Exhibition dates: 18th July – 9th November 2014

Victor Hugo (French, 1802-1885)
Les Misérables vol. 1
1845-1862
Autograph manuscript
Bibliothèque nationale de France
Devour the main course but don’t stay for dessert
This is an exhibition in two galleries. In the first you are not allowed to take photographs but in the second you can take as many as you want. You are told this as you enter the exhibition but the import of this incantation only becomes apparent much later in your visit.
The first gallery is a profound experience: manuscripts, letters, photographs, paintings, and posters that all relate to the great man and his work Les Misérables. The Charles Marville photographs are sublime (as always) with the width of the vertical prints being the element that I noticed most on this viewing. The space that Marville manages to capture in these vertical images makes them seem almost as wide as they are high giving them an almost panoramic feel, as though the space of the image goes on forever, from side to side and into the distance. There is a wonderful sense of volume in the atmosphere, tones and textures of these images. One juxtaposition is particularly tantalising, the pairing of Marville’s Rue Tirechape (1865) with engravings such as the demolition work for constructing the Boulevard St. Germain by Maxine Lalanne (1827-1886). The illusion that one could be the other is enlightening, and there is an established association (especially in Pictorialist photography) between representation in etching and photography.1
As Philip Ebury observes,
“It has often been said that Pictorial photographs resemble works in other media. The analogy with etchings is especially striking and the comparison is more than physical. Between 1890 and the late 1920s, etching and Pictorial photography had a shared history and many similar aims. Parallels between the two disciplines in Australia had their antecedents in England. In the late nineteenth century many photographers in that country were consciously promoting artistic, as opposed to documentary work. At the same time, printmakers were reviving the art of original etching as an expressive rather than a reproductive medium.”2
But the Charles Marville photographs are not the star of the show, oh no. That is left to five things:
a) An album of which you can see only one leaf in the exhibition, Les Proscrits (‘The Exiles’) (1856, below), but that one leaf is enough. The enigma, light and intimacy of this one page is just magnificent.
b) Equally impressive are the very small intense portraits of Victor Hugo such as the silver gelatin photograph attributed to Arsène Garnier (1820-1909) – dark, atmospheric with Neo-classical sculptures and chandeliers reflected in expansive mirrors, VH propped up by a favourite chair; or Charles Hugo’s salted paper print from a collodion negative of his father in Jersey leaning on the back of a chair (1853-1855). The intensity of these portraits is remarkable.
c) Victor Hugo’s own paintings, usually pen and brown ink wash on paper, are also very powerful. In images such as Ma destinée (My destiny) (1867, below) where VH wrote in direct conversation with the ocean and The bowels of the Leviathan (1866) – dark, dank labyrinthine Parisian sewers – Hugo draws you into a world of the disenfranchised, the poor, the destitute and their (and his) destiny.
d) The beautiful theatre posters (1880s-1910s) worth the price of admission on their own
e) Leaving the best till last, the autographed manuscript Volume 1 of Les Misérables in all its glory (the first time it has ever left France), complete with revisions, crossings out and the final version in red, resting innocuously in a glass display cabinet. The psychological weight of the volume is immense. This is getting as close to the ‘source’ as you can possibly get without touching it. I remember once holding a first edition of Oscar Wilde’s The Ballad of Reading Gaol in my hand. This had that same spine tingling effect.
.
The first gallery assembles this incredible story and builds a glorious intensity of experience. I was on such an elevated level it was great.
And then, in literally two minutes, it was gone… No, no, no, no!
The second gallery is such a let down. It features costumes, posters, pamphlets and video in an exploration of the musical ‘phenomena’ this is the (Disney-fied) Les Misérables. A stage set from the musical with cut our heads so people can have their photo taken, and for performances; very poor quality black and white images of the sets of the theatrical productions of Les Misérables; a cardboard cut-out two-wheeled cart that is the worst thing that you could possibly see; and videos of workshops with men explaining how they are using a bandsaw to create the stage for the musical (as if I want to see that after what has gone before!). From the sublime to the ridiculous. I’m sure the kids might like it but after seeing such an amazing first half of the exhibition, for me this was like being tied with a ball and chain and dropped over the side to sink like a stone. Why do curators insist on doing this. Do they think that they always have to have a “popular” space for the family and the kids these days. That more is really more?
In this case it quite ruined what was up till then an incredible experience. So visit the exhibition for the main course (and don’t take any photos), but if I were you I would turn around after the first gallery and walk out the way I came in, thinking to myself ‘less is more!
Dr Marcus Bunyan
- See Ebury, Frances. “Engravers and Etchers, Pictorialists and Photographers,” Part 2, Chapter 2 in Making Pictures: Australian Pictorial Photography as Art 1897 – 1957 Volume 1. Phd thesis, The University of Melbourne, 2001, p. 73.
- Ibid.,
.
Many thankx to the State Library of Victoria for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“As long as social damnation exists, through laws and customs, artificially creating hell at the heart of civilization and muddying a destiny that is divine with human calamity; as long as the three problems of the century – man’s debasement through the proletariat, woman’s demoralisation through hunger, the wasting of the child through darkness – are not resolved … as long as ignorance and misery exist in this world, books like the one you are about to read are, perhaps, not entirely useless.”
.
Victor Hugo, Hauteville House, 1 January 1862

Victor Hugo (French, 1802-1885)
Title page of Les Misérables vol. 1
1845-1862
Autograph manuscript
Bibliothèque nationale de France

Victor Hugo (French, 1802-1885)
Paris
Paris, 1867
Maison Littéraire de Victor Hugo
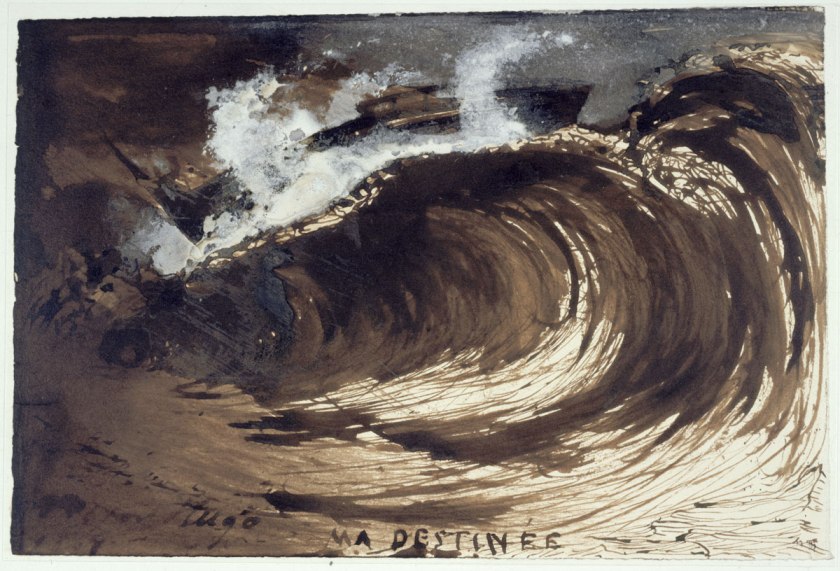

Victor Hugo (French, 1802-1885)
Ma destinée (My destiny)
1867
Ink and brown-ink wash
© Maisons de Victor Hugo / Roger-Viollet
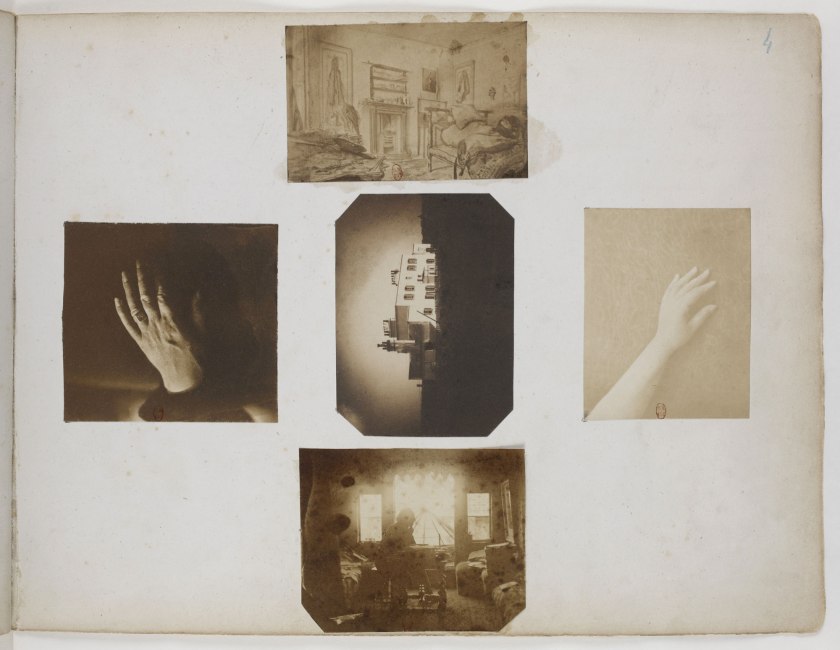

Les Proscrits (‘The Exiles’)
1856
Album of photographs
Bibliothèque nationale de France
Album The Exiles – Victor Hugo and his circle of friends in exile started in Guernsey on the 1st January 1856. The album creates an allegorical portrait of VH. His family is represented by Victor Hugo’s hand (left), Adele’s hand (right), Marine Terrace their home in Jersey 1852-1856 (centre) and VH posing at his desk in his study at Hauterville House, Guernsey, where he completed Les Misérables surrounded by sunlight. The page appears in the posting the correct way up, as it appears in the album.
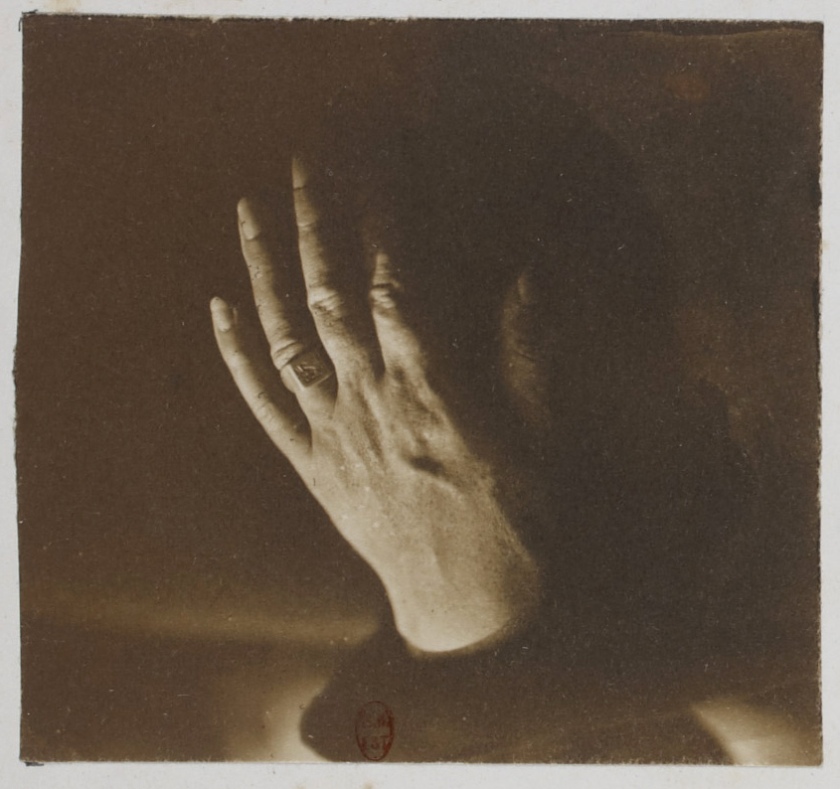

Victor Hugo’s hand
From the album Les Proscrits (‘The Exiles’) (detail of page)
1856
Album of photographs
Bibliothèque nationale de France
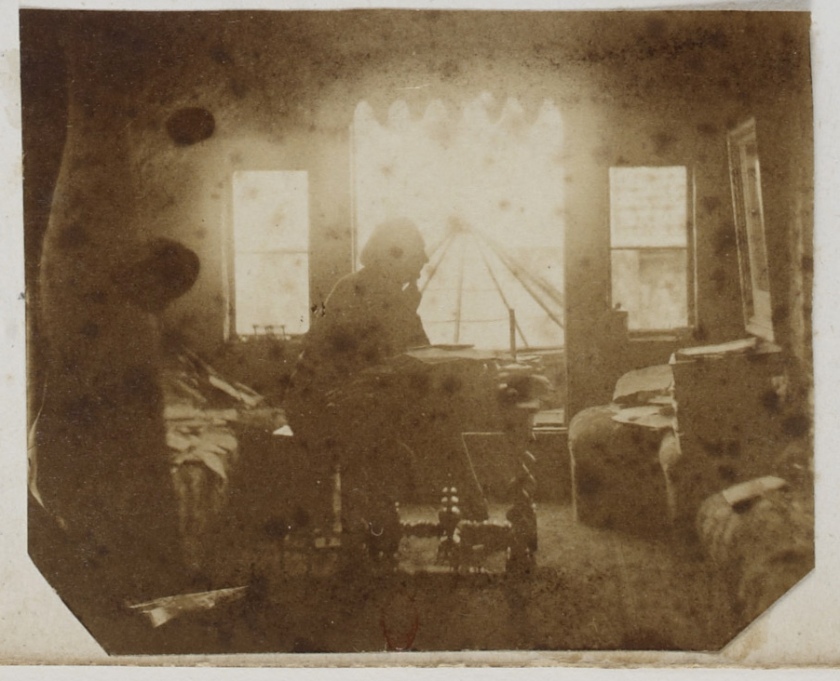

Victor Hugo posing at his desk in his study at Hauterville House, Guernsey
From the album Les Proscrits (‘The Exiles’) (detail of page)
1856
Album of photographs
Bibliothèque nationale de France
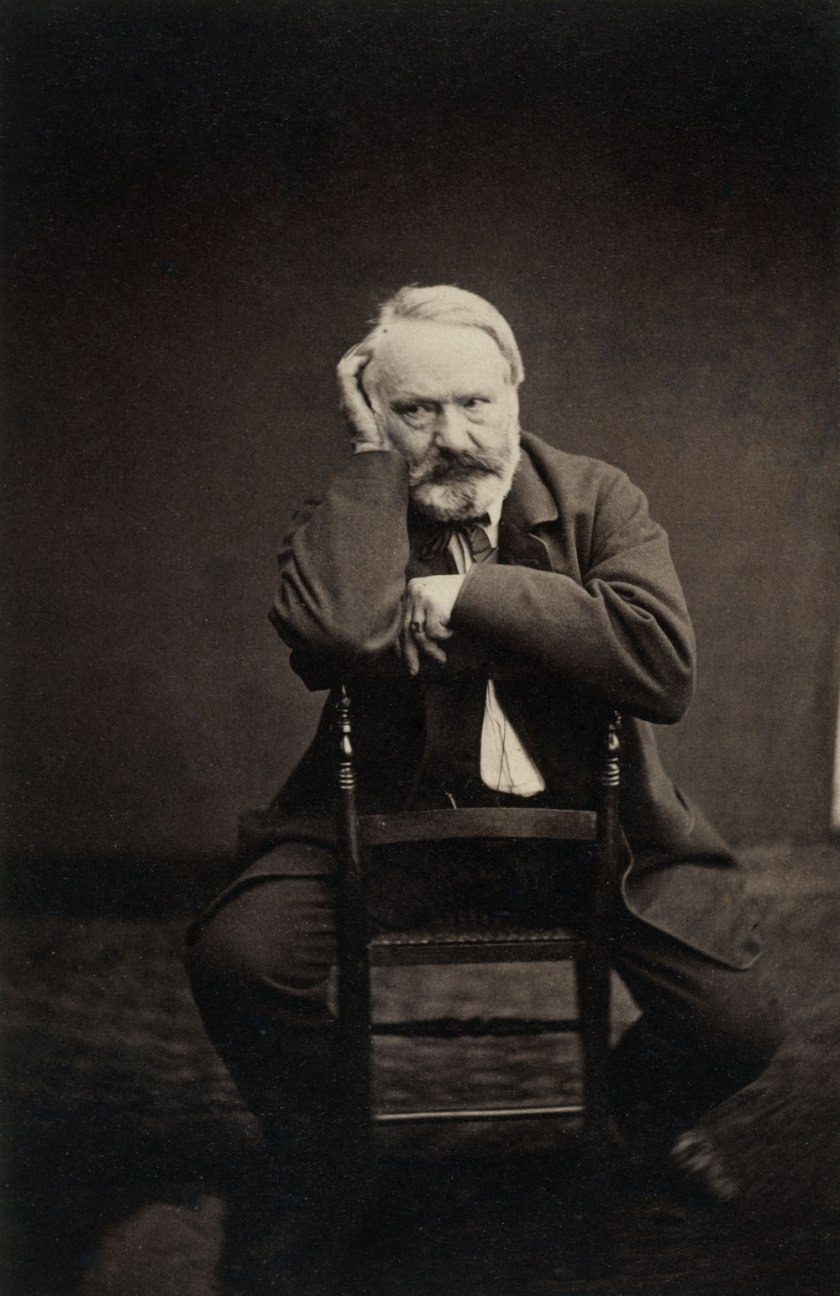
Edmond Bacot (French, 1814-1875)
Victor Hugo en 1862 (Victor Hugo in 1862)
1862
Maison de Victor Hugo
Image © Edmond Bacot / Maisons de Victor Hugo / Roger-Viollet
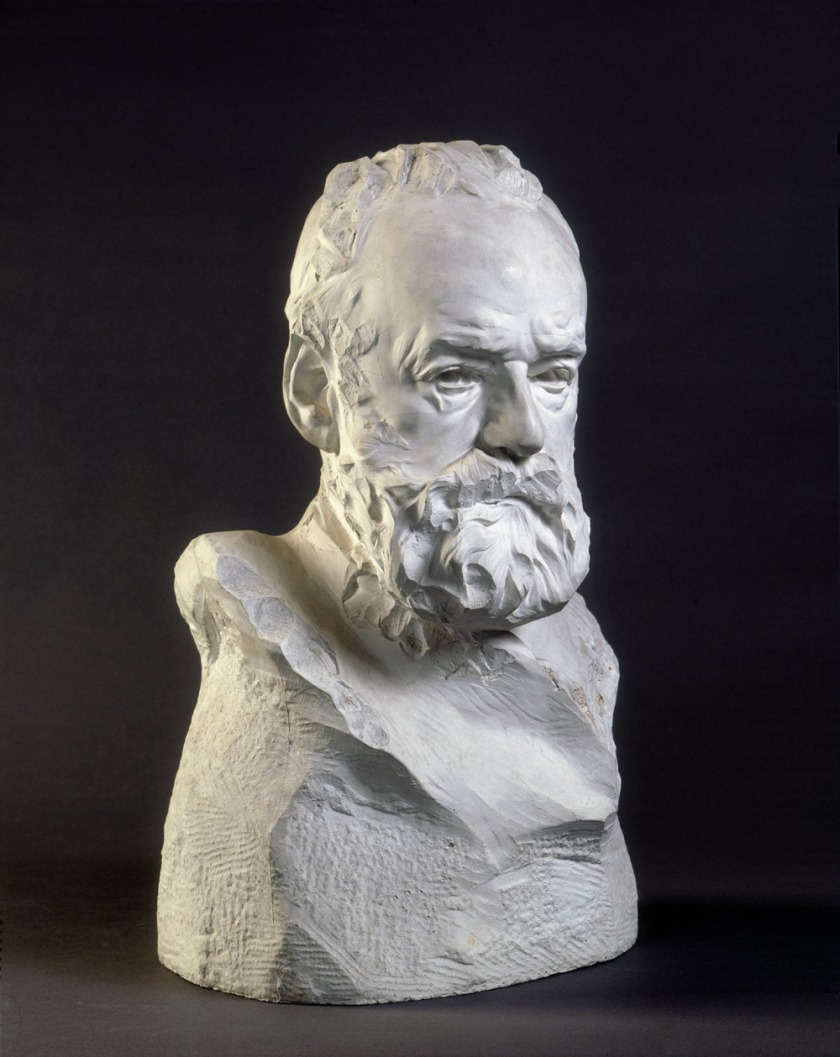

Auguste Rodin (French, 1840-1917)
Victor Hugo, buste dit À l’Illustre Maître (Victor Hugo, bust known as ‘To the illustrious master’)
1883
Musée Rodin
Rodin states that Hugo would not pose. “I worked out on the veranda. I observed him swiftly, but carefully as he refused to pose. He accepted to be looked at, from all angles, but he would not pose. And so I looked at his conscience. And this is how I was able to capture the real Hugo.”
When the first two volumes of Les Misérables arrived in Paris in April 1862, all 6000 copies sold in a day. Public readings were organised when copies sold out. Everyone was reading it, from the literary intelligentsia to the common people. It was also quickly translated into nine languages to reach a global audience. After only three months, 100,000 authorised copies (and countless editions on the black market) had been sold worldwide, making the novel into an unprecedented literary bestseller of western literature. In 1870 after the fall of Napoleon III, Hugo returned to France and was hailed a national hero.
Victor Hugo’s legacy and the iconic story of Les Misérables endure to this day with various adaptations being created around the world. There have been at least 48 films, 14 animated films or TV series, radio plays, 12 television miniseries, numerous comic books, and at least 286 editions of Les Misérables published, sung and spoken. The stage musical of Boublil and Schönberg’s Les Misérables is in itself a worldwide phenomenon. It is the longest running theatre performance in London and has been seen by over 65 million people in 43 countries and in 21 languages. It returns to Melbourne in June 2014.
About Victor Hugo
Victor Hugo is considered one of the most important and influential authors of the 19th century. Through his transformative literary works and political activism, French society’s most vulnerable were given a voice in a nation ruled by those with power and privilege. Best known for his novels Les Misérables and The Hunchback of Notre Dame Hugo is also acclaimed for his theatre, essays, drawings and poetry.
Born in Besançon, France in 1802, Hugo was the son of an atheist and anti-monarchist French General and a Catholic pro-monarchist mother. A precocious talent, Hugo’s first work was published at the age of 15. His debut as a professional writer soon followed with the release of his first volume of romantic poems; Ode et poésies diverses in 1822. Many of his early romantic works drew inspiration from his childhood sweetheart and wife Adele Foucher, with whom he had four children. Another powerful female influence on Hugo’s writings was his mistress of more than fifty years, Juliette Drouet.
As Hugo’s career progressed, his aptitude and fondness for romantic literature was matched by his passion for addressing themes of disadvantage and poverty. Hugo’s first major masterpiece The Hunchback of Notre Dame published in 1831 reflected his interest in highlighting such prejudices. However, it was his greatest masterpiece, Les Misérables, that first challenged and then changed the social and political understanding of poverty, disadvantage and inherited privilege in society. In Les Misérables Hugo casts an ex-convict, Jean Valjean, as the revered protagonist and paints a villain of the character representing authority and privilege, Inspector Javert.
Hugo dedicated 17 years of his life to plan and write the epic three part story beginning in the early 1840s and finally publishing the novel in 1862. In addition to his social and political sympathies, Hugo drew from many of his own personal experiences and professional turmoil to inform the characters and themes in Les Misérables. These included the tragic drowning of his eldest daughter, Leopoldine, in a boating accident in 1843, and Hugo’s exile from France by Louis Napoleon III in 1851 – a result of his public opposition to the increasingly authoritarian rule of the self-declared emperor.
From his exile on the Channel Islands of Jersey and Guernsey where he lived for 19 years, Hugo maintained his trenchent opposition to the political status quo and the death penalty, while also publishing widely and spending three years finishing his magnum opus Les Misérables. When Les Misérables finally hit the stands in Paris in 1862 the response by the public was explosive. All 6000 copies sold out in a day, and three months later the book was an international best seller and had been translated into nine languages. Following the success of Les Misérables Hugo returned to France in 1870 after the fall of Napoleon III and was hailed a national hero. He continued to work until he died on 22 May 1885. At his state funeral it was estimated that close to two million people attended. Hugo’s wish to be buried in a pauper’s coffin was granted and his body lay in state under the Arc de Triomphe until he was interred in the Panthéon.
Today Victor Hugo’s extraordinary legacy continues. Les Misérables has been published in at least 250 editions since 1862, 48 films have been made of the story and the Boublil and Schönberg Les Misérables musical has been seen by over 65 million people worldwide in 42 countries and 22 languages, and is one of the most popular musicals of all time. Victor Hugo is remembered as an international literary giant and a French national hero.
Themes
The possibility that the condemned can rise above poverty and degradation to become good and honourable, and perhaps above all to fight for freedom of body and soul.
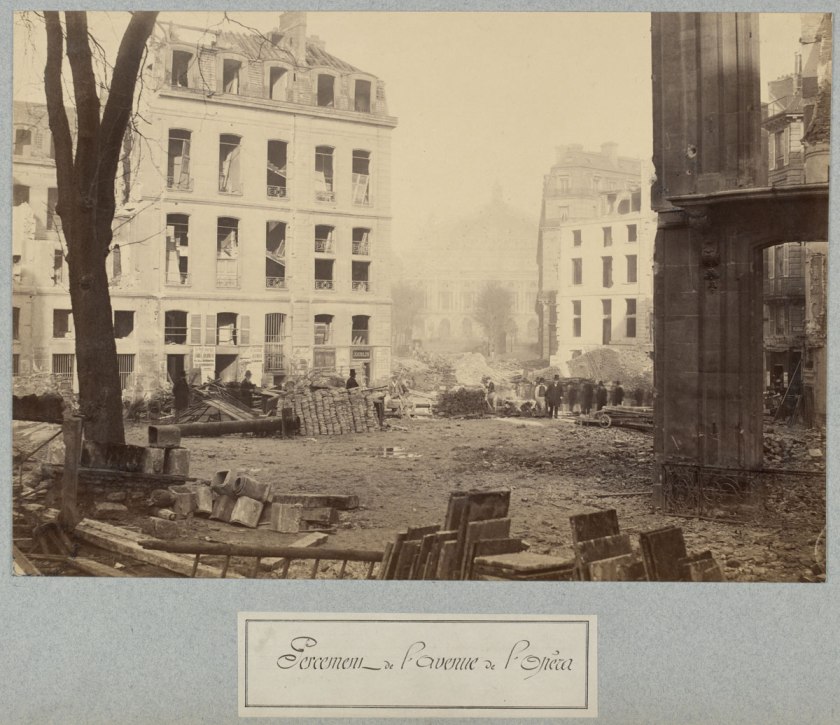

Charles Marville (French, 1813-1879)
Percement de l’avenue de l’Opéra (Clearing of the Avenue de l’Opéra)
c. 1876
State Library of Victoria
![Charles Marville. 'Rue Soufflot (pendant la démolition)' (Rue Soufflot [during demolition]) c. 1876-77](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/210_slv_marville_rue-soufflot-web.jpg?w=840)
Charles Marville (French, 1813-1879)
Rue Soufflot (pendant la démolition) (Rue Soufflot [during demolition])
c. 1876-1877
State Library of Victoria

Charles Marville (French, 1813-1879)
Avenue d’Iéna
c. 1877
State Library of Victoria

Charles Marville (French, 1813-1879)
Boulevard Haussmann
c. 1877
State Library of Victoria
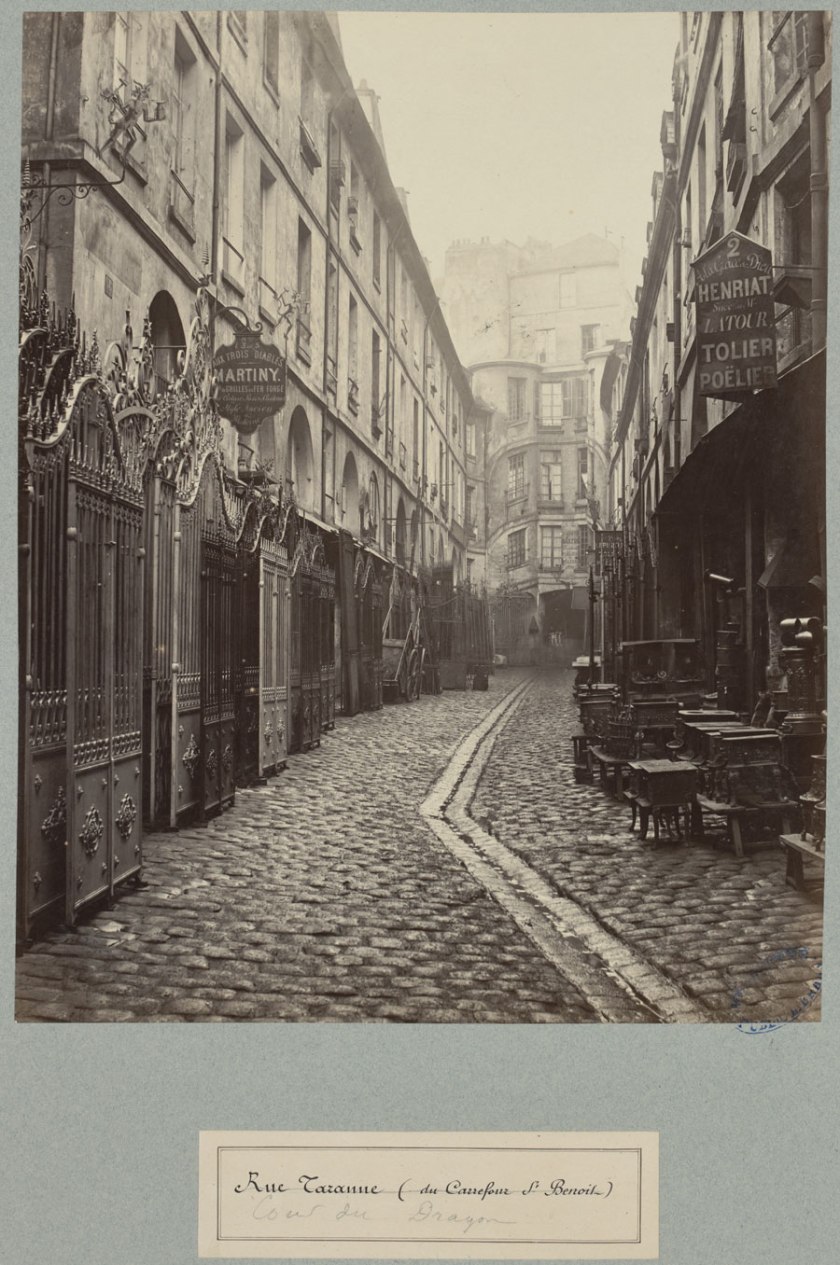

Charles Marville (French, 1813-1879)
Cour du Dragon, Rue de Taranne
c. 1863-1869
State Library of Victoria
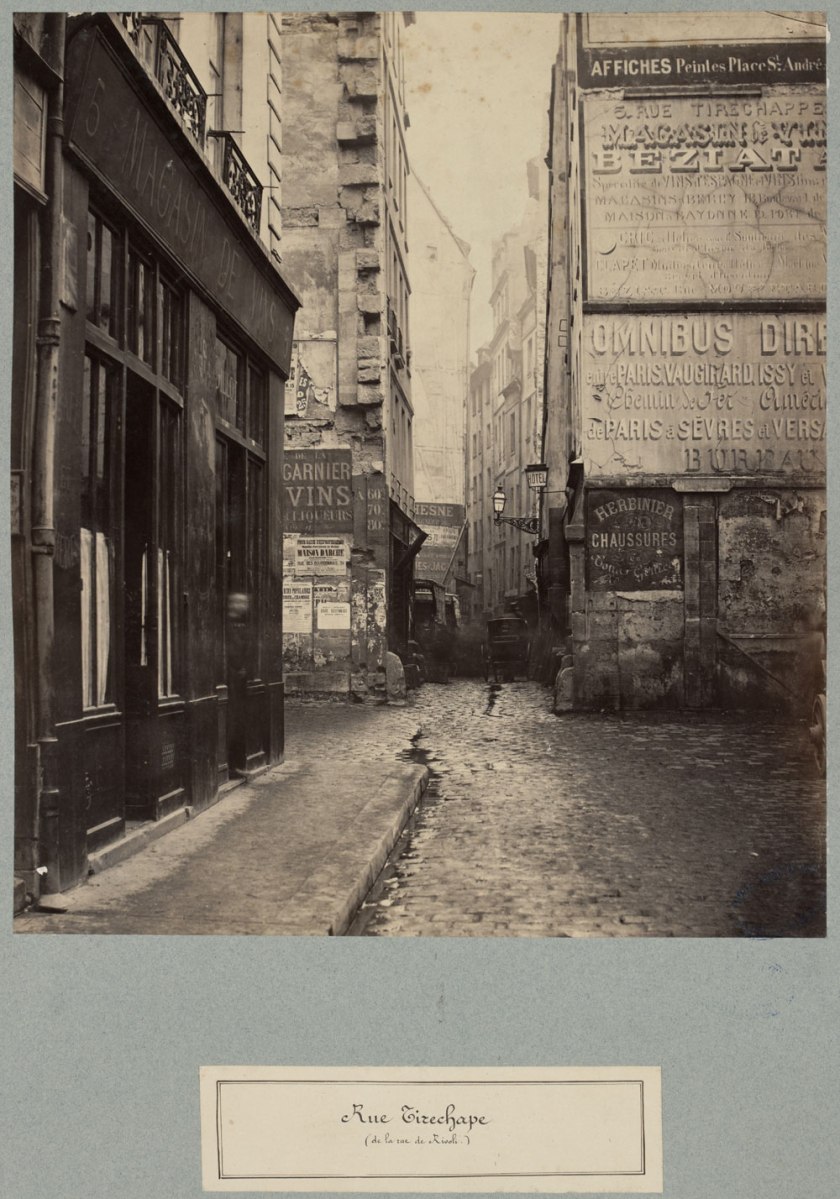

Charles Marville (French, 1813-1879)
Rue Tirechape
c. 1863-1869
State Library of Victoria
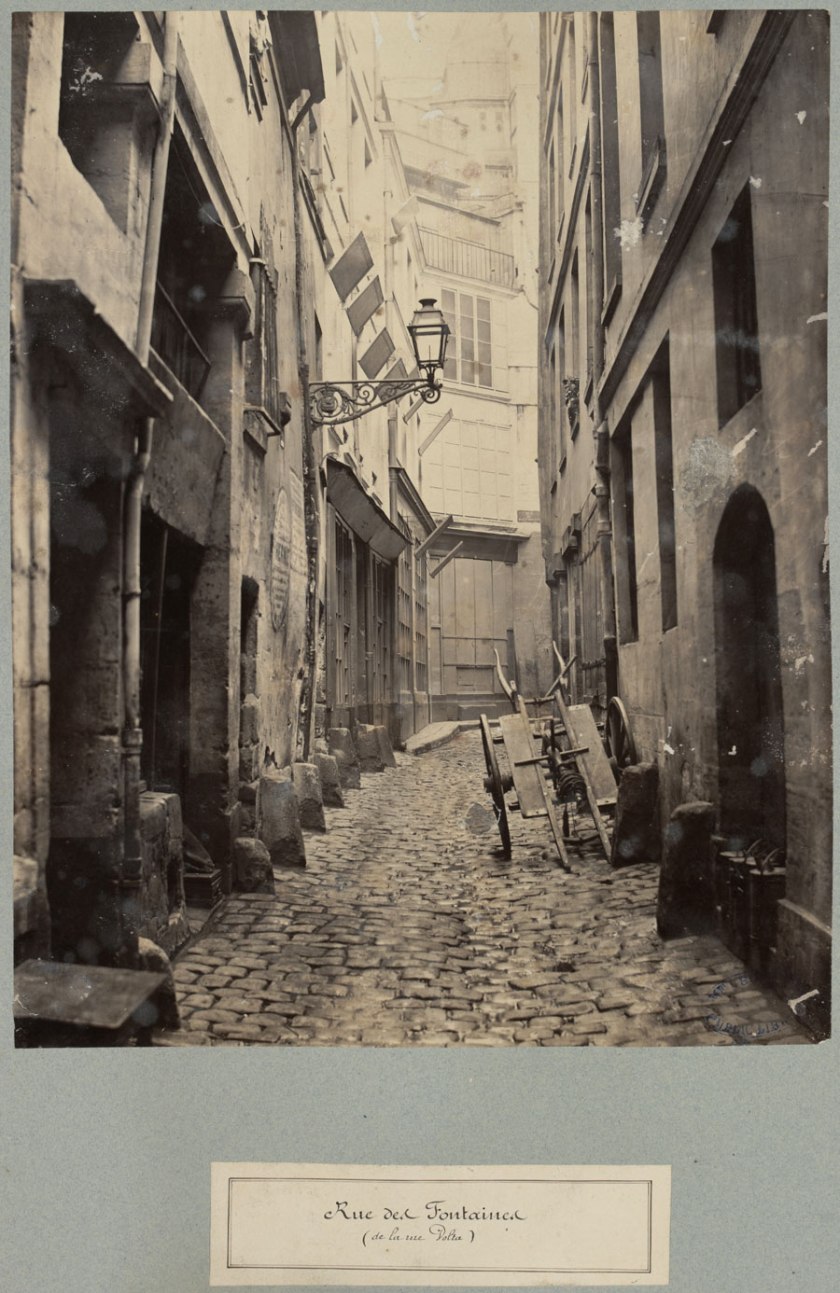

Charles Marville (French, 1813-1879)
Rue de Fontaines
c. 1863-1869
State Library of Victoria
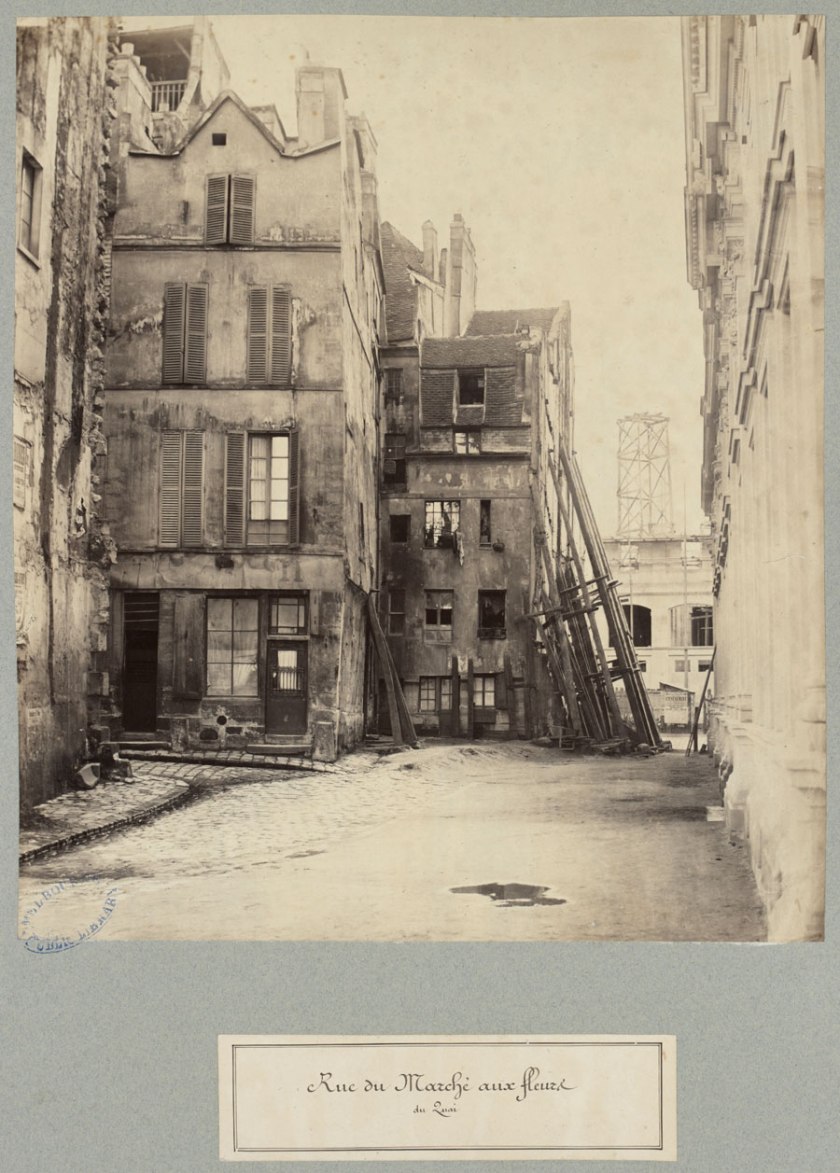

Charles Marville (French, 1813-1879)
Rue du Marche aux fleurs
c. 1863-1869
State Library of Victoria
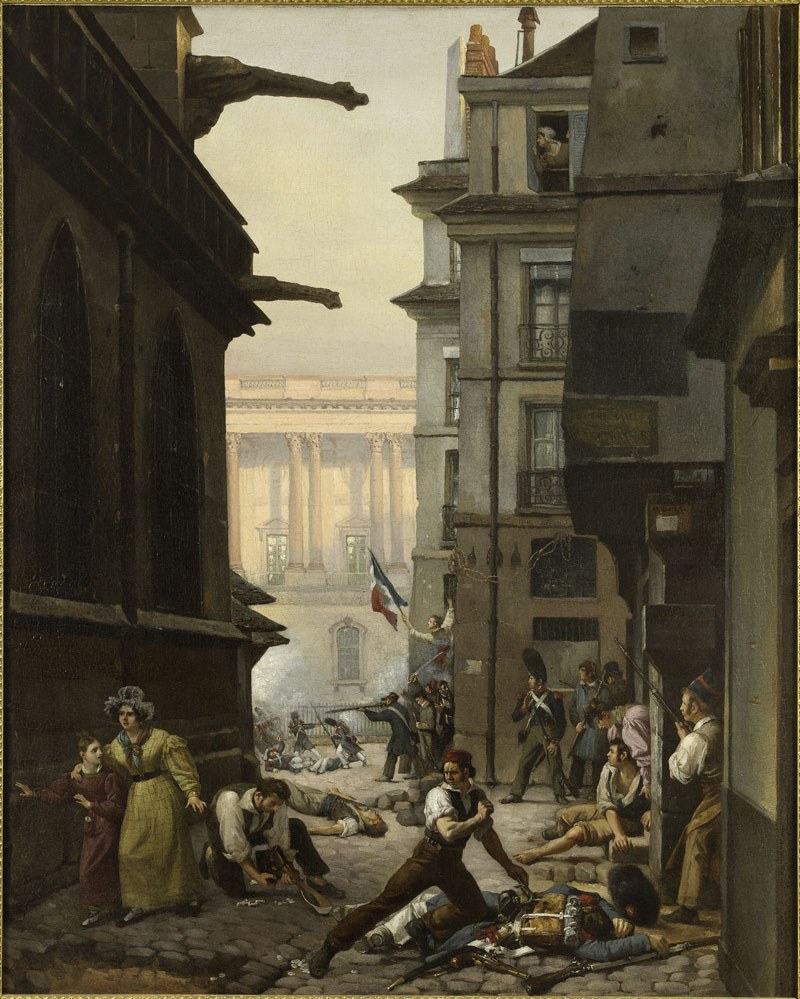

Paul Carpentier (French, 1787-1877)
Episode du 29 juillet 1830, rue Chilperic, face á la colonnade du Louvre (Event of 29 July 1830, rue Chilperic, before the colonnade of the Louvre)
1830
© Musée Carnavalet / Roger-Viollet
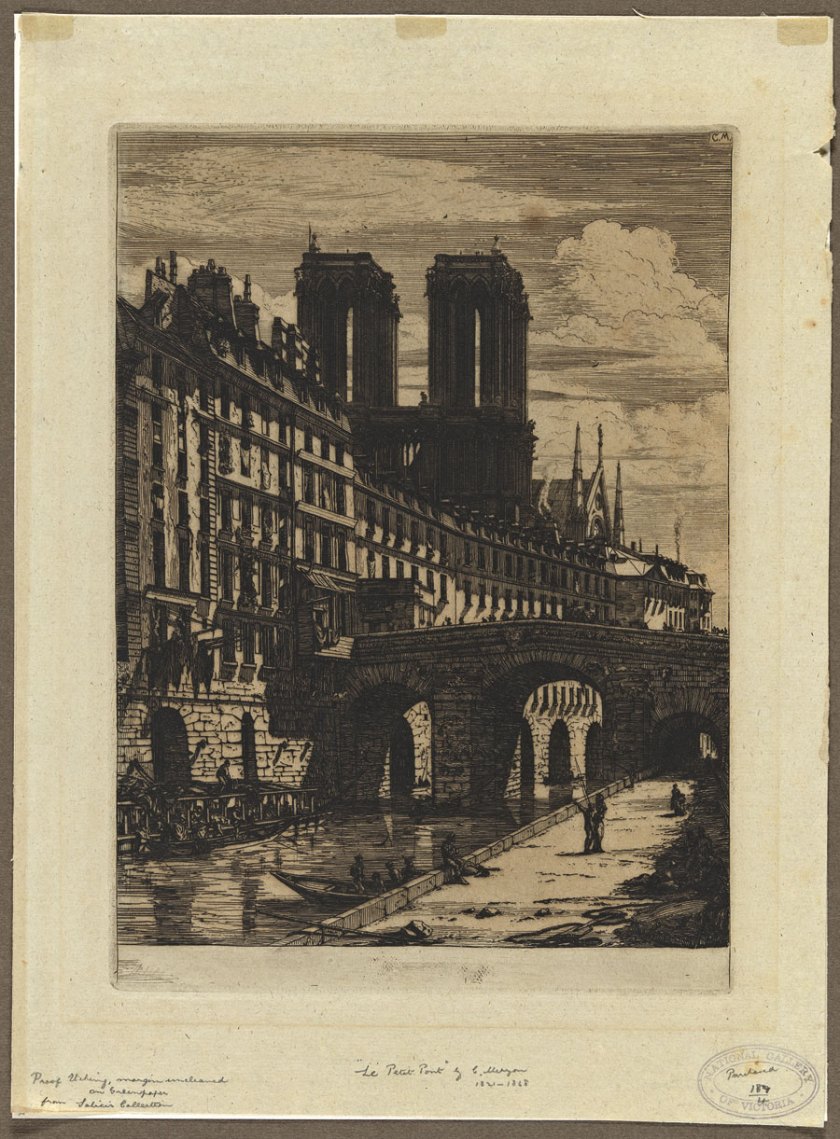

Charles Méryon (French, 1821-1868)
Le petit pont (The little bridge)
1850
National Gallery of Victoria, purchased 1891

Ottavio Rodella Tavio (Italian, 1864-1910)
Poster for I Miserabili di Victor Hugo (Les Misérables by Victor Hugo)
1890
Bibliothèque nationale de France

Les Misérables by Victor Hugo
New York, Classics Illustrated no. 9
1950
State Library of Victoria

Design by Slawomir Kitowski
Les Misérables poster
1989-2000
Teatr Muzyczny, Gdynia, Poland
Courtesy Cameron Mackintosh Ltd
State Library of Victoria
328 Swanston St,
Melbourne VIC 3000
Phone: (03) 8664 7000
Opening hours:
10am to 6pm daily
State Library of Victoria website
LIKE ART BLART ON FACEBOOK
Back to top








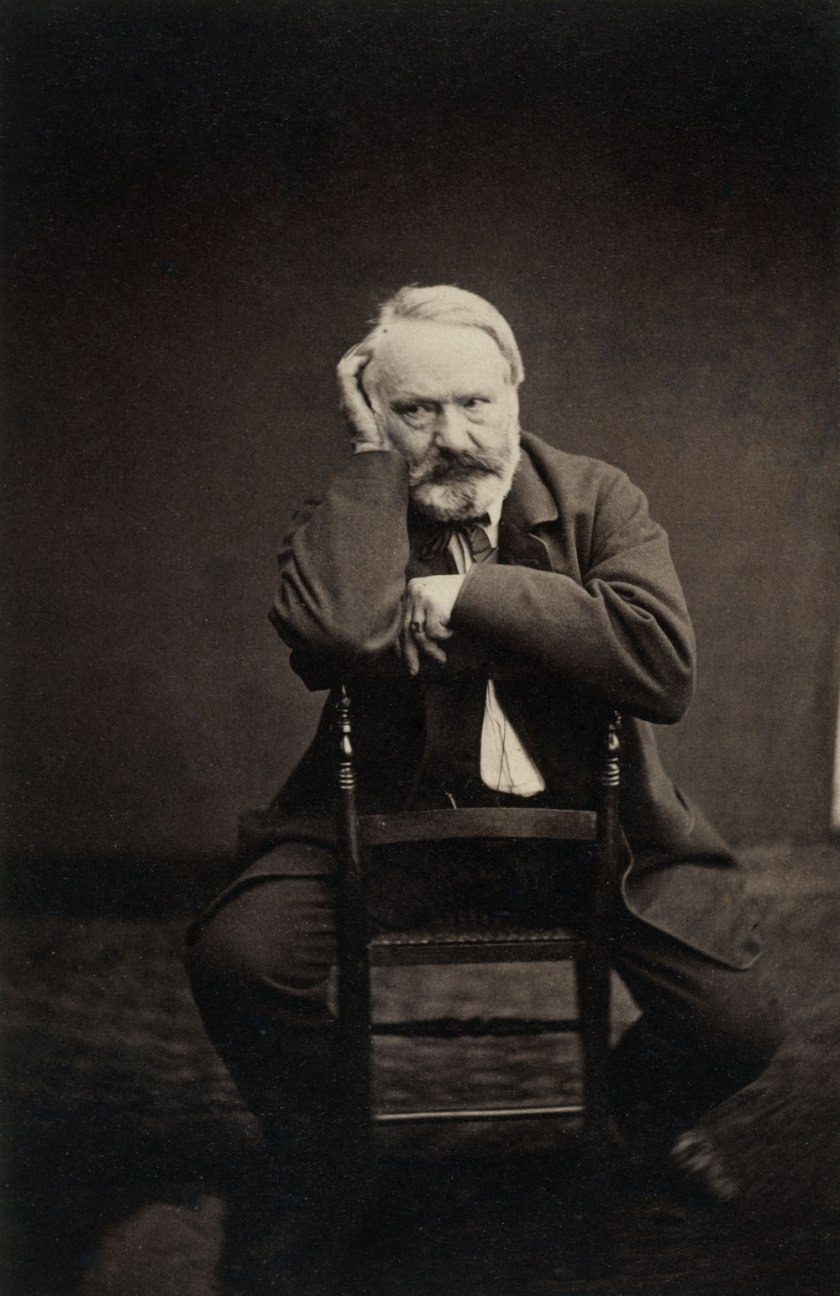


![Charles Marville. 'Rue Soufflot (pendant la démolition)' (Rue Soufflot [during demolition]) c. 1876-77](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/210_slv_marville_rue-soufflot-web.jpg?w=840)











You must be logged in to post a comment.