Exhibition dates: 1st October – 17th December 2022
Curators: Jonathan D. Katz, Curator and Johnny Willis, Associate Curator
Please note: This exhibition contains sexually explicit content. For mature audiences only.
Roberto Montenegro (Mexican, 1885-1968)
Retrato de un anticuario o Retrato de Chucho Reyes y autorretrato
Portrait of an antiquarian or Portrait of Chucho Reyes and self-portrait
1926
Oil on canvas
40.4 x 40.4 in (unframed), 41.7 x 41.6 x 1.6 in (framed)
Colección Pérez Simón, Mexico, © Arturo Piera
Short and sweet…
I believe that any artist that lives at the edge of desire, of creativity, of individuality, exploration and feeling – in seeing the world from different points of view – pushes the boundaries of what the conservative mass of humanity finds acceptable.
Defying the taboo is only possible because the taboo exists in the first place. The taboo against sensuality, eroticism and pleasure can only be broken by approaching those ecstatic and liminal spaces that lead to other states of consciousness, by being attentive to the dropping away of awareness so that we avoid the frequency of common intensities, instead illuminating spaces and languages where new cultural symbols and meanings can emerge. This is what artists and people of difference do: we approach the ‘Thing Itself’. We live on the edge of ecstasy, oblivion and revelation.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
PS. I have added bibliographic information to the posting where possible.
Many thankx to Wrightwood 659 for allowing me to publish the art work in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
The First Homosexuals: Global Depictions of a New Identity, 1869-1930 takes as its starting point the year 1869, when the word “homosexual” was first coined in Europe, inaugurating the idea of same-sex desire as the basis for a new identity category. On view will be more than 100 paintings, drawings, prints, photographs, and film clips – drawn from public and private collections around the globe and including a number of national treasures which have never before been allowed to travel outside their countries. This groundbreaking exhibition offers the first multi-medium survey of the very first self-consciously queer art, exploring what the “first homosexuals” understood themselves to be, how dominant culture, in turn, understood them, and how the codes of representation they employed offer us previously unknown glimpses into the social and cultural meanings of same-sex desire.
The First Homosexuals is being organised in two parts, due to COVID-related delays, with part one opening on October 1 with approximately 100 works, and on view only at Wrightwood 659. Three years from now, in 2025, 250 masterworks will be gathered at Wrightwood 659 for part two of The First Homosexuals in an exhibition which will travel internationally and be accompanied by a comprehensive catalogue.
The exhibition is being developed by a team of 23 international scholars led by art historian Jonathan D. Katz, Professor of Practice in the History of Art and Gender, Sexuality and Women’s Studies at the University of Pennsylvania, with associate curator Johnny Willis.
Alice Austen (American, 1866-1952)
Trude & I Masked, Short Skirts
1891
Print, 4 x 5 in
Historic Richmond Town
Elizabeth Alice Austen (March 17, 1866 – June 9, 1952) was an American photographer working in Staten Island.
One of America’s first female photographers to work outside of the studio, Austen often transported up to 50 pounds of photographic equipment on her bicycle to capture her world.[citation needed] Her photographs represent street and private life through the lens of a lesbian woman whose life spanned from 1866 to 1952. Austen was a rebel who broke away from the constraints of her Victorian environment and forged an independent life that broke boundaries of acceptable female behaviour and social rules. …
Alice Austen’s life and relationships with other women are crucial to an understanding of her work. Until very recently many interpretations of Austen’s work overlooked her intimate relationships. What is especially significant about Austen’s photographs is that they provide rare documentation of intimate relationships between Victorian women. Her non-traditional lifestyle and that of her friends, although intended for private viewing, is the subject of some of her most critically acclaimed photographs. Austen would spend 53 years in a devoted loving relationship with Gertrude Tate, 30 years of which were spent living together in her home which is now the site of the Alice Austen House Museum and a nationally designated site of LGBTQ history.
Austen’s wealth was lost in the stock market crash of 1929 and she and Tate were evicted from their beloved home in 1945. Tate and Austen were finally separated by family rejection of their relationship and poverty. Austen was moved to the Staten Island Farm Colony where Tate would visit her weekly. In 1951 Austen’s photographs were rediscovered by historian Oliver Jensen and money was raised by the publication of her photographs to place Austen in private nursing home care. On June 9, 1952 Austen passed away. The final wishes of Austen and Tate to be buried together were denied by their families.
Text from the Wikipedia website
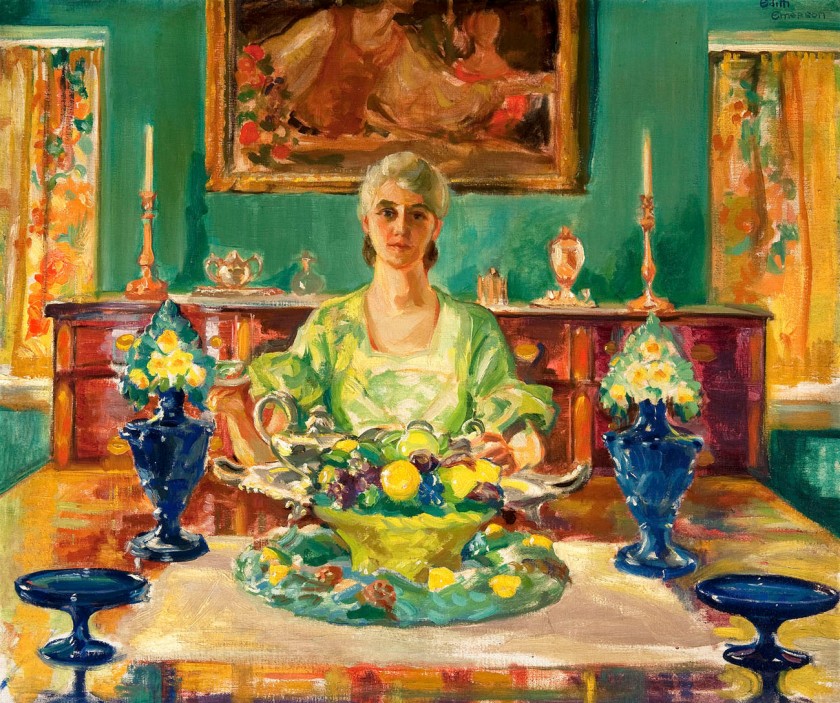
Violet Oakley (American, 1874-1961)
Edith Emerson Lecturing
c. 1935
Oil on canvas
35 x 45 in.
Woodmere Art Museum, Philadelphia, PA: gift of the Pennsylvania Academy of Fine Arts, 2012
Courtesy of Woodmere Art Museum
Violet Oakley (June 10, 1874 – February 25, 1961) was an American artist. She was the first American woman to receive a public mural commission. During the first quarter of the twentieth century, she was renowned as a pathbreaker in mural decoration, a field that had been exclusively practiced by men. Oakley excelled at murals and stained glass designs that addressed themes from history and literature in Renaissance-revival styles.
Edith Emerson (American, 1888-1981)
Portrait of Violet Oakley
Date unknown
Oil on canvas
25 x 30 in.
Woodmere Art Museum, Philadelphia, PA: gift of Jane and Noble Hall, 1998
Courtesy of Woodmere Art Museum
Edith Emerson (July 27, 1888 – November 21, 1981) was an American painter, muralist, illustrator, writer, and curator. She was the life partner of acclaimed muralist Violet Oakley and served as the vice-president, president, and curator of the Woodmere Art Museum in the Chestnut Hill neighbourhood of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, from 1940 to 1978. …
[Oakley’s] life partner, Edith Emerson, was a painter and, at one time, a student of Oakley’s. In 1916, Emerson moved into Oakley’s Mount Airy home, Cogslea, where Oakley had formed a communal household with three other women artists, calling themselves the Red Rose Girls. Emerson and Oakley’s relationship endured until Oakley’s death and Emerson subsequently established a foundation to memorialise Oakley’s life and legacy. The foundation dissolved in 1988 and the assets donated to the Smithsonian Museum.
Following Violet Oakley’s death in 1961, Emerson created the Violet Oakley Memorial Foundation to keep her teacher and companion’s memory and ideals alive. The foundation also sought to house and preserve the contents of Oakley’s studio, which was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1977 as the Violet Oakley Studio. Emerson served as the foundation’s president, as well as curator and general caretaker of the studio. The studio was opened to the public as a kind of museum, and Emerson organised various activities there, including concerts, exhibitions, poetry readings, and lectures on American art and illustration. Following Emerson’s death, the foundation dispersed the contents, sold the house, and disbanded.
In 1979, Emerson was instrumental in mounting an Oakley revival as an exhibition at the Philadelphia Museum of Art.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Owe Zerge (Swedish, 1894-1984)
Model Act
1919
Oil on canvas
53.1 x 19.7 in.
Private Collection
Role of Art in the Modern Construction of Same-Sex Desire Explored for First Time in Groundbreaking Two-Part Exhibition at Wrightwood 659 in Chicago
The First Homosexuals: Global Depictions of a New Identity, 1869-1930, begins in the year 1869, when the word “homosexual” was coined in Europe, inaugurating the idea of same-sex desire as the basis for a new identity category. With more than 100 paintings, drawings, prints, photographs, and film clips – drawn from public and private collections around the globe and including works which have never before been allowed to travel outside their countries – this large-scale international exhibition offers the first multi-media survey of some of the founding works of queer art. The First Homosexuals explores what the earliest homosexuals understood themselves to be, how dominant culture understood them, and how the codes of representation they employed offer previously unknown glimpses into the social and cultural meanings of same-sex desire.
The First Homosexuals is organised in two parts, due to Covid-related delays, with Part I on view only at Wrightwood 659 in Chicago from October 1 through December 17, 2022. Three years from now, in 2025, 250 masterworks will be gathered at Wrightwood 659 for Part II, in a major exhibition that will travel internationally, accompanied by a comprehensive catalogue.
Already three years in the making, the exhibition is being developed by a team of 23 international scholars, led by art historian Jonathan D. Katz, Professor of Practice in the History of Art and Gender, Sexuality and Women’s Studies at the University of Pennsylvania, with associate curator Johnny Willis.
The First Homosexuals rewrites conventional art history, in part by deepening the reading of works of art by familiar artists – whether it be Henry Fuseli, Thomas Eakins, or George Bellows – and in part by lifting the cover off works that previously have not been widely understood as declarations of same-sex attachment. The exhibition also introduces American museum goers to a number of artists who are little known in the United States but revered in their own countries, including Gerda Wegener (Denmark); Eugéne Jansson (Sweden); and Frances Hodgkins (New Zealand).
The First Homosexuals explores the cohesion of a new global identity at a liminal moment, one that art can tell uniquely well. While the written archive of the period must necessarily use accepted words to describe ideas, art is notably free of such consensus, allowing for the emergence of more idiosyncratic, contested, and exploratory forms.
“The First Homosexuals is an international project of an incredible scale. It perfectly fulfils our mission of presenting novel, socially engaged exhibitions,” says Chirag G. Badlani, Executive Director of Alphawood Foundation Chicago, which is presenting The First Homosexuals through Alphawood Exhibitions. “We are thrilled that the community can experience an important exhibition like this at Wrightwood 659 – given the content, it otherwise might not be seen.” He added, “We are particularly proud to show a collection of early Russian queer works borrowed from the Odesa Fine Arts Museum in Ukraine, amidst the ongoing war, helping to safeguard these important pieces of queer history from potential damage or destruction.”
Dr. Katz, notes, “The First Homosexuals demonstrates that as the language used to name same-sex desire narrowed into a simple binary of homosexual / heterosexual, art went the opposite direction, giving form to a range of sexualities and genders that can best be described as queer. Art became the place where the simplistic sexual binary could be nuanced and particularised, evoking emotions and responses that language couldn’t yet express.”
Dr. Katz continues, “The reality is that current-day conceptions about homosexuality are only roughly as old as the oldest living Americans. Our goal in this exhibition is to read queer desire as it manifested itself in this not-so-long-ago past, while being alert to the very different forms it took globally.”
The exhibition
Part I of The First Homosexuals is installed in nine sections, occupying the entire second floor of the Tadao Ando-designed galleries of Wrightwood 659. The first section, entitled Before Homosexuality, features 19th-century works that suggest how unself-consciously same-sex eroticism was portrayed before the coinage of the word homosexual. A highlight is a print depicting a sexual act between two men by Hokusai, the ukiyo-e master of Japan’s Edo period. Hokusai’s image would have been entirely uncontroversial in its day.
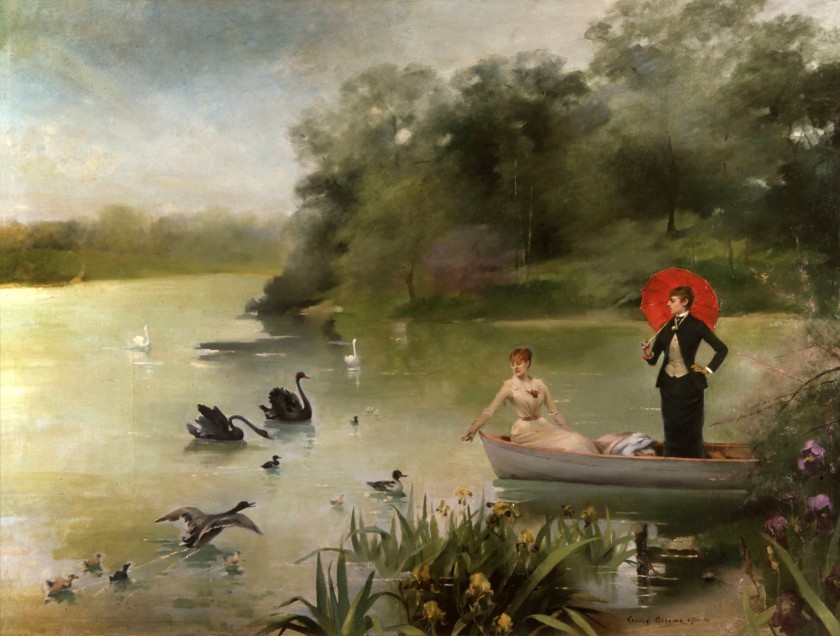
Among the works installed in Couples, the second section, is a leisurely boating scene by the French painter Louise Abbéma, showing herself in masculinate garb with her lover, the celebrated actress Sarah Bernhardt. Two other paintings represent reverse homages, wherein the American artist Edith Emerson paints her lover Violet Oakley and Oakley returns the favour by producing an oil study of Emerson. Also on view in this section is an illustration by Oakley that ran in the December 1903 issue of the popular The Century Magazine, depicting heaven as populated entirely by lithe young women in flowing gold and white robes.
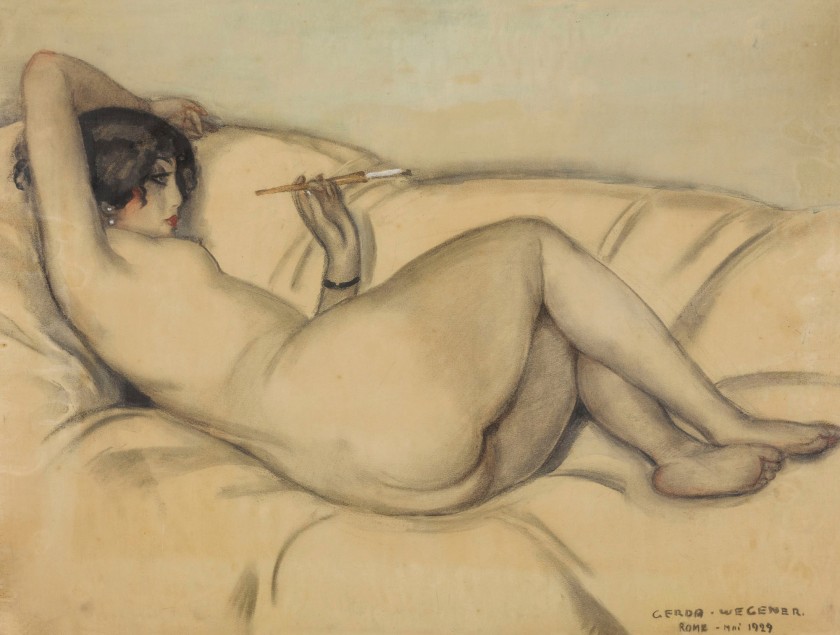
Especially notable in Between Genders is a seductive reclining nude, a painting of one of the first modern transgender women: Gerda Wegener’s Reclining Nude (Lili Elbe), 1929. Nearby, the Russian artist Konstantin Somov’s delicate Portrait of Cécile de Volanges, 1917, appears to portray an 18th-century aristocratic beauty; however, the face is the artist’s own.
Between Genders abounds with photographs documenting the social experiments of the time, including a postcard of the French chanteuse Josephine Baker in male evening attire; the Norwegian Marie Høeg dressed as a man in a variety of carte de visite poses, the calling cards of their day; the French surrealist Claude Cahun in a meditative position with a shaved head looking neither male nor female; and, from across the Atlantic, c. 1890s sepia-toned photographs of an African American man, perhaps once enslaved, performing female drag on the vaudeville stage. A film segment featuring Loïe Fuller performing her legendary Serpentine Dance, 1905, contrasts with another film clip by the Frères Lumière of a male dancer performing the same dance and dressed like Fuller in flowing, billowing robes.
In the section Pose is a famous portrait by the Mexican artist Roberto Montenegro of his friend, the antique and antiquities dealer Chucho Reyes. The limp wrist, the tilted chin, and the amused smile are legible tropes of queer codes even today. As well as picturing Reyes ensconced proudly among his treasures, including an oval miniature of a woman, Montenegro included in the foreground a silver ball reflecting his own visage, thus bringing himself into the picture.
A contrasting note is hit nearby where a recording of “Ma” Rainey’s blues song, “Prove It On Me,” will be played and a vintage advertisement for the vinyl record displayed. Rainey had been arrested for participating in a lesbian sex orgy, a notorious event that she shrewdly parlayed into the #1 best-selling record within the African American community in 1928.
Dr. Katz anchors the exhibition section called Archetypes around an acknowledged masterpiece of American painting, Thomas Eakins’s Salutat,1898. The painting is shown in The First Homosexuals as an example of a scene engineered to focus attention on an erotic part of the young male body. Dr. Katz observes that the crowd appears to be not so much cheering a boxing victory as absorbing a perfect specimen of male beauty.
Throughout this section, the viewer can track the ideal of male beauty evolving beyond the 19th-century ephebic (youthful male beauty idealised in ancient times) to a more masculinised ideal of perfection. A defining work here is a study by Swedish artist Eugène Jansson for his most famous painting, The Naval Bath House, 1907. The custom of young men swimming nude in all-male settings was universal in the West – as seen elsewhere in The First Homosexuals. In this drawing, Jansson carefully employs Cezanne-like strokes to work out seven different poses for as many young men.
The section entitled Desire brings together works of art that are stylistically varied, according to the visual language of the artist’s national culture and training, but alike in depicting same-gender sex or magnifying parts of the body for erotic effect. These include erotica from China, Japan, Iran, and India and a pair of seemingly sedate figure drawings by the French artist Jane Poupelet focusing on the rear view of female models, so as to eroticise women in a way that works to exclude the heterosexual male gaze.
In the section entitled Colonizing, the art on view reflects a number of dynamics, including the Euro-centric definition of early homosexuality, which often clashed with more indigenous forms, and the Western presumption that the East was decadent. European interlopers employed the latter to excuse otherwise forbidden sexual alliances as well as to justify political domination. Here are works as disparate as the Sri Lankan painter David Paynter’s modernist oil, L’après midi, 1935; F. Holland Day’s haunting double exposure photograph, The Vision, (Orpheus Scene), 1907; and a propaganda piece dropped by Japanese nationals into Russian territory to demoralise Russian troops during the Russo-Japanese War.
Following, in the section Public and Private, comes Charles Demuth’s ‘morning after’ scene of three young men in pyjamas and underwear in a stylish domestic interior; lesbian genre scenes set in Eastern Europe; and Marsden Hartley’s Berlin Ante War, 1914, a painting charting life, death, faith, sunrise, and sunset in symbolic forms and colours.
The centrepiece of the final thematic section, Past and Future, is a little-known masterpiece by the Finnish artist, Magnus Enckell, an impressionist-styled painting that reverses the classical myth of Leda and the swan, illustrating a nude man strangling the rapacious figure of Zeus in the form of a swan. Other works here evidence what is likely the earliest use of the rainbow as a symbol of same-sex love; photographs by Wilhelm von Gloeden that combine classical ruins and Sicilian youth; and the desire to acknowledge same-sex precedents in ancient history, as in the colour lithograph, Hadrian and Antinous, 1906, by Paul Avril (Édouard-Henri Avril).
The First Homosexuals documents The Elisarion, a temple to the arts built by the same-sex cultist and visionary Elisar von Kupffer in 1926 in Minusio, a tiny principality in Switzerland. Paintings of scenes illustrating same-sex desire once covered the walls of von Kupffer’s Sanctuarium. A cache of these were discovered recently in a municipal warehouse in Minusio by Dr. Katz and his team. This fall, the paintings will be seen for the first time in documentary photographs. In 2025, the actual large-scale paintings will be exhibited for the first time outside Switzerland in Part II of The First Homosexuals: Depictions of a New Identity, 1869-1930.
Press release from Wrightwood 659
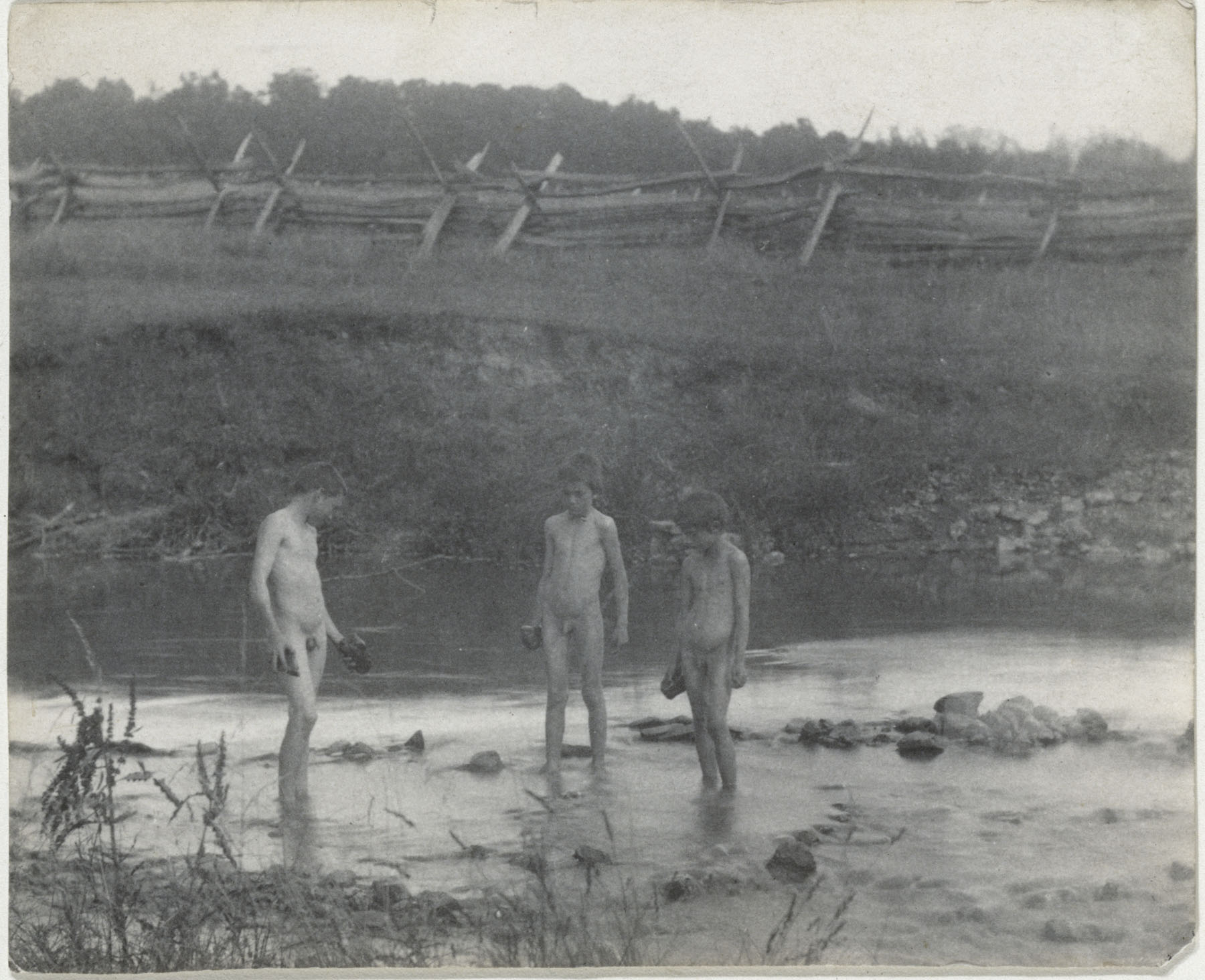
Berg & Høeg (Horten)
Bolette Berg (Norwegian, 1872-1944)
Marie Høeg (Norwegian, 1866-1949)
Untitled [Marie Høeg and her brother in the studio]
c. 1895-1903
Print, 2.4 x 3.1 in
Owner: Preus Museum Collection, Norway
Berg & Høeg (Horten)
Bolette Berg (Norwegian, 1872-1944)
Marie Høeg (Norwegian, 1866-1949)
Marie Høeg dressed as a man
1895-1903
Owner: Preus Museum Collection, Norway
Eugène Jansson (Swedish, 1862-1915)
Bath house study
Nd
Black chalk on paper
33 1/2 x 39 inches
Eugène Fredrik Jansson (18 March 1862, Stockholm – 15 June 1915, Skara) was a Swedish painter known for his night-time land- and cityscapes dominated by shades of blue. Towards the end of his life, from about 1904, he mainly painted male nudes. The earlier of these phases has caused him to sometimes be referred to as blåmålaren, “the blue-painter”. …
After 1904, when he had already achieved success with his Stockholm views, Jansson confessed to a friend that he felt absolutely exhausted and had no more wish to continue with what he had done until then. He stopped participating in exhibitions for several years and went over to figure painting. To combat the health issues he had suffered from since childhood, he became a diligent swimmer and winter bather, often visiting the navy bathhouse, where he found the new subjects for his paintings. He painted groups of sunbathing sailors, and young muscular nude men lifting weights or doing other physical exercises.
Art historians and critics have long avoided the issue of any possible homoerotic tendencies in this later phase of his art, but later studies (see Brummer 1999) have established that Jansson was in all probability homosexual and appears to have had a relationship with at least one of his models. His brother, Adrian Jansson, who was himself homosexual and survived Eugène by many years, burnt all his letters and many other papers, possibly to avoid scandal (homosexuality was illegal in Sweden until 1944).
Text from the Wikipedia website
F. Holland Day (American, 1864-1933)
The Vision (Orpheus Scene)
1907
Platinum print
Florence Carlyle (Canadian, 1864-1923)
The Guest, Venice
1913
Oil on canvas
28.9 x 15 in
Woodstock Art Gallery, Woodstock, Ontario, gift of Lenora McCartney
Photo Credit: John Tamblyn
Florence Carlyle
Florence Carlyle (1864-1923) was a Canadian painter born in Ontario. Carlyle studied painting in Paris beginning in 1890, where she exhibited work at Paris Salons while gaining recognition in Canada and the United States – achievements unusual for women of her time. After Carlyle returned to Canada in 1896, she continued to exhibit widely and contributed artworks to major exhibitions and museum collections. Influenced by the French Barbizon School, Impressionism, and the work of fellow female painters, Carlyle was known for intimate, domestic scenes of middle-class women’s lives.
In 1911, Carlyle traveled to Italy and England, where she met Judith Hastings, who would become her lifelong companion and model. In 1913, Carlyle and Hastings settled in Yew Tree Cottage in East Sussex. The Guest, Venice shows Hastings and Carlyle in conversation at sunset in a scene dominated by warm reds and yellows. The women’s poses and gestures seem to reflect each other – Hastings, seated, invitingly pulls on a long necklace while Carlyle leans comfortably on a windowsill, their complimentary poses suggesting an intimate relationship. The Threshold depicts Hastings as a bride. In place of a groom, Hastings stands across from an empty chair and a vase of flowers, this absence perhaps a subtle allusion to her relationship with Carlyle.
The First Homosexuals: Global Depictions of a New Identity, 1869-1930 is the first exhibition to display Carlyle’s artwork in the context of same-sex desire and relationships.
On view: Self Portrait, c. 1901, Oil on canvas; The Threshold, 1913, Oil on canvas; The Guest, Venice, 1913, Oil on canvas.
Florence Carlyle (Canadian, 1864-1923)
The Threshold
1913
Oil on canvas
117 x 96.5cm
Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Untitled [Self portrait in profile, sitting cross legged]
1920
Gelatin silver print
Claude Cahun and Marcel Moore
Claude Cahun (1894-1954) was a French photographer and writer known for works created in collaboration with their artistic and life partner Marcel Moore (1892-1972), an illustrator for magazines and avant-garde dance and theatre productions. Both artists adopted androgynous names in the 1910s and lived together in Paris by the early 1920s. In Paris, Cahun made theatrical and surrealist self-portraits, often dressing in masculine clothing with a shaved head or short-cropped hair and in elaborate costume, makeup, or masks.
Although Cahun considered themself a surrealist, and their images and writings presaged the 1924 Surrealist Manifesto, they were not aways readily accepted by Surrealist circles who celebrated images of women but rejected female artists. Despite this, many surrealists held Cahun in high regard, including Andre Breton, who recognised Cahun as, “one of the most curious spirits of our time.” Cahun’s 1930 surrealist autobiographical text Aveux non avenus combines non-linear stories and ideas with photomontages and self-portraits. In this text, Cahun also draws connections between their gender-fluid self-portraiture and identity, declaring that “neuter is the only gender that invariably suits me.”
On view: Illustration for Vues et Visions, 1919, Exhibition print; Untitled [Self portrait in profile, sitting cross legged], 1920, Exhibition print.
Anonymous photographer (France)
Untitled [Two Black actors (Charles Gregory and Jack Brown), one in drag, dance together on stage]
c. 1903
Print, 5.5 x 3.5 in
Wellcome Collection
Charles Gregory and Jack Brown
Charles Gregory and Jack Brown were American performing artists credited with introducing the wildly popular Cake-Walk dance to Paris in 1902. The Cake-Walk, which often featured gaudy and ostentatious costumes worn by both men and women, began as a parody of the European “Grand March” performed by Black enslaved people on antebellum Southern plantations. Although the dance was originally performed by and for Black communities, the Cake-Walk became popular with white slaveholders as well, who incorporated the dance into minstrel shows where it would be performed in blackface.
In the late 19th century, the Cake Walk took off as a dance craze, in the United States and Europe. Around the same time, the dance was also adopted by the underground Black queer community. William Dorsey Swann, the first self-proclaimed “queen of drag”, held the first drag balls in Washington, D.C., which featured Cake-Walk dances performed by men in women’s clothing. Drag balls went on to become a mainstay of Black queer and trans expression, becoming popular during the Harlem Renaissance and later in Chicago, Detroit, New Orleans, Washington, D.C., Philadelphia, and San Francisco. This film of Jack Brown and Charles Gregory is the first extant drag film, produced by those famed early innovators in cinema, the Lumière Brothers.
On view: Unknown artist, Le cake-walk. Dansé au Nouveau Cirque. Les nègres [Two black actors, Charles Gregory and Jack Brown, one in drag, dancing the Cake-Walk in Paris], 1903, Exhibition print; Untitled [Two black actors (Charles Gregory and Jack Brown), one in drag, dance together on stage], c. 1903, Exhibition print; Auguste and Louis Lumière, Nègres, [I], c. 1902-1903, Digital reproduction of film.
Nègres, [I] (1903) Lumière [incomplete]
Gerda Wegener (Danish, 1885-1940)
Venus and Amor
Nd
Oil on canvas
81 by 116cm (31 3/4 by 45 3/4in.)
Gerda Wegener (Danish, 1885-1940)
Reclining Nude (Lili Elbe)
1929
Watercolour on paper
20.8 x 26.9 in
The Shin Collection, New York
Image Courtesy of Shin Gallery, New York
Gerda Wegener and Lili Elbe
Gerda Wegener (1885-1940) and Lili Elbe (1882-1931) were Danish artists active in the early 20th century. The two met while students at the Royal Danish Academy of Fine Arts where Elbe was known by her birth name Einar Wegener. The couple married in 1904 and both worked as artists. Wegener was known for her illustrations, including female same-sex erotica; Elbe produced landscape paintings.
Lili Elbe began to understand herself as a woman as early as 1904. In 1912, Elbe and Wegener moved from Copenhagen to Paris, where Elbe openly dressed and identified as a woman. Throughout their partnership, Elbe was a favoured muse of Wegener and modelled for many of her paintings, including Art Deco and Art Nouveau images of the independent “New Woman.” Many of Wegener’s images depict female characters in erotic or homosocial environments – in the case of Venus and Amor, feminine and androgynous figures populate an idyllic allegorical scene. In 1930, Elbe traveled to Germany for the first of four sex reassignment surgeries, which was completed under the supervision of physician Magnus Hirschfeld, who had coined the term “transsexual” in 1923. Elbe died from complications of a fourth surgery in 1931.
In 2000, David Ebershoff depicted Wegener and Elbe’s relationship in his book The Danish Girl, which was adapted into a film in 2015.
On view: Lili Elbe (Einar Wegener), An Autumn Day at Bassin de Flore at Versailles, 1917, Oil on canvas; Gerda Wegener, Reclining Nude (Lili Elbe), 1919, Watercolour; Gerda Wegener, Venus and Amor, c. 1920, Oil on canvas; Gerda Wegener, Ulla Poulsen (Ballerina), c. 1927, Oil on canvas; Gerda Wegener, Erotic Scene, Ink and watercolour on paper.
Lili Elbe (Einar Wegener) (Danish, 1882-1931)
An Autumn Day at Bassin de Flore at Versailles
1917
Oil on canvas
Height: 61cm (24 in); width: 81cm (31.8 in)
Gerda Wegener (Danish, 1885-1940)
The Ballerina Ulla Poulsen in the Ballet Chopiniana
Paris, 1927
Oil on canvas
Konstantin Somov (Russian, 1869-1939)
Portrait of Cécile de Volanges
1934
Pencils on paper
Konstantin Somov
Konstantin Somov (1869-1939) was a Russian painter and a leading figure in the inter-disciplinary artistic movement and eponymous journal Mir iskusstva (World of Art), active from 1897 to the mid-1920s. Somov often depicted doll-like harlequin characters, women wearing masks, and French Rococo-style costume in his work. Some of these romantic or erotic compositions reference works by Aubrey Beardsley, an English illustrator who also evoked erotic masquerades in his artwork.
In Somov’s scenes, costumes often obscure the gender of couples engaging in romantic activity and reference an excessive game of love and emotion – a theme common to other artists associated with the Decadent movement and Russian Symbolism. Somov was also known for portraying women as ugly or masculine in images he described as encapsulating his frustration with his own same-sex attraction. Along with his erotic scenes, Somov painted male nudes and portraits of his close friends and partners. Somov also adopted the rainbow as a reference to homosexuality via the story of the biblical flood, in which the rainbow represents absolution and acceptance after divine punishment for corporeal sin.
On view: Standing Male Model from Back, 1896, Crayons and sauce-crayon on paper; A Shepard and a Dog, 1898, Exhibition print; Pierrot and Lady (The Fireworks), 1910, Watercolours and whitewash on paper; Les Tribades illustration for Le Livre de la Marquise, Watercolours and zincography on paper; Landscape with Rainbows, 1915, Oil on canvas; Portrait of Cécile de Volanges, 1917, Pencils on paper.
Konstantin Somov (Russian, 1869-1939)
Pierrot and Lady (The Fireworks)
1910
Watercolours and whitewash on paper
46 × 35cm
Lionel Wendt (Sri Lankan, 1900-1944)
Nude with a light bulb
c. 1935
Gelatin silver print
Lionel Wendt
Lionel Wendt (1900-1944) was a photographer, pianist, critic, and filmmaker born in Ceylon (modern-day Sri Lanka) to a Burgher father and a Sinhalese mother. As a young man, Wendt traveled to London, where he studied music and earned a law degree. In 1924, Wendt returned to Ceylon and became associated with prominent artists including Geoffrey Beyling, Ivan Peries, and George Keyt, with whom he founded the 43 Group. Recognised as the first modern art group in Ceylon, the 43 Group promoted artwork that departed from academic style and colonial tradition in favour of free expression.
Wendt is known for his photographs of Sinhalese subjects, documentation of indigenous ways of life, intimate portraits, and his experimental images, which deployed techniques the artist observed in Surrealist photography. Some of these images use photography to complicate the act of viewing or trouble the cohesion of Wendt’s subject. For example, Wendt’s Nude with a light bulb (c. 1935) deals with the concept of exposure in multiple registers. The image’s composition alternately exposes the male body and refuses identification, perhaps commenting on the alternately public and private nature of homosexuality. The image also references the techniques of photography itself; a single lightbulb literally exposes a domestic interior to reveal an assembly of jars, pitchers, and timer-tools; items often present in a dark room where a photographer makes an “exposure” of a negative to produce a print.
On view: Nude with a light bulb, c. 1935, Gelatin silver print.
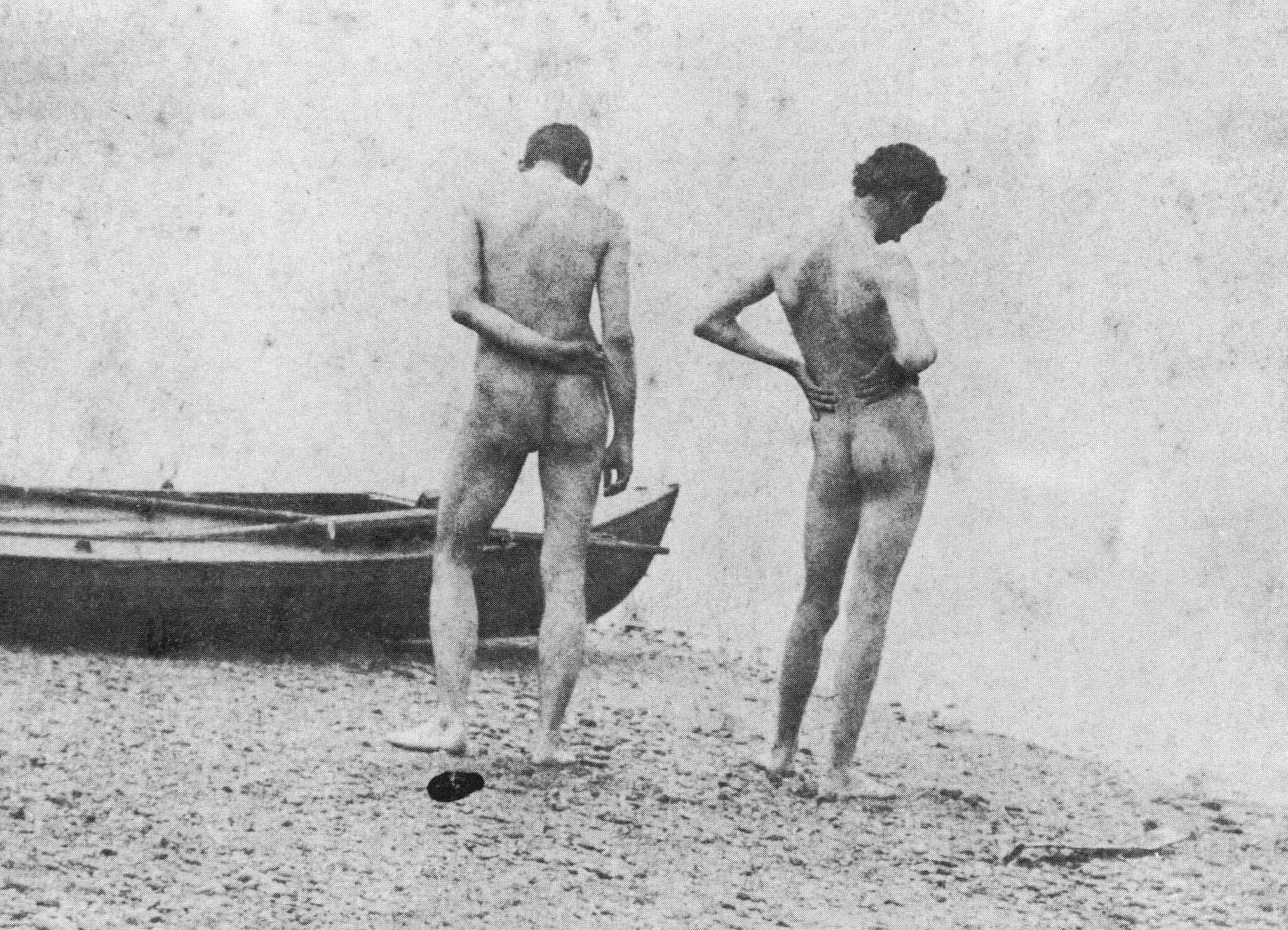
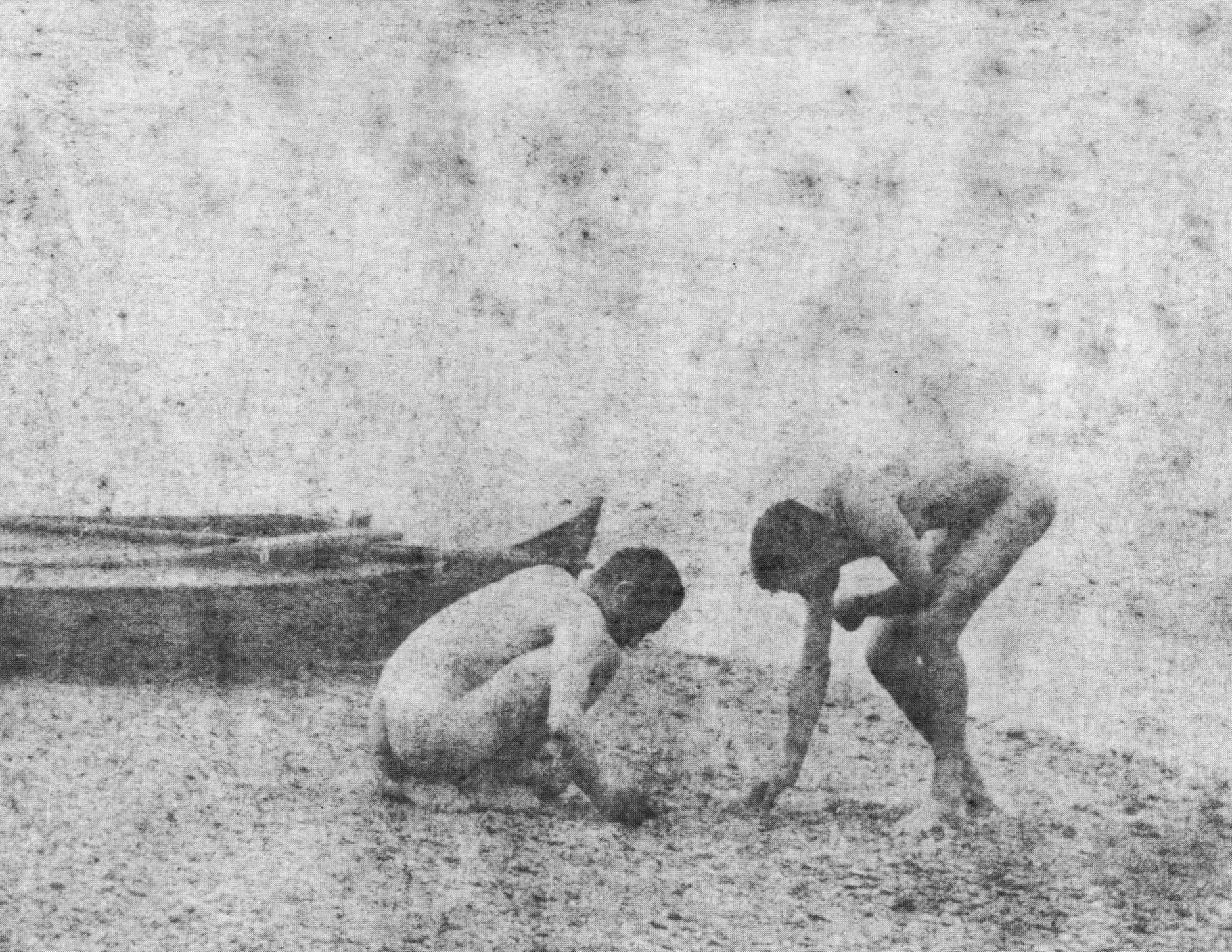
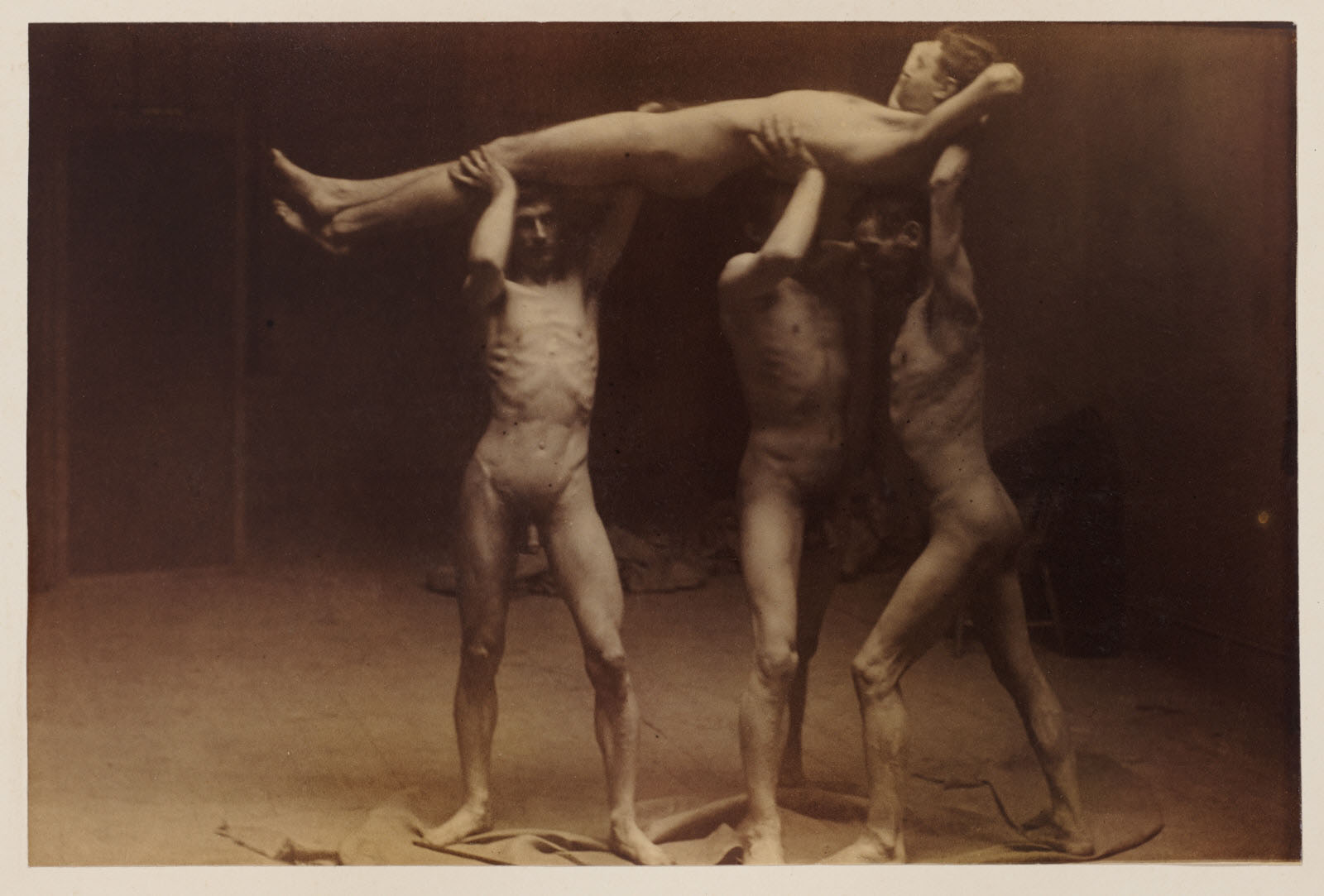
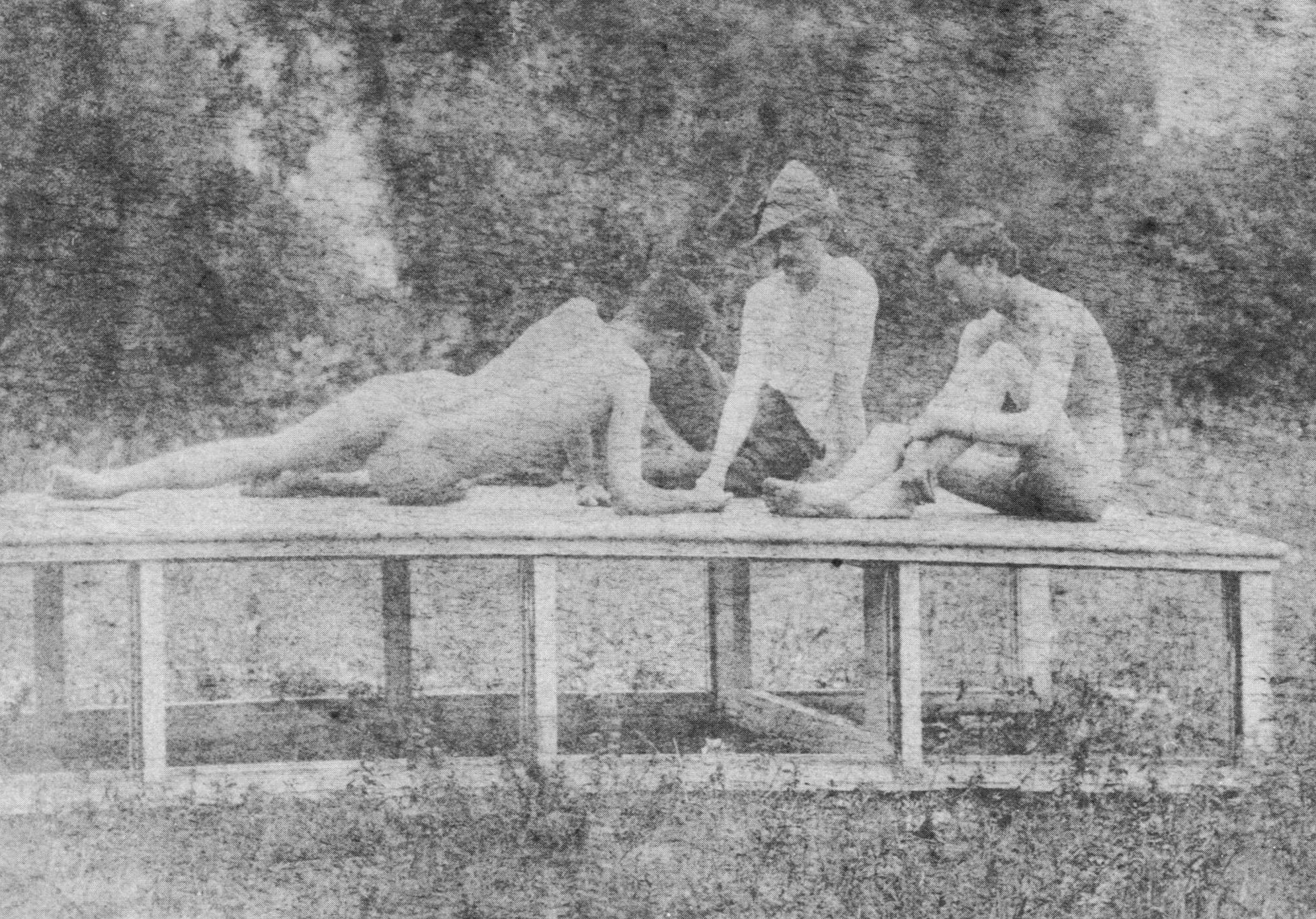
Circle of Eakins
Thomas Eakins and students, swimming nude
c. 1883
Platinum print
8 15/16 x 11 1/16 in. (22.7 x 28.1cm)
Courtesy of the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts, Philadelphia
Charles Bregler’s Thomas Eakins Collection, purchased with the partial support of the Pew Memorial Trust
Thomas Cowperthwait Eakins (July 25, 1844 – June 25, 1916) was an American realist painter, photographer, sculptor, and fine arts educator. He is widely acknowledged to be one of the most important American artists.
For the length of his professional career, from the early 1870s until his health began to fail some 40 years later, Eakins worked exactingly from life, choosing as his subject the people of his hometown of Philadelphia. He painted several hundred portraits, usually of friends, family members, or prominent people in the arts, sciences, medicine, and clergy. Taken en masse, the portraits offer an overview of the intellectual life of contemporary Philadelphia; individually, they are incisive depictions of thinking persons.
In addition, Eakins produced a number of large paintings that brought the portrait out of the drawing room and into the offices, streets, parks, rivers, arenas, and surgical amphitheaters of his city. These active outdoor venues allowed him to paint the subject that most inspired him: the nude or lightly clad figure in motion. In the process, he could model the forms of the body in full sunlight, and create images of deep space utilising his studies in perspective. Eakins also took a keen interest in the new technologies of motion photography, a field in which he is now seen as an innovator.
No less important in Eakins’ life was his work as a teacher. As an instructor he was a highly influential presence in American art. The difficulties which beset him as an artist seeking to paint the portrait and figure realistically were paralleled and even amplified in his career as an educator, where behavioural and sexual scandals truncated his success and damaged his reputation.
Eakins was a controversial figure whose work received little by way of official recognition during his lifetime. Since his death, he has been celebrated by American art historians as “the strongest, most profound realist in nineteenth- and early-twentieth-century American art”. …
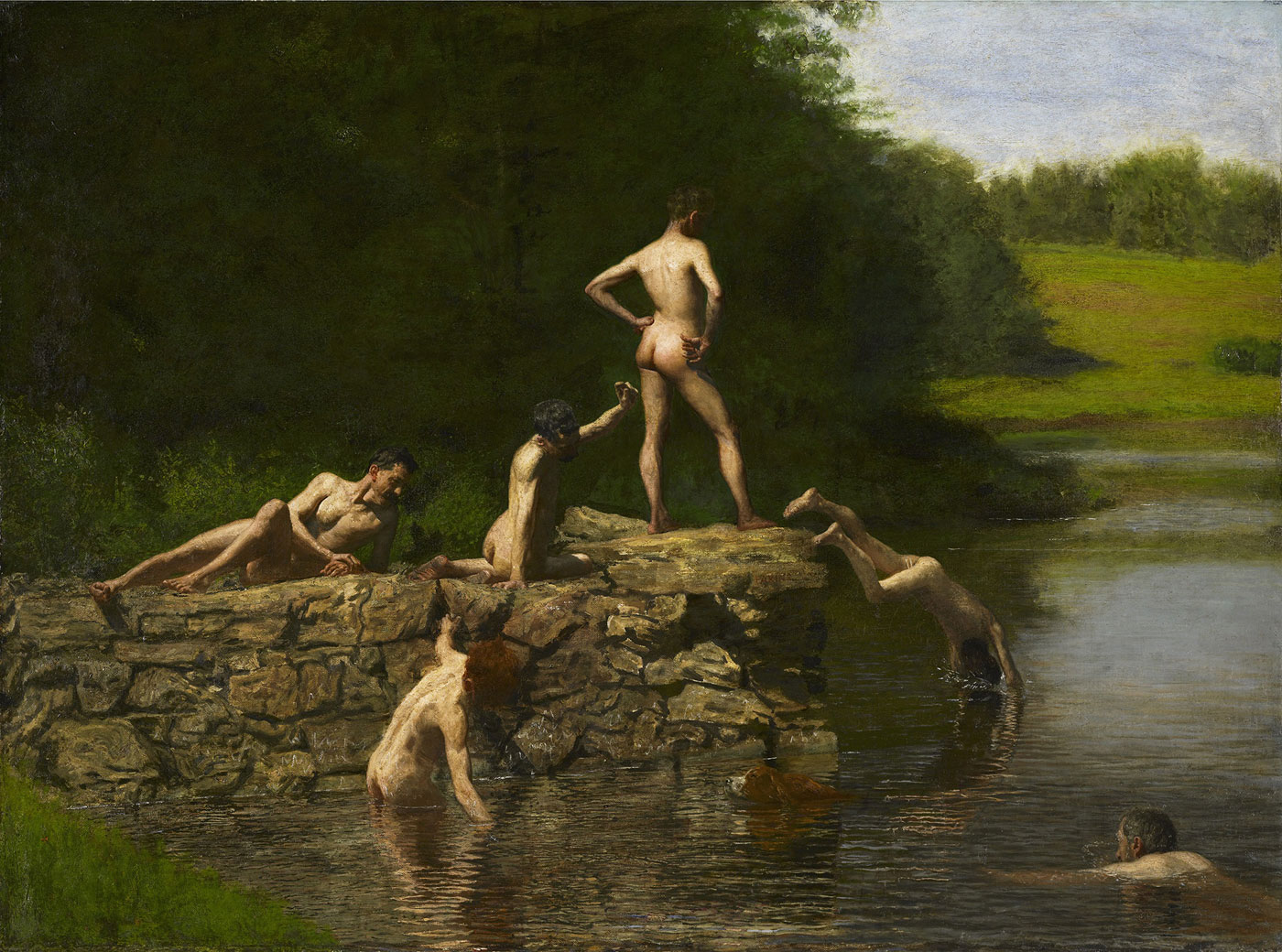
The Swimming Hole (1884-1885) features Eakins’ finest studies of the nude, in his most successfully constructed outdoor picture. The figures are those of his friends and students, and include a self-portrait. Although there are photographs by Eakins which relate to the painting, the picture’s powerful pyramidal composition and sculptural conception of the individual bodies are completely distinctive pictorial resolutions. The work was painted on commission, but was refused.
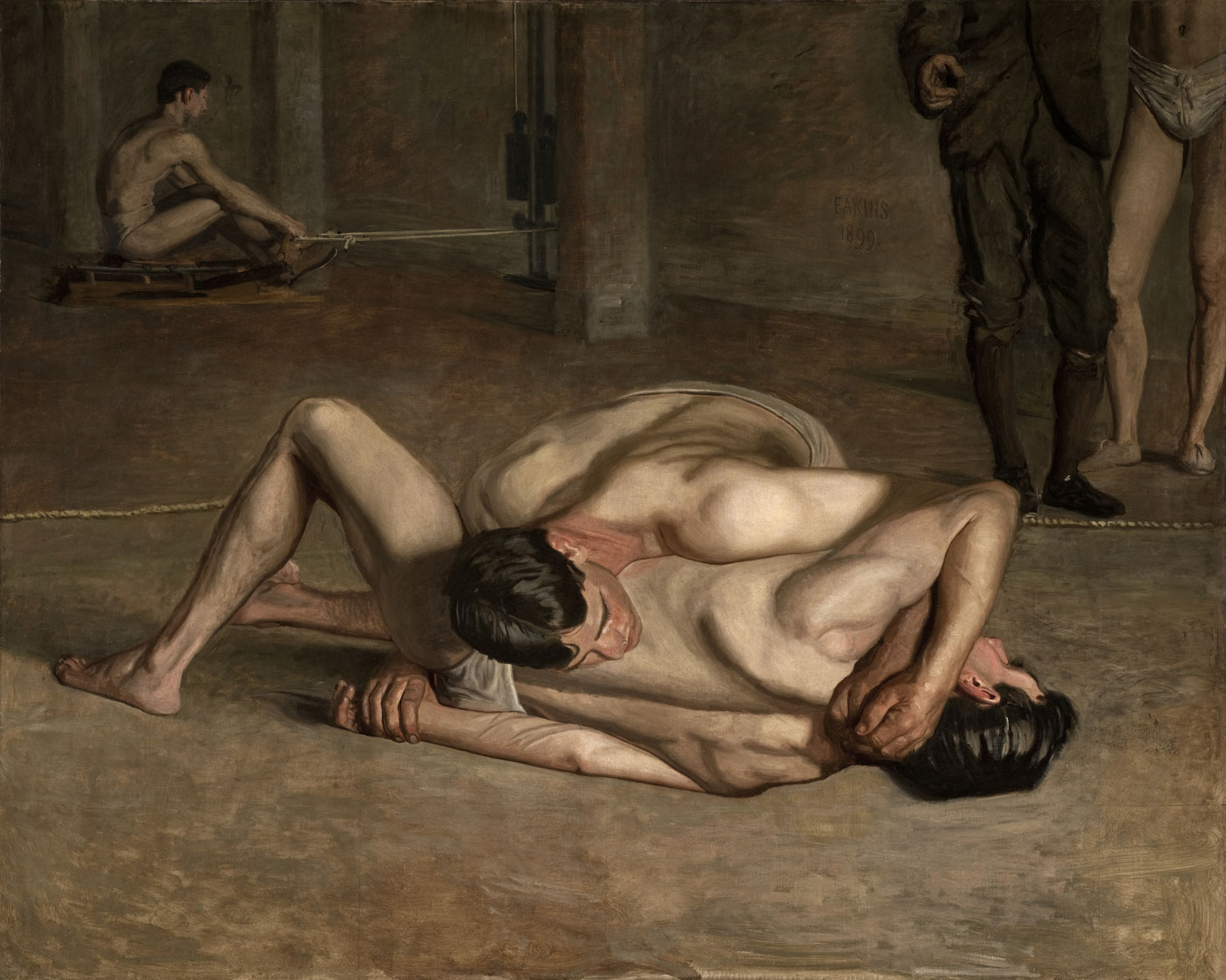
In the late 1890s Eakins returned to the male figure, this time in a more urban setting. Taking the Count (1896), a painting of a prizefight, was his second largest canvas, but not his most successful composition. The same may be said of Wrestlers (1899). More successful was Between Rounds (1899), for which boxer Billy Smith posed seated in his corner at Philadelphia’s Arena; in fact, all the principal figures were posed by models re-enacting what had been an actual fight. Salutat (1898), a frieze-like composition in which the main figure is isolated, “is one of Eakins’ finest achievements in figure-painting.” …
Personal life and marriage
The nature of Eakins’ sexuality and its impact on his art is a matter of intense scholarly debate. Strong circumstantial evidence points to discussion during Eakins’s lifetime that he had homosexual leanings, and there is little doubt that he was attracted to men, as evidenced in his photography, and three major paintings where male buttocks are a focal point: The Gross Clinic, Salutat, and The Swimming Hole. The last, in which Eakins appears, is increasingly seen as sensuous and autobiographical.
Until recently, major Eakins scholars persistently denied he was homosexual, and such discussion was marginalised. While there is still no consensus, today discussion of homoerotic desire plays a large role in Eakins scholarship. The discovery of a large trove of Eakins’ personal papers in 1984 has also driven reassessment of his life.
Text from the Wikipedia website
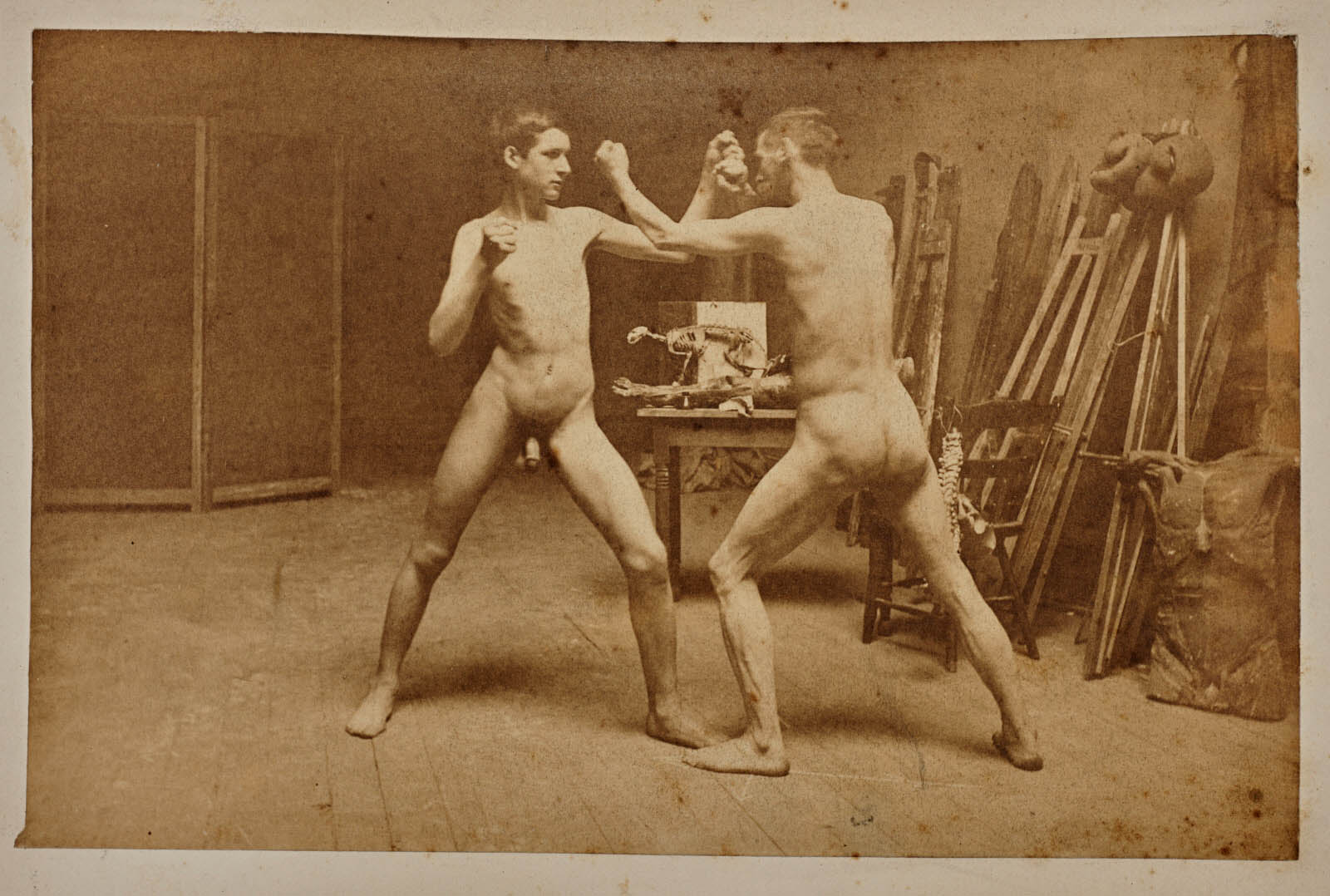
Salutat, Between Rounds (a portion of which was executed separately as Billy Smith) and Taking the Count are a series of three large boxing paintings done by Eakins. The former two depict events surrounding a boxing match that took place on April 22, 1898. Featherweight Tim Callahan fought featherweight Billy Smith in a match that was close until the final round, when Callahan gained the advantage and won the fight. However, for Salutat, Eakins chose to depict Smith as the winner. In the work, Smith raises his hand to salute the audience, in the style of a gladiator. On the painting’s original frame Eakins carved the words “DEXTRA VICTRICE CONCLAMANTES SALVTAT” (With the victorious right hand, he salutes those shouting [their approval]).
As with a number of other Eakins works, the rendering of the figures is extremely precise, such that it has allowed art historians to identify individual members of the audience. While working on the boxing pictures, friends would visit the studio, and Eakins invited them to “stay a while and I’ll put you in the picture.” For Salutat, audience members include Eakins’s friend Louis Kenton (wearing eyeglasses and a bow tie), sportswriter Clarence Cranmer (wearing a bowler hat), David Jordan (brother of Letitia Wilson Jordan, whom Eakins painted in Portrait of Letitia Wilson Jordan), photographer Louis Husson (next to Jordan), Eakins’s student Samuel Murray, and Eakins’s father Benjamin Eakins.
Smith is bathed in soft white light, which illuminates his muscles. Amid a general tonality of warm greys and browns that contains no strong chromatic notes, the skin tones of the three main figures are pale. All three men have the quality of relief sculpture, and with Smith’s figure separate from those of his seconds, they appear to move across the canvas in an arrangement reminiscent of a frieze.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Thomas Eakins (American, 1844-1916)
Salutat
1898
Oil on canvas
50 in. x 40 in. (127 cm x 101.6cm)
Addison Gallery of American Art, Phillips Academy, Andover, Massachusetts, gift of anonymous donor
Replica of Thomas Eakins’ original frame created and given as a partial gift by Eli Wilner & Company with the additional support of Maureen Barden and David Othmer
Katz told Windy City Times that being defined as a homosexual “was both a gift and a problem” for queer people during those years, depending on how the word affected their daily lives. For some, it clarified who they were and that was a benefit to them while for others their sexual possibilities were limited otherwise people would define them as a homosexual.
“The reason this is important is previously same-sex desire was understood not as a noun but as a verb,” said Katz. “It was something you did, not something you are. What we are trying to do is assess what happens after the identity category was created and a group of people fell under that name. The important theoretical point I am trying to make is that as language grew increasingly strict and binary, the menu of sexual and gender possibilities that was open to everybody grew increasingly constricted. What resulted out of that is as language became increasingly impoverished regarding sexuality and gender, art took up the slack. Art started to represent all sorts of sexual possibilities that language could no longer understand or name.” …
“These works will be looked at not just in the Euro-American frame, but in a global frame,” said Katz. “We are also assessing how, for example, following the lines of colonial domination European ideas were imposed over more local sexual definitions and names. What we have really is the first imaging of the first homosexuals. What is remarkable about this is some of these are among the most famous paintings among the most famous painters in their respective regions, but they have not been gathered under this rubric. The images are known, they just have not been interpreted in this way.” …
“This show resolutely demonstrates that we, as queer people, have a history, too – a rich, complex history that has been left out of the prevailing accounts of art history,” said Willis. “Too often we hear the accusation that queer, trans, and non-binary identities are something ‘new,’ and thus something without a history. The exhibition shuts down any such allegation, resurfacing this ‘lost’ generation of modern LGBTQ ancestry.” …
“I think this exhibition will begin to open up or underscore the way in which our language of binaries is way too delimited and poor of frame to understand the complexities of human behavior,” said Katz. “What this show does, and what art is great at because it does not have to use language, is depict all these variations. You will see therefore a range of possibilities of gender and sexual desire that our language does not have words for.”
Carrie Maxwell. “Jonathan D. Katz previews his upcoming ‘First Homosexuals’ exhibit,” on the Windy City Times website 17th September 2022 [Online] Cited 05/11/2022
Louise Abbéma (French, 1853-1927)
Sarah Bernhardt et Louise Abbéma sur un lac
1883
Oil on canvas
63 x 82.7 x 1.2 in (framed)
Collections Comédie-Française
Louise Abbéma (30 October 1853 – 29 July 1927) was a French painter, sculptor, and designer of the Belle Époque. …
She was a regular exhibitor at the Paris Salon, where she received an honourable mention for her panels in 1881. Abbéma was also among the female artists whose works were exhibited in the Women’s Building at the 1893 World Columbian Exposition in Chicago. A bust Sarah Bernhardt sculpted of Abbéma was also exhibited at the exposition.
Abbéma specialised in oil portraits and watercolours, and many of her works showed the influence from Chinese and Japanese painters, as well as contemporary masters such as Édouard Manet. She frequently depicted flowers in her works. Among her best-known works are The Seasons, April Morning, Place de la Concorde, Among the Flowers, Winter, and portraits of actress Jeanne Samary, Emperor Dom Pedro II of Brazil, Ferdinand de Lesseps, and Charles Garnier. …
New Woman
As educational opportunities were made more available in the 19th century, women artists became part of professional enterprises, including founding their own art associations. Artwork made by women was considered to be inferior, and to help overcome that stereotype women became “increasingly vocal and confident” in promoting women’s work, and thus became part of the emerging image of the educated, modern and freer “New Woman”. Artists then, “played crucial roles in representing the New Woman, both by drawing images of the icon and exemplifying this emerging type through their own lives,” including Abbéma who created androgynous self-portraits to “link intellectual life through emphasis on ocularity”. Many other portraits included androgynously dressed women, and women participating in intellectual and other pastimes traditionally associated with men.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Marsden Hartley (American, 1877-1943)
Berlin Ante War
1914
Oil on canvas with painted wood frame
34 x 43 in.
Columbus Museum of Art, Ohio: gift of Ferdinand Howald
“Berlin Ante War” (1914), or “Prewar,” explores the profound impact the city had on the artist.
Marsden Hartley (January 4, 1877 – September 2, 1943) was an American Modernist painter, poet, and essayist. Hartley developed his painting abilities by observing Cubist artists in Paris and Berlin. …
German sympathies
In April 1913 Hartley relocated to Berlin, the capital of the German Empire where he continued to paint, and became friends with the painters Wassily Kandinsky and Franz Marc. He also collected Bavarian folk art. His work during this period was a combination of abstraction and German Expressionism, fuelled by his personal brand of mysticism. Many of Hartley’s Berlin paintings were further inspired by the German military pageantry then on display, though his view of this subject changed after the outbreak of World War I, once war was no longer “a romantic but a real reality”.
Two of Hartley’s Cézanne-inspired still life paintings and six charcoal drawings were selected to be included in the landmark 1913 Armory Show in New York.
In Berlin, Hartley developed a close relationship with a Prussian lieutenant, Karl von Freyburg, who was the cousin of Hartley’s friend Arnold Ronnebeck. References to Freyburg were a recurring motif in Hartley’s work, most notably in Portrait of a German Officer (1914). Freyburg’s subsequent death during the war hit Hartley hard, and he afterward idealised their relationship. Many scholars interpreted his work regarding Freyburg as embodying homosexual feelings for him. Hartley lived in Berlin until December 1915.
Hartley returned to the U.S. from Berlin as a German sympathiser following World War I. Hartley created paintings with much German iconography. The homoerotic tones were overlooked as critics focused on the German point of view. According to Arthur Lubow, Hartley was disingenuous in arguing that there was “no hidden symbolism whatsoever”. …
Hartley was not overt about his homosexuality, often redirecting attention towards other aspects of his work. Works such as Portrait of a German Officer and Handsome Drinks are coded. The compositions honour lovers, friends, and inspirational sources. Hartley no longer felt unease at what people thought of his work once he reached his sixties. His figure paintings of athletic, muscular males, often nude or garbed only in briefs or thongs, became more intimate, such as Flaming American (Swim Champ), 1940 or Madawaska – Acadian Light-Heavy – Second Arrangement (both from 1940). As with Hartley’s German officer paintings, his late paintings of virile males are now assessed in terms of his affirmation of his homosexuality.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Duncan Grant (British, 1885-1978)
Bathers at the Pond
1920-1921
Oil on canvas
35 x 19 in.
© Estate of Duncan Grant. All rights reserved, DACS London / ARS, New York
Duncan James Corrowr Grant (21 January 1885 – 8 May 1978) was a British painter and designer of textiles, pottery, theatre sets and costumes. He was a member of the Bloomsbury Group.
Frances Hodgkins (New Zealand, 1869-1947)
Friends (Double Portrait) [Hannah Ritchie and Jane Saunders]
1922-1923
Oil on canvas
24 x 30.3 in.
Hocken Collections, Uare Taoka o Hākena, University of Otago
Frances Mary Hodgkins (28 April 1869 – 13 May 1947) was a New Zealand painter chiefly of landscape and still life, and for a short period was a designer of textiles. She was born and raised in New Zealand, but spent most of her working life in England. She is considered one of New Zealand’s most prestigious and influential painters, although it is the work from her life in Europe, rather than her home country, on which her reputation rests.
Hannah Ritchie and Jane Saunders were artists and taught art at the Manchester Girls High School. They were friends and supporters of artist Frances Hodgkins.
There is in Hodgkins’s life, however, evidence of an unconventional existence, supported, populated, and propelled by a roll call of LGBTQI+ people, including: Jane Saunders, Hannah Ritchie, Amy Krause, Dorothy Selby, Arthur Lett Haines, Cedric Morris, Norman Notley, David Brynley, Geoffrey Gorer, Christopher Wood, Philip and Lady Ottoline Morrell, Duncan Grant … and many more. While this is not proof that Hodgkins was a lesbian (if that should even be necessary), it signals an openness to a queer world – its people and their relationships – that makes for a fascinating investigation. …
In the early-to-mid-1920s, she lived off and on with lesbian partners Jane Saunders and Hannah Ritchie. These were desperate years for Hodgkins. Ritchie and Saunders housed and fed her, and gave her financial support in the form of an allowance. When Hodgkins was seriously thinking of returning to New Zealand, they gave her reason to stay in the United Kingdom. …
Ritchie and Saunders, both students of Hodgkins since 1911 and 1912, drew her into their milieu of influential literary and artistic friends. Their network included Forrest Hewit, chairman of the Calico Printers’ Association who helped her secure a job as a designer on a salary of £500 a year. The job-offer came just a month before Hodgkins was due to return home to New Zealand and changed the course of her life forever.
Joanne Drayton. “Frances Hodgkins: A portrait of queer love,” on the Te Papa Tongarewa website Nd [Online] Cited 06/11/2022
Unknown photographer
Hannah Richie, Frances Hodgkins, and Jane Saunders seated in a garden
c. 1925
Cellulose triacetate copy negative
12.5 x 10cm
National Library of New Zealand
Please note: Photograph not in exhibition
Curator of The First Homosexuals: Global Depictions of a New Identity, 1869-1930, Jonathan D. Katz, discusses Berlin Ante War by Mardsen Hartley.
Videography by Steve Rosofsky
Curator of The First Homosexuals: Global Depictions of a New Identity, 1869-1930, Jonathan D. Katz, discusses Salutat by Thomas Eakins.
Videography by Steve Rosofsky.
Introductory clip: A Representation of Loïe Fuller and her “Serpentine Dance” produced by Pathé Frères in 1905.
Curator of The First Homosexuals: Global Depictions of a New Identity, 1869-1930, Jonathan D. Katz, discusses the work of Louise Abbéma.
Videography by Steve Rosofsky.
Wrightwood 659
659 W. Wrightwood
Chicago, IL 60614
Opening hours:
Friday 12 – 7pm
Saturday 10am – 5pm






![Marie Høeg (Norwegian, 1866-1949) 'Untitled [Marie Høeg and her brother in the studio]' c. 1895-1903 Marie Høeg (Norwegian, 1866-1949) 'Untitled [Marie Høeg and her brother in the studio]' c. 1895-1903](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/image-10_berghoeg-c.-1895-1903.jpg?w=650&h=1014)





![Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954) 'Untitled [Self portrait in profile, sitting cross legged]' 1920 Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954) 'Untitled [Self portrait in profile, sitting cross legged]' 1920](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/claude-cahun-self-portrait-in-profile-sitting-cross-legged-1920.jpg?w=650&h=825)
![Anonymous photographer (France). 'Untitled [Two Black actors (Charles Gregory and Jack Brown), one in drag, dance together on stage]' c. 1903 Anonymous photographer (France). 'Untitled [Two Black actors (Charles Gregory and Jack Brown), one in drag, dance together on stage]' c. 1903](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/image-7_untitled-two-black-actors....jpg?w=650&h=989)












![Frances Hodgkins (New Zealand, 1869-1947) 'Friends (Double Portrait)' [Hannah Ritchie and Jane Saunders] 1922-1923 Frances Hodgkins (New Zealand, 1869-1947) 'Friends (Double Portrait)' [Hannah Ritchie and Jane Saunders] 1922-1923](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/image-13_frances-hodgkins-friends-double-portrait.jpg?w=840)



















You must be logged in to post a comment.