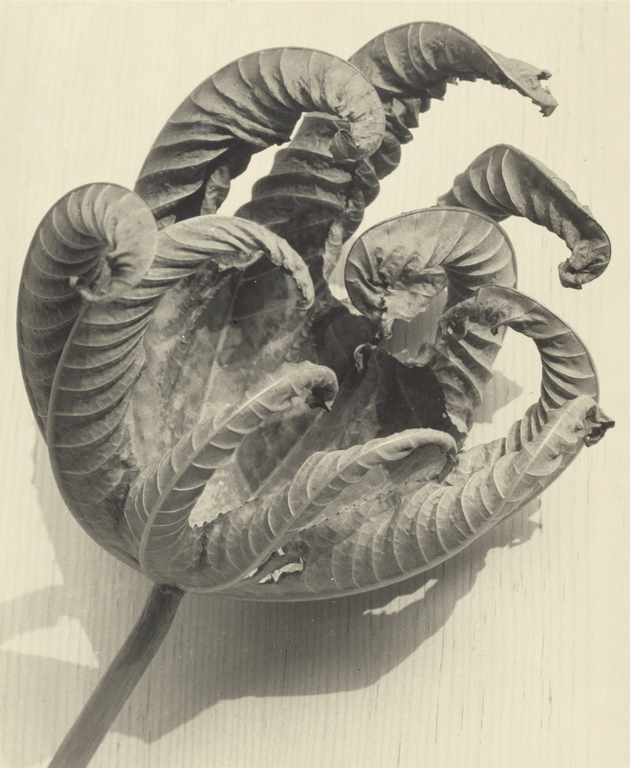
Nici Cumpston (Australian / Barkindji, b. 1963)
Nookamka – Lake Bonney
2007
watercolour and coloured pencils on ink on canvas
74.2 x 203cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, Victorian Foundation for Living Australian Artists, 2008
© Nici Cumpston
“It is this irreversibly modified world, from the polar caps to the equatorial forests, that is all the nature we have.”
Simon Schama. Landscape and Memory 1
“The term “landscape” can be ambiguous and is often used to describe a creative interpretation of the land by an artist and the terrain itself. But there is a clear distinction: the land is shaped by natural forces while the artist’s act of framing a piece of external reality involves exerting creative control. The terms of this ‘control’ have be theorised since the Renaissance and, while representations of nature have changed over the centuries, a landscape is essentially a mediated view of nature.”
Dr Isobel Crombie 2
“And, finally, what of the vexed, interrelated matter of non-Aboriginal Australians’ sense of belonging? While the Australian historian Manning Clark speculated that European settlers were eternal outsiders who could never know ‘heart’s ease in a foreign land, because … there live foreign ancestral spirits’, it now seems plausible that non-Aboriginal Australians are developing their own form of attachment, not to land as such, but to place. Indeed, it has recently been argued that for contemporary non-Aboriginal Australians, belonging may have no connection with land at all. Perhaps this is one of the reasons why art photographs of the natural landscape have lost their currency and are now far outnumbered by photographs of urban and suburban environments – after all, it is ‘here’ that most Australians live and ‘there’ that the tourist industry beckons them to escape.”
Helen Ennis. Photography and Australia 3
This review took a lot of research, reading, thinking and writing, all good stuff – I hope you enjoy it!
Heavy Weather: Photography and the Australian Land(e)scape
There is nothing fresh about the work in this exhibition. If feels like all the oxygen has been sucked out of the term ‘landscape’, the land itself gasping for air, for life. What the exhibition does evince is an “undercurrent of disruption and contradiction that suggests that all is not as it may appear” (wall text) – and on this evidence the process of photographing the Australian landscape seems to have become an escape from the land, a fragmented and dislocated scoping, mapping and photographing of mental aspects of the land that have little to do with the landscape itself. Landscape as a site of psychological performance. In this sense, the title Stormy Weather should perhaps have been Heavy Weather for contemporary photographic artists seem to make heavy going of photographing our sense of belonging to land, to place.
Is it the artists or the curators that seek to name this work ‘landscape photography’ for it is about everything but the landscape – an escape from the land, perhaps even a denial of it’s very existence. I believe it is the framing of landscape and its imaging in terms of another subject matter. While I am not going to critique individual works in the exhibition, what I am interested in is this framing of the work as ‘landscape photography’.
Since colonial settlement there has been a rich history of photographing the Australian landscape. In the early colonial period the emphasis was on documenting the building of new cities and communities through realist photography and later more picturesque and panoramic vistas of the Australian land as settlers sought comfort in familiar surroundings and a sense of ‘belonging’ to the land (for example day trippers and photographers travelling to the Blue Mountains). Photographers rarely accompanied expeditions into the interior, unlike the exploration and mapping of the land from the East Coast to the West Coast in the United States. Unlike America there has been little tradition of photographing sublime places in Australia because they are not of the same scale as in the USA. It is very difficult to photograph the vast horizon line of the Australian outback and make it sublime. Photographing the landscape then ventured through Pictorialism in the interwar years, Modernism after WWII through to the emergence of art photography in the 1970s (for example see my posting on Dr John Cato), wilderness and tourist photography. An excellent book to begin to understand the history of photography in Australia is Photography and Australia by Helen Ennis (London: Reaktion Books, 2007) that contains the chapter “Land and Landscape.” As Ennis comments in this chapter, “… landscape photography has been the practice of settler Australians and the expression of a settler-colonial culture … The viewpoint in landscape photography has therefore been almost exclusively European”4 although this culture has been changing in recent years with the emergence of Indigenous photographers.
Ennis observes that contemporary landscape photographers embrace internationalist styles, showing a distaste for totalising nationalist narratives and a rejection of essentialist or absolutist viewpoints, noting that an overarching framework like multiculturalism has lost its currency in favour of transnationalism (which is a social movement grown out of the heightened interconnectivity between people and the loosening of boundaries between countries) that does not disavow colonial inequalities and asymmetrical relations between countries and continents.5 Photographers have developed a “photographic language that allows for the expression of the contradictions inherent in contemporary settler Australians’ relations with the land,”6 whilst offering visual artists a “non-linear, non-didactic way of dealing with the complexities of Australia history and experience, and the relationship between past and present.”7
This much then is a given. Let us now look at the framing of the work in the exhibition as ‘landscape photography’.
Simon Schama in his erudite book Landscape and Memory (New York: Vintage, 1996) believes that there can never be a natural or neutral landscape (even the brilliant meadow-floor [at Yosemite] which suggested to its first eulogists a pristine Eden was in fact the result of regular fire-clearances by its Ahwahneechee Indian occupants) and that it is our shaping perception that makes the difference between raw matter and landscape. There was also a recognition that ‘nature’ was neither neutral nor beyond ideology during the 1970s-1980s. Hence there is a double mediation – by both nature and the artist.
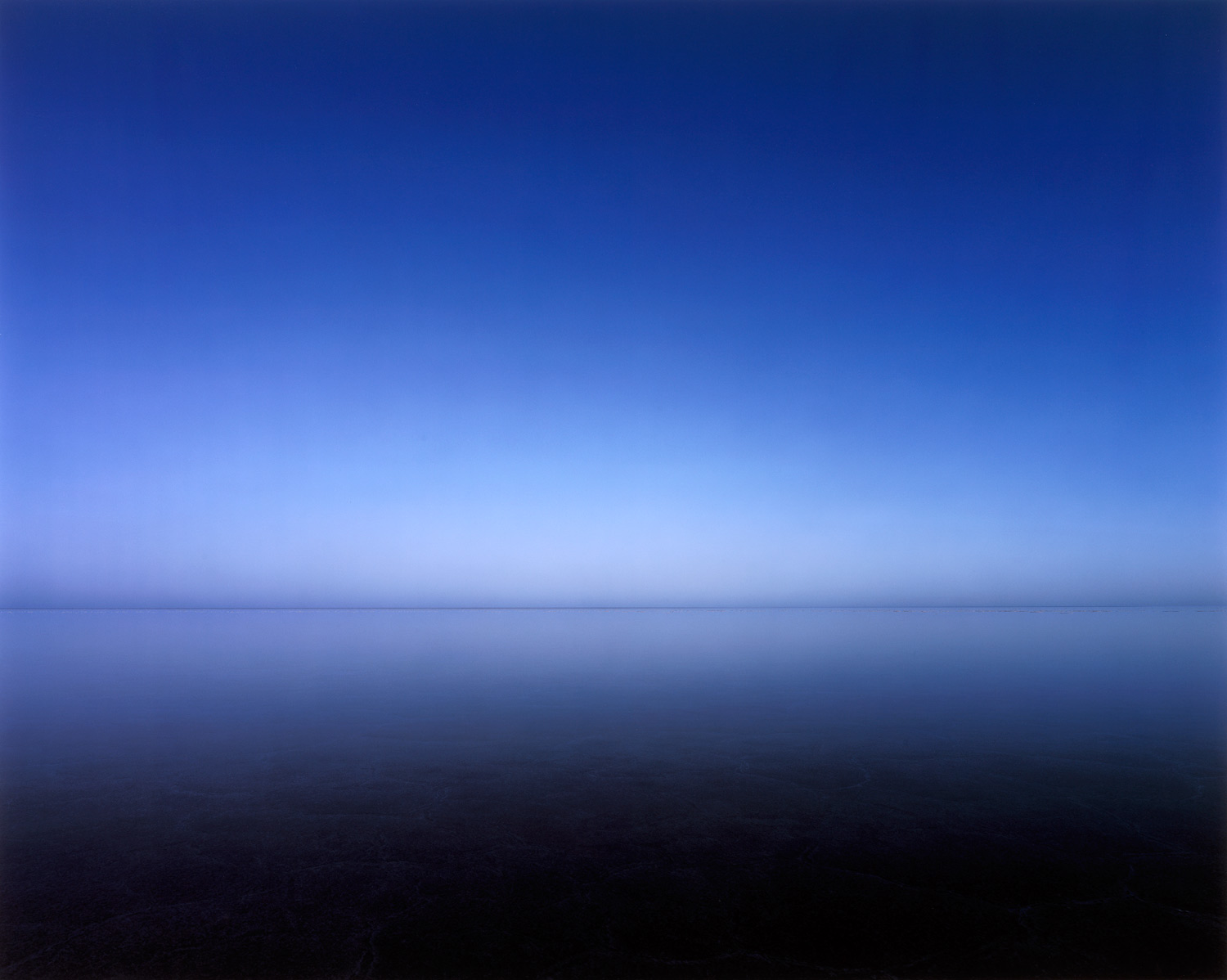
Despite the rejection of essentialist or absolutist viewpoints by contemporary photographers and an acknowledgment of the mediated view by/of nature one can say that there is not a single photograph in this exhibition that is just a ‘landscape’. Even the most sublime photographs in the exhibition, David Stephenson’s (Self-portrait), Reflected moon, Tasmania (1985) is cut up into a grid, or Murray Fredericks Salt photographs (2005, see below) where the photographer has waited agonisingly for weeks for just the right weather conditions to take his photographs which the general public, when visiting Lake Eyre, would have no chance of ever seeing. Through this mediation there seems to have emerged an abrogation or denial of landscape by the artists and curators conceptualisation of it, as though they are performing a particular condition, a style; working out a plan of what to do and say. Is it just a denial or is it an artistic strategy?
I believe that these are strategies that limit artists, not strategies that enable them. The curators are equally implicated in these strategies by their naming of these works ‘landscapes’. What purpose does this naming serve, in terms of the development of a sense of place, not nation, that people living in Australia seek to have? We can ask the question: Where do you stand in relationship to the landscape both philosophically and geographically?
After Butler, we can also ask: What forms of cultural myth making are “embedded” in the framing of landscape by the curators, the naming of such work as ‘landscape photography’?
Rarely is the framing recognised for what it is, when it is the viewer interpreting the interpretation that has been imposed upon us, that limits the visual discourse, producing a view of Australian landscape as fragmented norms enacted through visual narrative frames – that in this case efface the representation of land and place. This conceptual framing of what the work is about limits the grounds for discourse for a frame excludes as much as it corrals. The curators form an interpretative matrix of what is seen (or not seen, or withheld), reinforcing notions of landscape photography, the ‘landscape photography’ “that requires a certain kind of subject that actually institutes that conceptual requirement as part of its description and diagnosis.”8 In other words the description ‘landscape photography’ established by the curators becomes a limiting, self-fulfilling prophecy.
Personally, I think the problem with a landscape exhibition is that this is virtually an inane topic. Somehow “documentary” works as a topic because it is about a mental discipline. But “landscape” is no longer really a topic – it used to be a topic when landscape painters wanted to show the landscape (!) but does anyone really want to show this today? Even when the landscape painters wanted to show the sublime, the landscape was always treated with deference. No-one thinks of Minor White as a landscape photographer for he was a metaphysical photographer. And that’s what this exhibition needs – another word to give sense to a photographers efforts.
This is difficult subject matter. While artists may reject essentialist or absolutist viewpoints what has been substituted in their place is a framing, a definition that is post-nature, that undermines any sense of belonging to land, to place. The dissolutive pendulum has swung too far the other way; we look to theory to be inclusive and sometimes stand on our heads to achieve this to our detriment.
As of this moment we are not at the point where we can look back with some certainty and see that we have reached the beginning of the path of understanding. What I would propose to any artist is a photography that is broadly based, cumulative, offering a layered body of work that builds and refers back to an original body of work, much like the photographs of Robert Adams – photographs that do not make claims but ask questions and hint at a more responsive engagement with the landscape.
My hope is that a more broadly based view of place and our sense of belonging to the land emerges, one that challenges our contemporary understanding of the landscape, a viewpoint and line of sight that calm our troubled sense of reality. Robert Adams has written eloquently about photography and the art of seeing. Here is a quote from his seminal book Why People Photograph (Aperture Foundation, 1994) that aptly concludes this review.
“At our best and most fortunate we make pictures because of what stands in front of the camera, to honor what is greater and more interesting than we are. We never accomplish this perfectly, though in return we are given something perfect – a sense of inclusion. Our subject thus redefines us, and is part of the biography by which we want to be known.”9
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to Jemma Altmeier and the National Gallery of Victoria for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Addendum
Further to my argument above there is a session ‘Australian Identity: Australian Bio-diversity and the Landscape of the Imagination’ at the Festival of Ideas, Friday June 17th 2011 at the University of Melbourne where, in the details of the upcoming session, Ian Burn has been quoted about the loss of the landscape:
Details of the session: ‘The connection between landscape and national identity figures prominently in discussions of Australian experience. Recently the pairing of the two has taken a melancholic turn; artist Ian Burn has remarked that ‘A commitment to representing the landscape has come to be about the “loss” of the landscape’. Has the landscape that once supported the Australian legend disappeared? The landscape is represented not only in art but also through science, law and commerce. Are new landscapes and new identities now being imagined and discovered?’
Quotation: “The idea of landscape does not just invoke rival institutional discourses, but today attracts wider and more urgent reflections. A commitment to representing the landscape has become about the ‘loss’ of landscape in the twentieth century … that is about its necessity and impossibility at the same time. Seeing a landscape means focusing on a picture, implicating language in our seeing of the landscape.”
Burn, Ian quoted in Stephen, Ann (ed.,). Artists think: the late works of Ian Burn. Sydney: Power Publications in association with Monash University Gallery, Melbourne, 1996, p. 8.
Footnotes
1/ Schama, Simon. Landscape and Memory. New York: Vintage, 1996, p. 7
2/ Crombie, Isobel. Stormy Weather. Contemporary Landscape Photography (exhibition catalogue). Melbourne: National Gallery of Victoria, 2010, p. 15
3/ Clark, Manning quoted by Peter Read in “A Haunted Land No Longer? Changing Relationships to a Spiritualised Australia,” in Australian Book Review CCLXV (October 2004) pp. 28-33 in Ennis, Helen. “Land and Landscape,” in Photography and Australia. London: Reaktion Books, 2007, pp. 71-72
4/ Ennis, Helen. “Land and Landscape,” in Photography and Australia. London: Reaktion Books, 2007, pp. 51-52
5/ Ennis, Helen. “Land and Landscape,” in Photography and Australia. London: Reaktion Books, 2007, p. 123, p. 133
6/ Ibid., “Land and Landscape,” pp. 71-72
7/ Ibid., “Localism and Internationalism,” p. 128
8/ Butler, Judith. Frames of War: When is Life Grievable? London: Verso, 2010, p. 161
9/ Adams, Robert. Why People Photograph. New York: Aperture Foundation, 1994, p. 179
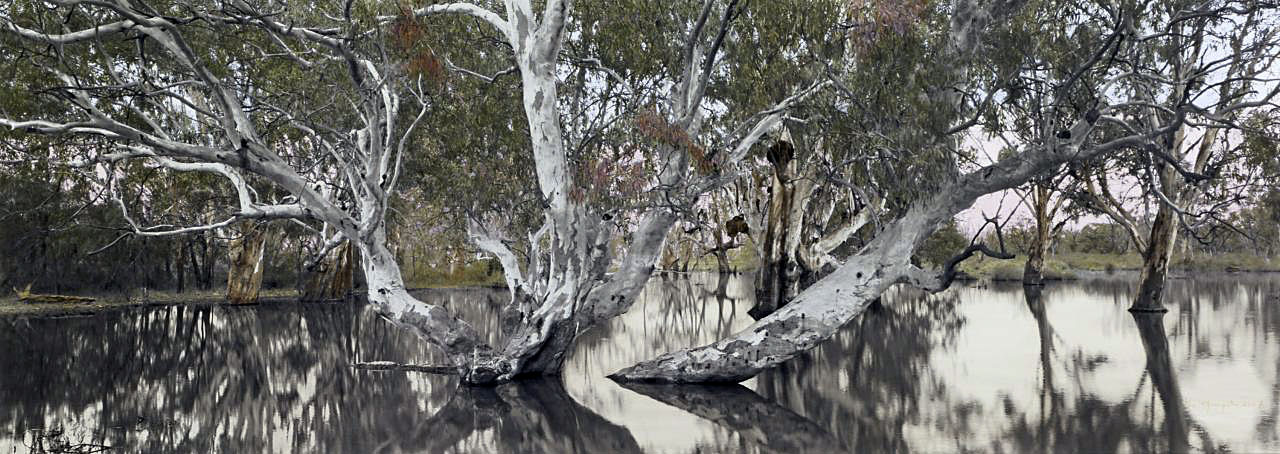
Nici Cumpston (Australian / Barkindji, b. 1963)
Flooded Gum, Katarapko Creek, Murray River National Park
2007
Watercolour and pencil on inkjet print on canvas
74.5 x 202.5cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, Victorian Foundation for Living Australian Artists, 2008
© Nici Cumpston
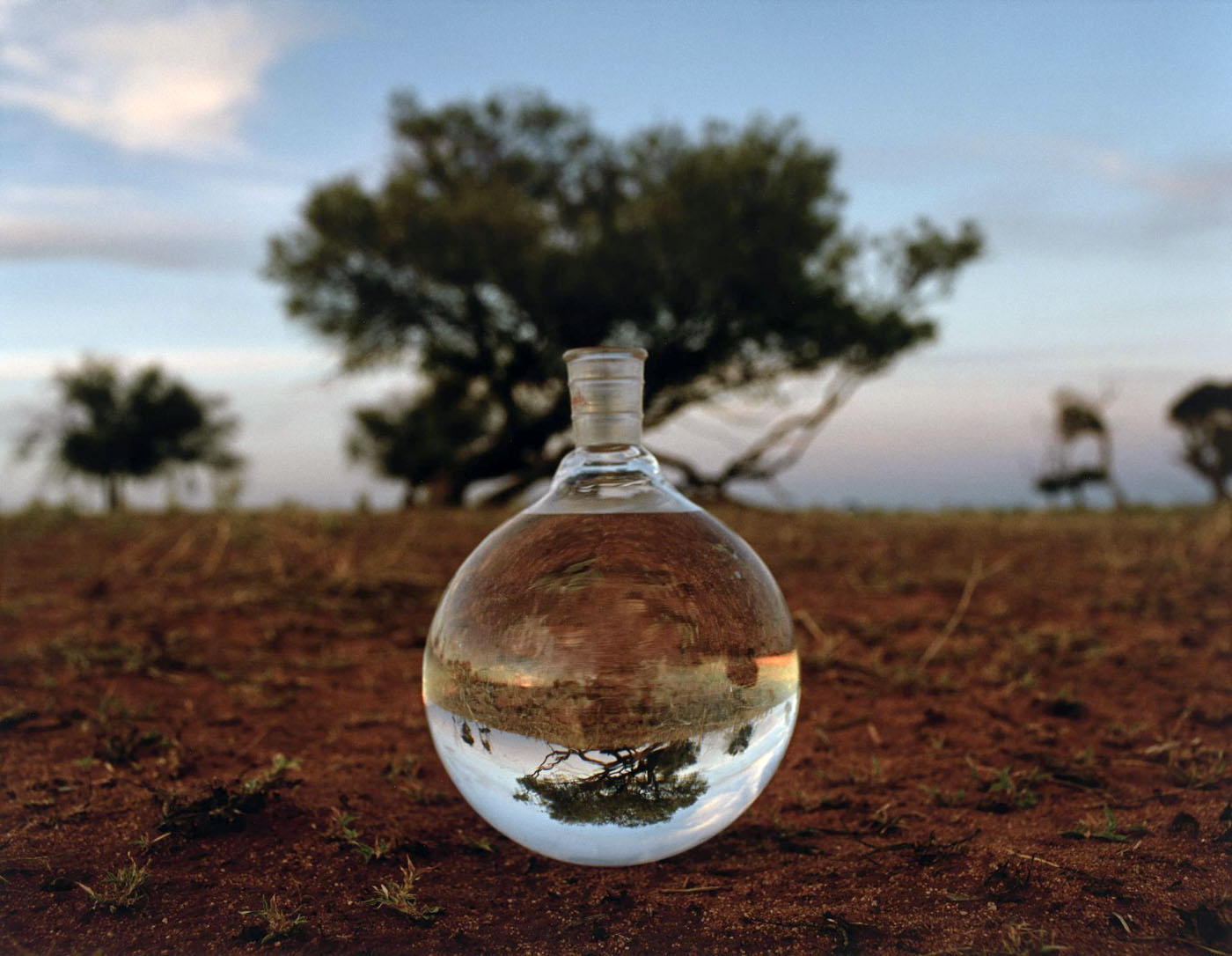

Stephanie Valentin (Australian, b. 1962)
Earthbound
2009
from the Earthbound series
inkjet photograph
70 x 90cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased with funds donated by Phillip Ross and Sophia Pavlovski-Ross, 2009
© Stephanie Valentin
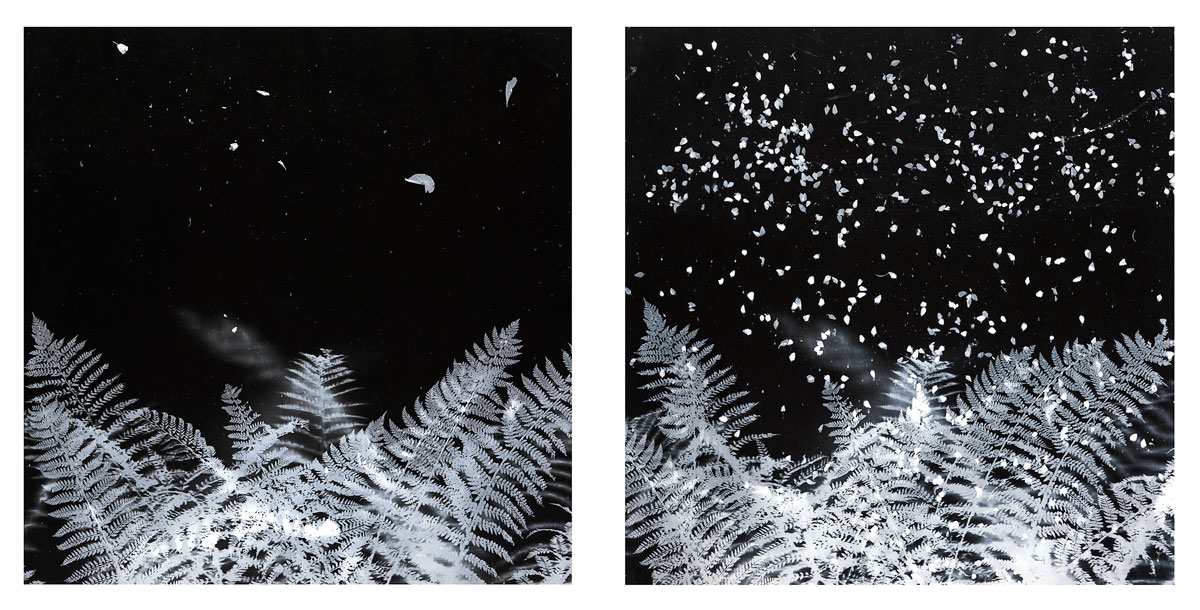
Harry Nankin (Australian, b. 1953)
Of Great Western tears / Duet 2
2006
From The rain series 2006-2007
Gelatin silver photographs
(a-b) 107.1 x 214.3cm (overall)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased NGV Foundation, 2007
© Harry Nankin
Stephanie Valentin (Australia, b. 1962)
Rainbook
2009
From the earthbound series 2009
Colour inkjet print
69.9 x 86.9cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased with funds donated by Philip Ross and Sophia Pavlovski-Ross, 2009
© Stephanie Valentin
Murray Fredericks (Australia, b. 1970)
Salt 154
2005
From the Salt series 2003-
Colour inkjet print
119.3 x 149.3cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, Victorian Foundation for Living Australian Artists, 2009
© Murray Fredericks
Siri Hayes (Australia, b. 1977)
Plein air explorers
2008
Type C photograph
104.3 x 134.8cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, Victorian Foundation for Living Australian Artists, 2009
© Siri Hayes
The work of the contemporary Australian photographers highlighted in this exhibition comes from a profound engagement with the lived landscape around them. The quiet intensity of their work comes from their close and sustained relationship to particular environments. These photographers may use that lived observation to reveal the layers of history in a landscape; to provoke ecological concerns; as the place for site specific performances; or to use the specific poetics of light to reveal the beauty of a place. However for all of them, the real world is the starting point for images of particularity.
Photographers’ interest in the landscape has increased in the last few years. Perhaps as a result of heightened environmental awareness, or an evolution in our engagement with Australian history, practitioners are again turning to the natural world as a site for critical practice and inspiration.
Drawn from the permanent collection the National Gallery of Victoria, the selected photographers in this exhibition have a particular focus that comes from their active relationship to various environments. The artists displayed here reveal history in a landscape; provoke ecological concerns; use the landscape as a site of performance; or reveal the distinctive beauty of a place.
Frequently underpinning these works of quiet intensity and considerable beauty is an undercurrent of disruption and contradiction that suggests all is not as it may first appear.
Text from the National Gallery of Victoria website [Online] Cited 26/02/2011 no longer available online

Rosemary Laing (Australia, b. 1959)
weather #9
2006
From the weather series 2006
Type C photograph
109.9 x 184.6cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, Victorian Foundation for Living Australian Artists, 2007
© Rosemary Laing and Tolarno Galleries, Melbourne
Jill Orr (Australia , b. 1952, lived in the Netherlands 1980-1984)
Southern Cross to bear and behold – Burning
2007
Colour inkjet print
65.5 x 134.9cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, Victorian Foundation for Living Australian Artists, 2010
Photographer: Naomi Herzog for Jill Orr
© Jill Orr
The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia
Federation Square
Corner of Russell and
Flinders Streets, Melbourne
Opening hours:
Open daily 10am – 5pm


































![Felix Gonzalez-Torres (American born Cuba, 1957–1996) '[No Title]' 1985 from the exhibition 'Between Here and There: Passages in Contemporary Photography' at The Metropolitan Museum of Art Felix Gonzalez-Torres (American born Cuba, 1957–1996) '[No Title]' 1985 from the exhibition 'Between Here and There: Passages in Contemporary Photography' at The Metropolitan Museum of Art](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/02/felix-gonzalez-torres-no-title-1985.jpg?w=284)
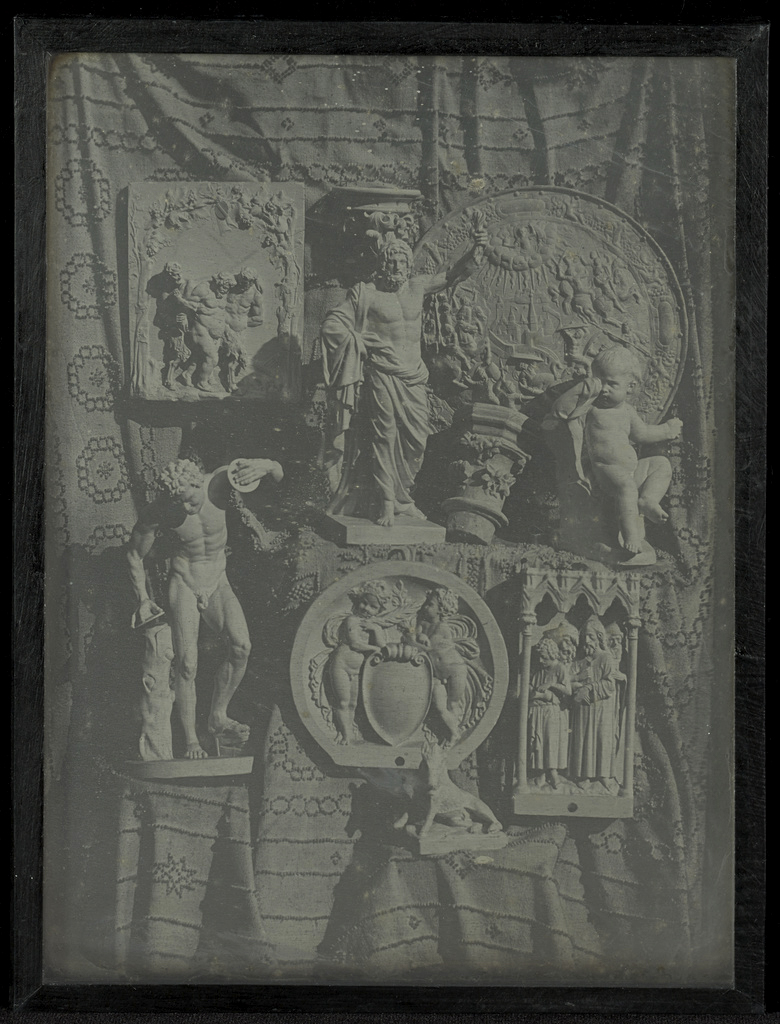

































![Louis-Rémy Robert (French, 1811-1882) '[Still Life with Statuette and Vases]' Negative 1855; print 1870s from the exhibition 'In Focus: Still Life' at The J. Paul Getty Museum Louis-Rémy Robert (French, 1811-1882) '[Still Life with Statuette and Vases]' Negative 1855; print 1870s from the exhibition 'In Focus: Still Life' at The J. Paul Getty Museum](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/robert-still-life-with-statuette-and-vases.jpg?w=830)
![Roger Fenton (English, 1819-1869) '[Still Life with Game and Gun]' about 1859 from the exhibition 'In Focus: Still Life' at The J. Paul Getty Museum Roger Fenton (English, 1819-1869) '[Still Life with Game and Gun]' about 1859 from the exhibition 'In Focus: Still Life' at The J. Paul Getty Museum](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/fenton-still-life-with-game-and-gun.jpg?w=969)
![Charles Aubry (French, 1811-1877) '[An Arrangement of Tobacco Leaves and Grass]' about 1864 from the exhibition 'In Focus: Still Life' at The J. Paul Getty Museum Charles Aubry (French, 1811-1877) '[An Arrangement of Tobacco Leaves and Grass]' about 1864 from the exhibition 'In Focus: Still Life' at The J. Paul Getty Museum](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/aubry-tobacco.jpg)
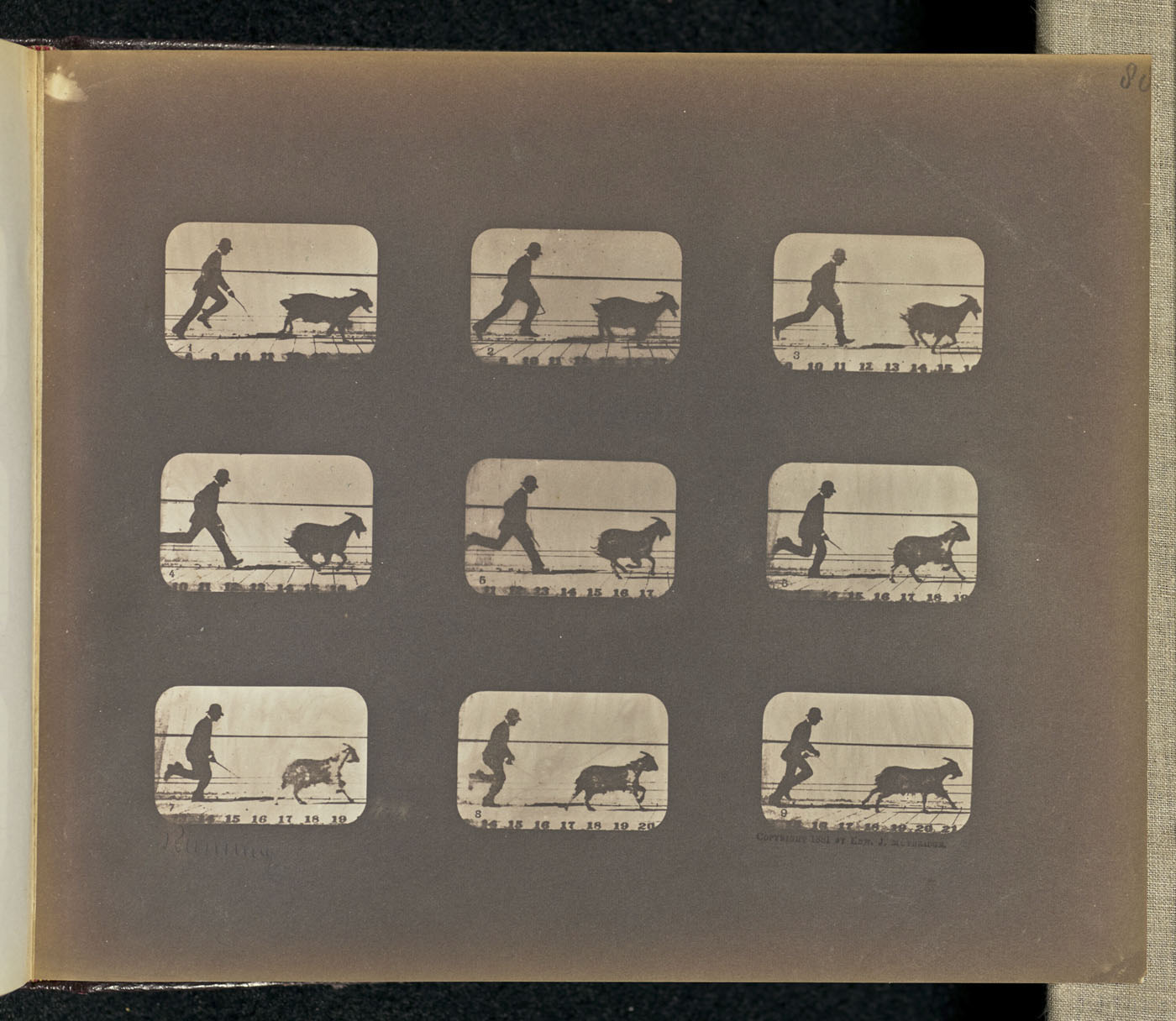
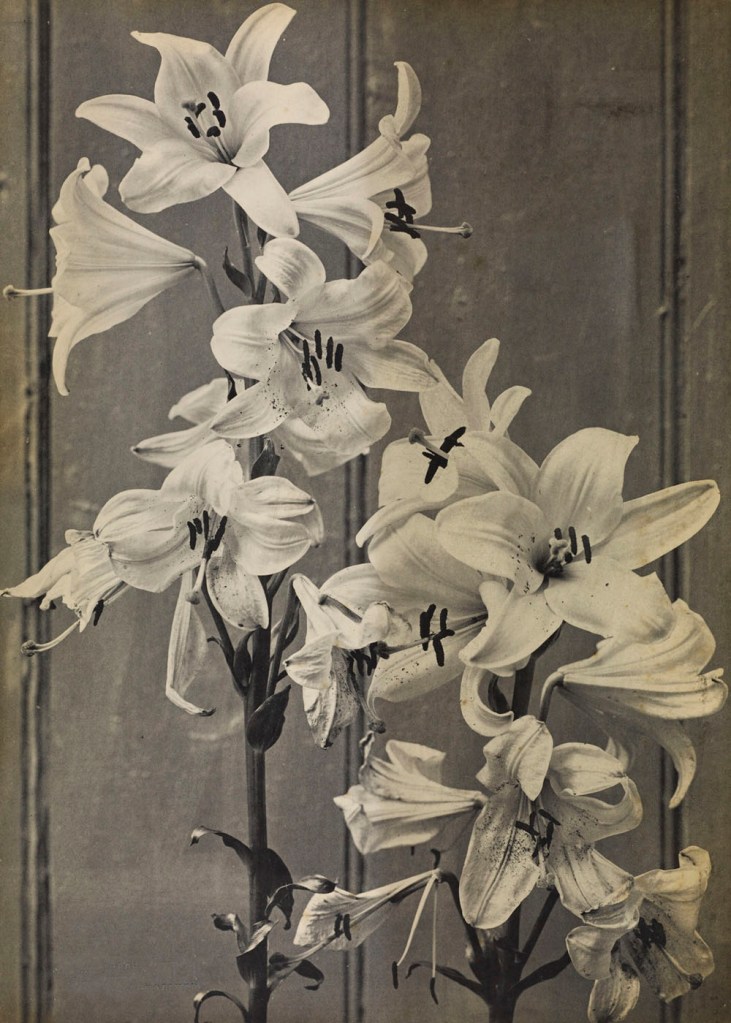
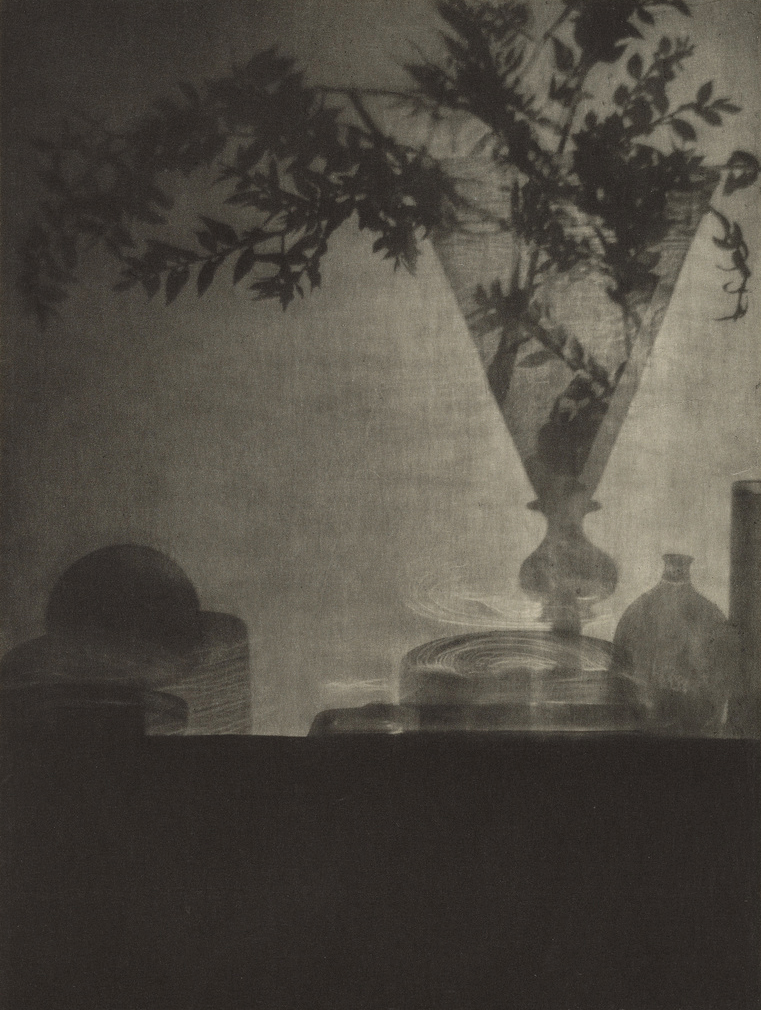



![Heinrich Kühn (Austrian born Germany, 1866-1944) '[Tea Still-life, Version III]' 1907 from the exhibition 'In Focus: Still Life' at The J. Paul Getty Museum Heinrich Kühn (Austrian born Germany, 1866-1944) '[Tea Still-life, Version III]' 1907 from the exhibition 'In Focus: Still Life' at The J. Paul Getty Museum](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/heinrich-kucc88hn-tea-sea-life.jpg)
![Paul Strand (American, 1890-1976) '[Black Bottle]' negative about 1919; print 1923-1939 from the exhibition 'In Focus: Still Life' at The J. Paul Getty Museum Paul Strand (American, 1890-1976) '[Black Bottle]' negative about 1919; print 1923-1939 from the exhibition 'In Focus: Still Life' at The J. Paul Getty Museum](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/strand-black-bottle.jpg)





![André Kertész (American born Hungary, 1894-1985) '[Bowl with Sugar Cubes]' 1928 from the exhibition 'In Focus: Still Life' at The J. Paul Getty Museum André Kertész (American born Hungary, 1894-1985) '[Bowl with Sugar Cubes]' 1928 from the exhibition 'In Focus: Still Life' at The J. Paul Getty Museum](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/kertesz-sugar.jpg)
























You must be logged in to post a comment.