Exhibition dates: 5th September, 2025 – 1st February, 2026
An exhibition by Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur in cooperation with the Bernd & Hilla Becher Studio, Düsseldorf

Anonyme Skulpturen. Eine Typologie technischer Bauten, Düsseldorf: Art-Press
Anonymous Sculptures: A Typology of Technical Buildings, Düsseldorf: Art-Press
1970 (Buchcover)
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Köln
When we think about the most influential photographers of the first five decades of the 20th century we conjure up names such as Eugène Atget, Alfred Stieglitz, Paul Strand, Walker Evans, László Moholy-Nagy, Dorothea Lange, and Berenice Abbott, to name just a few – and by influential, I mean those photographers that altered the intensification of the medium – the conceptualisation, creation, veracity, meaning and reception of the image.
In the last 50 years of the 20th century there are less of these medium-shifting artists that have really made a difference. Diane Arbus and Lee Friedlander are the two that readily spring to mind. And then there are the Bechers, Bernd & Hilla Becher. These German photographers changed the course of contemporary photographic practice, their conceptual art / objective photographic raison d’être still embedded at the heart of fine art photography today.
But, as I have argued elsewhere, their typologies and grids, their topographic state, their same same photographs and perspectives of industrial sculptures and landscapes are anything but objective. Their pictorial grammar, underlaid by a conceptual approach to subject matter, continuously reflected in the systematics of capture and display (the juxtaposition of works together), is constantly undermined by the ghost in the machine – those viral codes of mutation and difference which cannot be controlled.
While they professed to “eschew entirely entirely the aspects of beauty, emotion and opinion,” every photograph they took involves a subjective point of view, an element of uniqueness and beauty that can never be repeated.
“Despite protestations to the contrary (appeals to the objectivity of the image, eschewing entirely the aspects of beauty, emotion and opinion; the rigorous frontality of the individual images giving them the simplicity of diagrams, while their density of detail offers encyclopaedic richness) these are subjective images for all their objective desire. The paradox is the more a photographer strives for objectivity, the more ego drops away, the more the work becomes their own: subjective, beautiful, emotive.
Even though the Bechers’ demonstrate great photographic restraint with regard to documenting the object, the documentary gaze is always corrupted / mutated / distorted by personal interpretation: where to position the camera, what to include or exclude, how to interpret the context of place, how to crop or print the image, and how to display the image, in grids, sequences or singularly. In other words there are always multiple (con)texts to which artists conform or transgress. What makes great photographers, such as Eugène Atget, Walker Evans, August Sander and the Bechers, is the idiosyncratic “nature” of their vision: how Atget places his large view camera – at that particular height and angle to the subject – leaves an indelible feeling that only he could have made that image, to reveal the magic of that space in a photograph. It is their personal, unique thumbprint, recognisable in an instant. So it is with the Bechers.”1
For a deeper dive into the work of the Bechers, please see my text “Ghosts in the machine,” on the exhibition Bernd and Hilla Becher at the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, July – November, 2022.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
1/ Marcus Bunyan text on the exhibition Bernd and Hilla Becher: Mines and Mills – Industrial Landscapes at Fotomuseum Winterthur, Zurich, November 2011 – February 2012 [Online] Cited 05/12/2025
Many thankx to Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Cologne for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Installation view of the exhibition Bernd & Hilla Becher – History of a Method at Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Cologne
Installation view of the exhibition Bernd & Hilla Becher – History of a Method at Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Cologne
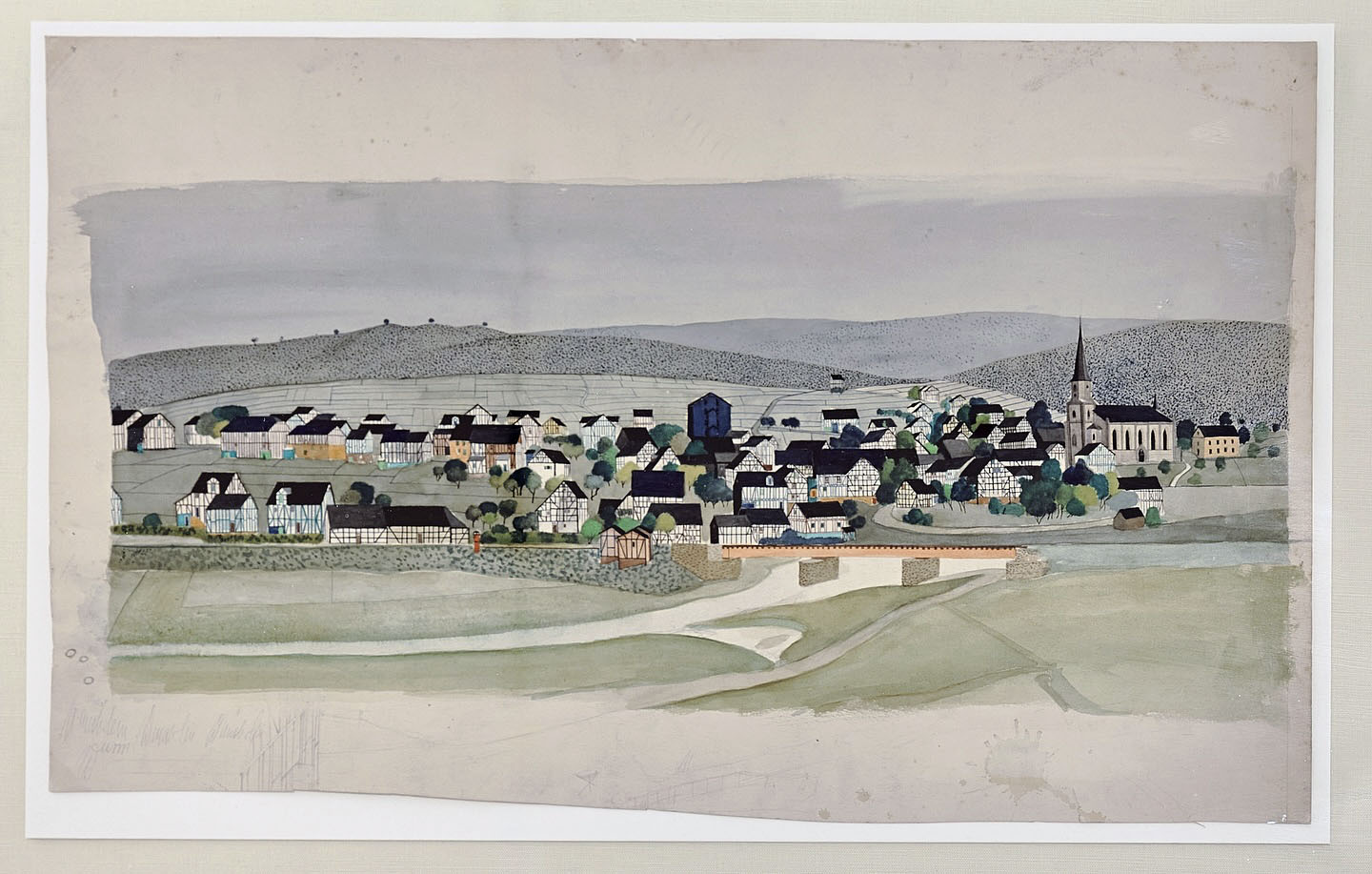
Bernd Becher (German, 1931-2007)
Mudersbach
1950s
Watercolour
35.5 x 59.9cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
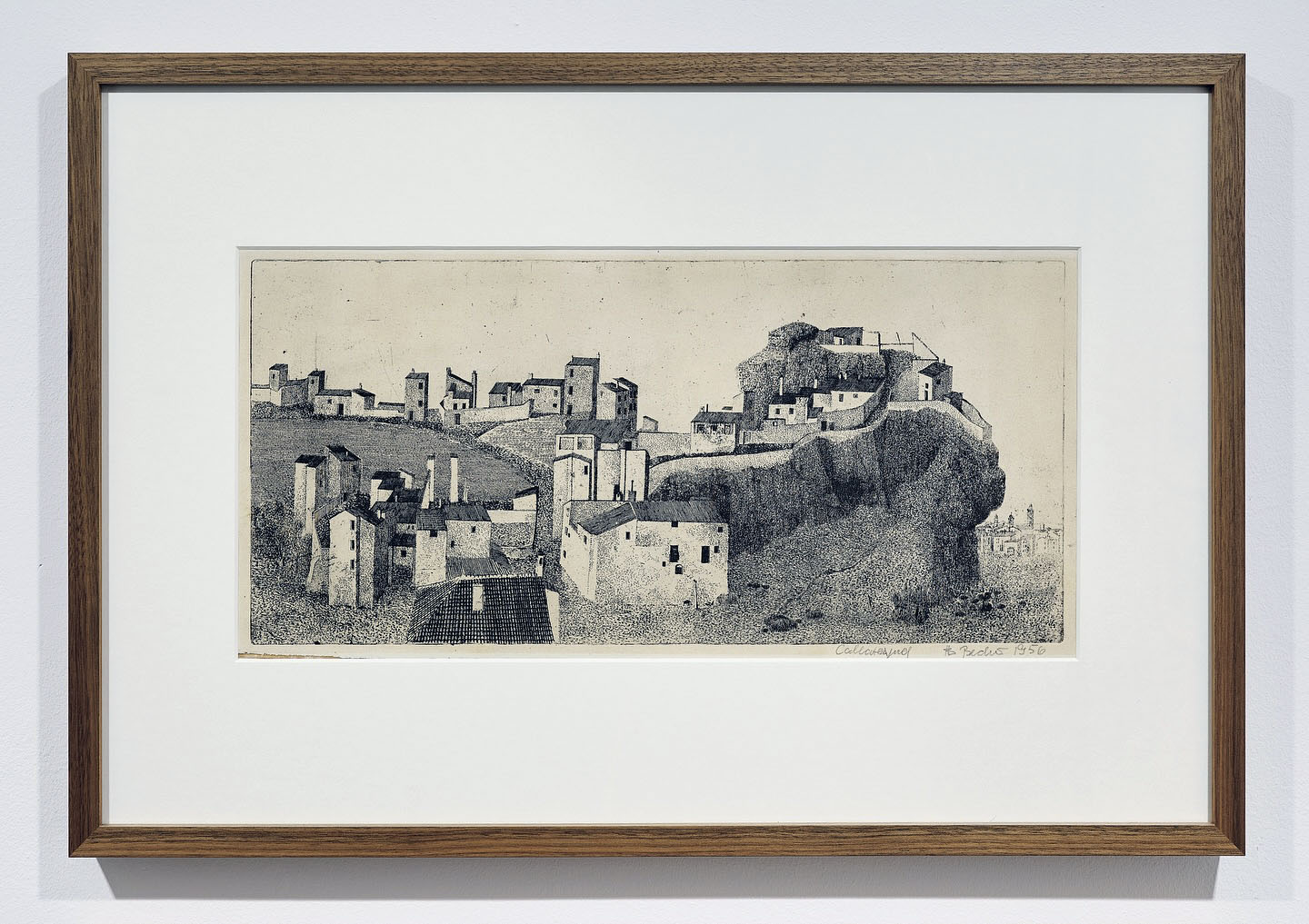
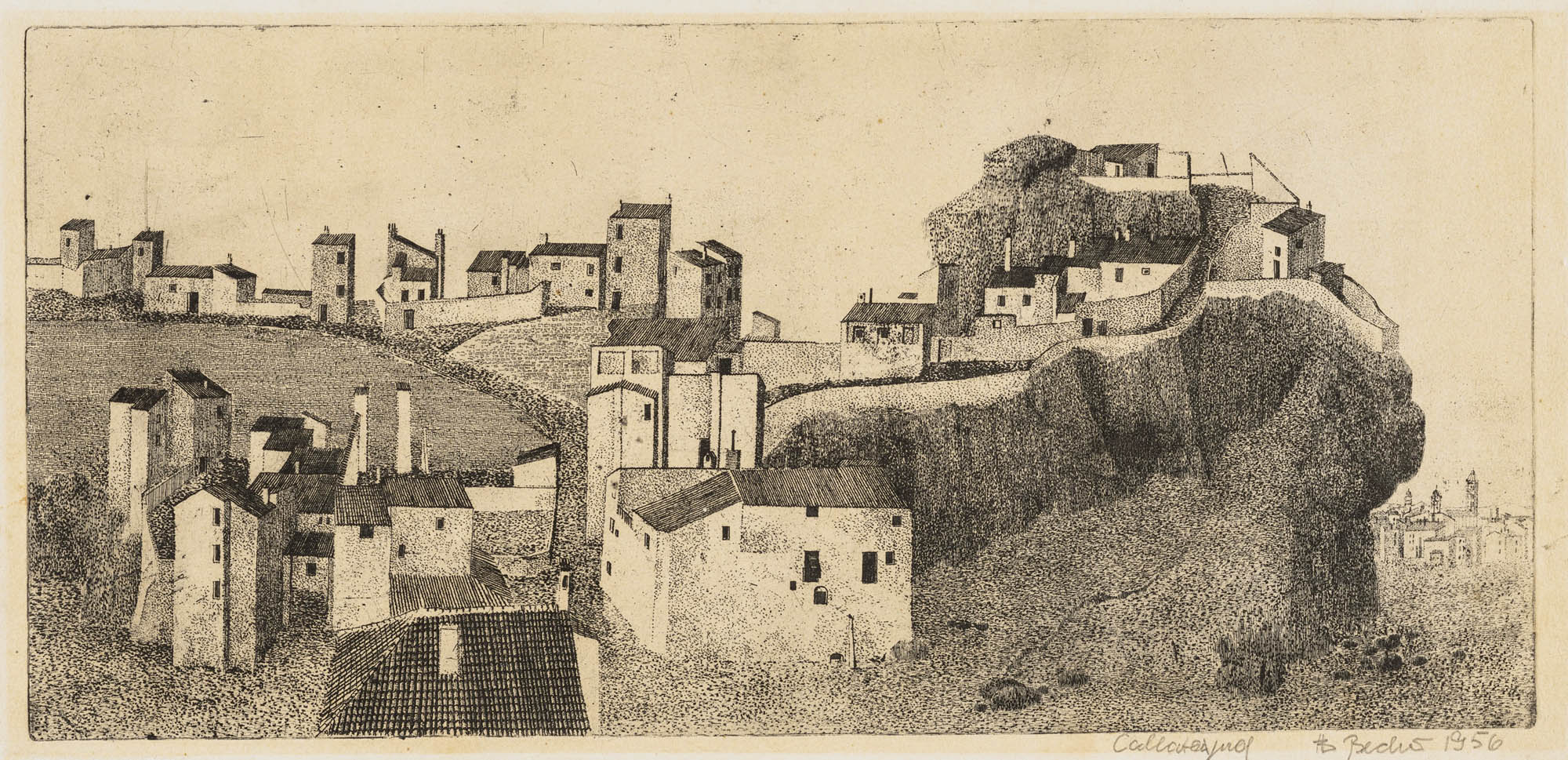
Installation view of the exhibition Bernd & Hilla Becher – History of a Method at Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Cologne showing Bernd Becher’s Calatayud 1956 (below)
Bernd Becher (German, 1931-2007)
Calatayud
1956
Aquatint on laid paper
20.8 x 44.0cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
Bernd Becher (German, 1931-2007)
Grube Eisernhardter Tiefbau, Eisern, D (Eisernhardter Tiefbau mine, Eisern, Germany)
1955/56
Pencil on paper
42.0 x 56.5cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
Installation view of the exhibition Bernd & Hilla Becher – History of a Method at Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Cologne

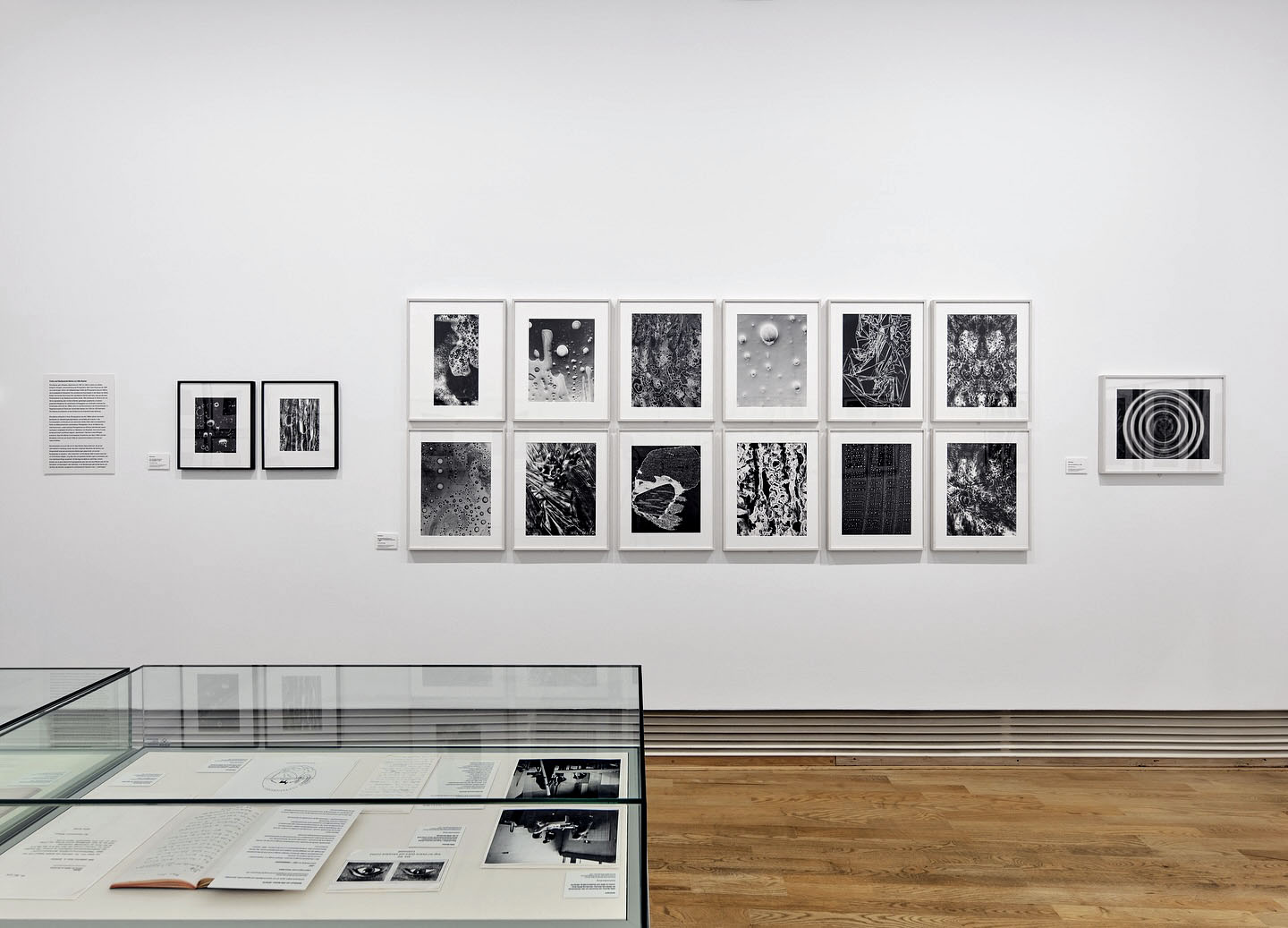
Installation view of the exhibition Bernd & Hilla Becher – History of a Method at Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Cologne showing Hilla Becher’s Untitled (Makroaufnahme von Schaum) (Macro shot of foam) c. 1960
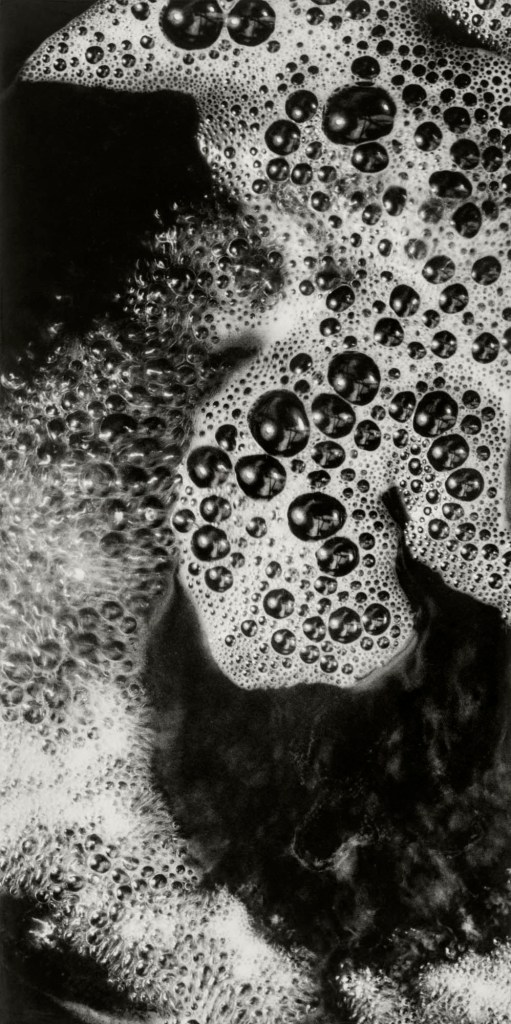
Hilla Becher (German, 1934-2015)
Untitled (Makroaufnahme von Schaum) (Macro shot of foam)
c. 1960
Gelatin silver print
38.9 x 19.4cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
Hilla Becher (née Wobeser) discovered photography as a teenager. Her mother had trained as a photographer at the Lette Verein in Berlin and supported her daughter’s interest. Accordingly, from 1951 to 1953, Hilla completed an apprenticeship as a photographer at the Walter Eichgrün studio in her hometown of Potsdam. In 1953, the family fled East Germany, and Hilla continued her career in West Germany. For example, in 1957 she worked at the Troost advertising agency in Düsseldorf, where she also met Bernd Becher.
The photograph shown above belongs to a series of surface and structural studies from around 1960. Nothing is known about the exact context of the photographs; however, their stylistic affinity to the “Subjective Photography” movement, which gained influence from the early 1950s onward, is interesting. Distortion techniques were an important tool in “Subjective Photography,” and Hilla Becher’s macro photographs utilise extreme proximity to the subject as a means of creating a sense of alienation.
Text from the SK Stiftung Kultur Die Photographische Sammlung Instagram page
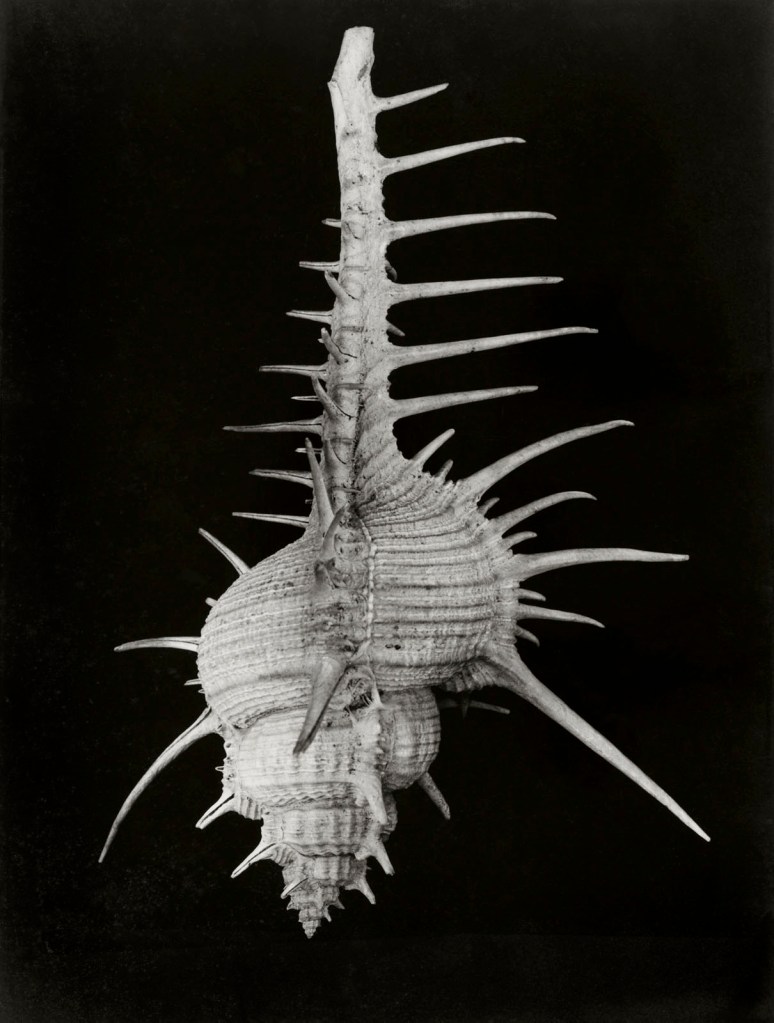
Hilla Becher (German, 1934-2015)
Meeresschnecke (Venuskamm) (Sea snail (Venus comb))
1960s
Gelatin silver print
39.6 x 30cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln

Hilla Becher (German, 1934-2015)
Pflanzenstudie, Photogramme (Plant study, photograms)
1960s
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
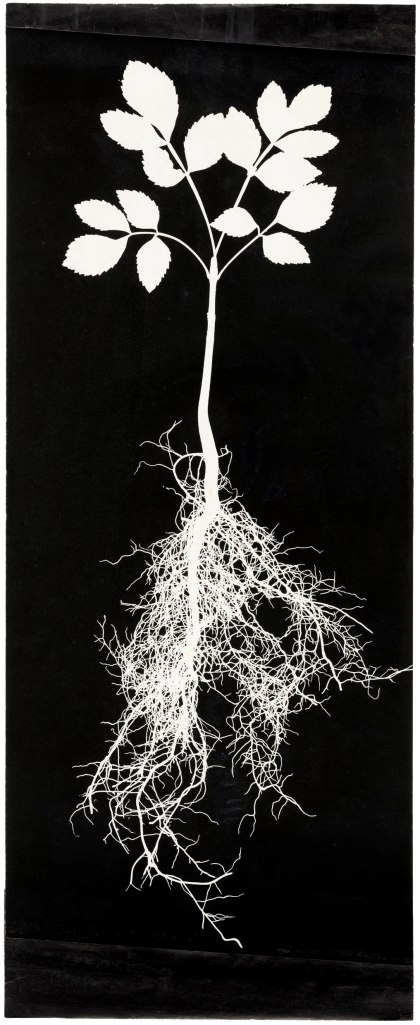
Hilla Becher (German, 1934-2015)
Pflanzenstudie, Photogramme (Plant study, photograms)
1960s
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
An exhibition of Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur in cooperation with the Bernd & Hilla Becher Studio, Düsseldorf
The artist couple Bernd and Hilla Becher (1931-2007/1934-2015) has written photographic history. With their joint work, which they developed from 1959 until the 2000s on the basis of an almost uninterrupted photographic activity in the industrial regions of Germany, the Benelux countries, Great Britain, France, Italy, the USA and Canada, they created a new artistically motivated documentary style.
For the first time in Europe, this exhibition will present the methodological and thematic range of their oeuvre in great detail with over 300 original black and white photographs and other exhibits by the artist couple. In the individual sections, almost all of Becher’s found subjects can be located in a compilation and sequencing largely determined by themselves. Photographs of landscapes, winding towers, blast furnaces, cooling towers, gas tanks or even views of entire collieries etc. are considered her trademark. The juxtaposition of the groups of works authentically conveys the pictorial grammar developed by Bernd and Hilla Becher and their continuously reflected systematics and conceptual approach.
The exhibits come from the Bernd and Hilla Becher Archive in Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur and the Bernd & Hilla Becher Studio, Düsseldorf, in collaboration with Max Becher under the supervision of the Bernd & Hilla Becher Estate. There are also loans from Sprüth Magers and the LVR-Landesmuseum Bonn.
The publication accompanying the exhibition will be published by Schirmer / Mosel Verlag, with texts by Max Becher, Gabriele Conrath-Scholl, Marianne Kapfer and Urs Stahel.
Text from the Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Cologne website

Installation view of the exhibition Bernd & Hilla Becher – History of a Method at Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Cologne showing Bernd and Hilla Becher’s photograph Kühlturm (Cooling tower) 1962, “Mont-Cenis” mine, Herne, Ruhr area 1965 (below)

Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Kühlturm (Cooling tower) 1962, “Mont-Cenis” mine, Herne, Ruhr area
1965
Gelatin silver print
40.3 x 31.5cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
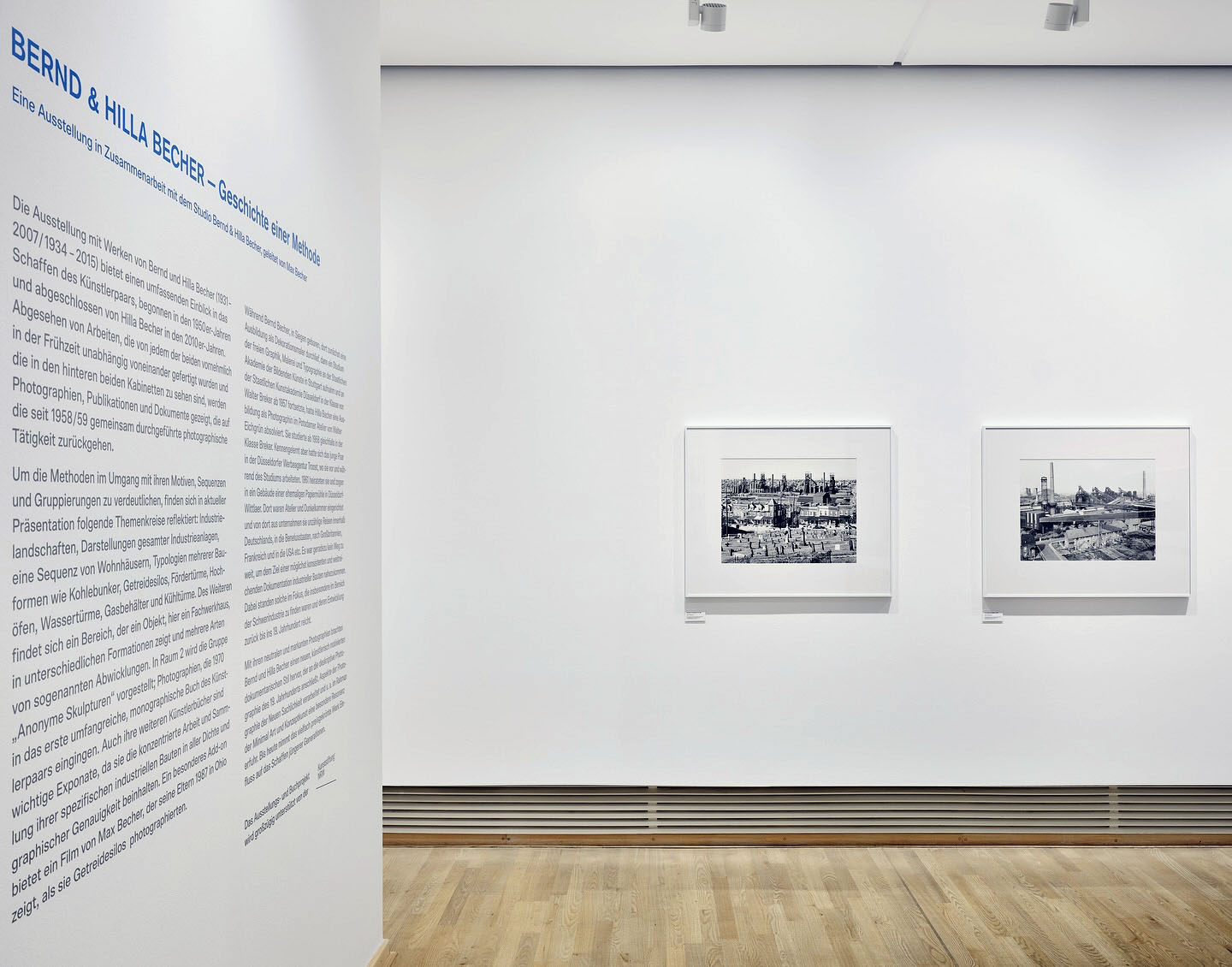
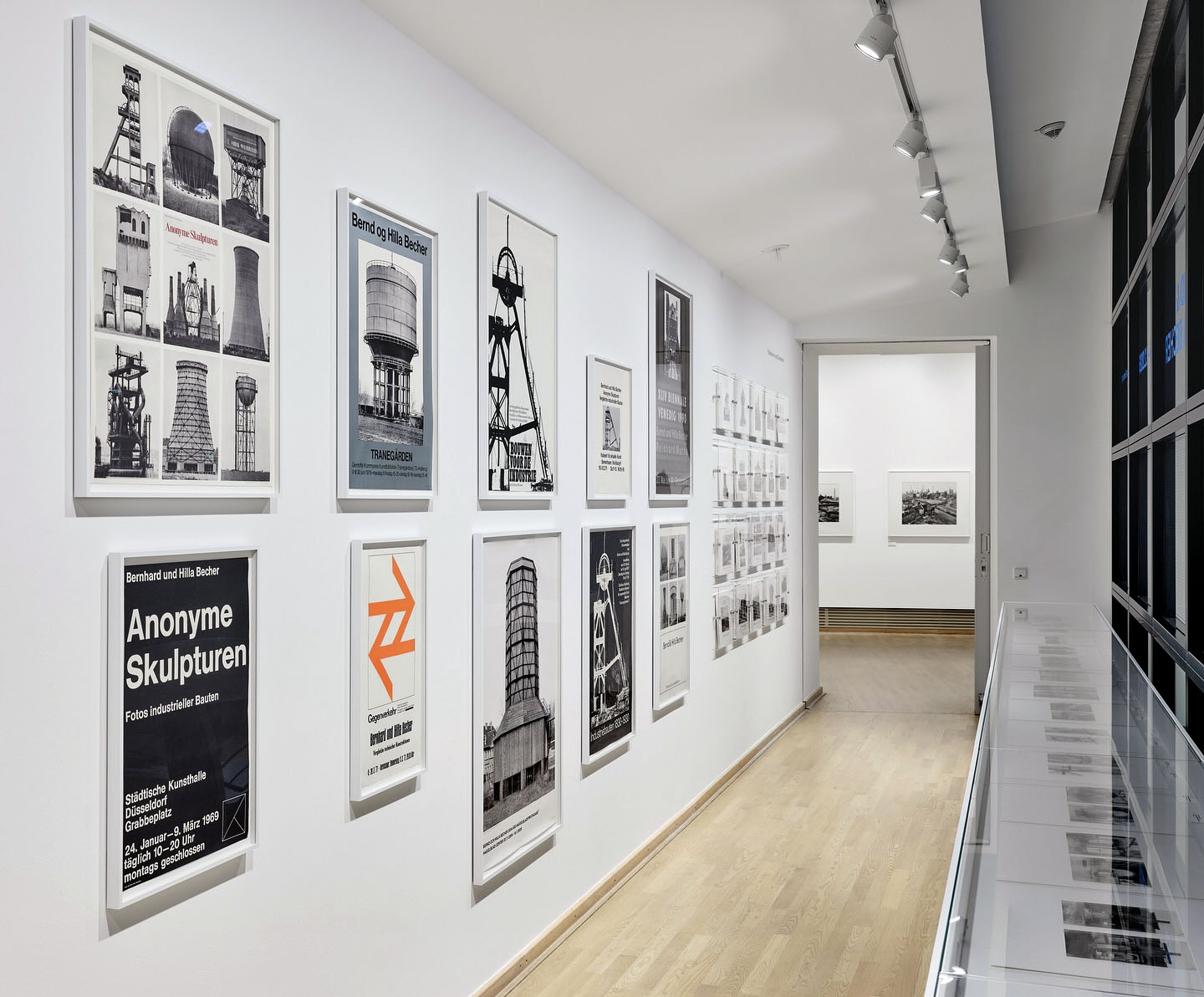
We have dedicated an entire room of our current exhibition to the group of “Anonymous Sculptures.” With this series of images, Bernd and Hilla Becher defined the building types that were important to them, such as cooling towers. The fundamental principle of the comparability of the motifs was introduced, and the work on publications, so crucial to Bernd and Hilla Becher’s artistic output, was also initiated.
You can trace the artists’ approach using 41 photographs that exemplify the building types presented in seven chapters of the 1970 publication “Anonymous Sculptures: A Typology of Technical Structures.” An exhibition at the Düsseldorf Municipal Art Gallery preceded the book in 1969 [see the book cover at the top of the posting].
The term “Anonymous Sculptures” establishes a link to conceptual art. This connection between Bernd and Hilla Becher’s work and the visual arts was important for their subsequent work and its presentation in museums and galleries.
Text from the SK Stiftung Kultur Die Photographische Sammlung Instagram page
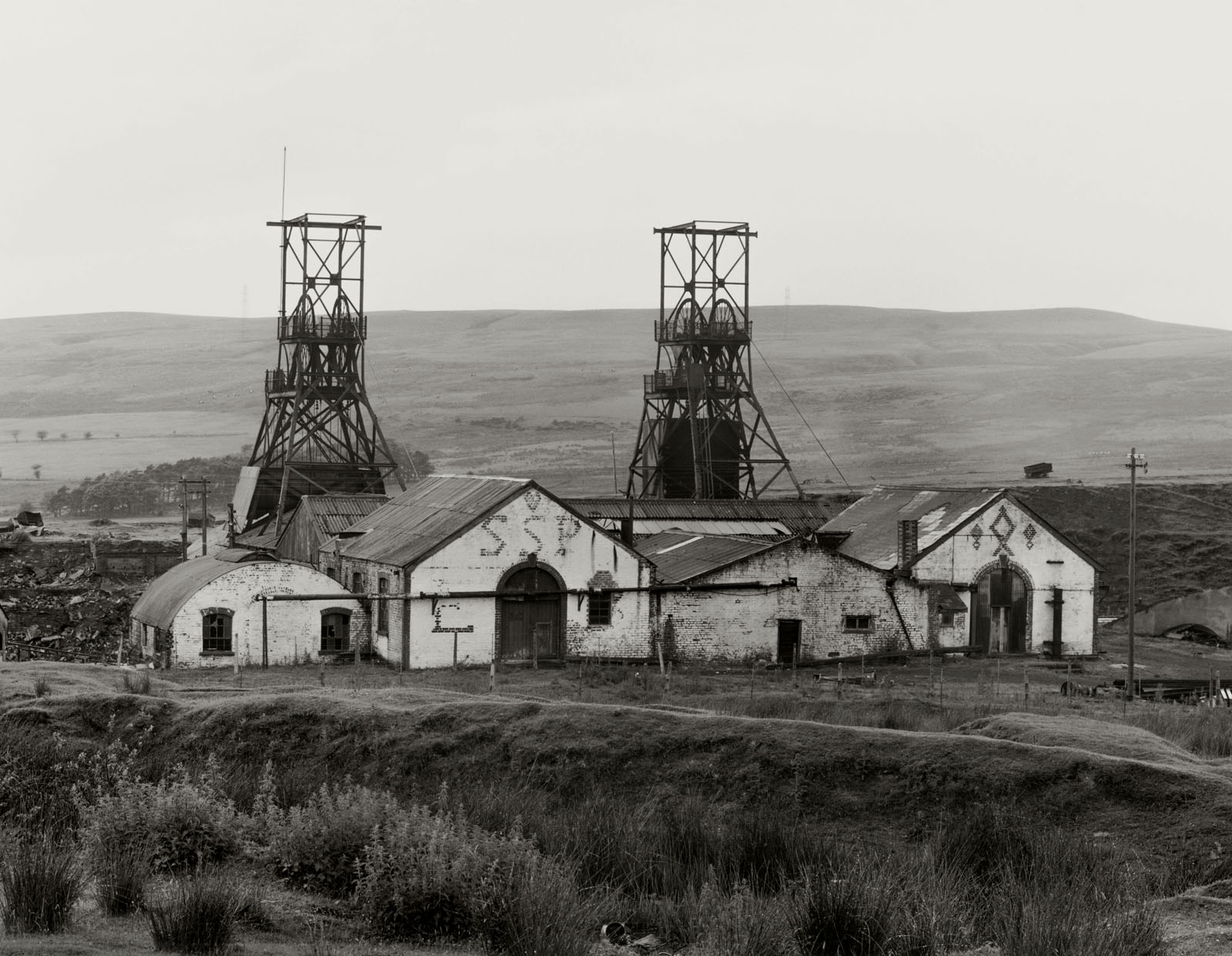
Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Seven Sisters Pit, South Wales, GB
1966
Gelatin silver print
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln, 2025
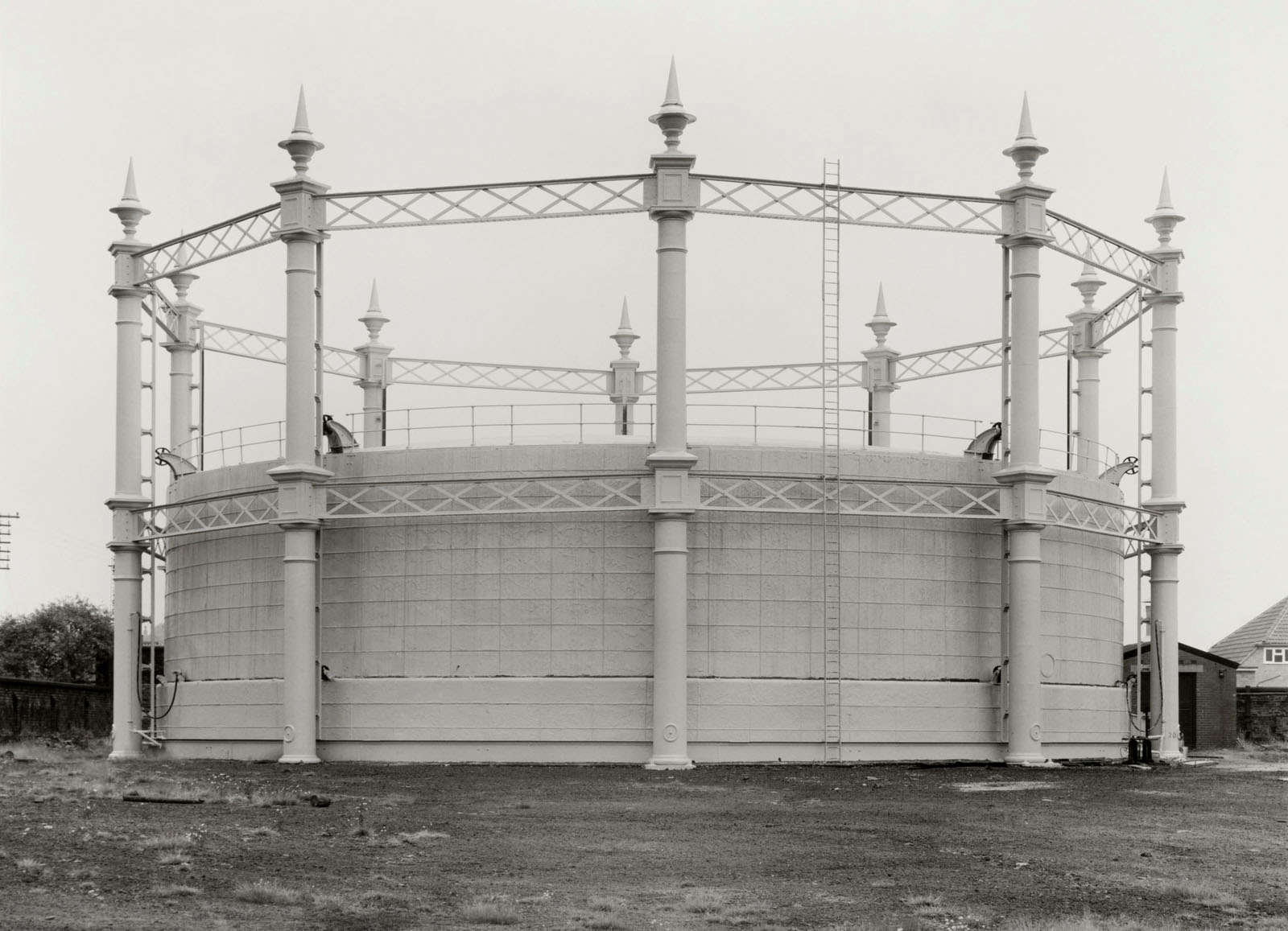
Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Gasbehälter (Gas container) 1886 Tyldesley near Manchester, UK
1966
Gelatin silver print
30.4 x 41.5cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
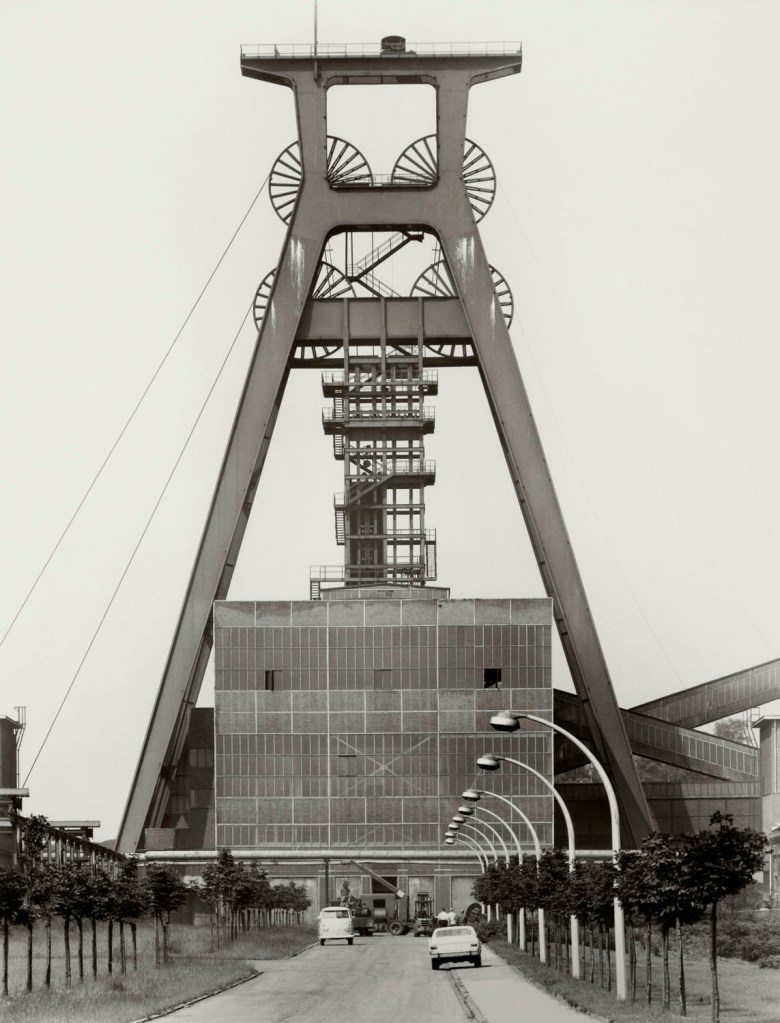

Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Förderturm (Conveyor tower) 1958 “Graf Bismarck” mine, Gelsenkirchen, Ruhr area
1967
Gelatin silver print
40.3 x 31.1cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
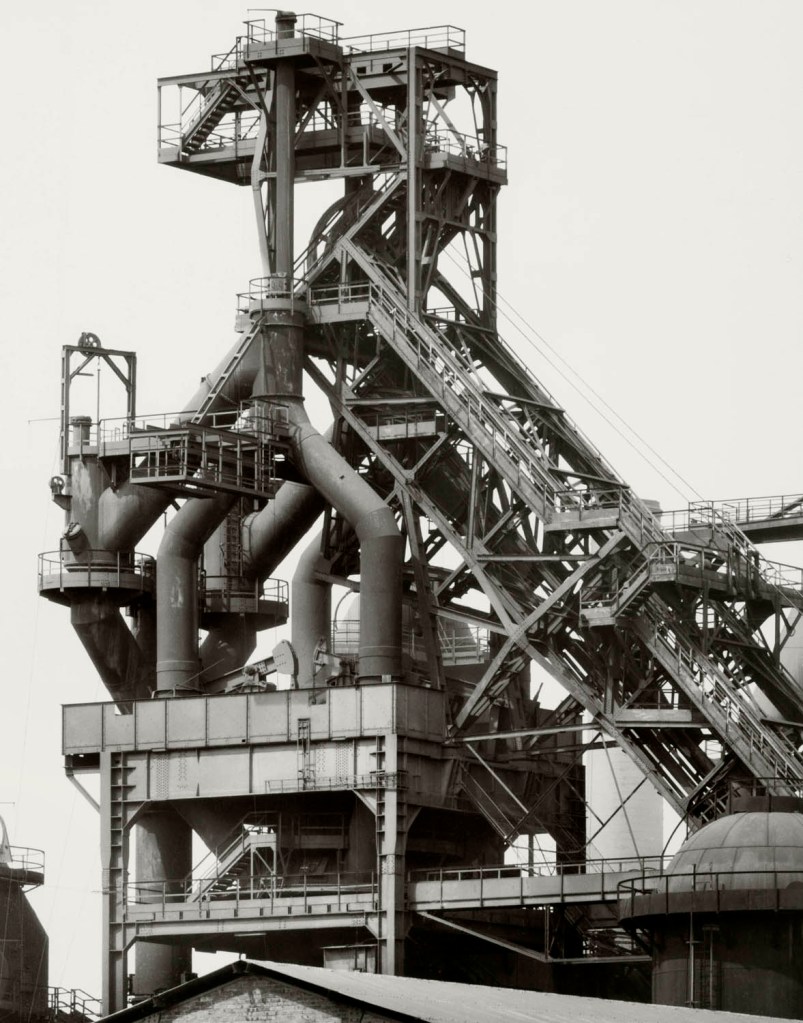

Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Hochofen (Blast furnace) c. 1930, Blast furnace plant, Esch, Luxembourg
1969
Gelatin silver print
40.4 x 31.5 cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Hochspannungsmast, Düsseldorf, D (High-voltage pylon, Düsseldorf, Germany)
1969
4 gelatin silver prints
Each approx. 41.3 x 30.4cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
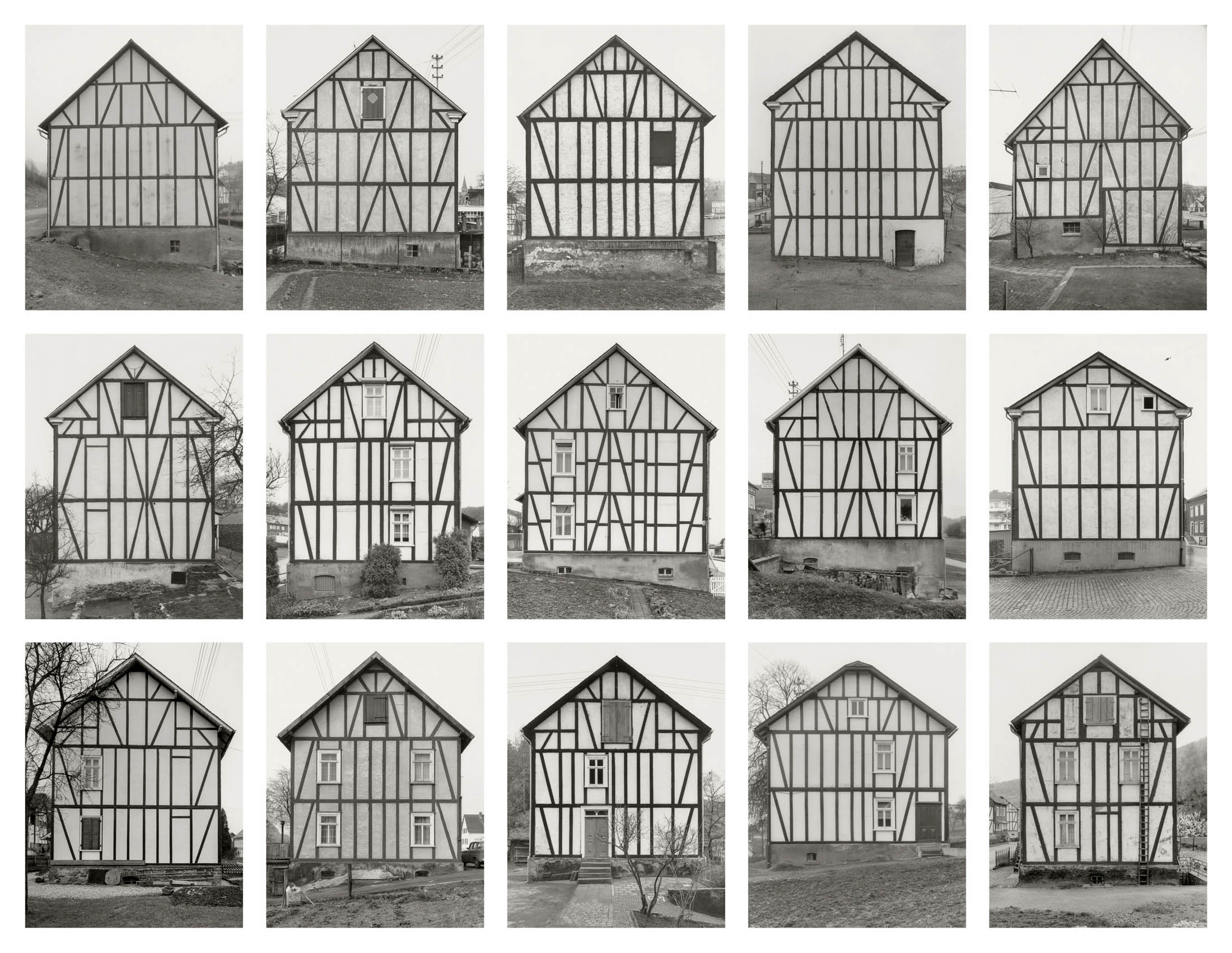
Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Giebelseiten Fachwerk, Siegerland D (Gable sides half-timbered, Siegerland D)
1959-1973
15 gelatin silver prints
Each approx. 40 x 31cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Museum für Gegenwartskunst Siegen und Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Köln
The first subjects Bernd and Hilla Becher photographed on their nearly fifty-year journey to documenting industrial buildings were half-timbered houses in the Siegerland region. For Bernd Becher, it was natural to photograph these “poor people’s houses,” as Hilla called them, from his childhood and youth. For the film “The Photographers Bernd and Hilla Becher,” we attempted to identify the Bechers’ subjects using the book “Siegerland Half-Timbered Houses” by Schirmer/Mosel. We asked locals and showed them the book. Although the Bechers provided the exact address of each house, they were often unrecognisable. Many, being drafty and cold, had been clad with asbestos cement, thus obscuring their exposed timber framing. Their original appearance is preserved only in the Bechers’ photographs.
Text from the Text from the SK Stiftung Kultur Facebook page

Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Bottrop, D
1976
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln, 2025
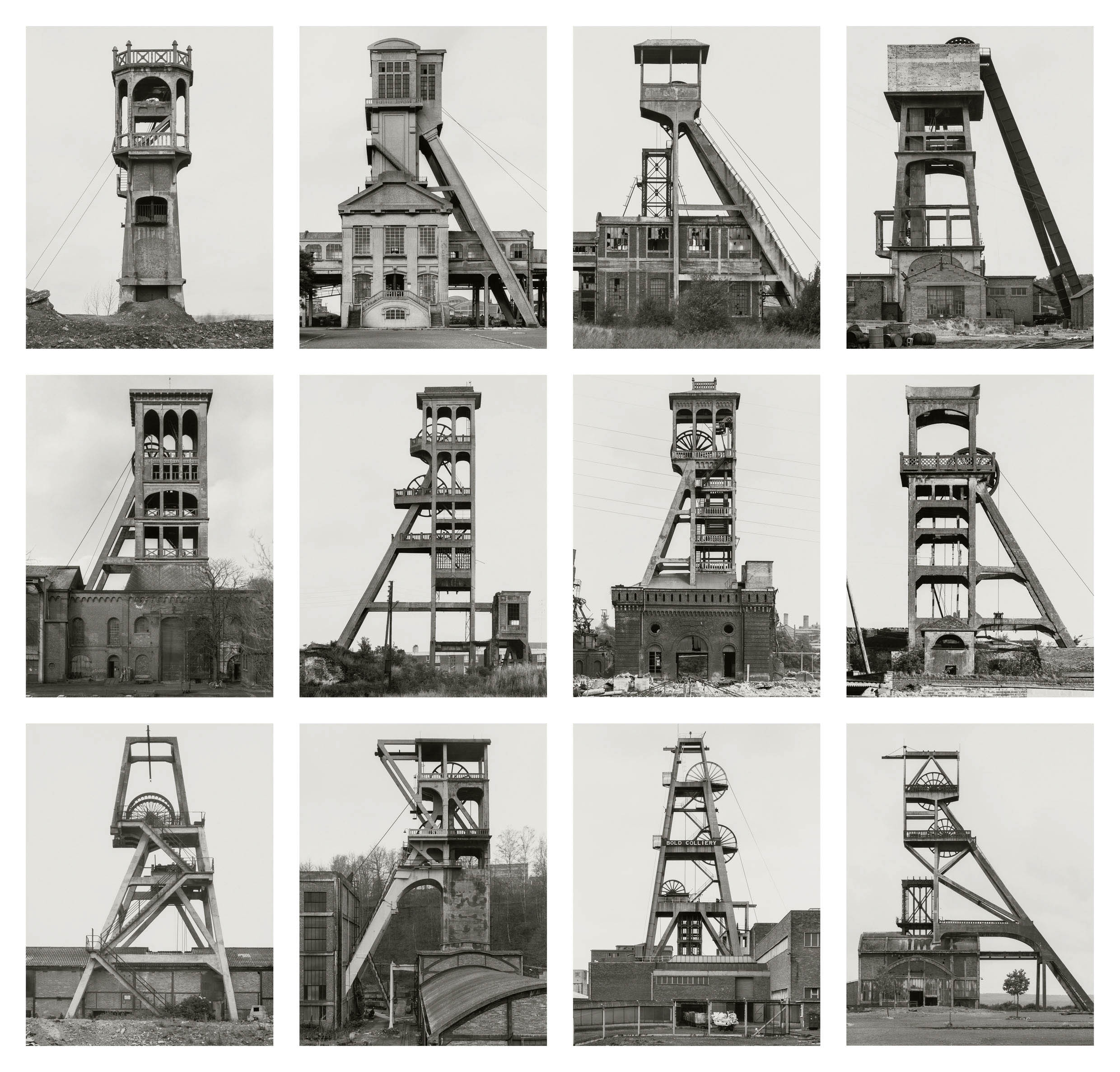

Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Fördertürme (Winding towers)
1966-1979
12 gelatin silver print
Each approx. 41 x 31cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
auf der Grube Ensdorf, Saarland (at the Ensdorf mine, Saarland)
1979
Gelatin silver print
12 x 14.1cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
The artist couple Bernd and Hilla Becher (1931-2007/1934-2015) set a benchmark in the history of photography with their work. Beginning in 1959, they collaborated almost continuously for decades on a joint oeuvre, developed across Germany, the Benelux countries, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, the United States, and Canada. Their artistic style, characterised by a precise, documentary visual language and methodical systematisation, resonated significantly with movements such as Minimal Art and Conceptual Art. Against the backdrop of New Objectivity and inspired by 19th-century documentary photography, they created a visual grammar whose influence remains palpable in contemporary photography.
For the first time in Europe, Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur presents an extensive retrospective featuring over 300 original black-and-white photographs and complementary exhibits, showcasing the formal and thematic breadth and depth of Bernd and Hilla Becher’s work. The exhibition centers on the themes and methods developed by the Bechers: consistent methodical approaches to the photographic motif that evolved and were variably applied over decades. The exhibition explores how these methods emerged, how they developed, and how they reflected the Bechers’ perspective on the different shapes, functions, and integration of industrial buildings into the landscape.
Rare early works from both artists – created between the 1950s and 1970s – are on view, many for the first time. These pieces provide insight into the evolution of their shared aesthetic.
Room 2 is dedicated to the book Anonyme Skulpturen. Eine Typologie technischer Bauten (Anonymous Sculptures. A Typology of Technical Constructions), 1970, considered the foundation of their work. This publication systematically catalogued industrial structures and remains a key reference point. Quoted texts on the function of the objects and original prints illuminate its significance within their oeuvre.
Industrial Landscapes and photographs of entire sites form another focus and demonstrate that the Bechers did not merely document isolated buildings, but also functional and spatial relationships. Featured works include views of the Zollern 2 coal mine in Dortmund (published 1977) and the Ewald Fortsetzung mine in Recklinghausen (1982-1985).
The exhibition also includes “portraits” of residential and settlement houses from the Ruhr region – especially from the post-war era – reflecting the everyday life and environment of industrial workers. A framework house from the Siegerland region is used to show how a single subject can take on different meanings depending on presentation and context.
“Sequences” or “unfoldings” are illustrated using various building groups, presenting structures from multiple perspectives, so that a sculptural image of the motifs is created.
Lastly, the exhibition presents typologies – photographic series of coal bunkers, grain silos, winding and water towers, blast furnaces, and cooling towers. These highlight how the Bechers used specific representational strategies, systematic arrangement, and variation to achieve artistic expression. Created between the 1960s and early 2000s across different countries, the works powerfully demonstrate the visual grammar developed by the Bechers.
A kind of “cinematic epilogue” is provided by a video created by Max Becher, who accompanied his parents on a work trip to Ohio in 1987, offering an evocative glimpse into their working process.
The works are drawn from the Bernd and Hilla Becher Archive at Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur and the Bernd & Hilla Becher Studio in Düsseldorf, directed by Max Becher. Additional loans are provided by Sprüth Magers and the LVR-Landesmuseum Bonn.
A catalogue will accompany the exhibition, published by Schirmer/Mosel Verlag, Munich, with texts by Max Becher, Gabriele Conrath-Scholl, Marianne Kapfer, and Urs Stahel. (Will be released in early November.)
Press release from Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur
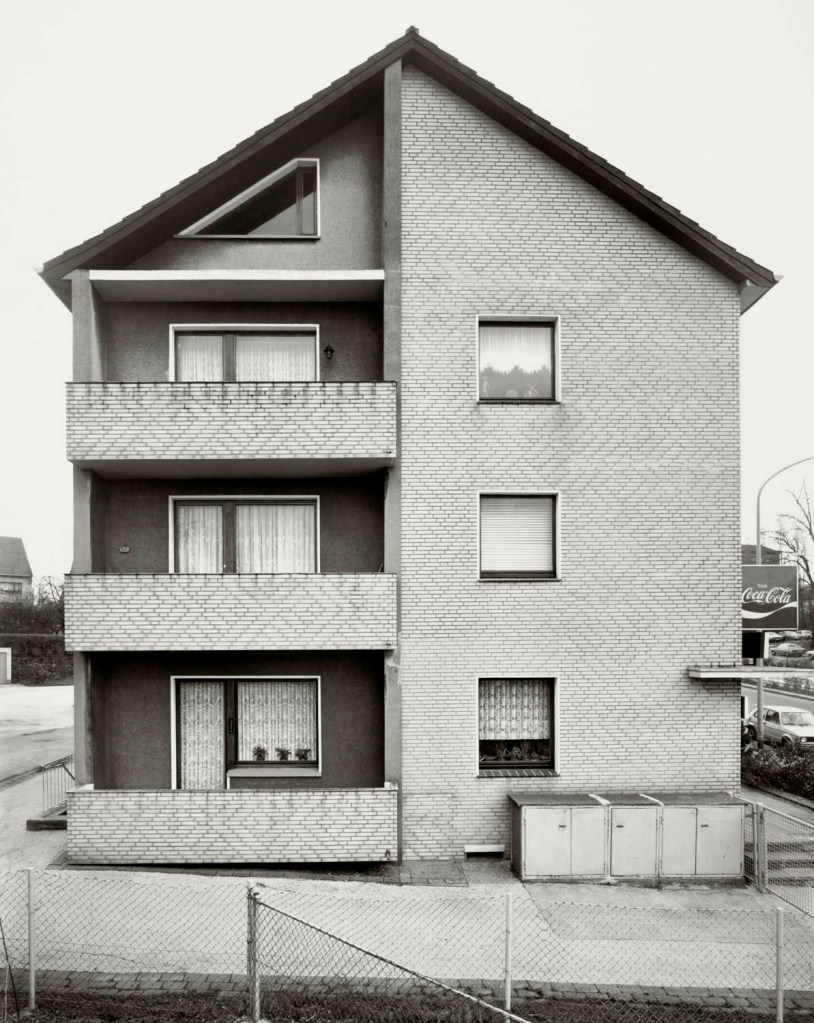

Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Essen-Schönebeck, D
1981
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
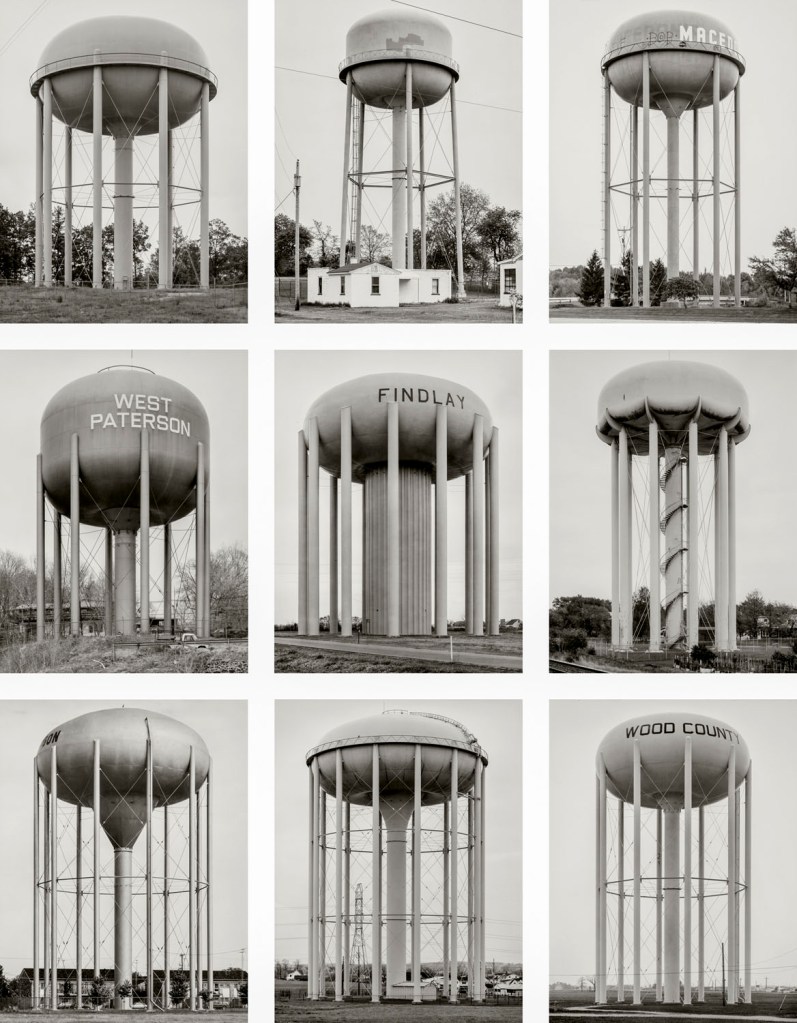

Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Wassertürme, USA (Water towers, USA)
1974-1983
Gelatin silver prints
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln, 2025
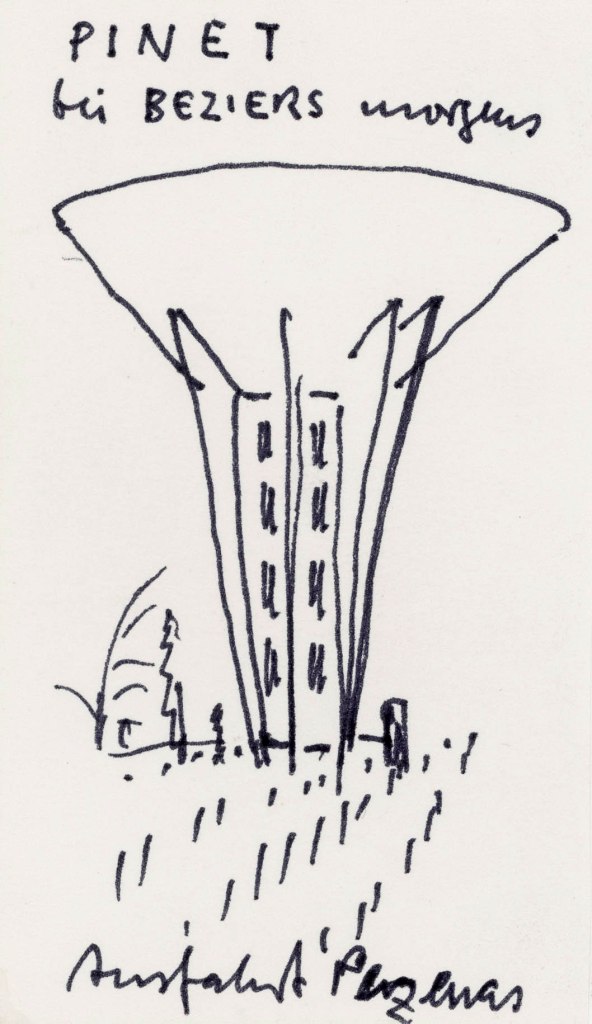

Bernd Becher (German, 1931-2007)
Untitled (Water tower, Béziers, Hérault, F)
c. 1984
Ink on paper
9 x 5.1cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln, 20255
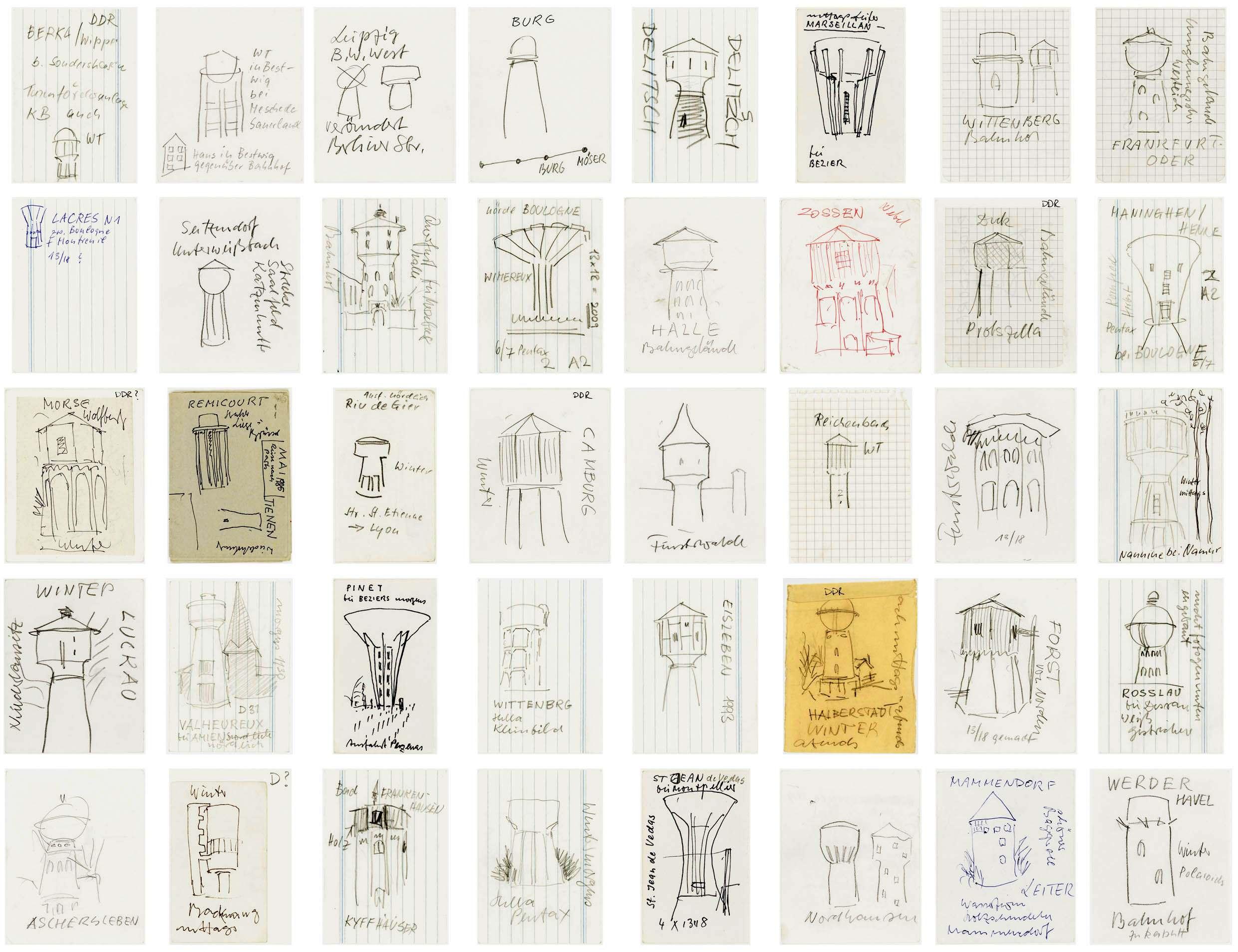

Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Wassertürme (Water tower)
1960s-1980s
Drawings with felt-tip pen, pencil, ballpoint pen on cardboard, paper, index cards
Various sizes around 10.5 x 8.5cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
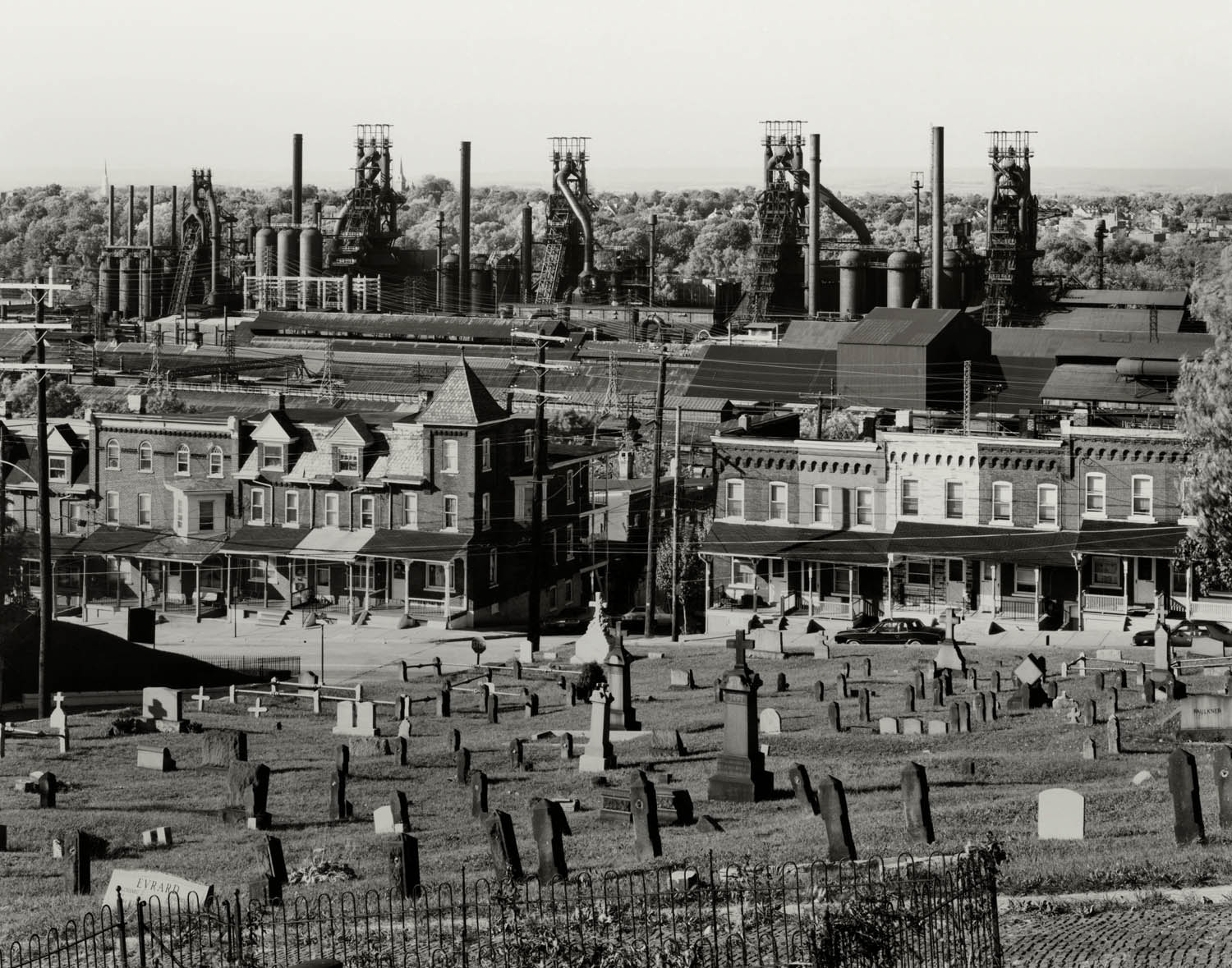
Walker Evans (United States of America 1903-1975)
Graveyard and steel mill, Bethlehem, Pennsylvania
1935
Gelatin silver print
Installation view of the exhibition Bernd & Hilla Becher – History of a Method at Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Cologne showing at left Bernd and Hilla Becher’s photograph Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, USA 1986 (below)
Installation view of the exhibition Bernd & Hilla Becher – History of a Method at Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Cologne showing Bernd and Hilla Becher’s photograph Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, USA 1986 (below)
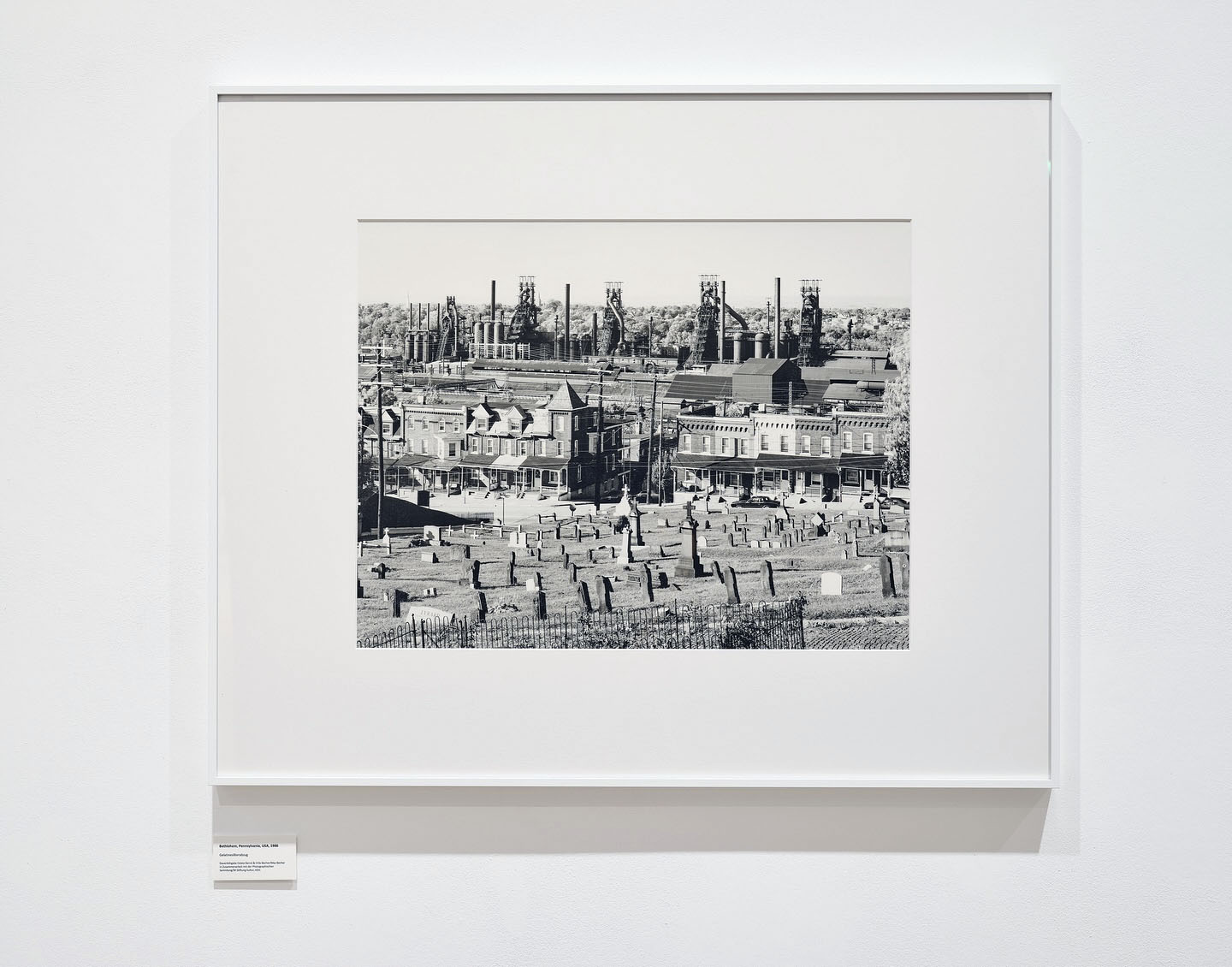
Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, USA
1986
Gelatin silver print
46.7 x 60cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
With their blast furnaces, chimneys, pipes, and conveyor belts, steelworks are less buildings than gigantic machines. They are among the most imposing industrial structures that Bernd and Hilla Becher have photographed since the late 1950s. Anatomically speaking, blast furnaces are like a body without skin, the artist couple wrote in 1990: excessively high temperatures, too much pressure, too many gases make cladding the steel shell impossible; they are nothing but function. In Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, the enormous work practically hangs over the town. Photographed from an elevated vantage point (similar to the one Walker Evans had chosen in 1935), the blast furnaces, houses, and the cemetery – work, life, death – are compressed into an inescapable proximity. Space compressed, time compressed.
Dr. Maria Müller-Schareck, art historian and member of the PS/SK management team
Text from the SK Stiftung Kultur Die Photographische Sammlung Instagram page
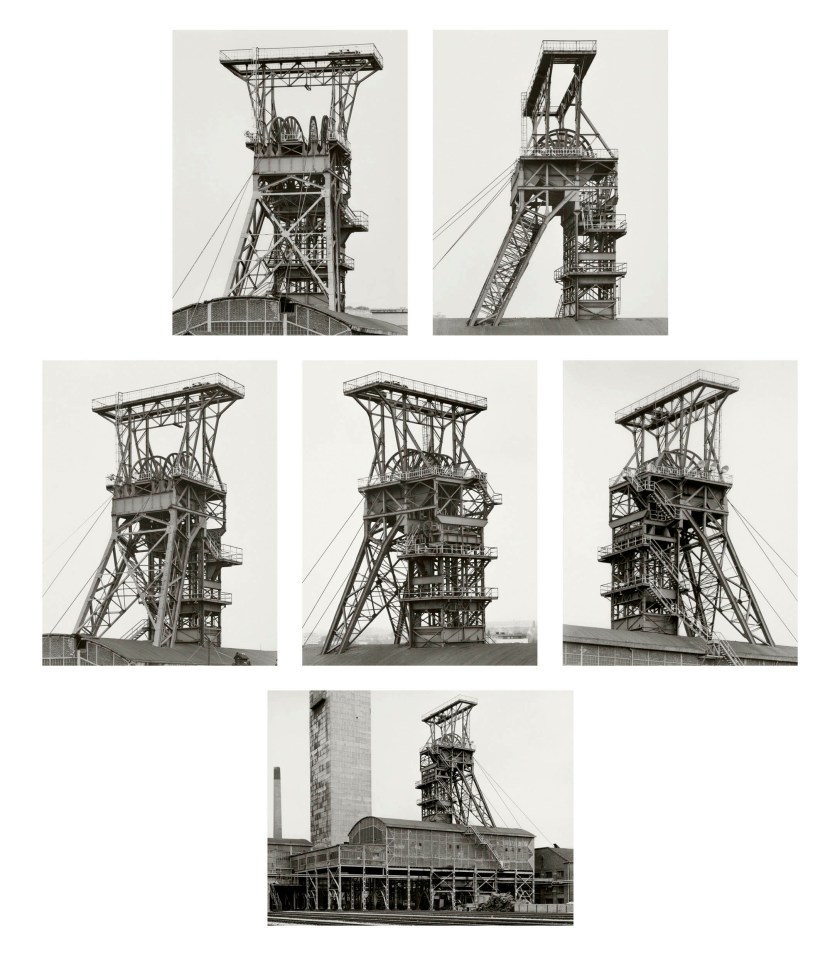

Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Förderturm, Schacht 2 (Winding tower, shaft 2)
1982
6 gelatin silver prints,
Each approx. 40 x 31cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
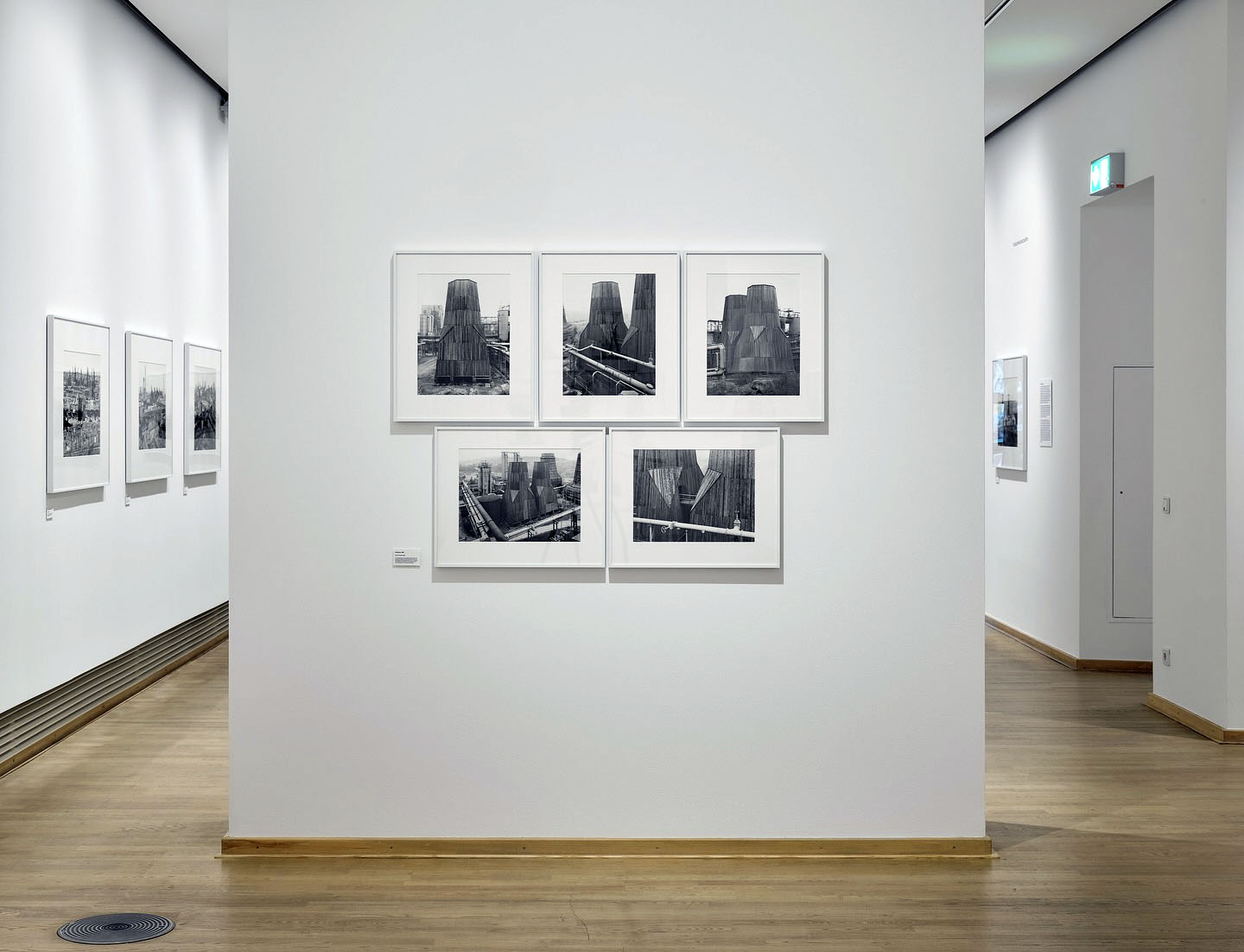
Installation views of the exhibition Bernd & Hilla Becher – History of a Method at Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Cologne showing Bernd and Hilla Becher’s Zeche Ewald Fortsetzung, Kühlturm/-türme (Ewald mine continuation, cooling tower(s)) 1985 (below)
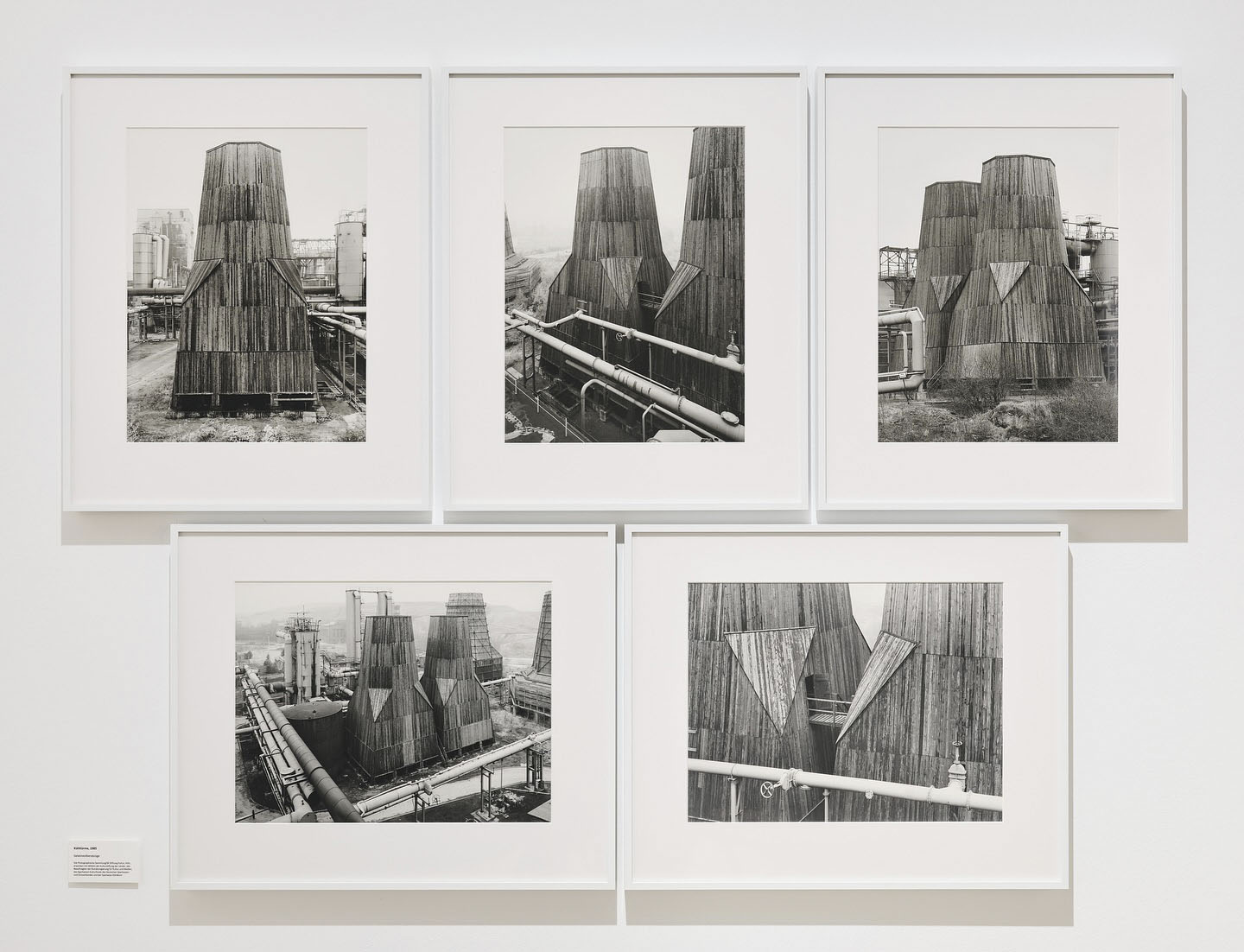
Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Zeche Ewald Fortsetzung, Kühlturm/-türme (Ewald mine continuation, cooling tower(s))
1985
5 gelatin silver prints
Each approx. 40.0 x 31.0cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
Over the course of their artistic career, Bernd and Hilla Becher documented approximately 200 industrial sites, including the Ewald Fortsetzung coal mine in Recklinghausen, which we are featuring in our exhibition.
These documentations are based on systematic walks through the industrial sites and surrounding areas. A panoramic photograph, often central to each site, provides an overview of the grounds and allows the individual buildings to be located and understood in relation to one another.
The subsequent photographs portray the individual building types, in this case, two cooling towers. The five images in this group clearly demonstrate how Bernd and Hilla Becher approach their subject, photographing the building from different sides and perspectives, and highlighting a specific detail. The aim of this approach was to depict the industrial buildings in a way that is both technically clear and aesthetically pleasing.
Text from the SK Stiftung Kultur Die Photographische Sammlung Instagram page
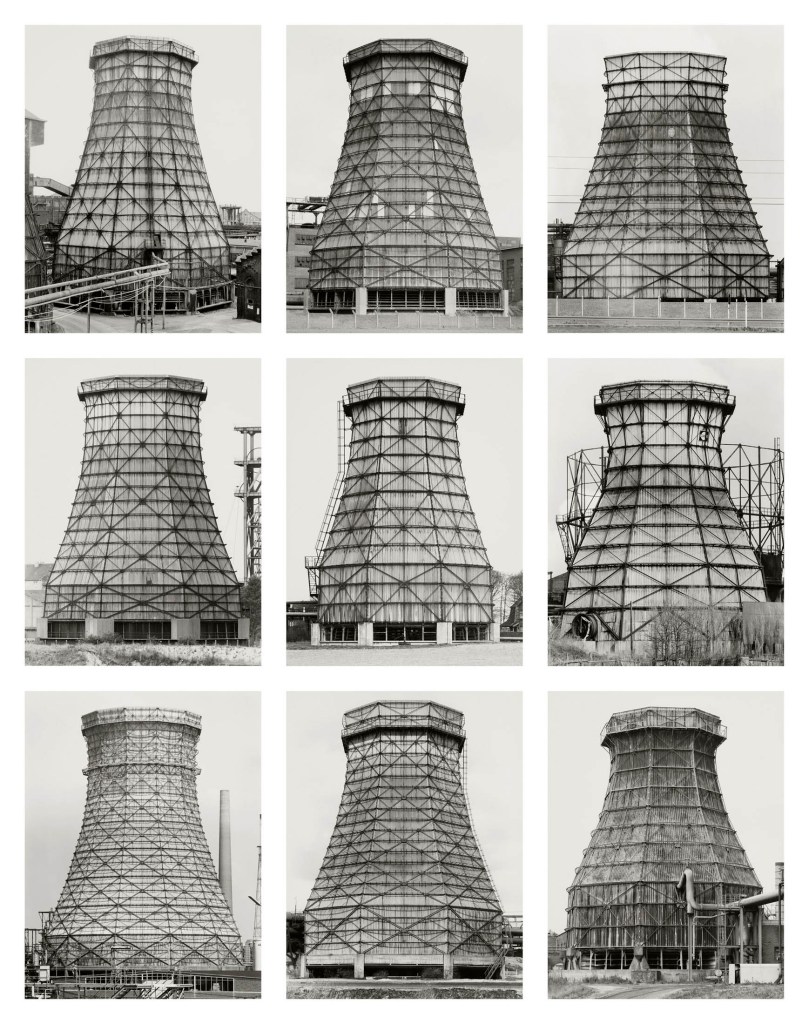

Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Kühltürme (Cooling towers)
1964-1993
9 gelatin silver prints
Each approx. 41 x 31cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur – Bernd und Hilla Becher Archiv, Köln
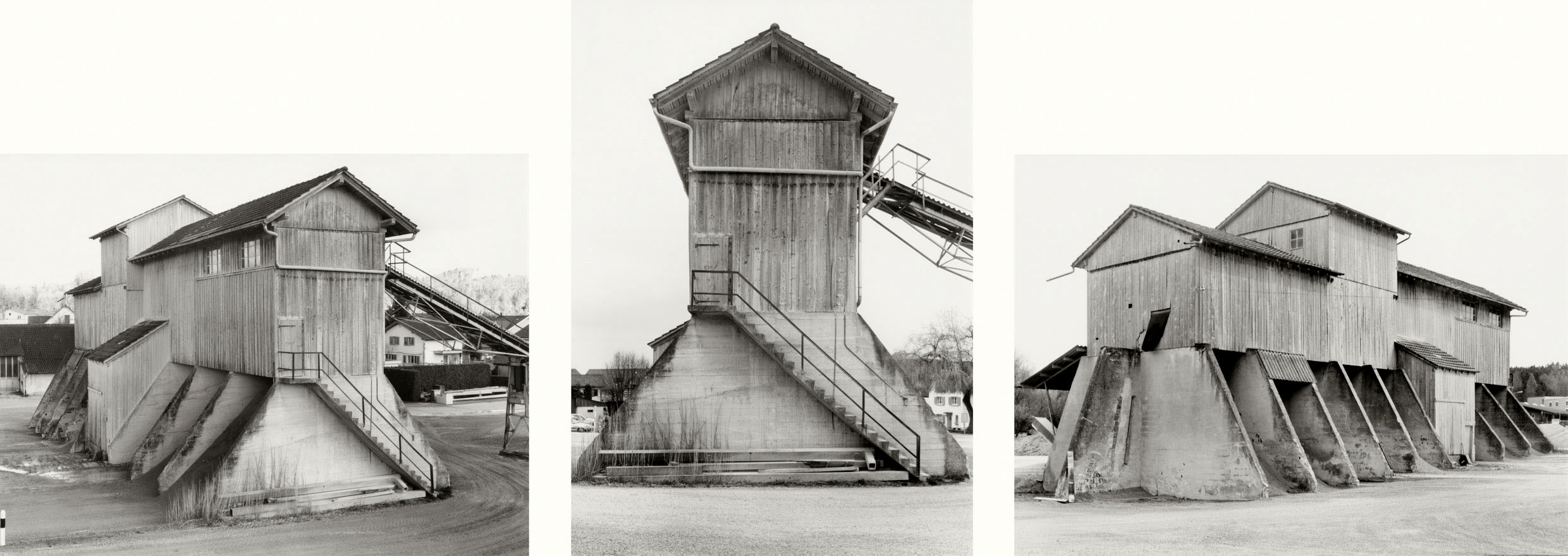
Bernd and Hilla Becher (German, 1931-2007/1934-2015)
Kies- und Schotterwerk, Oberbüren/St. Gallen, CH (Gravel and crushed stone works, Oberbüren/St. Gallen, CH)
2001
3 gelatin silver print
Each approx. 30 x 40cm
© Estate Bernd & Hilla Becher, vertreten durch Max Becher
Courtesy Sprüth Magers
Installation view of the exhibition Bernd & Hilla Becher – History of a Method at Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur, Cologne September, 2025 – February, 2026

Bernd & Hilla Becher – History of a Method book cover
Die Photographische Sammlung/SK Stiftung Kultur
Im Mediapark 7, 50670 Cologne
Phone: +49 221/888 95 300
Opening hours: Daily (except Wednesdays): 2pm – 7pm













































You must be logged in to post a comment.