Exhibition dates: 30th September – 12th November 2017
Curators: Naomi Cass and Pippa Milne
Living artists include: Laurence Aberhart, Brook Andrew, Rushdi Anwar, Warwick Baker, Paul Batt, Robert Billington, Christian Boltanski, Pat Brassington, Jane Brown, Daniel Bushaway, Sophie Calle, Murray Cammick, Christian Capurro, Steve Carr, Mohini Chandra, Miriam Charlie, Maree Clarke, Michael Cook, Bill Culbert, Christopher Day, Luc Delahaye, Ian Dodd, William Eggleston, Joyce Evans, Cherine Fahd, Fiona Foley, Juno Gemes, Simryn Gill, John Gollings, Helen Grace, Janina Green, Andy Guérif, Siri Hayes, Andrew Hazewinkel, Lisa Hilli, Eliza Hutchison, Therese Keogh, Leah King-Smith, Katrin Koenning, O Philip Korczynski, Mac Lawrence, Kirsten Lyttle, Jack Mannix, Jesse Marlow, Georgie Mattingley, Tracey Moffatt, Daido Moriyama, Harry Nankin, Jan Nelson, Phuong Ngo.
Historic photographers: Hippolyte Bayard (French, 1801-1887), Charles Bayliss (Australian born England, 1850-1897), Bernd and Hilla Becher (German; Bernd Becher 1931-2007, Hilla Becher 1934-2015), Lisa Bellear (Australian / Goernpil, 1962-2006), James E. Bray (Australian, 1832-1891), Jeff Carter (Australian, 1928-2010), Harold Cazneaux (Australian, 1878-1953), Olive Cotton (Australian, 1911-2003), Peter Dombrovskis (Australian, 1995-1996), Max Dupain (Australian, 1911-1992), Joyce Evans (Australian, 1929-2019), Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975), Sue Ford (Australian, 1943-2009), Marti Friedlander (New Zealand born Britain, 1928-2016), Kate Gollings (Australian, 1943-2017), André Kertész (Hungarian, 1894-1985), J. W. Lindt (Australian born Germany, 1845-1926), W. H. Moffitt (Australian, 1888-1948), David Moore (Australian, 1927-2003), Michael Riley (Australian / Wiradjuri/Kamilaroi, 1960-2004), Robert Rooney (Australian, 1937-2017), Joe Rosenthal (American, 1911-2006), Mark Strizic (Australian, 1928 -2012), Ingeborg Tyssen (Australian, 1945-2002), Aby Warburg (German, 1866-1929), Charles Woolley (Australian, 1834-1922).
(1) J W Lindt (Australian, 1845-1926)
Body of Joe Byrne, member of the Kelly Gang, hung up for photography, Benalla
1880
Courtesy State Library Victoria, Pictures Collection
Thought to be the first press photograph in Australia, this shows Joe Byrne, a member of the Kelly Gang, strung up for documentation days after his death, which followed the siege at Glenrowan. Byrne is displayed for an unknown photographer and the painter Julian Ashton who is standing to the left with possibly a sketchbook under his arm. Lindt’s photograph captures not only the spectacle of Byrne’s body but the contingent of documentarians who arrived from Melbourne to record and widely disseminate the event for public edification.
Double take
I was a curatorial interlocutor for this exhibition so it was very interesting to see this exhibition in the flesh.
An unorthodox flow of images is a strong exhibition, splendidly brought to fruition by curators Naomi Cass and Pippa Milne at the Centre for Contemporary Photography (CCP), Melbourne. To be able to bring so many themes, images, ideas and people together through a network of enabling, and a network of images, is an impressive achievement.
The exhibition explores the notion of connectivity between images in our media saturated world – across context, time and space. “With a nod to networked image viewing behaviour and image sharing – in one long line – the flow also impersonates the form of a sentence.” While the viewer makes their own flows through the works on view, they must interpret the interpolation of images (much like a remark interjected in a conversation) in order to understand their underlying patterns of connection. Like Deleuze and Guattari’s horizontal rhizome theory1 – where the viewer is offered a new way of seeing: that of infinite plateaus, nomadic thought and multiple choices – here the relationship between the photograph and its beholder as a confrontation between self and other, and the dynamic relation between time, subjectivity, memory and loss is investigated … with the viewer becoming an intermediary in an endless flow of non-hierarchical images/consciousness.
In this throng of dialects, the exhibition meanders through different “sections” which are undefined in terms of their beginning and end. The starting point for this flow is the public demonstration of trauma for the edification of society (the photographs of the aftermath of the siege of Ned Kelly and his gang at Glenrowan), notably what is thought to be the first press photograph in Australia, J W Lindt’s Body of Joe Byrne, member of the Kelly Gang, hung up for photography, Benalla (1880, above), and the flow then gathers its associations through concepts such as studio work, the gaze, disruption, truth, performance and traces, to name just a few. The exhibition ceaselessly establishes connections between semiotic chains, organisations of power and contextual circumstances, moving forward and backwards in time and space, jumping across the gallery walls, linking any point to any point if the beholder so desires. In this sense (that of an expanded way of thinking laterally to create a democracy of sight and understanding), the exhibition succeeds in fostering connections, offering multiple entryways into the flow of images that proposes a new cultural norm.
For Deleuze and Guattari these assemblages (of images in this case), “… are the processes by which various configurations of linked components function in an intersection with each other, a process that can be both productive and disruptive. Any such process involves a territorialization; there is a double movement where something accumulates meanings (re-territorialization), but does so co-extensively with a de-territorialization where the same thing is disinvested of meanings.”2 Now here’s the rub (or the trade-off if you like) of this exhibition, for everything in life is a trade-off: the accumulation of new meaning that such a flow of images creates is balanced by what has been lost. Both an accumulation and disinvestment of meaning.
I have a feeling that in such a flow of images the emotion and presence of the subject has been lost, subsumed into a networked, hypermedia flow where, “images become more and more layered until they are architectural in design, until their relationship to the context from which they have grown cannot be talked about through the simple models offered by referentiality, or by attributions of cause and effect.”3 The linear perspective developed during the Renaissance and its attendant evidence of truth / objective reality (the logic of immediacy) is disrupted. It is no longer about being there, about the desire for presence, but about a logic of hypermediacy that privileges fragmentation, process, and performance. Of course, immediacy / hypermediacy are part of a whole and are not exclusionary to each other. But here contemporary art, and in particular contemporary photography, keeps coming back to the surface, redefining conceptual and aesthetic spaces.
This is where I was plainly unmoved by the whole exhibition. Conceptually and intellectually the exhibition is very strong but sequentially and, more importantly, emotionally – the flow of images failed to engage me. The dissociative association proposed – like a dissociative identity disorder – ultimately becomes a form of ill/literation, in which the images seem drained of their passion, a degenerative illness in which all images loose their presence and power. In a media saturated world what does it mean to pluck these images from a variable spatio-temporal dimensionality and sequence them together and hope they give meaning to each other? Ultimately, it’s a mental exercise of identity organisation that is pure construct.
Further, this (re)iteration is a repetition that is supposed to bring you successively closer to the solution of a problem: what is the relevance of the stream of image consciousness in contemporary society? What happens to the referentiality and presence of the individual image?
With this in mind, let us return to the first image in the flow of images, J W Lindt’s Body of Joe Byrne, member of the Kelly Gang, hung up for photography, Benalla (1880, above). Here Byrne is displayed for an unknown photographer and the painter Julian Ashton who is standing to the left with possibly a sketchbook under his arm. Amongst other things, the image is by a photographer taking a photograph of another photographer taking a photograph of the body of Joe Byrne. Immediately, the triangular relationship of camera / subject / viewer (cause and effect) is disrupted with the addition of the second photographer. There is a doubling of space and time within this one image, as we imagine the image the photographer in the photograph would have taken. And then we can see two variations of that internal photograph: Photographer unknown Joe Byrne’s Body, Benalla Gaol, 29 June 1880 (below) and William J. Burman’s Joe Byrne’s Body, Benalla Gaol, 29 June 1880 (1880, below) which 1/ appears to solve who the “photographer unknown” is (unless Burman purchase the rights to use another’s photographers’ negatives); and 2/ is a more tightly framed image than the first iteration. If you look at the top of the head in the second image the hair goes over the metal hinge of the door behind… so the photographer (the same one) has moved closer and dropped the height of the camera, so that the camera looks up more, at the body.
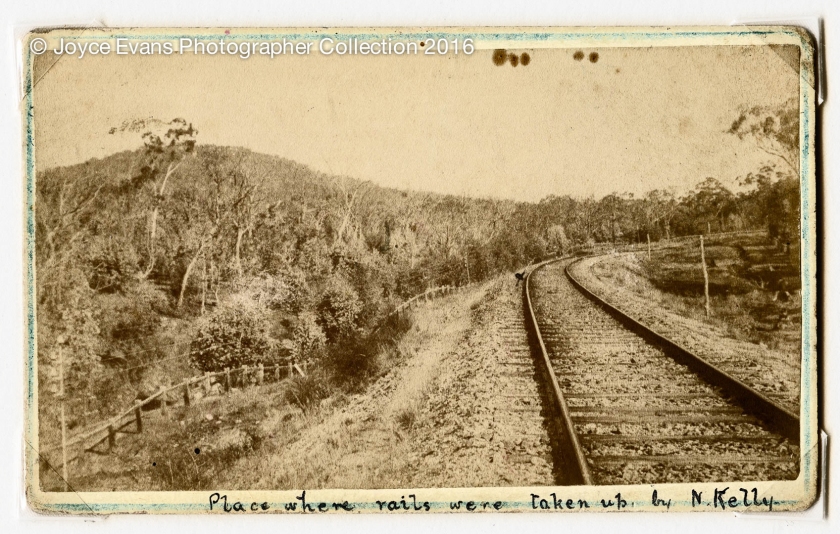
Other details fascinate. The ring on the left finger of Joe Byrne; his stripped shirt; the rope under his arms used to help support his weight; the rope disappearing out of picture to help string him up; and questions such as, how did they get his left hand to stay in that position? This is also, “an image of an audience as much as a portrait of the deceased … Members of the public are also documented; children, men – trackers perhaps, bearing witness to the public display of retribution that was intended to restore social order.” To the left we have what is presumably the photographers’ coat hung on a tree; a man wiping his nose with his thumb; and Aboriginal man; and a boy looking at the camera. Through his silhouette the Aboriginal man can probably be identified as Tracker Johnny, one of five trackers who helped track Ned Kelly, and we can see a portrait of him in an albumen photograph held by the Queensland Police Museum (1880, below). A picture of the ‘Other’, both outsiders, the outlaw and the Aboriginal, detailing the social order. The blurred image of the boy looking at the camera shows the length of the time exposure for the glass plate, but it is his “Janus-faced” visage that I am fascinated with… as he both looks forwards and backwards in time. Whilst most images within An unorthodox flow of images are conceptually grounded, they also evidence only one direct meaning in relationship to themselves within that network, “each one connected to those on either side,” – from point to point to point. Conversely, in this image the interpretation is open-ended, WITHIN THE ONE IMAGE. It is a network all of its own. I also remember, emotionally, the other images of the burnt out Glenrowan Inn, the place where the rails were taken up (I was there!), the bodies in the coffins, the preparation for the photograph of the Kelly Gang Armour laid out in a muddy field for documentation, and the burnt to a cinder, charred remains rescued from the ashes of the Glenrowan Inn laid out on a piece of wood. There is a physicality to these photographs, and an emotional charge, that no other photograph in this exhibition matches. I think, then, not of Joe Bryne’s lifeless body and its/the photographs morbidity, but of him as a younger man – standing legs crossed, one hand on hip, the other resting on the surface of a table, imagining his touch on that table in reality – a son, an outlaw, a living being.
I wish the curators had been braver. I wish that they had given these images more chance to breathe. I wish they had cut the number of images and sequenced them so that the space between them (what Minor White calls ice/fire, that frisson of space between two images that adds to their juxtaposed meaning) provided opportunity for a more emotional engagement with what was being presented. Yes, this is a strong exhibition but it could have been so much more powerful if the flow had not just meandered through the sentence, but cried out, and declaimed, and was quiet. Where was the punctum? Where was the life blood of the party, if only disappearing in a contiguous flow of images.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Word count: 1,642
Footnotes
1/ Deleuze, Gilles and Guattari, Felix. A Thousand Plateaus: Capitalism and Schizophrenia. Minneapolis and London: University of Minneapolis Press, 1987
2/ Wood, Aylish. “Fresh Kill: Information technologies as sites of resistance,” in Munt, Sally (ed.,). Technospaces: Inside the New Media. London: Continuum, 2001, p. 166
3/ Burnett, Ron. Cultures of Vision: Images, Media, & the Imaginary. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 1995, pp. 137-138.
Many thankx to the CCP for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image. The numbers in brackets refer to the number of the image in the field guide. The text is taken from the field guide to the exhibition [Online] Cited 01/11/2017. No longer available online.
An unorthodox flow of images commences with what is known as the first press photograph in Australia and unfurls through historic, press, portraiture, popular and art photography, some in their intended material form and others as reproductions. An unbroken thread connects this line of still and moving images, each tied to those on either side through visual, conceptual, temporal, material or circumstantial links.
This is a proposition about photography now. Relationships between images are sometimes real, and sometimes promiscuous. Unorthodox brings new contexts to existing artworks whilst celebrating the materiality of real photographs, in real time and critically, honouring the shared democratic experience of the public gallery space. (Text from the CCP website)
J W Lindt (Australian, 1845-1926)
Body of Joe Byrne, member of the Kelly Gang, hung up for photography, Benalla (details)
1880
Courtesy State Library Victoria, Pictures Collection
(2) Photographer unknown (Australian)
Joe Byrne’s Body, Benalla Gaol, 29 June
1880
Photographic print from glass plate
12 × 19.5cm
© Collection of Joyce Evans
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
This image appears to the one of the images taken by the photographer in J. W. Lindt’s Body of Joe Byrne, member of the Kelly Gang, hung up for photography, Benalla 1880 (above)
William J. Burman (Australian born England, 1814-1890)
Joe Byrne’s Body, Benalla Gaol, 29 June 1880
1880
At 209 Bourke Street, East Melbourne 1878-1888
Albumen carte de visite
6.5 × 10.5cm
This image appears to the one of the images taken by the photographer in J. W. Lindt’s Body of Joe Byrne, member of the Kelly Gang, hung up for photography, Benalla 1880.
Unknown photographer
Untitled [Portrait of Tracker Johnny from Maryborough District one of five trackers who helped track Ned Kelly] (detail, not in exhibition)
c. 1880
Albumen photograph
Queensland Police Museum
Non-commercial – Share Alike (cc)
(3) J. E. Bray (Australian, 1832-1891)
Kelly Gang Armour
1880
Albumen cabinet portrait
16.5 × 10.5cm
© Collection of Joyce Evans
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
“As objects of contemplation, images of the atrocious can answer to several different needs. To steel oneself against weakness. To make oneself more numb. To acknowledge the existence of the incorrigible.” ~ Susan Sontag, Regarding the Pain of Others (2003)
(4) Unknown photographer
Place where rails were taken up by Kelly gang
1880
Albumen carte de visite
6.5 × 10.5cm
© Collection of Joyce Evans
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
(5) J. E. Bray (Australian, 1832-1891)
The Glenrowan Inn after the Kelly Siege
1880
Albumen carte de visite
6.5 × 10.5cm
© Collection of Joyce Evans
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
(6) J. E. Bray (Australian, 1832-1891)
Charred remains from Kelly gang siege
1880
Albumen carte de visite
6.5 × 10.5cm
© Collection of Joyce Evans
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
In her comments on a related photograph by Bray, Helen Ennis writes, “What you see pictured, presumably as part of the official documentation are the thoroughly blackened remains of either Dan Kelly or Steve Hart… Relatives raked what remained of the bodies… from the ashes of the Glenrowan Inn. These were then photographed before family members took them home on horseback and buried them. … [These photographs] also underscore the brutality and barbarism of the post-mortem photographs – the violence physically enacted on the body in the first instance and then visually in terms of the photographic representation.”
Helen Ennis. “Portraiture in extremis” in Photogenic Essays / Photography / CCP 2000-2004, Daniel Palmer (ed.), 2005, CCP, pp. 23-39, p. 34
(7) J. E. Bray (Australian, 1832-1891)
Untitled [“McDonnell’s Tavern opposite Railway Station, remains of Dan Kelly and Hart in coffins”]
1880
Albumen cabinet portrait
16.5 × 10.5cm
© Collection of Joyce Evans
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
W. E. (William Edward) Barnes (Australian, 1841-1916)
Steve Hart (1859-1880) (front and verso, not in exhibition)
c. 1878
Albumen carte de visite
6.5 × 10.5cm
© Collection of Joyce Evans
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
W. E. (William Edward) Barnes (Australian, 1841-1916)
Steve Hart (1859-1880) (not in exhibition)
c. 1878
Albumen carte de visite
State Library of Victoria
(9) Piero della Francesca (Italian, 1415-1492)
Flagellation of Christ
1455-1460
Oil and tempera on wood, reproduced as digital print on wallpaper
58.4 × 81.5 cm, reproduced at 20 × 30 cm
The meaning of della Francesca’s Flagellation and exact identity of the three foreground figures in fifteenth century dress, is widely contested. In the context of this flow of images, the painting represents the pubic display of suffering as punishment, for the edification of society. In both J.W. Lindt’s documentary photograph and the possibly allegorical Flagellation, the broken body of Joe Byrne and that of Christ are isolated from other figures and subject of conversation and debate by gathered figures. Other formal similarities include framing of the tableau into shallow and deep space the organising role of architecture in signifying the key subject.
(10) Joosep Martinson
Police Hostage Situation Developing at the Lindt Café in Sydney
2014
Digital print on wallpaper
20 × 30cm
The scene outside the Lindt Cafe siege, caught by the photojournalist in a moment of public trauma. This bears formal resemblance to J.W. Lindt’s photograph of Joe Byrne, and even further back to Piero della Francesca.
(13) Tracey Moffatt (Australian, b. 1960)
I made a camera
2003
photolithograph
38 × 43cm, edition 201 of 750
Private collection
Returning to J.W. Lindt’s photograph in particular the hooded central figure photographing Joe Byrne – Tracey Moffatt’s picturing of children role-playing calls to mind the colonial photographer’s anthropological gesture.
(14) Siri Hayes (Australian, b. 1977)
In the far reaches of the familiar
2011
C-type print
88 × 70 cm, exhibition print
Courtesy the artist
The photographer’s hood is the photographer.
(15) Janina Green (Australian born Germany, b. 1944)
Self Portrait
1996
Digital version of a hand-coloured work in early Photoshop
44 × 60cm
Courtesy the artist and M.33, Melbourne
(16) Georgie Mattingly
Portrait IV (After Arthroplasty)
2016
Hand-tinted silver gelatin print
36 × 26cm
Unique hand print
Courtesy the artist
The photographer’s hood has become a meat-worker’s protective gear, tenderly hand-coloured. [And spattered with blood ~ Marcus]
(17) Lisa Hilli (Makurategete Vunatarai (clan) Gunantuna / Tolai People, Papua New Guinea)
In a Bind
2015
Pigment print on cotton rag
76 × 51.5cm
Courtesy the artist
‘The woven material that hoods the artist’s identity is a reference to collected Pacific artefacts, which are usually of a practical nature. Magimagi is a plaited coconut fibre used for reinforcing architectural structures and body adornment within the Pacific. Here it emphasises the artist’s feeling of being bound by derogatory Western and anthropological labels used by museums and the erasure of Pacific bodies and narratives within public displays of Pacific materiality.’ ~ Lisa Hilli 2017, in an email to the curator
In an era of ‘tumbling’ images, An unorthodox flow of images presents visual culture in a novel way: commencing with Australia’s first press photograph, 150 images unfurl in flowing, a-historical sequences throughout the gallery. Each work is connected to the one before through formal, conceptual or material links.
An unorthodox flow of images draws upon the photographic image in its many forms, from significant historical photographs by major Australian artists, such as J.W. Lindt, Olive Cotton and Max Dupain, through to contemporary international and Australian artists, such as Tracey Moffatt, Michael Parekowhai, Christian Boltanski and Daido Moriyama. This exhibition brings early career artists into the flow, including Georgie Mattingley, Jack Mannix and James Tylor.
Celebrating the breadth of photographic technologies from analogue through to digital, including hand made prints, a hand-held stereoscope, early use of Photoshop, iPhone videos and holography, An unorthodox flow of images propels the viewer through a novel encounter with technology, art, and the act of looking. Rather than a definitive narrative, this exhibition is a proposition about relationships between images: sometimes real and sometimes promiscuous, and is inevitably open to alternative readings. Contemporary culture necessitates quick, networked visual literacy. So viewers are invited to make their own readings of this unorthodox flow.
Akin to how images are experienced in our personal lives and perhaps to how artists are influenced by the multiverse of photography, this extraordinary gathering also includes spirited incursions from other kinds of images – rare prints of grizzly 19th century photojournalism abuts contemporary video first shared on Instagram, and surrealist French cinema nestles in with Australian image-makers.
This exhibition aims to bring new contexts to existing artworks to highlight networked image-viewing behaviour, whilst honouring the materiality of real photographs, in real time and critically, honouring the shared democratic experience of the public gallery space. An unorthodox flow of images is presented as part of the 2017 Melbourne Festival.
Press release from the CCP
(30)Siri Hayes (Australian, b. 1977)
Plein air explorers
2008
C-type print
108 × 135cm, edition 4 of 6
Collection of Jason Smith
An artist’s studio in the landscape.
(31) Robyn Stacey (Australian, b. 1952)
Wendy and Brett Whiteley’s Library
2016
From the series Dark Wonder
C-type print
110 × 159cm, edition of 5 + 3 artist proofs
Courtesy the artist and Jan Manton Gallery, Brisbane
The landscape brought into the studio by a camera obscura. Robyn Stacey captures the perfect moment of light and clarity, in this instance, also turning the egg-object into an orb of light.
(37) Pat Brassington (Australian, b. 1942)
Vedette
2015
Pigment print
75 × 60cm, edition of 8,
Courtesy the artist and ARC ONE Gallery, Melbourne and Bett Gallery, Hobart
Two orbs, a positive and a negative space.
(38) Anne Noble (New Zealand, b. 1954)
Ruby’s Room 10
1998-2004
Courtesy the artist and Two Rooms Gallery Auckland
(42) Daido Moriyama (Japanese, b. 1938)
DOCUMENTARY ’78
1986
Silver gelatin print
61 × 50.8cm
Private collection
(43) Leah King-Smith (Australian / Bigambul, b. 1957)
Untitled #3
1991
From the series Patterns of connection
C-type print
102 × 102cm, edition 6 of 25
Private collection
‘I was seeing the old photographs as both sacred family documents on one hand, and testaments of the early brutal days of white settlement on the other. I was thus wrestling with anger, resentment, powerlessness and guilt while at the same time encountering a sense of deep connectedness, of belonging and power in working with images of my fellow Indigenous human beings.’ ~ L King-Smith, White apron, black hands, Brisbane City Hall Gallery, 1994, p. 7. In this series, the artist superimposes the colonial portrait onto images of the subject’s own landscape, returning the dispossessed to country.
Unorthodox: a field guide
We could have started anywhere. Perhaps every image ever made connects with another image in some way. But, we have begun with what is known as the first press photograph in Australia – a grisly depiction of Kelly Gang member Joe Byrne, strung up some days after his execution, for a group of onlookers, including a group of documentarians who came in by train to record the event: a painter and several photographers. This is an image of an audience as much as a portrait of the deceased. A hooded photographer bends to his tripod, and a painter waits in line. Perhaps a seminal moment between competing technologies of record, magnificently captured by colonial photographer, J. W. Lindt (1845-1926): this is as decisive a moment as current technology permitted. Members of the public are also documented; children, men – trackers perhaps, bearing witness to the public display of retribution that was intended to restore social order.
From here, Unorthodox draws a thread of images together, each one connected to those on either side, whether through visual, conceptual, temporal, material or circumstantial ties, or by something even more diffuse and smoky – some images just conjure others, without a concrete reason for their bond. Spanning the entire gallery space, nearly 150 images unfurl with links that move through historic, press, portraiture, popular and art photography.
You are invited to wander through CCPs nautilus galleries, and make what you will of this flow because unlike a chain of custody, there is no singular narrative or forensic link: you are invited to explore not just connections between works but to see individual works in a new light.
At the core of this exhibition is an attempt to lay bare the way that images inform and seep into everyday life, underpinning the way that we see, interpret and understand the world. With a nod to networked image viewing behaviour and image sharing – in one long line – the flow also impersonates the form of a sentence.
The act of looking. Looking is a process, informed by context – where and when we see something, and what surrounds it. Here, images are unbuckled from their original context, indeed there are no museum labels on the wall. But this is often the way when viewing images on the internet, or reproduced in books, referenced in ads, reenacted in fashion shoots, or reinterpreted by artists. The notion of reproductions within photography is slippery, made more so by the rapid circulation of images whereby we sometimes only know certain originals through their reproductions. In this exhibition, sometimes we have the original images, at others we proffer ‘reproductions’, setting out a swathe of contemporary and historical approaches to the craft of photography and video, unhampered by traditional constraints of what we can or cannot show within a non-collecting contemporary art space.
This exhibition moves through a number of notional chapters, for example visual connections can be made between orbs made by soap bubbles (no. 32, 34) and moons (no. 33); eyes (no. 40, 41, 42), gaping mouths (no. 37), the balletic body in space (no. 45); and light from orbs (no. 44, 46) and then moonlight on the ocean (no. 47), which tumbles into salty connections, with photographs exposed by the light of the moon through seawater (no. 48) connecting to an image of salt mines (no. 50), and on to salt prints (no. 51).
We have been influenced by observing how audiences view exhibitions, traversing the space, seemingly drawing connections, making their own flows through works on view. In spite of its indexicality to the world, photography is particularly open to multiple readings due to its reproducibility and its vulnerability to manipulation. A key to this permeability is the intention of the photographer, which can become opaque over time. For example, installation artist Christian Boltanski’s found photograph (no. 137) has been taken out of its time and context so as to mean something quite different from what the photographer intended.
Importantly, due to their multiple readings, many works could be equally effective if placed in other sections of the exhibition. For example, of the many places to position Leah King-Smith’s Untitled #3 (no. 43), we have elected to locate it amongst compositions that include orbs. However, it is also a staged work; a constructed or collaged photograph; it embodies an Indigenous artist returning the colonial gaze and, due to the age of her source photograph, it represents a deceased person. And, in her own words King-Smith is responding to the trauma of settlement. ‘I was thus wrestling with anger, resentment, powerlessness… while at the same time encountering a sense of deep connectedness, of belonging and power in working with images of my fellow Indigenous human beings.’
A curious process indeed, we have been open to many repositories of images while gathering this flow – from our work with artists at CCP; to childhood memories of images and personal encounters with photography and video; to our trawling of the Internet and books; as well as conversations with writers, artists and collectors. From these stores, we have also considered which works were available in their material form, as opposed to reproductions on wallpaper, postcards and record covers. While we exhibit a broad timespan and multiple technologies, our primary desire as a contemporary art space is to create new contexts for the exhibition of contemporary photography and video.
Unorthodox is a proposition about relationships between images: sometimes real and sometimes promiscuous, and is inevitably open to alternative readings. It brings new contexts to existing artworks whilst celebrating the materiality of real photographs, in real time and critically, honouring the shared democratic experience of the public gallery space.
Naomi Cass and Pippa Milne
(62) Brook Andrew (Australian, b. 1970)
I Split Your Gaze
1997, printed 2005
Silver gelatin print
160 × 127cm
Private collection
Courtesy the artist and Tolarno Galleries, Melbourne; Roslyn Oxley9 Gallery, Sydney; and Galerie Nathalie Obadia, Paris and Brussels
(63) Brassaï (French, 1899-1984)
Young couple wearing a two-in-one suit at Bal De La Montagne Saint-Genevieve
c. 1931
Gelatin silver print
Reproduced as digital print on wallpaper
23.2 × 15.9cm, reproduced at 24.5 × 19cm
(64) William Yang (Australian, b. 1943)
Alter Ego
2000
from the series Self Portraits
Inkjet print, edition 2 of 30
68 × 88cm
Courtesy the artist
(65) Sue Ford (Australian, 1943-2009)
Lyn and Carol
1961
Silver gelatin print, edition 3 of 5
44 × 38cm
Courtesy Sue Ford Archive
(76) Harold Cazneaux (Australian, 1878-1953)
Spirit of Endurance
1937
Silver gelatin print
16.8 × 20.4cm
Private collection
In the following two works, a critical change of title by the artist reveals what, alone, the eye cannot see. This photograph had already achieved iconic status as a symbol of the noble Australian landscape when, following the loss of his son who died aged 21 at Tobruk in 1941, Cazneaux flipped the negative and presented the image under the new title Spirit of Endurance. The tree is now classified on the National Trust of South Australia’s Register of Significant Trees.
(77) Jeff Carter (Australian, 1928-2010)
The Eunuch, Marree, South Australia
1964
Silver gelatin print
37.5 × 27.2cm
Private collection
Changing a title can dramatically alter the meaning of an image. This work has had several titles:
Morning Break 1964;
Dreaming in the sun at Marree, outside the towns single store 1966;
At times there is not too much to do except just sit in the sun… 1968;
‘Pompey’ a well known resident of Marree;
and finally The Eunuch, Marree, South Australia 2000
Under early titles, the photograph appeared to be a simple portrait of “Pompey”, a local Aboriginal man in Marree who worked at the town’s bakery. The final title draws viewers’ attention away from what might have seemed to be the man’s relaxed approach to life, and towards the violence enacted on Aboriginal communities in castrating young boys.
(82) Photographer undisclosed
Persons Of Interest – ASIO surveillance images
1949 -1980
‘Frank Hardy under awning Caption: Author Frank Hardy shelters under an awning, in the doorway of the Building Workers Industrial Union, 535 George St, Sydney, August 1955’
C-type prints
22 × 29cm each
Private collection
The Australian Security and Intelligence Organisation (ASIO) employed photographers to spy on Australian citizens. The photographs which were annotated to indicate persons of interest, were retained by ASIO along with other forms of material gathered through espionage.
(85) Luc Delahaye (French, b. 1962)
L’Autre (detail)
1999
Book published by Phaidon Press, London
17 × 22cm
Private collection
In the footsteps of Walker Evans’ classic candid series, Rapid Transit 1956
(94) David Moore (Australian, 1927-2003)
Migrants arriving in Sydney
1966
Silver gelatin print
35.7 × 47cm
Private collection
In 2015, Judy Annear said of this famous photograph: “It’s great to consider that it’s not actually what it seems.” Years after the photo was published, it emerged that four of the passengers in it were not migrants but Sydneysiders returning home from holiday.
(95) Joe Rosenthal (American, 1911-2006)
Raising the Flag on Iwo Jima
1945
Digital print on wallpaper, reproduced at 20 × 25cm
While not present at the the raising of the first flag over Iwo Jima, Rosenthal witnessed the raising of the replacement flag. Some maintain that this Pulitzer Prize winning photograph was staged, while others hold that it depicts the replacement of the first flag with a larger one.
(103) Charles Kerry (Australian, 1857-1928)
Aboriginal Chief
c. 1901-1907
Carte de visite
13.7 × 8.5 cm
Private collection
No name or details are recorded of this sitter from Barron River, QLD. He was a member of the touring Wild West Aboriginal troupe, which staged corroborees, weapon skills and tableaux of notorious encounters between armed Native Police and unarmed local communities.
(104) Brook Andrew (Australian, b. 1970)
Sexy and Dangerous
1996
Computer-generated colour transparency on transparent synthetic polymer resin, included here as postcard of artwork
original 146.0 × 95.6cm, included here at 15.3 × 10.5cm
The artist is represented by Tolarno Galleries, Melbourne; Roslyn Oxley9 Gallery, Sydney; and Galerie Nathalie Obadia, Paris and Brussels
(116) William Eggleston (American, b. 1939)
Untitled (glass on plane)
1965-1974
C-type print
41 × 56cm
Private collection
(117) Bill Culbert (New Zealand, b. 1935)
Small glass pouring Light, France
1997
Silver gelatin print, edition of 25
40.5 × 40.5cm
Courtesy the artist and Roslyn Oxley9 Gallery, Sydney and Hopkinson Mossman Gallery, Auckland
(118) Olive Cotton (Australian, 1911-2003)
Teacup Ballet
1935
Silver gelatin print
35.5 × 28cm
Courtesy Tony Lee
(119) David Moore (Australian, 1927-2003)
Sisters of Charity
1956
Silver gelatin print
40.5 × 27.1cm
Private collection
(120) Bernd and Hilla Becher (German; Bernd Becher 1931-2007, Hilla Becher 1934-2015)
Kies-und Schotterwerke (Gravel Plants)
2006
Silver gelatin print
99 × 121cm
Private collection
(123) Max Dupain (Australian, 1911-1992)
Backyard, Forster, New South Wales
1940
Silver gelatin print
44 × 39cm
Private collection
(138) Joyce Evans (Australian, 1929-2019)
Budapest Festival
1949
Inkjet print
7.6 × 7.6cm
Courtesy the artist
(145) Jeff Wall (Canadian, b. 1946)
A sudden gust of wind (after Hokusai)
1993
Transparency on lightbox, included here as postcard of artwork
250 × 397 × 34cm, included here at 15.3 × 10.5cm
Artist is represented by Marian Goodman Gallery; Gagosian; and White Cube Gallery
(147) Masayoshi Sukita (Japanese, b. 1938)
David Bowie – Heroes
1977
Record cover
31 × 31cm
Sukita: In gesture and gaze, Sukita’s photograph for David Bowie’s 1977 cover harks back 60 years to Weimar Republic artist, Erich Heckel’s 1917 painting, Roquairol, which is in Bowie’s art collection.
(148) Francis Alÿs (Belgian based Mexico, b. 1959)
Railings (Fitzroy square)
London, 2004
4.03 min.
Francis Alÿs website
We posit Fitzroy Square at this point; in honour of your journey through this unorthodox flow of images.
Centre for Contemporary Photography
404 George St, Fitzroy
Victoria 3065, Australia
Phone: + 61 3 9417 1549
Opening Hours:
Wednesday – Sunday, 11am – 6pm











![J. E. Bray (Australian, 1832-1891) 'Untitled ["McDonnell's Tavern opposite Railway Station, remains of Dan Kelly and Hart in coffins"]' 1880 J. E. Bray (Australian, 1832-1891) 'Untitled ["McDonnell's Tavern opposite Railway Station, remains of Dan Kelly and Hart in coffins"]' 1880](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/bray-je-mcdonnells-railway-tavern-web.jpg?w=840)




































You must be logged in to post a comment.