Exhibition dates: 15th June, 2018 – 2nd June, 2019
Curator: Ann Shumard, Senior Curator of Photographs at the Smithsonian National Portrait Gallery, Washington, DC
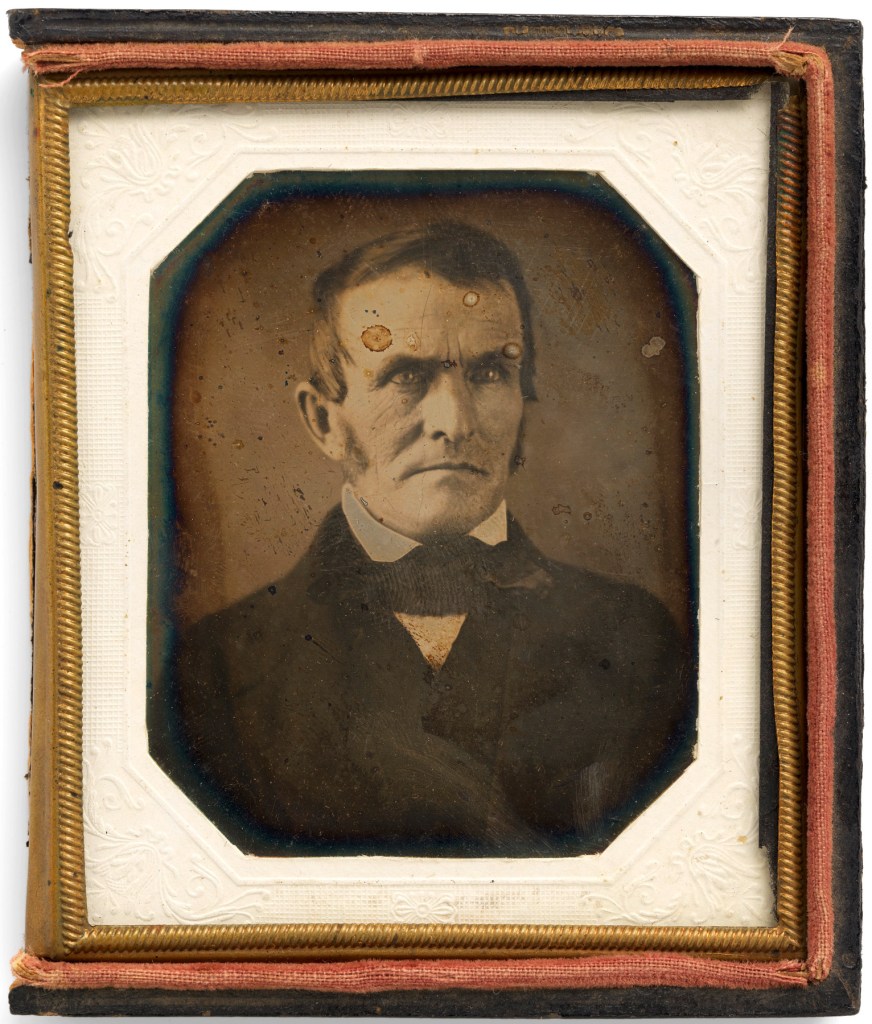

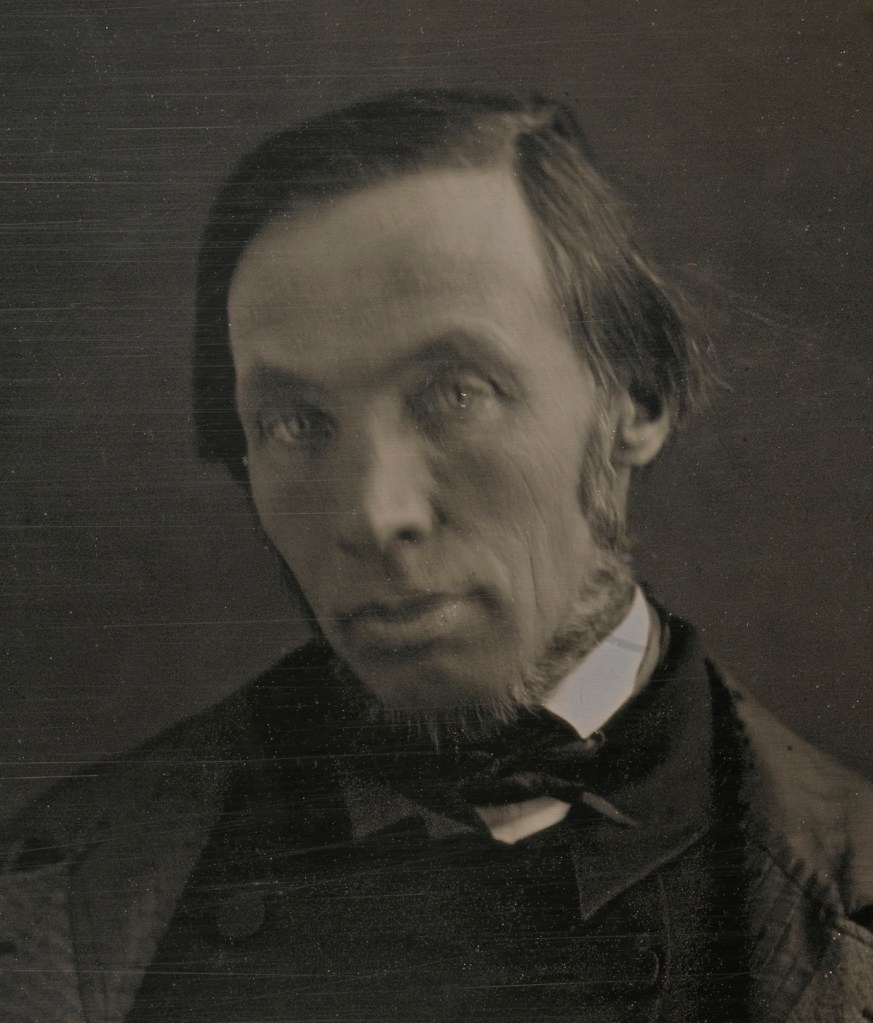
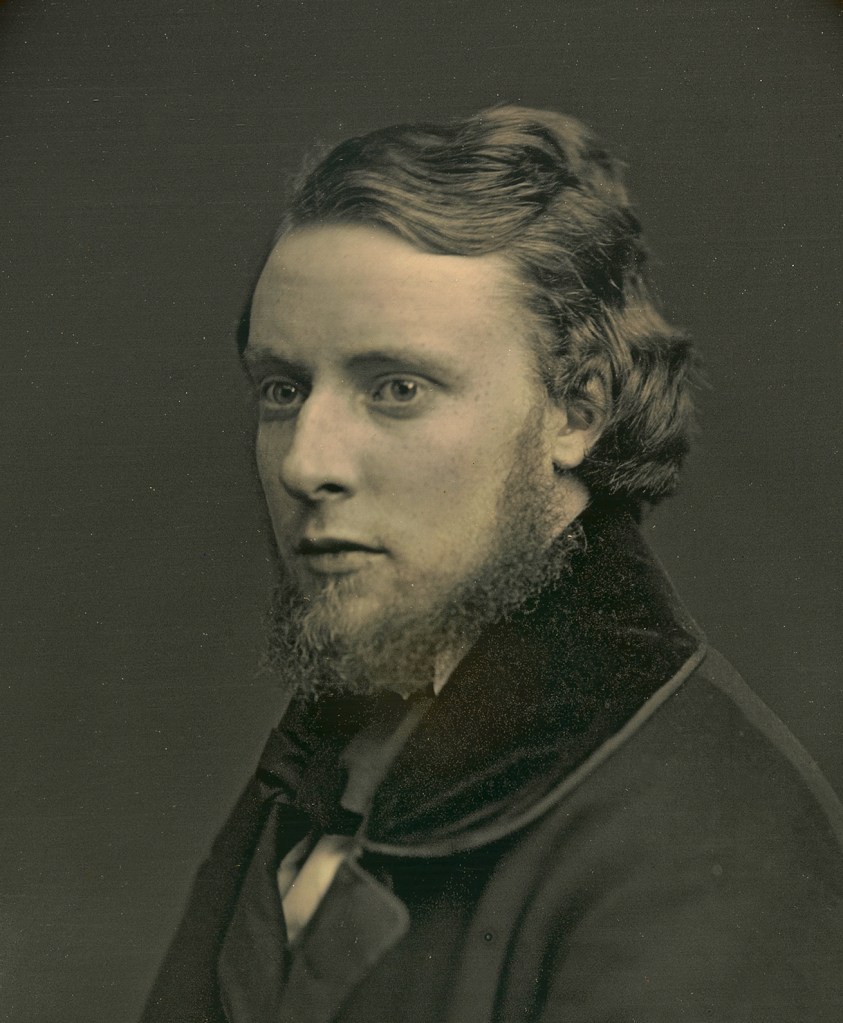
Bishop & Gray Studio (American, active c. 1843)
Dr. Rufus Priest
c. 1843
Sixth-plate daguerreotype
8.3cm x 7cm (3 1/4″ x 2 3/4″)
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution; gift of David Becker
What strong faces these people have, especially in the three-quarter or slightly oblique profile view with the subject not staring at the camera.
There is something incredibly powerful about these one off, cased mausoleum portraits that today’s throwaway representations struggle to match. As Montgomery P. Simons opines, “The delicacy, durability and wonderful minutiae of the daguerreotype has never been approached by any of the improved pictures recently introduced.” The contemporary Philadelphia daguerreotypist Marcus Aurelius Root paid them this praise: “Their style, indeed, is peculiar to themselves; presenting beautiful effects of light and shade, and giving depth and roundness together with a wonderful softness or mellowness. These traits have achieved for them a high reputation with all true artists and connoisseurs.” Indeed, their jewel-like aura seems to emanate from within.
I have added bibliographic details about the sitters and the photographers where possible to the posting, as well as artwork – paintings, illustrations, writing, postcards and drawings – and enlarged details of the daguerreotypes. Pictured are the great and good of the land. Surgeon, cardinal, poet, artist, actress, entrepreneur, president, social reformer, general, commodore, nurse and advocate for the mentally ill with minimal acknowledgement of Native American people (Seneca Chief Governor Blacksnake). This “man of rare intellectual and moral power” died on a reservation in December 1859.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Smithsonian National Portrait Gallery for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.

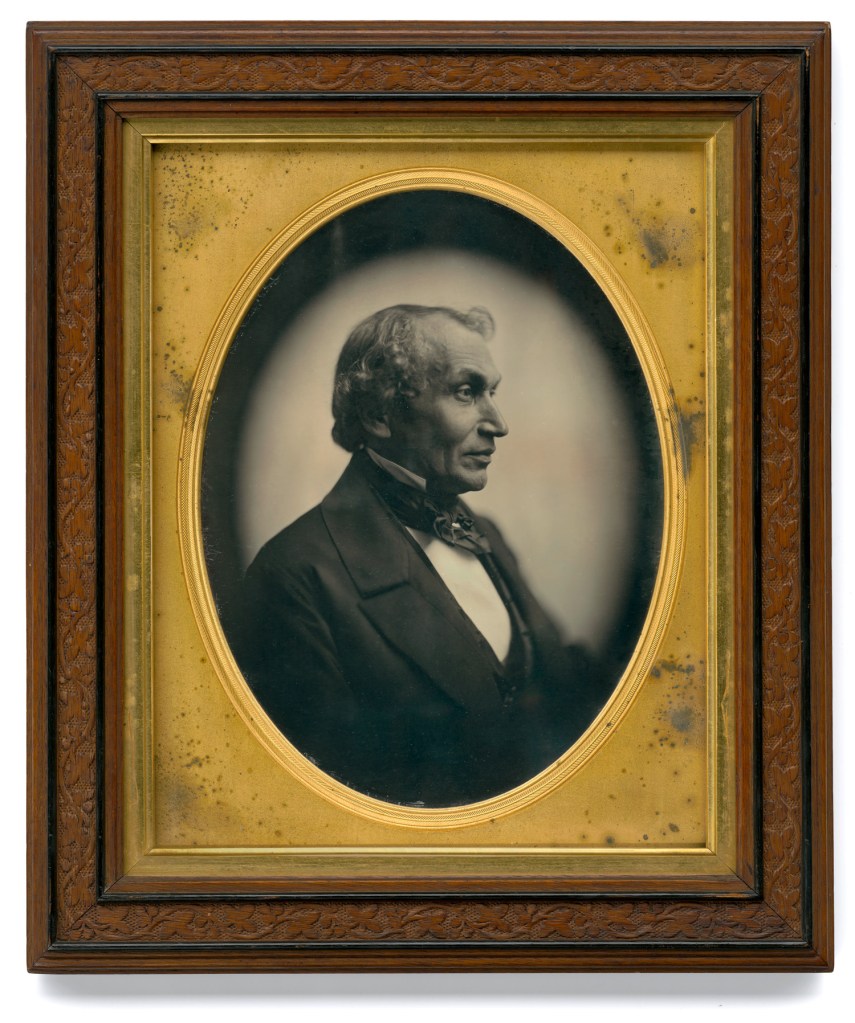
Marcus Aurelius Root (American, 1808-1888)
Thomas Buchanan Read (March 12, 1822 – May 11, 1872)
c. 1850
Half-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution; gift of Miss Eunice Chambers
Thomas Buchanan Read (American, 1822-1872)
Thomas Buchanan Read (March 12, 1822 – May 11, 1872), was an American poet and portrait painter. Read was born in Corner Ketch, a hamlet close to Downingtown, in Chester County, Pennsylvania on March 12, 1822.
Beside painting, Read wrote a prose romance, The Pilgrims of the Great St. Bernard, and several books of poetry, including The New Pastoral, The House by the Sea, Sylvia, and A Summer Story. Some of the shorter pieces included in these, e.g., Sheridan’s Ride, Drifting, The Angler, The Oath, and The Closing Scene, have great merit. Read was briefly associated with the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. His greatest artistic popularity took place in Florence. Among portraits he painted were Abraham Lincoln, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, Alfred Tennyson, Elizabeth Barrett Browning, Robert Browning and William Henry Harrison. Read died from injuries sustained in a carriage accident, which weakened him and led him to contract pneumonia while on shipboard returning to America.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Marcus Aurelius Root (American, 1808-1888)
Marcus Aurelius Root (1808-1888) was a writing teacher and photographer. He was born in Granville, Ohio and died in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
On 20 June 1846, he bought John Jabez Edwin Mayall’s Chestnut Street photography studio that was in the same building as Root’s residence in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Root had success as a daguerreotypist working with his brother, Samuel Root. The Root Brothers had a gallery in New York City from 1849 to 1857. Marcus Aurelius Root authored an important book on photography entitled The Camera and the Pencil.
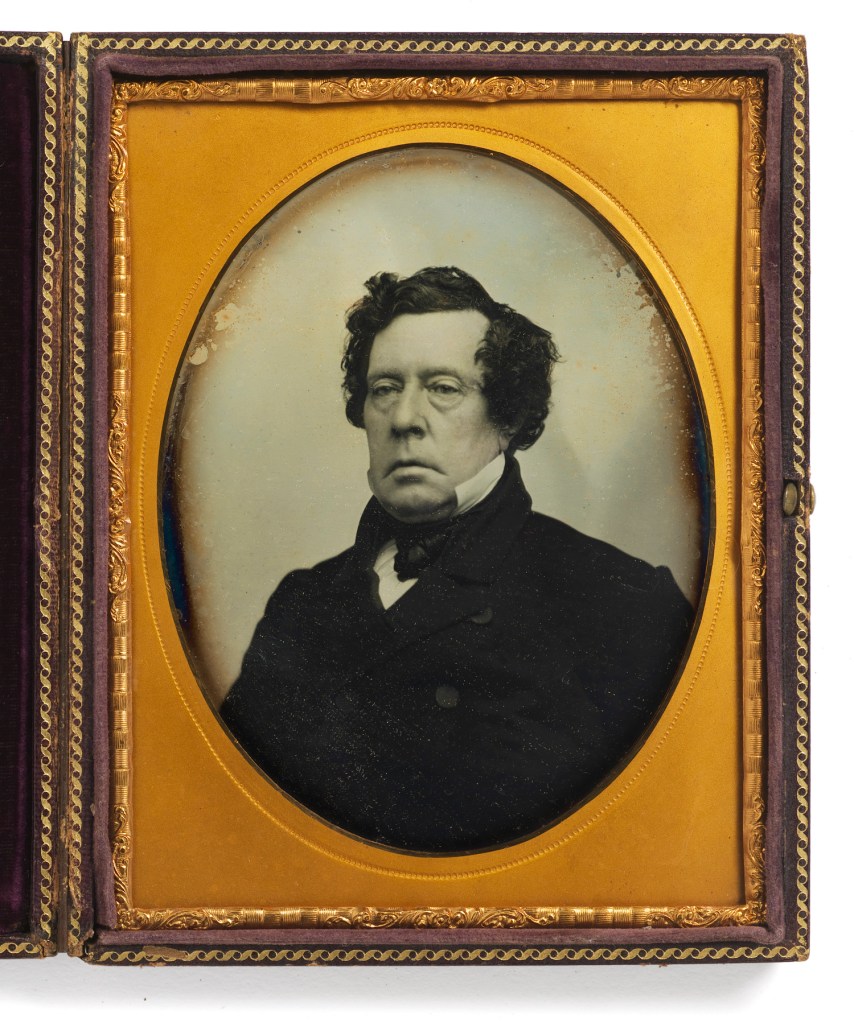

Beckers and Piard (American)
Alexander Beckers (American born Germany, 1815-1905, active 1842-1869)
Victor Piard (American born France, 1825-1901)
Matthew Calbraith Perry (April 10, 1794 – March 4, 1858)
c. 1855
Half-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Alexander Beckers (American born German, 1815-1905)
Alexander Beckers first saw a daguerreotype in Philadelphia, and subsequently went to work there for photographer Frederick David Langenheim in 1843. The following year he moved to New York, where he is credited with the first whole-plate daguerreotypes made in that city. Within months Beckers opened the Langenheim & Beckers studio in New York, which became Beckers & Piard in 1849. In 1857 he patented a revolving stereograph viewer and shortly thereafter sold his daguerreotype business in order to concentrate his attention on the manufacture of stereograph viewers.
Anonymous text. “Alexander Beckers,” on the J. Paul Getty Museum website [Online] Cited 15/03/2022
Matthew Calbraith Perry (American, 1794-1858)
Matthew Calbraith Perry (April 10, 1794 – March 4, 1858) was a Commodore of the United States Navy who commanded ships in several wars, including the War of 1812 and the Mexican-American War (1846-1848). He played a leading role in the opening of Japan to the West with the Convention of Kanagawa in 1854.
Perry was interested in the education of naval officers, and assisted in the development of an apprentice system that helped establish the curriculum at the United States Naval Academy. With the advent of the steam engine, he became a leading advocate of modernising the U.S. Navy and came to be considered “The Father of the Steam Navy” in the United States.
Text from the Wikipedia website
[Several] daguerreotypes of Matthew Calbraith Perry (1794-1858) [were] made in New York City, in the months following Commodore Perry’s triumphant return from Japan in January of 1855. The seminal achievement of his long naval career, Perry’s shrewd and persistent negotiations with Japan opened that isolated nation to the West for the first time in its history.
[These] portraits can be dated to 1855-1856, based on the date of Perry’s return to the United States and the years the Beckers & Piard studio operated at 264 Broadway. A variant, more conventional, portrait from this same sitting, previously unattributed, exists in three identical half-plates, one in the National Portrait Gallery (above), one in the New-York Historical Society, and one sold at Swann Galleries, New York, in 1988 (Sale 1468, Lot 186). In addition, there is a half-plate profile study of Perry in the U. S. Naval Academy Museum in Annapolis, also made by Beckers & Piard, that was the model for a commemorative medal struck in Perry’s honour in 1856; and a half-plate seated portrait of Perry in his full uniform and regalia, also owned by the New-York Historical Society.
The portraits can be dated to 1855 or 1856 based upon Perry’s arrival in New York, from Japan, in 1855, and by the address of the daguerreotypists stamped on the portrait’s mat. Alexander Beckers and Victor Piard were active at 264 Broadway, the address on the mat, from 1853 to 1856. At some point in 1856, the studio moved across the street to 261 Broadway. This portrait would, therefore, have to have been made in 1855 or 1856.
Anonymous text. “Catalogue note,” on the Sotheby’s website 2012 [Online] Cited 28/11/2018.
Unknown artist (Japanese)
Gasshukoku suishi teitoku kōjōgaki (Oral statement by the American Navy admiral)
c. 1854
Library of Congress
Public domain
A Japanese print showing three men, believed to be Commander Anan, age 54; Perry, age 49; and Captain Henry Adams, age 59, who opened up Japan to the west. The text being read may be President Fillmore’s letter to Emperor of Japan. This is a somewhat extensive restoration, meant to keep focus on the artwork, instead of the damage.

Unidentified artist (American)
Dorothea Lynde Dix
c. 1849
Half-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Dorothea Lynde Dix (American, 1802-1887)
Dorothea Lynde Dix (April 4, 1802 – July 17, 1887) was an American advocate on behalf of the indigent mentally ill who, through a vigorous and sustained program of lobbying state legislatures and the United States Congress, created the first generation of American mental asylums. During the Civil War, she served as a Superintendent of Army Nurses. (Wikipedia)
What a human being… read her full Wikipedia entry. A champion of the poor and mentally ill, Dix and her nurses cared for the wounded from both sides of the American Civil War.
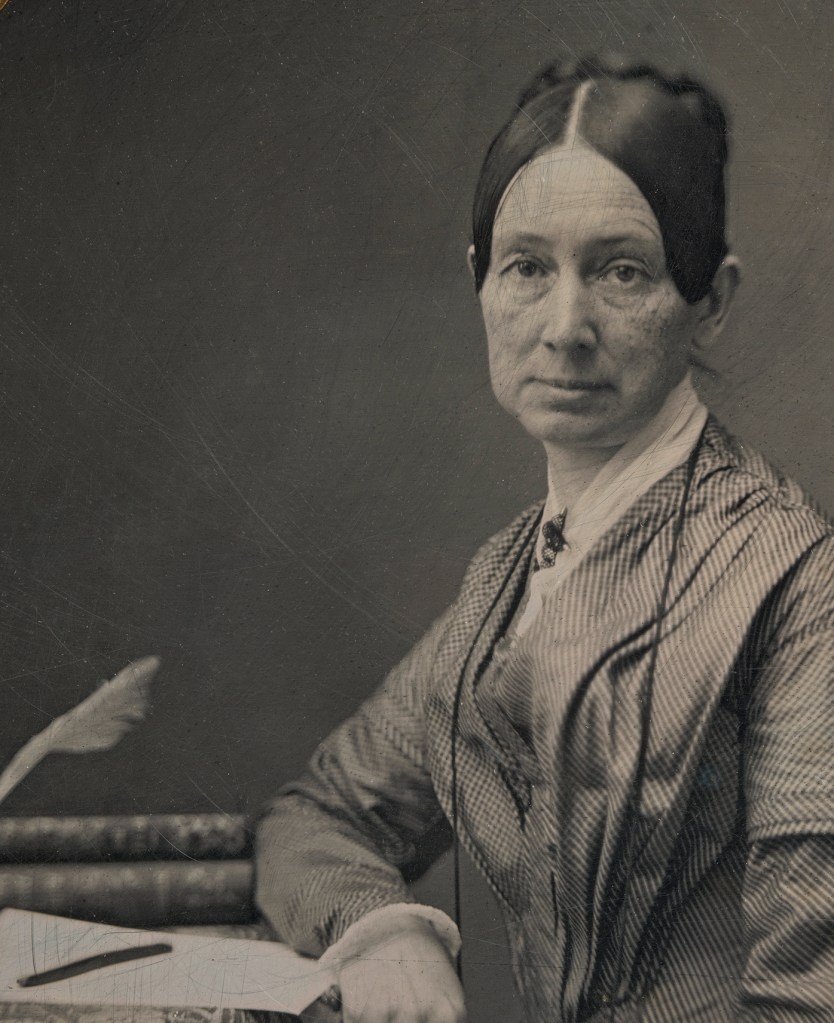

Unidentified artist (American)
Dorothea Lynde Dix (detail)
c. 1849
Half-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
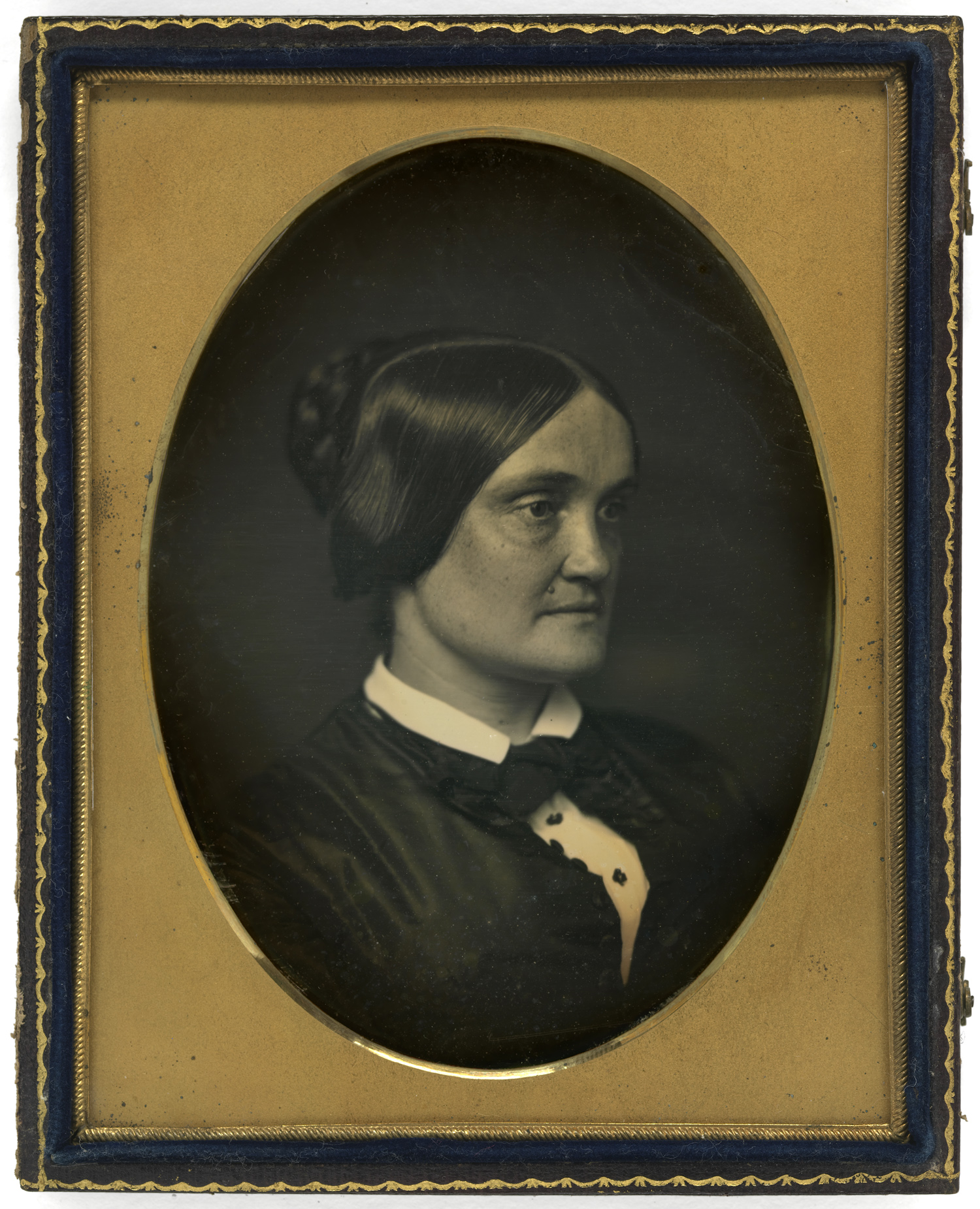

Unidentified artist (American)
Charlotte Cushman
c. 1850
Half-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Charlotte Saunders Cushman (July 23, 1816 – February 18, 1876) was an American stage actress. Her voice was noted for its full contralto register, and she was able to play both male and female parts. She lived intermittently in Rome, in an expatriate colony of prominent artists and sculptors, some of whom became part of her tempestuous private life.
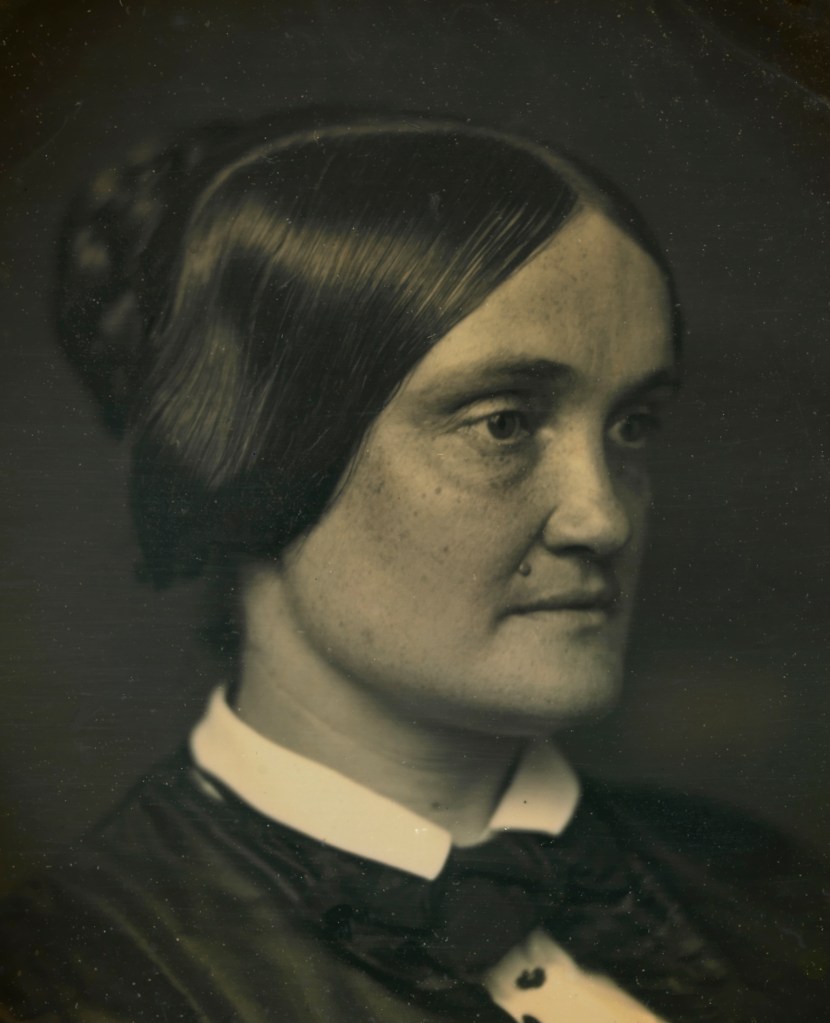

Unidentified artist (American)
Charlotte Cushman (detail)
c. 1850
Half-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution

Mathew Brady (American, 1822-1896)
Charlotte Saunders Cushman
between 1855 and 1865
Wet collodion glass negative
Library of Congress Prints and Photographs Division. Brady-Handy Photograph Collection
Public domain
Library of Congress description: “Charlotte Cushman as Meg Merriles”
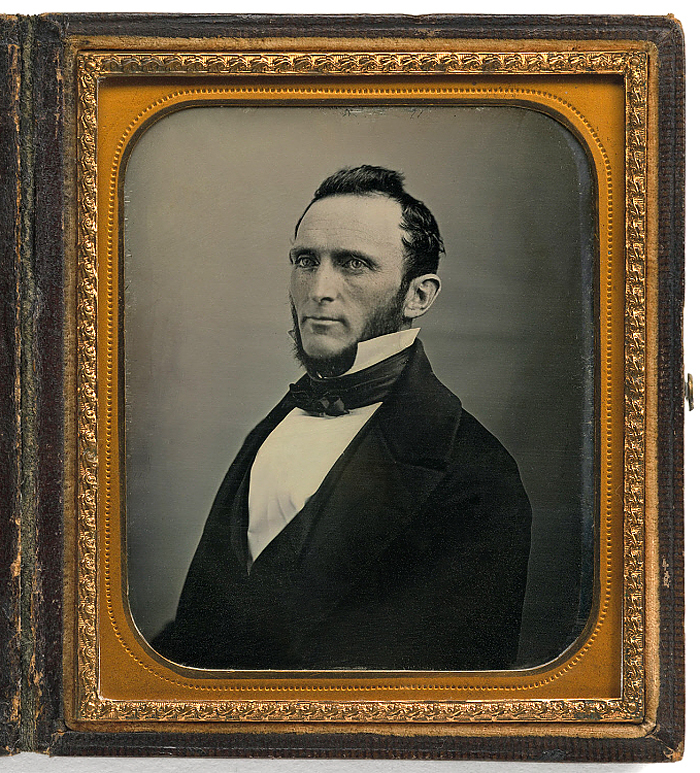

Henry B. Hull (American, active c. 1855)
Stonewall Jackson (Thomas Jonathan Jackson, 21 Jan 1824 – 10 May 1863)
1855
Sixth-plate daguerreotype
Image: 8.4 x 7.2cm (3 5/16 x 2 13/16″)
Case Open: 9.4 x 16.5 x 1.1cm (3 11/16 x 6 1/2 x 7/16″)
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Born Clarksburg, West Virginia
When future Confederate general Stonewall Jackson sat for this likeness in 1855, his emergence as one of the South’s most brilliant military tacticians lay six years away. A West Point graduate, Jackson had served with distinction in the Mexican American War, earning more citations for valour than any other American officer. He joined Virginia Military Institute as a professor of artillery tactics and natural philosophy in 1851, and later commanded the corps of VMI cadets that guarded the gallows at John Brown’s execution. Jackson had this daguerreotype made as a memento for his aunt and uncle while visiting them in the summer of 1855.
Text from the Smithsonian National Portrait Gallery website
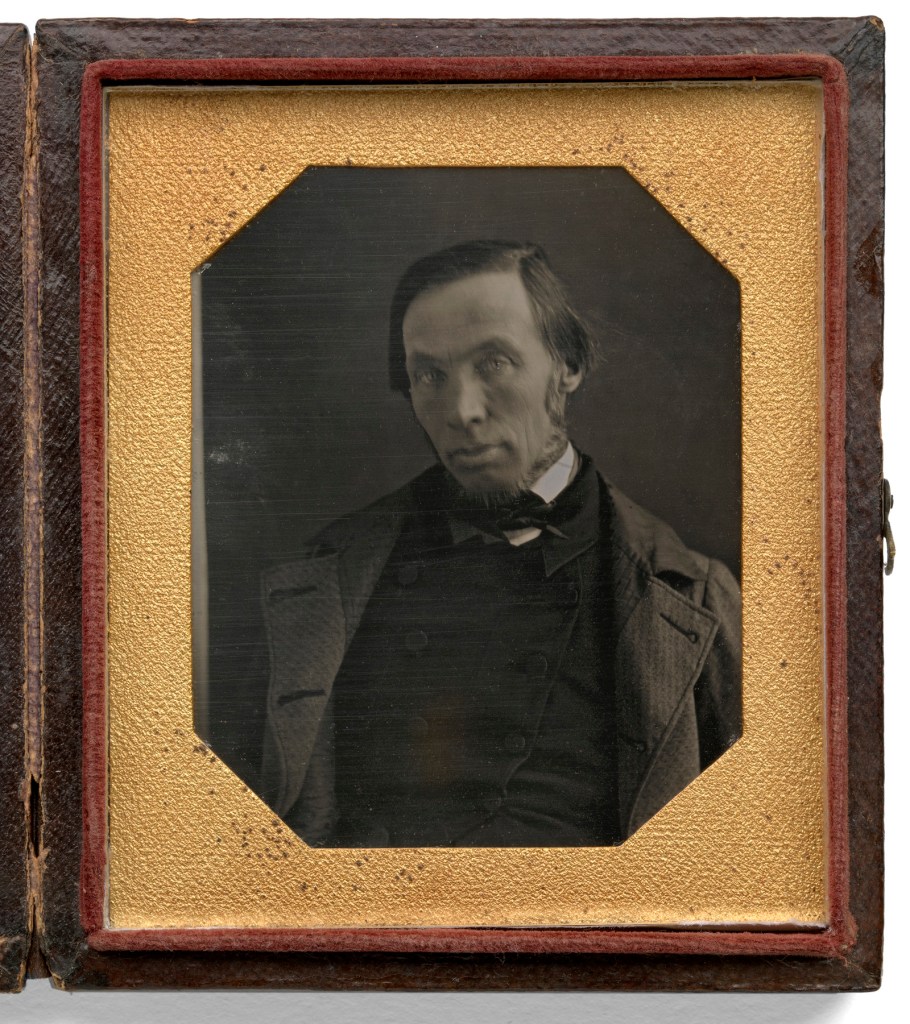

Unidentified artist (American)
Robert Dale Owen
c. 1847
Sixth-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution; gift of Andrew Oliver
Robert Owen Dale (American, 1801-1877)
Robert Dale Owen (November 7, 1801 – June 24, 1877) was a Scottish-born social reformer who immigrated to the United States in 1825, became a U.S. citizen, and was active in Indiana politics as member of the Democratic Party in the Indiana House of Representatives (1835-1839 and 1851-1853) and represented Indiana in the U.S. House of Representatives (1843-1847). As a member of Congress, Owen successfully pushed through the bill that established Smithsonian Institution and served on the Institution’s first Board of Regents. Owen also served as a delegate to the Indiana Constitutional Convention in 1850 and was appointed as U.S. chargé d’affaires (1853-1858) to Naples.
Owen was a knowledgeable exponent of the socialist doctrines of his father, Robert Owen, and managed the day-to-day operation of New Harmony, Indiana, the socialistic utopian community he helped establish with his father in 1825. Throughout his adult life, Robert Dale Owen wrote and published numerous pamphlets, speeches, books, and articles that described his personal and political views, including his belief in spiritualism. Owen co-edited the New-Harmony Gazette with Frances Wright in the late 1820s in Indiana and the Free Enquirer in the 1830s in New York City. Owen was an advocate of married women’s property and divorce rights, secured inclusion of an article in the Indiana Constitution of 1851 that provided tax-supported funding for a uniform system of free public schools, and established the position of Indiana Superintendent of Public Instruction. Owen is also noted for a series of open letters he wrote in 1862 that favoured the abolition of slavery and supported general emancipation, as well as a suggestion that the federal government should provide assistance to freedmen.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Unidentified artist (American)
Robert Dale Owen (detail)
c. 1847
Sixth-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution; gift of Andrew Oliver

Southworth & Hawes (American, active 1843-1862)
Albert Sands Southworth (12 Mar 1811 – 3 Mar 1894)
Josiah Johnson Hawes (20 Feb 1808 – 7 Aug 1901)
Franklin Pierce (23 Nov 1804 – 8 Oct 1869)
c. 1852
Quarter-plate daguerreotype
Image: 8.8 x 6.8cm (3 7/16 x 2 11/16″)
Case Closed: 11.9 x 9.4cm (4 11/16 x 3 11/16″)
Case Open: 11.9 x 18.7 x 1.2cm (4 11/16 x 7 3/8 x 1/2″)
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Franklin Pierce (American, 1804-1869)
Franklin Pierce (November 23, 1804 – October 8, 1869) was the 14th President of the United States (1853-1857), a northern Democrat who saw the abolitionist movement as a fundamental threat to the unity of the nation. He alienated anti-slavery groups by championing and signing the Kansas-Nebraska Act and enforcing the Fugitive Slave Act; yet he failed to stem conflict between North and South, setting the stage for Southern secession and the American Civil War.
Pierce was born in New Hampshire, and served in the U.S. House of Representatives and the Senate until he resigned from the Senate in 1842. His private law practice in New Hampshire was a success, and he was appointed U.S. Attorney for his state in 1845. He took part in the Mexican-American War as a brigadier general in the Army. He was seen by Democrats as a compromise candidate uniting northern and southern interests and was nominated as the party’s candidate for president on the 49th ballot at the 1852 Democratic National Convention. He and running mate William R. King easily defeated the Whig Party ticket of Winfield Scott and William A. Graham in the 1852 presidential election.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Southworth & Hawes (American, active 1843-1862)
Southworth & Hawes was an early photographic firm in Boston, 1843-1863. Its partners, Albert Sands Southworth (1811-1894) and Josiah Johnson Hawes (1808-1901), have been hailed as the first great American masters of photography, whose work elevated photographic portraits to the level of fine art. Their images are prominent in every major book and collection of early American photography.
Southworth & Hawes worked almost exclusively in the daguerreotype process. Working in the 8 1/2 x 6 1/2 inch whole plate format, their images are brilliant, mirror-like, and finely detailed. Writing in the Photographic and Fine Art Journal, August 1855, the contemporary Philadelphia daguerreotypist Marcus Aurelius Root paid them this praise: “Their style, indeed, is peculiar to themselves; presenting beautiful effects of light and shade, and giving depth and roundness together with a wonderful softness or mellowness. These traits have achieved for them a high reputation with all true artists and connoisseurs.” He further noted that the firm had devoted their time chiefly to daguerreotypes, with little attention to photography on paper. …
During their 20 years of collaboration, Southworth & Hawes catered to Boston society and the famous. Their advertisements drew a distinction between the appropriate styles for personal versus public portraiture. “A likeness for an intimate acquaintance or one’s own family should be marked by that amiability and cheerfulness, so appropriate to the social circle and the home fireside. Those for the public, of official dignitaries and celebrated characters admit of more firmness, sternness and soberness.” Among their sitters were Louisa May Alcott, Lyman Beecher, Benjamin Butler, William Ellery Channing, Rufus Choate, Cassius Marcellus Clay, Charlotte Cushman, Richard Henry Dana, Jr., Dorothea Dix, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Edward Everett, William Lloyd Garrison, Grace Greenwood, Oliver Wendell Holmes, Sam Houston, Thomas Starr King, Louis Kossuth, Jenny Lind, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, Horace Mann, Donald McKay, Lola Montez, George Peabody, William H. Prescott, Lemuel Shaw, Harriet Beecher Stowe, Charles Sumner, Daniel Webster, John Greenleaf Whittier, and Robert C. Winthrop.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Unidentified artist (American)
Brady’s New Daguerreotype Saloon, New York
Jun 11, 1853
Wood engraving on paper
36.6 × 24cm (14 7/16 × 9 7/16″)
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
During the 1850s, Manhattan continued to extend north, and Mathew Brady followed suit with the opening of a new gallery, elegantly furnished, at number 359 Broadway. On June 11, 1853, the New York newspaper Illustrated News published a view of the interior of the gallery with the following comment: “The reception room is furnished with richness and artistic taste. Adorning its walls an extensive collection of daguerreotypes of remarkable figures, excellently executed, which is well worth a visit by anyone who wishes to contemplate American and European celebrities. Residents and foreigners alike will enjoy observing the great progress of the art exhibited here, and we convey to Mr. Brady our cordial wishes for success in his new venture.”
Text from the Smithsonian National Portrait Gallery website

Mathew B. Brady (American, 1823? – 15 Jan 1896)
Thomas Cole (1 Feb 1801 – 11 Feb 1848)
c. 1845
Half-plate daguerreotype on silver-coated copper plate
Plate: 13.7 x 10.2cm (5 3/8 x 4″)
Case Open: 15.8 × 24.4 × 1cm (6 1/4 × 9 5/8 × 3/8″)
Case Closed: 15.8 × 12.3 × 2.7cm (6 1/4 × 4 13/16 × 1 1/16″)
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution; gift of Edith Cole Silberstein
Born Bolton-le-Moors, Lancashire, England
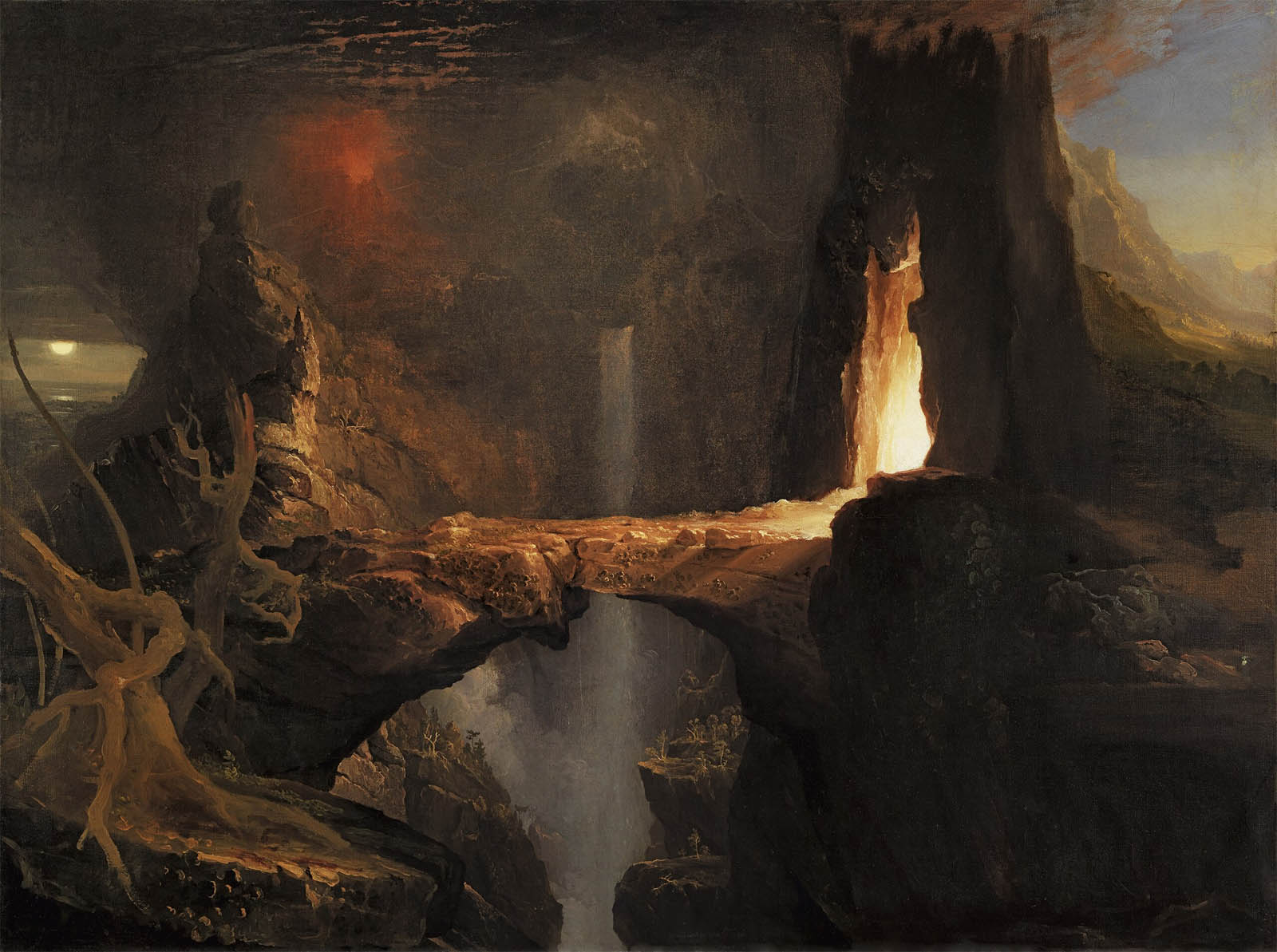
Artist Thomas Cole was a founding member of the Hudson River School of American painting, which sought to capture the sublime grandeur of the nation’s natural landscape. Believing that the best art also conveyed a moral lesson, Cole achieved his greatest fame with two series of allegorical paintings entitled The Course of Empire (1836) and The Voyage of Life (1841).
From the outset of his career, Mathew Brady courted major artists and welcomed the opportunity to daguerreotype them. This portrait is one of two known copies Brady made of his original daguerreotype of Cole, which is now in the collection of the Library of Congress.
Text from the Smithsonian National Portrait Gallery website
The Course of Empire is a series of five paintings created by Thomas Cole in the years 1833-1836. It is notable in part for reflecting popular American sentiments of the times, when many saw pastoralism as the ideal phase of human civilisation, fearing that empire would lead to gluttony and inevitable decay. The theme of cycles is one that Cole returned to frequently, such as in his The Voyage of Life series. The Course of Empire comprises the following works: The Course of Empire – The Savage State; The Arcadian or Pastoral State; The Consummation of Empire; Destruction; and Desolation. All the paintings are 39.5 inches by 63.5 inches (100cm by 161cm) except The Consummation of Empire which is 51″ by 76″ (130cm by 193cm).
The series of paintings depicts the growth and fall of an imaginary city, situated on the lower end of a river valley, near its meeting with a bay of the sea. The valley is distinctly identifiable in each of the paintings, in part because of an unusual landmark: a large boulder is situated atop a crag overlooking the valley. Some critics believe this is meant to contrast the immutability of the earth with the transience of man.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Thomas Cole (American, 1801-1848)
The Savage State
1834
From The Course of Empire
Oil on canvas
Height: 39.5 in (100.3cm)
Width: 63.5 in (161.2cm)
New-York Historical Society
Thomas Cole (American, 1801-1848)
The Consummation of Empire
1836
From The Course of the Empire
Oil on canvas
Height: 51 in (129.5cm)
Width: 76 in (193cm)
New-York Historical Society
The Voyage of Life is a series of paintings created by Thomas Cole in 1842, representing an allegory of the four stages of human life: childhood, youth, manhood, and old age. The paintings depict a voyager who travels in a boat on a river through the mid-19th-century American wilderness. In each painting the voyager rides the boat on the River of Life accompanied by a guardian angel. The landscape, each reflecting one of the four seasons of the year, plays a major role in conveying the story. With each instalment the boat’s direction of travel is reversed from the previous picture. In childhood, the infant glides from a dark cave into a rich, green landscape. As a youth, the boy takes control of the boat and aims for a shining castle in the sky. In manhood, the adult relies on prayer and religious faith to sustain him through rough waters and a threatening landscape. Finally, the man becomes old and the angel guides him to heaven across the waters of eternity.
Cole’s renowned four-part series traces the journey of an archetypal hero along the “River of Life.” Confidently assuming control of his destiny and oblivious to the dangers that await him, the voyager boldly strives to reach an aerial castle, emblematic of the daydreams of “Youth” and its aspirations for glory and fame. As the traveler approaches his goal, the ever more turbulent stream deviates from its course and relentlessly carries him toward the next picture in the series, where nature’s fury, evil demons, and self-doubt will threaten his very existence. Only prayer, Cole suggests, can save the voyager from a dark and tragic fate.
From the innocence of childhood, to the flush of youthful overconfidence, through the trials and tribulations of middle age, to the hero’s triumphant salvation, The Voyage of Life seems intrinsically linked to the Christian doctrine of death and resurrection. Cole’s intrepid voyager also may be read as a personification of America, itself at an adolescent stage of development. The artist may have been issuing a dire warning to those caught up in the feverish quest for Manifest Destiny: that unbridled westward expansion and industrialisation would have tragic consequences for both man and the land itself.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Thomas Cole (American, 1801-1848)
The Voyage of Life: Youth
1842
Oil on canvas
134 × 194cm (53 in × 76 in)
National Gallery of Art
Thomas Cole (American, 1801-1848)
The Voyage of Life: Manhood
1842
Oil on canvas
132.8 × 198.1cm (52.3 in × 78.0 in)
National Gallery of Art
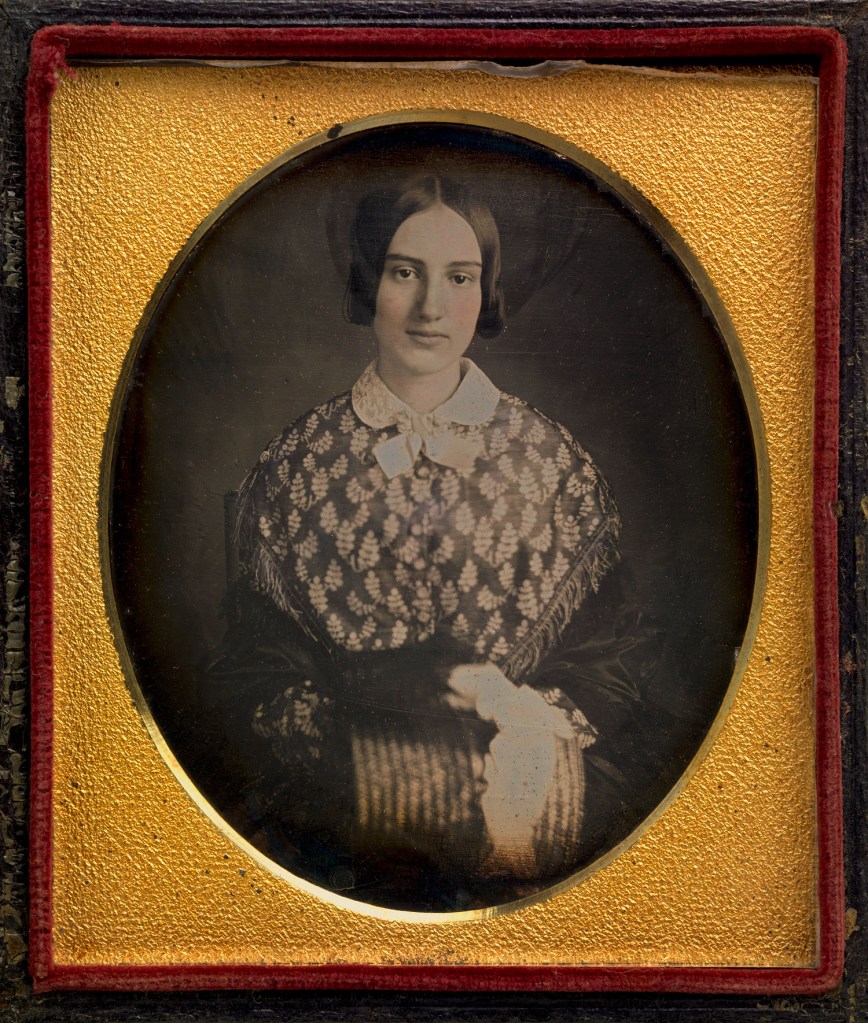

Unidentified artist (American)
Julia Catherine Seymour Conkling
1848
Sixth-plate daguerreotype
Plate: 8.2 x 6.8cm (3 1/4″ x 2 11/16″)
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
In addition to being the wife of Senator Roscoe Conkling, Julia Seymour was the sister of New York Governor and 1868 Democratic presidential nominee Horatio Seymour. In 1893 Julia Conkling founded the Oneida Chapter of the Daughters of the American Revolution, the fourth chapter formed after the 1890 founding of the national D.A.R.
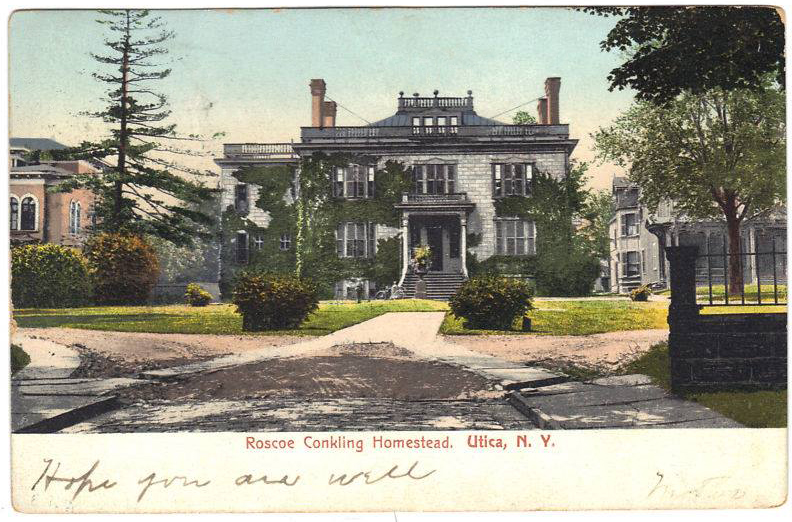
A linen postcard of Conkling House, #3 Rutger Park, Rutger Street, Utica NY (The Landmarks Society of Greater Utica)
The first commercially viable form of photography, daguerreotypes brought portraiture within reach of average Americans in the mid-1800s. Today, they are an essential part of the museum’s collection. Daguerreotypes: Five Decades of Collecting celebrates the Portrait Gallery’s tradition of collecting with this intimate exhibition of 13 small-scale, one-of-a-kind portraits of early American influencers. The exhibition opens June 15 and will be on display on the museum’s first floor through June 2, 2019.
The presentation, organised by Ann Shumard, senior curator of photographs, celebrates the museum’s golden anniversary and highlights its extraordinary collection. With more than 23,000 objects, the Portrait Gallery holds some of the most important photographic portraits, including prized glass-plate negatives by Mathew Brady and the acclaimed 2017 acquisition of an 1843 daguerreotype likeness of President John Quincy Adams by artist Philip Haas, on permanent view in the museum’s America’s Presidents gallery.
The Portrait Gallery’s first photographic acquisition was a daguerreotype, which arrived as a gift in 1965 – three years before the museum opened its doors to the public. The image was a portrait by Marcus Aurelius Root of poet, painter and sculptor Thomas Buchanan Read, whose equestrian portrait of Union army general Philip Sheridan is on exhibit in the museum’s Civil War galleries.
When an Act of Congress established the National Portrait Gallery in 1962, the new museum was not initially authorised to collect photographs. An exception was made to accommodate gifts to its Support Collection. This enabled the Portrait Gallery to accept several significant daguerreotype portraits before 1976, when its charter was amended to allow for the acquisition of photographs. The museum’s collection now includes more than 150 daguerreotypes representing individuals as diverse in their achievements as showman P.T. Barnum, Seneca Nation leader Blacksnake, actress Charlotte Cushman, humanitarian Dorothea Dix, surgeon Thomas D. Mütter, U.S. Navy Commodore Matthew C. Perry and writer Henry David Thoreau.
“These daguerreotypes are remarkable artefacts from the dawn of American photography,” Shumard said. “Each is truly, as Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr. said, a ‘mirror with a memory.'”
A daguerreotype is a one-of-a-kind, direct-positive image produced on a sensitised plate of silver-clad copper. The process was introduced by French artist Louis-Jacques-Mandé Daguerre, but American practitioners were the ones who recognised the daguerreotype’s potential as a portrait medium. Through technical innovations, they transformed it from an experimental process into a commercially viable one within months of its introduction in August 1839. For nearly 20 years, the daguerreotype flourished in the United States as Americans flocked to studios in communities large and small to pose for their portraits.
Press release from the Smithsonian National Portrait Gallery
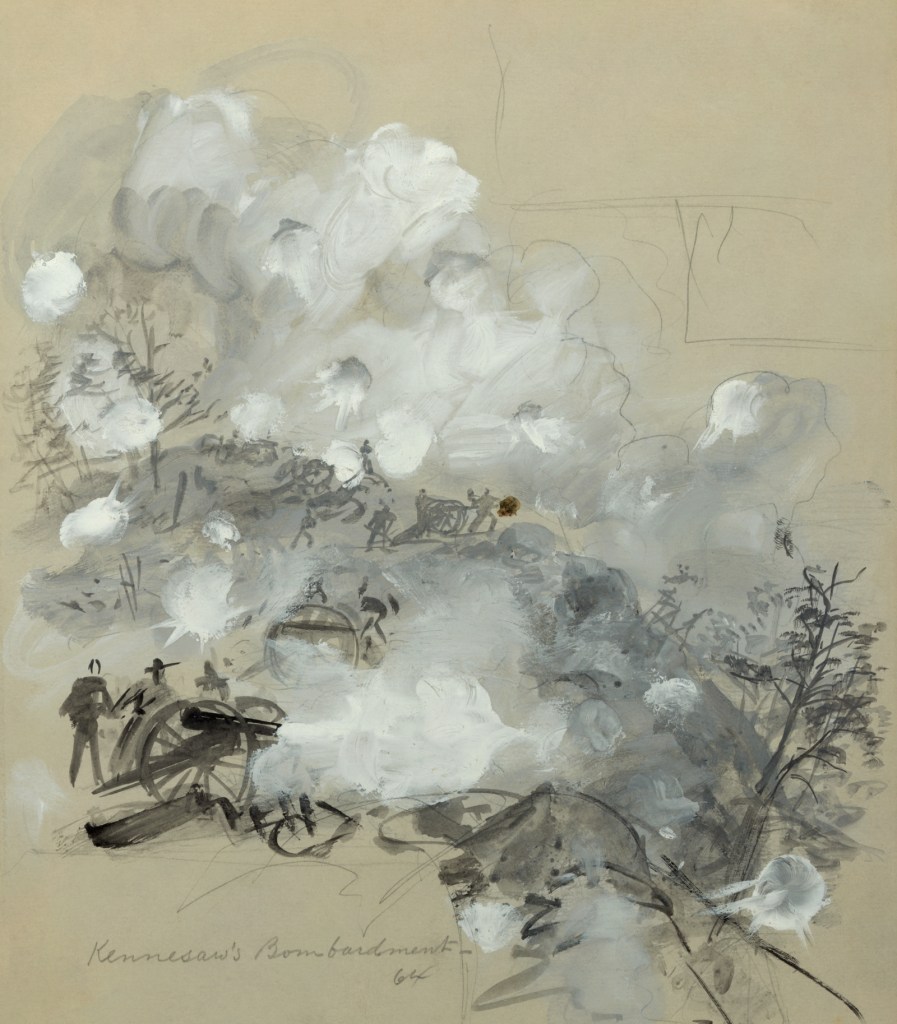

Alfred R. Waud (Alfred Rudolph) (American, 1828-1891)
Kennesaw’s Bombardment, 64
June 27, 1864
Drawing on light gray paper: pencil, Chinese white, and black ink wash
Digitised from original
Library of Congress
Public domain
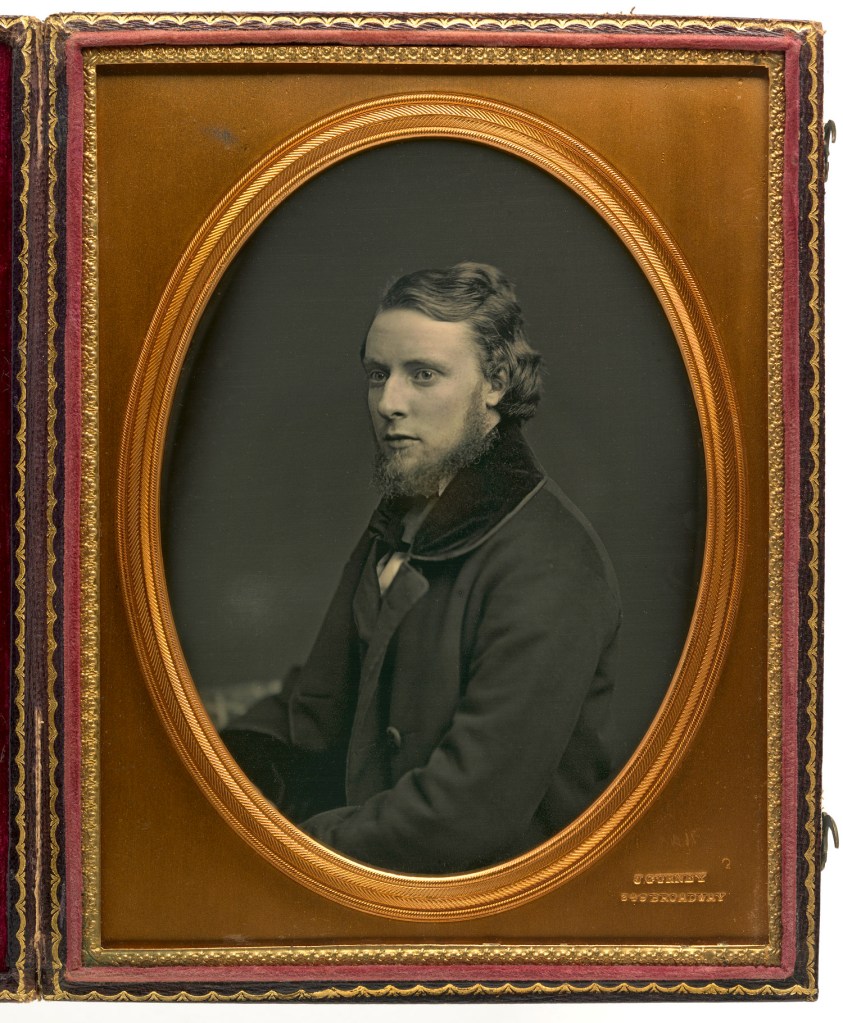

Jeremiah Gurney (American, 17 October 1812 – 21 April 1895)
Alfred R. Waud
c. 1852
Half-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Alfred Rudolph Waud (wōd) (October 2, 1828 – April 6, 1891) was an American artist and illustrator, born in London, England. He is most notable for the sketches he made as an artist correspondent during the American Civil War.
Jeremiah Gurney (American, 1812-1895)
Jeremiah Gurney (October 17, 1812 – April 21, 1895), was an American daguerreotype photographer operating in New York.
Gurney worked in the jewellery trade in Little Falls, New York, but soon moved his business to New York City and shortly after turned to photography, having been instructed and inspired by Samuel Morse. He was one of the pioneering practitioners of the daguerreotype process, opening the first American photo gallery at 189 Broadway in 1840, and charging $5 for a portrait.
He created remarkably detailed portraits, using to the full the remarkable tonal rendition of the process. He selected his clients from New York’s society elite, calling them “Distinguished Persons of the Age” and eschewing the political and entertainment figures favoured by his rival, Mathew Brady. The quality of Gurney’s portraits soon ensconced him as the finest daguerreotypist in Gotham.
Gurney’s photographic skills received numerous accolades, including a write-up in the Scientific American of 5 December 1846. The New York Illustrated News, in an 1853 article, wrote that his establishment at 349 Broadway “consisted of nine spacious rooms, devoted exclusively to this art.” In the 1840s Gurney showed his images at numerous exhibitions such as the American Institute Fair and later at the Crystal Palace in London, achieving international renown. His business flourished and in 1858 he built a three-story white marble studio at 707 Broadway to house his pictures, and it was the first building built for the sole purpose of photography in the United States.
Gurney played a leading role in the training of the first wave of pioneering photographers such as Mathew Brady, who made a name for himself as a civil war photographer. Brady had been employed as a journeyman making jewellery cases for E. Anthony & Co., and also made display cases for Gurney’s daguerreotypes. One of the things Gurney is best known for is having taken the only known photograph of Abraham Lincoln in death.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Jeremiah Gurney (American, 17 October 1812 – 21 April 1895)
Alfred R. Waud (detail)
c. 1852
Half-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Leslie & Hooper (engravers)
Gurney’s Daguerreian Saloon at 349 Broadway, NYC
12 November, 1853
From Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper
Public domain
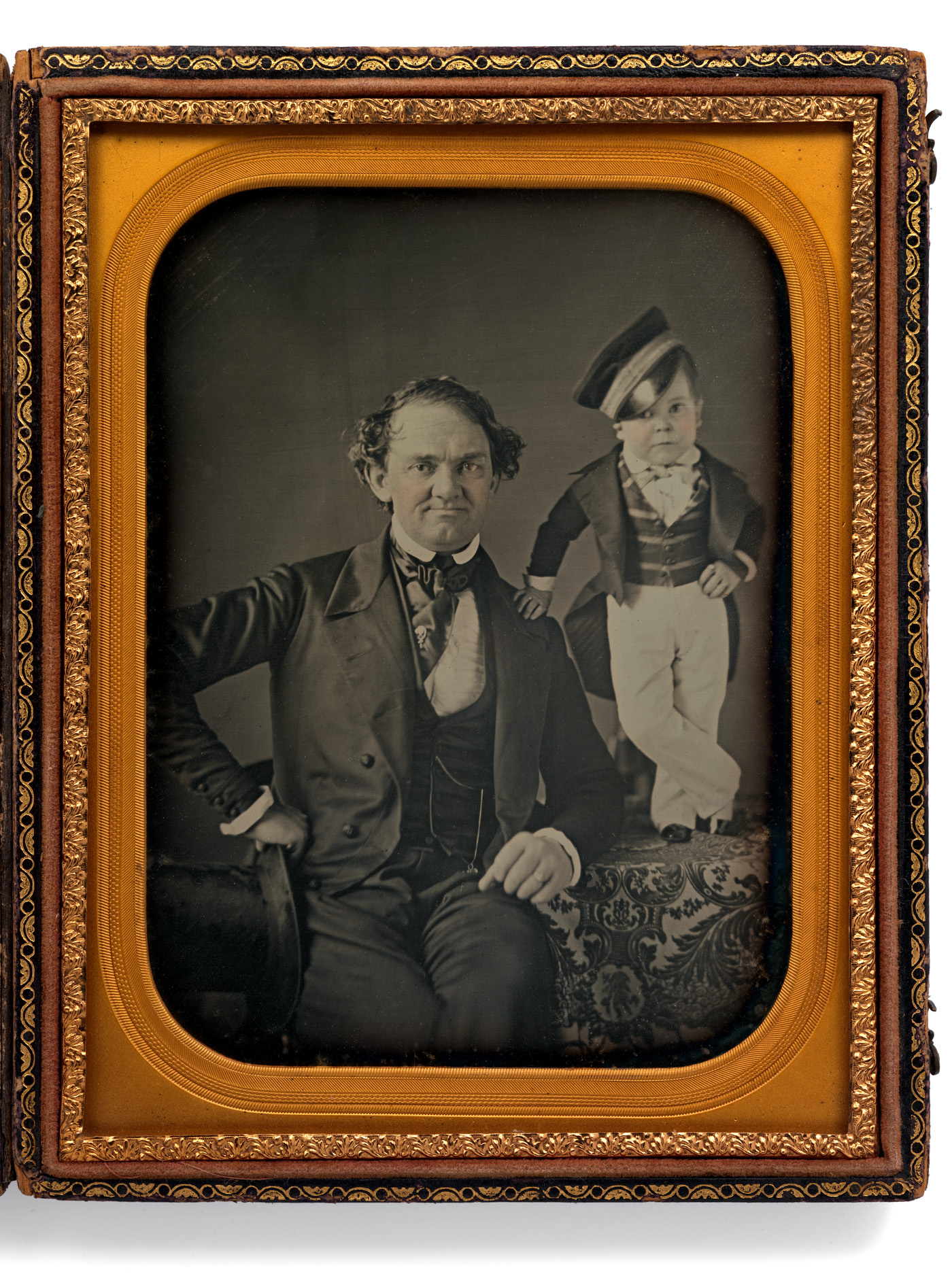

Samuel Root and Marcus Aurelius Root (American)
Samuel Root (American, c. 1820-1889)
Marcus Aurelius Root (American, 1808-1888)
P.T. Barnum and General Tom Thumb
c. 1850
Half-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Samuel Root (American, c. 1820-1889)
Marcus Aurelius Root (American, 1808-1888)
Samuel Root, was born circa 1820. Marcus spent his childhood in Ohio and briefly attended Ohio University before contracting pleurisy forced him to drop out. After working briefly as a portrait artist, Marcus began teaching penmanship at the encouragement of painter Thomas Sully, and opened his own school in Philadelphia in 1835. During this period, he wrote several books on penmanship, including Philosophical Theory and Practice of Penmanship (1842).
Marcus Root‘s interest in daguerreian art began when Louis Daguerre’s process was introduced in Philadelphia in 1839. He studied under famed daguerreian Robert Cornelius. For him, daguerreotype was more than just a new art form; it was an expression of nationalist ideals. After opening a series of galleries in various locations, he returned to Philadelphia, where he was joined by his younger brother Samuel, to whom he taught the daguerreian art. Together, the siblings opened a gallery at 363 Broadway in New York City in 1849, which Samuel managed. Marcus eventually sold his interest in the gallery to Josiah W. Thompson so that he could concentrate on the Philadelphia gallery.
By the 1850s, Marcus Root had become one of America’s most respected daguerreians, and Samuel Root’s artistry was also receiving national attention. He completed the first daguerreotype of Swedish opera singer Jenny Lind and such prominent political officials as Henry Clay and George M. Dallas. When major daguerreotype dealer Edward Anthony held the first national photographic contest, Samuel Root received the second prize, a pair of goblets.
After selling the Philadelphia gallery in 1856, Marcus Root heavily invested in the Mount Vernon Hotel in Cape May, New Jersey. However, shortly thereafter, the uninsured structure was destroyed in a fire. His misfortunes continued when he was seriously injured in a train accident while preparing for a New York City gallery opening. His one leg was crushed, and despite undergoing a lengthy and arduous recovery, Marcus Root remained crippled for the rest of his life. Samuel Root was also enduring his share of hardship. His first wife died, leaving him with a young son. He married Harriet Furman in 1856, and the couple settled in Dubuque, Iowa, where Samuel opened a gallery at 166 Main Street. He became a respected member of the community, and published several photographic texts on Dubuque, including Views of Dubuque and Stereoscopic Views of Dubuque and Surrounding Scenery.
During his long recovery, Marcus Root worked on an exhaustive history of American photography, which was later published as The Camera and the Pencil; Or the Heliographic Art. He was well enough to exhibit his daguerreotype portraits of famous people at the 1876 Centennial Celebration, but a serious fall from a streetcar in 1885 ended his active life, which was spent in relative seclusion until his death on April 12, 1888 at the age of 79. Samuel Root was not one to let adversity get him down, and after a hailstorm destroyed his gallery’s skylight, he photographed and sold the four-inch hailstones. He sold his Dubuque gallery on May 27, 1887, and while on a visit to his sister-in-law in New York, Samuel Root died suddenly of a cerebral haemorrhage on March 11, 1889. The Root brothers were two of America’s earliest and most commercially successful photographic pioneers.
Anonymous text. “Marcus and Samuel Root,” on the Historic Camera website 07/11/2013 [Online] Cited 15/03/2022
Charles Sherwood Stratton “General Tom Thumb” (American, 1838-1883)
Charles Sherwood Stratton (January 4, 1838 – July 15, 1883), better known by his stage name “General Tom Thumb”, was a dwarf who achieved great fame as a performer under circus pioneer P.T. Barnum. …
Phineas T. Barnum, a distant relative (half fifth cousin, twice removed), heard about Stratton and after contacting his parents, taught the boy how to sing, dance, mime, and impersonate famous people. Barnum also went into business with Stratton’s father, who died in 1855. Stratton made his first tour of America at the age of five, with routines that included impersonating characters such as Cupid and Napoleon Bonaparte as well as singing, dancing and comical banter with another performer who acted as a straight man. It was a huge success and the tour expanded.
A year later, Barnum took young Stratton on a tour of Europe, making him an international celebrity. Stratton appeared twice before Victoria of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. He also met the three-year-old Prince of Wales, who would become King Edward VII. In 1845, he triumphed at the Théâtre du Vaudeville (France) in the play Le petit Poucet of Dumanoir and Clairville. The tour was a huge success, with crowds mobbing him wherever he went. After his three-year tour in Europe, Stratton began his rise to stardom in the United States. Stratton’s fame grew at an astonishing rate, and his popularity and celebrity surpassed that of any actor within his lifetime. …
Stratton’s first performances in New York marked a turning point in the history of freak show entertainment. Prior to Stratton’s debut, the presentation of ‘human curiosities’ for the purpose of entertainment was deemed dishonourable and seen as an unpleasing carnival attraction. However, after viewers were introduced to Stratton and performances, he was able to change the perception people held toward freak shows. Stratton’s lively and entertaining performances made these types of carnival shows one of the most favoured forms of theatrical entertainment in the United States.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Southworth & Hawes (American, active 1843-1862)
Albert Sands Southworth (12 Mar 1811 – 3 Mar 1894)
Josiah Johnson Hawes (20 Feb 1808 – 7 Aug 1901)
Jonas Chickering (April 5, 1798 – December 8, 1853)
1853
Whole-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Jonas Chickering (April 5, 1798 – December 8, 1853) was a piano manufacturer in Boston, Massachusetts.
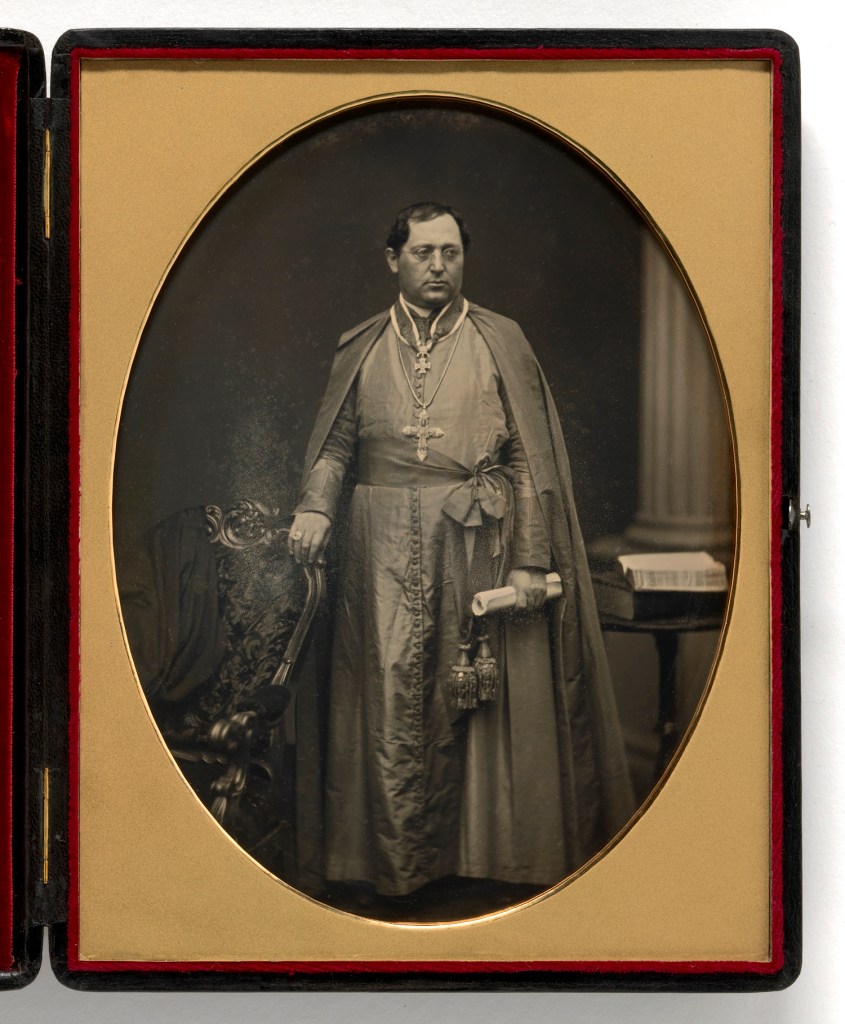

Southworth & Hawes (American, active 1843-1862)
Albert Sands Southworth (12 Mar 1811 – 3 Mar 1894)
Josiah Johnson Hawes (20 Feb 1808 – 7 Aug 1901)
Gaetano Bedini
1853
Whole-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Gaetano Bedini (Italian, 1806-1864)
Gaetano Bedini (15 May 1806 – 6 September 1864) was an Italian ecclesiastic, Cardinal and diplomat of the Catholic Church.
On 15 March 1852 he was named titular Archbishop of Thebes, and, three days after, Apostolic Nuncio in Brazil. Once he received the archiepiscopal order on 4 July 1852 from cardinal Luigi Lambruschini, he decided to leave for Brazil, but he could not enter the country because of a plague epidemic, so he went to the United States. He was the first Papal Nuncio in the United States.
He arrived in New York on 30 June 1853. He became the target of attacks by non-Catholics because of his role in overthrowing the Anti-Papal Roman Republic in 1849, and his visit triggered the Cincinnati Riot of 1853 in which several hundred men marched in protest against his visit.
While travelling, Bedini met the president of the United States, Franklin Pierce, to whom he delivered a letter from the Pope, and the American Secretary of State, William L. Marcy. He ordained some new bishops, amongst whom were James Roosevelt Bayley, archbishop of the Archdiocese of Newark, John Loughlin, bishop of the Diocese of Brooklyn, and Louis De Goesbriand, bishop of the Diocese of Burlington. After visiting New York, Pittsburgh, Louisville, Baltimore and Philadelphia, he returned to Rome from New Orleans in January 1854.
Text from the Wikipedia website

F. C. Flint (American)
Seneca Chief Governor Blacksnake
c. 1850
Quarter-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Governor Blacksnake (Tah-won-ne-ahs, born c. 1737-1760 – died 1859)
Tah-won-ne-ahs or Thaonawyuthe “The Nephew” (born between 1737 and 1760, died 1859), known in English as either Governor Blacksnake or Chainbreaker, was a Seneca war chief and leader. Along with other Iroquois war chiefs (most notably Mohawk leader Joseph Brant), he led warriors to fight on the side of the British during the American Revolutionary War from 1777 to 1783. He was prominent for his role at the Battle of Oriskany, in which the Loyalist and allied forces ambushed a force of rebels (now called Patriots). After the war he supported his maternal uncle Handsome Lake, as a prominent religious leader. Governor Blacksnake allied with the United States in the War of 1812 and later encouraged some accommodation to European-American settlers, allowing missionaries and teachers on the Seneca reservation.
Importantly, he also led a successful postwar struggle in New York in the 1850s after white men illegally bought reservation land. He helped gain a New York State Appeals Court ruling in 1861 that restored the Oil Springs Reservation to the Seneca. …
Blacksnake died on the Allegany Reservation in Cattaraugus County, New York in late December 1859. He is remembered by the Seneca Nation as “a man of rare intellectual and moral power.”
Text from the Wikipedia website
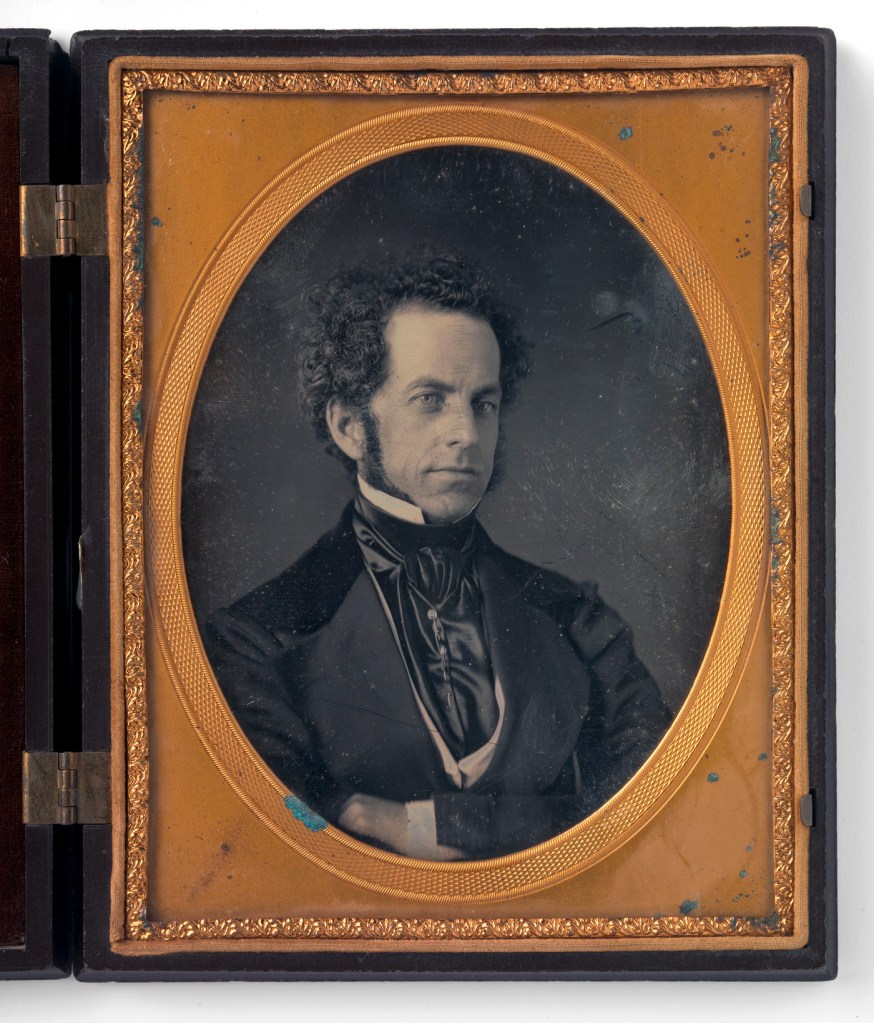

Montgomery P. Simons (American, 1817-1877, active Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 1840s-1870s)
Dr. Thomas Dent Mutter (1811-1858)
1846
Half-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution; purchased through the Marc Pachter Acquisitions Fund, Jon and Lillian Lovelace; partial gift of Stanley B. Burns, MD and The Burns Archive
Thomas Dent Mutter (American, 1811-1858)
Born in Richmond Virginia in 1811, Thomas Dent Mutter lost his brother, mother, father, and guardian grandmother to illness by the time he was seven. As a sickly orphan, Mutter developed an interest in medicine, enrolling in the University of Pennsylvania medical school at age 17.
Then as now, Philadelphia was the leading city in the nation for medical education. Founded in 1765, Mutter’s alma mater was the first hospital and medical school in North America. Today, Penn is one of five med schools in the city educating nearly 20% of all doctors in America. Visitors to Philadelphia can still see the stately Pennsylvania Hospital building at 8th and Spruce streets.
After graduating from Penn, young Mutter followed the path of many American doctors of the time and continued his education among the surgeons of Paris, France. There he learnt the innovative techniques of les operations plastiques (plastic surgery): cosmetic procedures to repair skin and tissue damaged by burns, tumors, or congenital defects.
In Paris, Mutter obtained an item since seen by thousands of museum-goers: a wax head-cast of a “horned” lady, a young woman with a thick brown protrusion extending from her forehead to below her chin. It was the first of many wax models, skeletons, and preserved body parts he would collect over the next few decades.
On returning to Philadelphia, Mütter (as he now styled himself, adding an umlaut to appear more European) became a prominent plastic surgeon. He was soon named chair of surgery at Jefferson Medical College, the city’s second-oldest medical school (now Thomas Jefferson University). There, he used his growing collection of one-of-a-kind medical specimens as a teaching tool to demonstrate the varied maladies which could affect the human body. “He wanted a well-rounded collection,” says Robert Hicks, director of the Mütter Museum. “One that reflected what a physician might see in practice.”
At Jefferson, Mütter built a reputation as a flamboyant and popular lecturer, a precocious young doctor at the forefront of a wave of new surgical techniques. He was an early adopter of anaesthesia and sterilisation, developments which made operations significantly less painful and risky. Tickets to his public surgeries were a hot commodity, and aspiring students praised his teaching skills and the specimens from his growing collection, which he wove into his lectures “so as to impress yet not confuse,” as he wrote at the time.
The later years of Mütter’s life were plagued by illness, including painful attacks of gout – a swelling of the joints often caused by poor nutrition – which made it impossible for the doctor to perform surgeries. Seeing that his days were numbered, the physician sought a permanent home for his extensive holdings of pathological specimens, waxworks, and diagrams so that they would be useful to future generations of doctors.
Extract from Christopher Munden. “A Weird History: Dr. Thomas Dent Mütter and his peculiar museum,” on the Phindie website May 23, 2016 [Online] Cited 01 November 2018



Montgomery P. Simons (American, 1817-1877)
Photography in a nut shell; or, The experience of an artist in photography, on paper, glass and silver : with illustrations
1858
King & Baird, printer
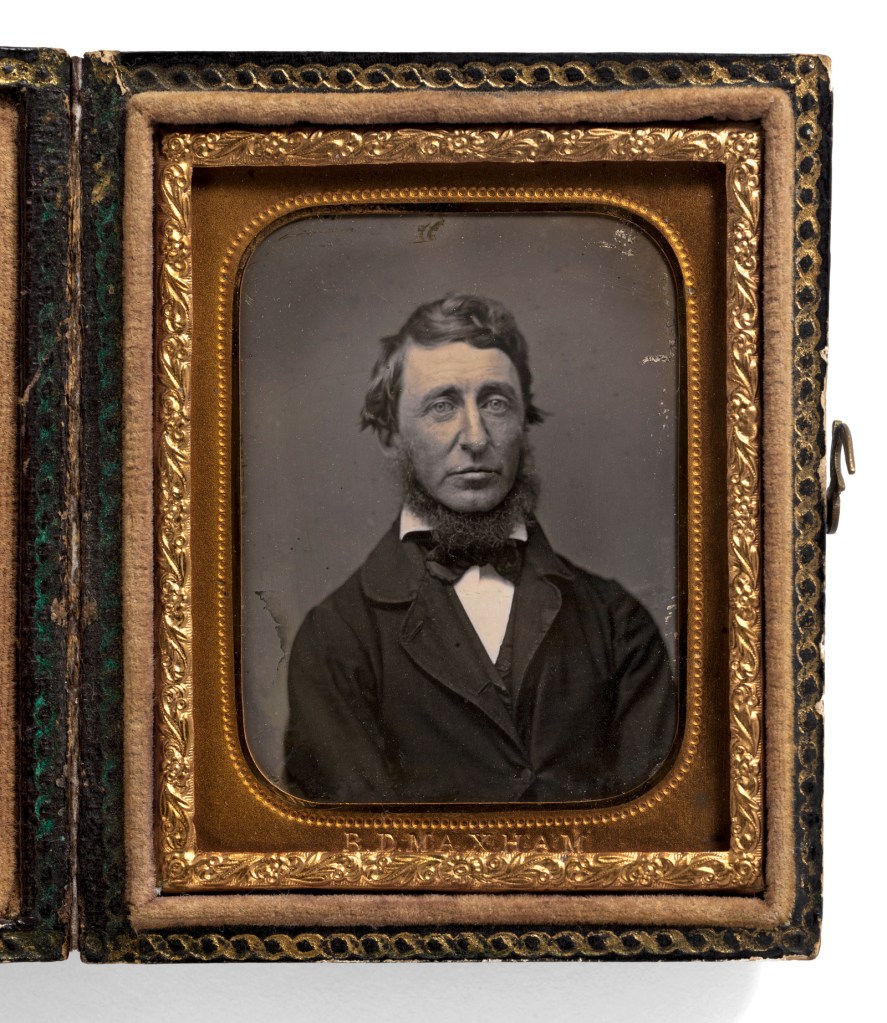

Benjamin D. Maxham (American, 1821-1899, active 1848-1858)
Henry David Thoreau (July 12, 1817 – May 6, 1862)
1856
Ninth-plate daguerreotype
Height: 63mm (2.48 in)
Width: 47mm (1.85 in)
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution; gift of anonymous donor
Calvin R. Greene was a Thoreau “disciple” who lived in Rochester, Michigan, and who first began corresponding with Thoreau in January 1856. When Greene asked for a photographic image of the author, Thoreau initially replied: “You may rely on it that you have the best of me in my books, and that I am not worth seeing personally – the stuttering, blundering, clodhopper that I am.” Yet Greene repeated his request and sent money for the sitting. Thoreau must have kept this commitment to his fan in the back of his mind for the next several months. On June 18, 1856, during a trip to Worcester, Massachusetts, Henry Thoreau visited the Daguerrean Palace of Benjamin D. Maxham at 16 Huntington Street and had three daguerreotypes taken for fifty cents each. He gave two of the prints to his Worcester friends and hosts, H.G.O. Blake and Theophilius Brown. The third he sent to Calvin Greene in Michigan. “While in Worcester this week I obtained the accompanying daguerreotype – which my friends think is pretty good – though better looking than I,” Thoreau wrote.
Text from the Wikipedia website
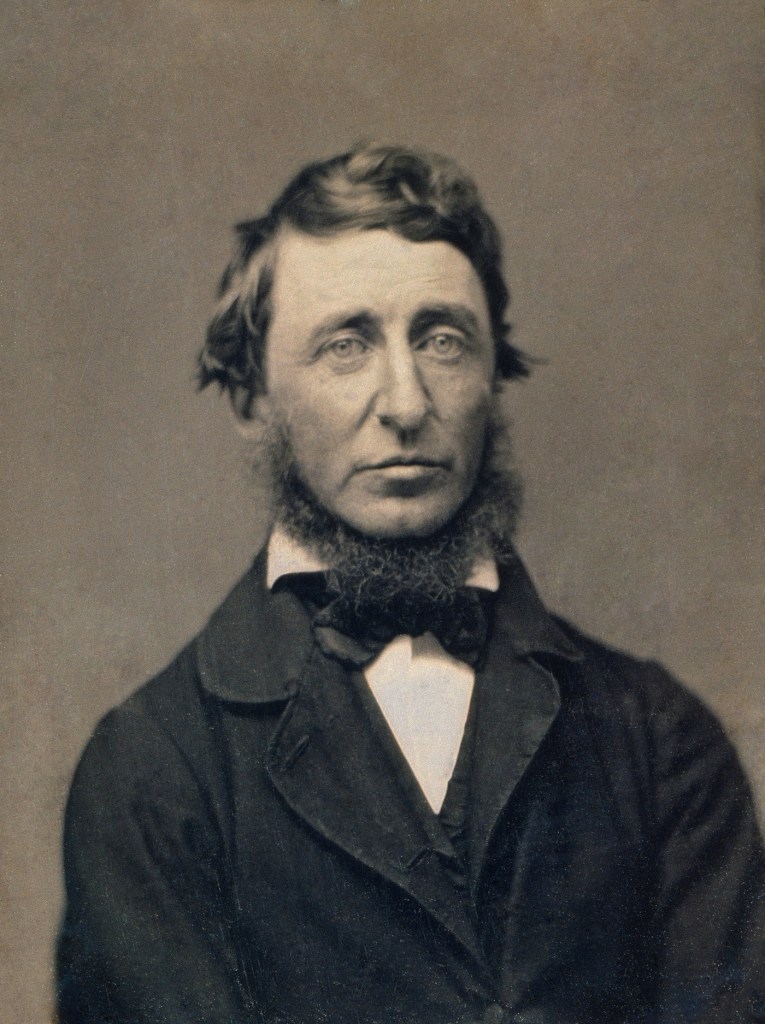

Benjamin D. Maxham (American, 1821-1899, active 1848-1858)
Henry David Thoreau (July 12, 1817 – May 6, 1862) (detail, restored)
1856
Ninth-plate daguerreotype
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution; gift of anonymous donor
Henry David Thoreau (American, 1817-1862)
Henry David Thoreau (July 12, 1817 – May 6, 1862) was an American essayist, poet, philosopher, abolitionist, naturalist, tax resister, development critic, surveyor, and historian. A leading transcendentalist, Thoreau is best known for his book Walden, a reflection upon simple living in natural surroundings, and his essay “Civil Disobedience” (originally published as “Resistance to Civil Government”), an argument for disobedience to an unjust state.
Thoreau’s books, articles, essays, journals, and poetry amount to more than 20 volumes. Among his lasting contributions are his writings on natural history and philosophy, in which he anticipated the methods and findings of ecology and environmental history, two sources of modern-day environmentalism. His literary style interweaves close observation of nature, personal experience, pointed rhetoric, symbolic meanings, and historical lore, while displaying a poetic sensibility, philosophical austerity, and Yankee attention to practical detail. He was also deeply interested in the idea of survival in the face of hostile elements, historical change, and natural decay; at the same time he advocated abandoning waste and illusion in order to discover life’s true essential needs.
He was a lifelong abolitionist, delivering lectures that attacked the Fugitive Slave Law while praising the writings of Wendell Phillips and defending the abolitionist John Brown. Thoreau’s philosophy of civil disobedience later influenced the political thoughts and actions of such notable figures as Leo Tolstoy, Mahatma Gandhi, and Martin Luther King Jr.
Thoreau is sometimes referred to as an anarchist. Though “Civil Disobedience” seems to call for improving rather than abolishing government – “I ask for, not at once no government, but at once a better government” – the direction of this improvement contrarily points toward anarchism: “‘That government is best which governs not at all;’ and when men are prepared for it, that will be the kind of government which they will have.”
Transcendentalism
A core belief of transcendentalism is in the inherent goodness of people and nature. Adherents believe that society and its institutions have corrupted the purity of the individual, and they have faith that people are at their best when truly “self-reliant” and independent.
Transcendentalism emphasises subjective intuition over objective empiricism. Adherents believe that individuals are capable of generating completely original insights with little attention and deference to past masters.
Text from the Wikipedia website
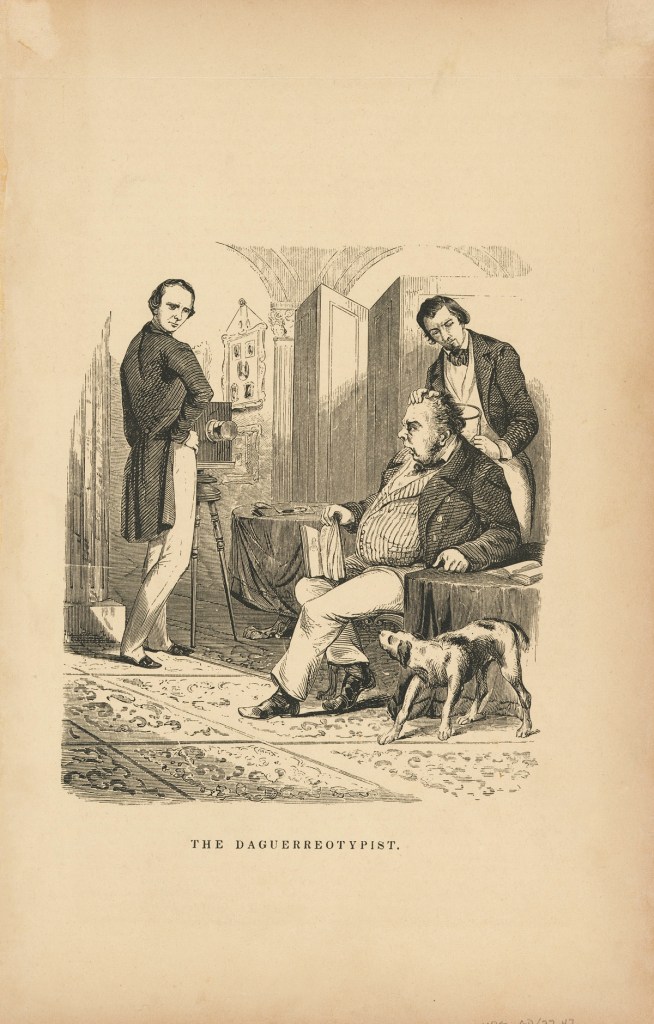

Unidentified artist (American)
The Daguerreotypist
1849
Wood engraving on paper
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Smithsonian National Portrait Gallery
8th and F Sts NW
Washington, DC 20001
Opening hours:
11.30am – 7.00pm daily
























































You must be logged in to post a comment.