Exhibition dates: 12th October 2018 – 23rd April 2019
Curators: Curated by Tracey Bashkoff, Director of Collections and Senior Curator, with the assistance of David Horowitz, Curatorial Assistant, and organised with the cooperation of the Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm.
The exhibition Hilma af Klint: Paintings for the Future has attracted more than 600,000 visitors since its opening, making it the most-visited show in the history of the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum. The survey of Hilma af Klint’s work is the first major solo exhibition in the United States devoted to the Swedish artist.
“For me, the 2018-19 art season will always belong to the Swedish painter Hilma af Klint (1862-1944). I say this simply as a measure of the psychic and historical shift caused by the Guggenheim Museum’s extraordinary full-dress retrospective of her nearly 40-year career.” ~ Roberta Smith, The New York Times
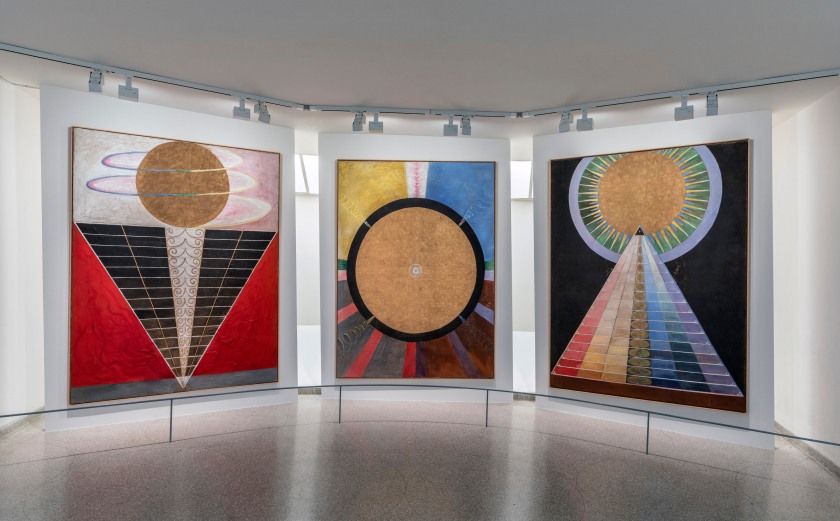
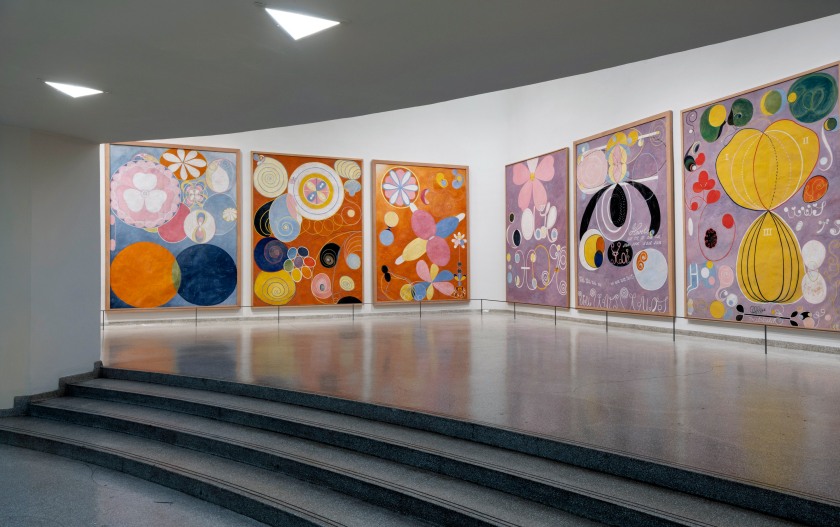
Installation view of the exhibition Hilma af Klint: Paintings for the Future, Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum, New York, October 12, 2018 – April 23, 2019
Photo: David Heald
What can one say…
Magical, mystical, enchanted; chakra, mandala, golden ratio; music, spirit, energy.
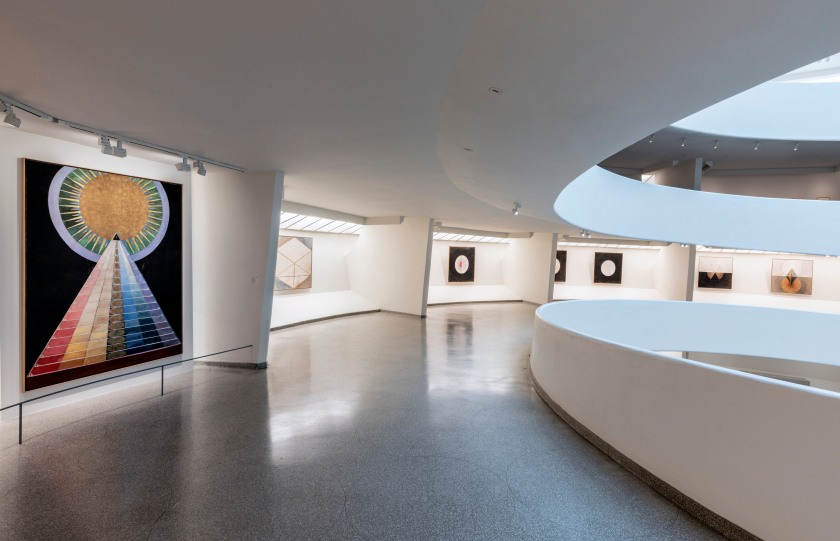
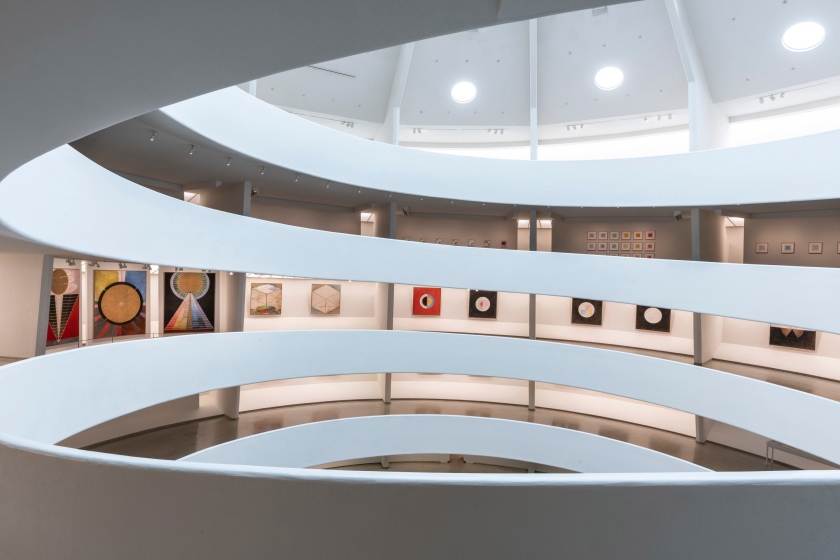
Af Klint imagined displaying these works in a spiral temple, but the building never came to fruition. Now they are displayed in the spiral of the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum, New York. I think she would have been very pleased.
She stipulated that her paintings not be shown for 20 years following her death, convinced the world was not ready for them. She was probably correct in that assumption. But now, now we are ravished by her creativity and prescience.
If she only knew how much she is now loved and adored. An enigmatic star that burns so very bright in the cosmos.
For Joyce Evans
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
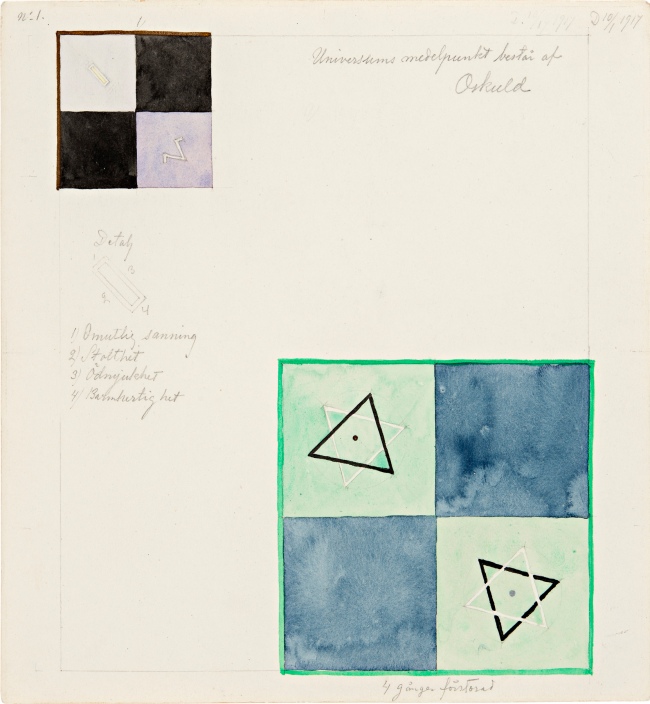
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
Group X, No. 1, Altarpiece (Grupp X, nr 1, Altarbild) (detail)
1915
From Altarpieces (Altarbilder)
Oil and metal leaf on canvas
237.5 x 179.5cm
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström, the Moderna Museet, Stockholm
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
Group X, No. 1, Altarpiece (Grupp X, nr 1, Altarbild)
1915
From Altarpieces (Altarbilder)
Oil and metal leaf on canvas
237.5 x 179.5cm
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström, the Moderna Museet, Stockholm
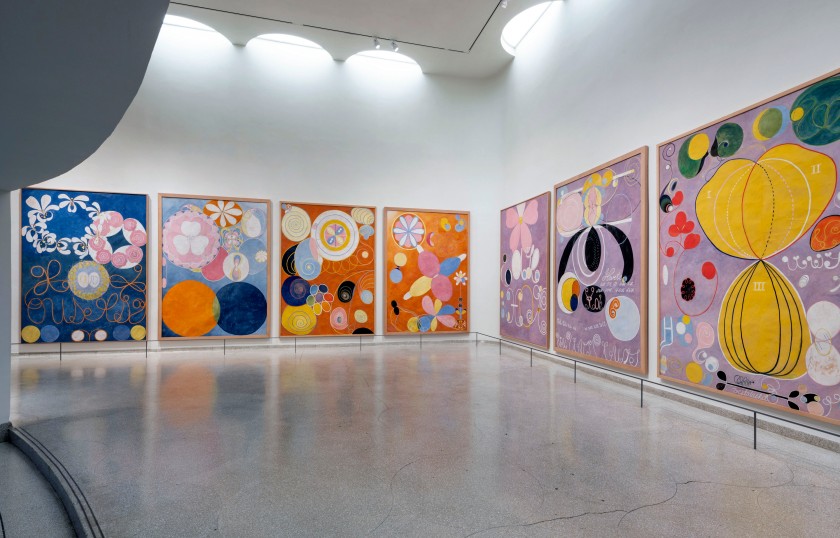
Installation views of the exhibition Hilma af Klint: Paintings for the Future, Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum, New York, October 12, 2018 – April 23, 2019
Photos: David Heald
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
The Ten Largest, No. 7., Adulthood, Group IV [The age of men]
1907
Tempera on paper mounted on canvas
315 x 235cm
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström/Moderna Museet
From October 12, 2018, to April 23, 2019, the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum presents the first major solo exhibition in the United States of the Swedish artist Hilma af Klint (1862-1944). When af Klint began creating radically abstract paintings in 1906, they were like little that had been seen before: bold, colourful, and untethered from recognisable references to the physical world. It was several years before Vasily Kandinsky, Kazimir Malevich, Piet Mondrian, and others would take similar strides to free their own artwork of representational content. Yet af Klint rarely exhibited her remarkably forward-looking paintings and, convinced the world was not ready for them, stipulated that they not be shown for 20 years following her death. Ultimately, her work was not exhibited until 1986, and it is only over the past three decades that her paintings and works on paper have received serious attention.
Hilma af Klint: Paintings for the Future offers an opportunity to experience af Klint’s artistic achievements in the Guggenheim’s rotunda more than a century after she began her daring work. Curated by Tracey Bashkoff, Director of Collections and Senior Curator, with the assistance of David Horowitz, Curatorial Assistant, and organised with the cooperation of the Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm, the exhibition features more than 170 of af Klint’s artworks and focus on the artist’s breakthrough years, 1906-20. It is during this period that she began to produce nonobjective and stunningly imaginative paintings, creating a singular body of work that invites a reevaluation of modernism and its development.
Hilma af Klint was born in Stockholm in 1862 and went on to study painting at the city’s Royal Academy of Fine Arts, graduating with honours in 1887. She soon established herself as a respected painter in Stockholm, exhibiting deftly rendered figurative paintings and serving briefly as secretary of the Society for Swedish Women Artists. During these years, she also became deeply engaged with spiritualism, Rosicrucianism, and Theosophy. These forms of spirituality, which were also of keen interest to other artists, including Kandinsky, František Kupka, Malevich, and Mondrian, were widely popular across Europe and the United States, as people sought to reconcile long-held religious beliefs with scientific advances and a new awareness of the global plurality of religions.
Af Klint developed her new approach to art making together with her spiritual practice, outside of Stockholm’s male-dominated art world. She had begun to regularly hold séances with four other women by 1896. During a meeting in 1906, one of the spirits that the group often channeled asked af Klint to create a cycle of paintings. Af Klint immediately accepted. She worked on the project between 1906 and 1915, completing 193 paintings and works on paper collectively called The Paintings for the Temple. These works, which included her first forays into non-objectivity, were a radical break from the more staid paintings she produced as part of her public practice. Stylistically, they are strikingly diverse, utilising biomorphic and geometric forms, expansive and intimate scales, and maximalist and reductivist approaches to composition and colour. She imagined installing them in a spiral temple, but the building never came to fruition. Af Klint described the final group of The Paintings for the Temple, called the Altarpieces, as “the summary of the series so far.” Recent research suggests this group of paintings was exhibited in 1928 at the World Conference of Spiritual Science and Its Practical Applications in London – the only known public display of The Paintings for the Temple during the artist’s lifetime. After she completed The Paintings for the Temple, af Klint continued to test the limits of her new abstract vocabulary. In these years, she experimented with form, theme, and seriality, creating some of her most incisive works.
Exhibition catalogue
Hilma af Klint: Paintings for the Future is accompanied by an illustrated catalogue representing her groundbreaking painting series while expanding recent scholarship to present the fullest picture yet of her life and art. Edited by Tracey Bashkoff, the volume includes contributions by Tessel M. Bauduin, Daniel Birnbaum, Briony Fer, Vivien Greene, Ylva Hillström, David Max Horowitz, Andrea Kollnitz, Helen Molesworth, and Julia Voss. Essays explore the social, intellectual, and artistic context of af Klint’s 1906 break with figuration and her subsequent development, placing her in the context of Swedish modernism and folk art traditions, contemporary scientific discoveries, and spiritualist and occult movements. A roundtable discussion among contemporary artists, scholars, and curators considers af Klint’s sources and relevance to art in the 21st century. The volume also delves into her unrealised plans for a spiral-shaped temple in which to display her art – a wish that finds a fortuitous answer in the Guggenheim Museum’s rotunda, the site of the exhibition.
Press release from the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum website [Online] Cited 11/03/2019
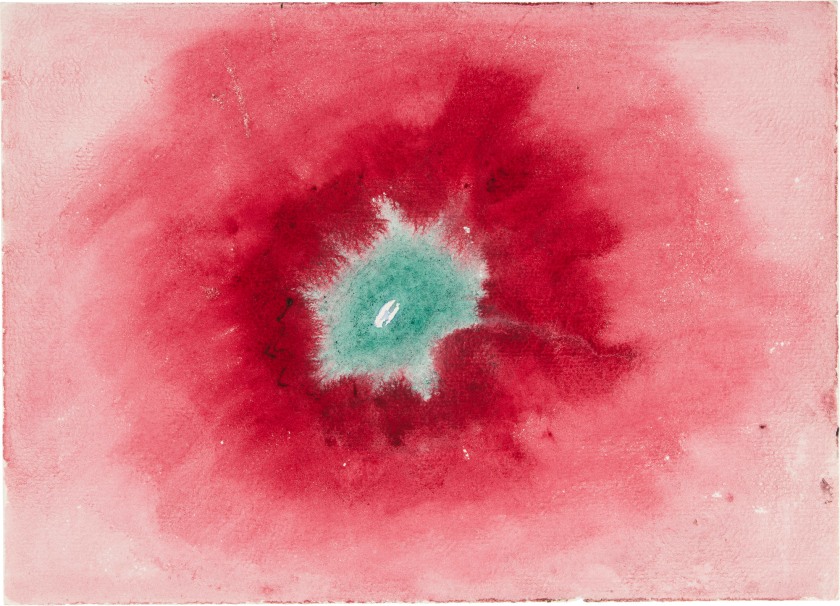
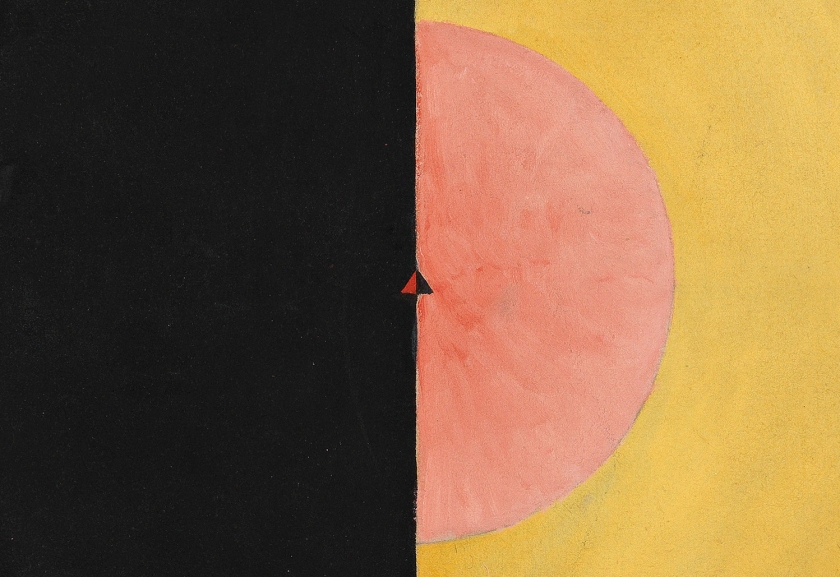
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
Untitled
1920
From On the Viewing of Flowers and Trees (Vid betraktande av blommor och träd)
Watercolor on paper
17.9 x 25cm
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström, the Moderna Museet, Stockholm
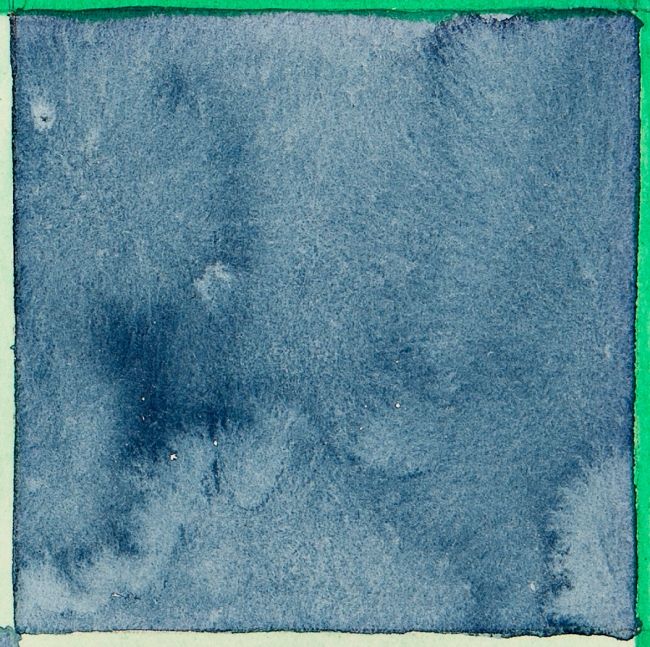
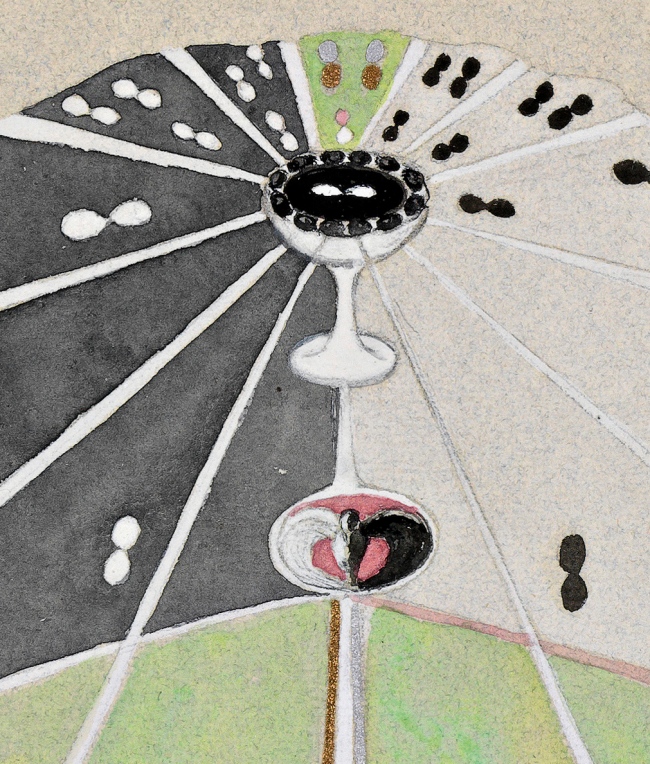
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
No. 1 (Nr 1) (detail)
1917
From The Atom Series (Serie Atom)
Watercolor on paper
27 x 25cm
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström, the Moderna Museet, Stockholm
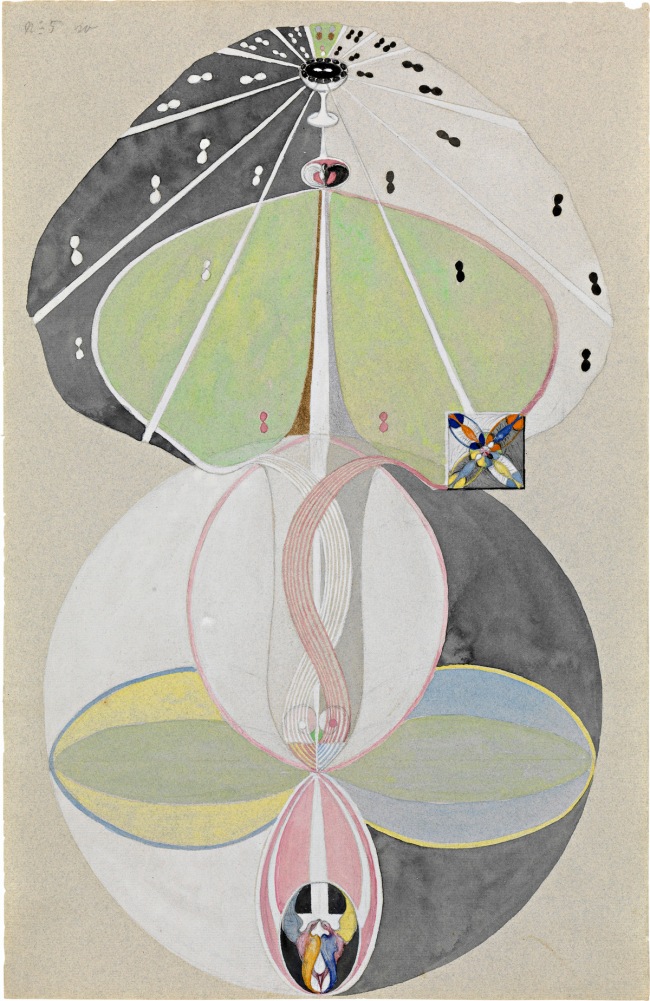
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
No. 1 (Nr 1)
1917
From The Atom Series (Serie Atom)
Watercolor on paper
27 x 25cm
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström, the Moderna Museet, Stockholm
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
Group IX/SUW, The Swan, No. 17 (Grupp IX/SUW, Svanen, nr 17)
1915
From The SUW/UW Series (Serie SUW/UW)
Oil on canvas
150.5 x 151cm
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström, the Moderna Museet, Stockholm
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
Group IX/SUW, The Swan, No. 17 (Grupp IX/SUW, Svanen, nr 17) (detail)
1915
From The SUW/UW Series (Serie SUW/UW)
Oil on canvas
150.5 x 151cm
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström, the Moderna Museet, Stockholm
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
No. 2a, The Current Standpoint of the Mahatmas (Nr 2a, Mahatmernas nuvarande ståndpunkt)
1920
From Series II (Serie II)
Oil on canvas, 36.5 x 27cm
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström, the Moderna Museet, Stockholm
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
Group I, Primordial Chaos, No. 16 (Grupp 1, Urkaos, nr 16)
1906-1907
From The WU/Rose Series (Serie WU/Rosen)
Oil on canvas
53 x 37cm
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström, the Moderna Museet, Stockholm
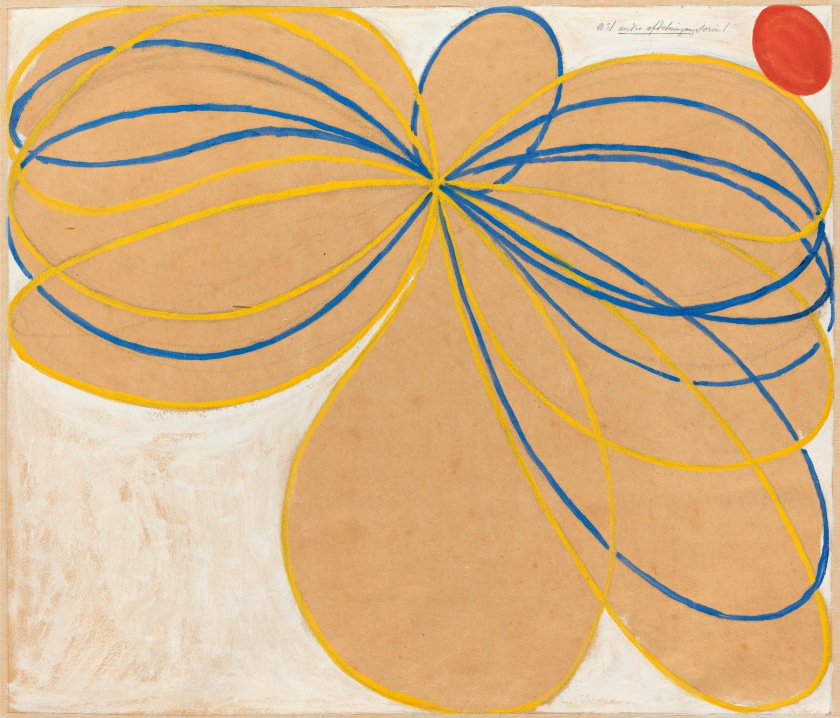
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
Group V, The Seven-Pointed Star, No. 1n (Grupp V, Sjustjärnan, nr 1)
1908
From The WUS/Seven-Pointed Star Series (Serie WUS/Sjustjärnan)
Tempera, gouache and graphite on paper mounted on canvas
62.5 x 76cm
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström, the Moderna Museet, Stockholm
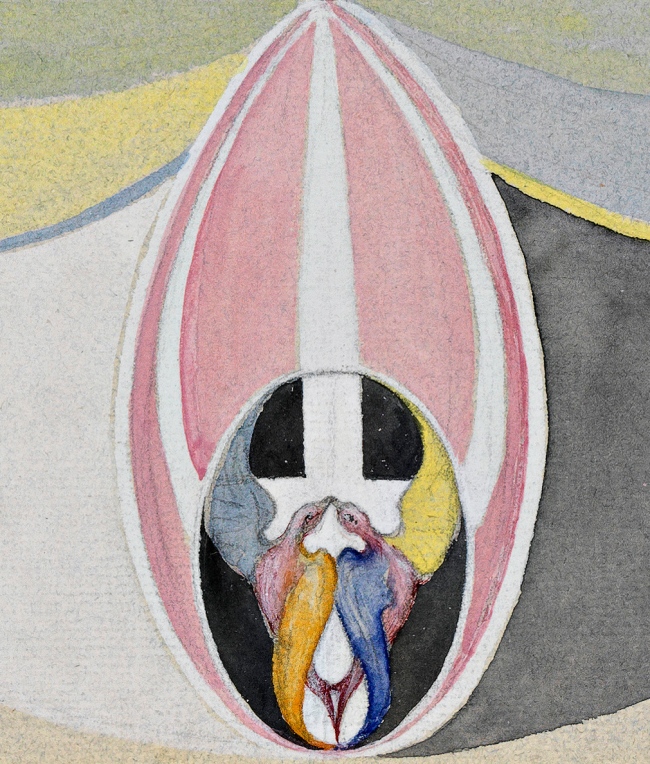
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
Tree of Knowledge, No. 5 (Kunskapens träd, nr 5) (detail)
1915
From The W Series (Serie W)
Watercolor, gouache, graphite and metallic paint on paper
18 1/16 x 11 5/8 inches (45.8 x 29.5cm)
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström, the Moderna Museet, Stockholm
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
Tree of Knowledge, No. 5 (Kunskapens träd, nr 5)
1915
From The W Series (Serie W)
Watercolor, gouache, graphite and metallic paint on paper
18 1/16 x 11 5/8 inches (45.8 x 29.5cm)
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström, the Moderna Museet, Stockholm
Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944)
Tree of Knowledge, No. 5 (Kunskapens träd, nr 5) (detail)
1915
From The W Series (Serie W)
Watercolor, gouache, graphite and metallic paint on paper
18 1/16 x 11 5/8 inches (45.8 x 29.5cm)
© The Hilma af Klint Foundation, Stockholm
Photo: Albin Dahlström, the Moderna Museet, Stockholm
Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum
1071 5th Avenue (at 89th Street)
New York
Opening hours:
Open daily 11am – 6pm
Saturdays until 8pm








![Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944) 'The Ten Largest, No. 7., Adulthood, Group IV' [The age of men] 1907 Hilma af Klint (Swedish, 1862-1944) 'The Ten Largest, No. 7., Adulthood, Group IV' [The age of men] 1907](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/hilma-af-klint-groupiv-the-ten-largest-no.7-web.jpg?w=650&h=874)























You must be logged in to post a comment.