Exhibition dates: August 2014
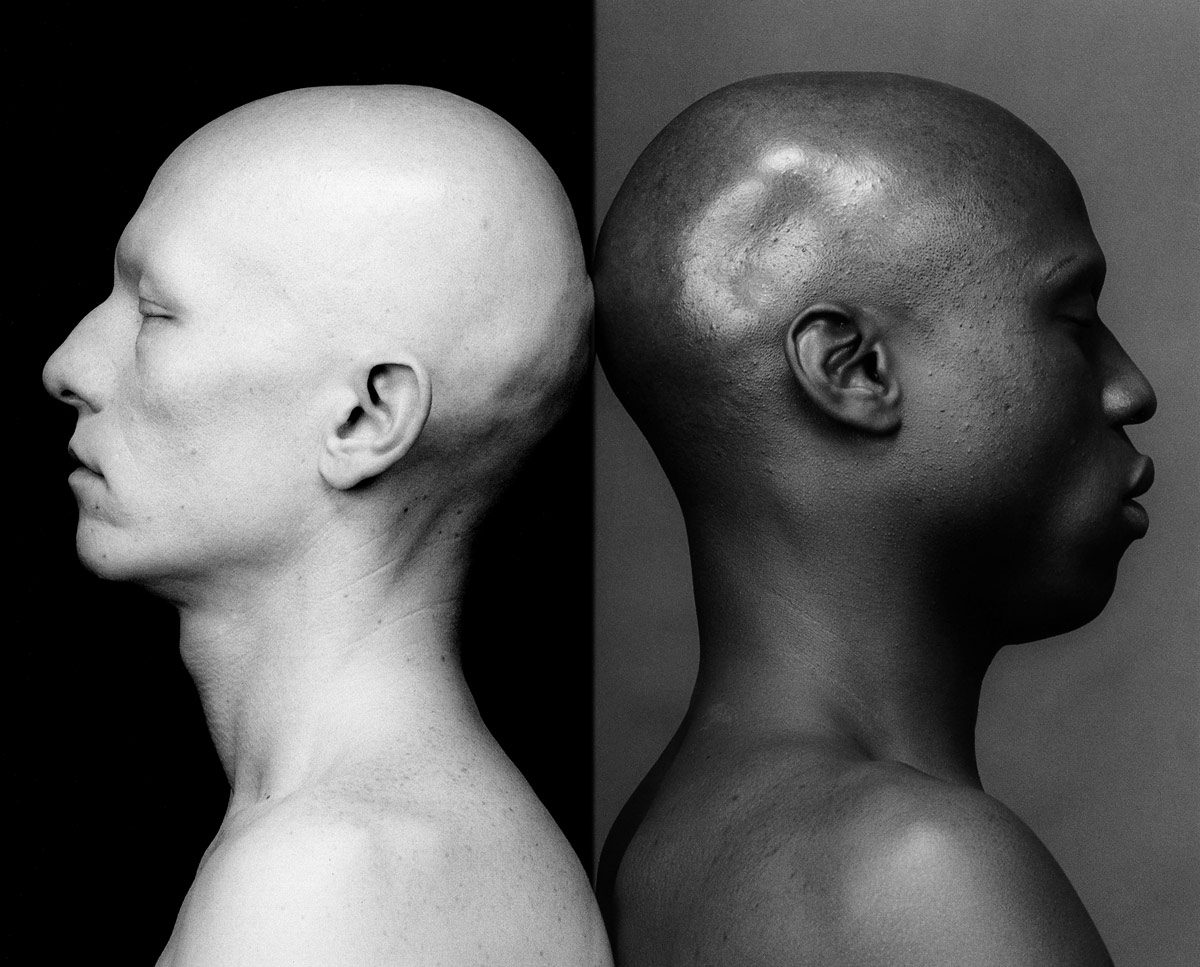
Marcus Bunyan (Australian, b. 1958)
Zen
1984
From the series First experiments
Silver gelatin print
© Marcus Bunyan
This is the catalogue essay for the exhibition Hidden Talents, an exhibition of the hidden talents of professional staff at the Faculty of the VCA & MCM, The University of Melbourne, Australia. The exhibition has been postponed until a later date but I did not want the catalogue essay to metaphorically sit under the bed with no one reading it.
The essay was written without seeing any of the art work for the exhibition (which is going to consist of knitting, performance, video, sculpture, painting, etc…). I have used my imagination to write about the subject matter, asking why it is important to reveal hidden aspects of the self.
Curator Tracey Claire observes, “Practicing artists are as likely to be found behind a desk as in front of a class at the VCA & MCM… Be it dancing, cycling, sailing, knitting, painting, writing, film making or performing, all the individuals in this exhibition are creative artists thriving in a melting hot pot of creativity… Professional staff tend to go about their business quietly, excelling in the dark arts of spreadsheet wizardry and effortless administration but in their private lives, conjuring mysterious creations. Toiling endlessly in the hours beyond their professional lives, yet inspired and nurtured by precisely this environment, they distill these experiences and produce magic.“
This catalogue essay examines the significance of these activities and is accompanied by 5 of the very first black and white images that I ever took, long before I ever started studying photography in 1989.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Keywords
Hidden Talents, The Self, Aspects of the Self, self-expression, image man, essence man, actual self, networked society, perfomative self, citational self, cosmopolitanism, hybridity, visibility, bricolage, Goethe, hybrid identities, identity formation, self actualisation, social transparency, The University of Melbourne, Australia, Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne Conservatorium of Music, VCA.
Download the Aspects of the Self (Revealed) catalogue essay (2.6Mb pdf). Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Marcus Bunyan (Australian, b. 1958)
Brighton Pier (horizontal)
1984
From the series First experiments
Silver gelatin print
© Marcus Bunyan
Aspects of the Self (Revealed)
Dr Marcus Bunyan
“In our era of internet ubiquity, the line that separates our selves from the media with which we self-express has dissolved, and the distinction between medium and maker is confused. As we publicise our private stories, and perpetually alter, rebrand, and repaint ourselves to the world, performances of self are status quo and everyone is an artist.”
Josephine Skinner 1
We are all performance artists. And this text is a performance piece, an aspect of myself as I choose to express it in this place and time. An aspect – appearance, look, character, view, interpretation, phase, countenance2 – which, like the word itself, is both stable and fluid, and will change at any time: perhaps even now; or in the future.
Having noted the amorphous nature of the wor(l)d, what I will do in this performance is examine the truths and separate them from the platitudes of Josephine Skinner’s quotation (above) in order to understand not only that the private be made public but also why the hidden should be revealed. Of course, our sense of self changes when the private becomes open, public and possibly universal. I will ask why this is important and how it affects our sense of connection to other human beings. To do this I will examine my own private story, not to rebrand or repaint myself to the world, far from it, but because every life path has important lessons for us all.
In the beginning, I grew up on a farm. My parents were impoverished. It was subsistence living and we were the working poor. We had no running hot water and my mother used to have to boil water on a stove and fill a bathtub on the kitchen floor so that we could be cleaned. I used to explore the remote reaches of the land, out behind the pond at the front of the farmhouse and up the cart path into the forests, creating fantasy worlds to escape what was going on at home. There, fantasies became a form of escapism, for my imagination, for action,3 a place where I could create new worlds of magic, light and freedom.
My mother was a piano teacher and my father was a part-time singer. I started to study piano at the age of 5 years old under my mother’s tutelage. I had a natural gift and became a child prodigy, the youngest person at that time to attain a distinction in Associated Board Grade 8 examination, at age 11. I was sent to boarding school on a music scholarship at the age of 12, leaving all my school friends behind. There, in that upper class boarding school, I was ostracised because they found out I was gay (just as I was discovering it myself), and because I was a music scholar. My parent’s adage to life was what I would come to call Protestant work ethic: ‘you never work hard enough, you’ll never be good enough, you’ll never make anything of yourself.” This damnation has stuck with me and I have struggled against its prophecy, working hard to make something of myself, something I can be proud of. Even now my mother (I don’t see my father) still fails to recognise my achievements, my life path.
At boarding school I developed what I was told was depression but which was actually bipolar disorder, undiagnosed until I was in my forties. At the age of 16, I was one of the youngest people to go to the Royal Academy of Music and at 17 I went to the Royal College of Music full time. I moved away from home, which was a blessing, and started living on my own. It was a tough initiation into adult life but I was determined not to be dependent on anyone else. My parents finally divorced when I was 17 and, at the same age, the stress of my hidden sexuality leading me to have a nervous breakdown. After nearly a year recovering I came out as a gay man. I graduated with my degree at 21 and gave up being a concert pianist the same year. The time to start living my own life had begun.
I worked in pubs around London for years. I hated classical music (a rejection of the past) and was really into the funk scene. I was a dilettante, a person without real commitment or knowledge. Not once did I ever think of myself as intelligent or creative, it just wasn’t in my vocabulary. I enjoyed partying, holidays, friends and motor racing and started taking a few photographs. That was it until I was about 28 when I returned to Year 12 and university to study, study, study, to read Carlos Castaneda, Robert Johnson and Joseph Campbell, to devour Borges, Jung and Foucault – not the usual university curriculum for an artist, but I was searching for a spiritual way in life. These authors offered wisdom and learning, and a network to other authors and artists investigating similar subject matter. The start of a path had been found and an inquiring mind slowly emerged. I tell you all of this simply as a statement of fact – this was my beginning, this is what I went through, and this journey and learning informs my being and relation to other people and to the world.
Today, we need to understand our own paradigm of sharing, what we are prepared to reveal of ourselves now that we live in a networked society. In a networked society the private and the public self are no longer two endpoints of a linear dichotomy for the boundaries have well and truly been breached: mobile technologies, computers and social media bring the outside world into our home and we willingly promote our point of view to others. Our interior thoughts are advertised through our exterior relations and appearance – on videos, on mobile phones, through millions of images and informational flows that surround us everyday. Our performative self, our citational self constantly performs and citationally quotes our relations of our self to others through different nodal points, or contexts of connection. But our interiority is still different from our exteriority, even as we perform the self.
Yet, while it is correct that in our era of internet ubiquity, the line that separates our selves from the media with which we self-express has dissolved – we are still not yet fully immersed in this system. Critically, we still have a choice about what we reveal of ourselves to others. My degree as a concert pianist may appear at the bottom of my CV, and I may not tell many people about it, but how I imagine my art, how I write my words and my worlds, is inherently related to the line and ‘magic’ of music. How I relate to other people is based on my core values (strong moral code, loyalty, love of helping people) developed during childhood, core values that have remained stable but whose context may have changed over the journey from youth to adulthood. And because of our class (our position in the world and our contexts), we inhabit the privilege of that disclosure. In this moment, we can still prioritise what other people know of us. What we should not do is divest this choice from our whole selves, partitioning ourselves off in different contexts. We cannot act within our core values in one situation and not in another – unless we want to deceive ourselves and those around us – AND YET WE DO!
While our fundamental values remain consistent (the actual self) what is rapidly changing is the environment in which our social self operates.4 As Sally Shaw notes, “We are experiencing an important cultural moment: the next generation will not be able to recall a time without smartphones, the internet or other enhanced means of communication.”5 Globalised mass media, technological advances in communications, future generations’ normalising of the constant barrage of information and the endless pursuit of “stuff”6 (materialism gone mad) means that “image man” takes precedence over “essence man.”7 But all is not lost if we are prepared to be open to possibilities, to be brave in our choice of engagement with others, and be accepting in our attitude and perspective on life. As the artist Bill Henson observes, “Of course, we live with each other and get along using “civilisational logic” – go at a green light, stop at a red light. But there is a deeper logic – no less exacting or emphatic.”8
This deeper logic, a logic that opens up spaces of inquiry, has links to creative, moderate cosmopolitanism,9 hybridity,10 bricolage and visibility. It is how creativity is changing how our talents are recognised by our friendship networks, our work colleagues or students, without having to justify or hide their existence. It is how the networked personality extends along a horizontal consciousness (not a vertical hierarchy), in which interior / exterior, self / other, is re/formed. Through respect, authenticity (and not anxiety about it!) and openness, we can embed the self into naturalised flows of increasingly open (media) systems. We have a new freedom to construct social relations across time and space for the horizon of social relationship – my body, the social body, the actual self – can become open constellations. Here there is fluidity in identity representation in which stable dimensions, persistent appearances and secure meanings are disavowed. This is coupled, however, with a paradoxical insecurity of those in power, evidenced by the proliferation of borders, walls, security cameras and protected areas.11
This new process of self actualisation enables a creative context, the context for understanding creativity, intelligence, self and what you bring to an encounter, what you are prepared to reveal of your self during that encounter – whether it be baking cakes, knitting scarves, making a video, documenting the self or creating, as I did in my childhood and still do in my art, imaginative worlds to express inner self. Through the lived practice of social transformation we, as social actors, have to rethink our hybrid identities and the function of our imagination as a world-making process.12 This process is about the exposure of the hidden; it is about social transparency; and it is about the emergence of something new.13
Finally, we can say it is neither about the roles we play nor the destination that many seek, but it is about the journey that we take and about rejoicing in that journey. It’s about the moment before ecstasy, the anticipation: of company, of environment, of friends, places, being human, that joy of being human. It’s an inquiring instability that leads, as in Beethoven, to the resolution of stability, a love of the human being and our existence. It’s about understanding the personality and possibility of being.
Instead of the byte sized tweet (in which we understand everything, in an instant), we understand our hybrid being only by moving mentally and physically through heterogenous spaces via flows, nodes and lexias, accessing different perspectives and viewpoints. If we are attentive and aware of these viewpoints, we can open up lines of inquiry and access spaces of plurality which may allow us to be better informed as to the value of self and others. Through an understanding of difference. Through an understanding of the obligation of all human beings to each other.
This challenge to established rhythms, institutions and boundaries – the polity of the state, the indifference of the masses, and the speed of informational flows – can be accomplished by both stepping back and contemplating but also by moving forward and engaging in acts of informed choice, thinking, believing, and relating to other people. This is where I disagree with Josephine Skinner’s quote at the beginning of this aspect of myself: performances of self should never become just so, status quo – for we must not be afraid to reveal aspects of our self and expose the hidden to light. In the day-to-day world, the roles we play and the masks we wear must never come to define who we really are. As Lou Benson observes, “If people begin to see their roles as their true selves and deny thoughts and feelings that are really present, they become estranged from themselves.”14
By not being secret but secreting wisdom and seeking creation we may ultimately find better paths through life. This journey is about being extra/ordinary, however that may be. It is about the ‘making present’ of our imagination in the moment we are in, being consciously aware of that moment, being happy in that moment without ego. It’s about what you do and who you are, not cowering behind the bulkheads.
“O God, how the world and heaven shrink together when our heart cowers in its barriers.”
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
© Dr Marcus Bunyan
August 2014
Word count: 2,164
Marcus Bunyan (Australian, b. 1958)
Craig in his Docs
1984
From the series First experiments
Silver gelatin print
© Marcus Bunyan
Endnotes
1/ Skinner, Josephine. “Totally Looks Like.” Exhibition catalogue. Stills Gallery, Sydney, June 2014.
2/ as·pect [as-pekt]
noun
~ Appearance to the eye or mind; look: the physical aspect of the country.
~ Nature; quality; character: the superficial aspect of the situation.
~ A way in which a thing may be viewed or regarded; interpretation; view: both aspects of a decision.
~ Part; feature; phase: That is the aspect of the problem that interests me most.
~ Facial expression; countenance: He wore an aspect of gloom. Hers was an aspect of happy optimism.
Aspect as defined on the Dictionary.com website [Online] Cited 22/06/2014 http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/aspect
3/ “The ubiquity of images and the constant enhancement of the modes for public participation have not only disrupted the conventional division between the agency of the artist and collective authorship but also underscore the necessity to rethink the function of the imagination as world-making process. Arjun Appadurai stated it most succinctly: ‘the imagination is today a staging ground for action, and not only escape’.”
Appadurai, Arjun. Modernity at Large. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1996, p. 7 quoted in Papastergiadis, Nikos. Cosmopolitanism and Culture. Cambridge: Polity Press, 2012, p. 95.
4/ “A natural extension of social comparison theory is the development of the self-concept. Self-concept is a person’s perceptions and perceptual organization of his/her own characteristics, roles, abilities and appearance. One’s self-concept is based in part on how one compares to other individuals with regards to traits, opinions and abilities … Self concept can have a number of dimensions which evolve from social comparisons and evaluations. The self-concept consists of:
~ the actual self (how a person perceives him/herself),
~ the ideal self (how a person would like to perceive him/herself), and
~ the social self (how a person presents him/herself to others).
Sproles, George and Burns, Leslie Davis. Changing Appearances: Understanding Dress in Contemporary Society. New York: Fairchild Publications, 1994, pp. 208-209.
5/ Shaw, Sally quoted in Beesley, Ruby. “Challenging Normality,” in Aesthetica, Issue 59, June/July 2014, p. 52.
6/ Ibid.,
7/ “Essence man approaches life from the standpoint of being who he is without concern for the way he is perceived by others. Image man, on the other hand, focuses on what he wishes to appear to be. In reality, Buber admits, we are all a combination of both. But the tendency is to develop a life-style that is dominated by one pole of this duality.”
Benson, Lou. Images, Heroes and Self-Perceptions. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, 1974, pp. 26-29.
8/ Henson, Bill. “Unfinished Symphony,” in the Weekend Australian Review, June 14-15, 2014, p. 5.
9/ “The more moderate [cosmopolitan] alternative “is to say that, in addition one to one’s relationships and affiliations with particular individuals and groups, one also stands in an ethically significant relation to other human beings in general” … This second approach starts with rights rather than obligations, and holds that wherever people are joined in significant social relations they have a collective right to share in control of these.”
Calhoun, Craig. “‘Belonging’ in the cosmopolitan imaginary,” in Ethnicities, 3 (4), 2003, pp. 531-553.
10/ “At the first level, hybridity refers to the visible effects of difference within identity as a consequence of the incorporation of foreign elements… Recognition of the second level refers to the process by which cultural differences are either naturalized or neutralized within the body of the host culture… The third level of hybridity is linked to aesthetic processes and can be thematized through the early modernist techniques of juxtaposition, collage, montage and bricolage.”
Papastergiadis, Op. cit., p. 117.
11/ For these ideas I am indebted to the “Introduction: The Uncanny Home,” in McQuire, Scott. The Media City: Media, Architecture and Urban Space. London: Sage Publications, 2008, pp. 22-24.
12/ Papastergiadis, Op. cit., p. 95.
13/ “Hybridity refers not only to the ambivalent consequences of mixture but also to the shift in the mode of consciousness. By mixing thing that were previously kept apart there is both a stimulus for the emergence of something new and a shift in position that can offer a perspective for seeing newness as it emerges.”
Papastergiadis, Op. cit., p. 131.
14/ “This is not to say that it is possible or even desirable to try to live in the day-to-day world without playing certain roles and wearing certain masks. Societies function through the role play of their inhabitants. But if people begin to see their roles as their true selves and deny thoughts and feelings that are really present, they become estranged from themselves.”
Benson, Lou. Images, Heroes and Self-Perceptions. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, 1974, pp. 26-29.
Marcus Bunyan (Australian, b. 1958)
Craig with halo
1984
From the series First experiments
Silver gelatin print
© Marcus Bunyan
Marcus Bunyan (Australian, b. 1958)
Brighton Pier (vertical)
1984
From the series First experiments
Silver gelatin print
© Marcus Bunyan



















You must be logged in to post a comment.