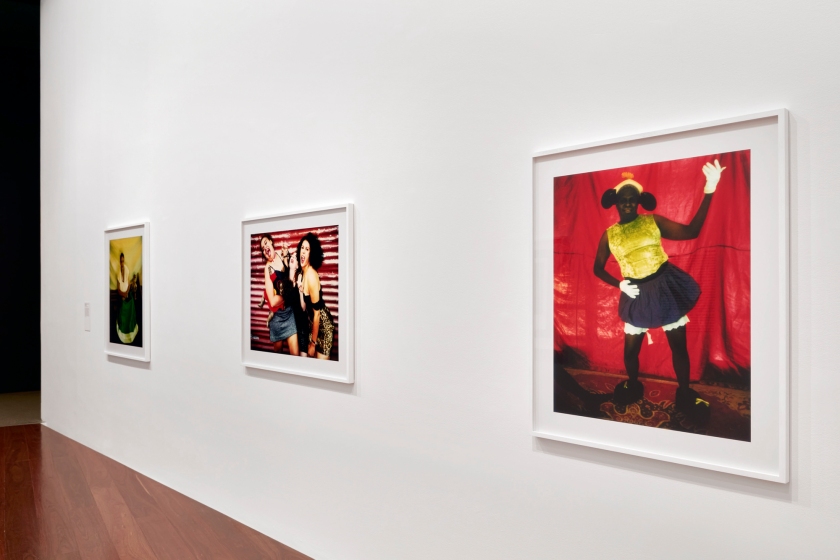
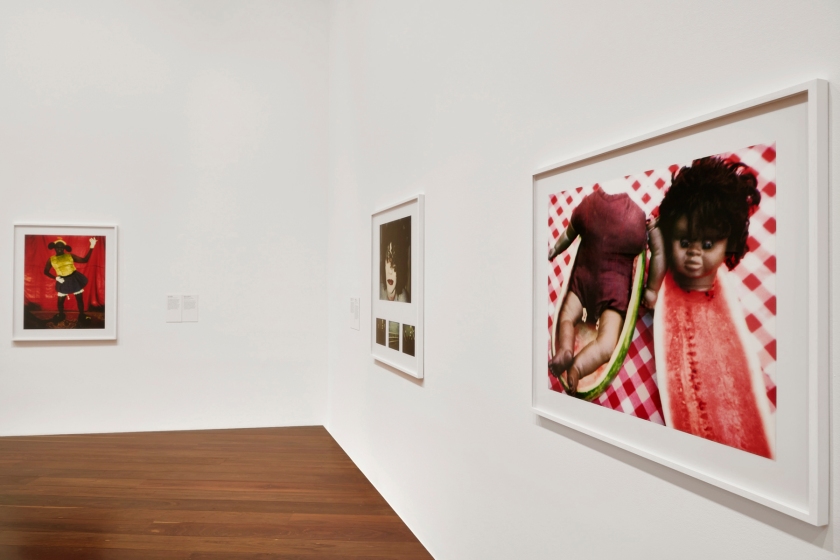
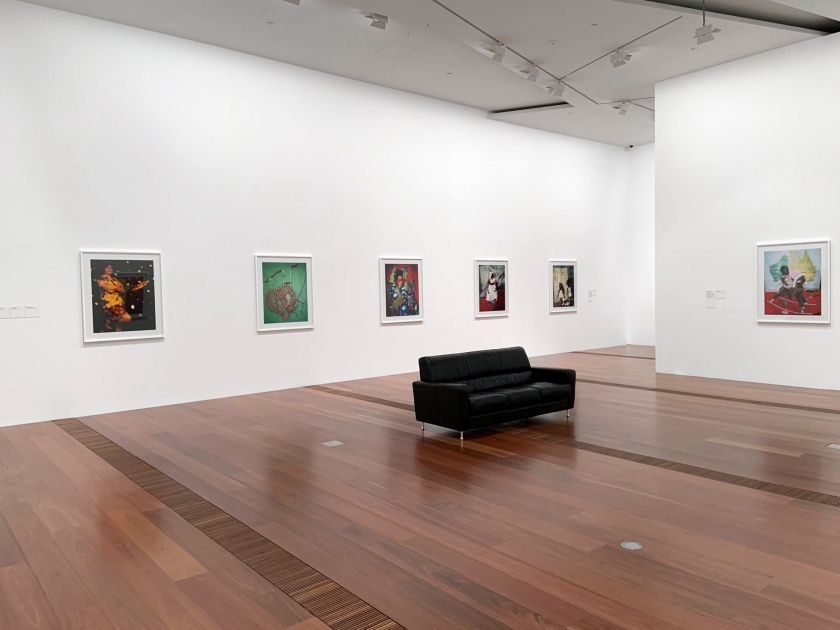
Exhibition dates: 23rd November 2020 – 14th February 2021
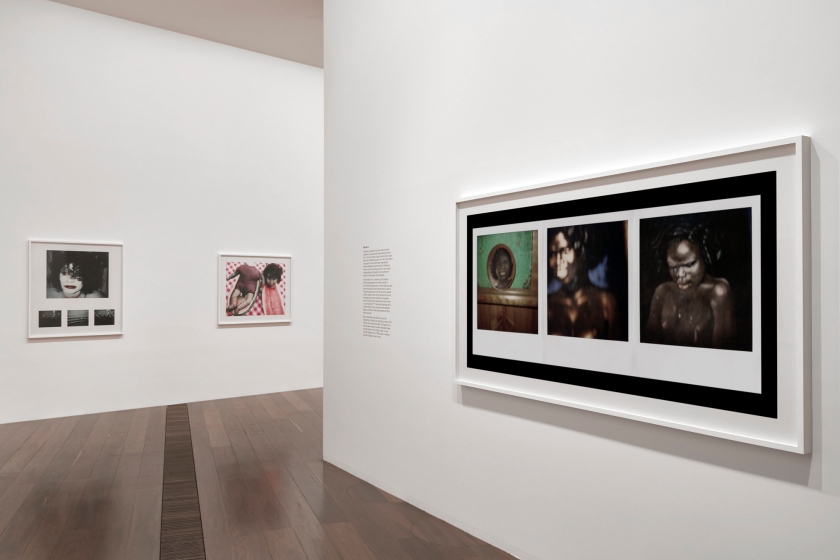
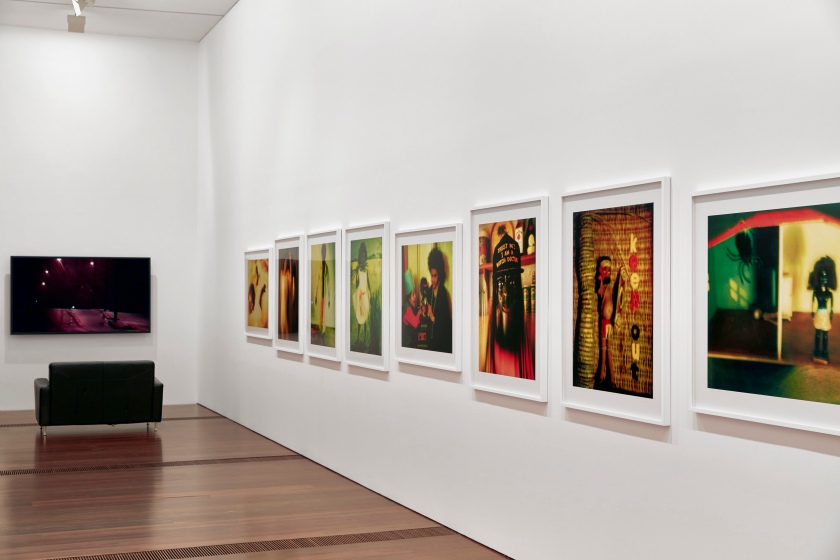
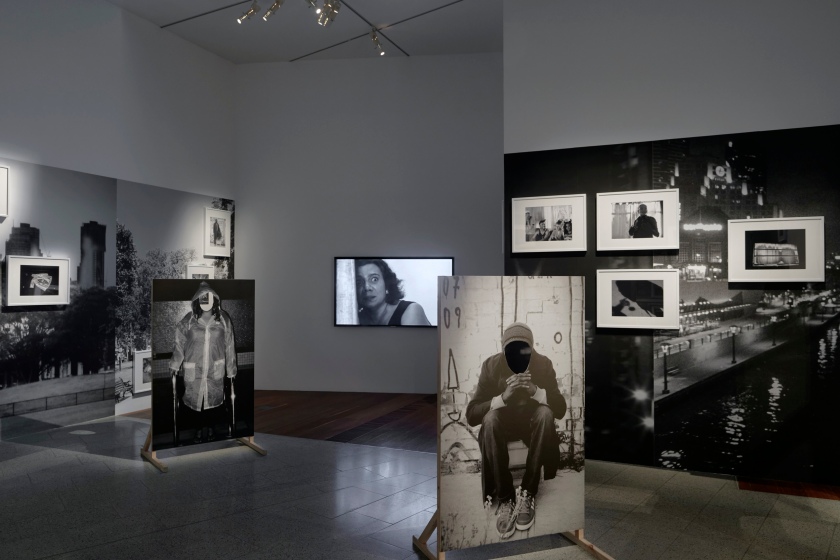
Installation view of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020
Photo: Tom Ross
“There is no excuse for ignorance, and you should make an effort to understand what happens in our world. How else can you be contemporary?”
Destiny Deacon
Embodied Ab/origin
This is a strong, powerful if rather repetitive exhibition by Destiny Deacon at NGV Australia, Melbourne. It’s like being hit over the head with a blakly ironic blunt object many times over, just like Aboriginal people have had both physical and cultural violence enacted upon them many times over since the arrival of the white man in terra nullius, a misnomer if ever there was one.
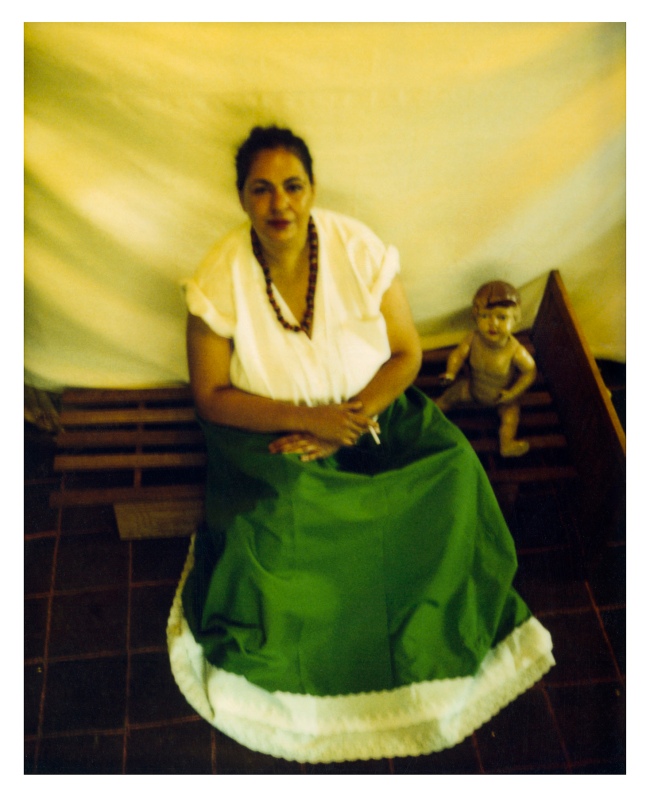
“Drawing from her vast collection of Aboriginalia, Deacon interrogates the way in which Aboriginal people have been, and continue to be, misrepresented within popular culture.” Aboriginalia is repurposed “historicised, interpreted and recast through Aboriginal eyes”, especially through the use of white-appropriated and conceptualised Blak dolly models that allegedly “possess a liveliness and personality, making the violence enacted on to them all the more confronting.” Deacon photographs her reclaimed dollies using Polaroids from which colour prints are enlarged. Technically and aesthetically this means the photographs loose the uniqueness, size and aura of a Polaroid, perhaps not the best outcome for the use of the instant photography process in the making of memorable images.
The exhibition never strays far from its theme: that whities will never understand the symbols of racism perpetrated against Blaks embedded in white culture, unless they are pointed out to them. This concept is expressed through the silent voice of the archetypal Blak doll – dis/embodied, headless, amputated, tied up, trapped in a blizzard, over the fence, adopted – inserted placelessly into whatever scenario bigotry and racism rears its head, a snatched headline of dispossession and grief. While the Blak dolls are a paradigm that Deacon uses to represent the “collective lives” of Aborigines under the heal of a repressive regime, no idea is ever investigated fully for the viewer is only given a snippet of information. Holistically, these snippets add up to a terrible indictment of a dominant race lording it over a vanquished one.
“Marcia Langton once described Destiny Deacon’s work as a ‘barometer of postcolonial anxiety’.” Personally, I don’t feel any sense of postcolonial anxiety when I look at Deacon’s work. I just feel sad, very sad and guilty. Sad for the invasion, sad and guilty for the lives lost, dispossession, poor health, shorter life spans, racism and inequality, the ongoing discrimination and neglect. It’s like sticking the knife in over and over again. I so wish it was different. We KNOW, if we are informed sentient beings, the injustices that Aboriginal people suffered and continue to suffer. As Deacon says, there is no excuse for ignorance. But this is preaching to the converted. How many Joe Public will come and see this exhibition to be informed and to change their mind? As a friend of mine succinctly said, “Don’t come to this exhibition if you don’t want your racism challenged.” Many will not bother. For others this will be a confronting exhibition. And in all this reclaiming of Aboriginalia, all this confrontation, all this looking back, the dredging up of every little inequality – it leaves me thinking: what is the future, where is the positiveness, where is the forward looking cultural creativity of a great people?
I believe that this contemporary reconceptualisation of history from a singular standpoint – that of a unified Ab/original people represented by Blak dolly – is pure hokum. Aboriginal culture is made up of many mobs, many voices, reflecting the difference in backgrounds and experiences of different communities which come together in diversity to present “a statement about the unity of Aboriginal people, the defiant continuity of their cultural traditions and the personal search of many individual artists for their own Aboriginal identity.”1 In this exhibition, where are the homosexual Aboriginals, the lesbian Aboriginals, the transgender Sista Girls, or an investigation into interracial marriages that are loving and kind, instead of just more and more works that reinforce injustices (of history) in the here and now, through the dis/embodied plastic body of a silent doll. Where is the positivity for the future, for example an acknowledgement of the thousands of people that attended Invasion Day rallies this year?
Collectively, the exhibition powerfully questions the processes of a problematic cultural assimilation using repurposed Aboriginalia but today Aboriginal identities, like all identities, are in a state of transformation and flux. I look at the work of contemporary African artists and I see joy, hope, colour, movement, new identities, new sites of conceptualisation in the evolving struggle to engage new definitions of nationhood in relation to the autonomous, self-governing body. They acknowledge history, discrimination, the struggle for freedom, but are more forward looking, more engaged with the possibilities of the future rather than the deficits of the past expressed in the inequalities of the present. When is a positive voice of embodied (not disembodied, decapitated) Ab/origin going to emerge in contemporary art?
Dr Marcus Bunyan
1/ Jennifer Isaacs. “Introduction,” in Jennifer Isaacs (ed.,). Aboriginality: Contemporary Aboriginal Paintings and Prints. University of Queensland Press, 1996, p. 8.
Many thankx to the NGV for allowing me to publish some of the photographs in the posting. All the other images, as noted, are iPhone images of the exhibition by Marcus Bunyan. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Destiny Deacon is one of Australia’s boldest and most acclaimed contemporary artists. In the largest retrospective of her work to date, DESTINY marks the artist’s first solo show in over 15 years. Featuring more than 100 multi-disciplinary works made over a 30-year period, the exhibition includes the premiere of newly-commissioned works. Numerous early video works created with the late Wiradjuri / Kamilaroi photographer Michael Riley and West Australian performance artist Erin Hefferon are also on display.
A descendant of the Kuku and Erub / Mer people from Far North Queensland and Torres Strait, Deacon is internationally known for a body of work depicting her darkly comic, idiosyncratic worldview. Offering a nuanced, thoughtful and, at times, intensely funny snapshot of contemporary Australian life, Deacon reminds us that ‘serious’ art can also have a sense of humour.
Melbourne-based, Deacon works across photography, video, sculpture and installation to explore dichotomies such as childhood and adulthood, comedy and tragedy, and theft and reclamation. Her chaotic worlds, where disgraced dolls play out sinister scenes for audience amusement, subvert cultural phenomena to reflect and parody the environments around us.
Installation view of Destiny Deacon and Virginia Fraser’s Abi see da classroom 2006 on display in DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020
Photo: Tom Ross
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Virginia Fraser (Australian, d. 2021)
Abi see da classroom (stills)
2006
10 min. sound
National Gallery of Victoria
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
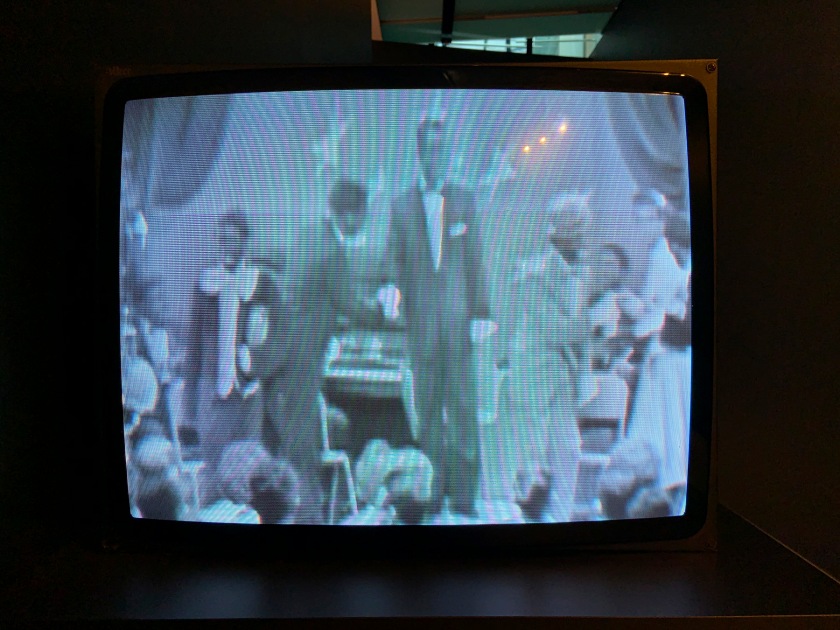
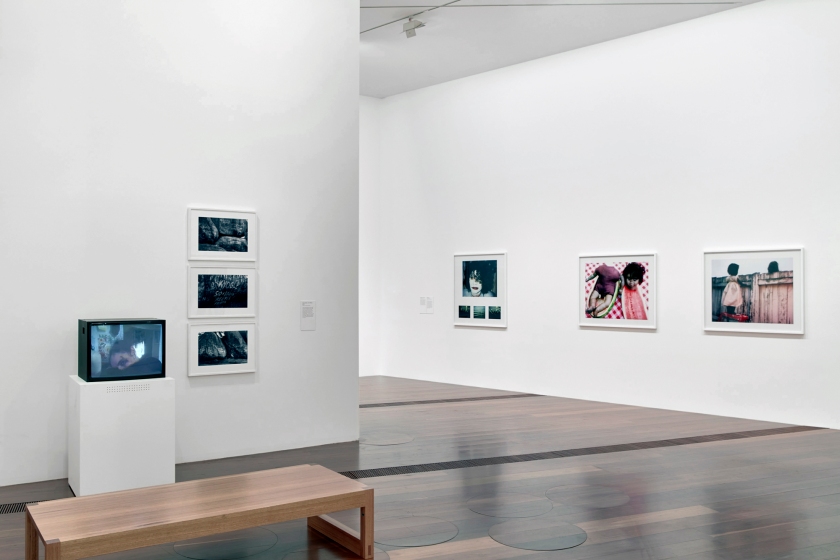
Abi see da classroom
For the fiftieth anniversary of the Australian Broadcasting Commission (ABC), Destiny Deacon and her long-time collaborator Virginia Fraser were given unrestricted access to the ABC’s archive, possibly the most significant collection of film and television held in Australia. By searching for any keywords that started with ‘Aborigin’ they were able to uncover a large assortment of videos.
In this installation, two CRT television screens play alongside each other, creating a mashup of noise and black-and-white moving images. The television on the right shows archival footage of Aboriginal children attending school, reading and playing musical instruments, while the television on the left presents a series of short clips of people in varying degrees of blackface. Switching from uncomfortable to distasteful, to overtly racist, the two channels juxtapose extreme versions of how Aboriginal people have historically been depicted on television. The footage is problematic and offensive; though, some might say ‘it was a different time’. The flashback to the 1950s prompts audiences to consider Australia’s legacy of televised racism and poses the question: how far have we actually come?
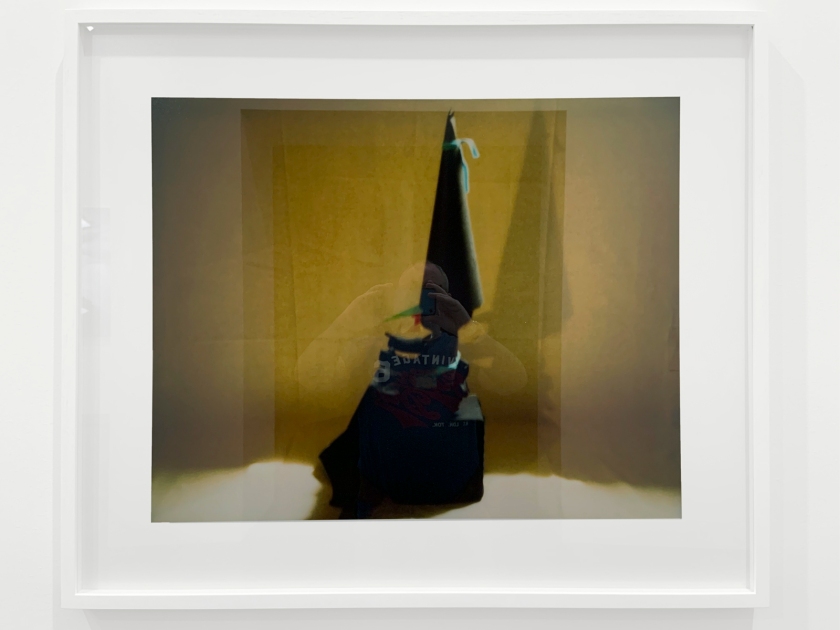
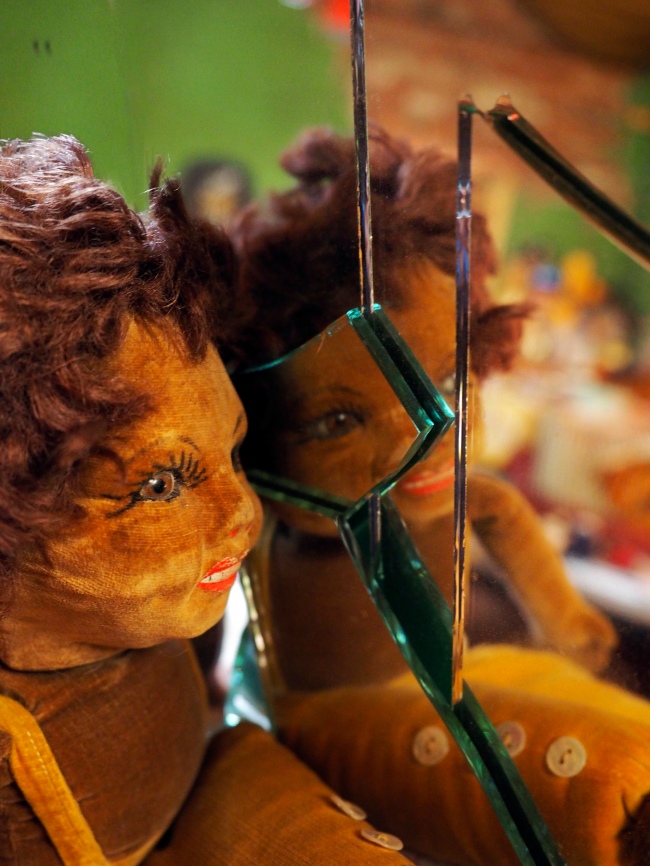
Installation view of Destiny Deacon’s Blak lik mi 1991 on display in DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020
Photo: Tom Ross
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Blak lik mi
1991, printed 1995
Exhibition version printed 202
Colour laser print from Polaroid original
80.0 x 100.0cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
© Destiny Deacon
Blak lik mi
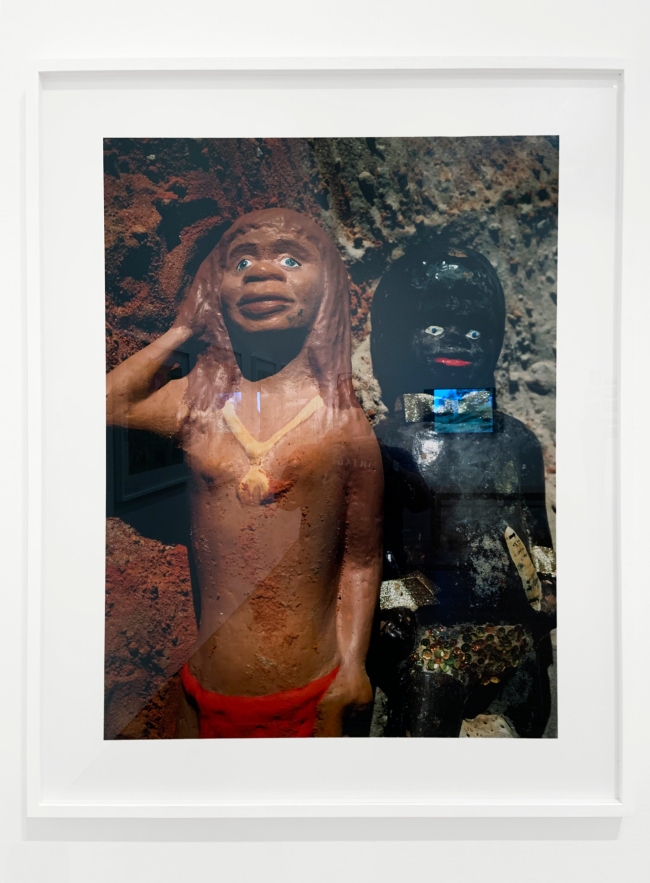
Historically photography has been used as a tool to categorise and document Aboriginal people and their lives. In this work Destiny Deacon reclaims three images taken from a 1960s reproduction of a 1957 Axel Poignant photograph, from his photo essay, originally titled Picaninny Walkabout, later renamed Bush Walkabout. Deacon turns the colonial gaze back on the coloniser, photographing the photograph, and subverting her position as both subject and photographer.
The title Blak lik mi is a reference to John Howard Griffin’s autobiographical novel, Black Like Me, in which Griffin took large doses of an anti-vitiligo drug and spent hour daily under an ultraviolet lamp in order to change the appearance of his skin so that he ‘passed’ as Black. Deacon’s work offers a window into her own interrogation about what constitutes her Aboriginal identity. On this, Deacon often jokes that she ‘took the c, out of black little c**t’. Rude words beginning with ‘c’, of which there are many, are often used as offensive slights, and Deacon recalls being taunted with these words as a child.
‘Blak’, unlike ‘Black’, was Deacon’s way of self-determining her identity, and originating a version of the self that comes entirely from within. The legacy of this work has been massive. Countless Aboriginal people now self-determine their identity as Blak, so much so that a Google search of ‘Blak’ returns a nearly all Australian Indigenous search result.
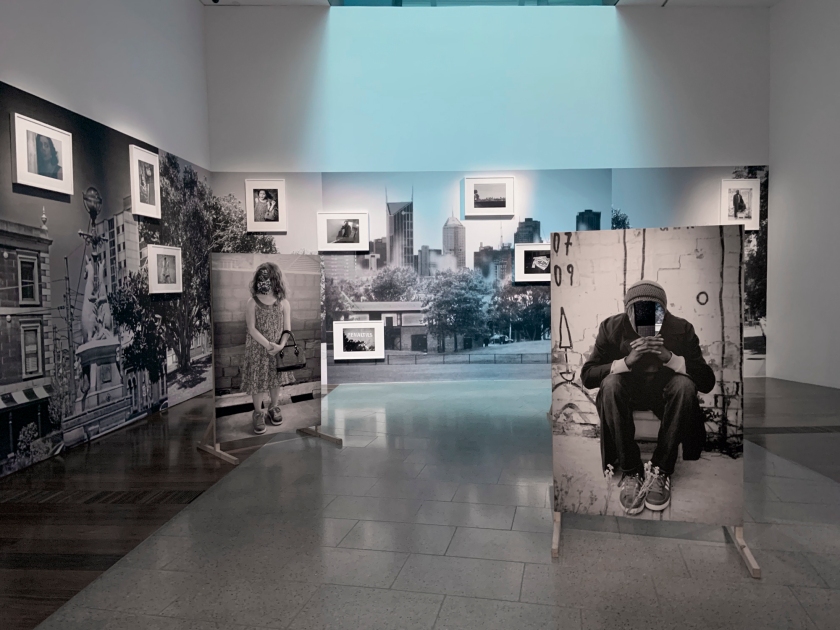
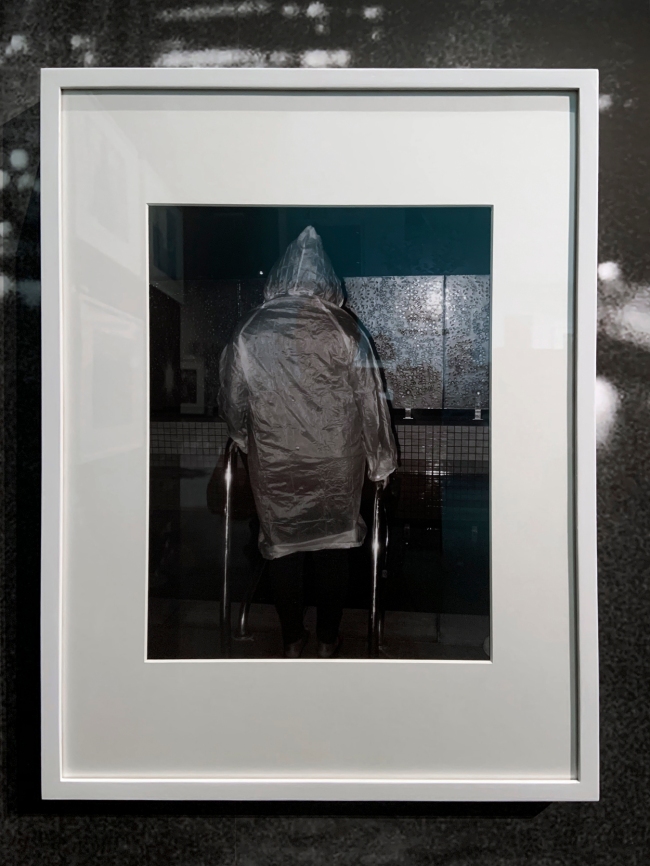
Installation view of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020
Photo: Tom Ross
Installation view of Destiny Deacon’s Me and Virginia’s doll (Me and Carol) 1997 at left, Last laughs 1995 at centre, and Where’s Mickey 2002 at right, on display in DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020
Destiny Deacon (Australian, Kuku/Erub/Mer b. 1957)
Me and Virginia’s doll (Me and Carol)
1997, printed 2020
Lightjet print from Polaroid original
Destiny Deacon began her professional career in photography in her late thirties as a way to express herself and her political beliefs. A self-taught artist, Deacon is primarily known for her photographs and videos where she subverts familiar icons with humour and wit. Often when Deacon photographs people she poses them like paintings. In this image, Deacon presents herself as Frida, staging the image as an homage to Kahlo’s 1937 painting Me and my doll.
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Last laughs
1995
Lightjet photograph from Polaroid photograph
80.0 x 100.0cm
Courtesy of the artist
© Destiny Deacon
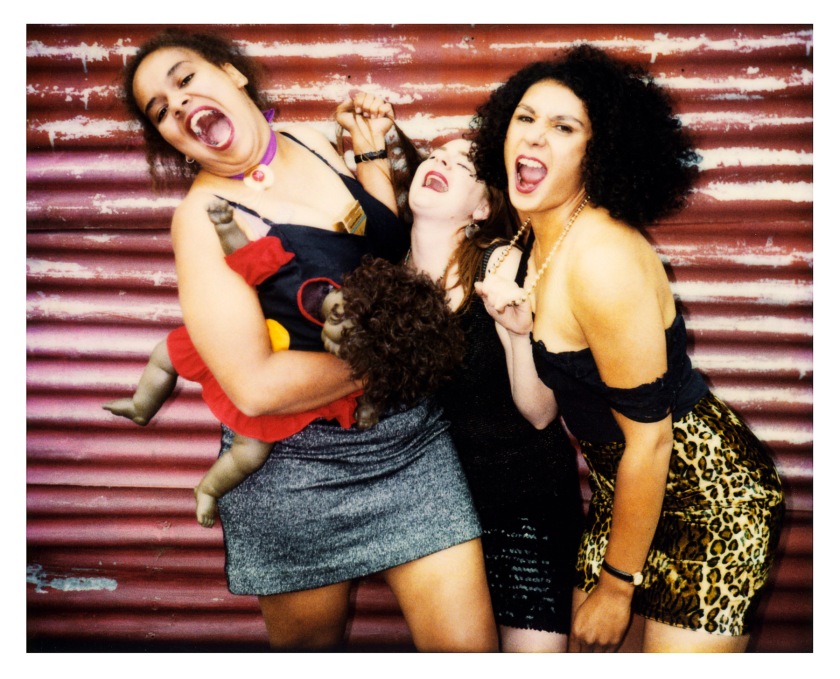
In this image Deacon both reclaims and ridicules a genre of colonial photography, which historically depicted Aboriginal women as a highly sexualised or exotic ‘other’. In the nineteenth century it was commonplace for Aboriginal women to appear naked in ethnographic photographs that were mass reproduced and distributed as souvenirs around the world. In Last laughs three Blak women pose for the camera, limbs intertwined, performing their sexuality. Unlike in the colonial photography it references, the subjects in this work are the ones in control.
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Where’s Mickey?
2002, printed 2016
Exhibition version printed 2020
Lightjet print from Polaroid original
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
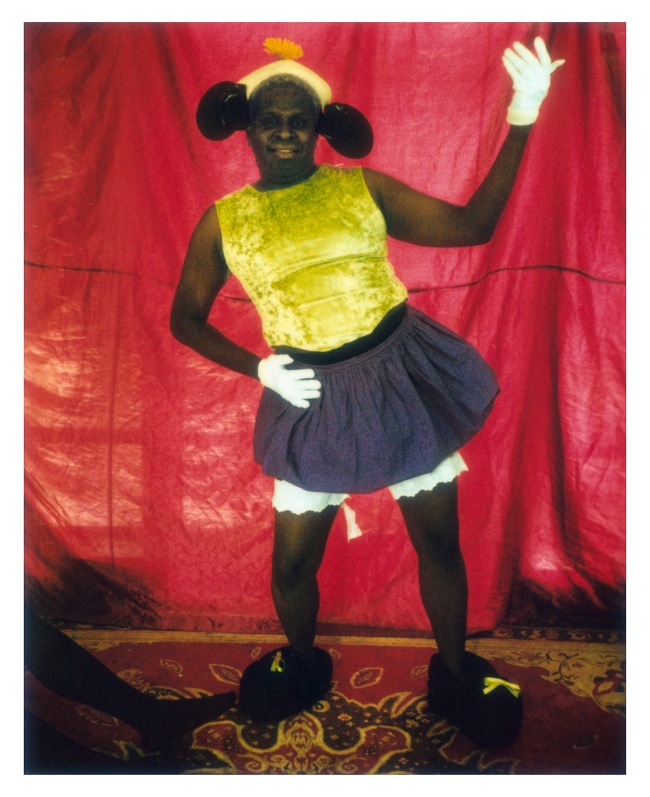
Where’s Mickey? plays on the Australian slang phrase ‘Mickey Mouse’, used to refer to something that is substandard, poorly executed or amateurish. Mickey Mouse is also the archetypal figure of an (often white) American consumerist culture. In this portrait of Luke Captain, Deacon pokes fun at the cartoon icon, suggesting his animated spirit has possessed the body of an Aboriginal Australian man, who is dressed as a woman.
Installation view of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing at left, Where’s Mickey? 2002, and at right Meloncholy 2000
Photo: Tom Ross
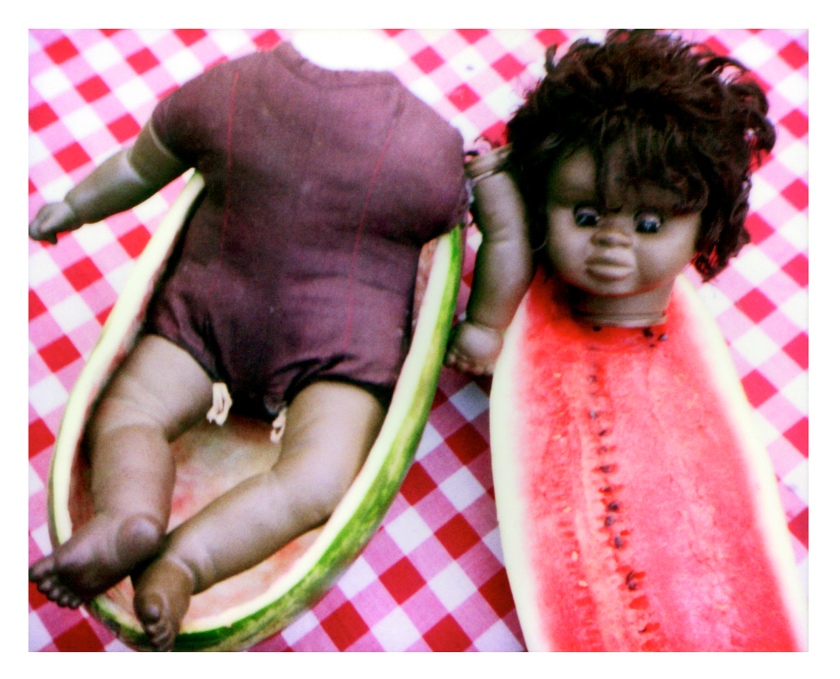
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Meloncholy
2000
From the Sad & Bad series
Lightjet photograph from Polaroid photograph
80.0 x 100.0cm
Courtesy of the artist
© Destiny Deacon
In 1970 African-American film director, Melvin Van Peebles released Watermelon Man, a movie in which a fictional, white insurance salesman wakes up one morning only to discover he has turned Black overnight. The film is inspired by John Howard Griffin’s autobiographical novel, Black Like Me. In this image Deacon gives the watermelon a double meaning. The emptied peel of the melon cradles the doll’s body, kind of like the coolamon [Coolamon is an anglicised NSW Aboriginal word used to describe an Australian Aboriginal carrying vessel], but it is also a fruit that has been severed from its skin. She challenges the relationship between identity, skin colour, and how the world perceives and responds to both Blackness and Blakness.
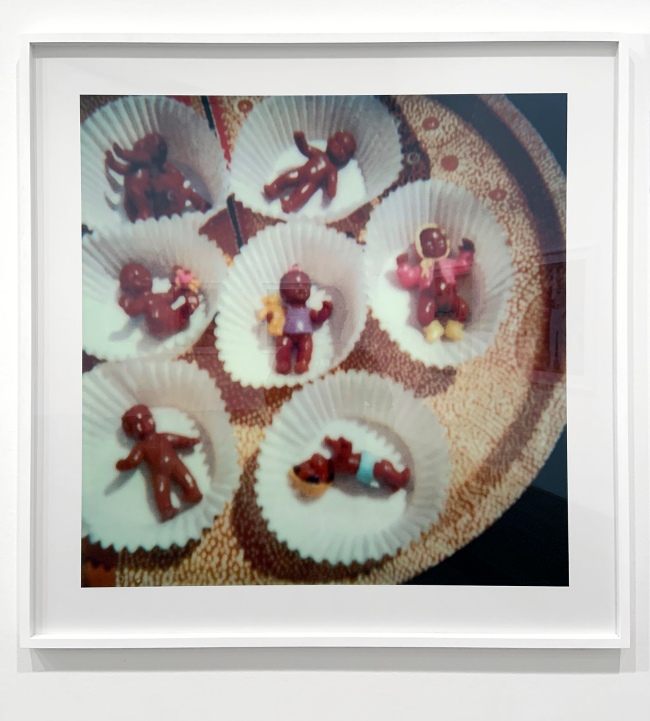
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Adoption (installation view)
2000; printed 2020
Lightjet print from Polaroid original
Purchased, Victorian Foundation for Living Australian Artists, 2016; copy printed 2020
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
In this image Destiny Deacon has placed a collection of plastic, black toy babies into paper cupcake shells. Titled Adoption, this work directly references Australia’s shameful history of government-sanctioned Aboriginal child removal. In addition, Adoption also pokes fun at the deeply offensive misnomer of the nineteenth century that Aboriginal mothers were both infanticidal, as well as cannibals of their newborns. Deacon describes how she came to collect dolls, saying ‘in the beginning I wanted to rescue them, because otherwise they’d end up in a white home or something, somewhere no one would appreciate them’.
Destiny Deacon, one of Australia’s boldest and most acclaimed contemporary artists, will be celebrated in her largest retrospective to date opening at the National Gallery of Victoria on 23 November 2020.
DESTINY will mark Deacon’s first solo show in over 15 years, featuring more than 100 multi-disciplinary works made over a 30-year period, and including the premiere of newly-commissioned works created with the artist and her long-term collaborator Virginia Fraser. The exhibition will also feature a number of early video works created with the late Wiradjuri / Kamilaroi photographer Michael Riley and West Australian performance artist Erin Hefferon.
A descendant of the Kuku and Erub / Mer people from Far North Queensland and Torres Strait, Deacon is internationally known for a body of work depicting her darkly comic, idiosyncratic world view. Offering a nuanced, thoughtful and, at times, intensely funny snapshot of contemporary Australian life, Deacon reminds us that art can have both pathos and humour.
Melbourne-based, Deacon works across photography, video, sculpture, and installation to explore dichotomies such as childhood and adulthood, comedy and tragedy, and theft and reclamation. Her chaotic worlds, where disgraced dolls play out sinister scenes for audience amusement, subvert cultural phenomena to reflect and parody the environments around us.
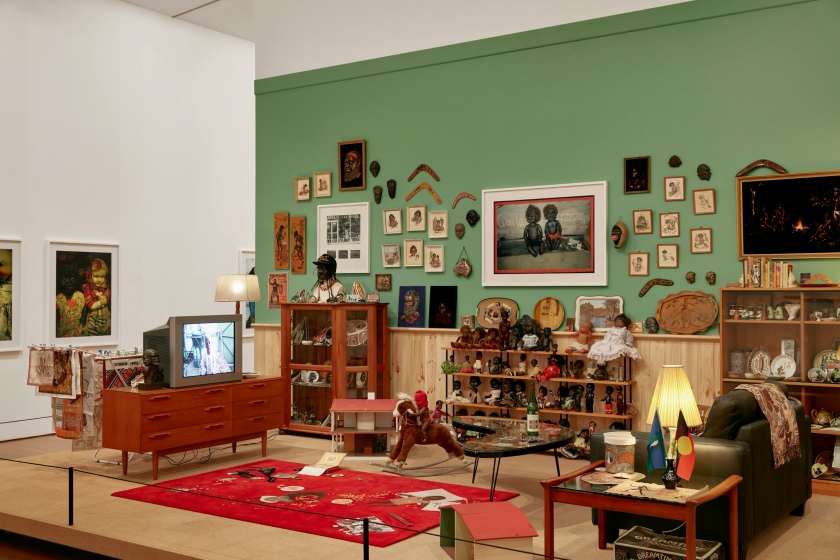
Featuring early videos which mock negative stereotypes of Aboriginal Australians – Home video 1987, Welcome to my Koori world 1992, I don’t wanna be a bludger 1999 – the exhibition will also feature an installation of a lounge room housing Deacon’s own collection of ‘Koori kitsch’. Deacon and Fraser’s highly acclaimed installation Colourblinded 2005 will also be on display. A powerful combination of photographs, sculptures, and video projections, this interactive work leaves the viewer both literally and metaphorically ‘colourblinded’.
“Featuring new NGV commissions and some of the highlights of Deacon’s 30-year career, the retrospective DESTINY pays tribute to an artist who has been challenging audiences for more than 30 years,” said Tony Ellwood AM, Director, National Gallery of Victoria. “Destiny Deacon has never shied away from confronting our country’s difficult history and her work continues to make a vital contribution to Australian cultural discourse,” said Ellwood.
Press release from the National Gallery of Victoria
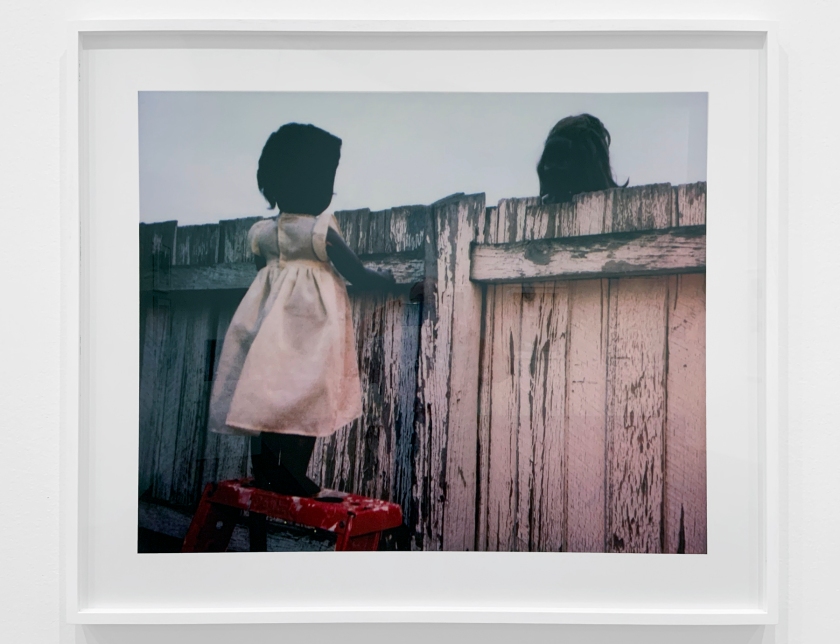
Installation view of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing at second right, Meloncholy 2000 and at right, Over the fence 2000
Photo: Tom Ross
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Over the fence (installation view)
2000, printed 2000
Exhibition version printed 2020
From the Sad & Bad series
Lightjet print from Polaroid original
Purchased, Victorian Foundation for Living Australian Artists, 2016
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
The nostalgic qualities in Deacon’s poignant photograph Over the fence reinforce a narrative familiar to many Aboriginal people. Two segregated dollies peer at each other across a suburban, wooden fence, leaving the audience wondering who is fenced in, and who is fenced out? The image illustrates an ‘us’ and ‘them’ mentality towards race, which many Aboriginal people would recognise beneath this seemingly ‘friendly’ neighbourhood encounter.
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Portrait of Peter Blazey, writer (installation view)
2004, printed 2020
Lightjet print from Polaroid original
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Peter Blazey, journalist, author and gay activist.
Blazey was born in Melbourne in 1939 and worked for The Australian, the National Times and as a regular columnist for OutRage, a gay magazine. He published a number of books, including a political biography of Henry Bolte, and was co-editor of the short fiction anthology, Love Cries. His personal memoir, Screw Loose, appeared after his death from AIDS in 1997.
“Peter was someone with a lion’s head of loose ends that could never fit into some ideologically sound and tidy space. Storyteller, mythomane, and one of the last great conversationalists in a country wary of the free flow of uncensored language, he was a comet who flashed his tail at everyone.” ~ Tim Herbert, OutRage, 1997.
Text from the University of Melbourne Scholarship website [Online] Cited 29/01/2021
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Portrait of Gary Foley, activist (installation view)
1995, printed 2020
Lightjet print from Polaroid original
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Often in Deacon’s portrait photography, sitters are posed like those in paintings. In these three images, Deacon presents Gary Foley, an Aboriginal Gumbainggir activist, academic, writer and actor; Peter Blazey, the late journalist, author and gay activist; and Richard Bell, and activist and artist of the Kamilaroi, Kooma, Jiman and Gurang Gurang communities. All three men are posed in a near identical way to the 1932 painting The boy at the basin by Australian landscape and portrait artist William Dobell.
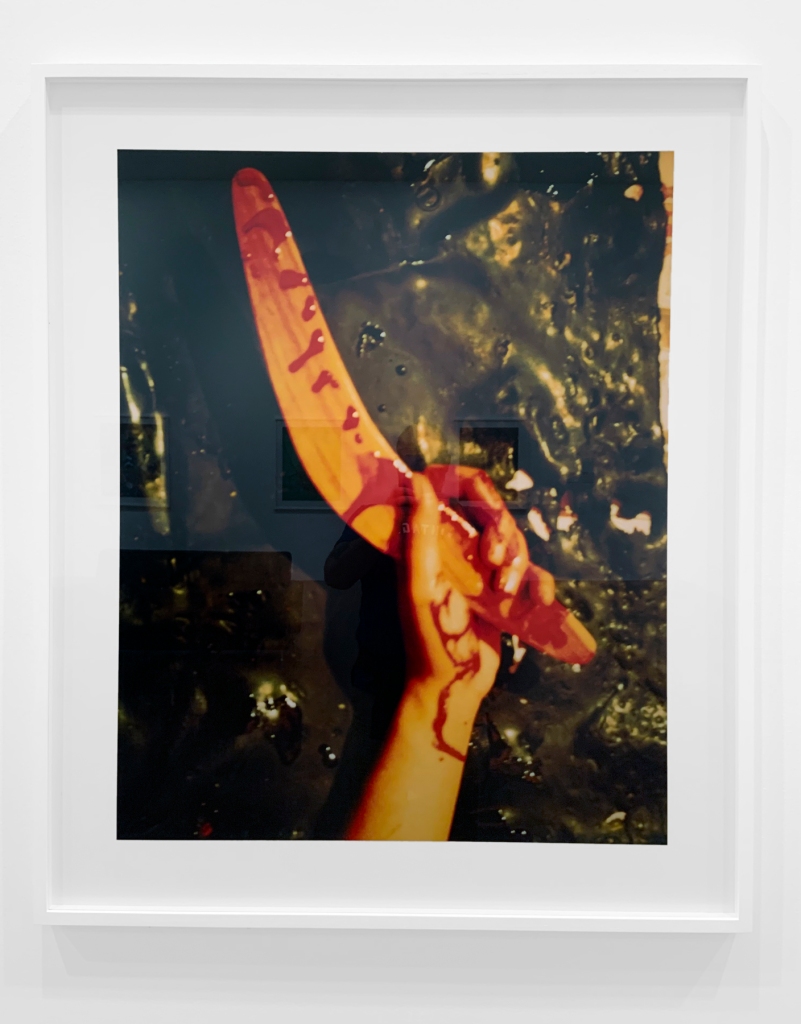
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
My boomerang did come back (installation view)
2003, printed 2020
Lightjet photograph from Polaroid photograph
80.0 x 100.0cm
Courtesy of the artist
© Destiny Deacon
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
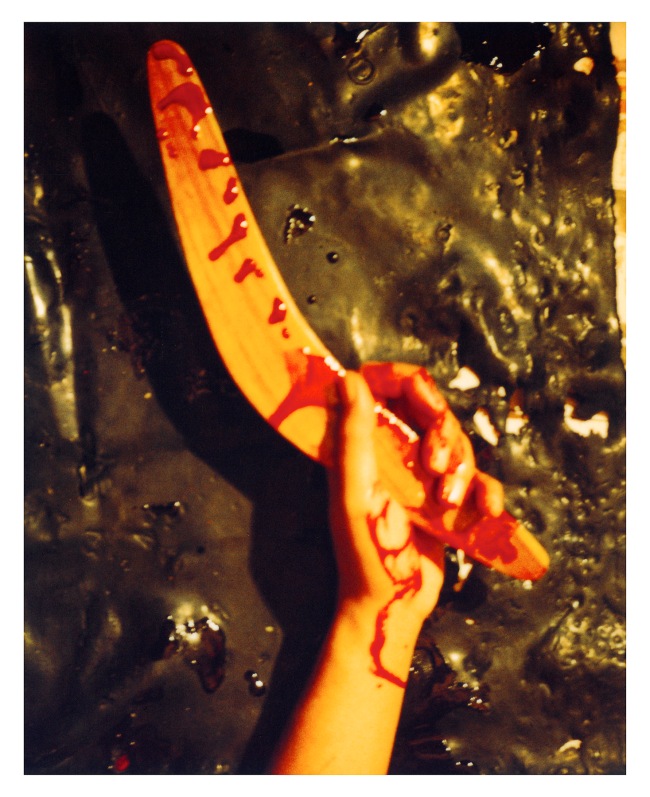
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
My boomerang did come back
2003, printed 2020
Lightjet photograph from Polaroid photograph
80.0 x 100.0cm
Courtesy of the artist
© Destiny Deacon
This image is a reference to Charlie Drake’s 1961 song ‘My Boomerang Won’t Come Back’. Drake sings in a halting and staccato manner, wildly grunting ‘ho’ and ‘ugh’ as he narrates the story of an effeminate young Aboriginal boy named Mac, who has been banished from his tribe because he is ‘a big disgrace to the Aborigine [sic] race’ because his ‘boomerang won’t come back’. A single hand (Lisa Bellear’s) reachers upward, grasping a bloody boomerang in front of a black background. Deacon suggests that Drake, whose song is at best a kind of vaudevillian blackface, has assassinated himself.
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Hear come the judge (installation view)
2006
Exhibition version printed 2020
Lightjet print from Polaroid original
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Deacon references the 1968 comedic funk song ‘Here Comes the Judge’ by American entertained Dewey ‘Pigmeat’ Markham, which is regarded by many to be the first recorded hip-hop song. Markham’s lyrics ridicule the formalities of courtroom etiquette by painting a picture of a make-believe world where justice is in the hands of Black people. Deacon’s photograph uses humour to disarm and interrogate something that is inherently unfunny. The Blak / Black judge is only comical because it is supposedly unbelievable, a notion Deacon challenges audiences to reconsider.
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Border patrol (installation view)
2006, printed 2020
Lightjet print from Polaroid original
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
“And they figured a dispossessed people as racial types, suggesting that authentic Aboriginal identity was purely tribal and something to be trivialised as curios and knick-knacks…
But the figurines of a racialised people, of warriors, beautiful girls and adorable children, took this interest into a different realm of curiosity, namely objectification.
Elder women, who were often savagely vilified in popular newspapers as “unsightly frights”, never appear among these figurines. Lithe young women, deep-chested warrior tribesmen, dignified elder “noble savages” and sweetly smiling “piccaninnies” were particularly prized. In the early prints of artists Peg Maltby and Brownie Downing, endearing Aboriginal children are orphaned by the bush rather than being at home in the country of their birthright. They find playmates with baby native animals but are divested of family and community. They seem to be crying out for the care that only the state, it was thought, could properly provide. …
The figures found in Aboriginalia evoke a troubling presence, in which visual appeal, sometimes libidinal, stands in for the profound ambivalence at the heart of settler-colonialism, which has benefited from the violent dispossession of a people.
While townships were campaigning to exclude Aboriginal kids from schools, families from housing and adults from pubs, these nostalgic, perplexing images were being taken into white homes in the form of bric-a-brac.
Sociologist Adrian Franklin has described the “semiotic drenching” of souvenirs with Aboriginal motifs and argues “these objects became ‘repositories of recognition’ of what was often entirely absent, denied or undermined in the everyday political and policy spheres”.
These objects, he suggests, gave some expression to the sadness surrounding dispossession and removal. In more recent years, Indigenous artists such as Destiny Deacon and Tony Albert have repurposed Aboriginalia.
Thus it is finally being historicised, interpreted and recast through Aboriginal eyes.
Deacon uses dolls and kitsch ephemera from her own extensive collection to turn the tables on the uncritical consumption of racist imagery. In one of her best backhanders, she puts plastic, black babies in cupcake shells and titles the photograph Adoption.”
Extract from Dr Liz Conor. “Friday essay: the politics of Aboriginal kitsch,” on The Conversation website March 3, 2017 [Online] Cited 29/01/2021 CC
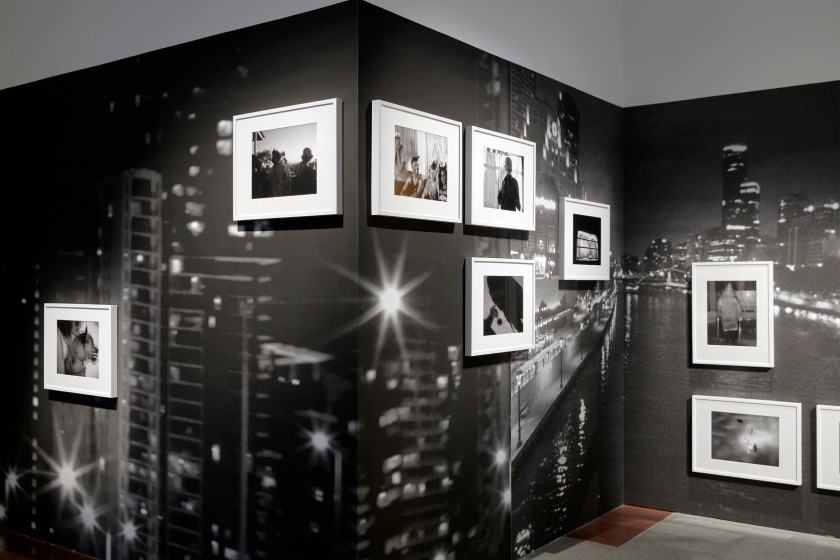
Installation views of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing at right Border patrol 2006
Photos: Tom Ross
Installation view of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing at second left, Heart broken 2006
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
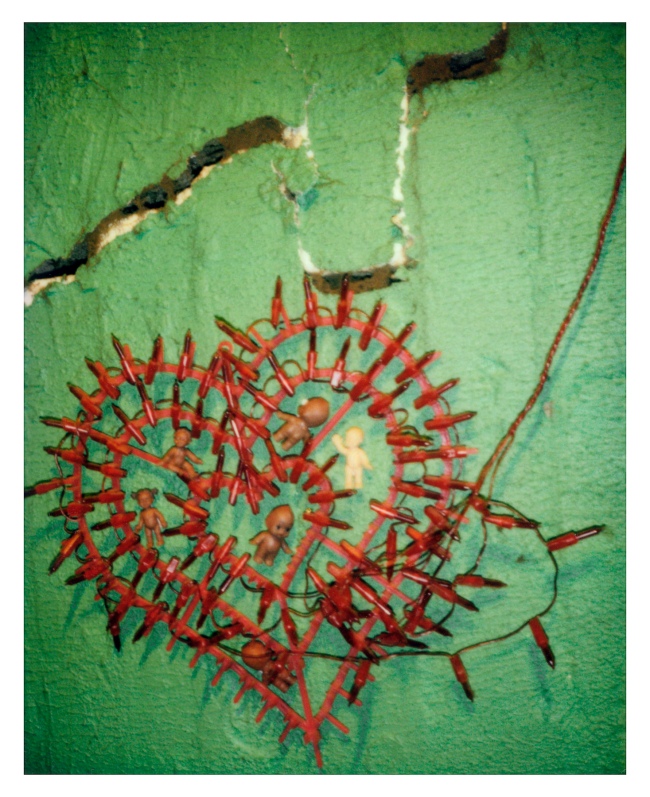
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Heart broken
2006
Lightjet photograph from Polaroid photograph
80.0 x 100.0cm
Courtesy of the artist
© Destiny Deacon
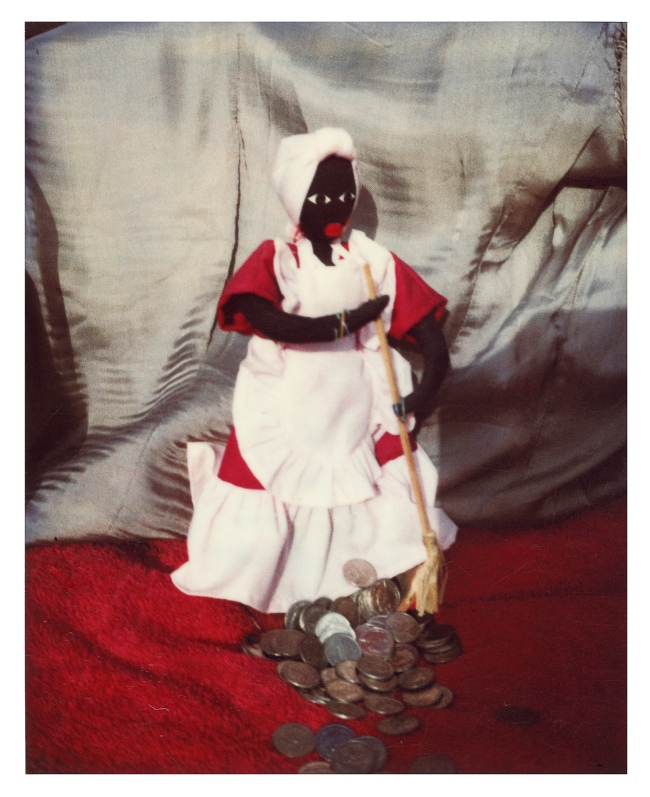
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Ask your mother for sixpence
1995
Lightjet photograph from Polaroid photograph
80.0 x 100.0cm
Courtesy of the artist © Destiny Deacon
This image takes its name from a cheeky nursery rhyme Deacon recalls learning when living in Port Melbourne as a child. The playful limerick teases audiences with the threat of a rude word: ‘Ask your mum for sixpence, to see the big giraffe, pimples on his whiskers, and pimples on his – ask your mum for sixpence’. The work was originally displayed in juxtaposition with a photograph of a half-built Crown Casino in Melbourne, challenging audiences to consider the dynamic between the main character, a Blak woman working in service sweeping up coins, and the multinational gambling corporation.
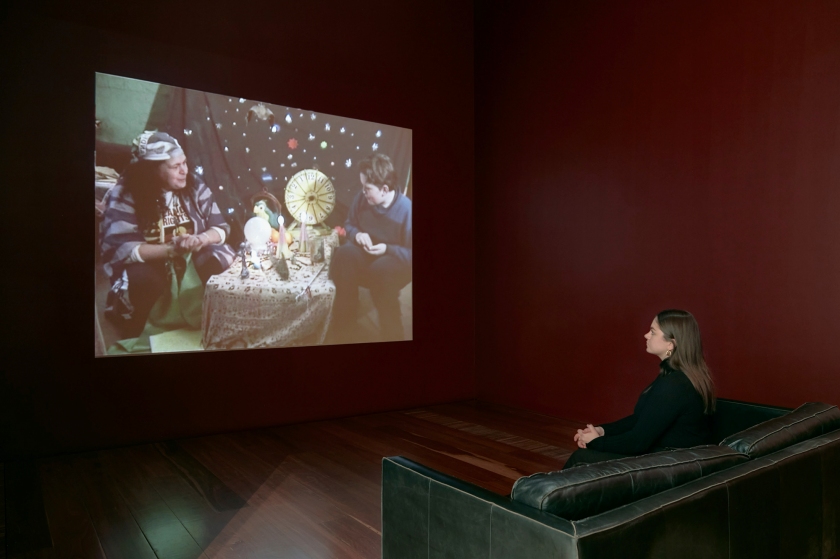
Installation views of Destiny Deacon and Michael Riley’s I don’t wanna be a bludger 1999 on display in DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020. Photos: Tom Ross
Wall text from the exhibition
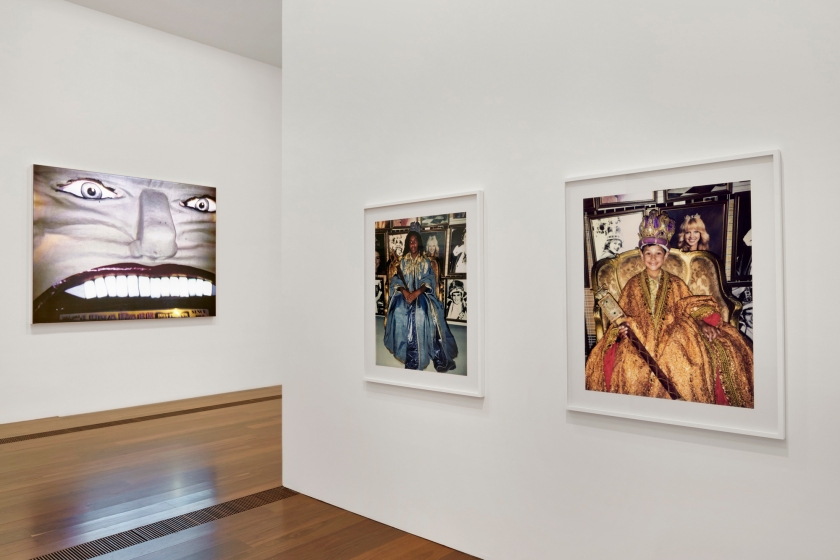
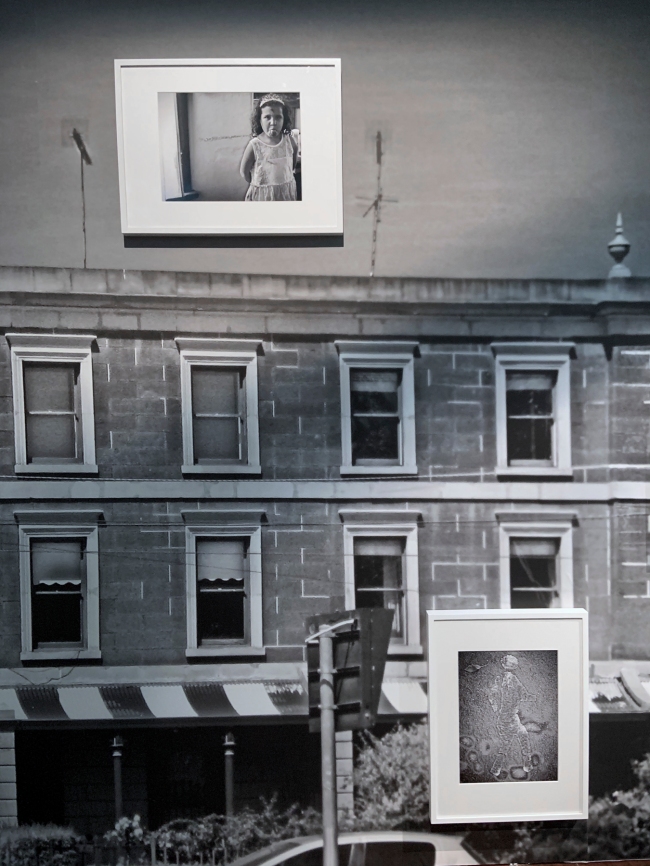
Installation view of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 with at left, Whitey’s watching 1994; and at right, Moomba princess and Moomba princeling (both 2004)
Photo: Tom Ross
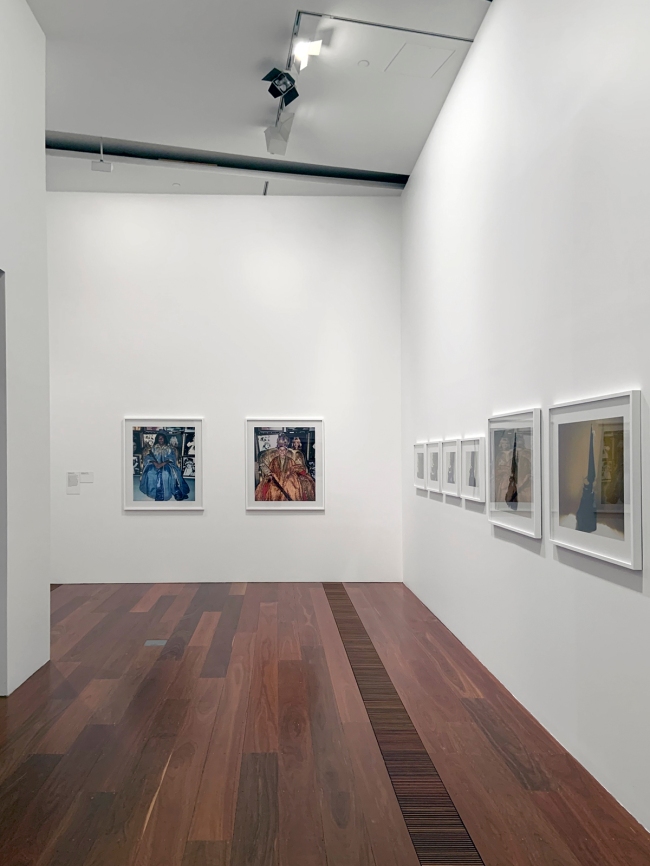
Installation view of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing at centre, Moomba princess and Moomba princeling (both 2004), and at right Thought cone (A-F) 1997
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
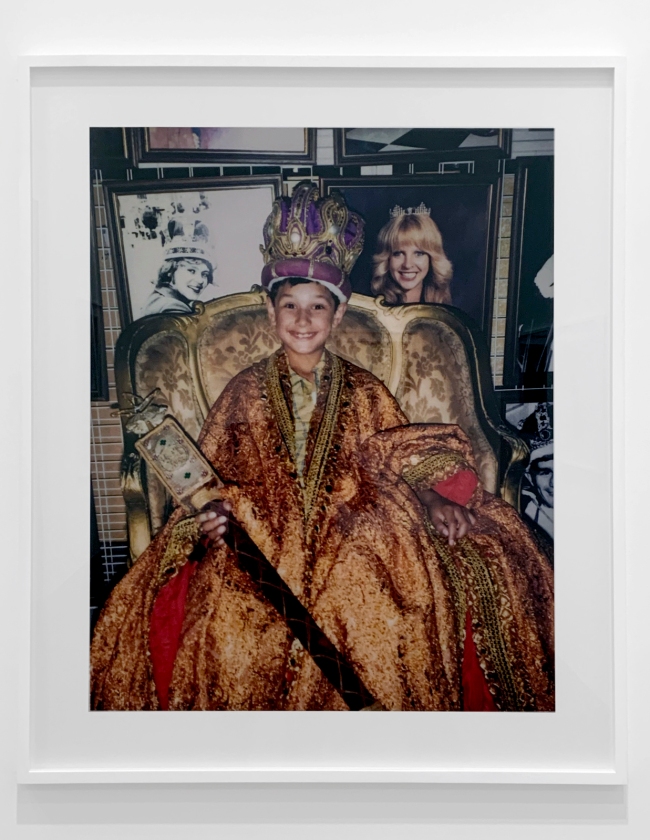
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Moomba princess (installation view)
2004, printed 2020
Lightjet print from Polaroid original
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Moomba princess and Moomba princeling show Deacon’s young niece and nephew dressed in the robes and regalia of Moomba sovereigns. Moomba is an annual parade and community festival held in Melbourne, which each year crowns a ‘Moomba monarch’. The portraits reference Elizabethan Armada portraiture, a style of painting which first depicted the Tudor queen seated in royal garb and surrounded by symbols against a backdrop depicting the defeat of the Spanish Armada in 1588. At first glance, the Moomba portraits can be read as innocent children playing dress ups, but by presenting two Aboriginal models in this type of colonial ceremonial dress, Deacon challenges audiences to consider the legacy and impact of British invasion.
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Moomba princeling (installation view)
2004, printed 2020
Lightjet print from Polaroid original
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
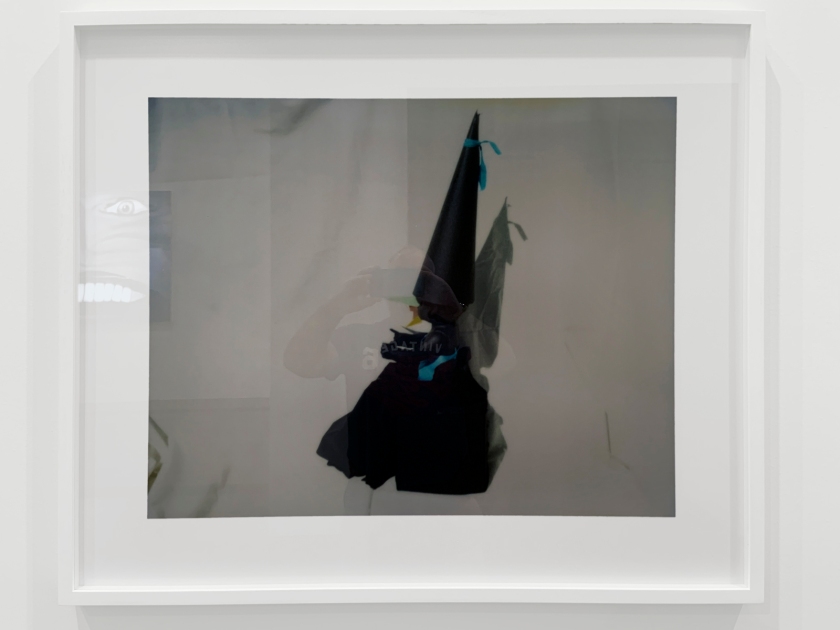
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Thought cone (A-F) (installation view details)
1997, printed 2020
Lightjet print from Polaroid original
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Installation view of Destiny Deacon’s Whitey’s watching 1994 on display in DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020
Photo: Tom Ross
Installation view of Destiny Deacon’s Whitey’s watching 1994 on display in DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
For more than thirty years Destiny Deacon has forged a path as an international artist with a distinct brand of artistic humour unlike any other. Descended from the Kuku and Erub / Mer peoples of Far North Queensland and the Torres Strait, Deacon has been living and working in Melbourne since she arrived here as a small child.
Deacon’s work sits in the uncomfortable but compelling space between comedy and tragedy, and contrasts seemingly innocuous childhood imagery with scenes from the dark side of adulthood. She actively resists interpretation and so called ‘art speak’, instead choosing to let her work speak for itself. The more we look, the greater we understand that the world Deacon conjures is a complex one. Drawing from her vast collection of Aboriginalia, Deacon interrogates the way in which Aboriginal people have been, and continue to be, misrepresented within popular culture. Decapitated, amputated, pants down, tied up, trapped in a blizzard or flying through the air, the characters in Deacon’s world both reflect and parody the one in which we live.
Installation view of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing at right, Regal eagles (A-B) 1994
Photo: Tom Ross
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Regal eagles (A-B) (installation views)
1994, printed 2020
Lightjet print from Polaroid original
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
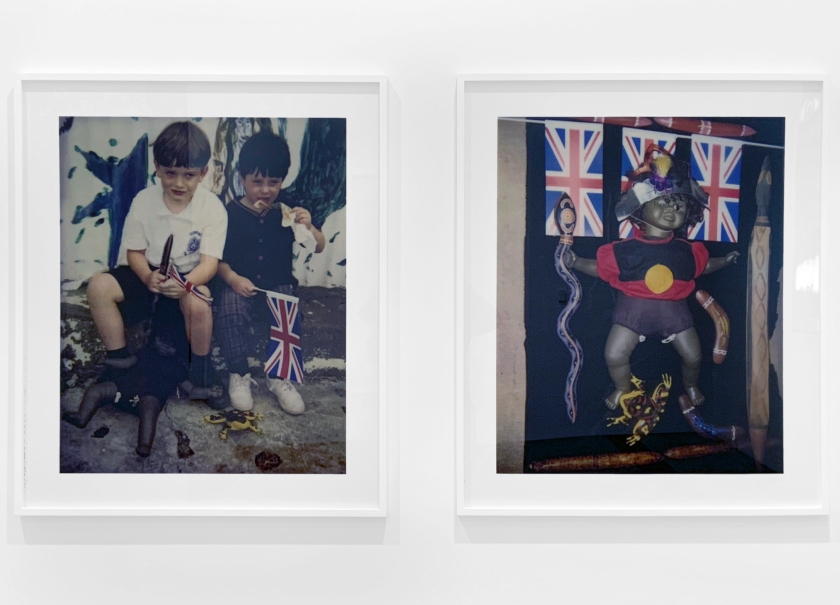
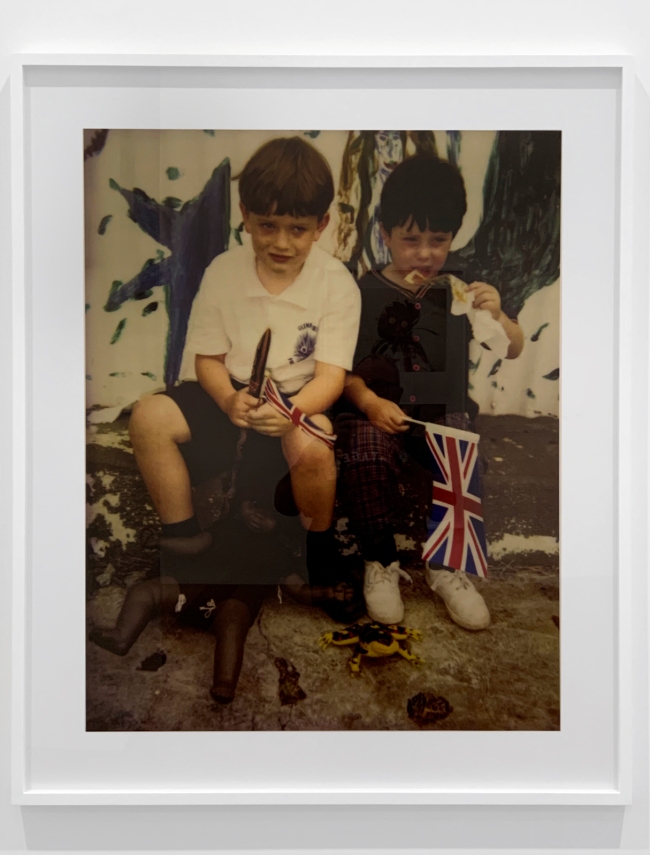
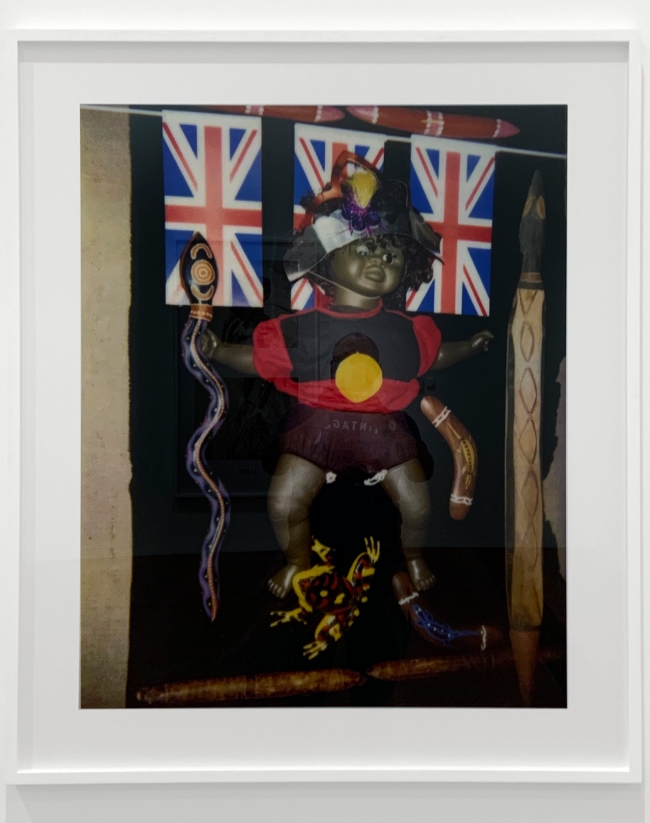
Academic, historian and Indigenous rights activist Marcia Langton once described Destiny Deacon’s work as a ‘barometer of postcolonial anxiety’. This diptych combines two congruent images: the photo on the left shows a pair of young, white boys holding plastic Union Jacks and eating in front of a disregarded, spread-eagled Black doll. The image on the right shows another Black dolly in a Koori flag T-shirt pinned onto a board surrounded by appropriated Aboriginalia. As always in Deacon’s work, the dolls possess a liveliness and personality, making the violence enacted on to them all the more confronting.
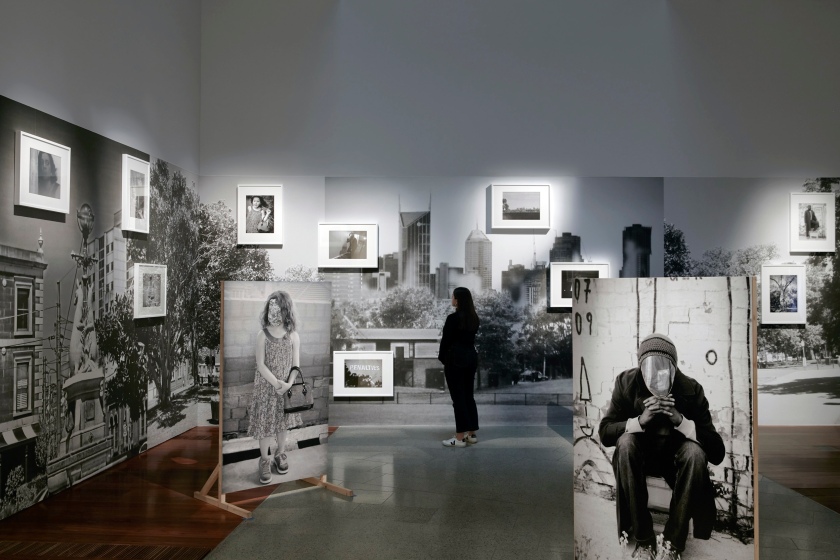
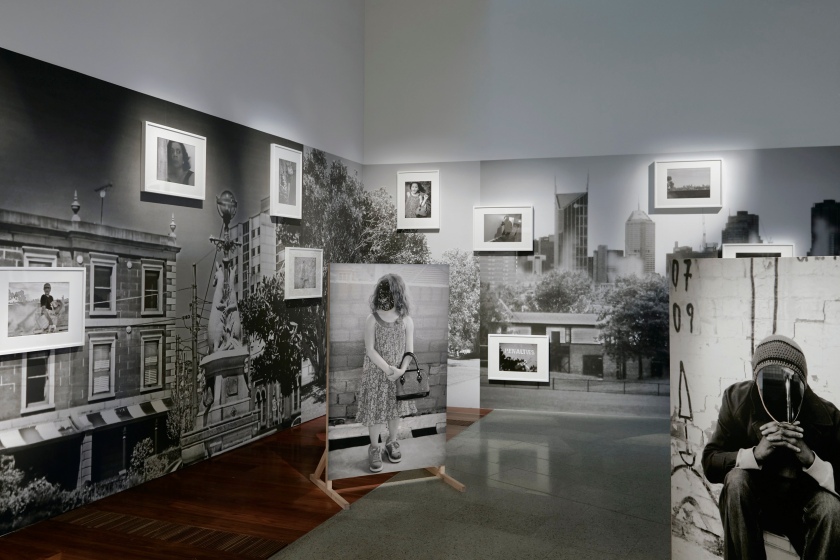
Installation views of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020
Photos: Tom Ross
Installation views of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing Destiny Deacon and Virginia Fraser’s Melbourne Noir 2013
Photos: Tom Ross
Adapting the quotidian formats of snapshot photography, home videos, community TV and performance modes drawn from vaudeville and minstrel shows, Deacon’s artistic practice is marked by a wicked yet melancholy comedic and satirical disposition. In decidedly lo-fi vignettes, friends, family and members of Melbourne’s Indigenous community appear in mischievous narratives that amplify and deconstruct stereotypes of Indigenous identity and national history. For Melbourne Now, Deacon and Fraser present a trailer for a film noir that does not exist, a suite of photographs and a carnivalesque diorama. The pair’s playful political critiques underscore a prevailing sense of postcolonial unease, while connecting their work to wider global discourses concerned with racial struggle and cultural identity.
Text from Exhibition: ‘Melbourne Now’ at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne, Part 1
Installation views of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing Destiny Deacon and Virginia Fraser’s Melbourne Noir 2013
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Digital prints, Digital prints on plywood, wood, gelatin silver photographs, high-definition video, sound
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Wall text from the exhibition
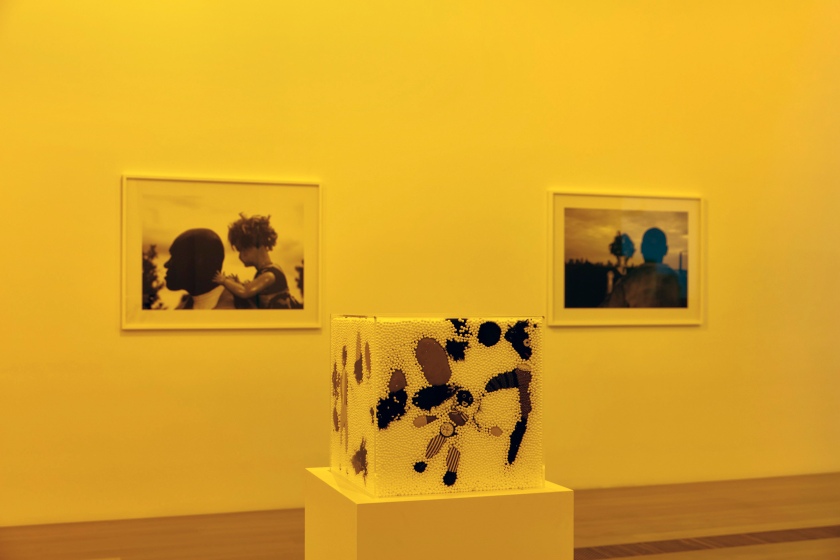
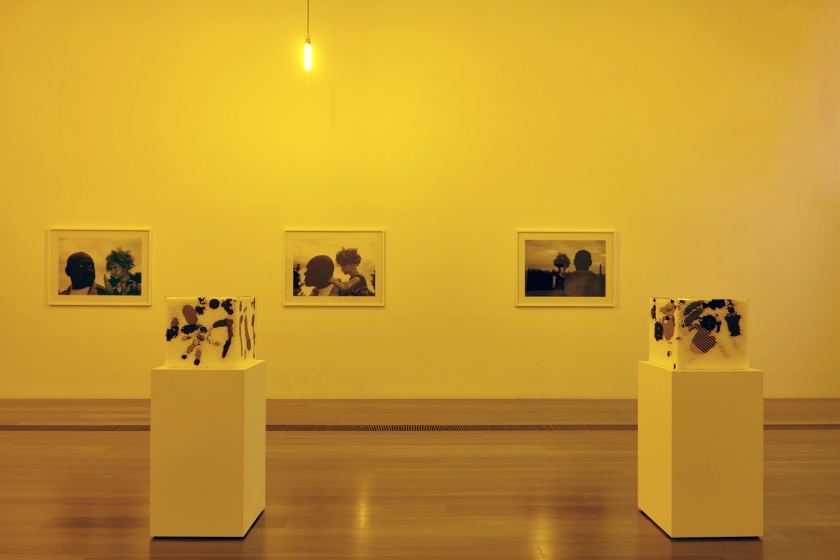
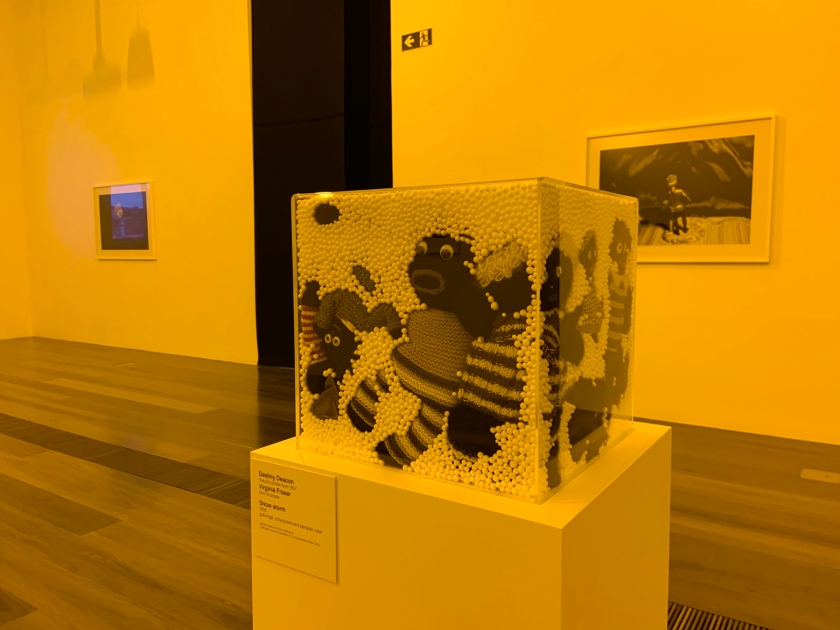
Installation views of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing in the foreground Snow storm 2005
Photos: Tom Ross
Colour Blinded
Man & doll (a)
Man & doll (b)
Man & doll (c)
Baby boomer
Back up
Pacified
2005, printed 2020
Lightfoot print from orthochromatic film negative
Wall text from the exhibition
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Virginia Fraser (Australian)
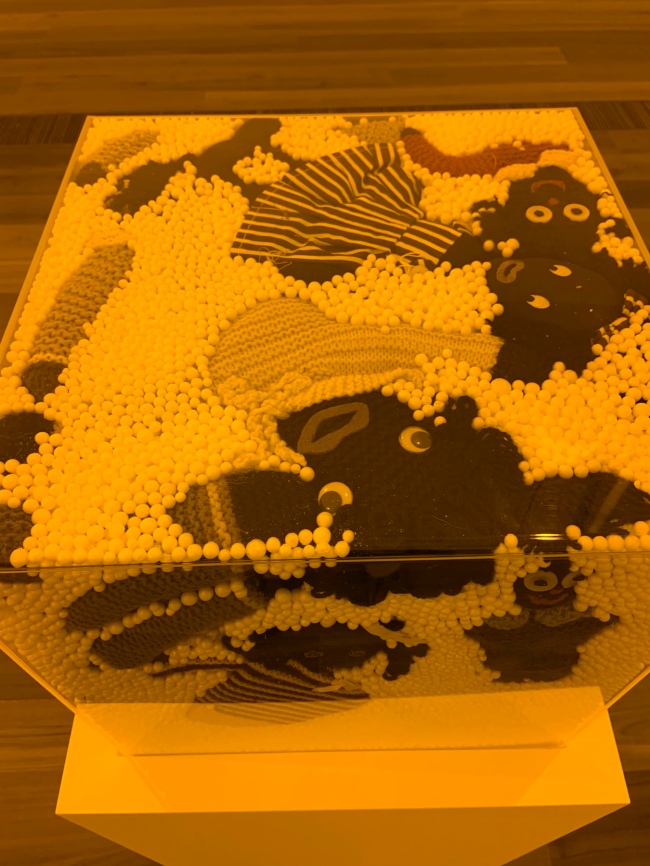
Snow storm (installation views)
2005
Golliwogs, polystyrene and perspex cube
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Man & doll (installation view details)
2005, printed 2020
Lightfoot print from orthochromatic film negative
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
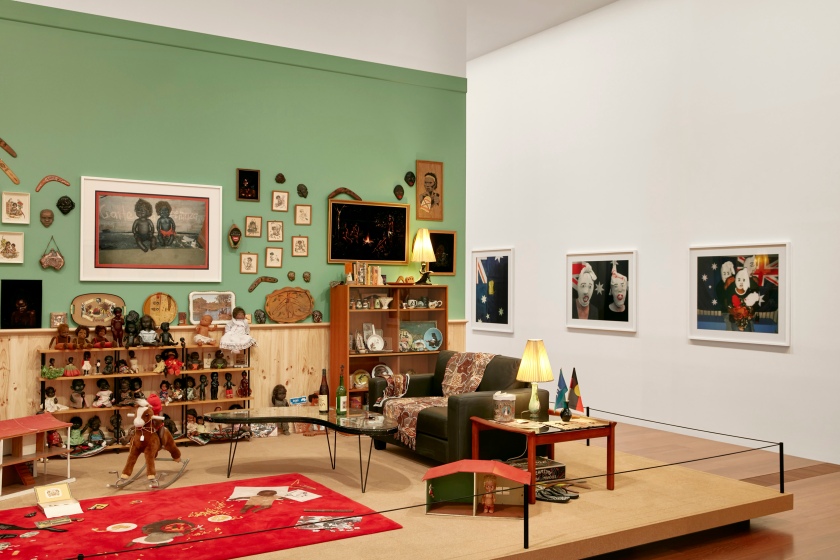
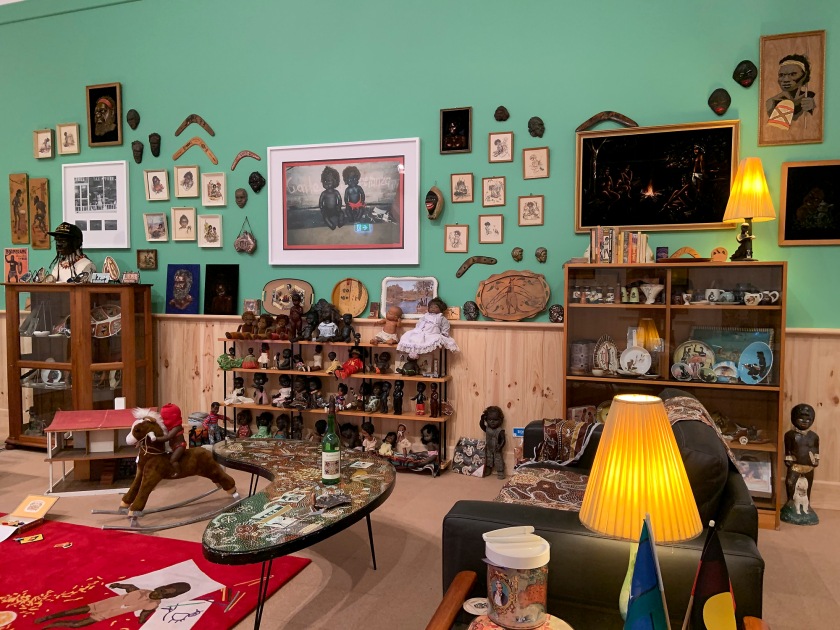
Installation views of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing Destiny Deacon and Virginia Fraser’s Koori lounge room 2021
Photos: Tom Ross
Wall text from the exhibition
Installation views of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing Destiny Deacon and Virginia Fraser’s Koori lounge room 2021
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Ebony and Ivy face race (installation view)
2016, printed 2020
Lightjet print
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Sand minding / Sand grabs (installation views)
2017, printed 2020
Inkjet print from digital image on archival paper
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
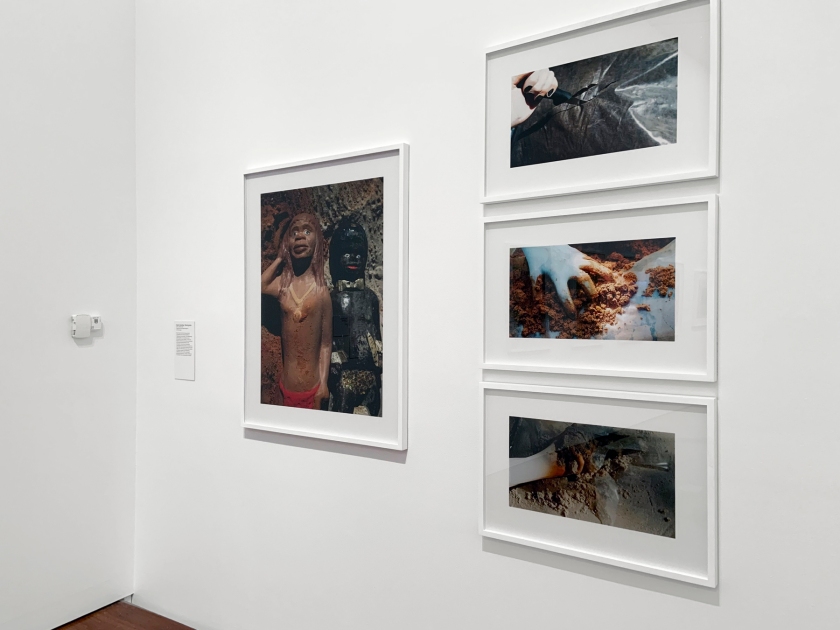
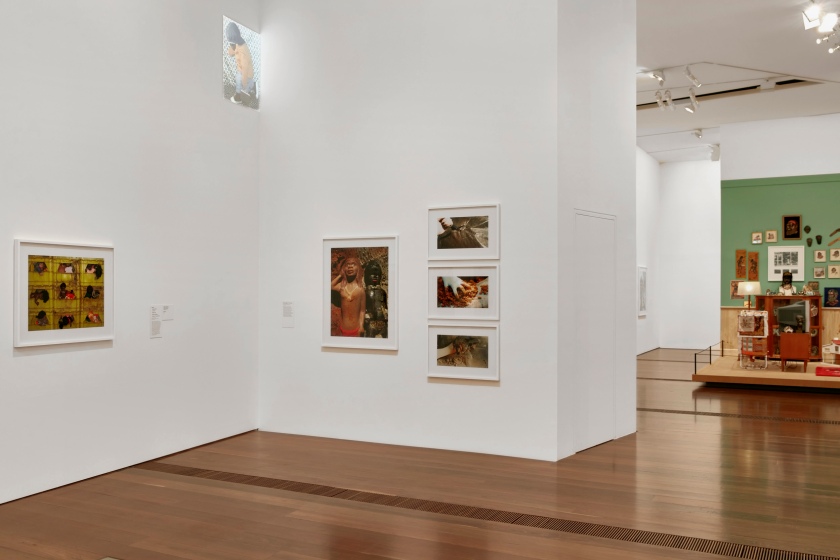
More than half of all mining projects in Australia are in close proximity to Indigenous communities. This relationship has long been, and continues to be, the source of much debate. In this work Deacon condemns the violence committed by the sand mining industry on the ecosystem, the land and its people. A latex-gloved hand makes an incision in a bag of soil, destructively releasing the sand inside. The white hand grasps the contents and takes a handful. Two disturbing characters look on with a seemingly perplexed expression, perhaps inviting us to consider the consequences of mining.
Installation views of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing at left, Arrears windows 2009; at centre, Sand minding / Sand grabs 2017; and in the background Koori lounge room 2021
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Arrears windows
2009
From the series Gazette
Inkjet print from digital image on archival paper
60.0 x 80.0cm
Courtesy of the artist
© Destiny Deacon
Gazette
Gossip walks
Look out!
Action men
Arrears windows
Come on in my kitchen
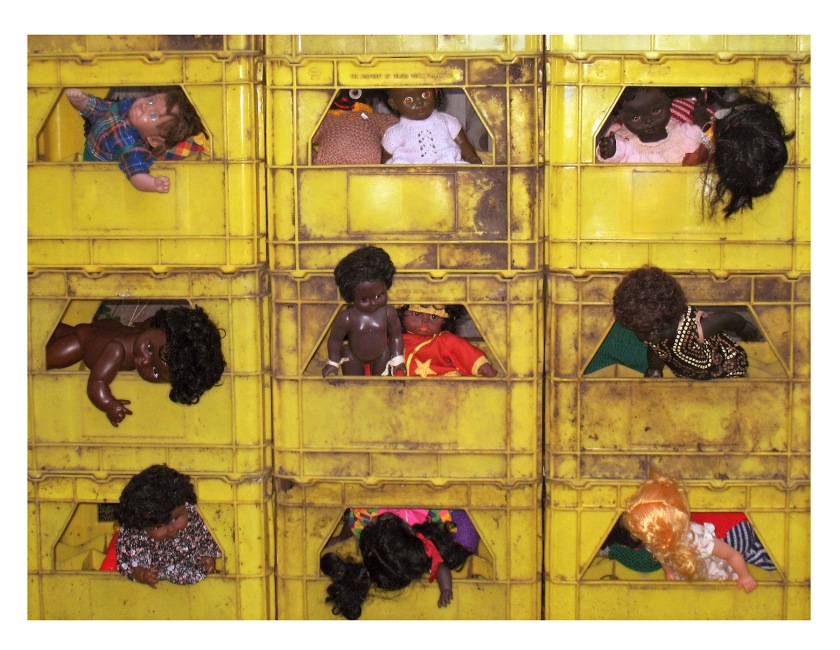
In 2009 Deacon produced the series Gazette. These now eerily familiar scenes appear like vignettes, offering windows into the lives of those living inside Melbourne’s public housing towers. Recent scenes from the news are echoed in Arrears windows, which shows Deacon’s collection of black and brown dolls crammed into yellow plastic tubs. The series draws attention to the individual lives and struggles of residents within these buildings, while also reminding viewers of the often-overcrowded conditions these residents live in. Each image brings to light Deacon’s idiosyncratic take on current global and national events with her semi-autobiographical edge.
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Action men
2009
From the series Gazette
Inkjet print from digital image on archival paper
80.0 x 60cm
Courtesy of the artist
© Destiny Deacon
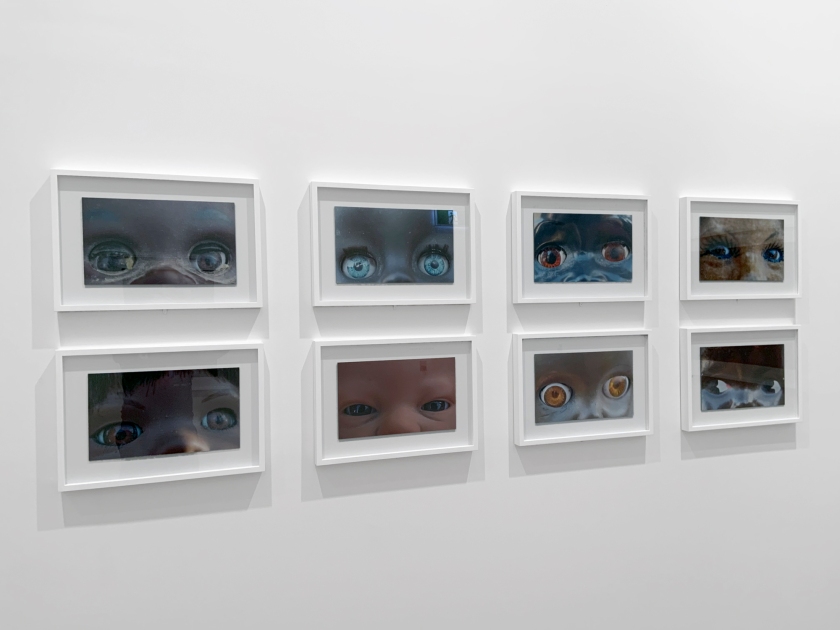
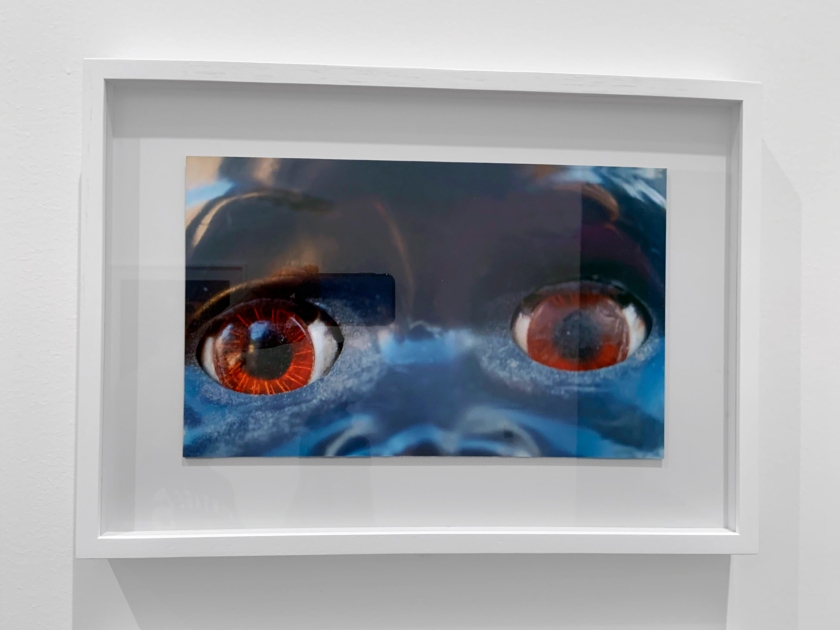
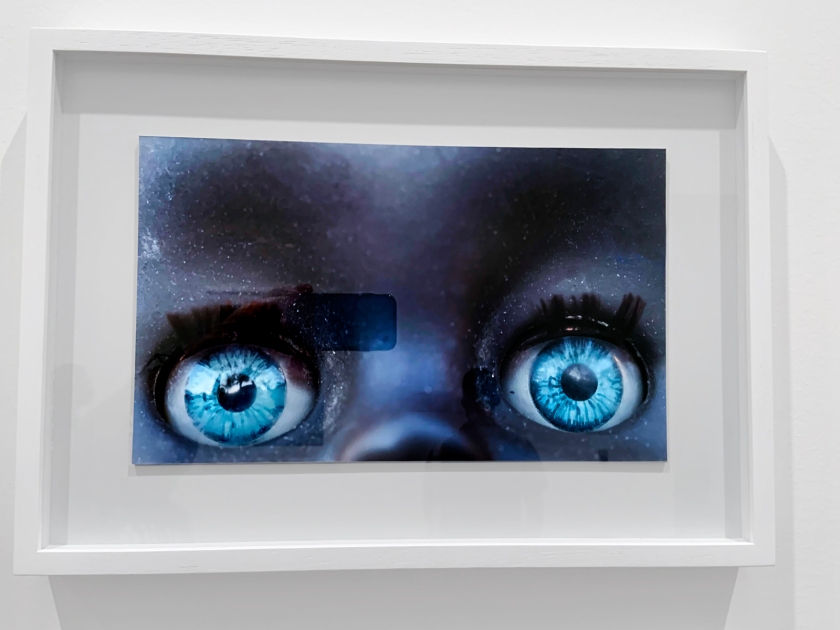
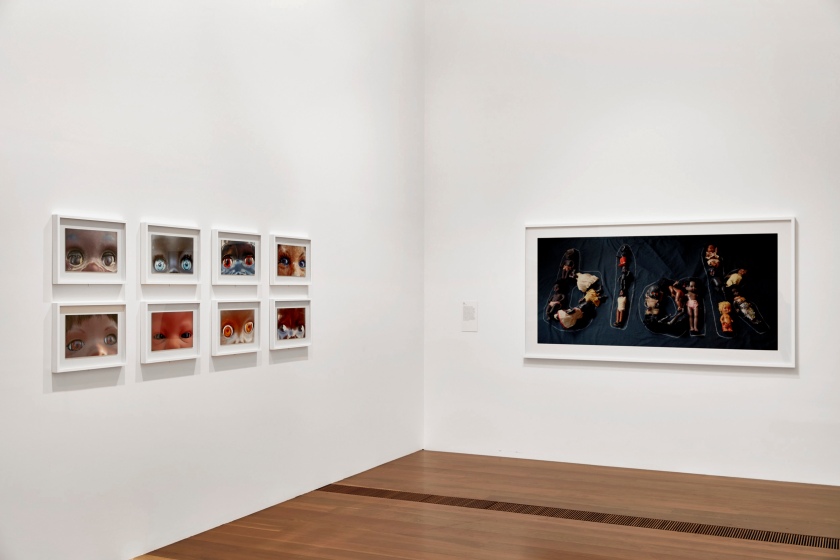
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Dolly eyes (A-H)
2020
Lightjet print
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
A doll with piercing blue eyes and dark brown skin is among the unblinking, manic faces that make up Destiny Deacon’s most recent series, Dolly Eyes, 2020. While people of colour can and do have an array of different-coloured eyes, blue eyes are often seen as a signifier of whiteness. Deacon’s tightly cropped images reduce these dollies to just eyes and skin tone, highlighting the problematic nature of using physical features to signify of racial identity.
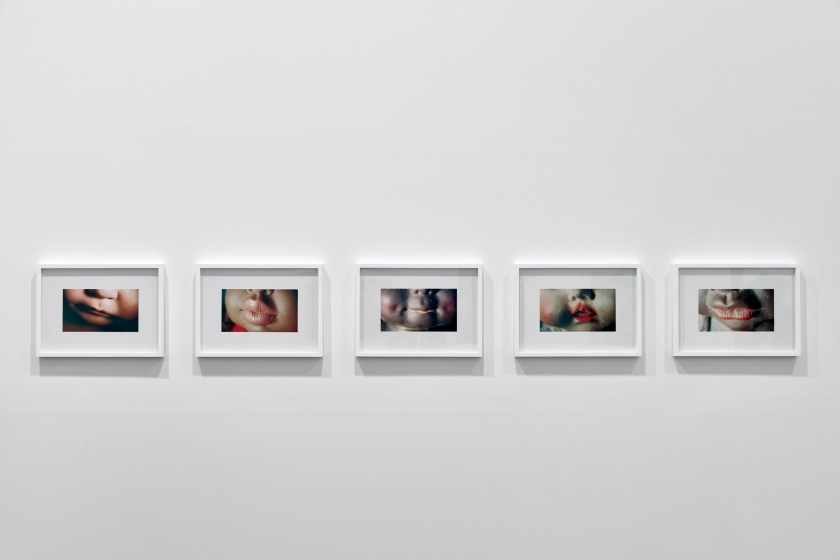
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Dolly lips (A-E)
2017, printed 2020
Lightjet print
Photo: Tom Ross
Dolly lips extracts surprising expressions from some of Deacon’s regular models. Some of these dolls have been posing for Deacon for decades, but these sensitive and suggestive images show them in a new light.
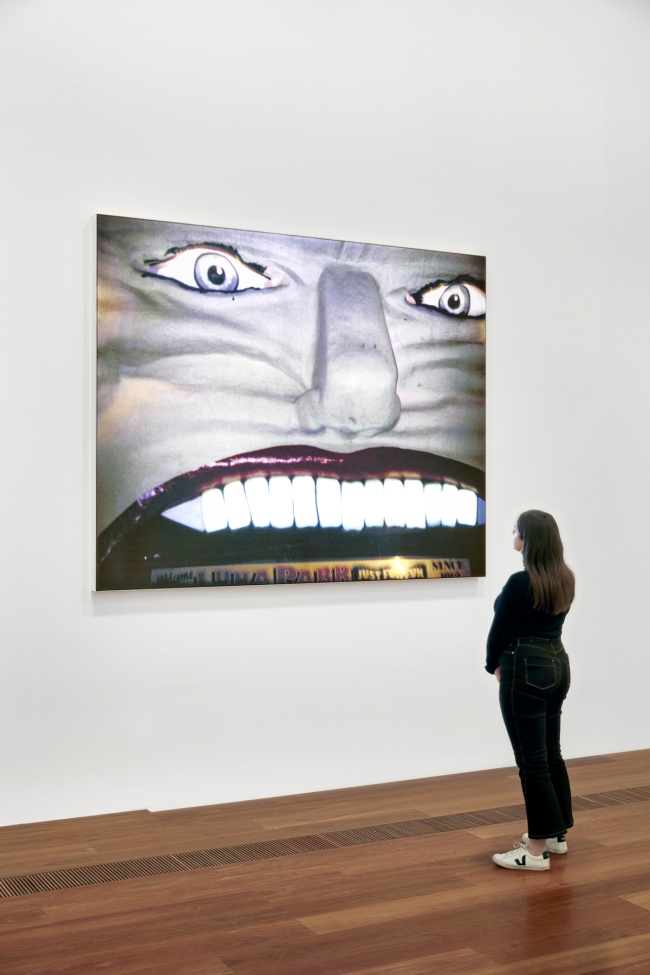
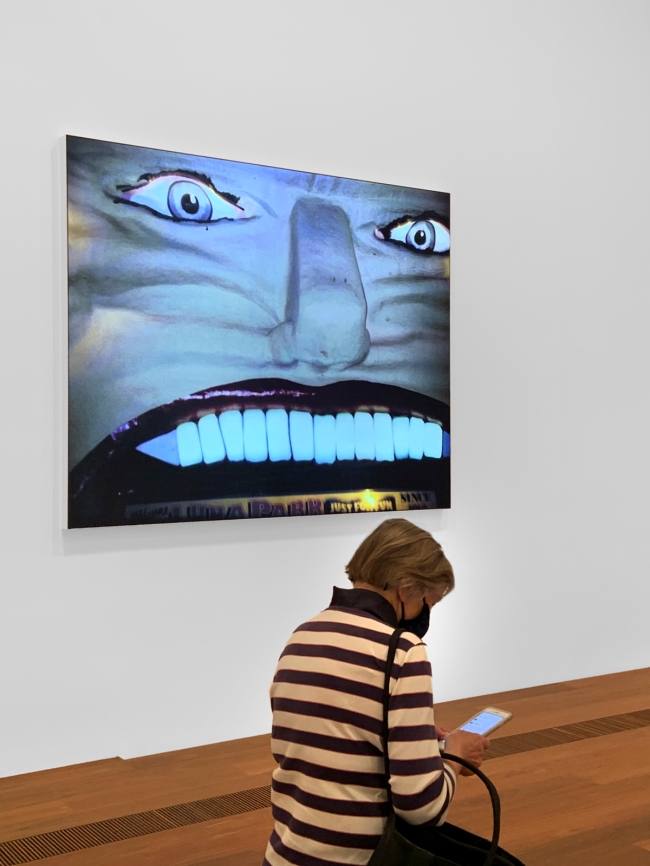
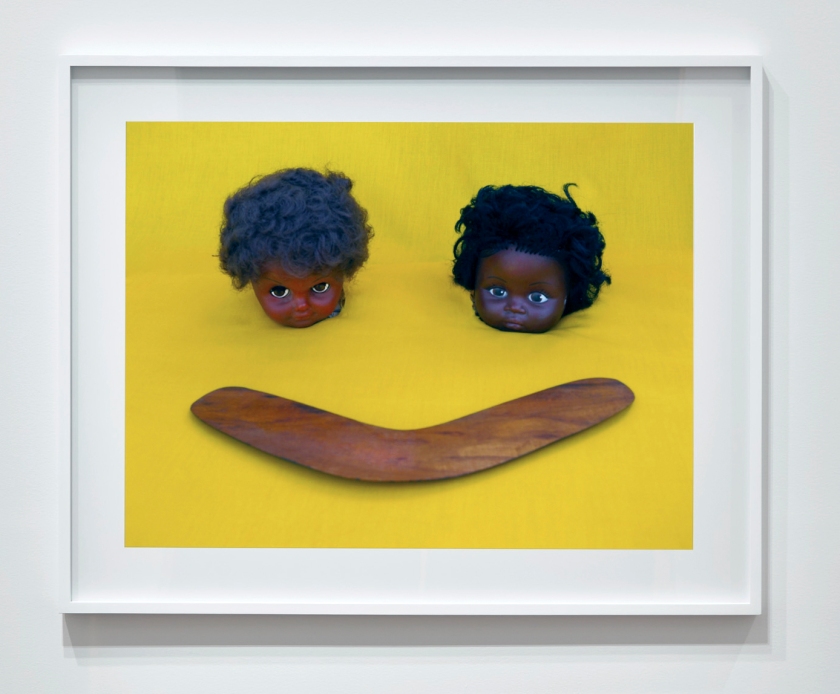
Installation view of Destiny Deacon’s Smile 2017 on display in DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020
Photo: Tom Ross
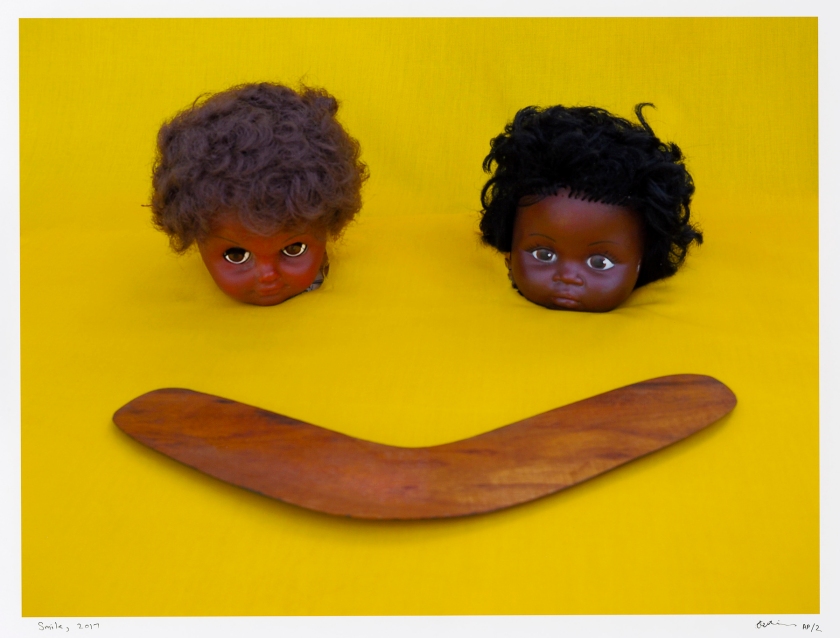
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Smile
2017
Exhibition version printed 2020
Lightjet photograph from Polaroid photograph
80.0 x 100.0cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, Victorian Foundation for Living Australian Artists, 2016
© Destiny Deacon
Deacon undercuts our trust in the innocuous smiley face emoji and prompts the viewer to look more closely at the everyday symbols that proliferate in our lives. The dolls appear decapitated, but perhaps even more ominously the disembodied heads are actually poking through a yellow sheet. Deacon uses an op-shop boomerang to complete the smile. When broken down, the individual features that make up the happy face are all racially charged. However, when viewed at a glance, all people see is the familiar smiley face emoji.
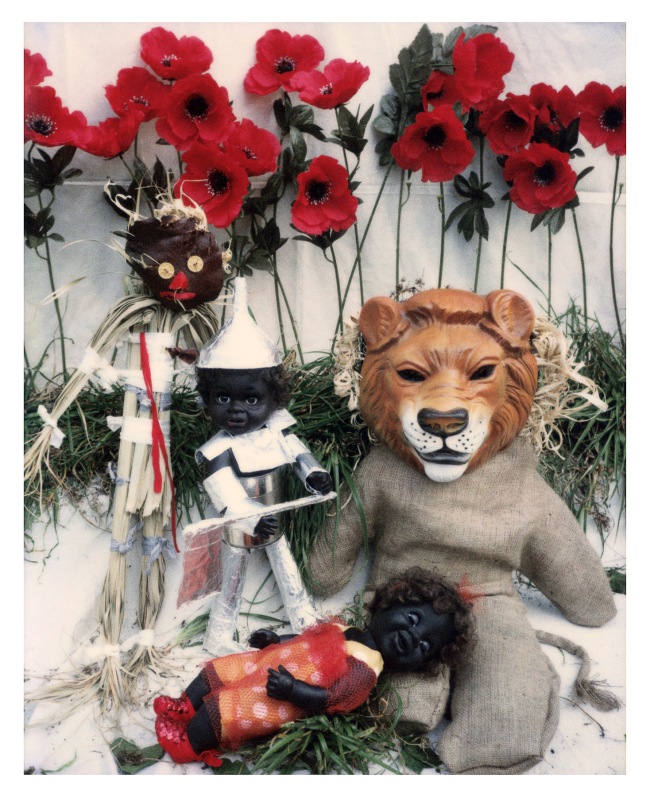
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Oz Games – Under the spell of the tall poppies
1998
Lightjet photograph from Polaroid photograph
80.0 x 100.0cm
Courtesy of the artist
© Destiny Deacon
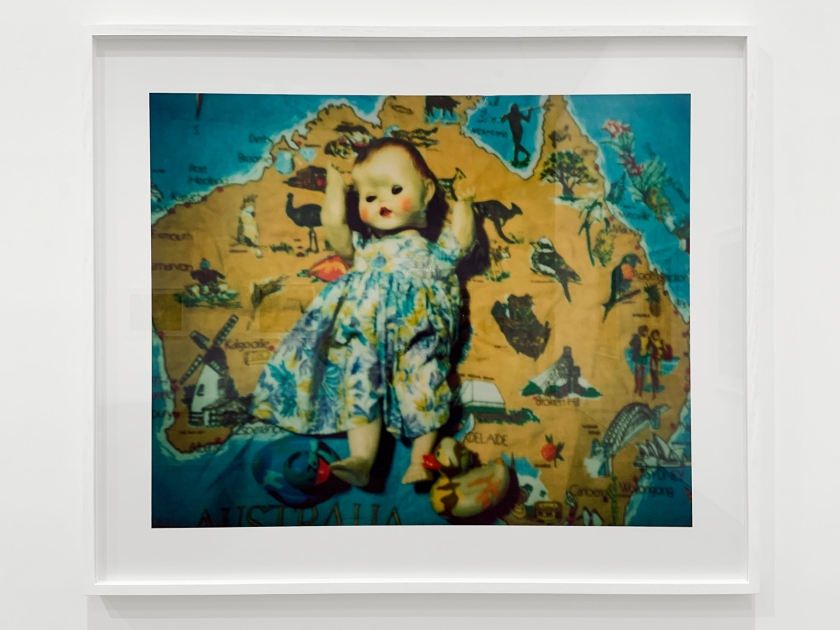
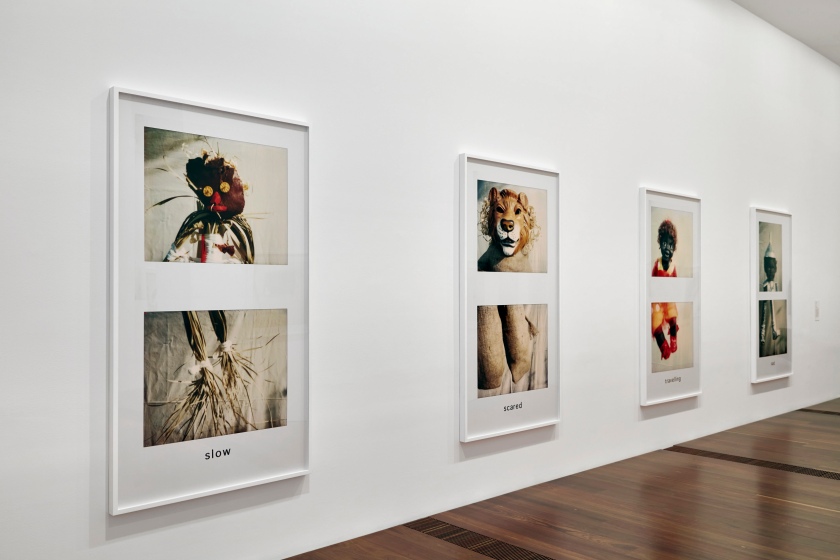
In the lead-up to the Sydney 2000 Olympics, Deacon produced Oz, a series of works parodying the 1939 film The Wizard of Oz. In the original film, Dorothy Gale is swept away from a farmhouse in Kansas to the magical land of Oz. In this series, Deacon transforms the journey undertaken by the original characters into a contemporary recognition of Aboriginality. Dorothy, now known as the ‘traveller’, appears alongside a ‘sad’ tin man, a ‘slow’ scarecrow in blackface and a ‘scared’ cowardly lion. The character’s quest for self-realisation resembles the personal journeys many Aboriginal people go through every day.
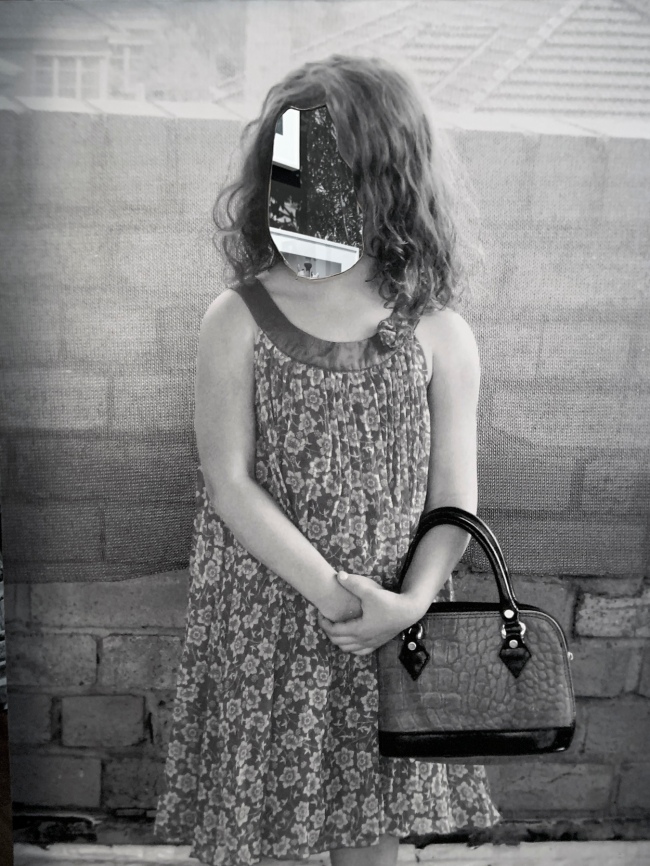
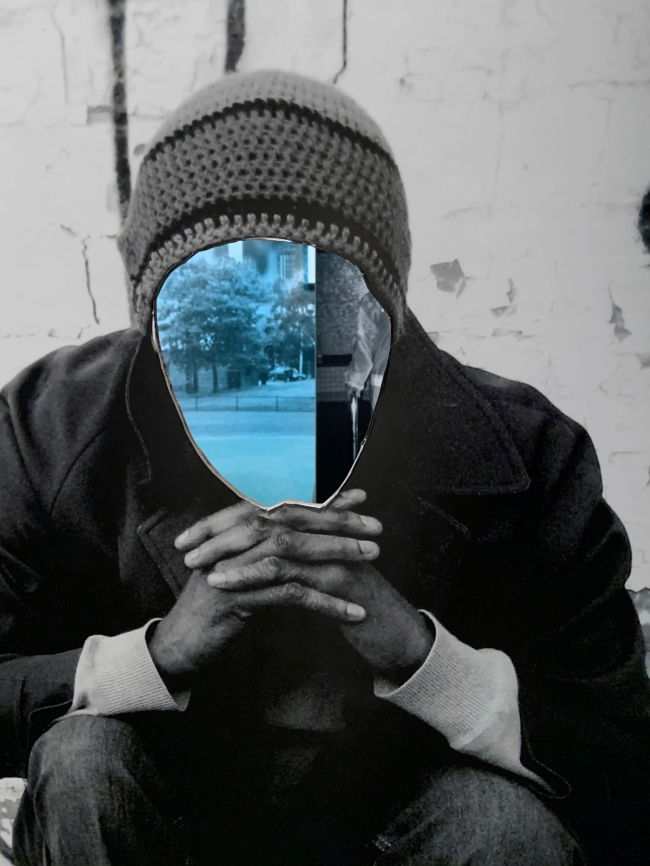
Installation views of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing at right, On reflection 2019 (below)
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
On reflection
2019
Lightjet print
100.0 x 80.0cm
Collection of the artist
© Destiny Deacon, courtesy Roslyn Oxley9 Gallery, Sydney
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Escape – From the whacking spoon
2007
Lightjet photograph from Polaroid photograph
80.0 x 100.0cm
Courtesy of the artist
© Destiny Deacon
Whacked
Escape – from the whacking spoon
Whacked to sleep (B)
Fence sitters (A)
The goodie hoodie family
Waiting for the bust
Whacked & coming home
2007, printed 2020
Lightjet print
This series of photographs references familiar imagery from news media and contemporary culture, making a link between themes of terrorism, surveillance, suppression and Australian nationalism. Playing with stereotypes, Deacon and her friends have masked themselves in long johns with disturbing painted faces. The images use sinister humour to highlight shared similarities between fanatics around the world.
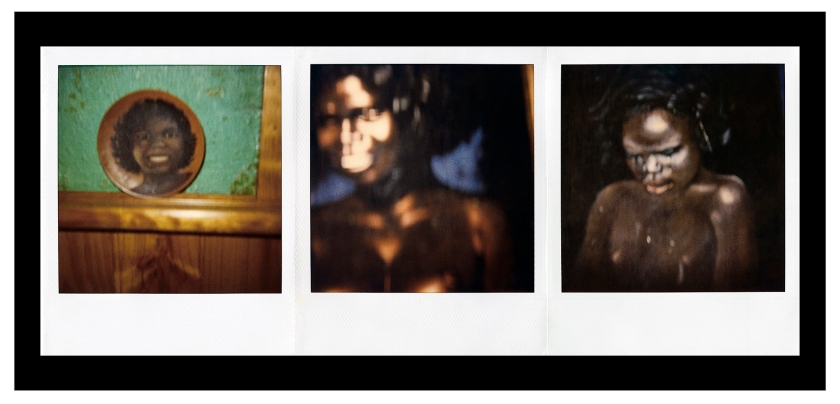
Installation view of Destiny Deacon’s Postcards from Mummy 1998 on display in DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020
Photo: Tom Ross
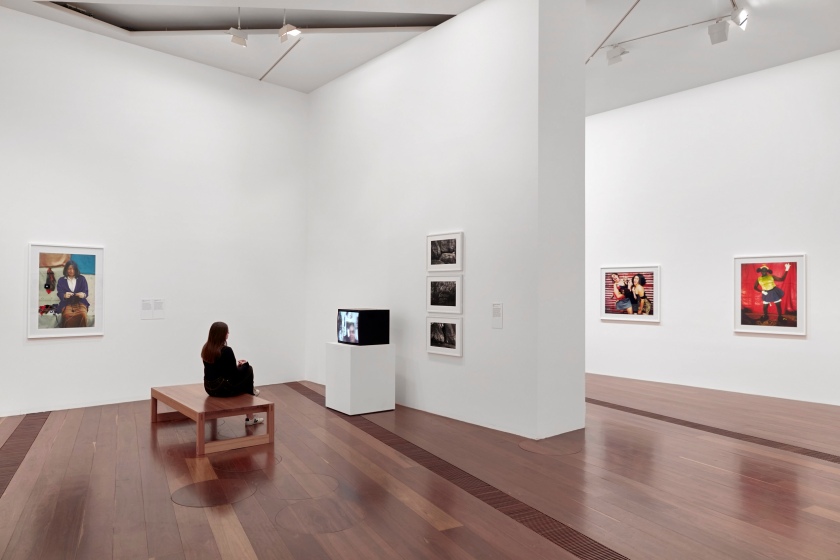
Installation view of DESTINY at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne, 2020 showing at left Dolly eyes (A-H) 2020; and at right, Blak 2020
Photo: Tom Ross
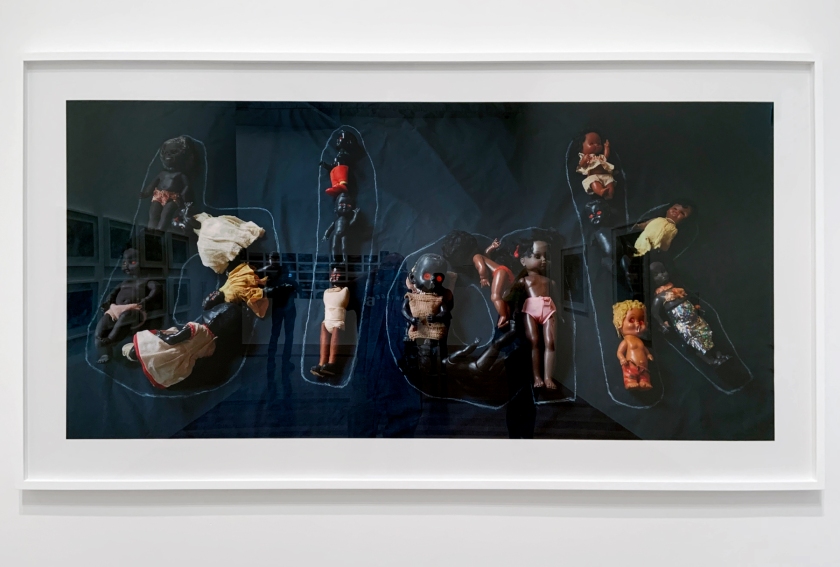
Throughout her career, this cast of characters has become central to Deacon’s practice, as has her subversive use of language. For Deacon, language, and in particular spelling, has provided an opportunity to reframe and assert her identity on her own terms. In its deceptive simplicity the recasting of ‘Black’ to ‘Blak’ resonated with Aboriginal communities everywhere. What started as Deacon asserting her personal identity as a Kuku / Erub / Mer woman, has since morphed into a Community-owned declaration of Aboriginal pride. It is fitting to conclude this exhibition with a singular photographic work: the letters b-l-a-k emblazoned across the surface with seventeen of Deacon’s regular dolly models.
Destiny Deacon (Kuku/Erub/Mer b. Australia 1957)
Blak (installation view)
2020
Light jet print
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia
Federation Square
Corner of Russell and
Flinders Streets, Melbourne
Opening hours:
Daily 10am – 5pm





































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.