Wednesday 5th December 2012
We were asked to choose our favourite photograph, one that we could nominate as a great photograph. I chose a slightly different take on proceedings.
Marcus
Many thankx to my fellow speakers for their talks and to Director of the Centre for Contemporary Photography Naomi Cass for inviting me to speak at a wonderful evening. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
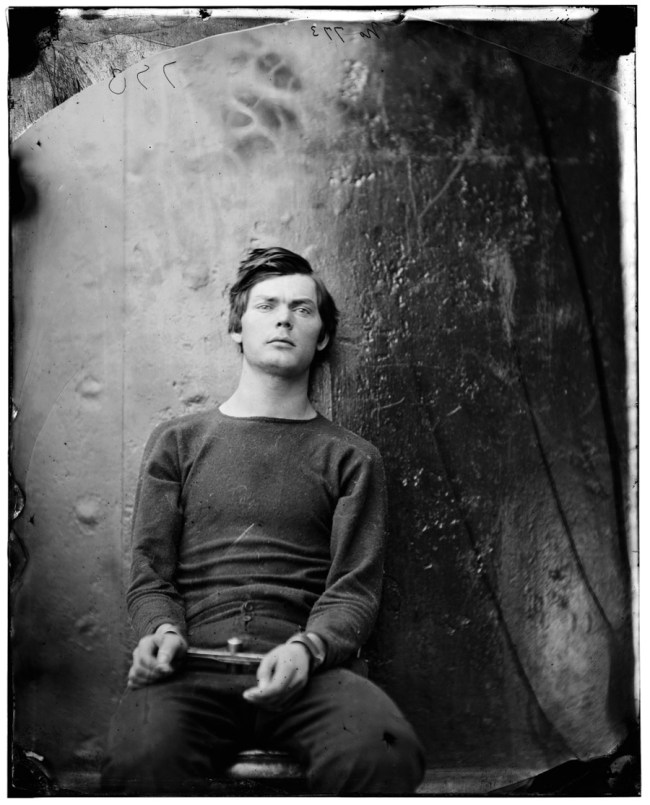

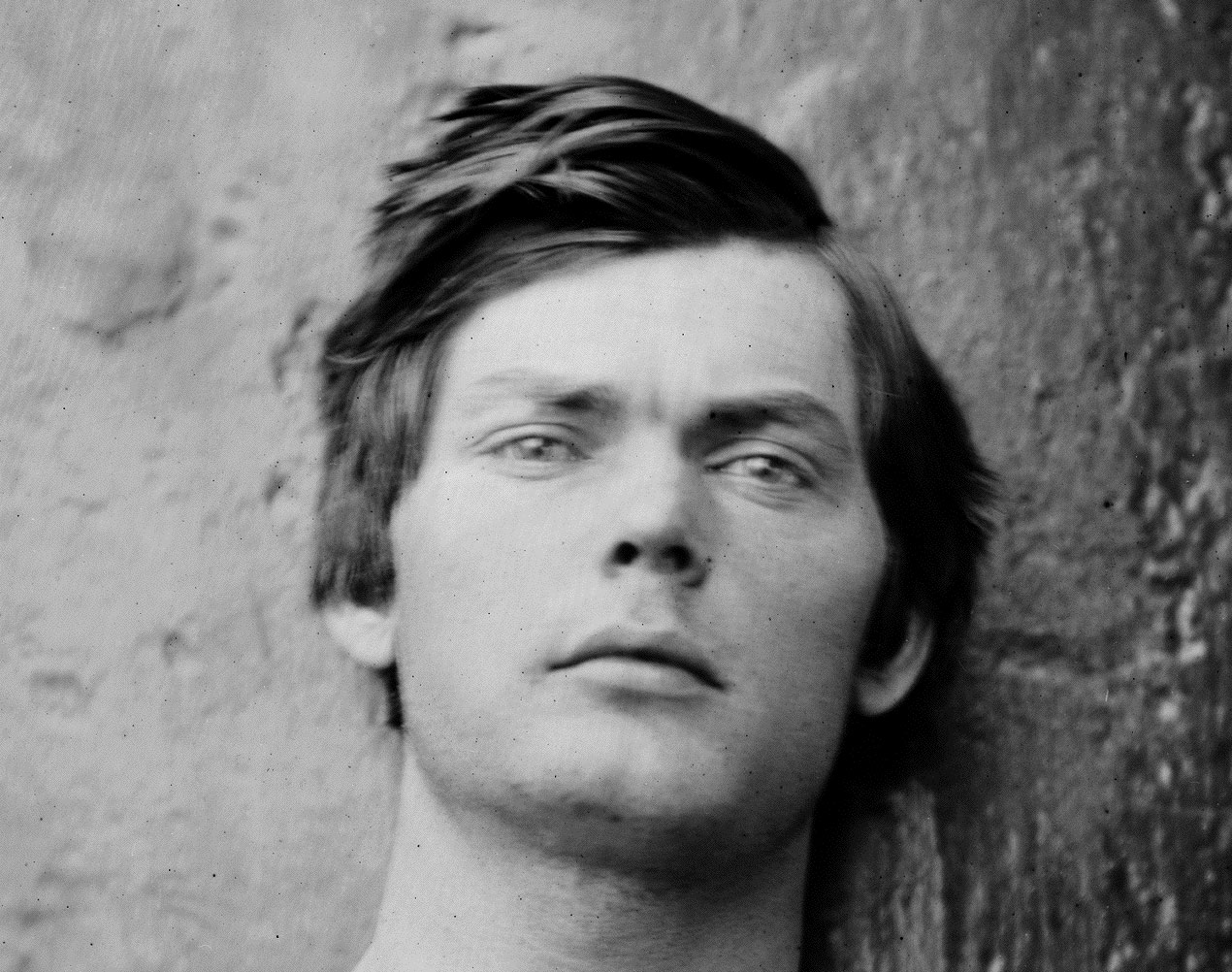
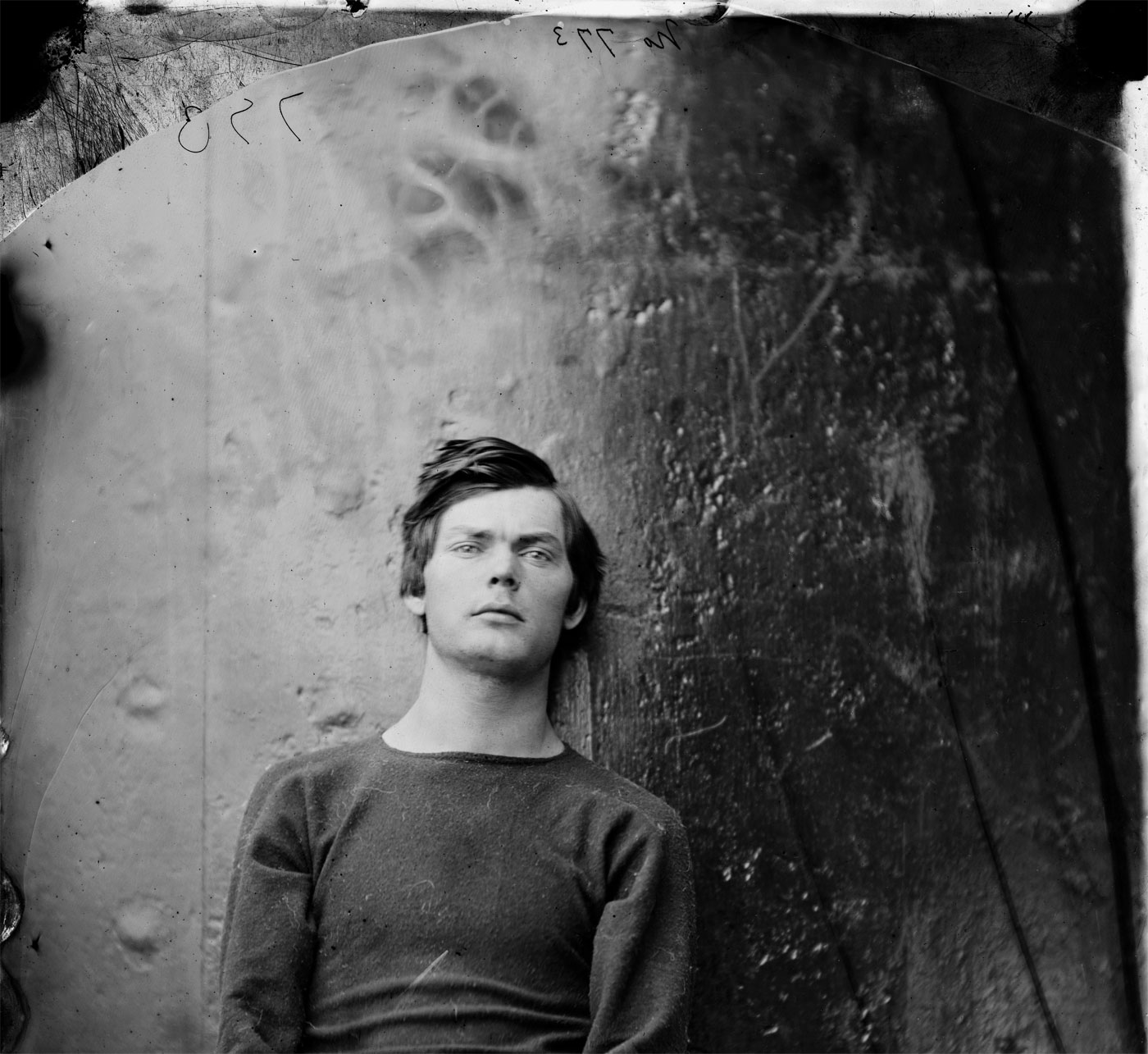
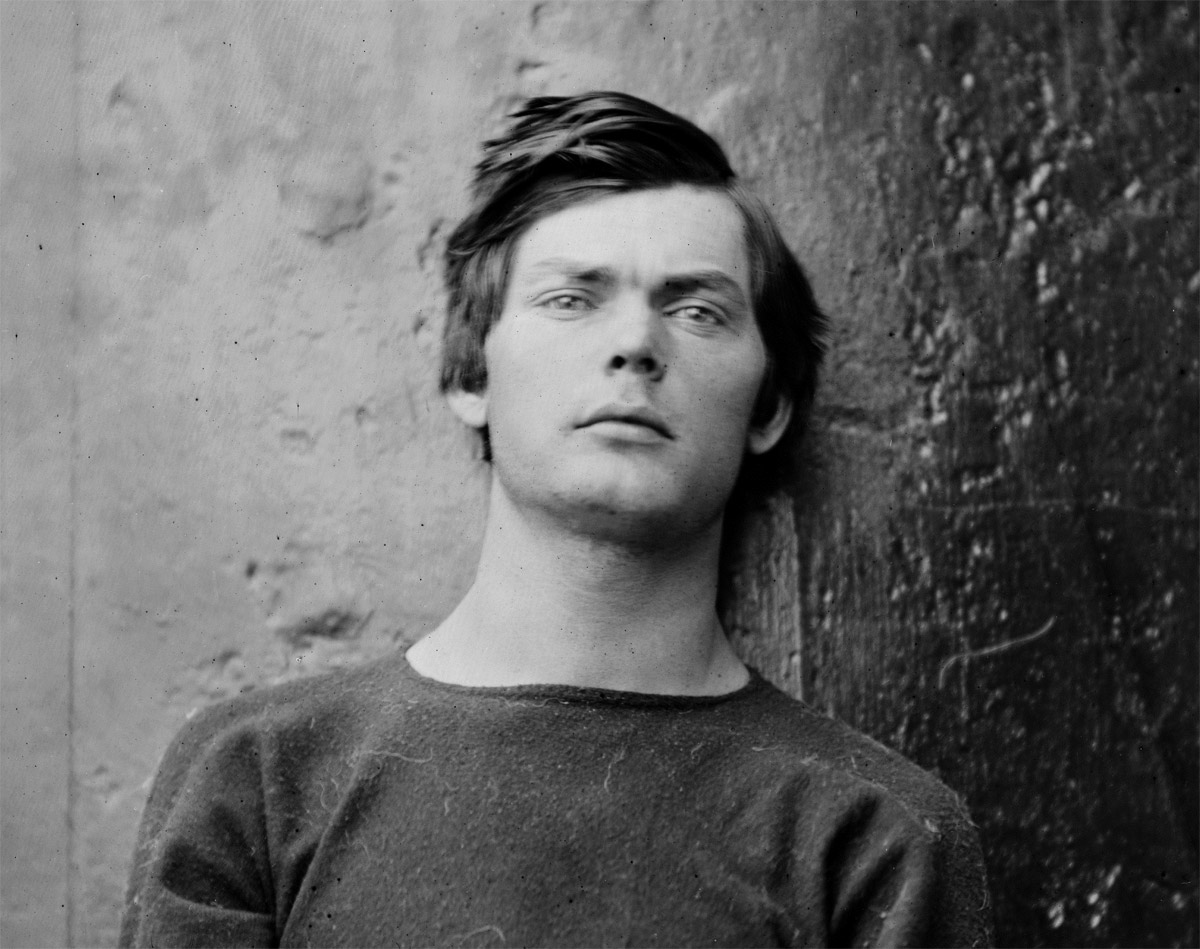
Alexander Gardner (American, 1821-1882)
Lewis Paine
26th April, 1865
Albumen silver print from a Collodion glass plate negative
This is not my favourite photograph
A minute’s silence…
This is not my favourite photograph
Nor may it be a great photograph…
More interestingly to me, it is a remarkable photograph – one that you are able to make remarks on.
It is also a photograph that has haunted me for years.
Taken by Alexander Gardner in April 1865, this photograph is a portrait of Lewis Thornton Powell (aka Lewis Payne or Paine) who was one of the conspirators in the assassination of Abraham Lincoln which had happened the same month. The photograph has a background of dark metal, and was taken on one of the ironclads U.S.S. Montauk or Saugus, where the conspirators were for a time confined. Paine was executed in July 1865 just eight short weeks later.
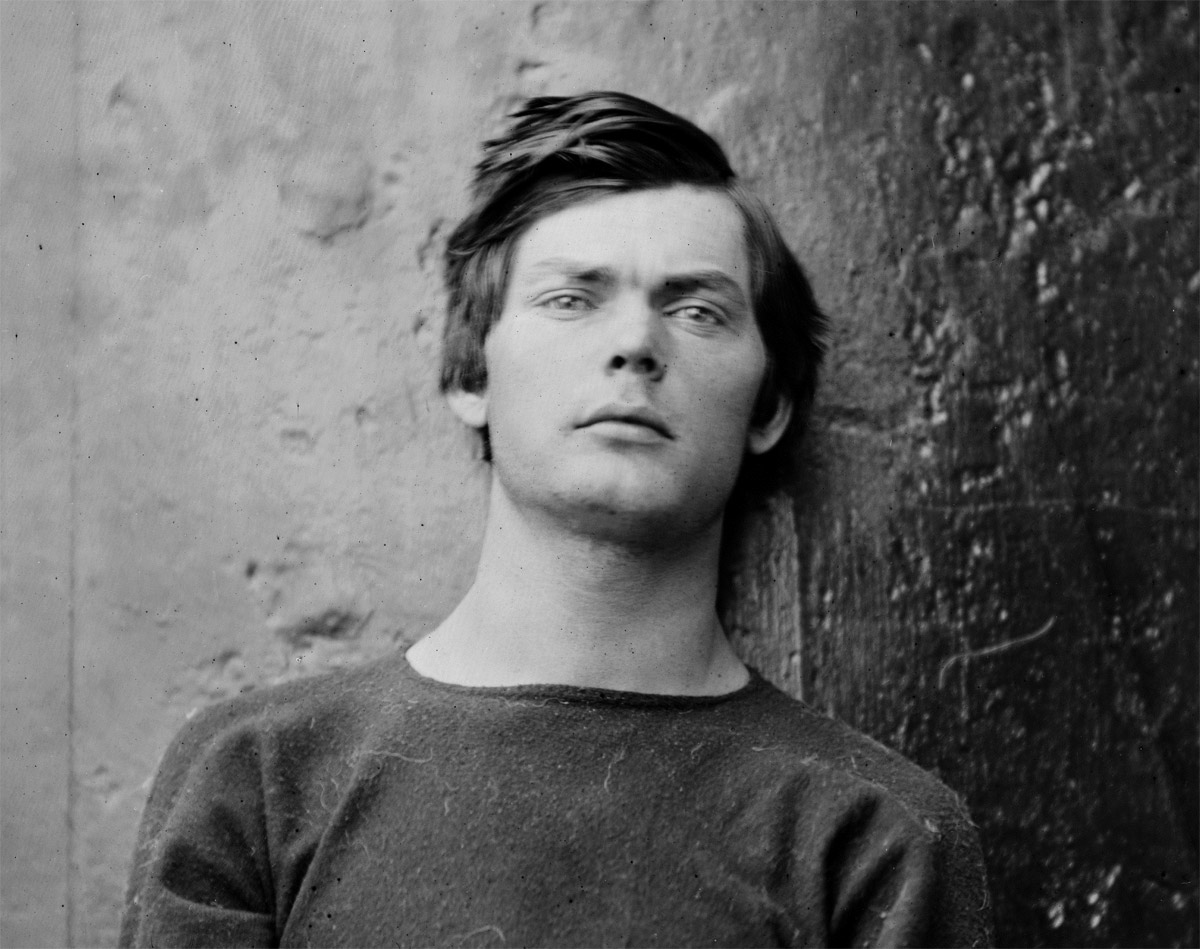
Alexander Gardner (American, 1821-1882)
Three photographs of Lewis Paine
26th April, 1865
This is the triptych of photographs by Gardner in the form they are usually displayed, like a three-panel renaissance altar-piece. The left and right hand photographs were taken within minutes of each other, with the camera in the same position, whereas in the centre photograph the camera has been lowered to show more of the body, and the image has been cropped at the top. In the central plate the figure of Paine has been raised up in the frame – almost prematurely brought back to life by his placement.
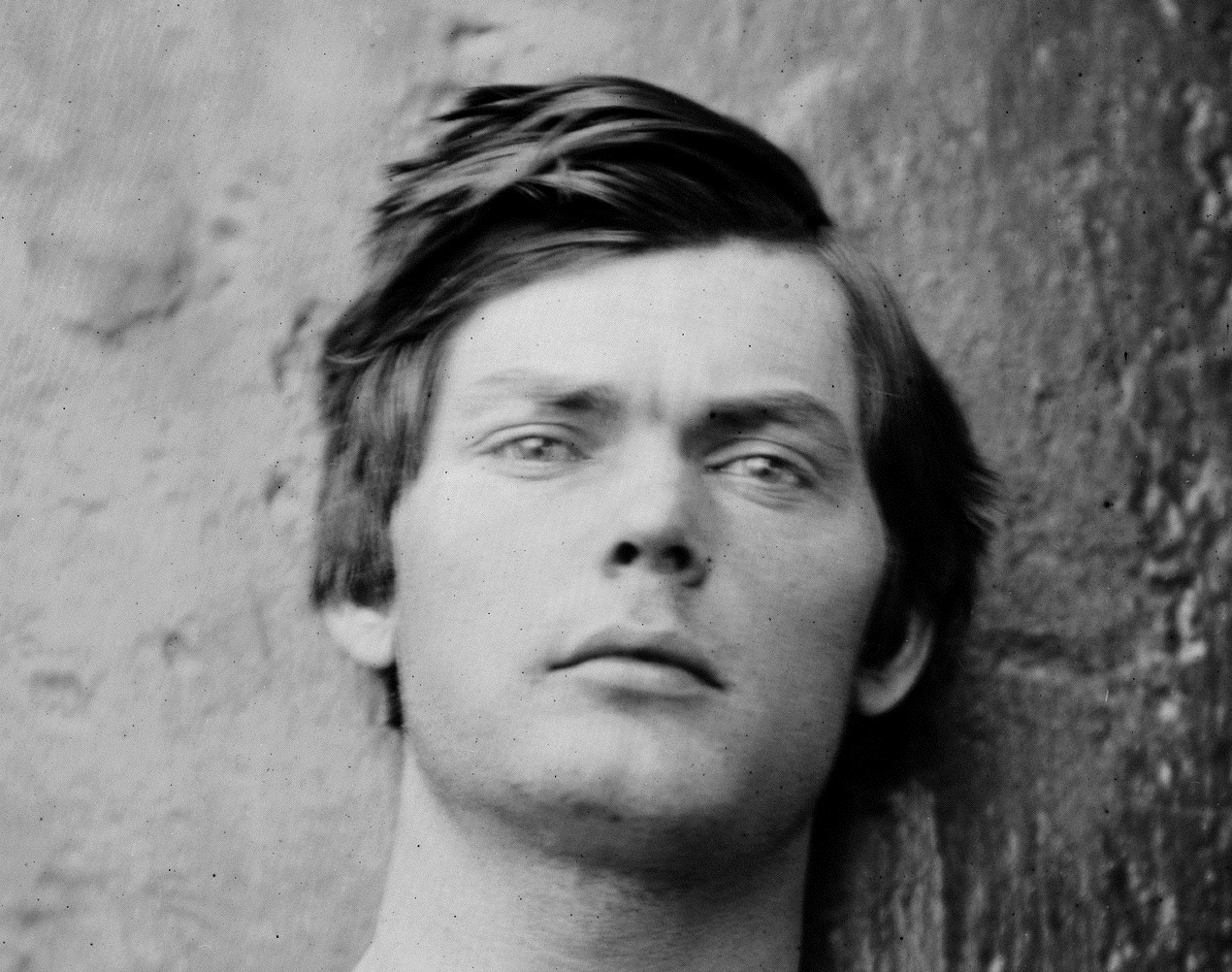
The centre image is the only one where Paine stares directly at the camera. He surveys the viewer with a gaze I find enigmatic.
This is a very modern face, a very contemporary face. His hair is just like Justin Beiber’s.
Who brushed his hair across for this picture, and would it normally be this long, or has it just been ignored because of his fate?
He still has good muscle tone – has he been exercising in his cell?
And finally his clothing – is it navy issue, as his top appears to have been given to him, perhaps the coarse, navy blue wool of the Northern states.

Noel Cordle
Hot Dead Guys: Lewis Powell
Posted on September 5th, 2010
Mere Musings blog [Online] Cited 01/12/2012 no longer available online
There’s even a web page dedicated to him on “hot dead guys” where there’s that awkward moment when one of Lincoln’s conspirators is so sexy its ridiculous…
He wasn’t all bad. Biographers of Powell describe him as a quiet, introverted boy who enjoyed fishing and caring for sick and injured animals. Apparently, Lewis was an intelligent, sensitive, soul with great potential.

Descriptions of Lewis from “The Life, Crime and Capture”
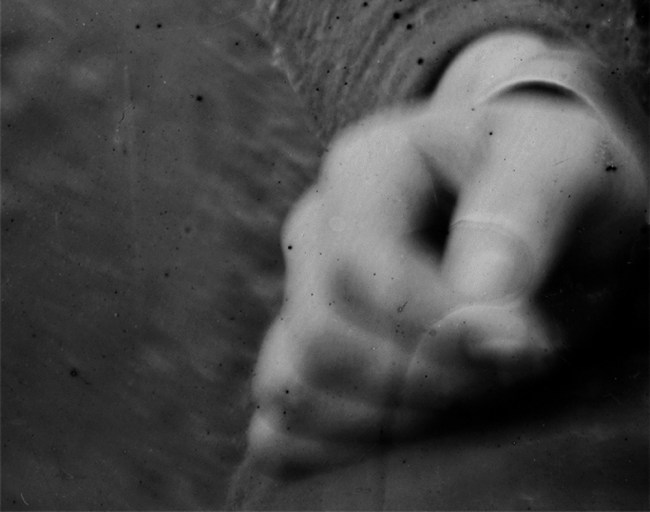

.
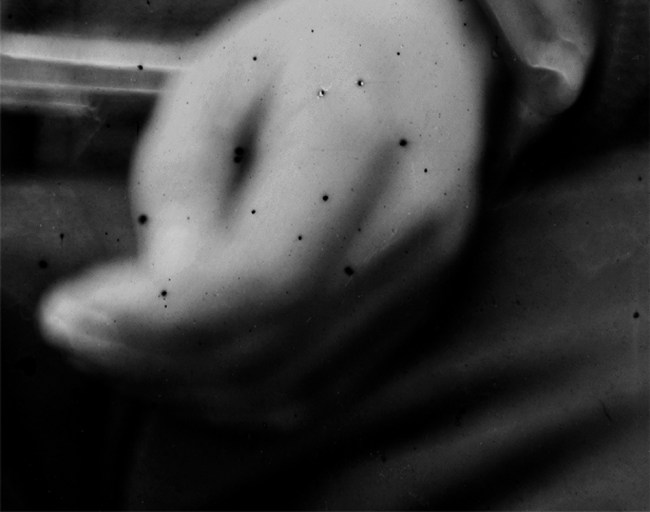
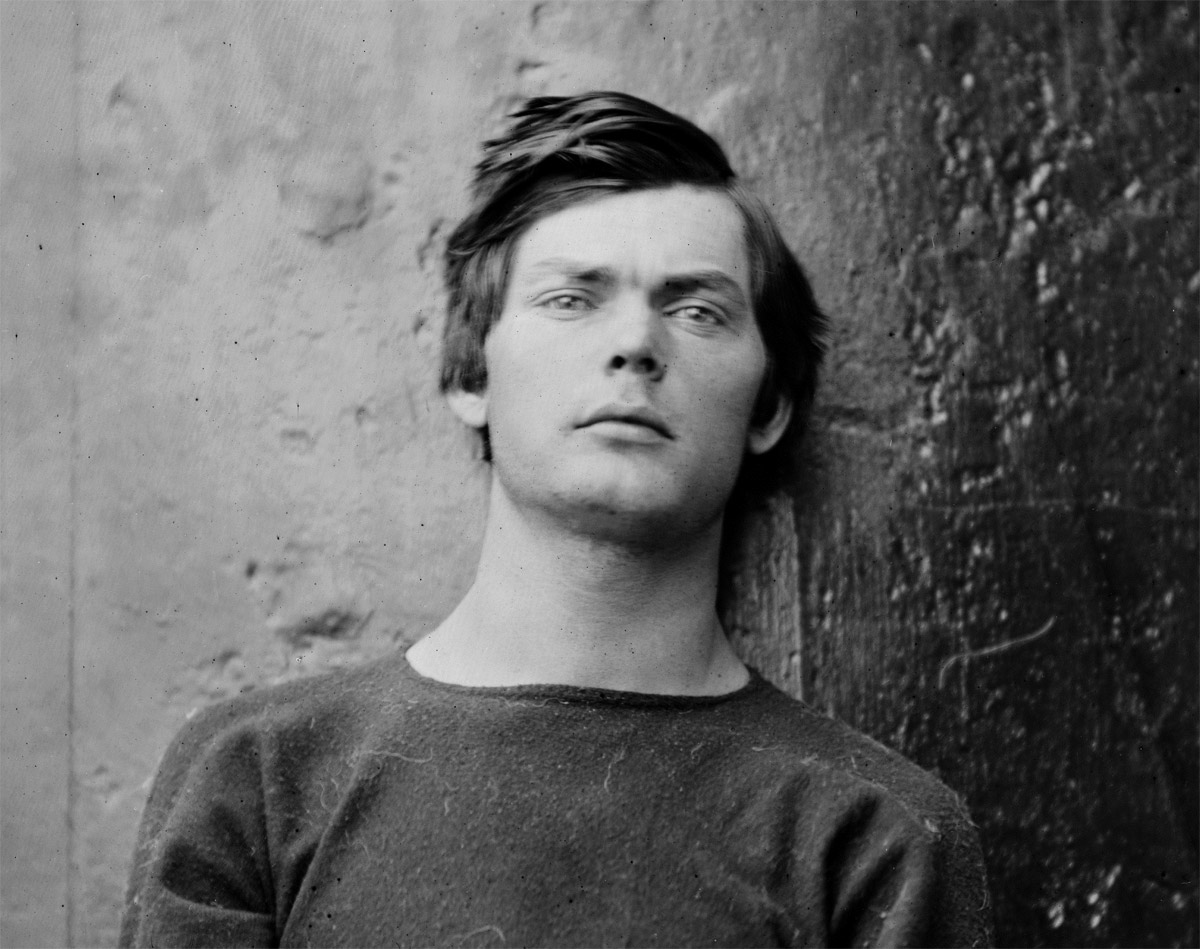
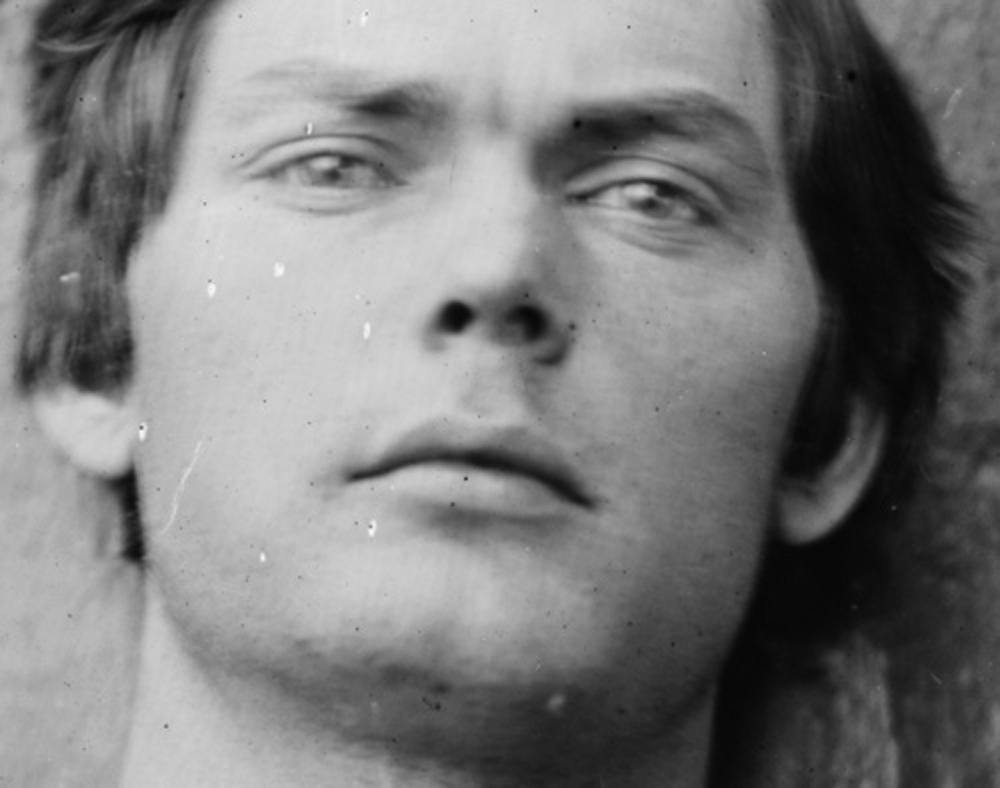
Alexander Gardner (American, 1821-1882)
Lewis Paine (detail)
26th April, 1865
Albumen silver print from a Collodion glass plate negative
Could we say that he is left-handed given the different size of his fingers (?)
Roland Barthes (French, 1915-1980)
Camera Lucida (La Chambre claire)
1980
Roland Barthes in his seminal work Camera Lucida said in Section 39: “He is dead and he is going to die…
“The photograph is handsome, as is the boy: that is the studium. But the punctum is: he is going to die. I read at the same time: this will be and this has been; I observe with horror an anterior future of which death is the stake. By giving me the absolute past of the pose, the photograph tells me death in the future. What pricks me is the discovery of this equivalence.”

If we were to place this image within the metaphysical school of photography which peaked with Paul Caponigro and Minor White we could say:
Hovering above his head, has his spirit already begun to leave his body?

One reading of his gaze is that he is really interested in what the photographer is doing – almost the gaze of an apprentice wanting to apply these skills in the future.
Given his fate is he insane because of his interest?
What is really going on in his mind – what is his perspective?
Another reading could be as looking out to the future in the hope of finding that he will be judged in another way.
And another is the immediacy of his gaze – it is a gaze that is happening now!
The other thing that I find quite mysterious is the distance of the photographer from the subject.
Was it fear that stopped him getting any closer or are there deck fittings we cannot see that prevented his approach?
What brought Paine to this place?
Michel Foucault calls the methods and techniques through which human beings constitute themselves, “Technologies of the self.” Foucault argued that we as subjects are perpetually engaged in processes whereby we define and produce our own ethical self-understanding. According to Foucault, technologies of the self are the forms of knowledge and strategies that “permit individuals to effect by their own means or with the help of others a certain number of operations on their own bodies and souls, thoughts, conduct, and way of being, so as to transform themselves in order to attain a certain state of immortality.”1
As we look into his eyes he knows that we know he is going to die, has already died but the intensity of that knowledge is brought into present time. What Paine emanates is a form of i-mortality.
I wonder, did Gardner ever show him the finished photographs before he died?
This is Barthes anterior future, a moment where truth is interpreted in the mind of the photographer, not out there but in here [points to head and heart], where past, present and future coalesce into single point in time – his death and our death are connected through his gaze, the knowledge of our discontinuity. Eons contracted into an eternal moment.
In this moment in time, what we are doing is we are making a list about the human condition when we talk about something that is remarkable. We are moving towards a language that defines the human condition…
But ultimately language can never fully describe the human condition, much as it may try… and this is why this photograph is remarkable, because it is ineffable, unknowable.
This photograph inhabits you, it haunts you like few others.
Early Wittgenstein described a world of facts pictured by thoughts. he said, “Don’t Think, But Look!”
I would add “Don’t think, but feel and look”
This photograph is a memoriam to a young man and his present death. As such it is a REMARKABLE photograph that haunts us all.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
December 2012
1/ Foucault, Michel. “Technologies of the self,” in L. H. Martin, H. Gutman and P. H. Hutton (eds.). Technologies of the self. Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press, 1988, p. 18.
Postscript

George Cook (American, 1819-1902)
Union ironclads firing on Fort Moultrie, S.C.,
8th September 1863
Photo courtesy of the Cook Collection, Valentine Richmond History
George Cook’s photograph of Union ironclads firing on Fort Moultrie, S.C., believed to be the world’s first combat photograph. Monitors engage Confederate batteries on Sullivan’s Island, Charleston, South Carolina. Photographed from one of the Confederate emplacements, the ships are identified as (from left to right): Weehawken, Montauk and Passaic. The monitor on the right appears to be firing its guns. Date is given as 8 September 1863, when other U.S. Navy ships were providing cover for Weehawken, which had gone aground on the previous day. She was refloated on the 8th after receiving heavy gunfire from the Confederate fortifications.
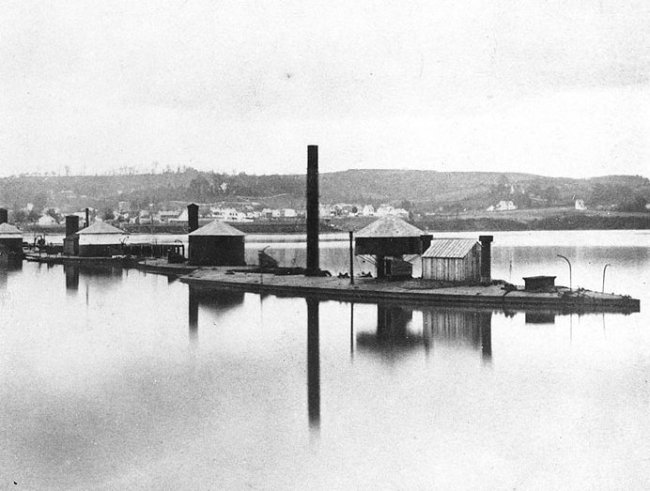

Kilburn Brothers (Edward and Benjamin Kilburn, American)
Four monitors laid up in the Anacostia River, off the Washington Navy Yard
c. 1866
Ships are (from left to right): USS Mahopac, USS Saugus, USS Montauk (probably), and either USS Casco or USS Chimo
Photo mounted on a stereograph card, marked: “Photographed and published by Kilburn Brothers, Littleton, N.H.”
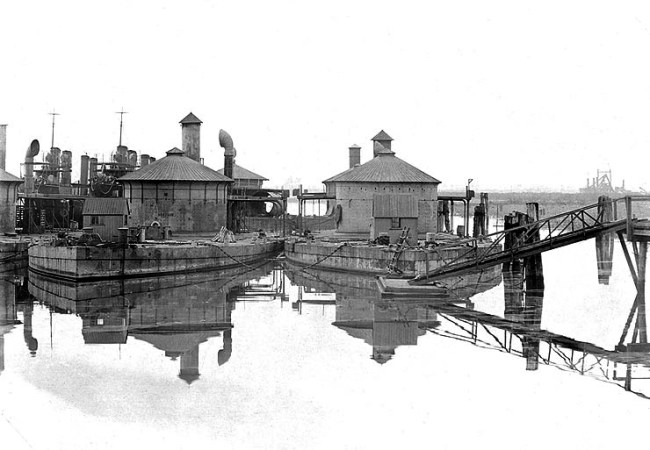

Anonymous photographer
‘Montauk’ at left, and ‘Lehigh’ at right, laid up at the Philadelphia Navy Yard, Pennsylvania
c. late 1902 or early 1903
U.S. Naval Historical Center photograph
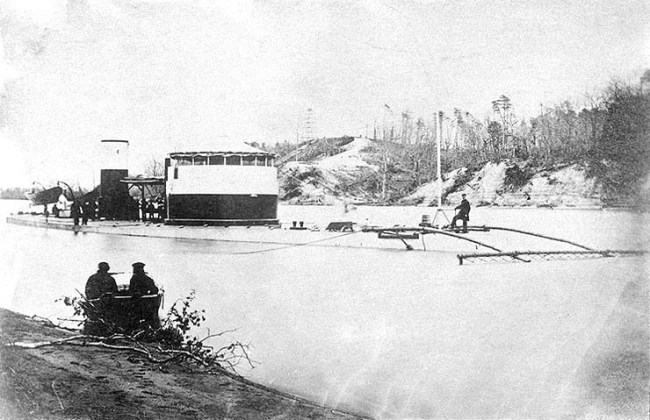

Anonymous photographer
Saugus, in Trent’s Reach on the James River, Virginia
c. early 1865
Note the mine sweeping “rake” attached to her bow
U.S. Naval Historical Center photograph
Anonymous photographer
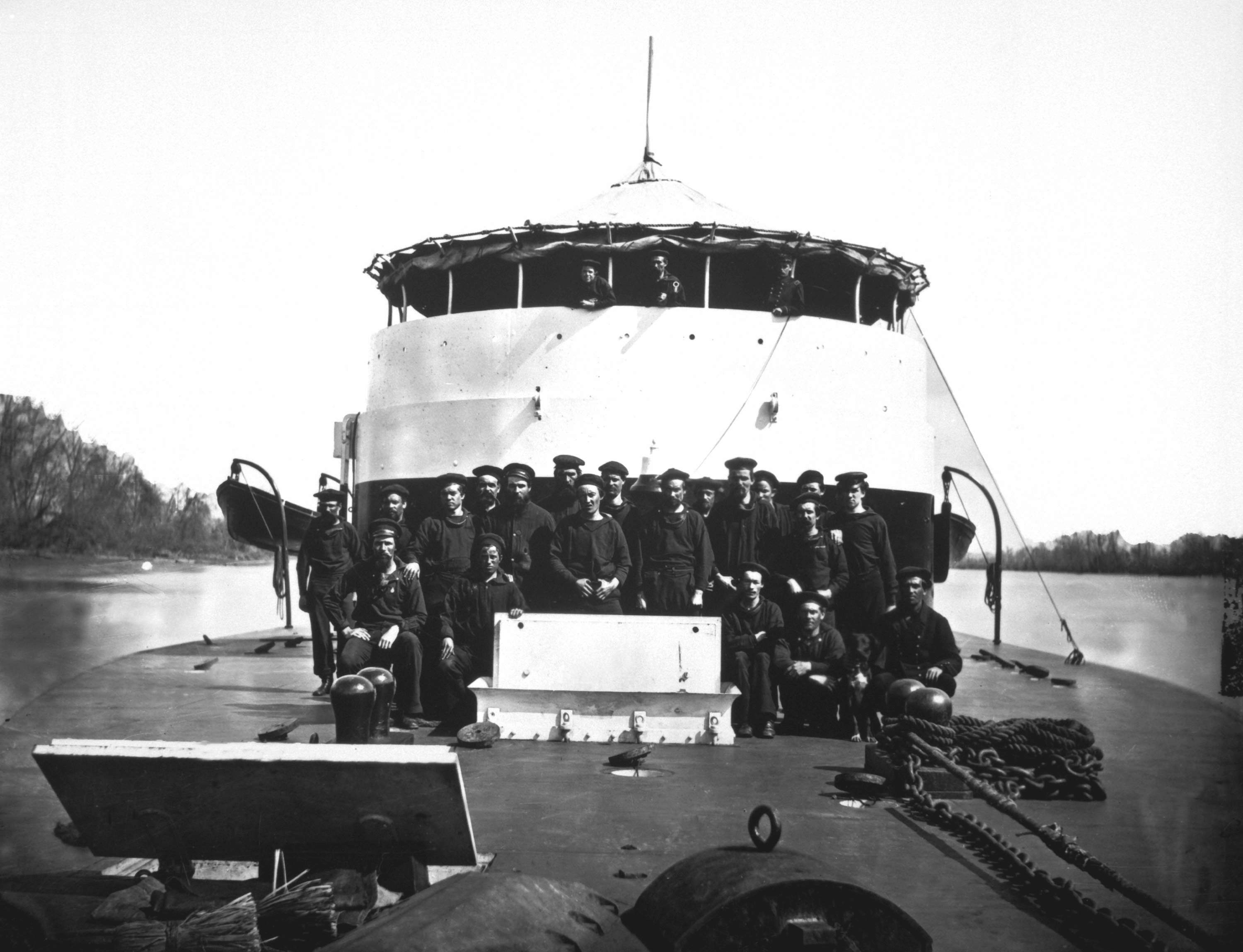
Officers pose on deck of the Saugus, in front of the gun turret, probably while the ship was serving on the James River, Virginia
c. early 1865
Note ship’s bell and other details of the turret and deck fittings
U.S. Naval Historical Center photograph
Centre for Contemporary Photography
No permanent exhibition space at the moment














![Judith Wright (Australian, b. 1945) 'Desire [14]' 2009 from the exhibition 'Desire' paintings and video by Judith Wright at Sophie Gannon Gallery, Melbourne, May - June, 2009 Judith Wright (Australian, b. 1945) 'Desire [14]' 2009 from the exhibition 'Desire' paintings and video by Judith Wright at Sophie Gannon Gallery, Melbourne, May - June, 2009](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/05/wright-desiresgg14-xlg.jpg?w=602)
![Judith Wright (Australian, b. 1945) 'Desire [5]' 2009 from the exhibition 'Desire' paintings and video by Judith Wright at Sophie Gannon Gallery, Melbourne, May - June, 2009 Judith Wright (Australian, b. 1945) 'Desire [5]' 2009 from the exhibition 'Desire' paintings and video by Judith Wright at Sophie Gannon Gallery, Melbourne, May - June, 2009](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/05/wright-desiresgg5-xlg.jpg?w=613)
![Judith Wright (Australian, b. 1945) 'Desire [7]' 2009 Judith Wright (Australian, b. 1945) 'Desire [7]' 2009](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/05/wright-desiresgg7-xlg2.jpg?w=604)
![Judith Wright (Australian, b. 1945) Desire [16]' 2009 Judith Wright (Australian, b. 1945) Desire [16]' 2009](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/05/wright-desiresgg16-xlg.jpg?w=607)
![Judith Wright (Australian, b. 1945) 'The Gift [2]' 2009 Judith Wright (Australian, b. 1945) 'The Gift [2]' 2009](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/05/wright-the_gift2-xlg.jpg)
![Judith Wright (Australian, b. 1945) 'The Gift [7]' 2008 Judith Wright (Australian, b. 1945) 'The Gift [7]' 2008](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/05/wright-the_gift7-xlg.jpg)
You must be logged in to post a comment.