Exhibition dates: 10th March – 8th July 2012
List of Photographers Included: Katya Brailovsky, Lola Alvarez Bravo, Manuel Alvarez Bravo, Manuel Carrillo, Alejandro Cartagena, Eduardo del Valle and Mirta Gomez, Pia Elizondo, Dave Gatley, Oscar Fernando Gomez, Héctor Garcia, Lourdes Grobet, Graciela Iturbide, Geoffrey James, Mark Klett, Pablo Lopez Luz, Elsa Medina, Susan Meiselas, Enrique Metinides, Pedro Meyer, Tina Modotti, Rodrigo Moya, Pablo Ortiz Monasterio, Paolo Pellegrin, Antonio Reynoso, Daniela Rossell, Mark Ruwedel, Victoria Sambunaris, Alec Soth, Paul Strand, Yvonne Venegas, Brett Weston, Edward Weston, and Mariana Yampolsky.
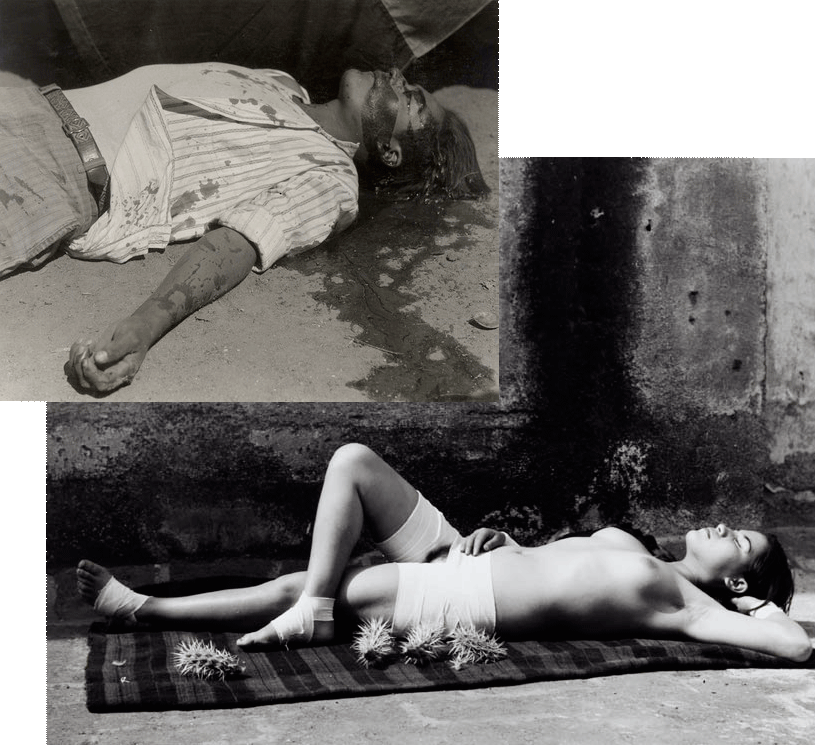
Manuel Alvarez Bravo (Mexican, 1902-2002)
Obrero en huelga, asesinado (Striking Worker, Assassinated)
1934
Gelatin silver print
19.2 x 23.8cm
Manuel Alvarez Bravo (Mexican, 1902-2002)
La buena fama durmiendo (The Good Reputation Sleeping)
1939
Gelatin silver print
20.3 x 25.4cm
Compilation by Dr Marcus Bunyan
“There is no one ‘Mexican photography,’ but one strand that runs throughout is a synthesis of aesthetics and politics. We see that with Manuel Alvarez Bravo, and we still see it in work made decades later.”
Jessica S. McDonald
One of my early heroes in photography was Manuel Alvarez Bravo whom I rate as one of the best photographers that has ever lived, up there with Atget and Sudek. His photograph Parabola optica (Optical Parable, 1931, below) lays the foundation for an inherent language of Mexican photography: that of a parable, a short allegorical story designed to illustrate or teach some truth, religious principle, or moral lesson. Many Mexican photographs tell such stories based on the mythology of the country: there are elements of the absurd, surrealism, macabre, revolution, political and socio-economic issues, also of death, violence, beauty, youth, sexuality and religion to name but a few – a search for national identity that is balanced in the photographs of Bravo by a sense of inner peace and redemption. This potent mix of issues and emotions is what makes Mexican photography so powerful and substantive. In the “presence” (or present, the awareness of the here and now) of Mexican photography there is a definite calligraphy of the body in space in most of the work. This handwriting is idiosyncratic and emotive; it draws the viewer into an intimate narrative embrace.
Two famous photographs by Bravo illustrate some of these themes (Apollonian / Dionysian; utopian / dystopian). When placed together they seem to have a strange attraction one to the other (see photographs above).
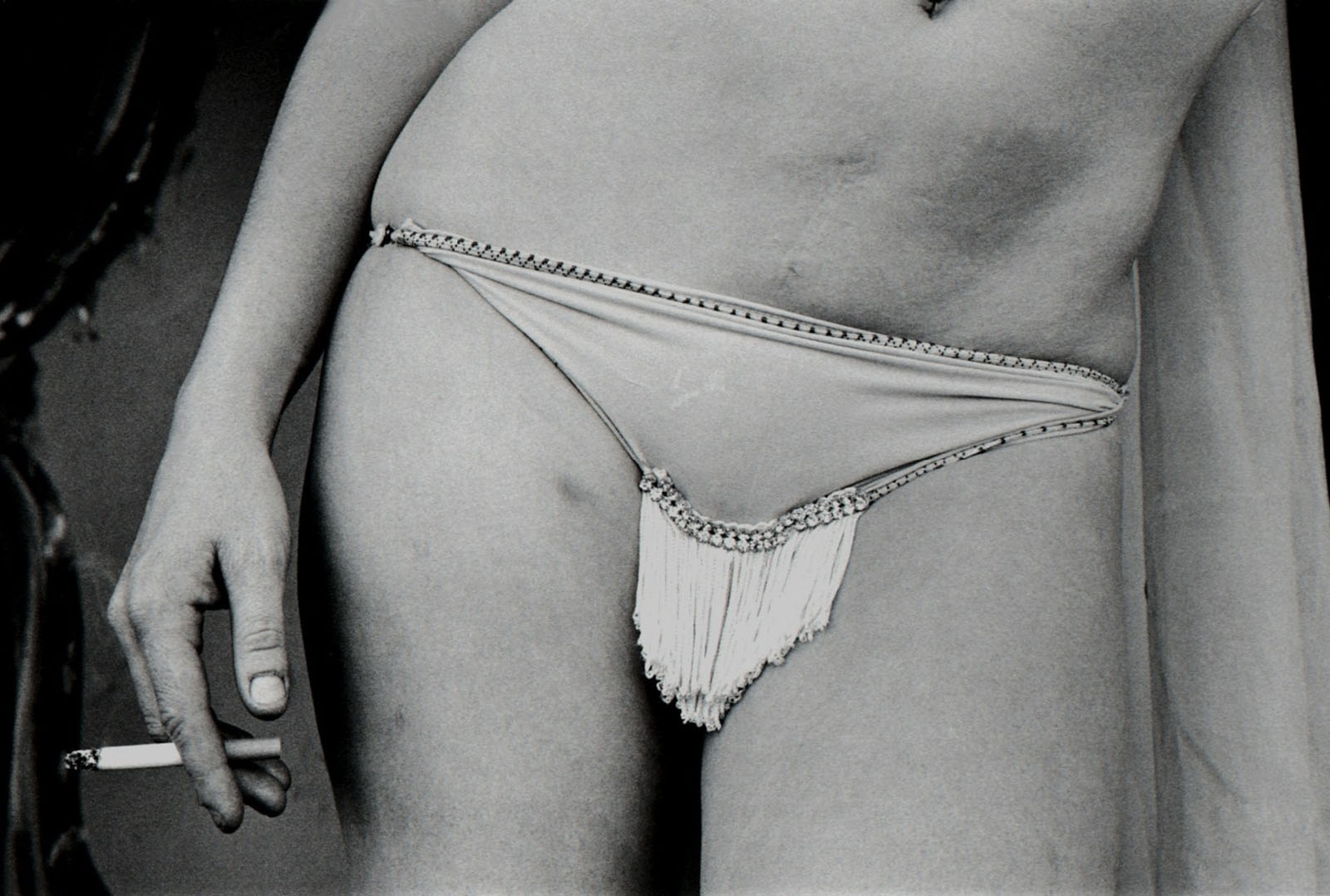
Unlike most Australian documentary photography where there is an observational distance present in the photographs – a physical space between the camera/photographer and the subject – Mexican documentary photography is imbued with a revolutionary spirit and validated by the investment of the photographer in the subject itself, as though the image is the country is the photographer. There is an essence and energy to the Mexican photographs that seems to turn narrative on its head, unlike the closed loop present in the tradition of Australian story telling. The intimate, swirling narratives of Mexican photography could almost be termed lyrical socio-realist. The halo of the golden child of Yvonne Venegas’ Nirvana (2006, below) menaced by the upturned forks is a perfect example.
Some of the themes mentioned above are evidenced in the photographs in this posting. Not the placid nude or heroic pyramid of Weston but the howl of the masked animal and surrealism of Our Lady of the Iguanas demands our close engagement. I only wish Australian photographers could be as forthright in their investigation of the morals and ethics of this country and our seemingly never ending search for a national identity (other than war, mateship, the beach, sport and the appropriation of Aboriginal painting exported as the Australian art “identity”).
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to SFMoMA for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
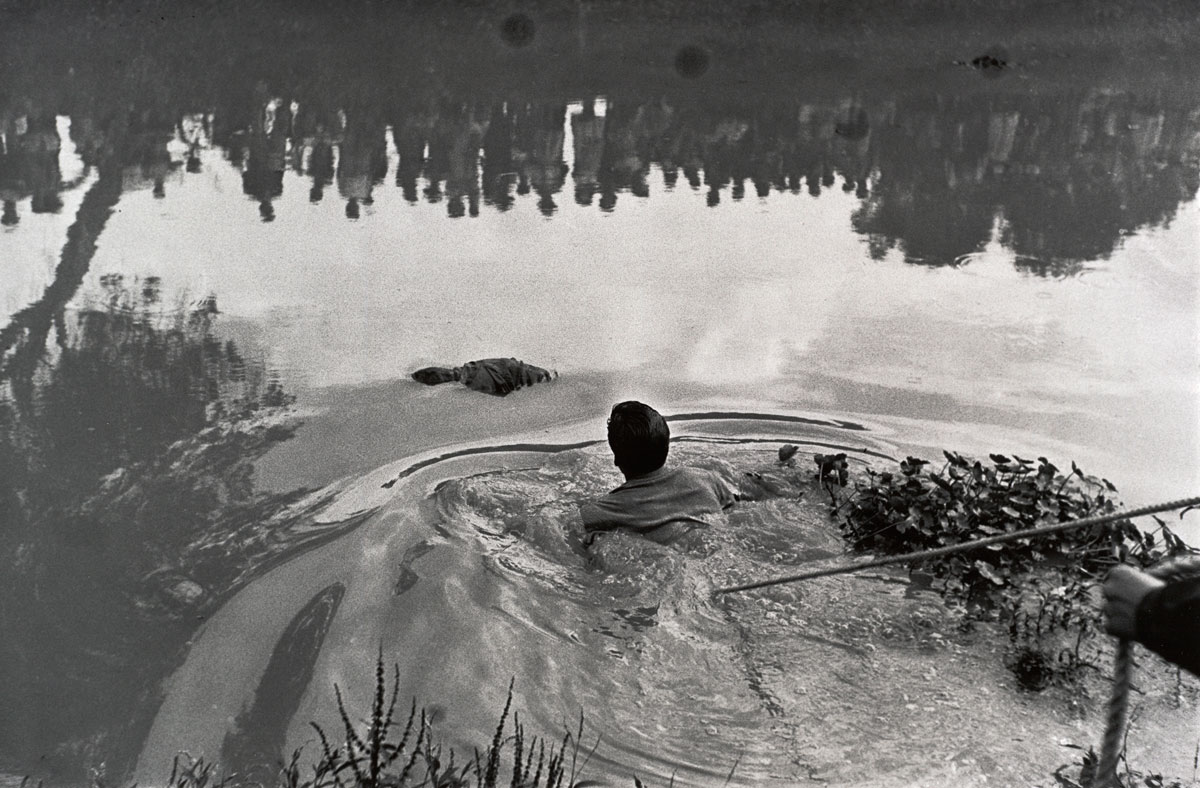
Enrique Metinides (Mexican, 1934-2022)
Rescate de un ahogado en Xochimilco con público reflejado en el agua (Retrieval of a drowned body from Lake Xochimilco with the public reflected in the water)
1960
Gelatin silver print
13 3/4 x 20 3/4 in
San Francisco Museum of Modern Art, Anonymous Fund purchase
© Enrique Metinides
Pablo Ortiz Monasterio (Mexican, b. 1952)
Y es plata, cemento o brisa
c. 1985
Gelatin silver print
8 9/16 x 12 3/4 in (21.75 cm x 32.39cm)
Collection of Daniel Greenberg and Susan Steinhauser
© Pablo Ortiz Monasterio
Yvonne Venegas (American, b. 1970)
Nirvana from the series Maria Elvia De Hank
2006
Inkjet print
19 1/2 x 24 in (49.53 cm x 60.96cm)
Collection of the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art
© Yvonne Venegas
Oscar Fernando Gómez (Mexican, b. 1970)
Untitled from the series The Windows
2008-2010
Inkjet print
17 1/4 x 24 in (43.82 cm x 60.96cm)
Collection of the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art
© Oscar Fernando Gómez
Paolo Pellegrin (Italian, b. 1964)
USA. El Paso, Texas. May 17, 2011. Two men, who illegally attempted to enter the U.S., run across the dry Rio Grande river back to Juarez, Mexico after being spotted by the US Border Patrol
2011
Inkjet print
15 3/16 x 22 3/4 in (38.58 cm x 57.79cm)
Collection of the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art
© Paolo Pellegrin
From March 10 through July 8, 2012, the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art (SFMOMA) will present the exhibition Photography in Mexico: Selected Works from the Collections of SFMOMA and Daniel Greenberg and Susan Steinhauser. Exploring the distinctively rich and diverse tradition of photography in Mexico from the 1920s to the present, the exhibition showcases works by important Mexican photographers as well as major American and European artists who found Mexico to be a place of great artistic inspiration.
Organised by SFMOMA Assistant Curator of Photography Jessica S. McDonald, the selection of more than 150 works draws from SFMOMA’s world-class photography holdings and highlights recent major gifts and loans from collectors Daniel Greenberg and Susan Steinhauser. The presentation reflects the collections’ particular strengths, featuring photographs made in Mexico by Tina Modotti, Paul Strand, and Edward Weston, along with works by key Mexican photographers including Lola Alvarez Bravo, Manuel Alvarez Bravo, Manuel Carrillo, Héctor Garcia, Lourdes Grobet, Graciela Iturbide, Enrique Metinides, Pedro Meyer, Pablo Ortiz Monasterio, and Mariana Yampolsky.
The exhibition begins with the first artistic flowering of photography in Mexico after the Mexican Revolution (1910-1920) and goes on to look at the explosion of the illustrated press at midcentury; the documentary investigations of cultural traditions and urban politics that emerged in the 1970s and 1980s; and more recent considerations of urban life, globalisation, and issues particular to the U.S.-Mexico border region. Rather than attempting to define a national style, the exhibition considers the range of approaches and concerns that photographers in Mexico have pursued over time. As McDonald notes, “There is no one ‘Mexican photography,’ but one strand that runs throughout is a synthesis of aesthetics and politics. We see that with Manuel Alvarez Bravo, and we still see it in work made decades later.”
As arts and culture flourished in Mexico after the Revolution, many European and American artists were drawn to the country. Among them were Edward Weston and Tina Modotti, who arrived in Mexico in 1923. Inspired by what they saw there, Weston and Modotti in turn motivated Mexican photographers to pursue the medium’s artistic possibilities; their influence helped “give Mexican photographers confidence that art photography was a viable path,” says McDonald. Hence, the exhibition opens with a selection of works made in Mexico by Modotti, Weston, his son Brett Weston, and Paul Strand during the 1920s and 1930s.
One of the Mexican photographers encouraged by Modotti and Weston was Manuel Alvarez Bravo, who went on to become one of the most influential photographers and teachers in the country’s history as well as a key figure in the broader international history of the medium. The exhibition features a substantial number of major works by the photographer, many of them donated or loaned to SFMOMA by Daniel Greenberg and Susan Steinhauser. In considering Alvarez Bravo’s career, the exhibition illuminates the birth and development of a tradition of art photography in Mexico. The presentation also includes a selection of works by Alvarez Bravo’s first wife, Lola Alvarez Bravo, an important photographer in her own right who established a successful commercial and artistic practice.
In mid-20th-century Mexico, as in the United States and Europe, earning an adequate income as an art photographer was an unlikely proposition. Instead, many photographers made a living through photojournalism, contributing to the numerous illustrated publications in circulation during this period. In the decades following the Revolution, there was great interest in traditional ways of life and in defining what it meant to be Mexican. Some photographers, such as Manuel Carrillo, created images documenting the nation’s traditions and celebrating its common people. Others, like Hector Garcia and Rodrigo Moya, rejected this sentimental approach, focusing instead on contemporary concerns and the political and social turbulence that continued to influence post-revolutionary Mexican life.
The late 1960s and 1970s saw the rise of critical theory and a new interest in investigating the nature of photography as a medium; in Mexico as elsewhere, there were more opportunities to study photography and to pursue noncommercial projects. A number of Mexican photographers, such as Lourdes Grobet, Graciela Iturbide, Pedro Meyer, and Pablo Ortiz Monasterio, created extended documentary series. Iturbide lived among indigenous people and recorded the details of their daily lives; Grobet focused on wrestling and the cultural concept of the mask; Ortiz Monasterio captured gritty, dystopian views of Mexico City. The exhibition draws extensively on gifts from Daniel Greenberg and Susan Steinhauser to represent directions in Mexican photography of the 1970s and 1980s.
Since the 1990s, the attention of many Mexican photographers has turned away from cultural traditions and rural landscapes and toward the cities and suburbs where many Mexicans now live. Works by Katya Brailovsky, Alejandro Cartagena, Pablo Lopez Luz, Daniela Rossell, and Yvonne Venegas reflect this interest in the changing social landscape, looking at issues of wealth and class, urbanization and land use, and the effects of the globalised economy. The exhibition closes with contemporary international photographers’ perspectives on U.S.-Mexico border issues. Images by Mark Klett, Victoria Sambunaris, and Alec Soth consider the border as landscape, while works by Elsa Medina, Susan Meiselas, and Paolo Pellegrin document the experiences of migrant workers and people trying, successfully or unsuccessfully, to cross into the United States.
About Daniel Greenberg and Susan Steinhauser
Based in Los Angeles, Daniel Greenberg and Susan Steinhauser have a deep and longstanding interest in Mexican photography, which they have been collecting since 1995. The photography department at SFMOMA has benefited greatly from their generosity: they have donated more than 175 works to the museum over the last six years. Their recent major gift of Mexican work, including over 50 photographs by Manuel Alvarez Bravo, Graciela Iturbide, and others, has created an ideal opportunity for SFMOMA to present this exhibition exploring photography in Mexico.
Press release from SFMOMA website
Edward Weston (American, 1886-1958)
Pirámide del Sol, Teotihuacán
1923
Gelatin silver print
7 9/16 x 9 1/2 in
San Francisco Museum of Modern art, gift of Brett Weston
© 1981 Center for Creative Photography, Arizona Board of Regents
Edward Weston (American, 1886-1958)
Tina Modotti, Half-Nude in Kimono
1924
Gelatin silver print
9 5/8 x 4 11/16 in
San Francisco Museum of Modern Art, Albert M. Bender Collection, Albert M. Bender Bequest Fund purchase
© 1981 Center for Creative Photography, Arizona Board of Regents
Manuel Alvarez Bravo (Mexican, 1902-2002)
Parabola optica (Optical Parable)
1931
Gelatin silver print
9 3/4 x 7 1/4 in. (24.77 x 18.42cm)
Collection of Daniel Greenberg and Susan Steinhauser
© Colette Urbajtel / Asociación Manuel Álvarez Bravo
Lola Álvarez Bravo (Mexican, 1907-1993)
Los gorrones
c. 1955, printed later
Gelatin silver print
9 5/8 x 11 3/4 in (24.45 cm x 29.85cm)
Collection of Daniel Greenberg and Susan Steinhauser
© 1995 Center for Creative Photography, The University of Arizona Foundation
Hector Garcia (Mexican, 1923-2012)
Aquelarre Cargadores con Diablos
1971
Gelatin silver print
Hector Garcia Cobo (August 23, 1923 – June 2, 2012) was a Mexican photographer and photojournalist who had a sixty-year career chronicling Mexico’s social classes, Mexico City and various events of the 20th century, such as the 1968 student uprising. He was born poor but discovered photography in his teens and early 20s, deciding to study it seriously after his attempt to photograph the death of a co-worker failed. He was sent to the Academia Mexicana de Artes y Ciencias Cinematográficas by magazine director Edmundo Valdés who recognised García’s talent. Most of García’s career was related to photojournalism, working with publications both inside and outside of Mexico. However, a substantial amount of his work had more artistic and critical qualities. Many of these were exhibited in galleries and museums, with sixty five individual exhibitions during his lifetime. This not only included portraits of artists and intellectuals (including a famous portrait of David Alfaro Siqueiros at Lecumberri Prison) but also portraits of common and poor people. He was also the first photojournalist to explicitly criticise Mexico’s elite, either making fun of them or contrasting them to the very poor.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Lourdes Grobet (Mexican, 1940-2022)
Ponzoña, Arena Coliseo
c. 1983
Gelatin silver print
14 x 11 in
San Francisco Museum of Modern Art, gift of Jane and Larry Reed
© Lourdes Grobet
Lourdes Grobet Argüelles (1940-2022)
Lourdes Grobet Argüelles (25 July 1940 – 15 July 2022) was a Mexican contemporary photographer, known for her photographs of Mexican lucha libre wrestlers.
Grobet spent some time as a painter before focussing on photography. Her photography led her to explore lucha libre, and she spent a lot of time getting to know the luchadores (wrestlers). Grobet did some theatre and video, and published several books. Grobet’s work has been the subject of numerous exhibitions, and she received many grants and awards for her work.
Career
Kati Horna introduced Grobet to the world of photography, though the main influences in her early career were Mathias Goeritz, Gilberto Aceves Navarro, El Santo and others. Grobet studied as a painter in Mexico for some time and then took a trip to Paris in 1968; it changed her life and the way that she viewed the art world.
While she was in Paris, Grobet visited many art galleries and discovered kinetic art; because of this, she liked working with multimedia. She spent some time working at a jazz concert, controlling lighting and kinetic projections. When Grobet returned to Mexico, she decided that she wanted to focus on photography; after she got back home, she decided to burn all of her old work and start over.
In 1981 Grobet released her first set of photographs. At the beginning of her career in photography, she was part of a group called Consejo Mexicano de Fotografía (Mexican Council of Photography), formed by Pedro Meyer in 1977. With her participation in this group, she was able to revitalise photography in Mexico,[citation needed] which led to a movement called the Grupos. Grobet was focused on establishing a community-based perspective.
Grobet spent some time with indigenous people during a time of great struggle for them. She took the time to learn more about them and photograph them in a theatrical way. She wanted to relate to indigenous people using her artistic initiative, so they made costumes and scenery of their own and she then took their photos. Later on, Grobet took interest in the Mayan culture. Wanting to learn more about the Mayans she went to the suburbs; while this was not a common thing to do, she wanted to steer clear of any tourists. She wanted to get accurate information about the people she documented and explore an area less traveled. She discovered temples that were made by an unknown civilisation and she decided they were to be called the Olmayazetec.
After her education and her travels, Grobet came back to México City. She once again started to explore her childhood interest of luchadores. She found that there was very little information pertaining to the luchadores, and so she decided that she wanted to make them more known to the world.
Grobet spent thirty years devoted to taking pictures of the luchadores and studying their way of life. She spent time photographing lucha libre wrestlers inside and outside of the ring, both in their masks, but also in their own homes. Grobet wanted to show that they lived normal lives, just like everyone else. She got very close with well known Lucha Libre wrestlers such as: El Santo, Blue Demon, Mil Mascaras, Sagrada, Octagon, Misioneros de la Muerte, Los Perros del Mal, and Los Brazos. Influenced greatly by Mathias Goeritz, the Polish sculptor from Gdańsk, and by Gilberto Aceves Navarro, a Mexican master of art murals, who were her teachers, Grobet worked on pictures of El Santo, one of the most important Mexican wrestlers, and a hero of lucha libre who starred in more than 50 films. Since 1975, she has published more than 11,000 photographs of the sport, including those on the sport in the United States since the 1930s, and as an important part of Mexican popular culture, adopting a sociological attitude. The sport involves many costumes and masks, leading it to a sport-carnival air which is much appreciated by Mexicans.
She also ventured into cinema. In her 2013 movie Bering. Balance and Resistance, Grobet questions the political separation between the Big Diomede Island (Russia) and the Little Diomede Island (USA) in the Bering Strait, a border between the United States and Russia. Showing the consequences of the separation between both Islands. After the American-Soviet conflict of the 21st century, the Beringia region was divided in two, which caused the separation of complete Nanook families and also, paradoxically, separated the place where the first human beings that populated the American continent crossed.
Grobet has had over one hundred exhibitions of her photographs, both group and solo exhibitions. She had her work exhibited at the London Mexfest festival in 2012. She won an award at the Second Biennal in Fine Art Photography. In 1975, for the exhibition Hora y media, she transformed a gallery into a photographic laboratory. She developed the photographs, but without fixing them, and displayed them on three walls. While the public looked at the photographs, the lights from the gallery made it look like they disappeared.
In 1977, Grobet presented Travelling, an exhibition of photography on an escalator. Among her other works were Paisajes pintados, Teatro campesino, Strip Tease.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Graciela Iturbide (Mexican, b. 1942)
La Nuestra Senora de las Iguanas, Juchitan, Oaxaca, Mexico (Our Lady of the Iguanas, Juchitan, Oxaca, Mexico)
1979
Gelatin silver print
17 5/16 x 14 7/16 in
San Francisco Museum of Modern Art, gift of the artist
© Graciela Iturbide
Graciela Iturbide (Mexican, b. 1942)
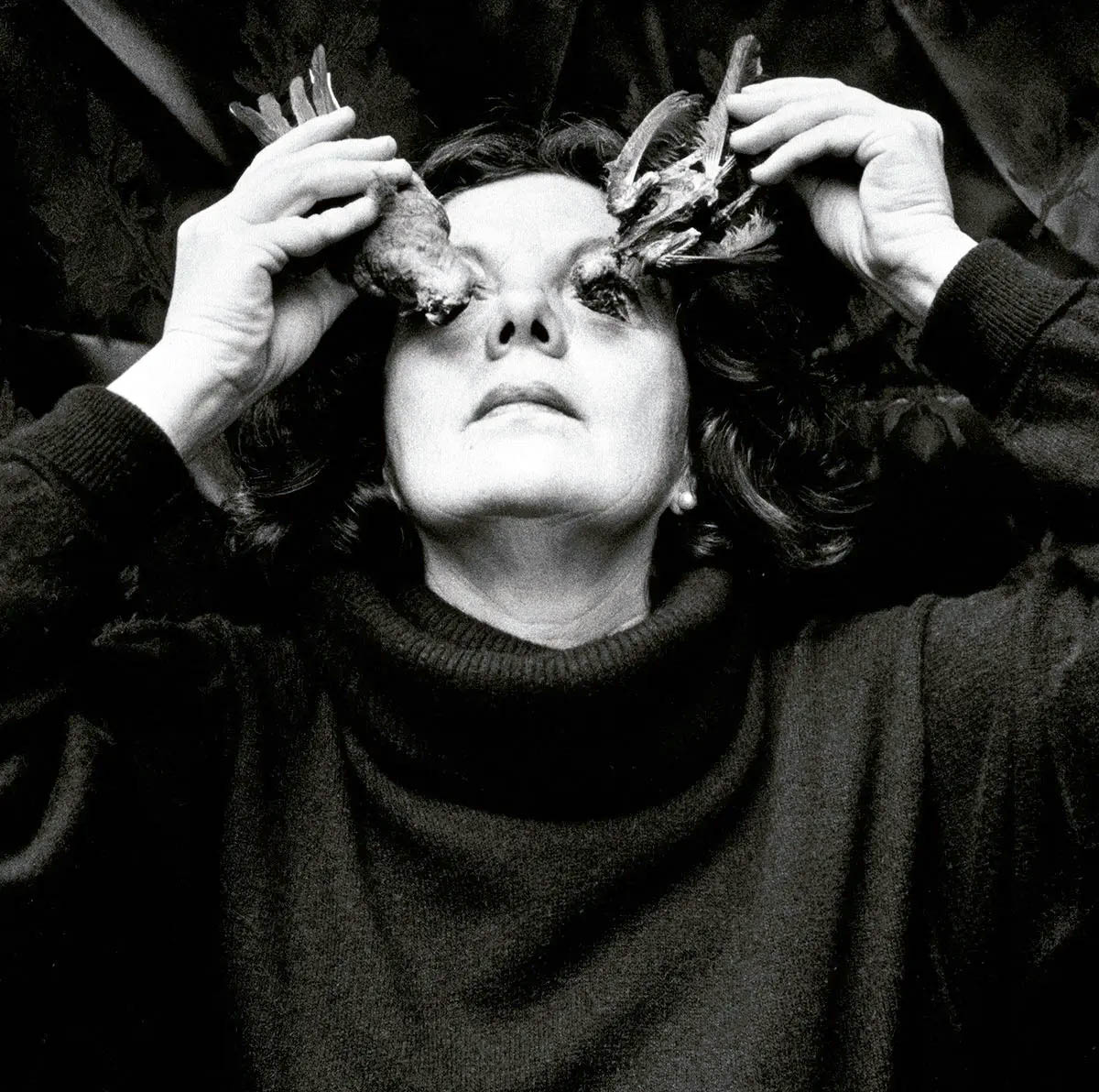
¿Ojos para volar?, Coyoacán, Ciudad de México (Eyes to Fly With?, Coyoacan, Mexico City)
1991
Platinum print
19.5 × 19.5cm
© Graciela Iturbide
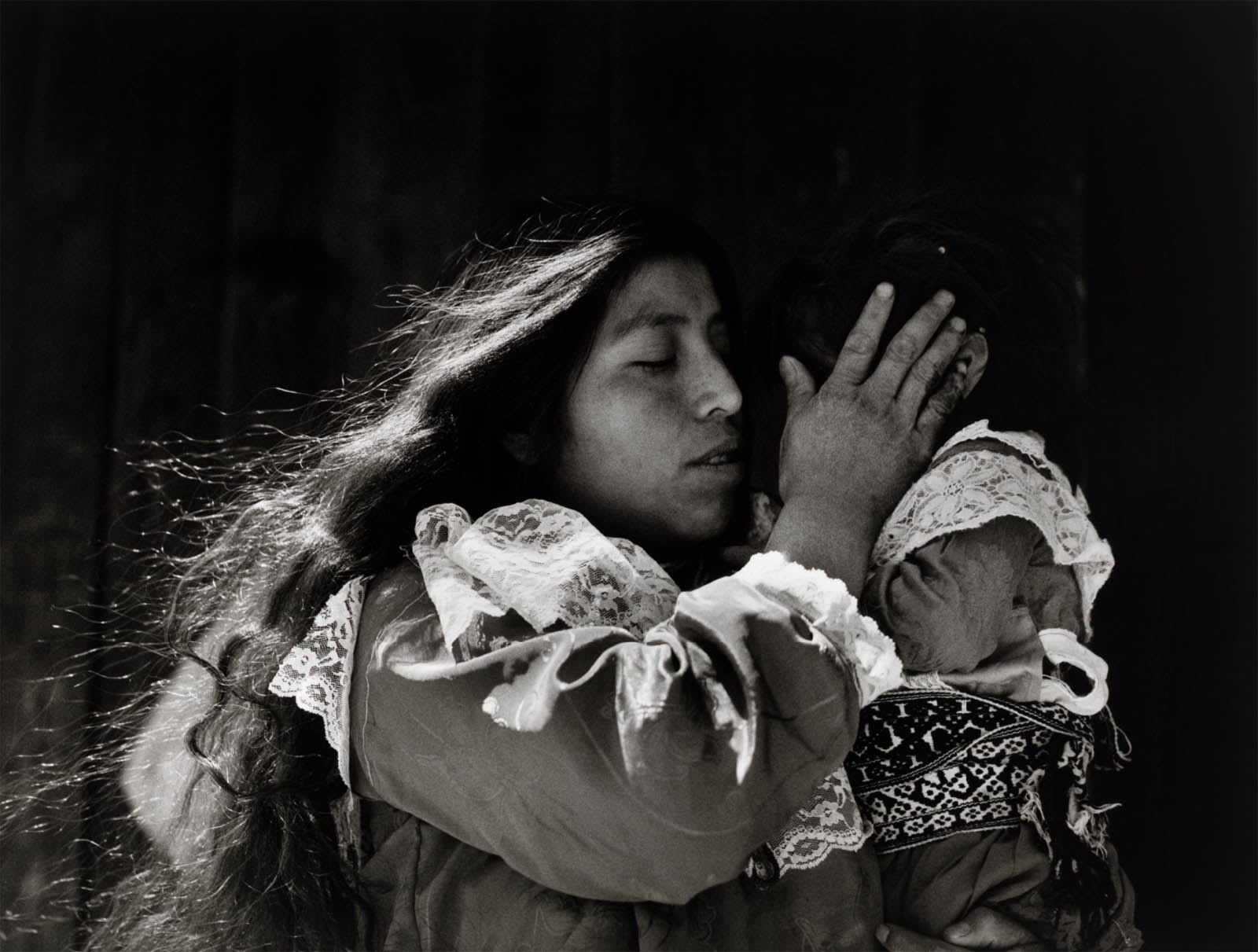
Mariana Yampolsky (Mexican, 1925–2002)
Caricia (Caress)
1989
Gelatin silver print
13 3/8 × 17 1/2 in (34 × 44.5cm)
San Francisco Museum of Modern Art
Susan Meiselas (American, b. 1948)
Shortie on the Bally, Barton, VT
1974
Gelatin silver print
The exhibition closes with contemporary international photographers’ perspectives on U.S.-Mexico border issues. Images by Mark Klett, Victoria Sambunaris, and Alec Soth consider the border as landscape, while works by Elsa Medina, Susan Meiselas, and Paolo Pellegrin document the experiences of migrant workers and people trying, successfully or unsuccessfully, to cross into the United States.
Anonymous. “Major Mexican Photographers at the SFMOMA,” on the Literal, Latin American Voices magazine website 15th November 2011 [Online] Cited 18/09/2024
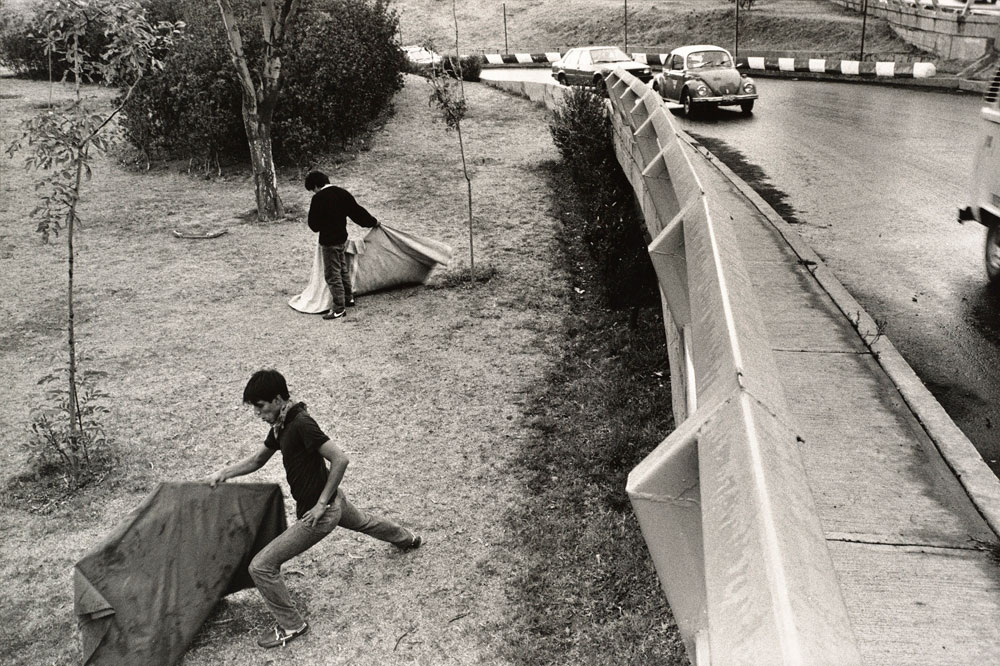
Alejandro Cartagena (Mexican, b. 1977)
Fragmented Cities, Juarez #2
2007
From the series Suburbia Mexicana
Inkjet print
20 x 24 in
San Francisco Museum of Modern Art, Accessions Committee Fund purchase
© Alejandro Cartagena
San Francisco Museum of Modern Art (SFMOMA)
151 Third Street (between Mission + Howard)
San Francisco CA 94103
Opening hours:
Monday – Tuesday: 10am – 5pm
Wednesday: Closed
Thursday: 1 – 8pm
Fri – Sun: 10am – 5pm










































































You must be logged in to post a comment.