Exhibition dates: 2nd May – 14th October, 2018
Curators: Simon Baker, Senior Curator, International Art (Photography) and Shoair Mavlian, Assistant Curator, Tate Modern, with Emmanuelle de l’Ecotais, Curator for Photographs
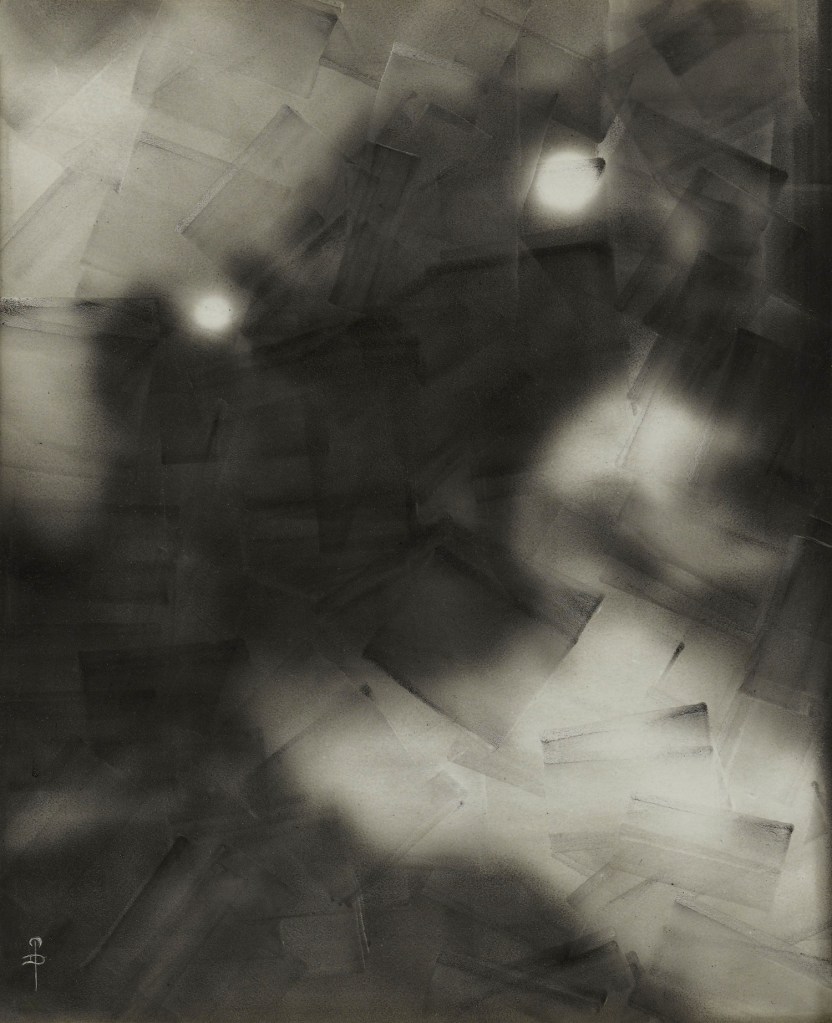

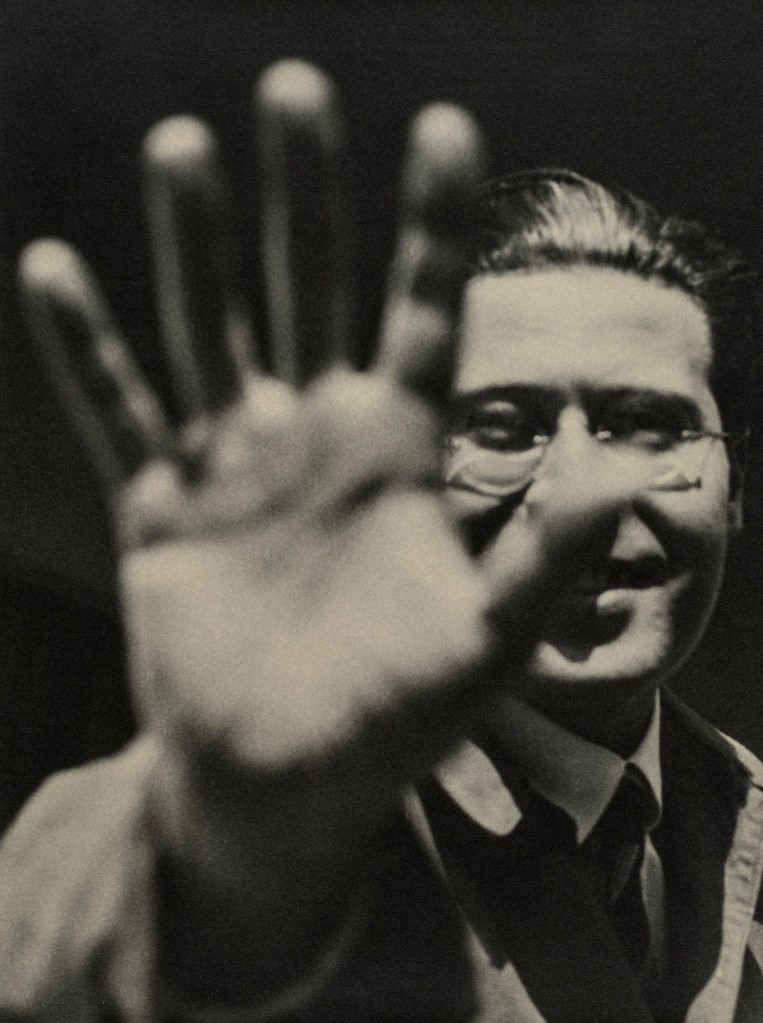
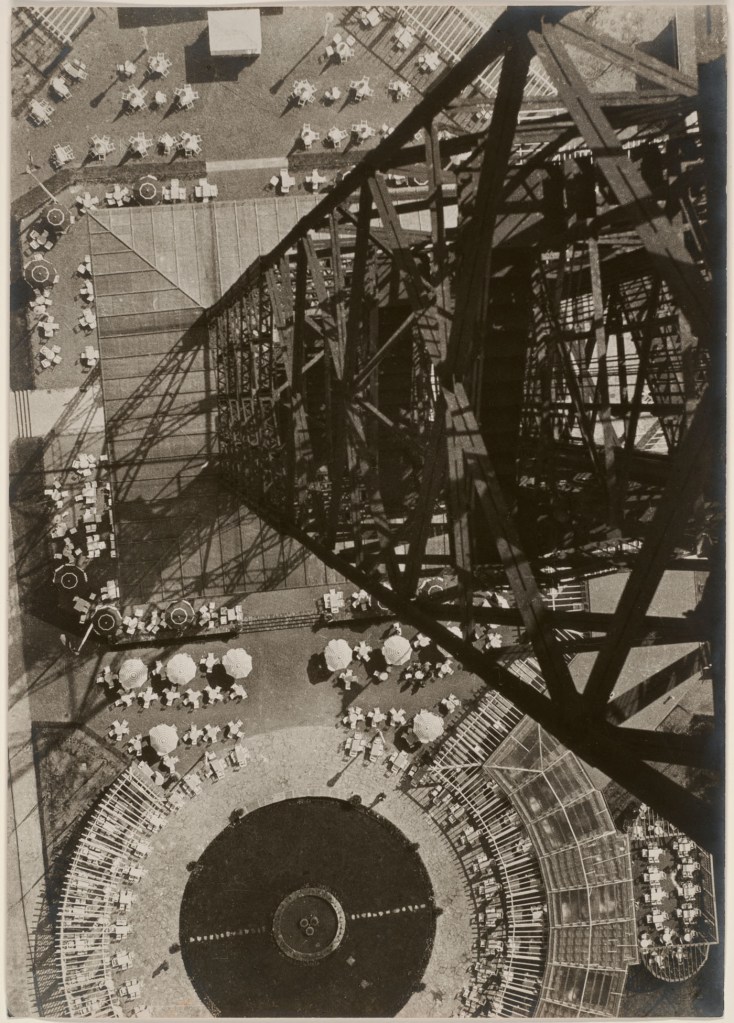
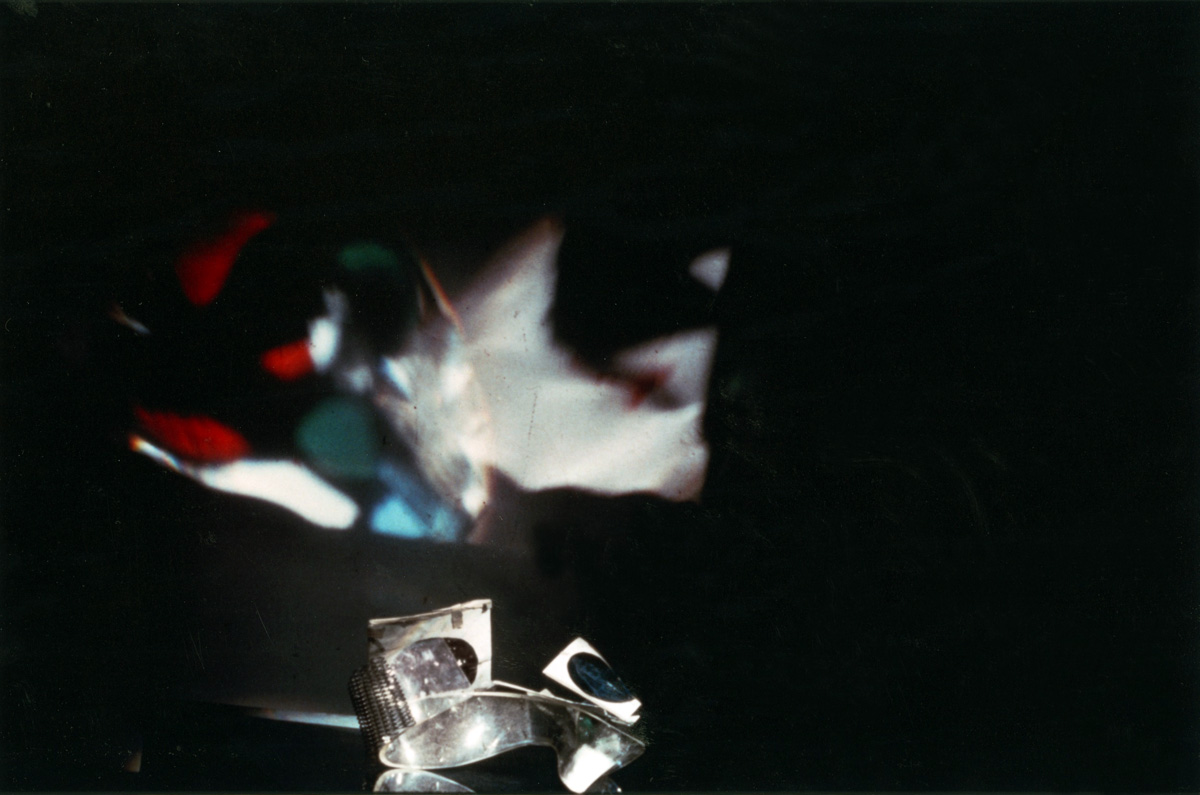
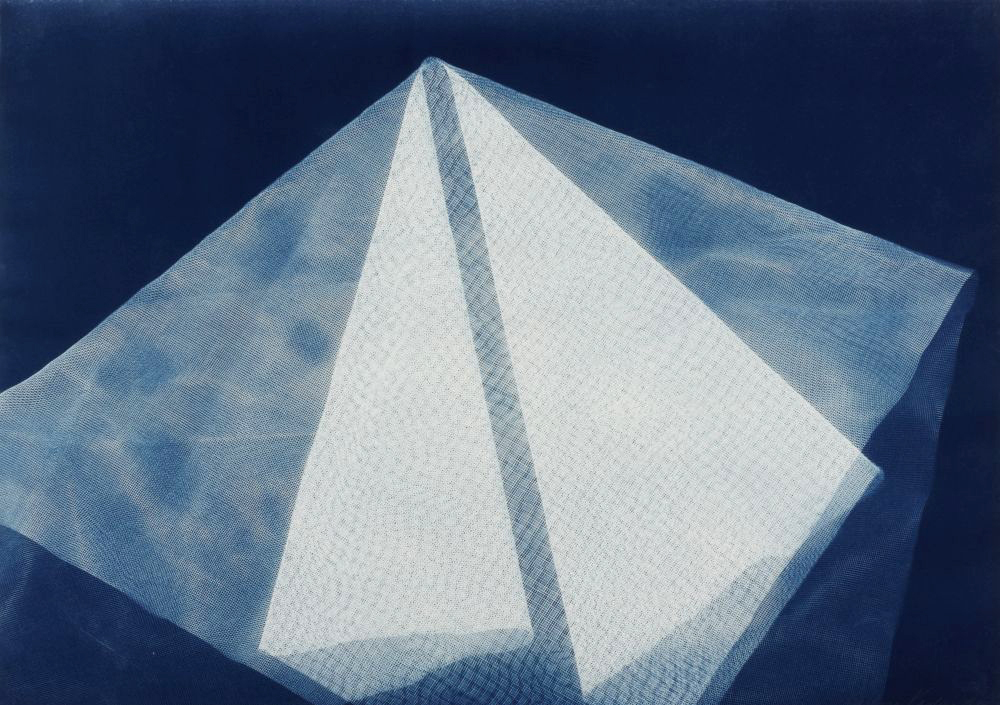
Pierre Dubreuil (French, 1872-1944)
Interpretation Picasso, The Railway
1911
Gelatin silver print on paper
238 x 194mm
Centre Pompidou, Paris
Musée National d’Art Moderne / Centre de Création Industrielle
Purchased, 1987
An interesting premise –
“a premise is an assumption that something is true. In logic, an argument requires a set of (at least) two declarative sentences (or “propositions”) known as the premises or premisses along with another declarative sentence (or “proposition”) known as the conclusion” (Wikipedia)
– that the stories (the declarative sentences) of abstract art and abstract photography are intertwined (the conclusion). The two premises and one conclusion forms the basic argumentative structure of the exhibition.
Unfortunately in this exhibition, the abstract art and abstract photographs (declarations), seem to add up to less than the sum of its parts (conclusion).
Why is this so?
The reason these two bedfellows sit so uncomfortably together is that they are of a completely different order, one to the other.
Take painting for example. There is that ultimate linkage between brain, eye and hand as the artist “reaches out” into the unknown, and conjures an abstract representation from his imagination. This has a quality beyond my recognition. The closest that photography gets to this intuition is the cameraless Photogram, as the artist paints with light, from his imagination, onto the paper surface, the physical presence of the print.
Conversely, we grapple with the dual nature of photography, its relation to reality, to the real, and its interpretation of that reality through a physical, mechanical process – light entering a camera (metal, glass, digital chips, plastic film) to be developed in chemicals or on the computer, stored as a physical piece of paper or in binary code – but then we LOOK and FEEL what else a photograph can be. What it is, and what else it can be.
Initially, to take a photograph is to recognise something physical in the world which can then be abstracted. Here is a tree, a Platonic ideal, now here is the bark of the tree, or cracks in dried mud, or Aaron Siskind’s Pleasures and Terrors of Levitation in which, in our imagination, the body is no longer human. This archaeology of photography is a learnt behaviour (from the world, from abstract paintings) where ones learns to turn over the truth to something else, a recognition of something else. Where one digs a clod of earth, inspects it, and then turns it over to see what else it can be.
We can look at something in the world just for what it is and take a photograph of it, but then we can look at the same object for what else it can be (for example, Man Ray’s image Dust Breeding (1920), which is actually dust motes on the top of Duchamp’s Large Glass). Photographers love these possibilities within the physicality of the medium, its processes and outcomes. Photographers love changing scale, perspective, distortion using their intuition to perhaps uncover spiritual truths. Here I are not talking about making doodles – whoopee look what I can make as a photographer! it’s important because I can do it and show it and I said it’s important because I am an artist! the problem with lots of contemporary photography – it is something entirely different. It is the integrity of the emotional and intellectual process.
Not a reaching out through the arm and hand, but an unearthing (a reaching in?) of the possibilities of what else photography can be (other than a recording process). As Stieglitz understood in his Equivalents, and so Minor White espoused through his art and in one of his three canons:
When the image mirrors the man
And the man mirrors the subject
Something might take over
And that revelation is something completely different from the revelation of abstract art.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Tate Modern for allowing me to publish the art work in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“Despite its roll call of stellar names, the show’s adrenaline soon slumps. A rhythm sets in, as each gallery offers perhaps a single non photographic work and dozens of medium format black and white abstracts arranged on an allied theme: extreme close ups, engineered structures, worms’ and birds’ eye views, moving light, the human body, urban fabric.
Individually each photograph is quite wonderful, but they echo each other so closely in their authors’ attraction to diagonal arrangements, rich surface textures, dramatic shadows, odd perspectives and close cropping, that the same ‘point’ is being made a dozen times with little to distinguish between the variants. …
By the present day, abstract photography has given in to its already Ouroboros-like tendencies, and swallowed itself whole, offering abstract photographs about the process of photography, and the action of light on its materials. This is a gesture I relished in Wolfgang Tillmans’s show in the same space this time last year, when it was broken up by a plethora of other ideas and perspectives on photography. Here it feels like another level of earnest self-absorption with a century-long backstory.”
Hettie Judah. “By halfway round I actually felt faint,” on the iNews website May 5th 2018 [Online] Cited 14/07/2018. No longer available online
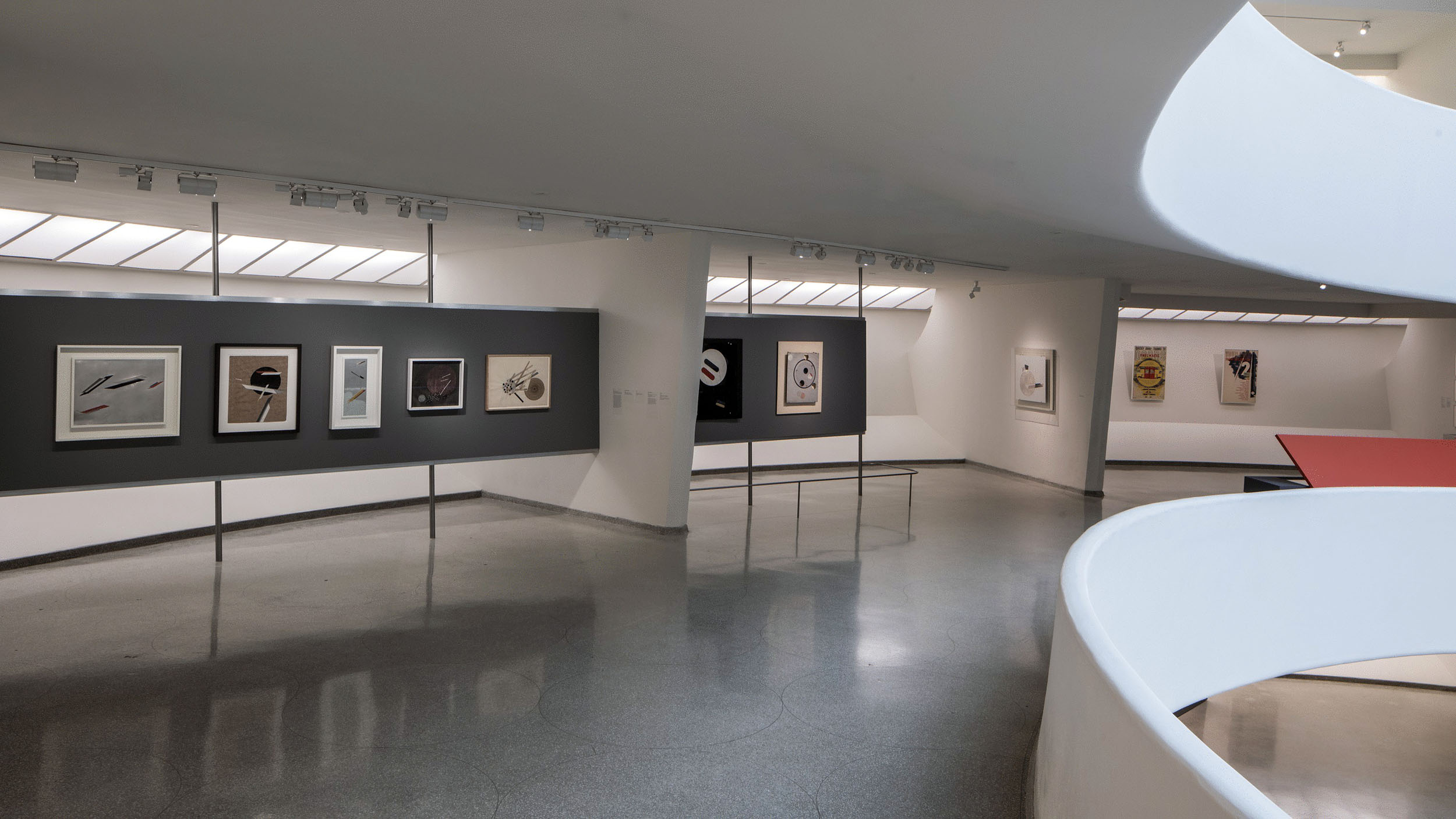
For the first time, Tate Modern tells the intertwined stories of photography and abstract art. The birth of abstract art and the invention of photography were both defining moments in modern visual culture, but these two stories are often told separately.
Shape of Light is the first major exhibition to explore the relationship between the two, spanning the century from the 1910s to the present day. It brings to life the innovation and originality of photographers over this period, and shows how they responded and contributed to the development of abstraction.
Key photographs are brought together from pioneers including Man Ray and Alfred Stieglitz, major contemporary artists such as Barbara Kasten and Thomas Ruff, right up to exciting new work by Antony Cairns, Maya Rochat and Daisuke Yokota, made especially for the exhibition.
Shape of Light | First Look
Tate Curator, Simon Baker, meets Caroline von Courten from leading photography Magazine, Foam. Together they explore the exhibition Shape of Light: 100 Years of Photography and Abstract Art at Tate Modern.
Exhibition Review – Shape of Light: 100 years of Photography and Abstract Art at Tate Modern

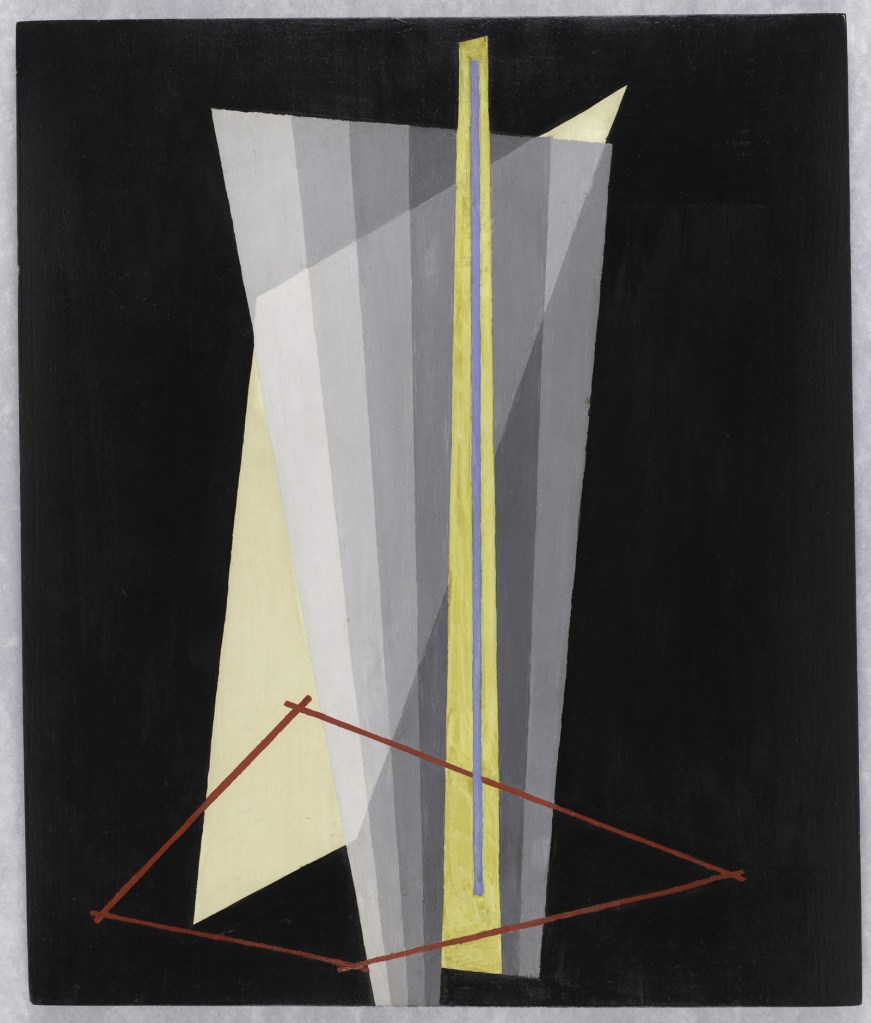
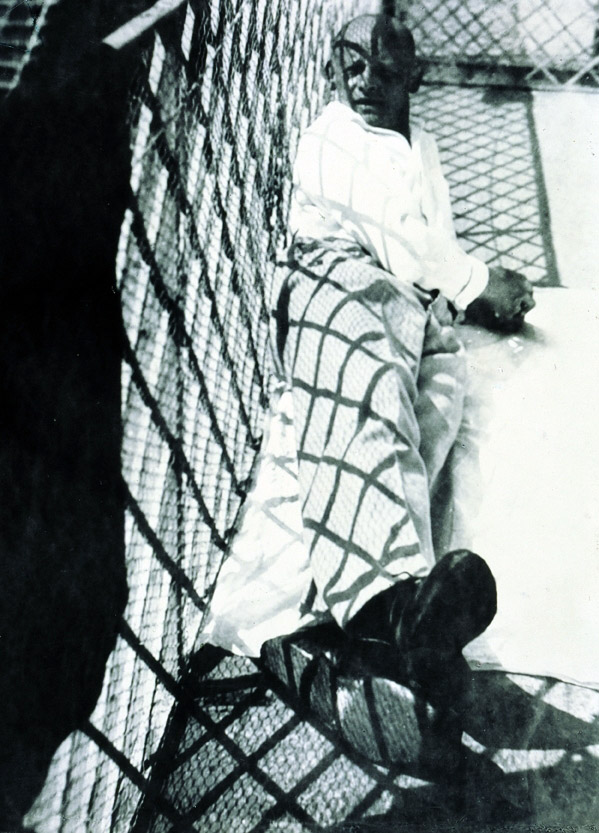
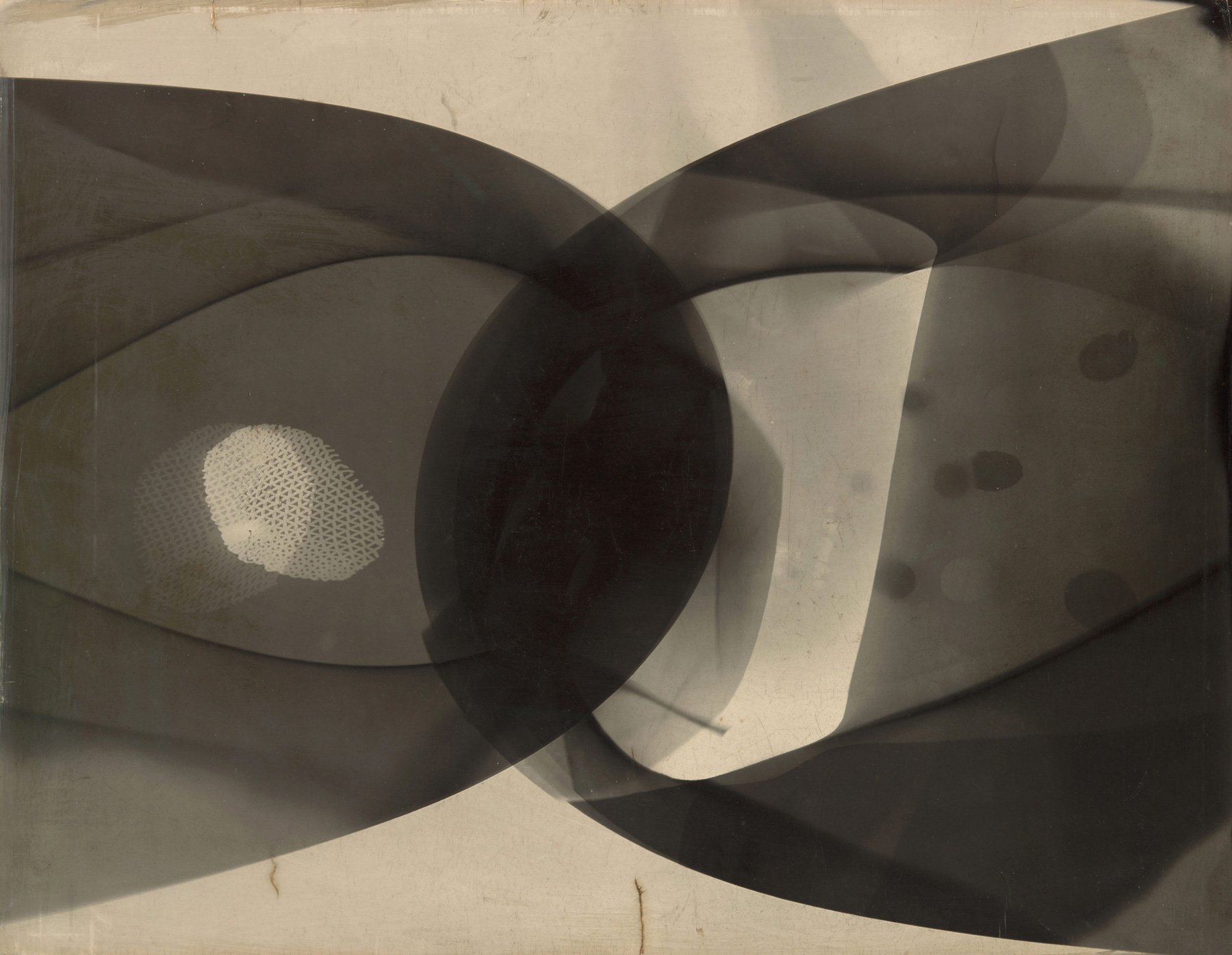
Wyndham Lewis (British, 1882-1957)
Workshop (installation view)
c. 1914-1915
Tate
Purchased 1974
© Wyndham Lewis and the estate of Mrs G A Wyndham Lewis by kind permission of the Wyndham Lewis Memorial Trust (a registered charity)
Percy Wyndham Lewis (18 November 1882 – 7 March 1957) was a British writer, painter, and critic. He was a co-founder of the Vorticist movement in art and edited BLAST, the literary magazine of the Vorticists.
His novels include Tarr (1918) and The Human Age trilogy, composed of The Childermass (1928), Monstre Gai (1955) and Malign Fiesta (1955). A fourth volume, titled The Trial of Man, was unfinished at the time of his death. He also wrote two autobiographical volumes: Blasting and Bombardiering (1937) and Rude Assignment: A Narrative of my Career Up-to-Date (1950).
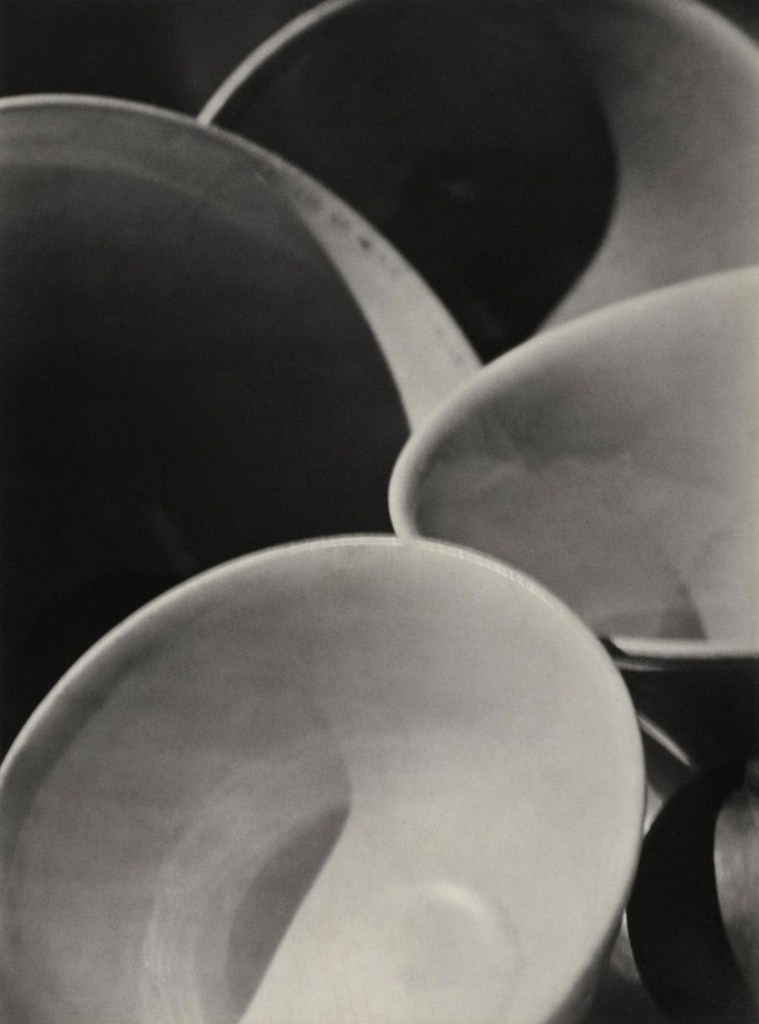

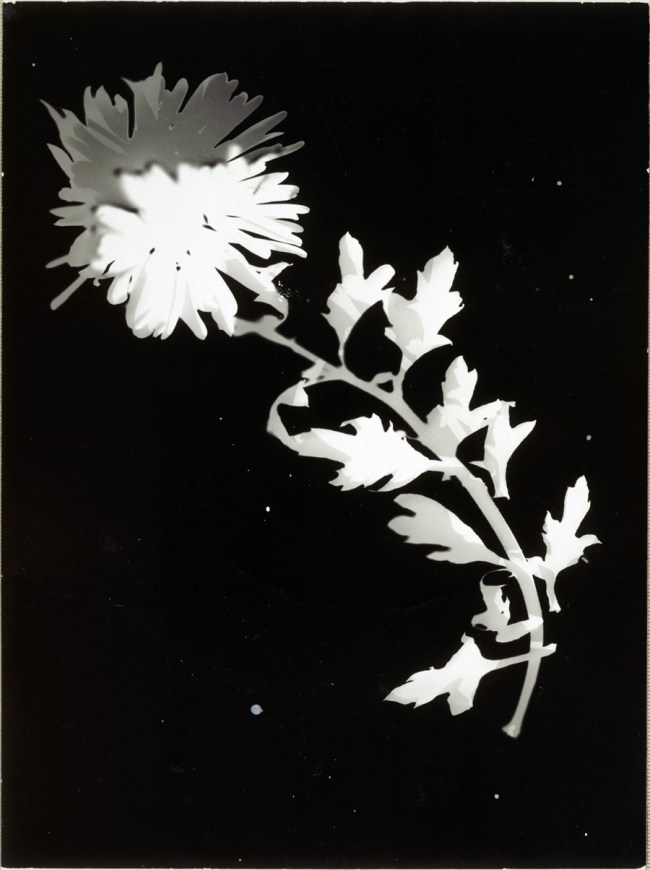
Paul Strand (American, 1890-1976)
Abstraction Bowls, Twin Lakes, Connecticut
1916
Silver gelatin print
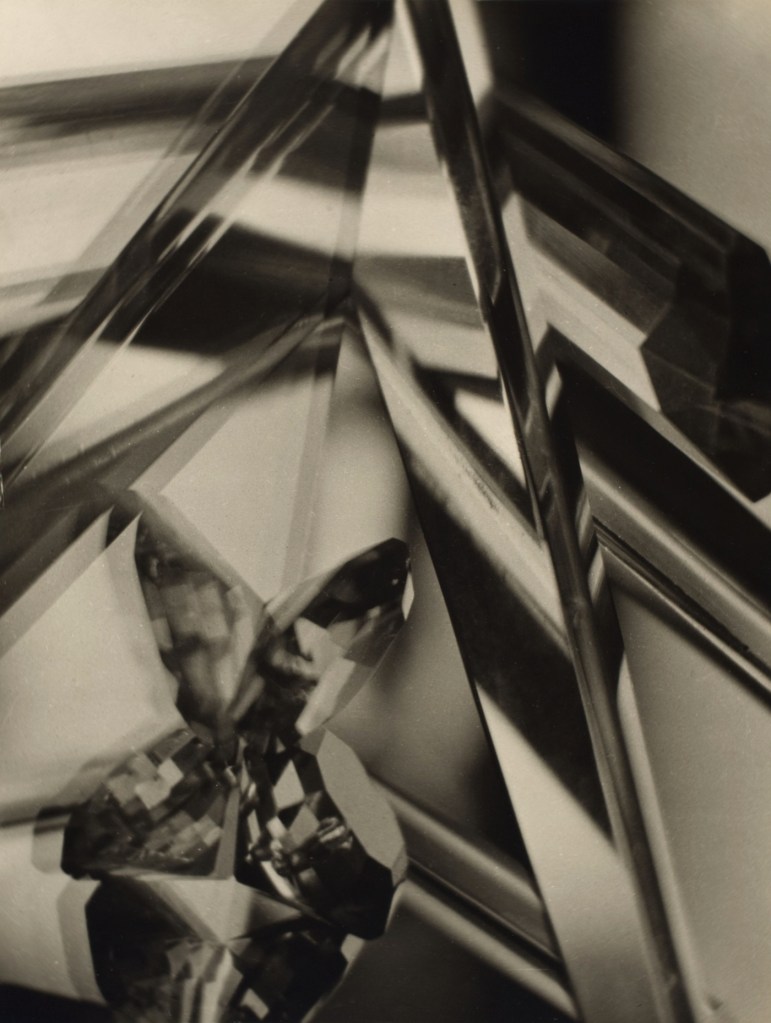

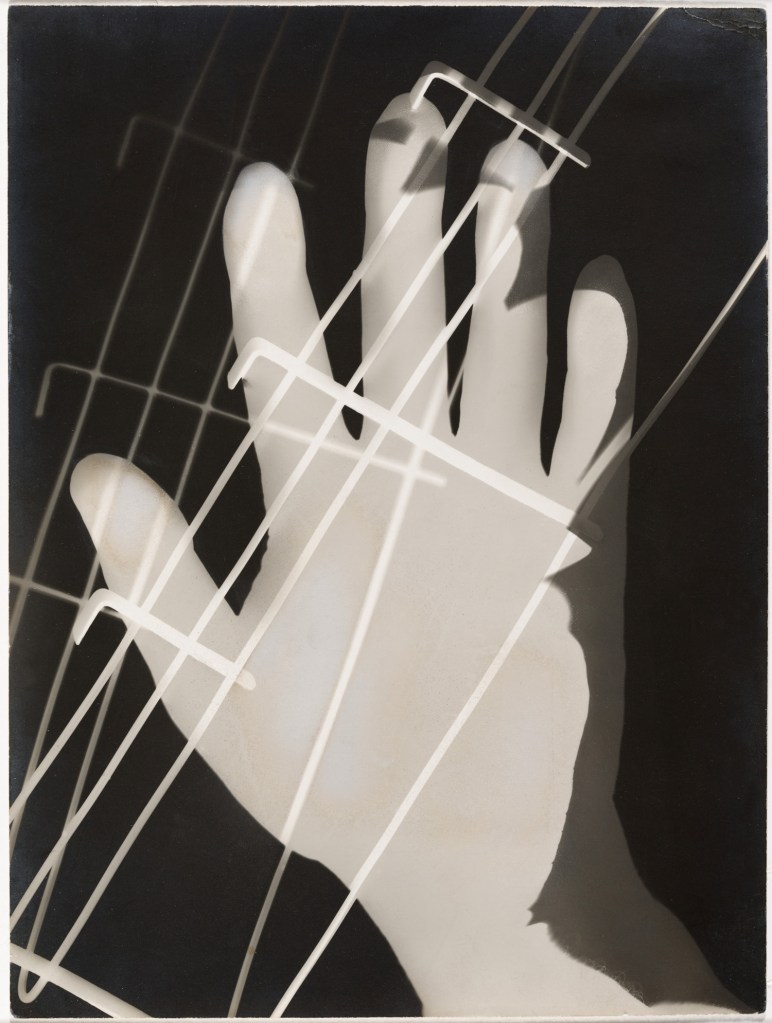
Alvin Langdon Coburn (American, 1882-1966)
Vortograph
1917
Gelatin silver print on paper
283 x 214mm
Courtesy of the George Eastman Museum NY
© The Universal Order
Installation view of the exhibition Shape of Light: 100 Years of Photography and Abstract Art at Tate Modern, London showing László Moholy-Nagy’s K VII at centre
Photo: © Tate / Andrew Dunkley
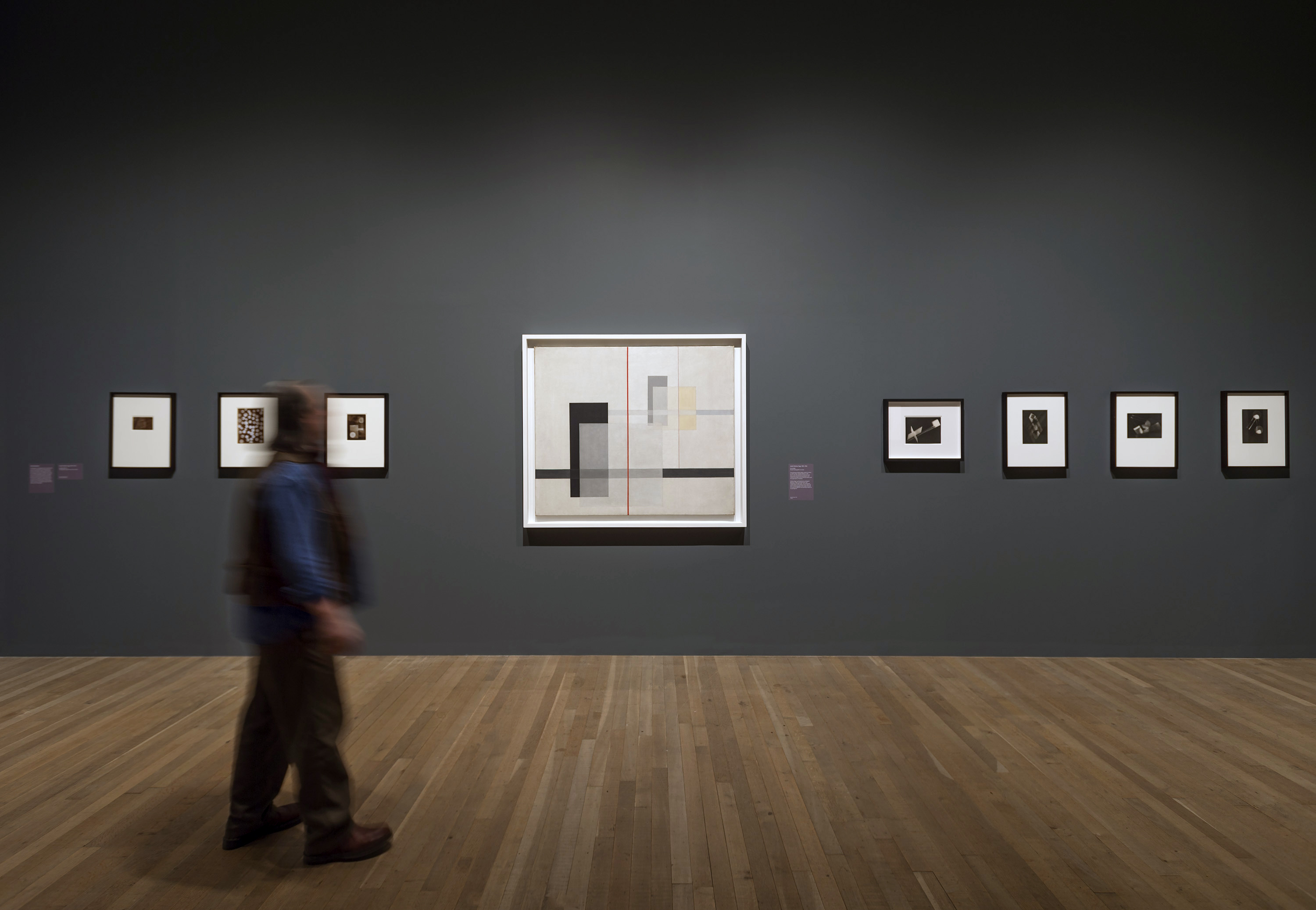
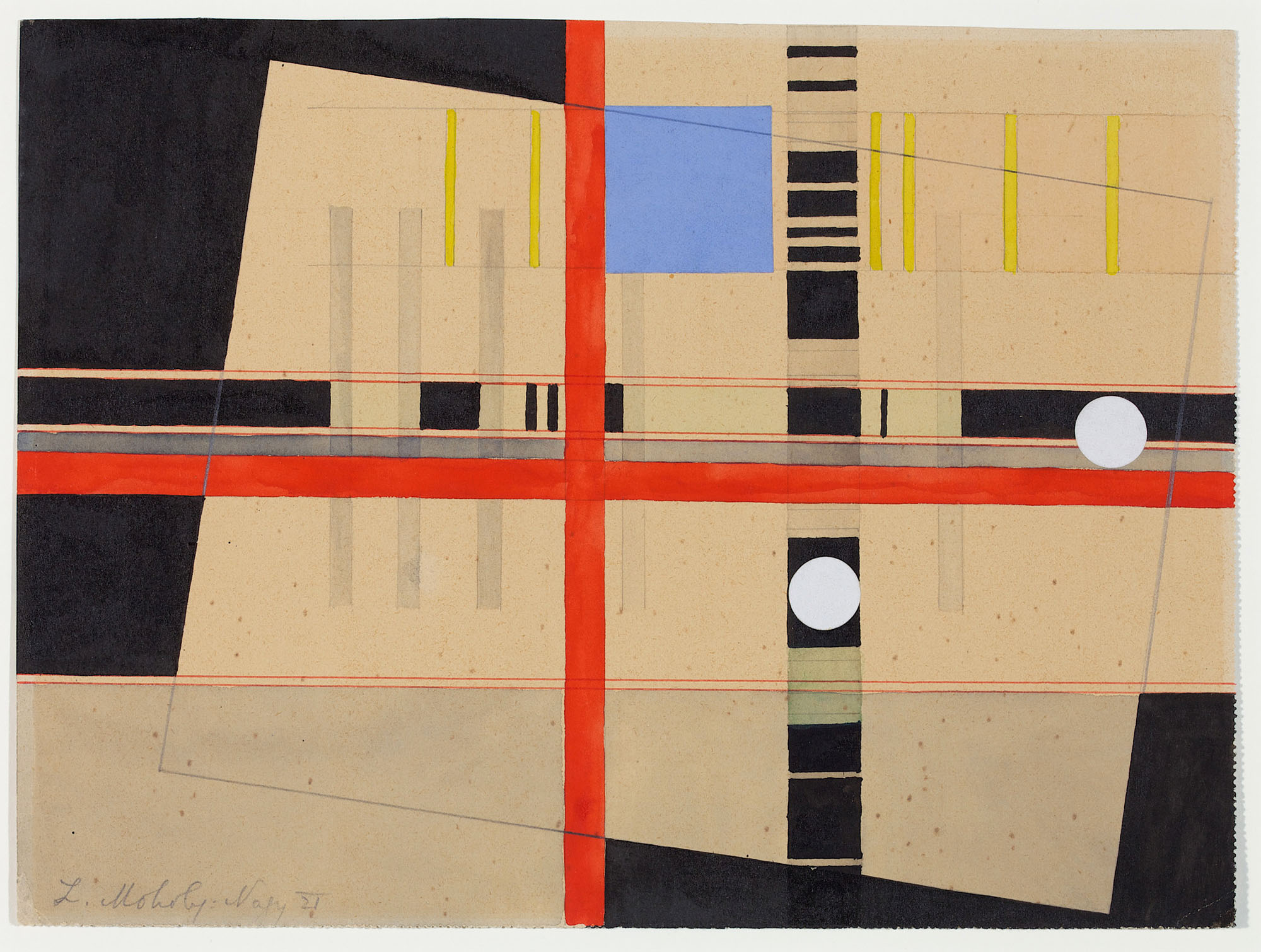
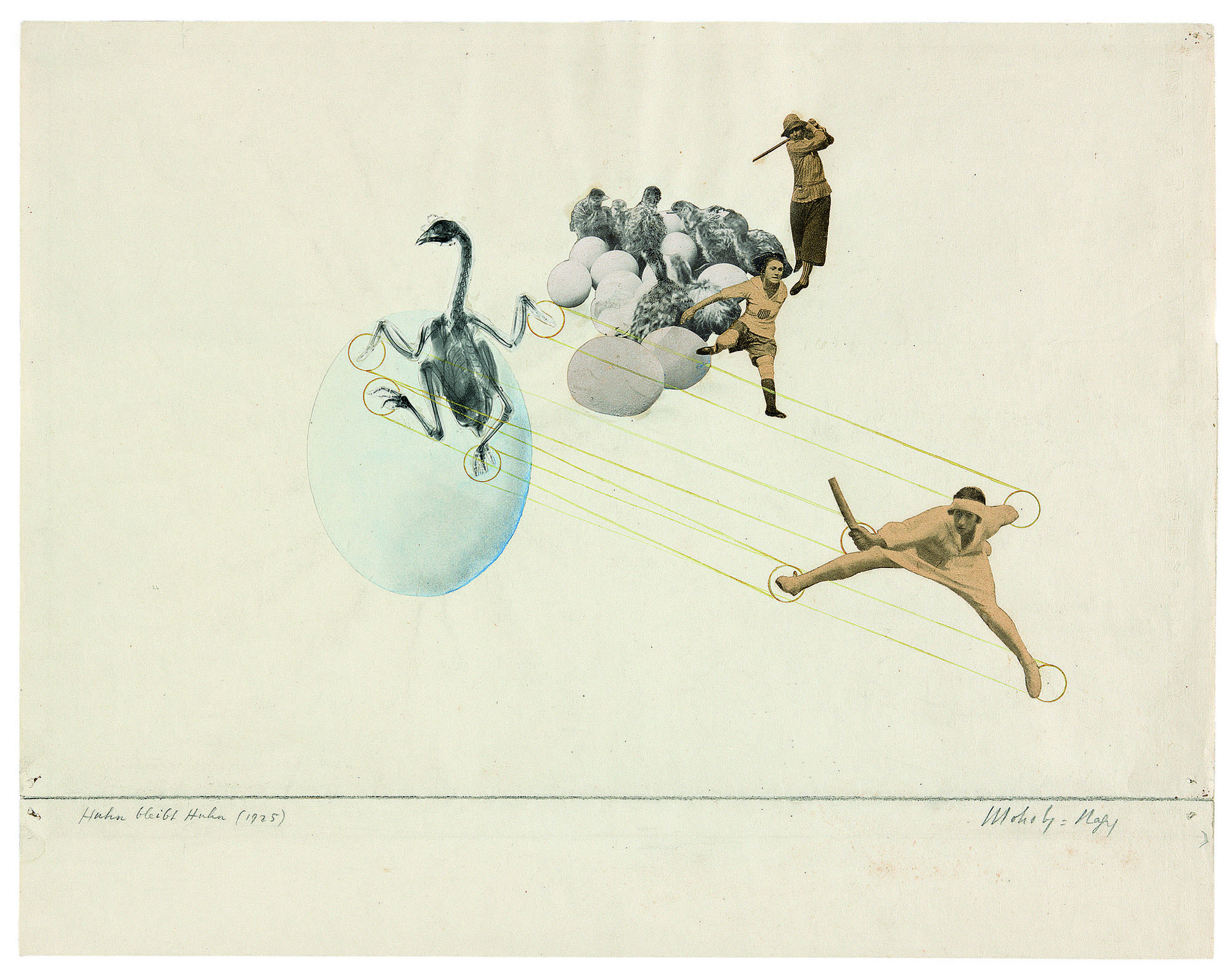
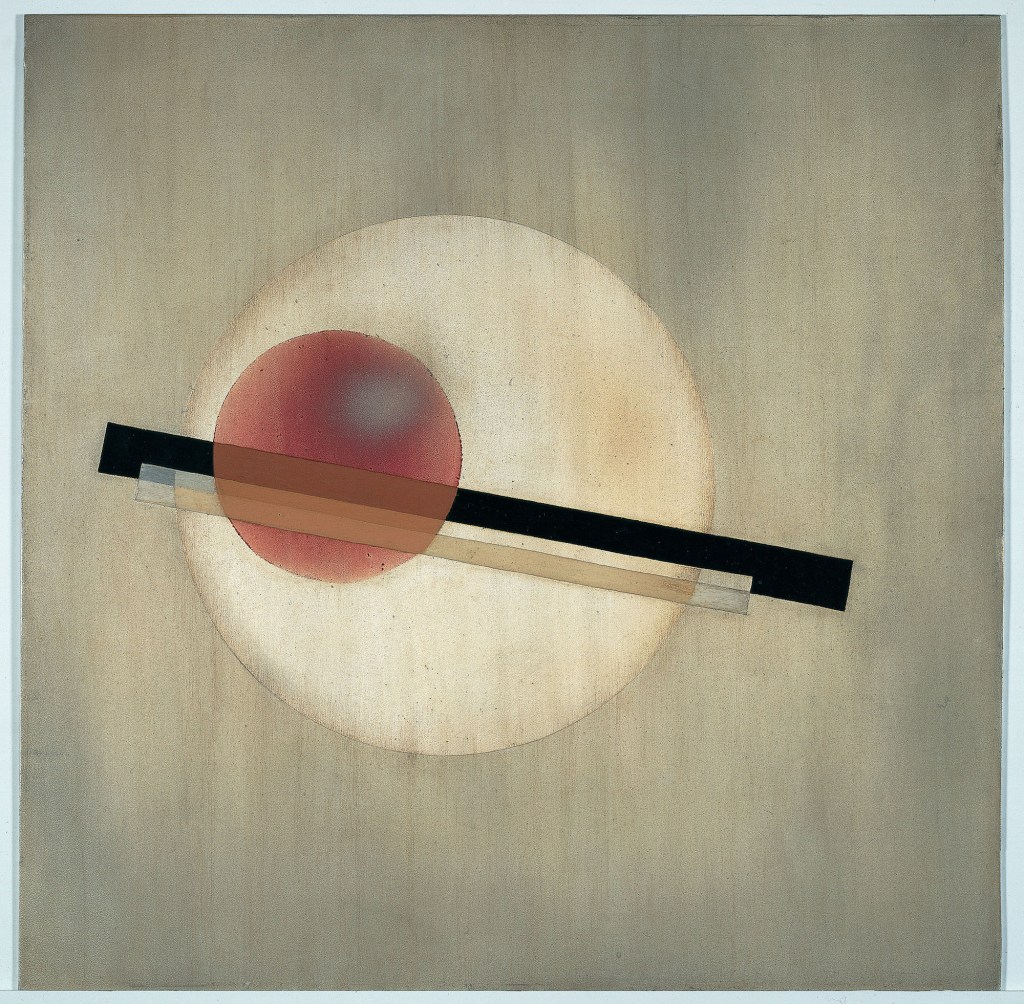
László Moholy-Nagy (Hungarian, 1895-1946)
K VII
1922
Oil paint and graphite on canvas
Frame: 1308 x 1512 x 80mm
Tate
Purchased 1961
The ‘K’ in the title of K VII stands for the German word Konstruktion (‘construction’), and the painting’s ordered, geometrical forms are typical of Moholy-Nagy’s technocratic Utopianism. The year after it was painted, he was appointed to teach the one year-preliminary course at the recently founded Bauhaus in Weimar. Moholy-Nagy’s appointment signalled a major shift in the school’s philosophy away from its earlier crafts ethos towards a closer alignment with the demands of modern industry, and a programme of simple design and unadorned functionalism.
Gallery label, April 2012
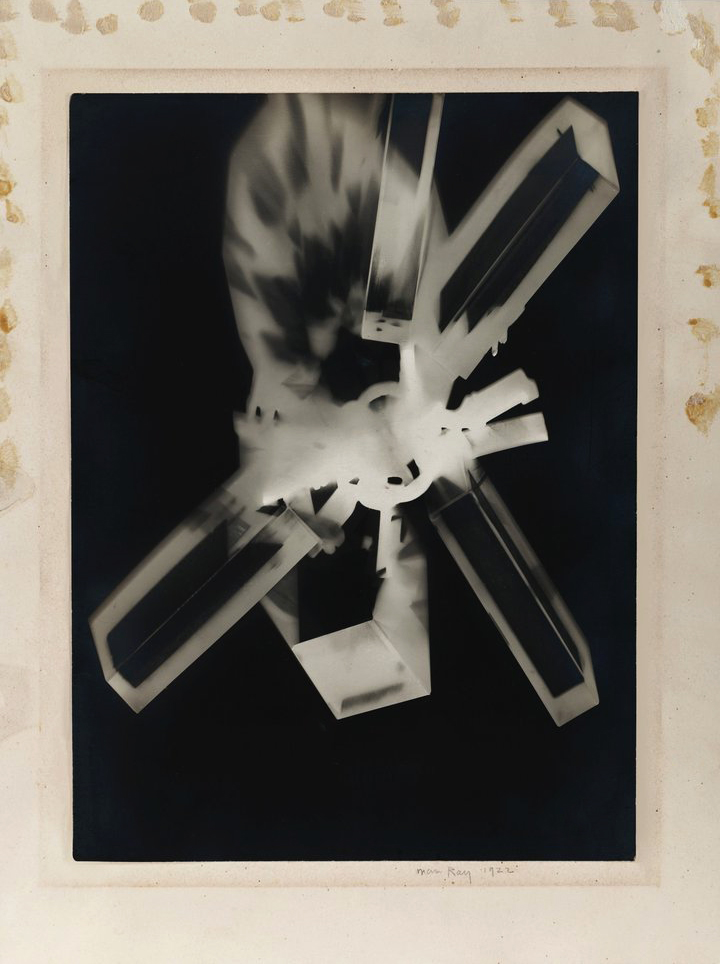

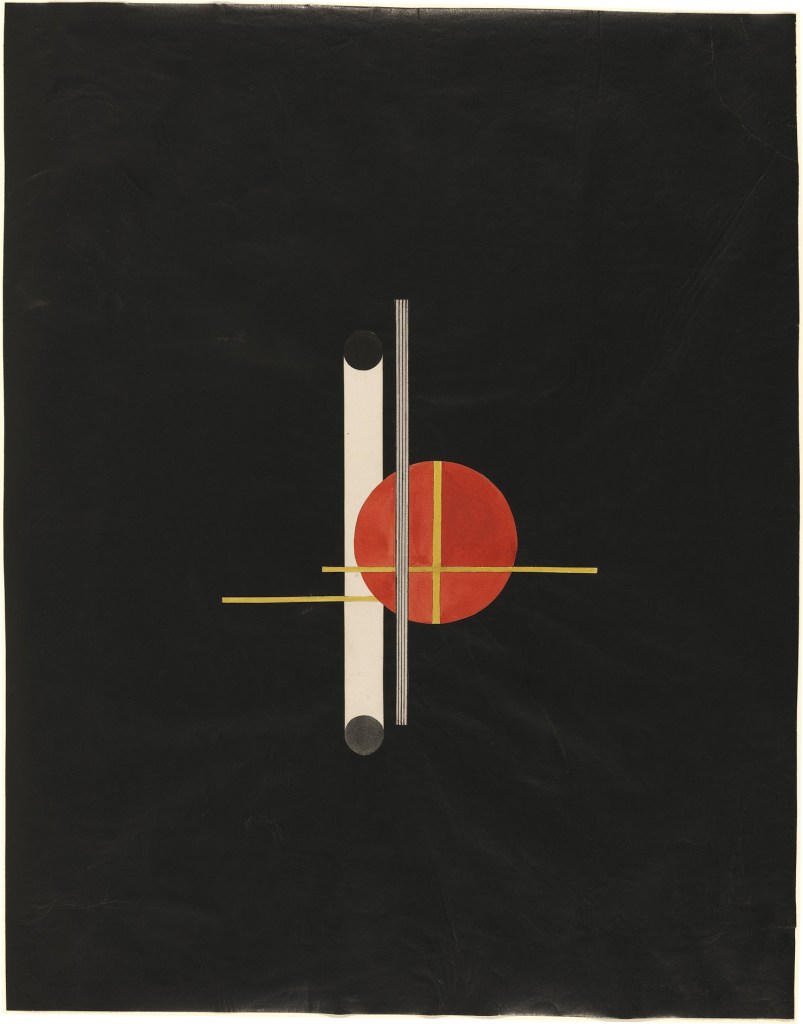
Man Ray (American, 1890-1976)
Rayograph
1922
Gelatin silver print on paper
Private Collection
© Man Ray Trust/ADAGP, Paris and DACS, London 2018
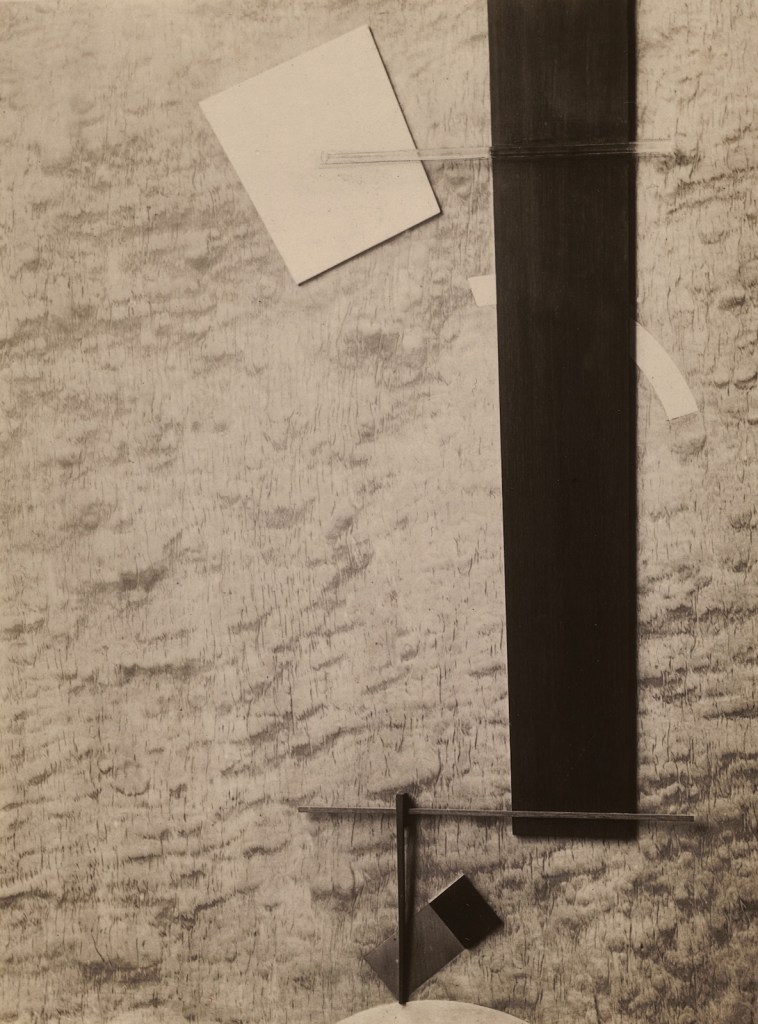

El Lissitzky (Russian, 1890-1941)
Proun in Material (Proun 83)
1924
Gelatin silver print on paper
140 x 102mm
© Imogen Cunningham Trust. All rights reserved
László Moholy-Nagy (Hungarian, 1895-1946)
Photogram
c. 1925
Gelatin silver print on paper
Photo: Jack Kirkland Collection, Nottingham

Wassily Kandinsky (Russian, 1866-1944)
Swinging
1925
Oil paint on board
705 x 502mm
Tate
![Edward Steichen (American, 1879-1973) 'Bird in Space' [L'Oiseau dans l'espace] 1926 Edward Steichen (American, 1879-1973) 'Bird in Space' [L'Oiseau dans l'espace] 1926](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/edward-steichen-bird-in-space-sculpture-by-brancusi-1926-web.jpg?w=765)
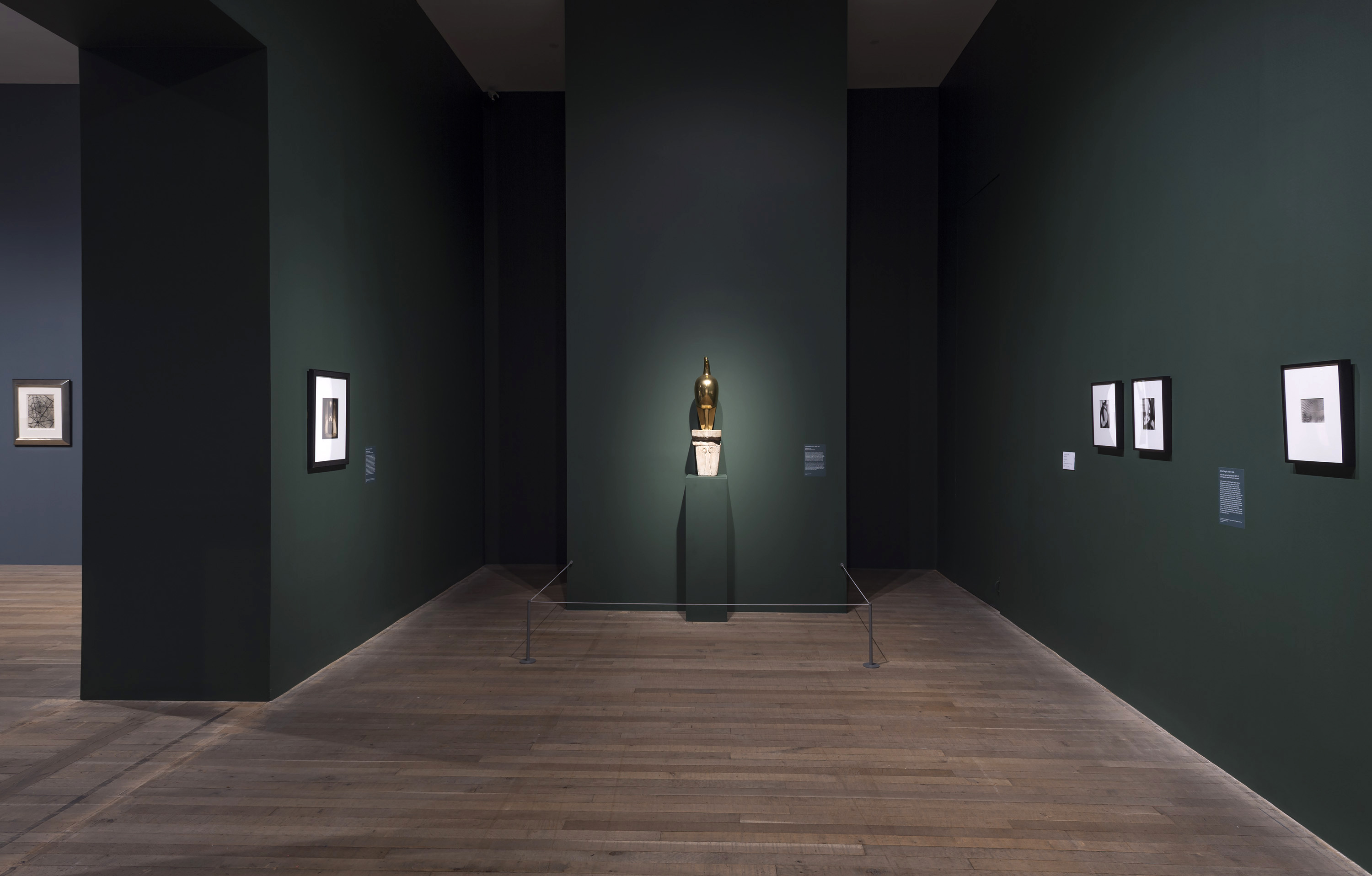
Edward Steichen (American, 1879-1973)
Bird in Space (L’Oiseau dans l’espace)
1926
Gelatin silver print on paper
253 x 202mm
Bequest of Constantin Brancusi, 1957
Centre Pompidou, Paris
Musée National d’Art Moderne / Centre de Création Industrielle
Installation view of the exhibition Shape of Light: 100 Years of Photography and Abstract Art at Tate Modern, London showing at centre, Constantin Brancusi’s bronze and stone sculpture Maiastra (1911)
Photo: © Tate / Andrew Dunkley
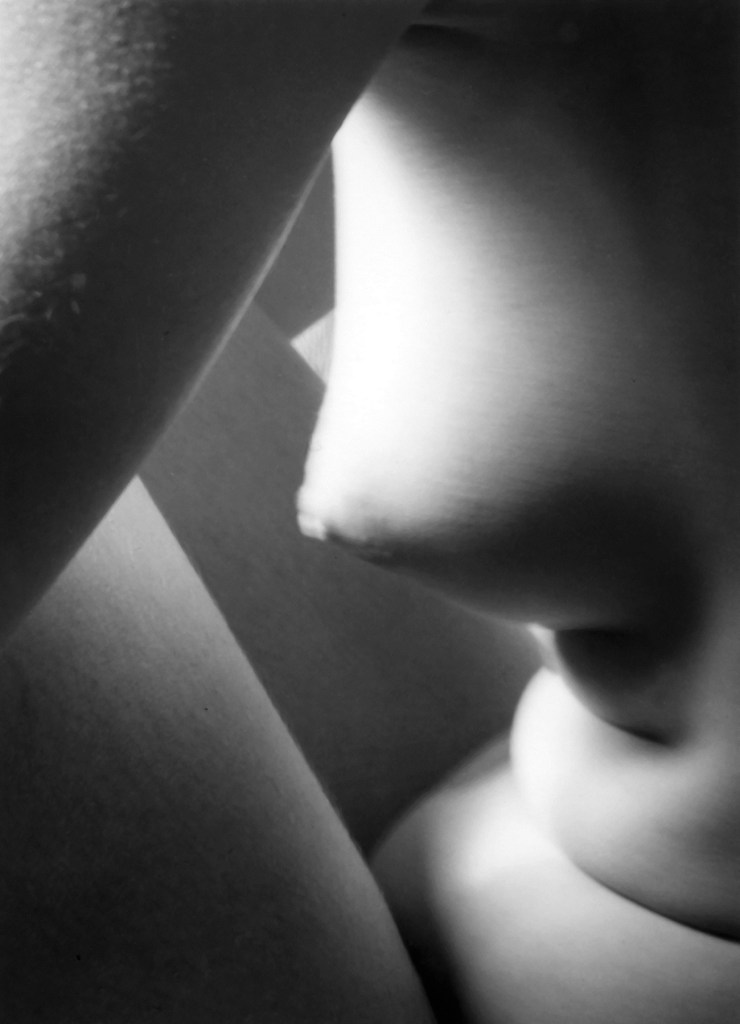

Imogen Cunningham (American, 1883-1976)
Triangles
1928, printed 1947-1960
Gelatin silver print on paper
119 x 93mm
Pierre Brahm
© Imogen Cunningham Trust. All rights reserved
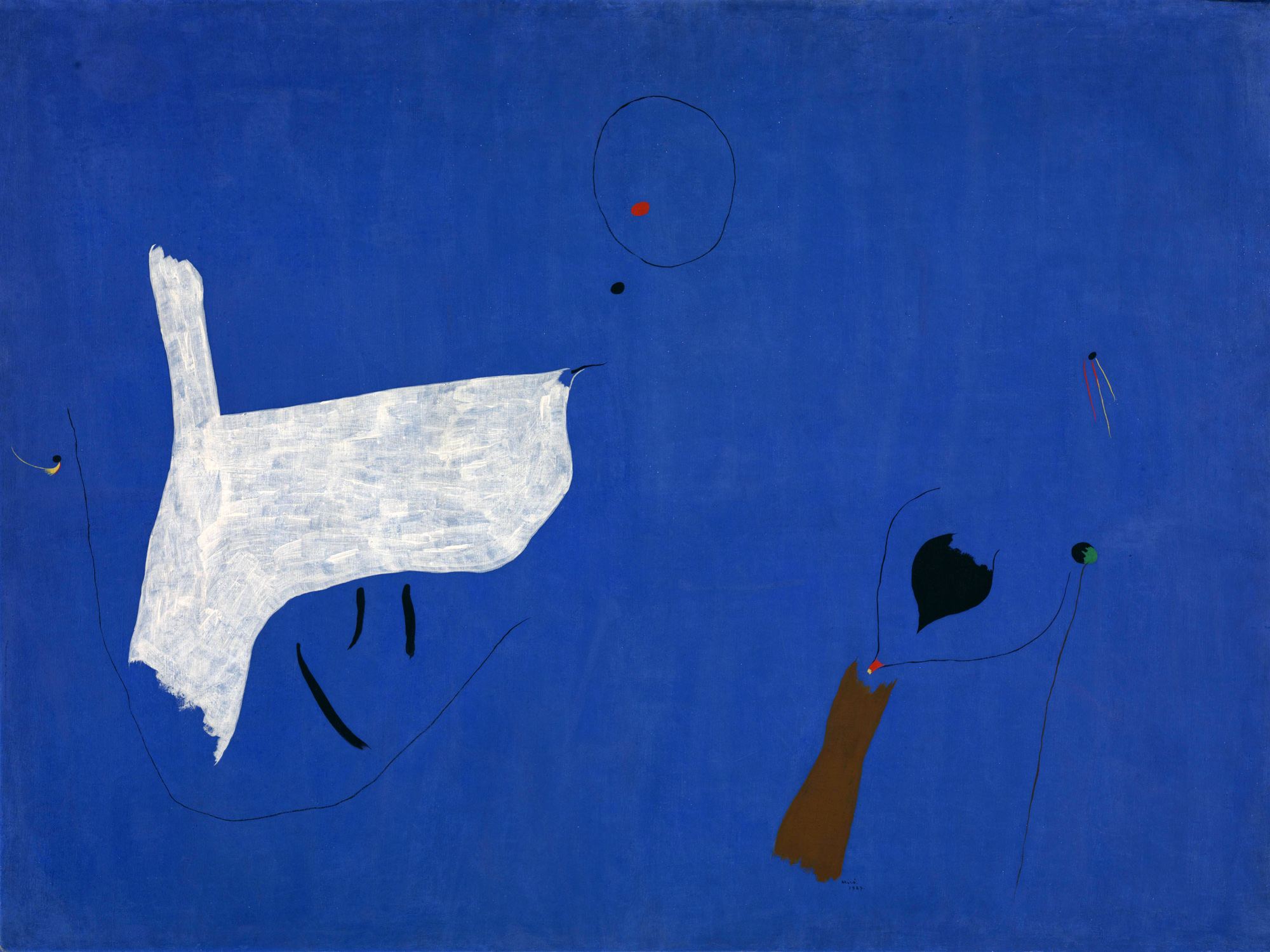
Joan Miró (Spanish, 1893-1983)
Painting
1927
Tempera and oil paint on canvas
972 x 1302mm
Tate
© Succession Miro/ADAGP, Paris and DACS, London 2018
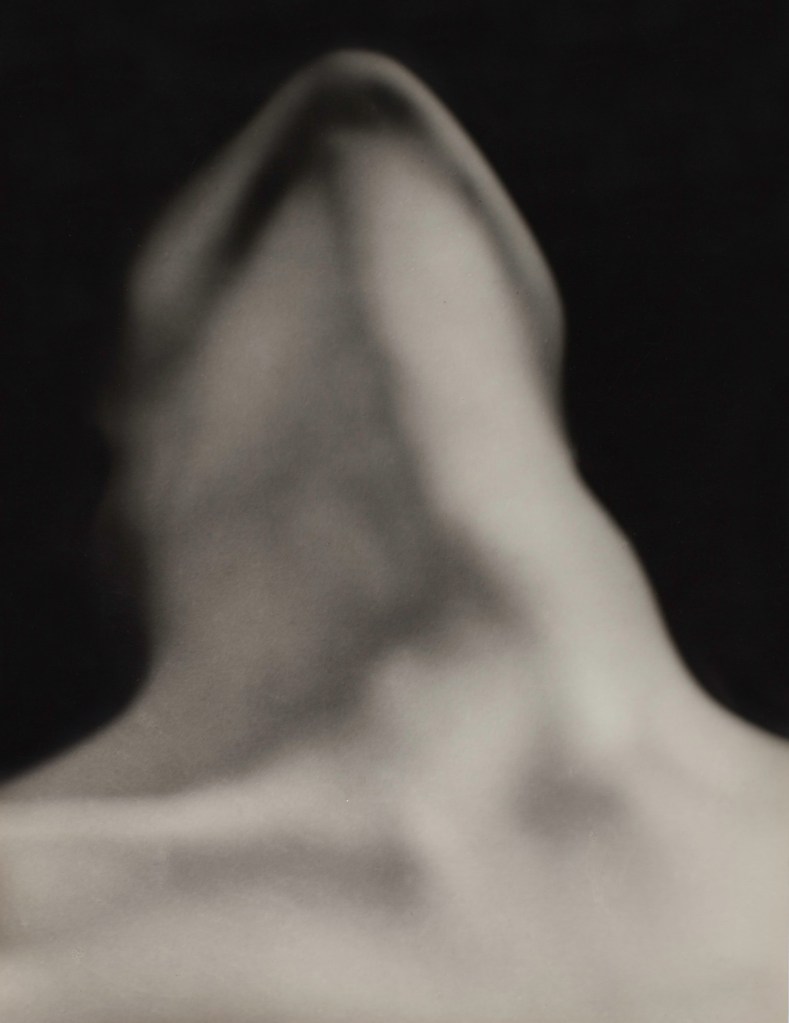

Man Ray (American, 1890-1976)
Anatomies
1930
Photo: © Man Ray Trust/ADAGP, Paris and DACS, London 2016
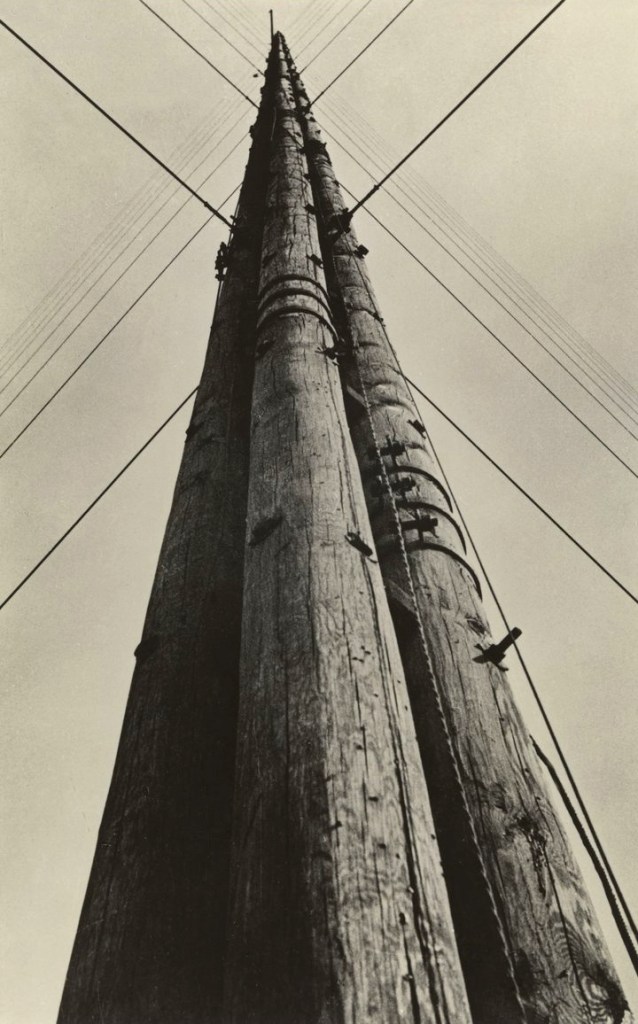

Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Radio Station Power
1929
Gelatin silver print on paper
Lent by Jack Kirkland Collection, Nottingham
© A. Rodchenko and V. Stepanova Archive. DACS, RAO 2018
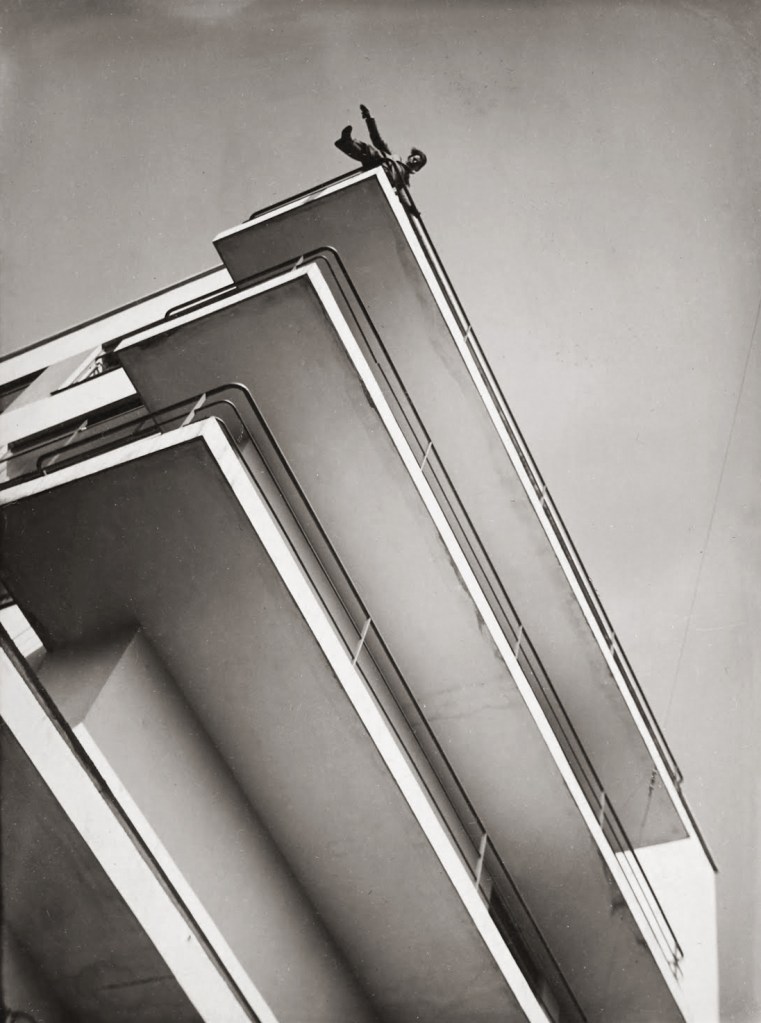

László Moholy-Nagy (Hungarian, 1895-1946)
Xanti Schawinsky on the balcony of the Bauhaus
1929
Gelatin silver print on paper
Luo Bonian (Chinese, 1911-2002)
Untitled
1930s
Gelatin silver print on paper
Courtesy The Three Shadows Photography Art Centre, Beijing
© Luo Bonian

Marta Hoepffner (German, 1912-2000)
Homage to de Falla
1937
Gelatin silver print on paper
387 x 278mm
Stadtmuseum Hofheim am Taunus
© Estate Marta Hoepffner
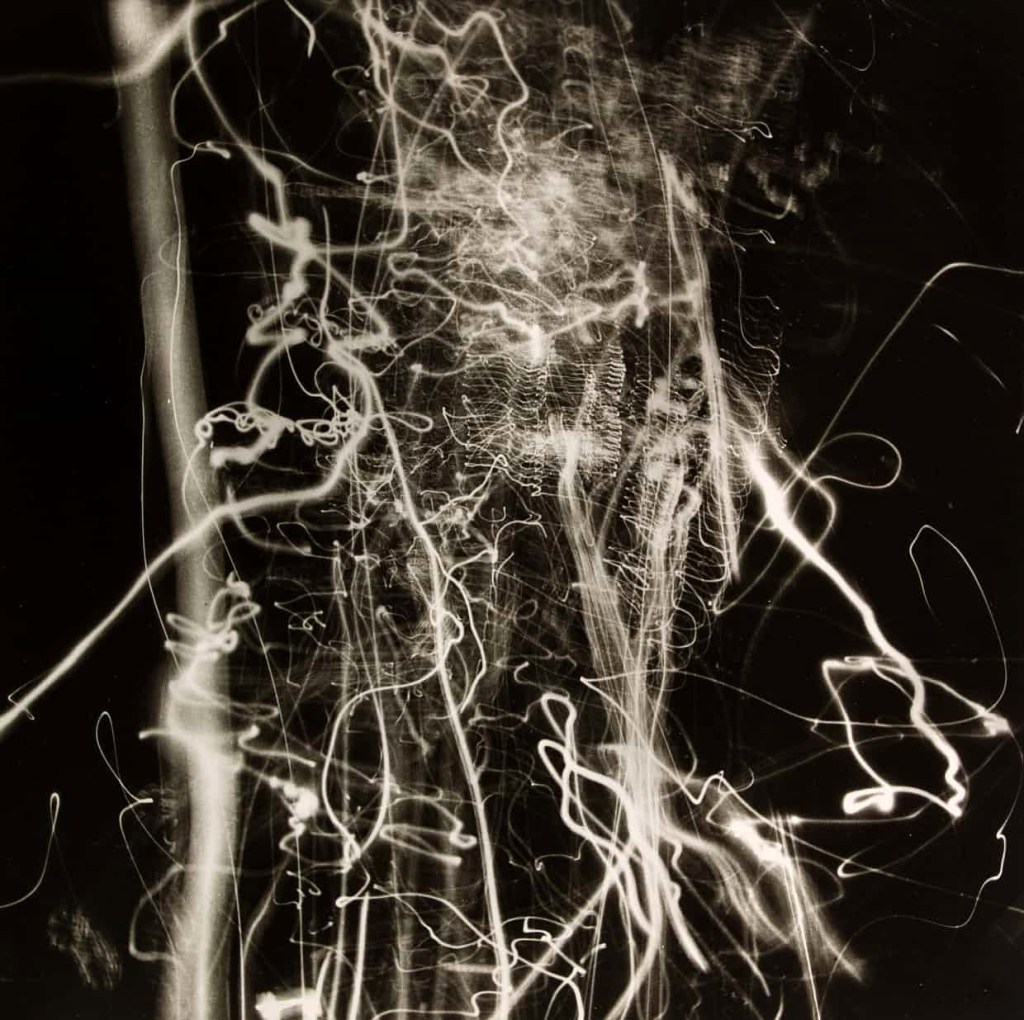
Nathan Lerner (American, 1913-1997)
Light Tapestry
1939
Gelatin silver print on paper
401 x 504mm
Musée d’Art Moderne de la Ville de Paris
Gift of Mrs Kiyoko Lerner, 2014
Photo: Nathan Lerner/© ARS, NY and DACS, London
Luigi Veronesi (Italian, 1908-1998)
Construction
1938
Gelatin silver print on paper
286 x 388mm
Tate
Accepted under the Cultural Gifts Scheme by HM Government from Massimo Prelz Oltramonti and allocated to Tate 2015

Luigi Veronesi (Italian, 1908-1998)
Photo n.145
1940, printed 1970s
Gelatin silver print on paper
310 x 280mm
Tate
Accepted under the Cultural Gifts Scheme by HM Government from Massimo Prelz Oltramonti and allocated to Tate 2015
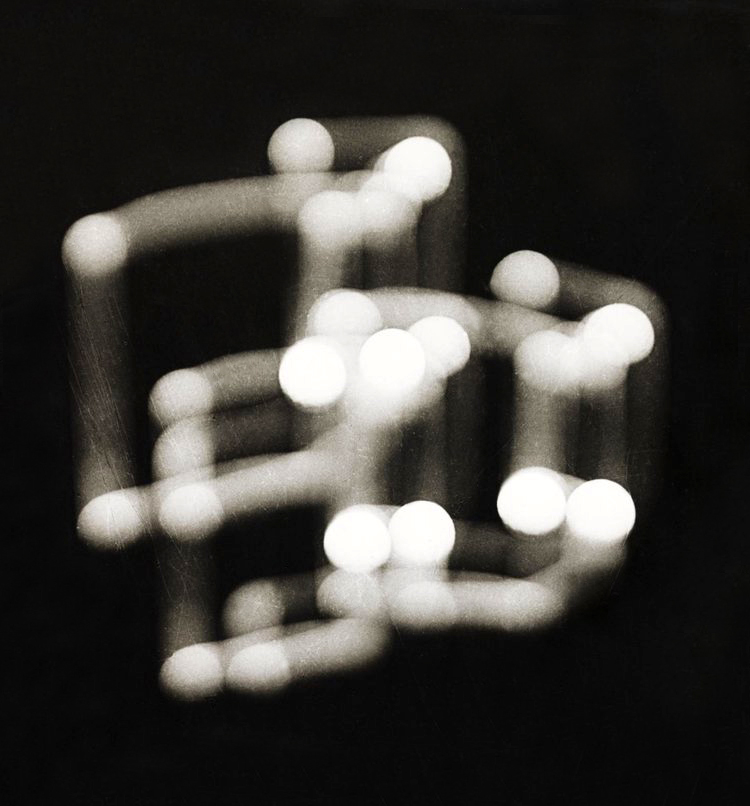

Luigi Veronesi (Italian, 1908-1998)
Photo n.152
1940, printed 1970s
Gelatin silver print on paper
320 x 298mm
Tate
Accepted under the Cultural Gifts Scheme by HM Government from Massimo Prelz Oltramonti and allocated to Tate 2015
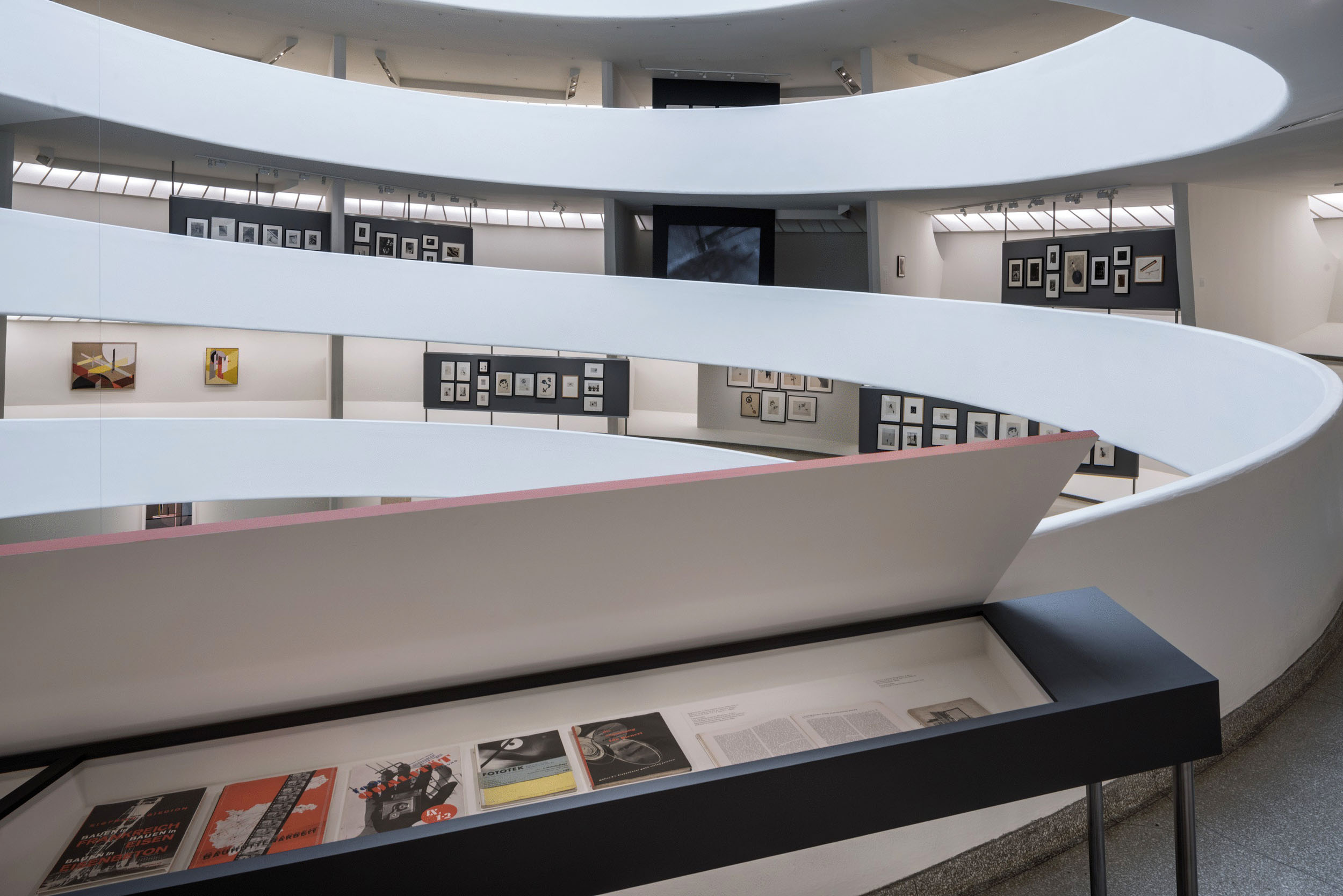
A major new exhibition at Tate Modern will reveal the intertwined stories of photography and abstract art. Shape of Light: 100 Years of Photography and Abstract Art will be the first show of this scale to explore photography in relation to the development of abstraction, from the early experiments of the 1910s to the digital innovations of the 21st century. Featuring over 300 works by more than 100 artists, the exhibition will explore the history of abstract photography side-by-side with iconic paintings and sculptures.
Shape of Light will place moments of radical innovation in photography within the wider context of abstract art, such as Alvin Langdon Coburn’s pioneering ‘vortographs’ from 1917. This relationship between media will be explored through the juxtaposition of works by painters and photographers, such as cubist works by George Braque and Pierre Dubreuil or the abstract expressionism of Jackson Pollock and Otto Steinert’s ‘luminograms’. Abstractions from the human body associated with surrealism will include André Kertesz’s Distorsions, Imogen Cunningham’s Triangles and Bill Brandt’s Baie des Anges, Frances 1958, exhibited together with a major painting by Joan Miró. Elsewhere the focus will be on artists whose practice spans diverse media, such as László Moholy-Nagy and Man Ray.
The exhibition will also acknowledge the impact of MoMA’s landmark photography exhibition of 1960, The Sense of Abstraction. Installation photographs of this pioneering show will be displayed with some of the works originally featured in the exhibition, including important works by Edward Weston, Aaron Siskind and a series by Man Ray that has not been exhibited since the MoMA show, 58 years ago.
The connections between breakthroughs in photography and new techniques in painting will be examined, with rooms devoted to Op Art and Kinetic Art from the 1960s, featuring striking paintings by Bridget Riley and installations of key photographic works from the era by artists including Floris Neussis and Gottfried Jaeger. Rooms will also be dedicated to the minimal and conceptual practices of the 1970s and 80s. The exhibition will culminate in a series of new works by contemporary artists, Tony Cairns, Maya Rochat and Daisuke Yokota, exploring photography and abstraction today.
Shape of Light is curated by Simon Baker, Senior Curator, International Art (Photography) and Shoair Mavlian, Assistant Curator, Tate Modern, with Emmanuelle de l’Ecotais, Curator for Photographs, Musée d’Art Moderne de la Ville de Paris. The exhibition will be accompanied by a fully illustrated catalogue from Tate Publishing and a programme of talks and events in the gallery.
Press release from Tate Modern

Otto Steinert (German, 1915-1978)
Composition of Forms
1949
Gelatin silver print on paper
290 x 227mm
Jack Kirkland Collection, Nottingham
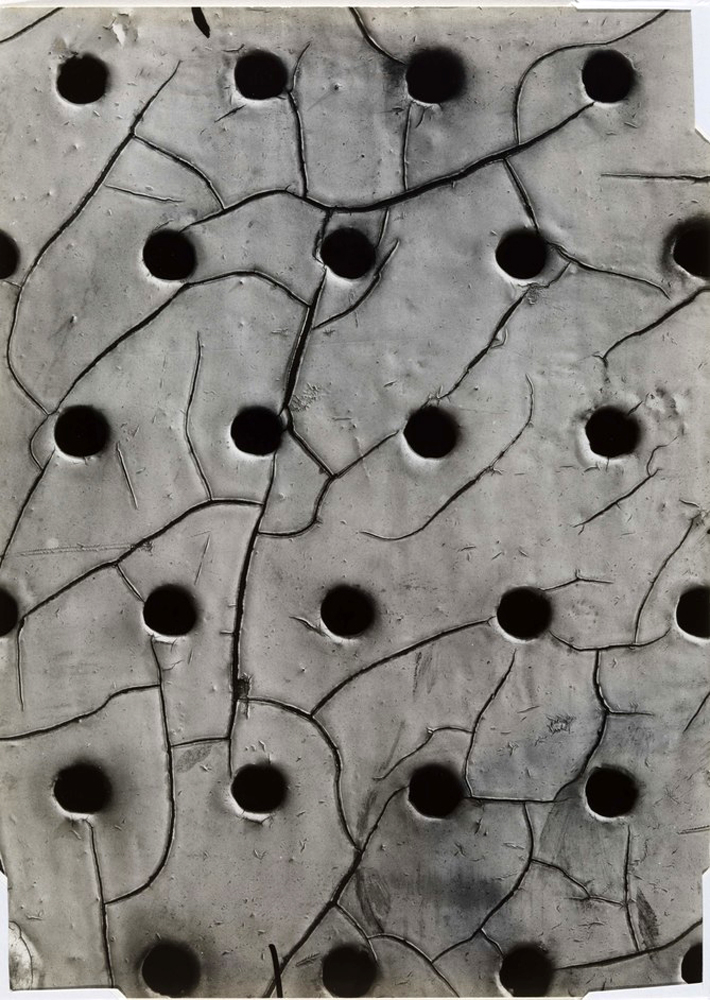

Guy Bourdin (French, 1928-1991)
Untitled
1952
Gelatin silver print on paper
277 x 164mm
Purchased with funds provided by the Photography Acquisitions Committee 2015
© The Guy Bourdin Estate
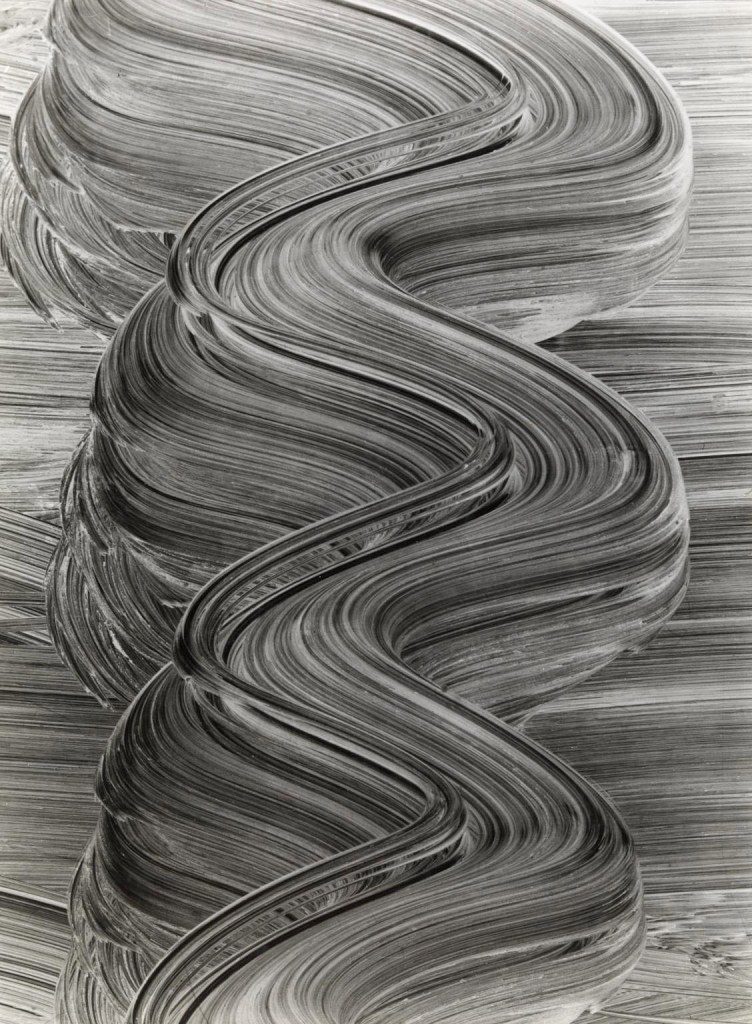

Guy Bourdin (French, 1928-1991)
Untitled
1952
Gelatin silver print on paper
232 x 169mm
Purchased with funds provided by the Photography Acquisitions Committee 2015
© The Guy Bourdin Estate
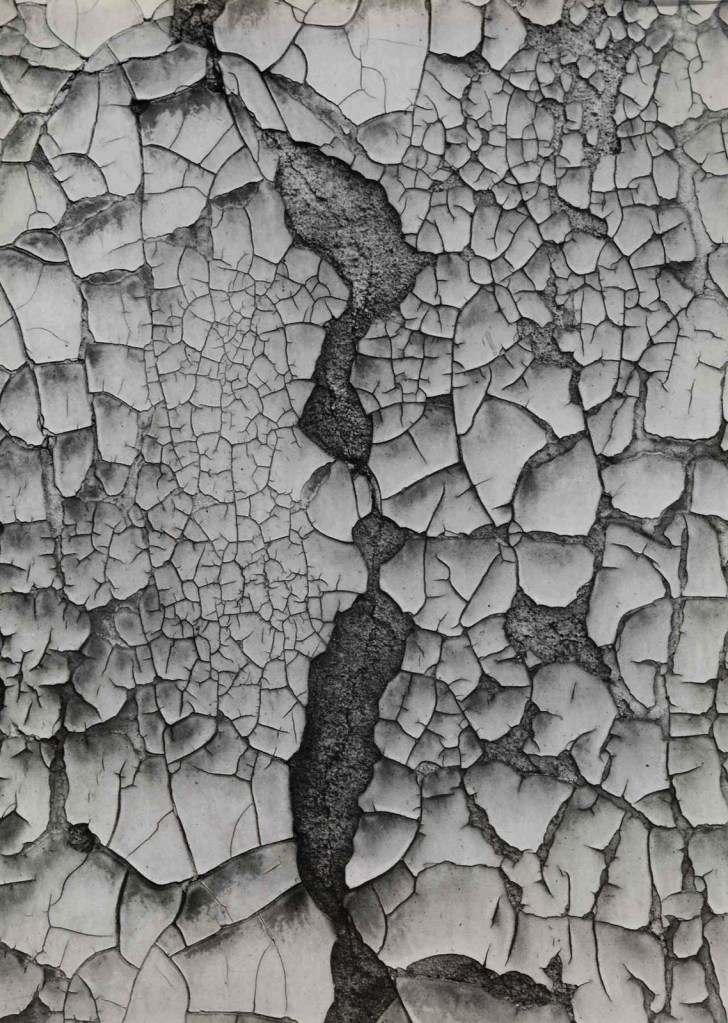

Guy Bourdin (French, 1928-1991)
Untitled
c. 1950s
Gelatin silver print on paper
239 x 179mm
Purchased with funds provided by the Photography Acquisitions Committee 2015
© The Guy Bourdin Estate
Untitled c.1950s is a black and white photograph by the French photographer Guy Bourdin. The entirety of the frame is taken up by a close-up of peeling paint. The paint sections fragment the image into uneven geometric shapes, which are interrupted by a strip of the dark surface beneath that winds from the top to the bottom of the frame. There is little sense of scale or contextual detail, resulting in a near-abstract composition.
Bourdin is best known for his experimental colour fashion photography produced while working for French Vogue between 1955 and 1977. This photograph belongs to an earlier period of experimentation, before he began to use colour and work in fashion. Taken outside the studio, it shows Bourdin’s sensitivity to the natural world and his attempt to transform the everyday into abstract compositions, bridging the gap between surrealism and subjective photography. Bourdin’s early work was heavily influenced by surrealism, as well as by pioneers of photography as a fine art such as Edward Weston, Paul Strand and Bill Brandt. His surrealist aesthetic can be attributed to his close relationship with Man Ray, who wrote the foreword to the catalogue for Bourdin’s first solo exhibition of black and white photographs at Galerie 29, Paris, in 1952.
This and other early works in Tate’s collection (such as Untitled (Sotteville, Normandy) c. 1950s, Tate P81205, and Solange 1957, Tate P81216) are typical of Subjektive Fotografie (‘subjective photography’), a tendency in the medium in the late 1940s and early 1950s. Led by the German photographer and teacher Otto Steinert, who organised three exhibitions under the title Subjektive Fotografie in 1951, 1954 and 1958, the movement advocated artistic self-expression – in the form of the artist’s creative approach to composition, processing and developing – above factual representation. Subjektive Fotografie’s emphasis on, and encouragement of, individual perspectives invited both the photographer and the viewer to interpret and reflect on the world through images. Bourdin’s interest in this can be seen in his early use of texture and abstraction, evident in close-up studies of cracked paint peeling off an external wall or a piece of torn fabric. These still lives were often dark in subject matter and tone, highlighting Bourdin’s interest in surrealist compositions and the intersection between death and sexuality. The works made use of the photographer’s urban environment, with deep black and high contrast printing techniques employed to create a sombre mood.
This approach was also important for Bourdin’s early portraiture, which anticipated his subsequent work in fashion. The subject of his portraits – often Solange Gèze, to whom the artist was married from 1961 until her death in 1971 – is usually framed subtly, rarely appearing in the centre or as the main focus of the image. In these works the figure is secondary, showing how Bourdin let the natural or urban environment frame the subject and integrate the body into its immediate surroundings. Bourdin was meticulous about the creative process from start to finish, sketching out images on paper and then recreating them in the landscape, using the natural environment as a stage set for his work.
Shoair Mavlian
August 2014
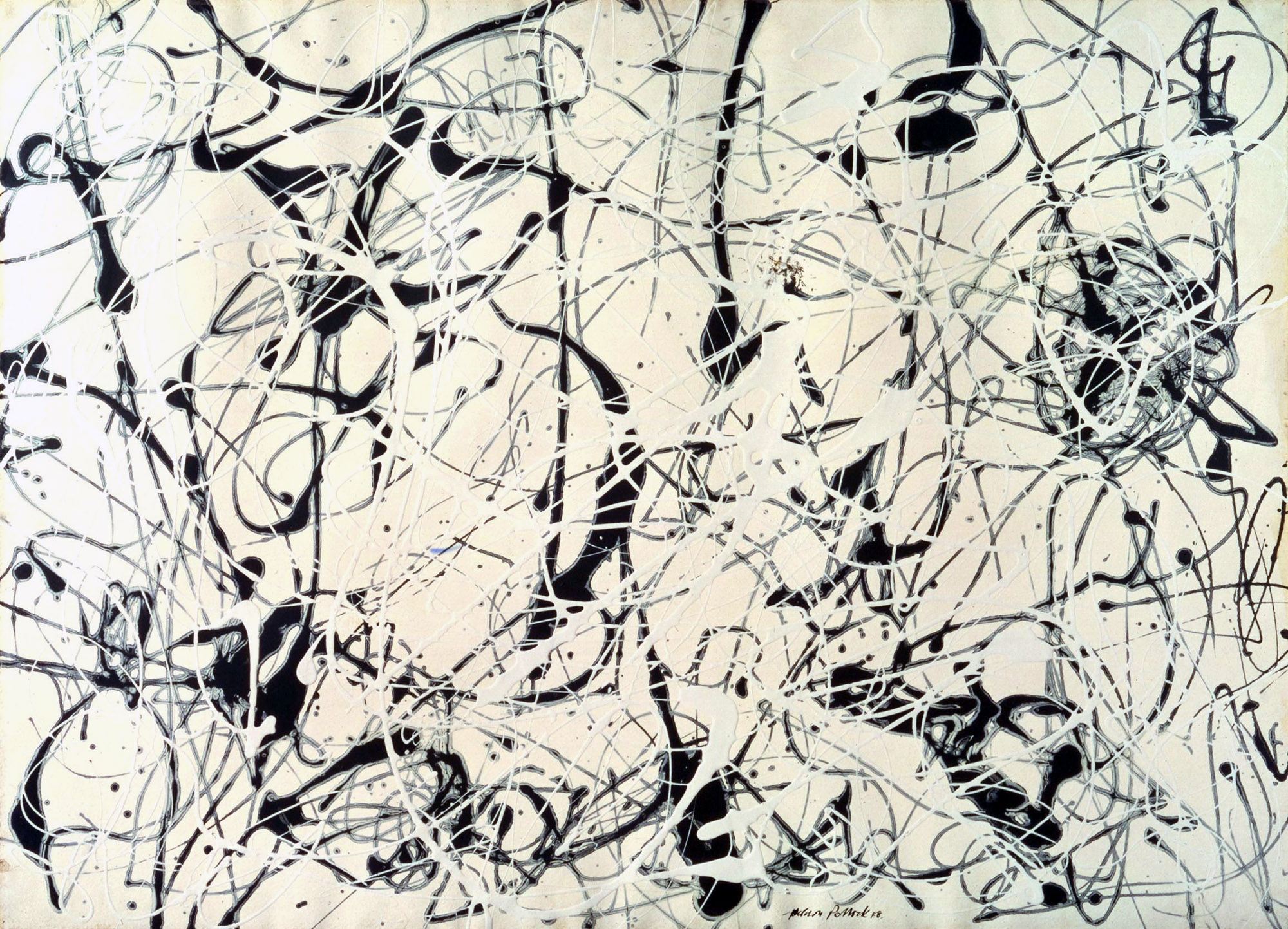
Jackson Pollock (American, 1912-1956)
Number 23
1948
Enamel on gesso on paper
575 x 784mm
Tate: Presented by the Friends of the Tate Gallery (purchased out of funds provided by Mr and Mrs H.J. Heinz II and H.J. Heinz Co. Ltd) 1960
© ARS, NY and DACS, London 2018
Installation view of the exhibition Shape of Light: 100 Years of Photography and Abstract Art at Tate Modern, London showing at left Jackson Pollock’s Number 23 (1948, above)
Photo: © Tate / Sepharina Neville
Installation view of the exhibition Shape of Light: 100 Years of Photography and Abstract Art at Tate Modern, London showing at top left, Nathan Lerner’s Light Tapestry; and at centre right, Otto Steinert’s Luminogram II (1952, below)
Photo: © Tate / Sepharina Neville
Otto Steinert (German, 1915-1978)
Luminogram II
1952
Gelatin silver print on paper
302 x 401mm
Jack Kirkland Collection Nottingham
© Estate Otto Steinert, Museum Folkwang, Essen
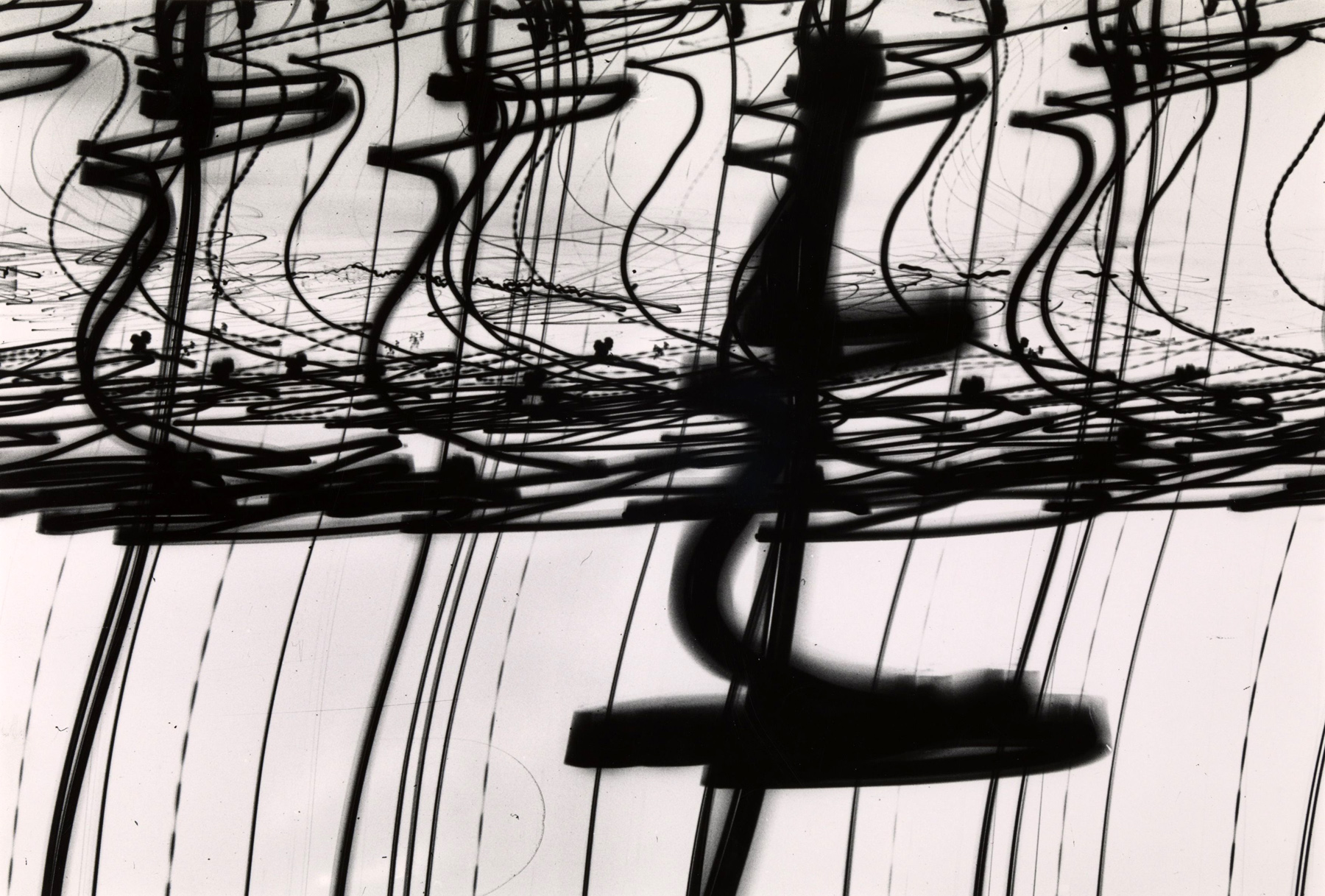
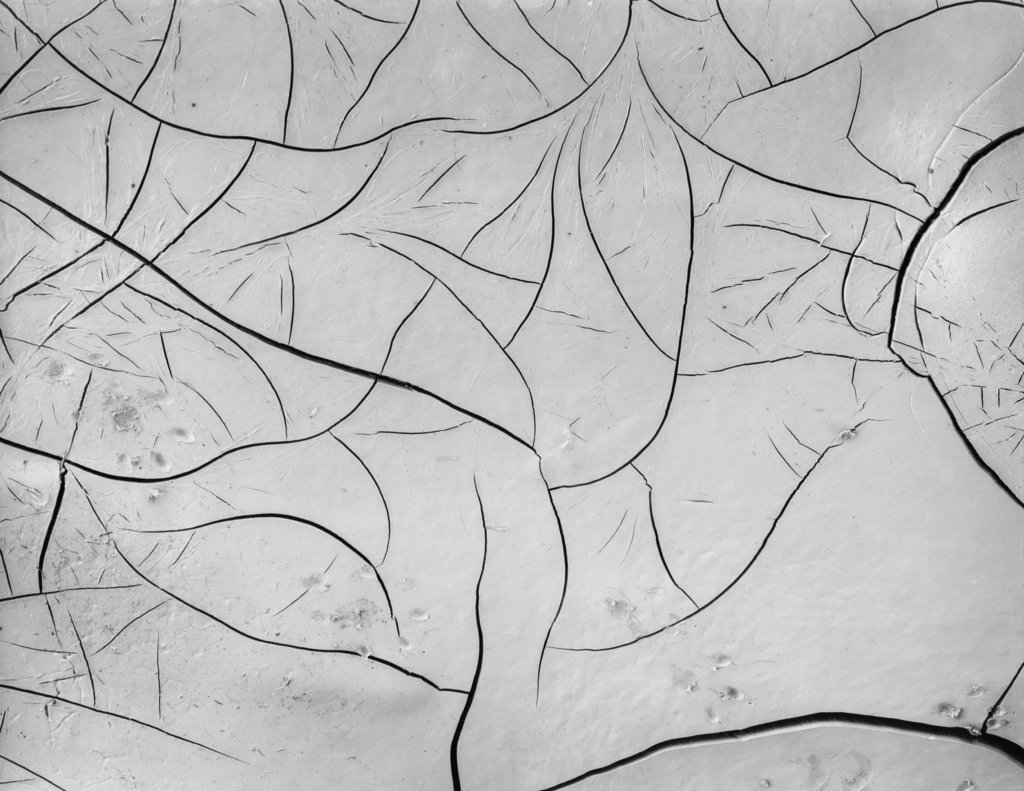
Brett Weston (American, 1911-1993)
Mud Cracks
1955
Silver gelatin print
203 x 254mm
Lent by the Tate Americas Foundation, courtesy of Christian Keesee Collection 2013
© The Brett Weston Archive/CORBIS
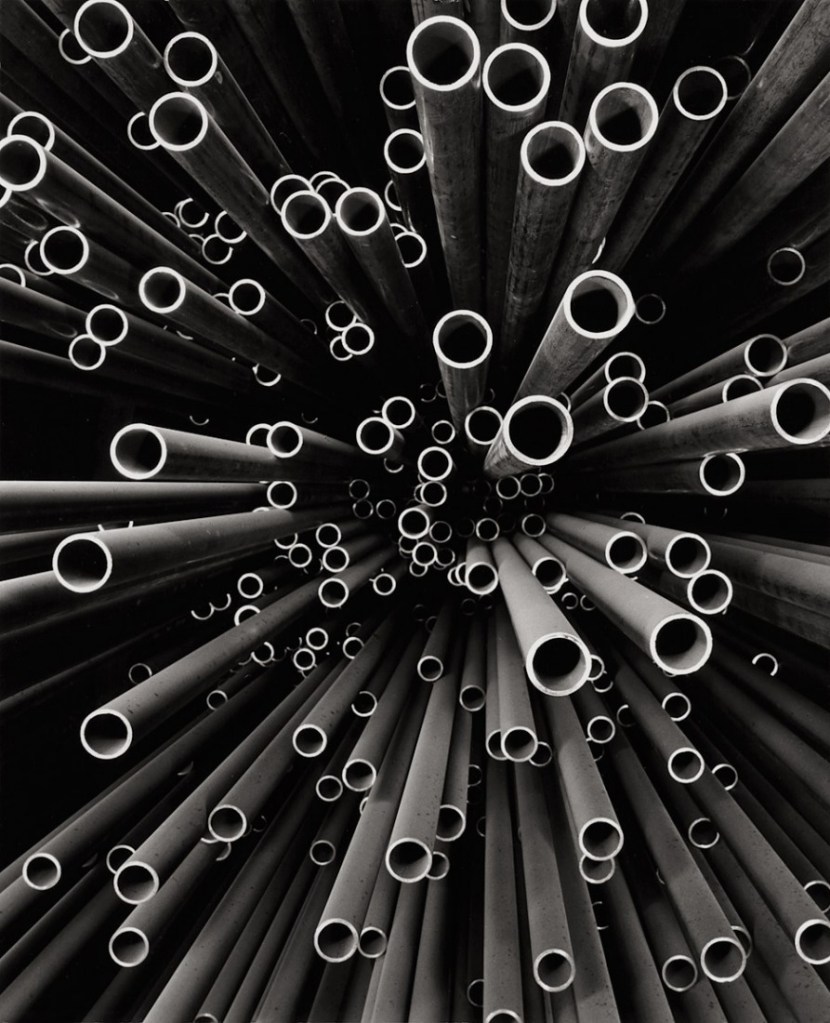

Peter Keetman (German, 1916-2005)
Steel Pipes, Maximilian Smelter
1958
Gelatin silver print on paper
508 x 427mm
F.C. Gundlach Foundation
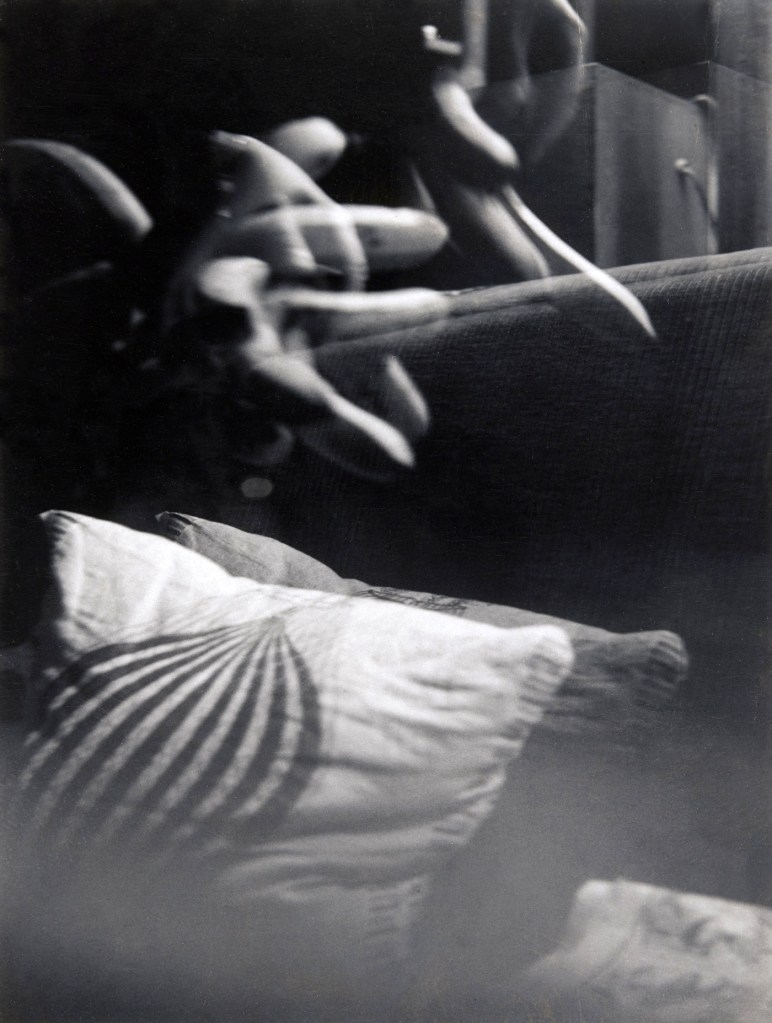

Man Ray (American, 1890-1976)
Unconcerned Photograph
1959
Museum of Modern Art, New York
© Man Ray Trust/ADAGP, Paris and DACS, London 2018

Jacques Mahé de la Villeglé (French, 1926-2022)
Jazzmen
1961
Printed papers on canvas
2170 x 1770mm
Presented by the Friends of the Tate Gallery 2000
© Jacques Mahé de la Villeglé
The Jazzmen is a section of what Jacques Villeglé termed affiches lacérées, posters torn down from the walls of Paris. These particular ones were taken on 10 December 1961. Following his established practice, Villeglé removed the section from a billboard and, having mounted it on canvas, presented it as a work of art. In ‘Des Réalités collectives’ of 1958 (‘Collective Realities’, reprinted in 1960: Les Nouveaux Réalistes, pp. 259-60) he acknowledged that he occasionally tore the surface of the posters himself, although he subsequently restricted interventions to repairs during the mounting process. The large blue and green advertisements for Radinola (at the top right and lower left) provide the main visible surface for The Jazzmen. These establish a compositional unity for the accumulated layers. Overlaid are fragmentary music posters and fly-posters, some dated to September 1961, including the images of the red guitarists that lend the work its title. The artist’s records give the source as rue de Tolbiac, a thoroughfare in the 13th arrondissement in south-east Paris. Villeglé usually uses the street as his title, but has suggested (interview with the author, February 2000) that the title The Jazzmen may have been invented for the work’s inclusion in the exhibition L’Art du jazz (Musée Galliera, Paris 1967).
Villeglé worked together with Raymond Hains (b. 1926) in presenting torn posters as works of art. They collaborated on such works as Ach Alma Manetro, 1949 (Musée nationale d’art moderne, Centre Georges Pompidou, Paris), in which typography dominates the composition. They first showed their affiches lacérées in May 1957 at the Galerie Colette Allendy, Paris, in a joint exhibition named Loi du 29 juillet 1881 ou le lyrisme à la sauvette (The Law of 29 July 1881 or Lyricism through Salvage) in reference to the law forbidding fly-posting. Villeglé sees a social complexity in the developments in the style, typography and subject of the source posters. He also considers the processes of the overlaying and the pealing of the posters by passers-by to be a manifestation of a liberated art of the street. Both aspects are implicitly political. As Villeglé points out, anonymity differentiates the torn posters from the collages of the Cubists or of the German artist Kurt Schwitters. In ‘Des Réalités collectives’ Villeglé wrote: ‘To collages, which originate in the interplay of many possible attitudes, the affiches lacérées, as a spontaneous manifestation, oppose their immediate vivacity’. He saw the results as extending the conceptual basis of Marcel Duchamp’s readymades, whereby an object selected by an artist is declared as art. However, this reduction of the artist’s traditional role brought an end to Villeglé’s collaboration with Hains, who held more orthodox views of creative invention.
In 1960 Villeglé, Hains and François Dufrêne (1930-1982), who also used torn posters, joined the Nouveaux Réalistes group gathered by the critic Pierre Restany (b.1930). Distinguished by the use of very disparate materials and techniques, the Nouveaux Réalistes – who also included Arman (b.1928), Yves Klein (1928-1962) and Jean Tinguely (1925-1991) – were united by what Villeglé has called their ‘distance from the act of painting’ as characterised by the dominant abstraction of the period (interview February 2000). In this way, Klein’s monochrome paintings (see Tate T01513) and Villeglé’s affiches lacérées (lacerated posters) conform to the group’s joint declaration of 27 October 1960: ‘The Nouveaux Réalistes have become aware of their collective singularity. Nouveau Réalisme = new perceptual approaches to reality.’ The Jazzmen, of the following year, embodies Villeglé’s understanding of his ‘singularity’ as a conduit for anonymous public expression.
Matthew Gale
June 2000
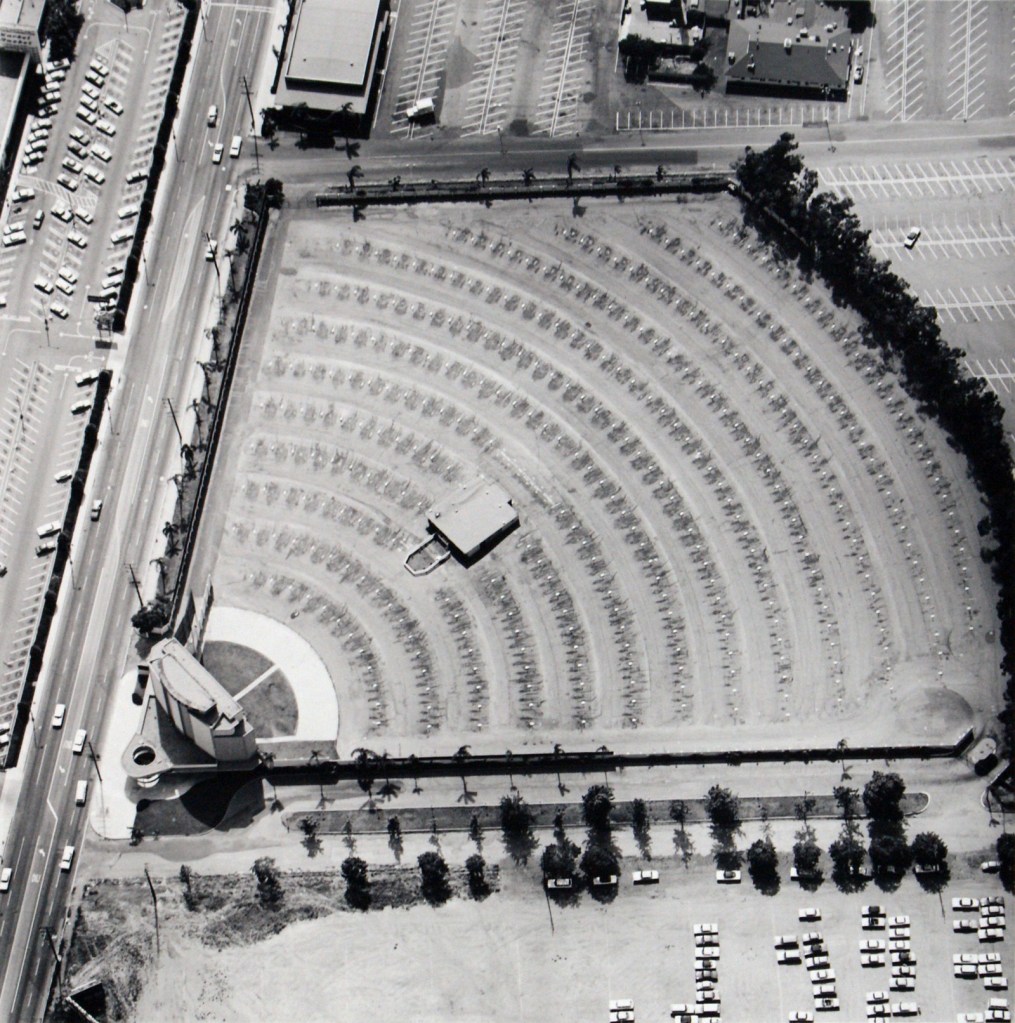

Edward Ruscha (American, b. 1937)
Gilmore Drive-In Theater – 6201 W. Third St.
1967, printed 2013
Gelatin silver prints on paper
356 x 279mm
Courtesy Ed Ruscha and Gagosian Gallery
© Ed Ruscha
Installation view of the exhibition Shape of Light: 100 Years of Photography and Abstract Art at Tate Modern, London
Photo: © Tate / Andrew Dunkley
Installation view of the exhibition Shape of Light: 100 Years of Photography and Abstract Art at Tate Modern, London showing Gregorio Vardanega’s Circular Chromatic Spaces 1967. Musée d’Art moderne de la Ville de Paris
Photo: © Tate / Andrew Dunkley
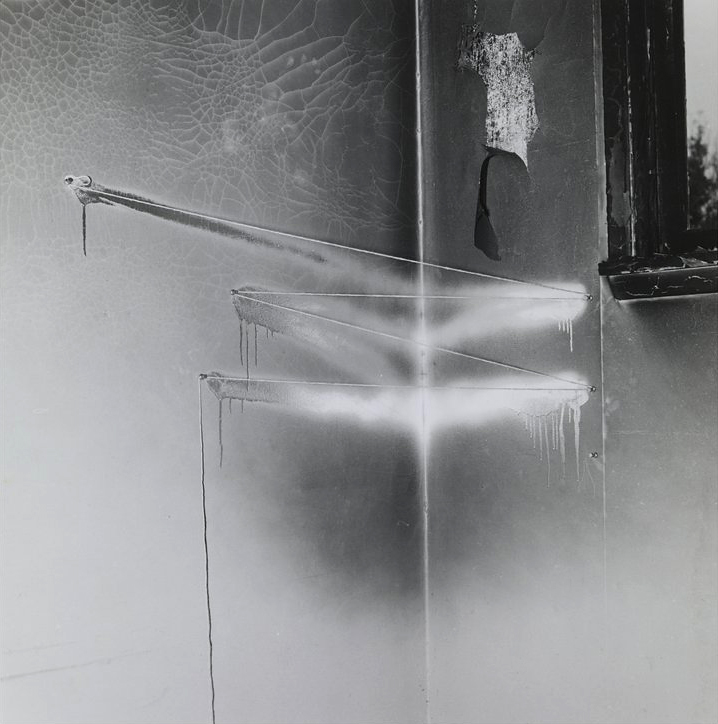

John Divola (American, b. 1949)
74V11
1974
Silver gelatin print
Jack Kirkland Collection, Nottingham
© John Divola
Barbara Kasten (American, b. 1936)
Photogenic Painting, Untitled 74/13 (ID187)
1974
Salted paper print
558 x 762mm
Courtesy the artist, Thomas Dane Gallery and Bortolami Gallery, New York
© Barbara Kasten
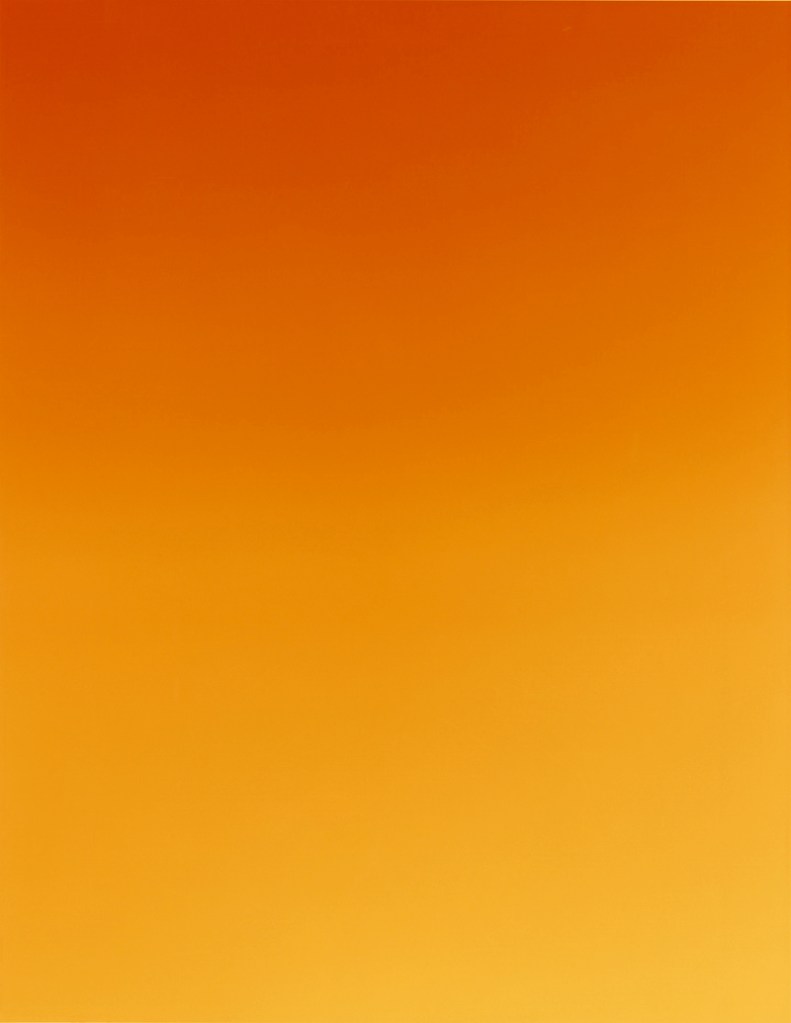

James Welling (American, b. 1951)
Untitled
1986
C-print on paper
254 x 203mm
Jack Kirkland Collection, Nottingham
© James Welling. Courtesy the artist and David Zwirner, New York/London/Hong Kong and Maureen Paley, London
Installation view of the exhibition Shape of Light: 100 Years of Photography and Abstract Art at Tate Modern, London showing Sigmar Polke’s Untitled (Uranium Green) 1992. Hans Georg Näder © The Estate of Sigmar Polke / VG Bild-Kunst Bonn and DACS London, 2018
Photo: © Tate / Seraphina Neville
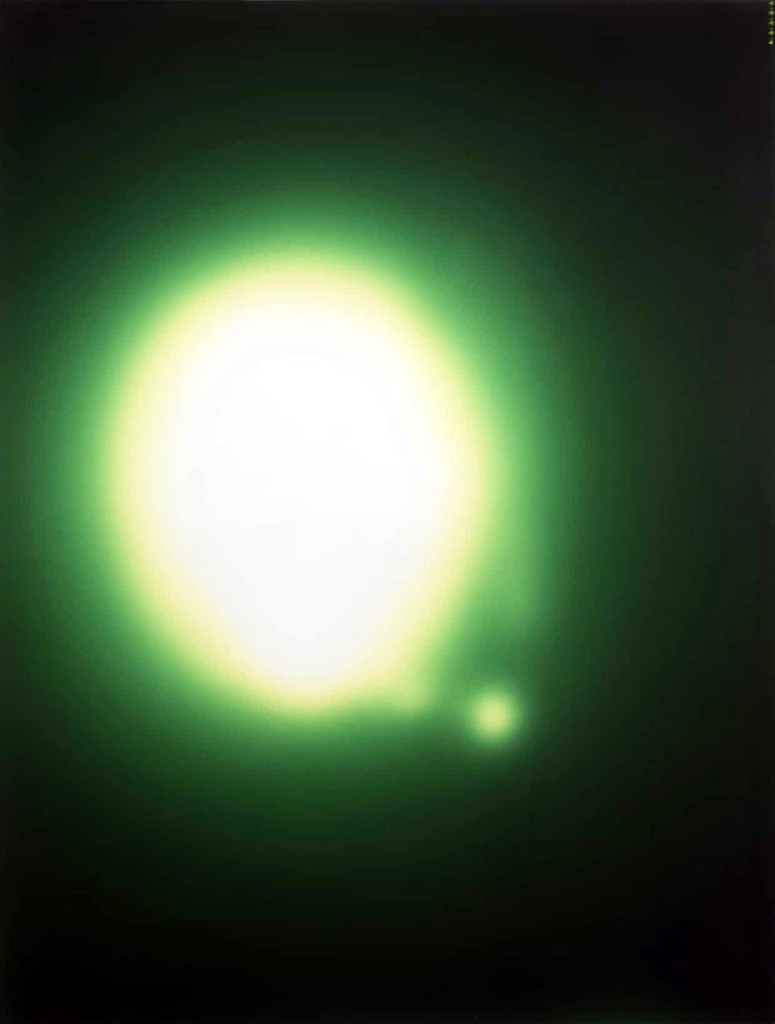

Sigmar Polke (German, 1941-1910)
Untitled (Uranium Green) (detail)
1992
10 Photographs, C-print on paper
Image, each: 610 x 508mm
The Estate of Sigmar Polke / VG Bild-Kunst Bonn 2017
Photo: Adam Reich/The Estate of Sigmar Polke / VG Bild-Kunst Bonn and DACS London, 2018
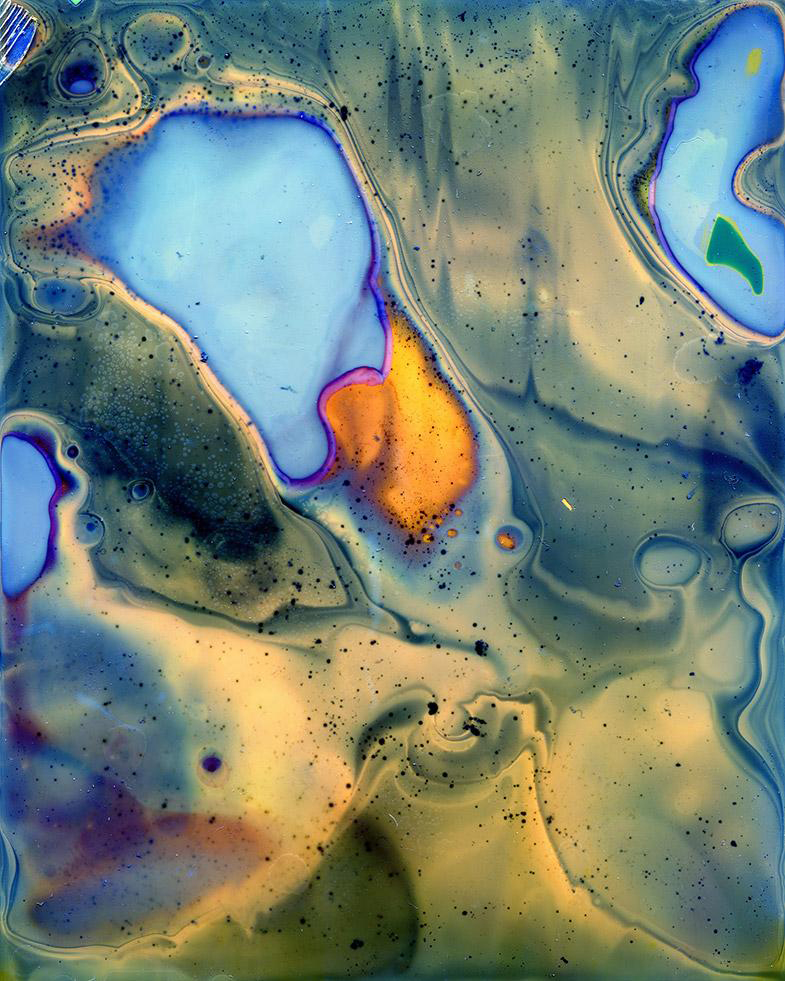
Daisuke Yokota (Japanese, b. 1983)
Untitled
2014
from Abstracts series
© Daisuke Yokota
Courtesy of the artist and Jean-Kenta Gauthier Gallery
Process is at the core of Yokota’s photographs. For his black-and-white work, such as the series Linger or Site/Cloud, Yokota sifts through an archive of more than 10 years of photographs in his Tokyo apartment. When he finds something that speaks to him – a nude figure, a chair, a building, a grove of trees – he makes a digital image of it, develops it, and rephotographs the image up to 15 times, until it becomes increasingly degraded. He develops the film in ways that are intentionally “incorrect,” allowing light to leak in, or singeing the negatives, using boiling water, or acetic acid. The purported subject fades, and shadows, textures, spots and other sorts of visual noise emerge. For his recent colour work, trippy, sensual abstractions, the process is similar, except that it is cameraless; he doesn’t start with a preexisting image. “I wanted to focus on the emulsion, on the different textures, more than on a subject being photographed,” says Yokota.
IN THE STUDIO
Daisuke Yokota
By Jean Dykstra
November – December 2015. No longer available online
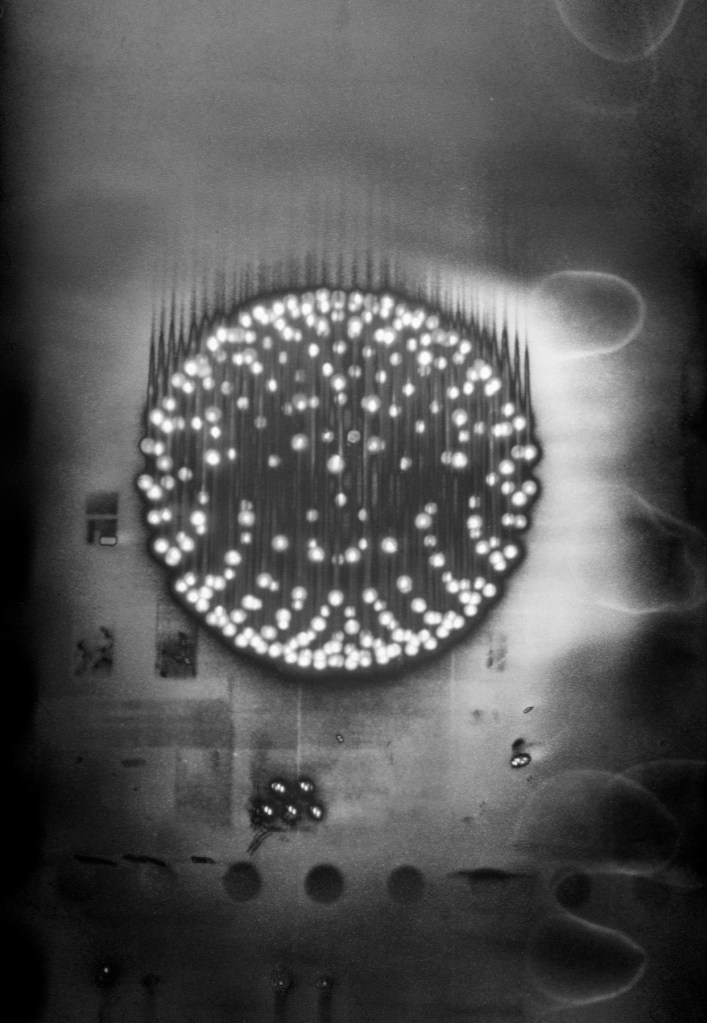

Antony Cairns (British, b. 1980)
LDN5_051
2017
Courtesy of the artist
© Antony Cairns
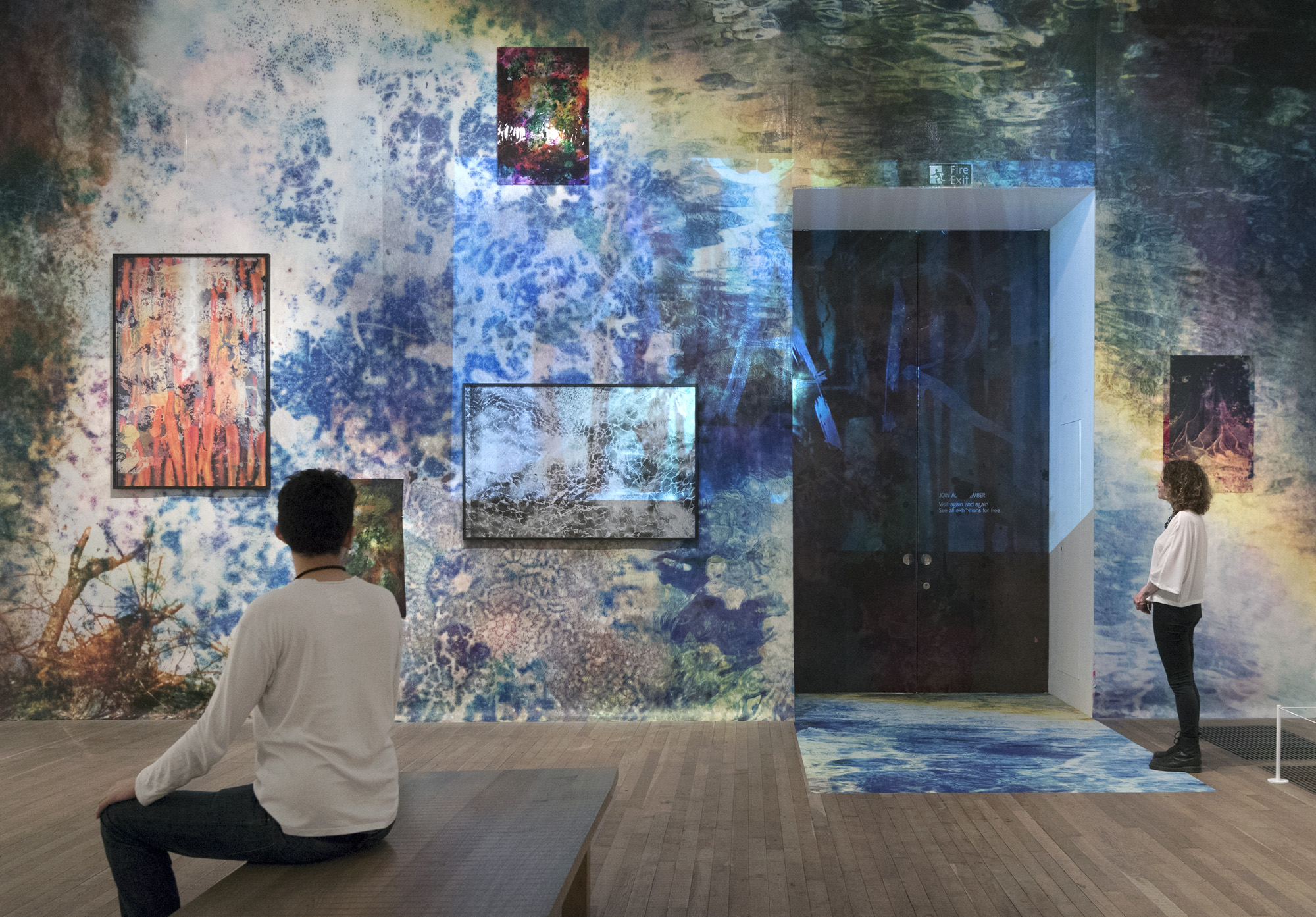
Installation view of the exhibition Shape of Light: 100 Years of Photography and Abstract Art at Tate Modern, London showing the installation A Rock Is A River, 2018 by the artist Maya Rochat. Courtesy Lily Robert and VITRINE, London | Basel © Maya Rochat
Photo: © Tate / Sepharina Neville
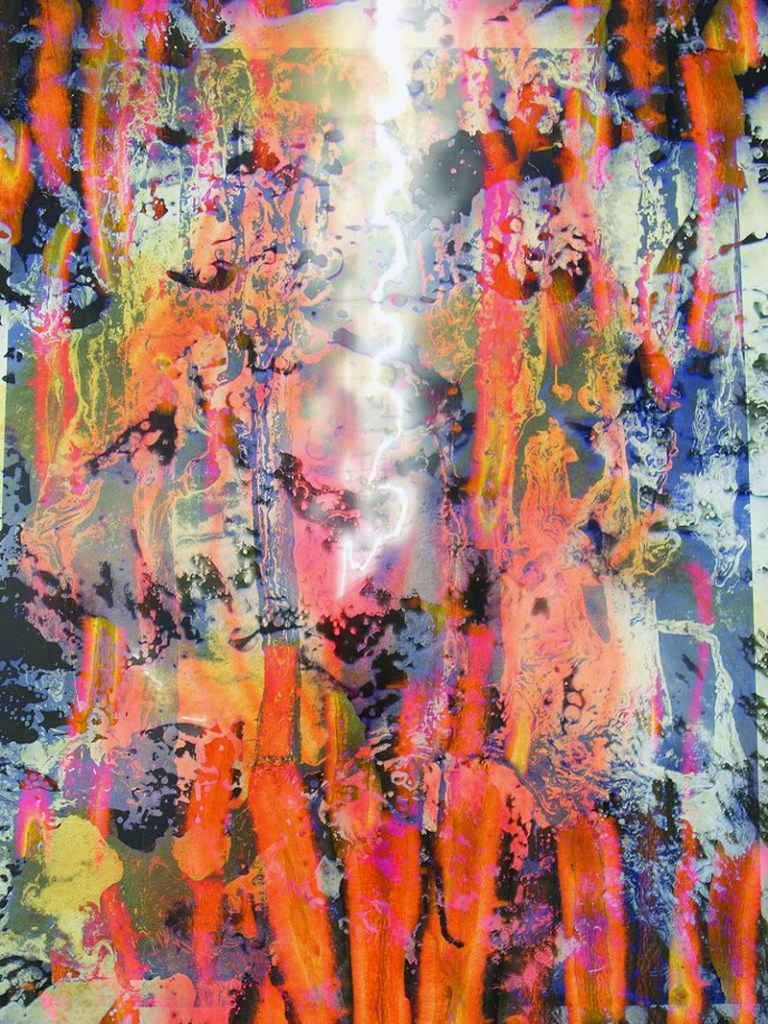

Maya Rochat (German, b. 1985)
A Rock is a River (META CARROTS)
2017
Courtesy Lily Robert
© Maya Rochat
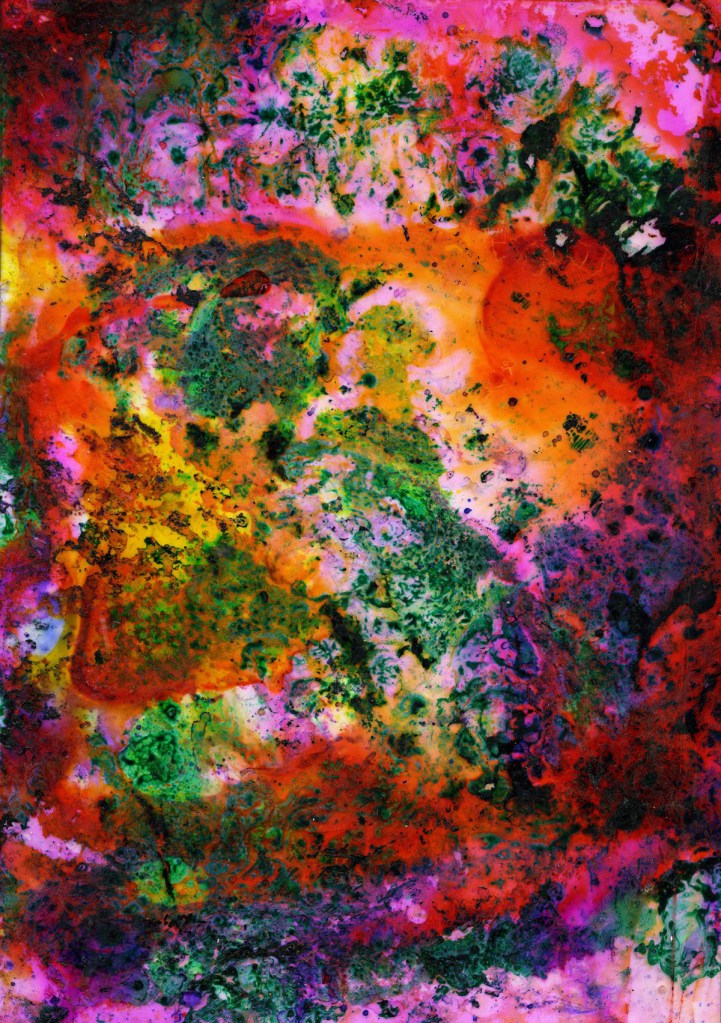

Maya Rochat (German, b. 1985)
A Rock is a River (META RIVER)
2017
Courtesy Lily Robert
© Maya Rochat
Tate Modern
Bankside
London SE1 9TG
United Kingdom
Opening hours:
Daily 10am – 5pm






























































You must be logged in to post a comment.