Exhibition dates: 10th October, 2025 – 22nd February, 2026
Curator: Taous Dahmani, art historian and writer. The exhibition was developed in collaboration with Autofoto (Rafael Hortala Vallve and Corinne Quin) and features archival material from Raynal Pellicer
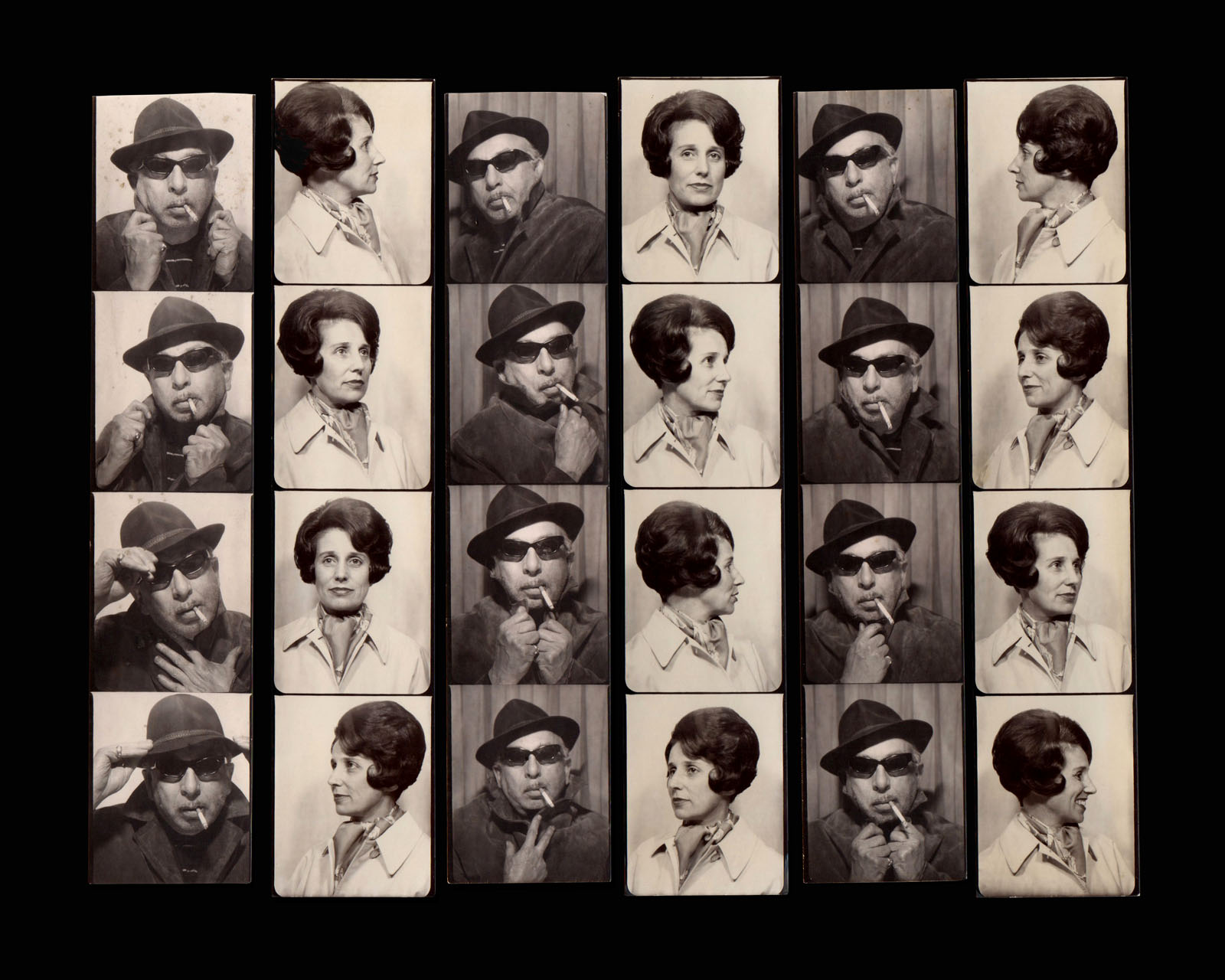
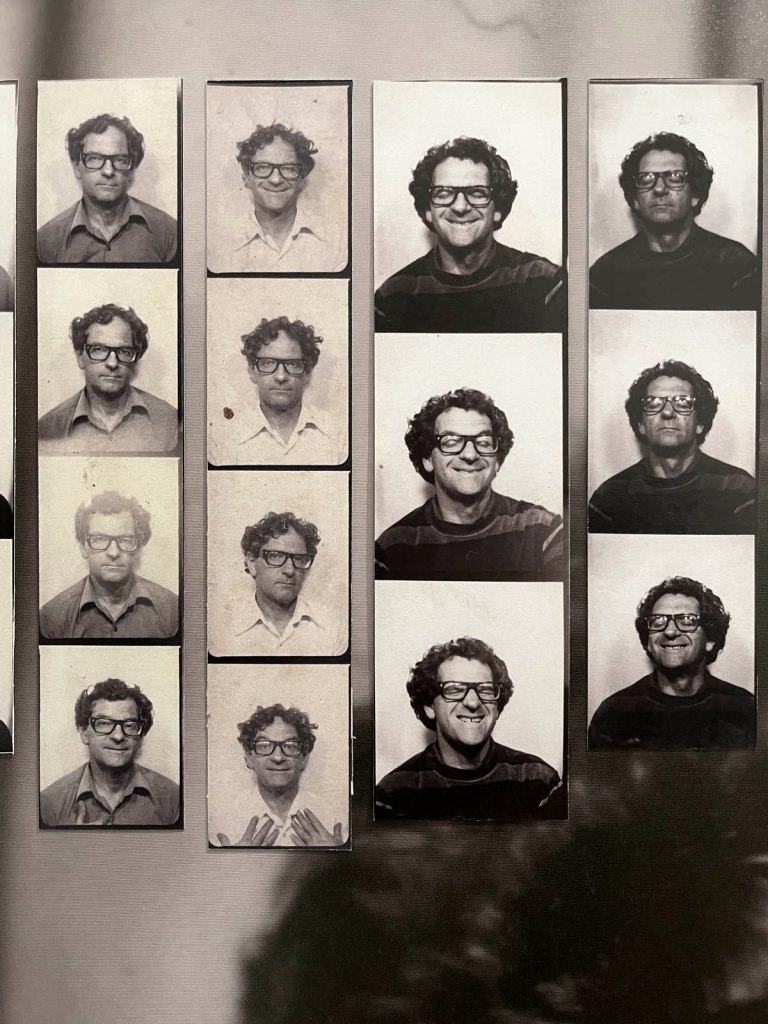
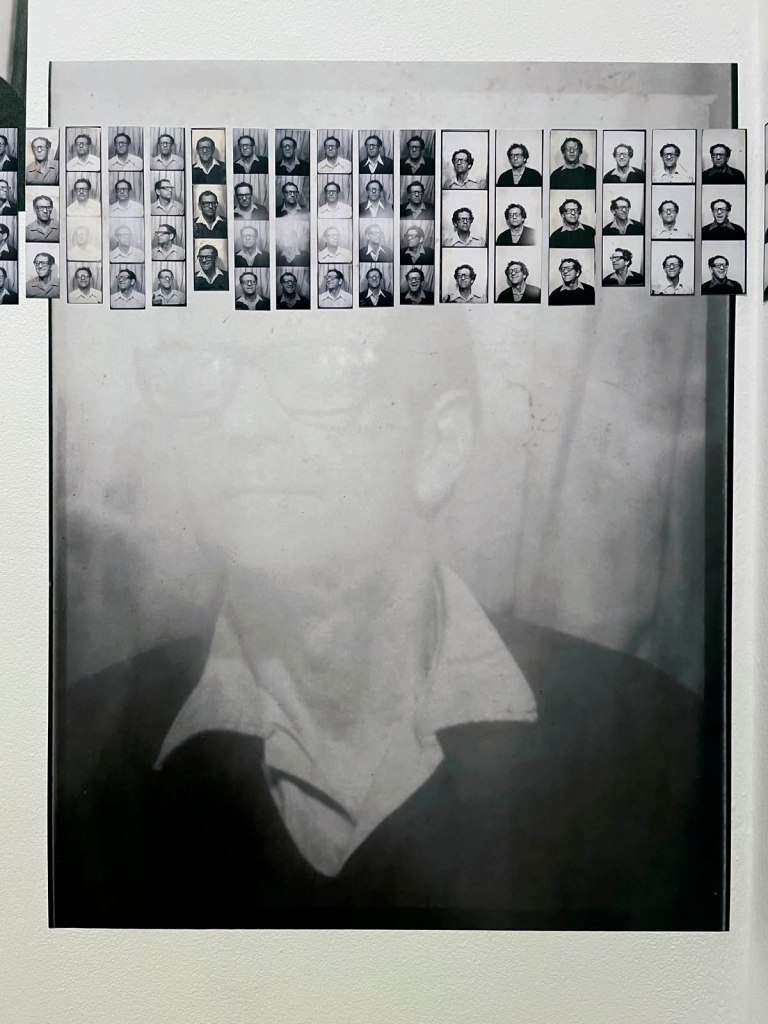
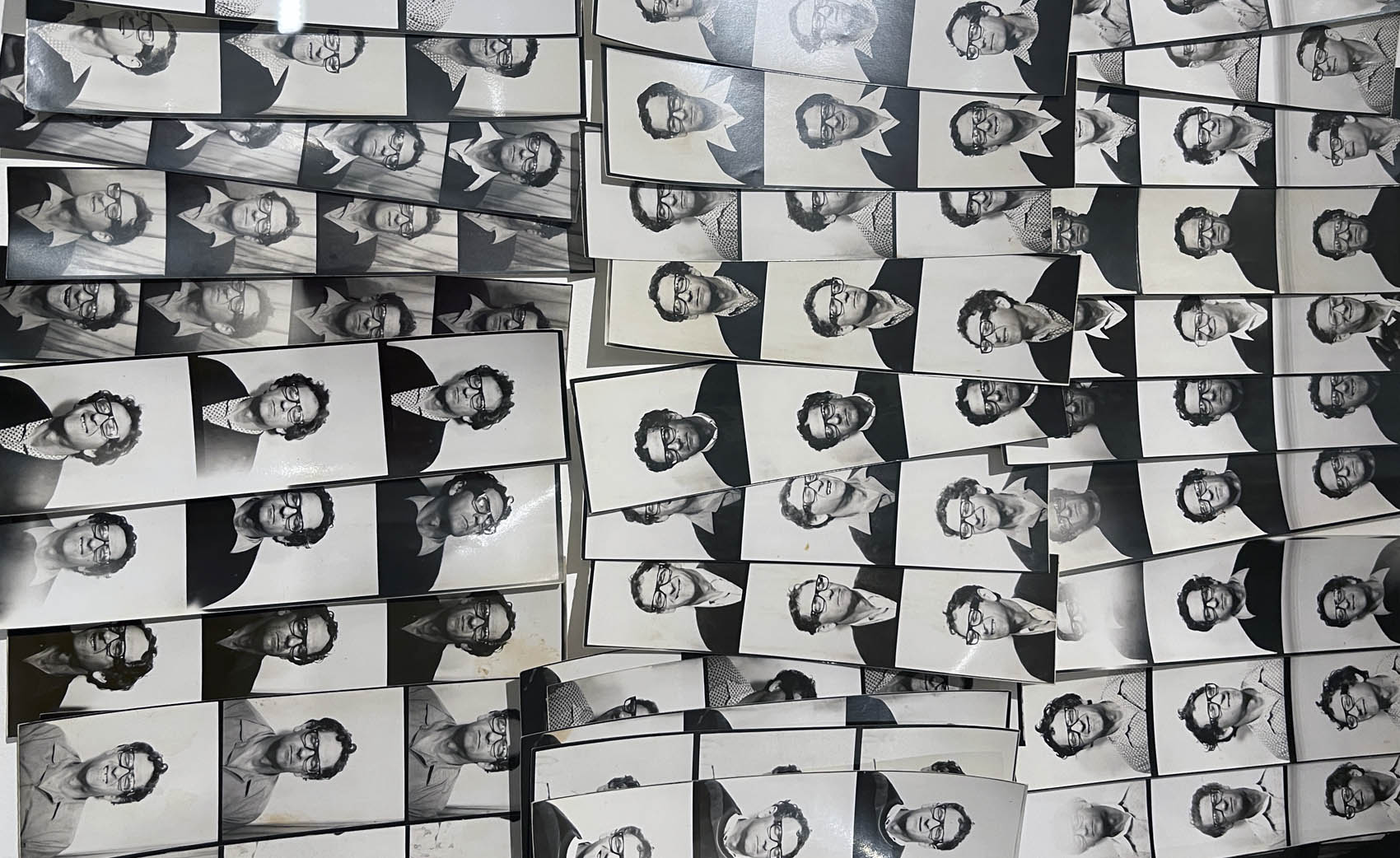
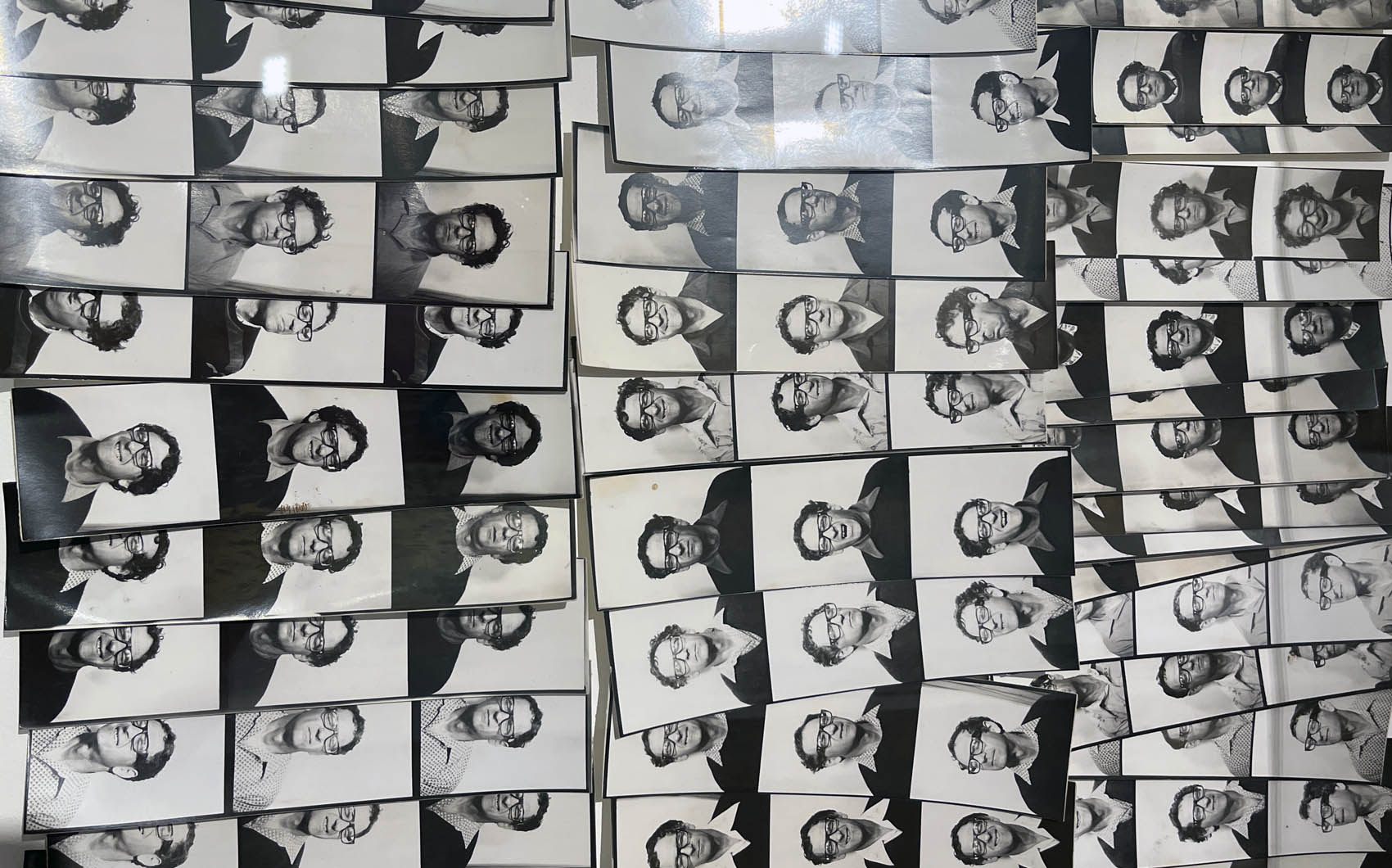
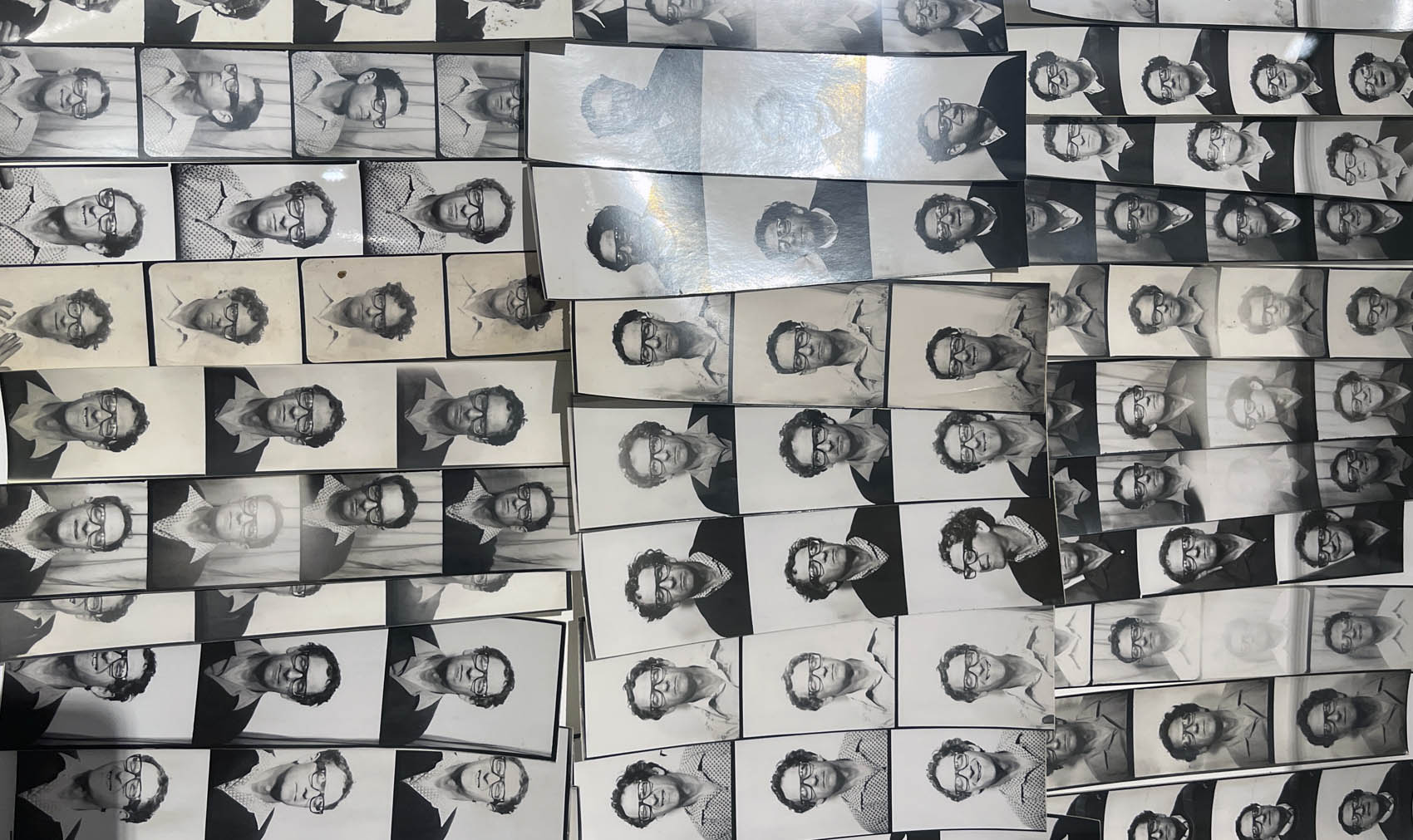
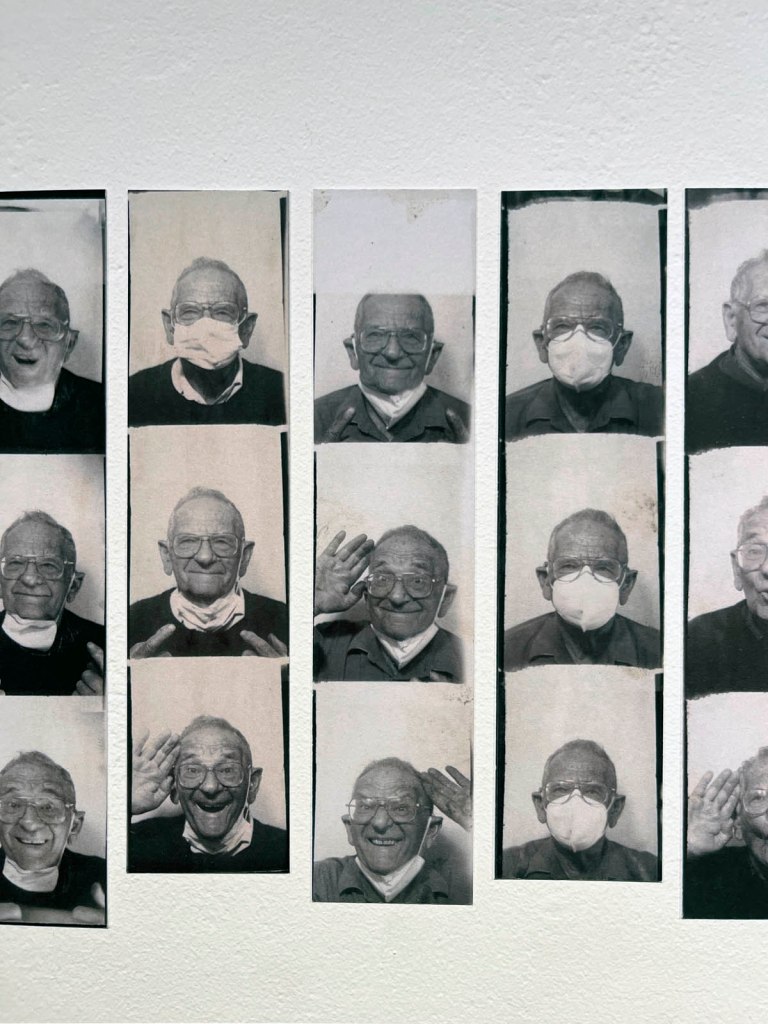
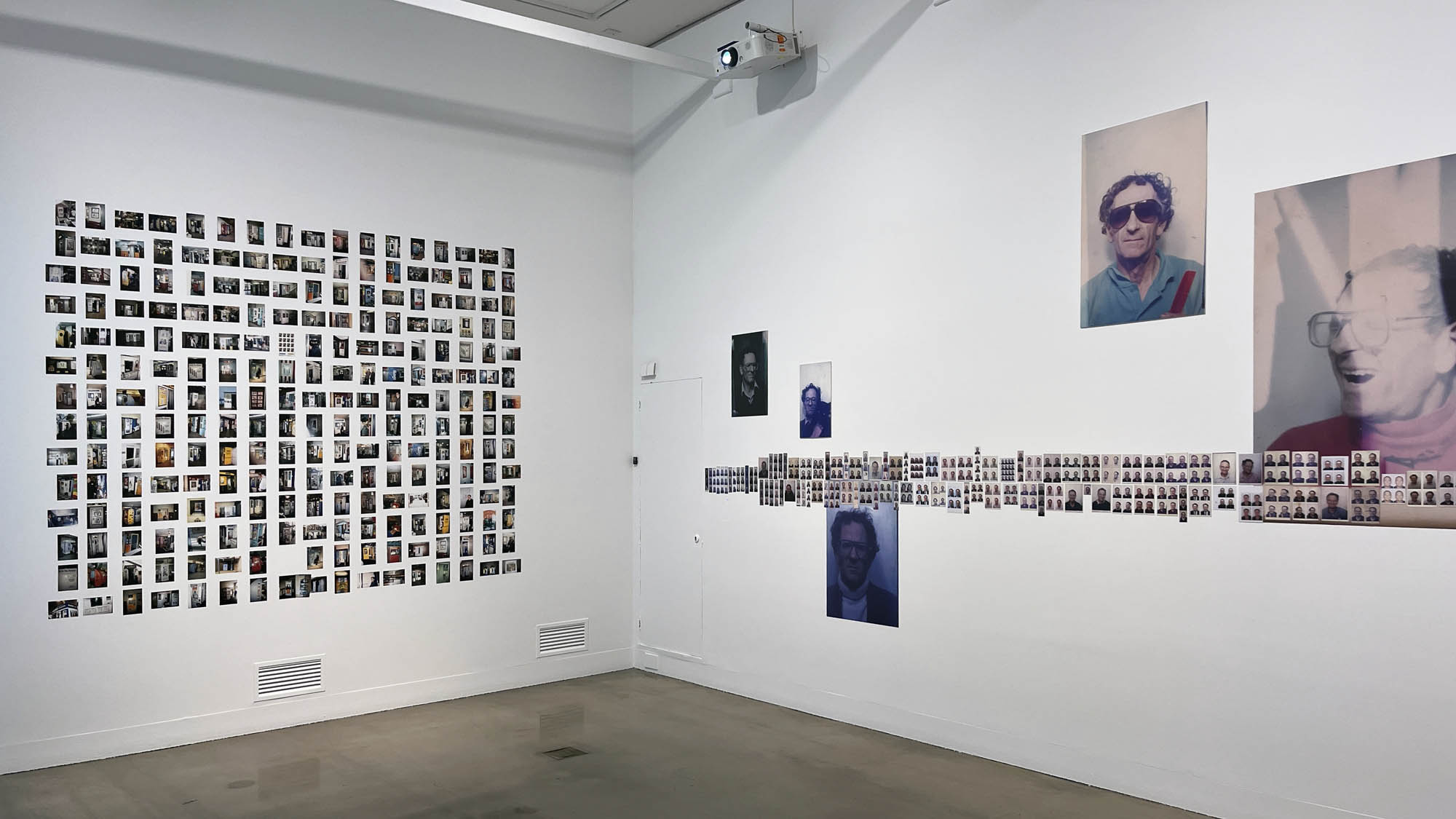
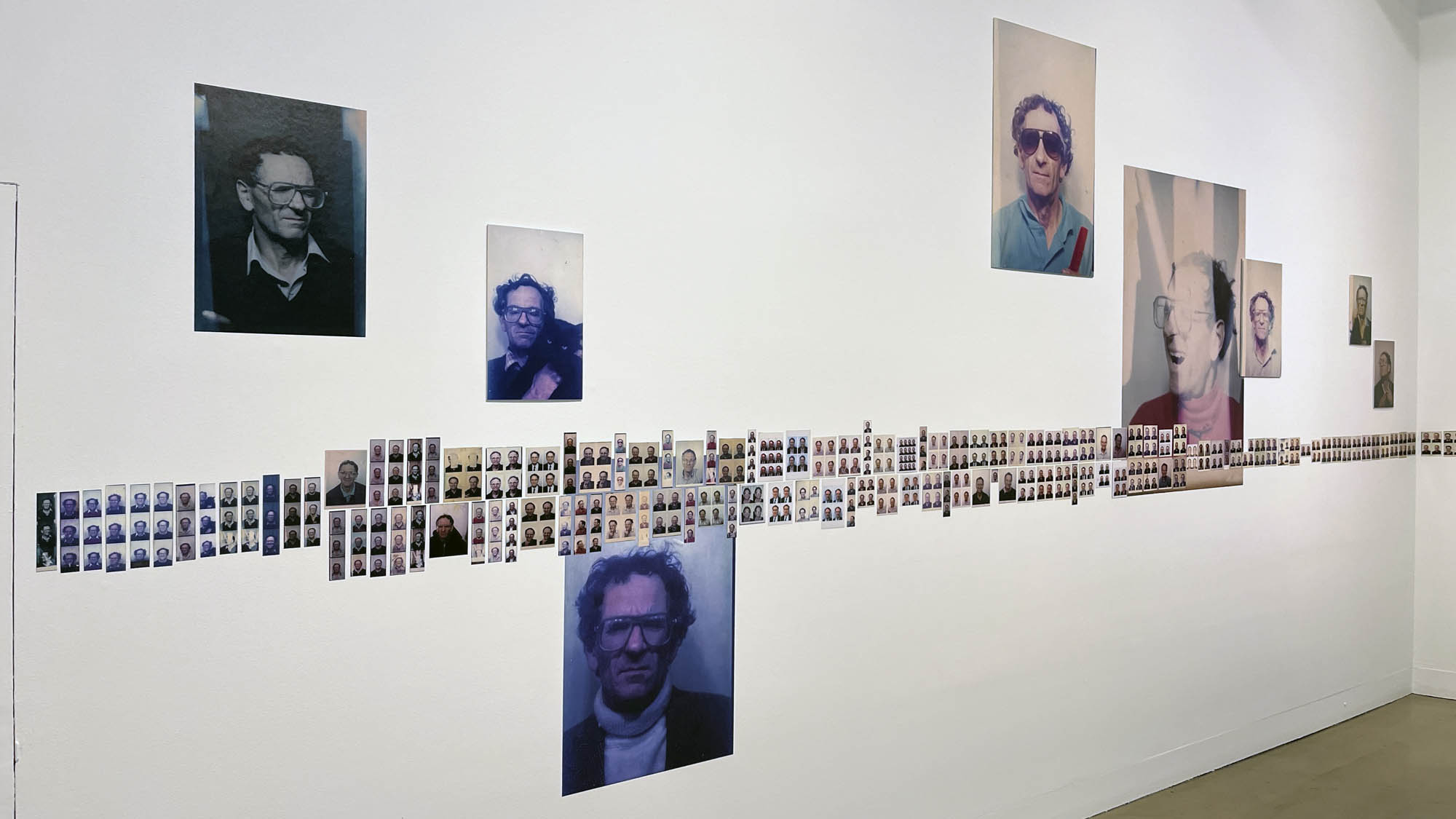
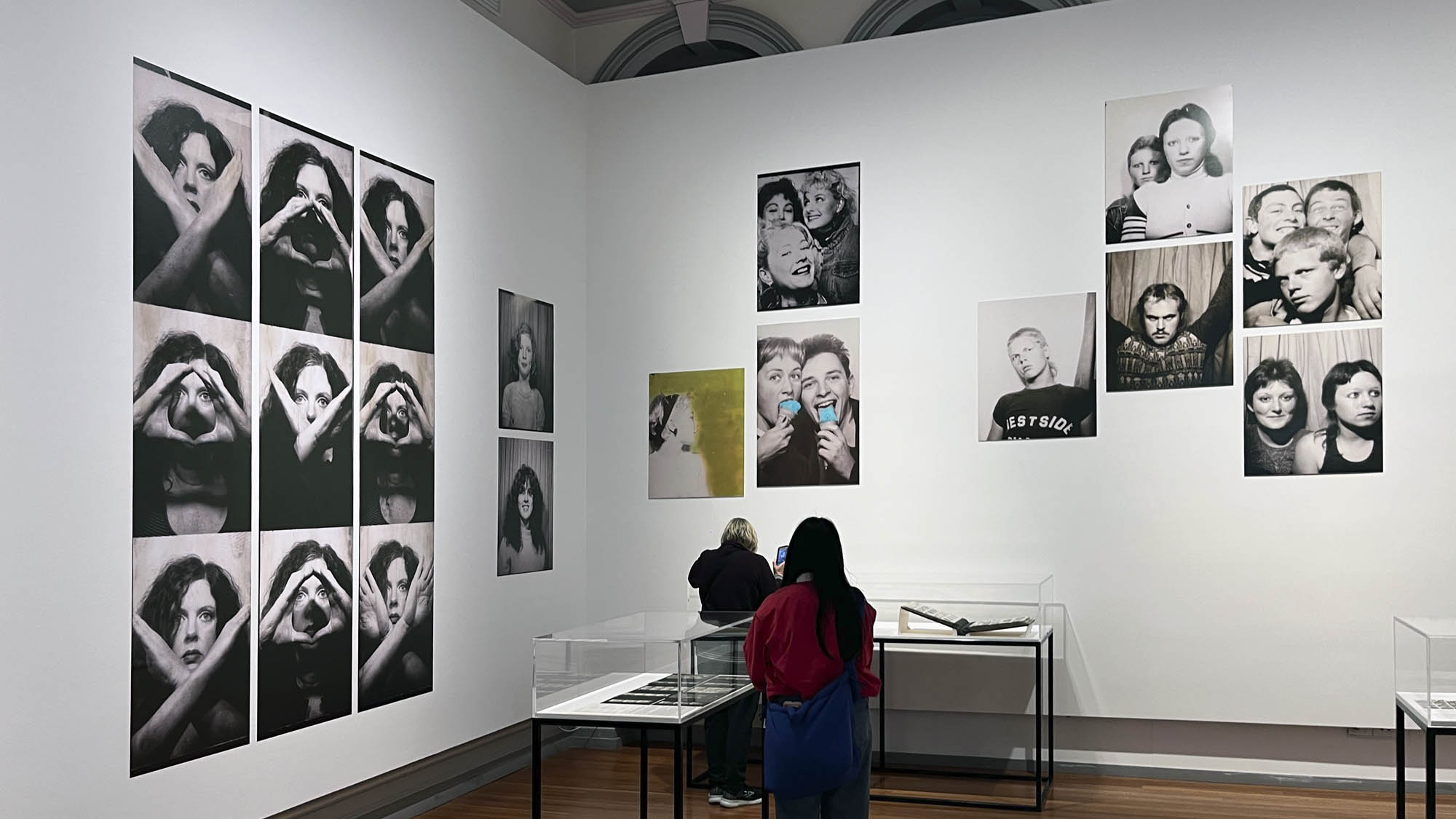
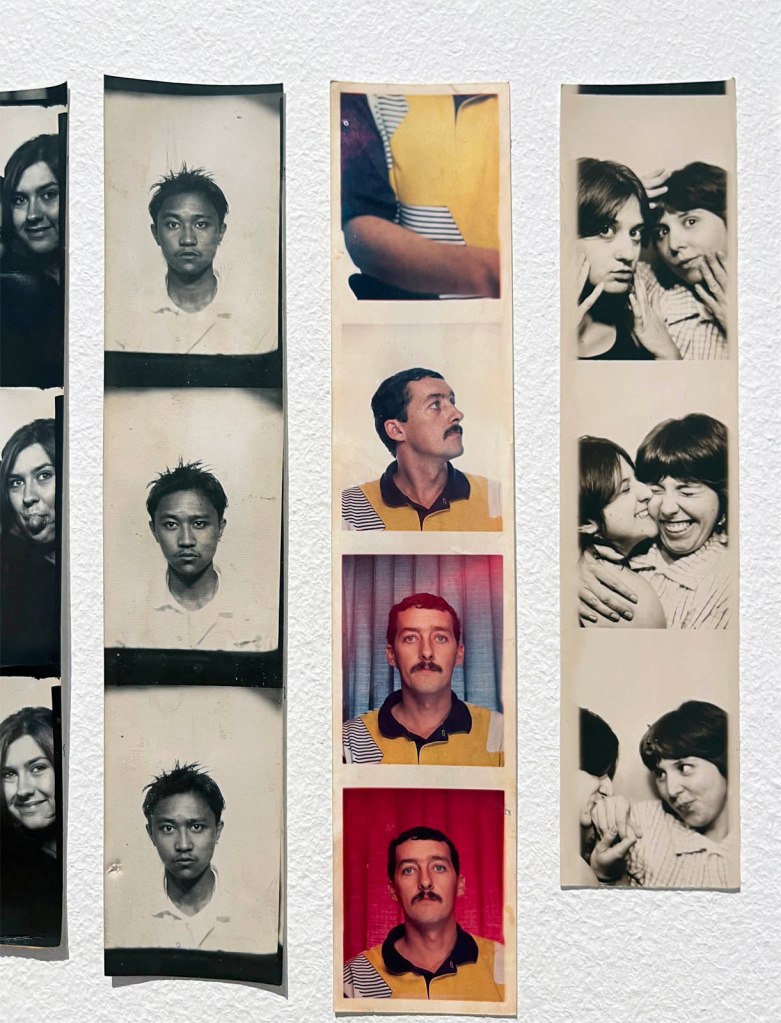
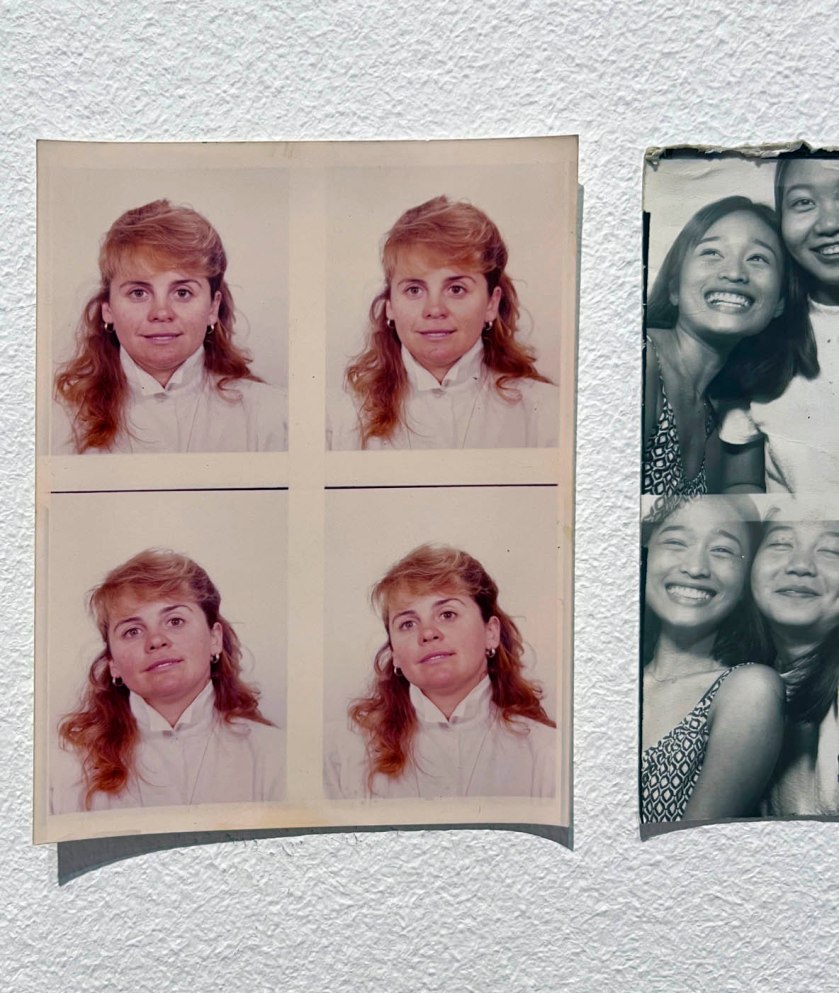
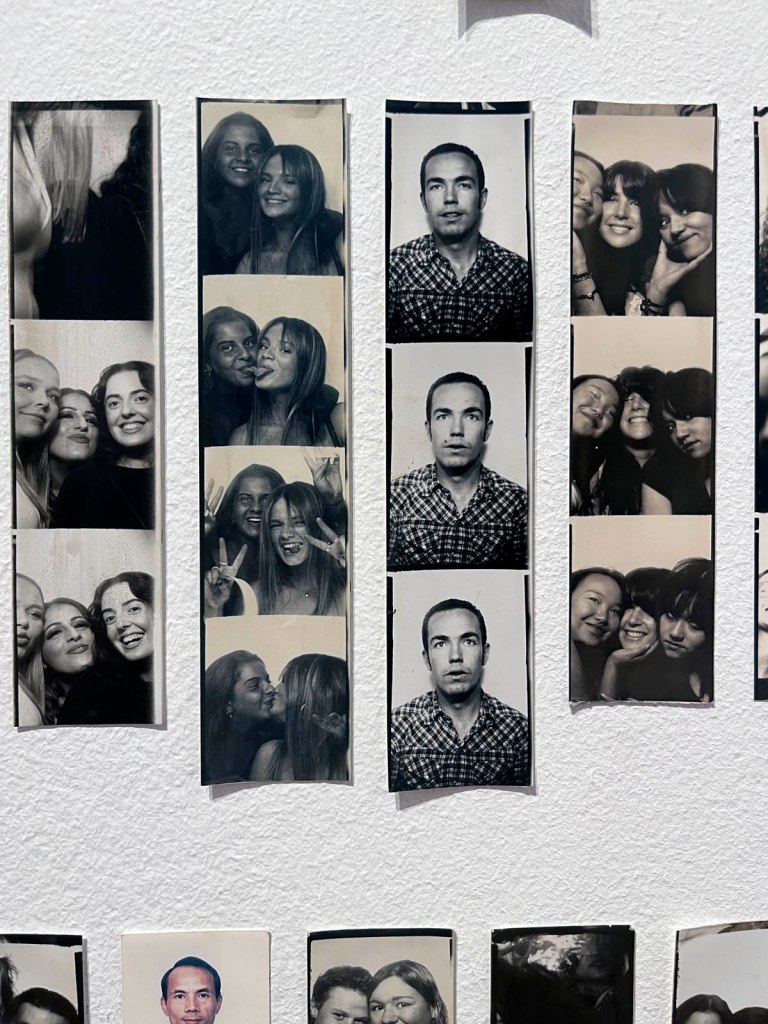
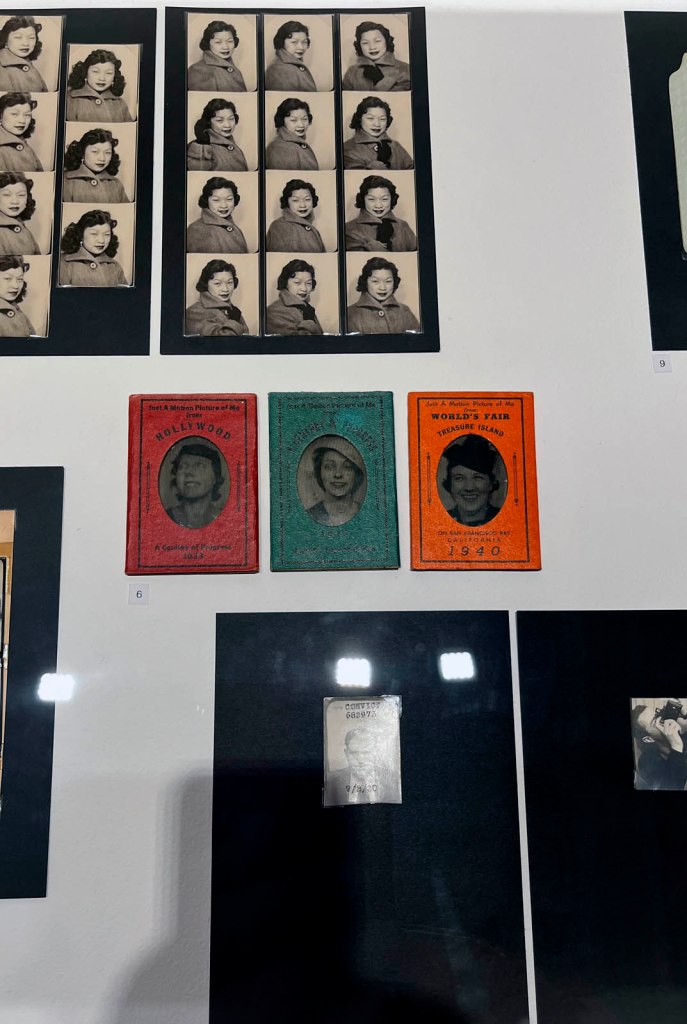
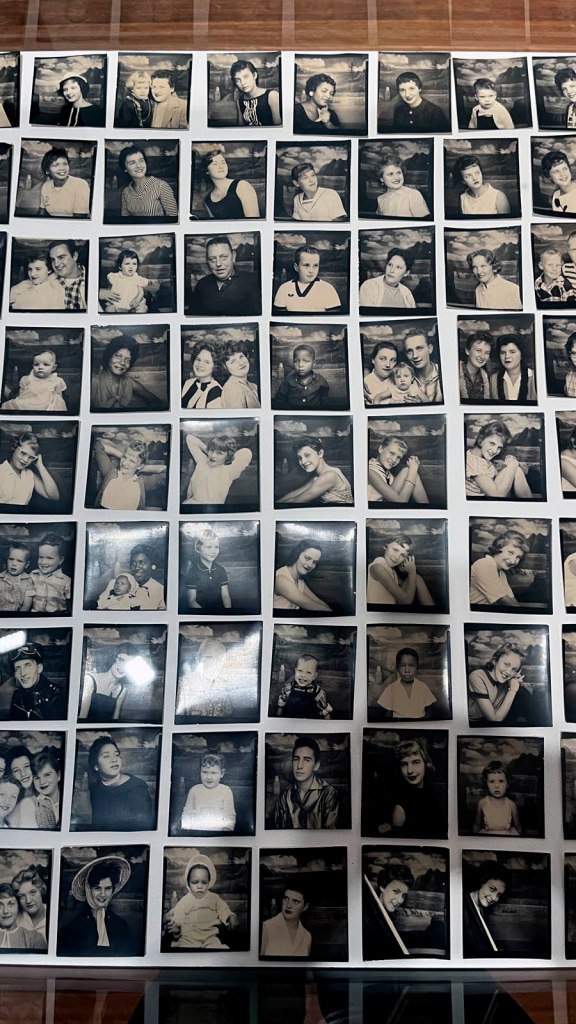
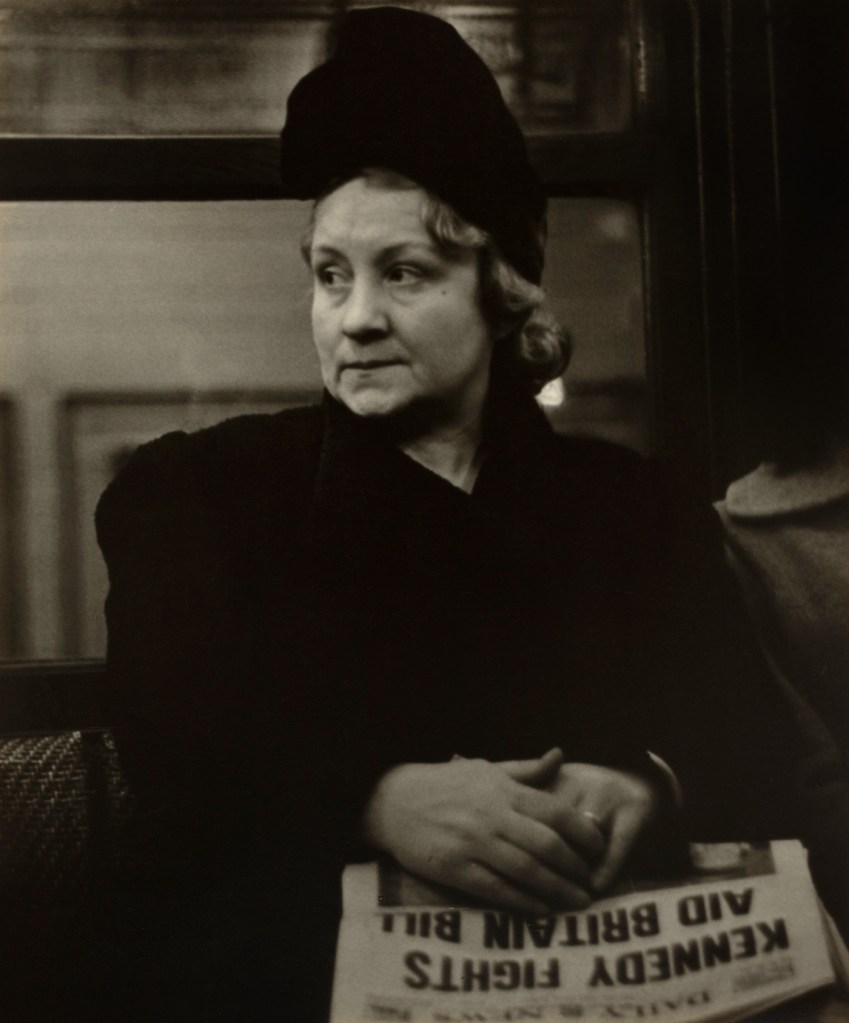
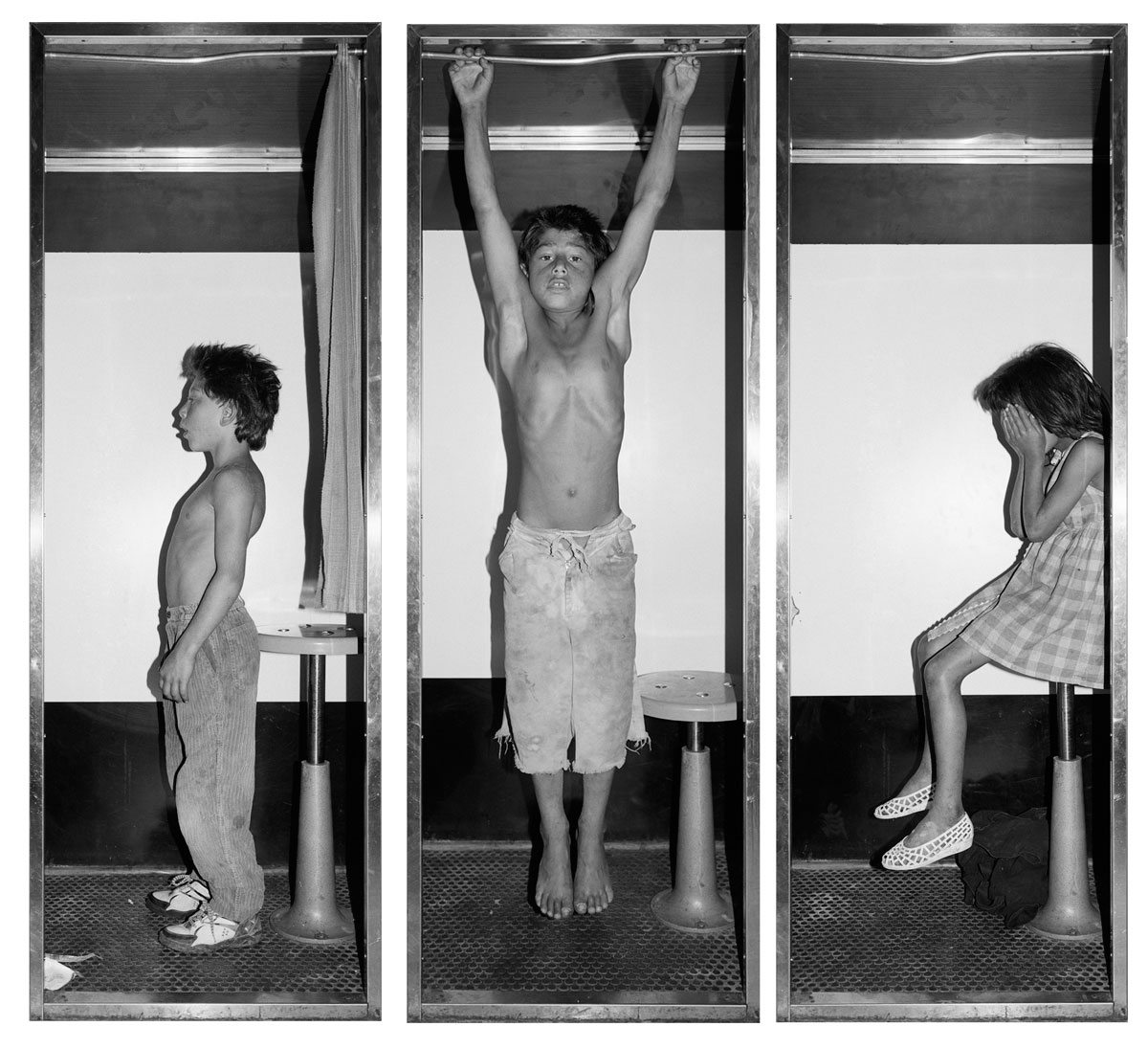
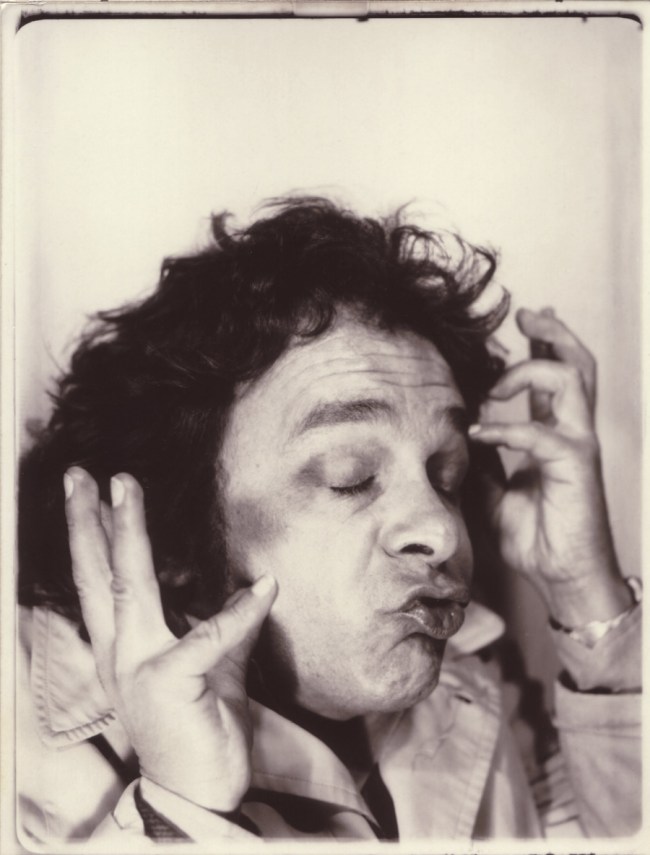
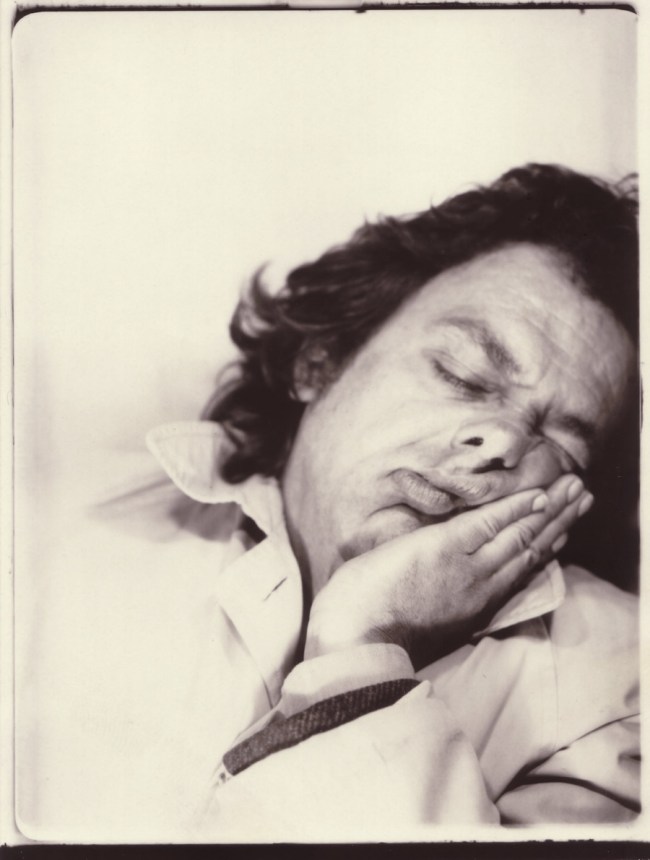
Untitled [Women Photobooth Portraits]
c. 1940s-1950s
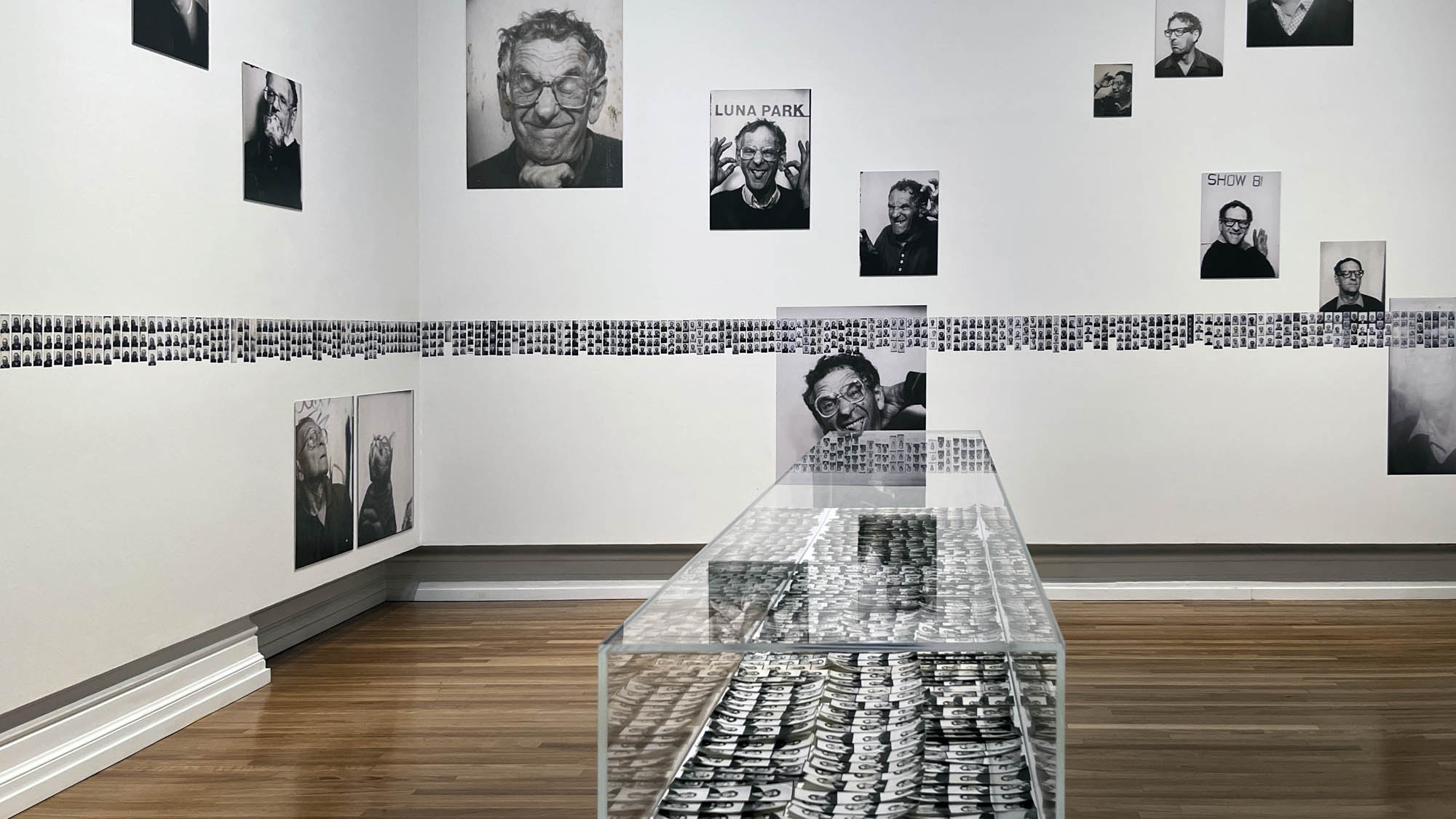
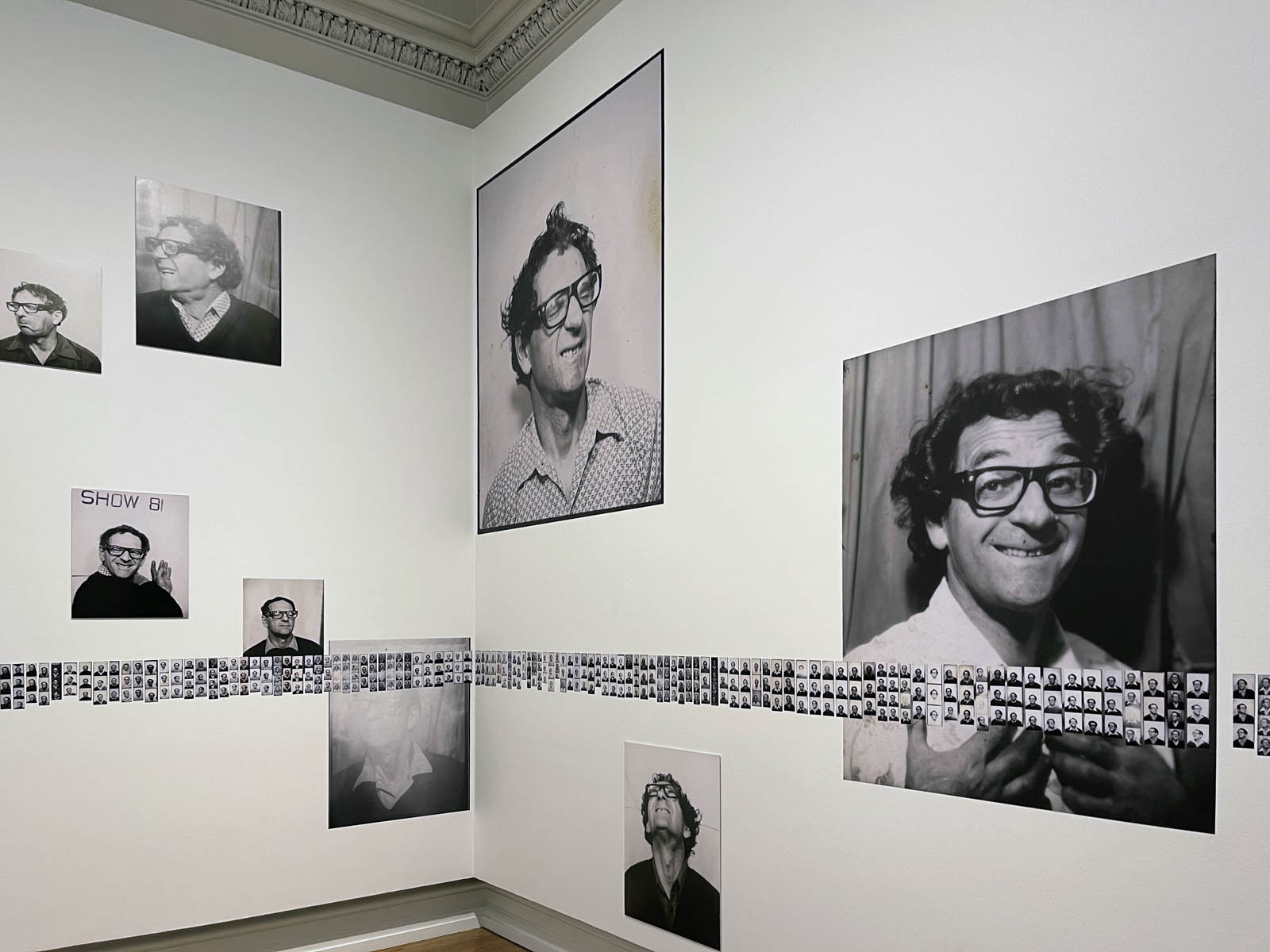
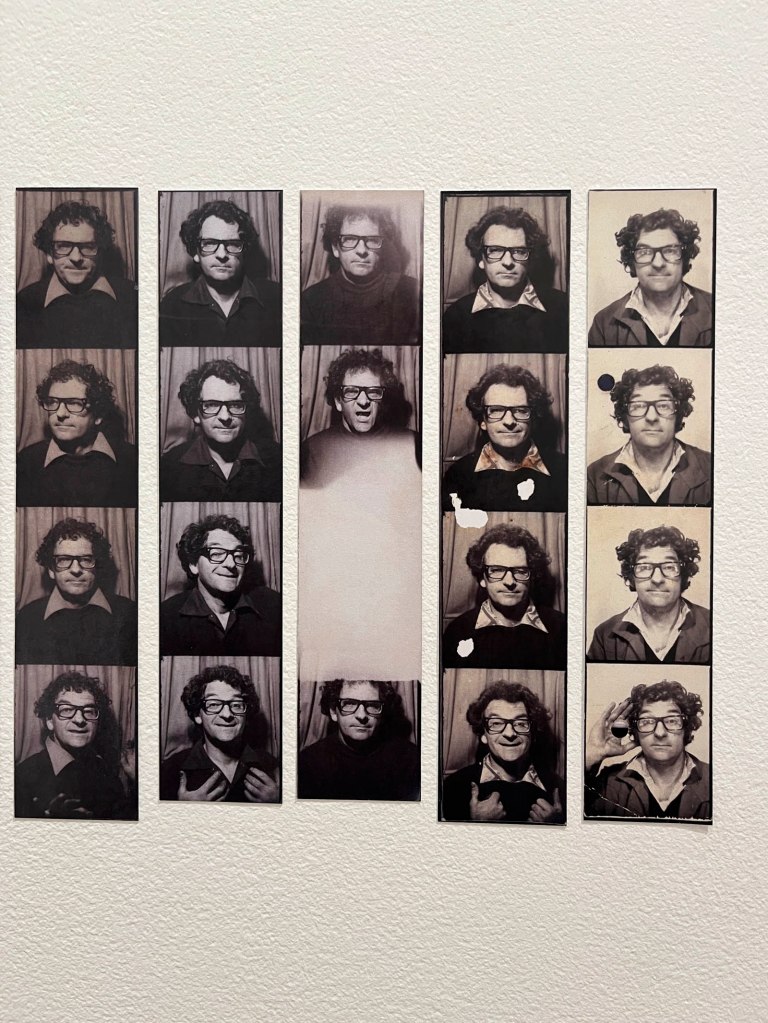
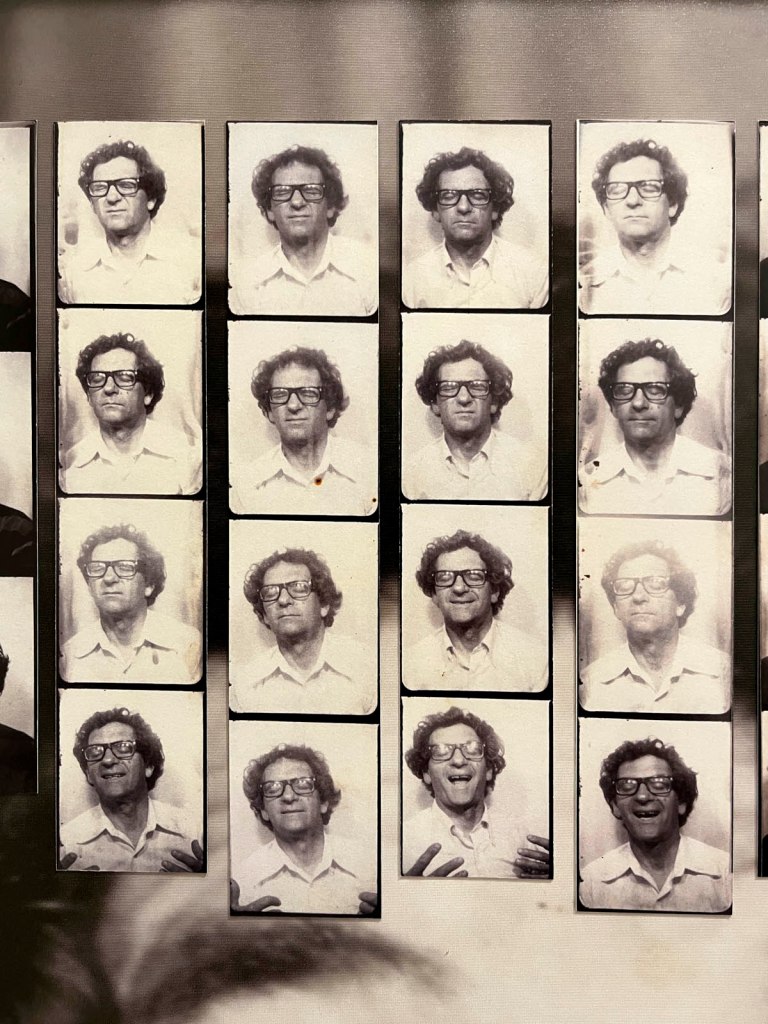
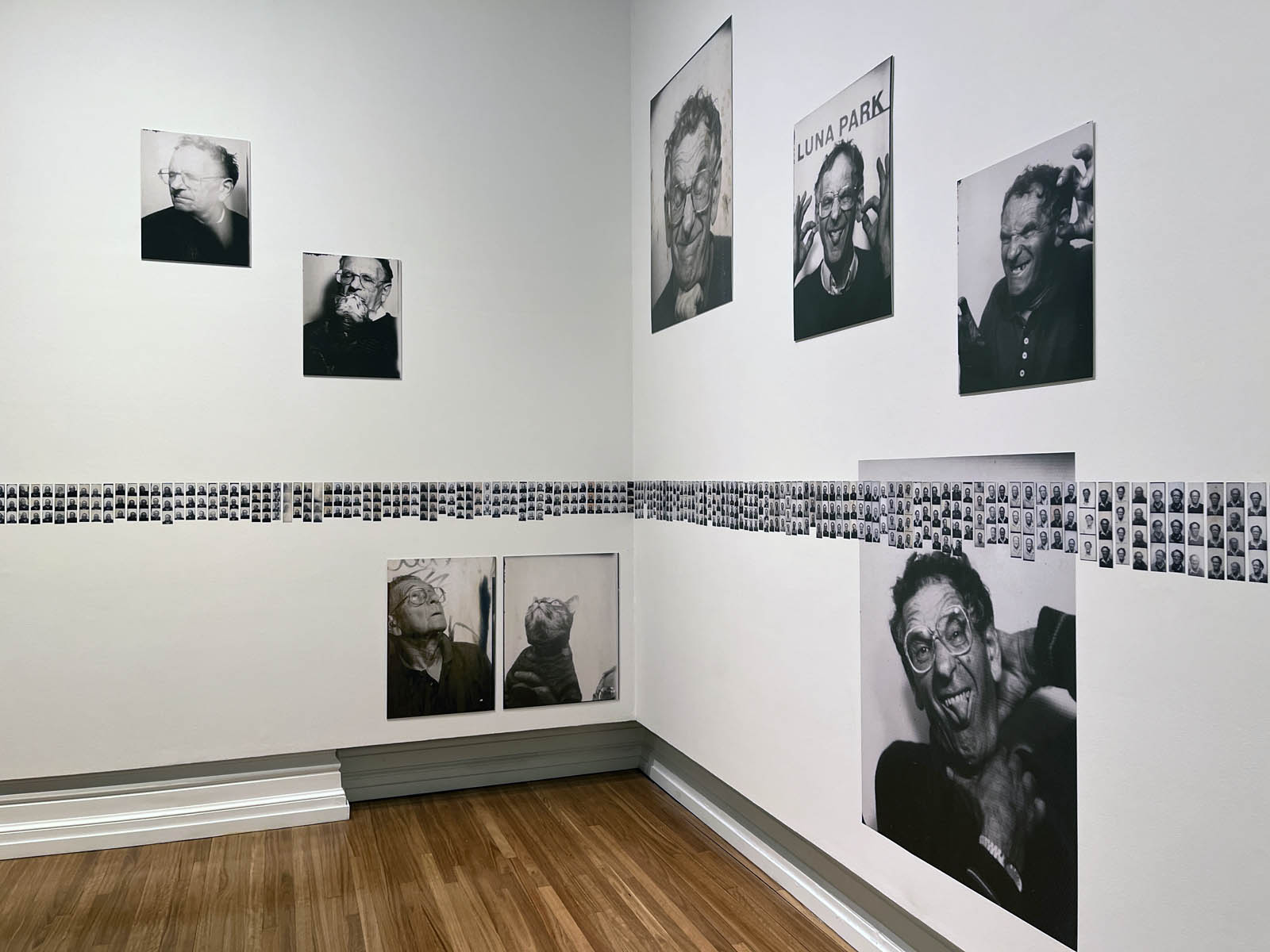
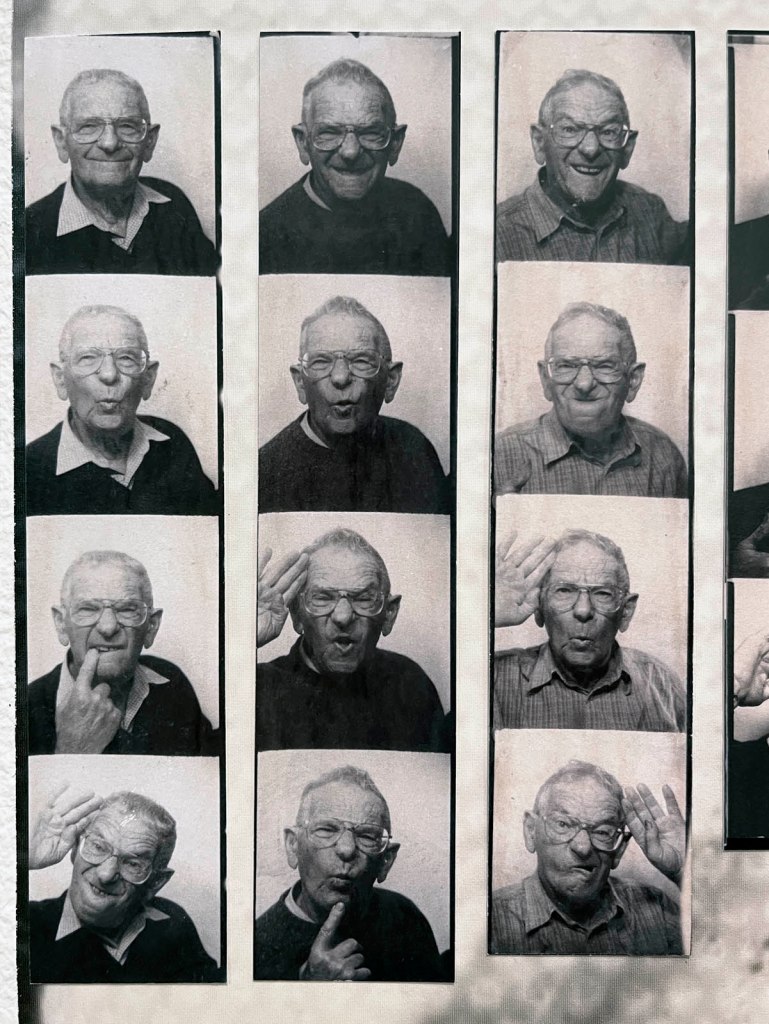
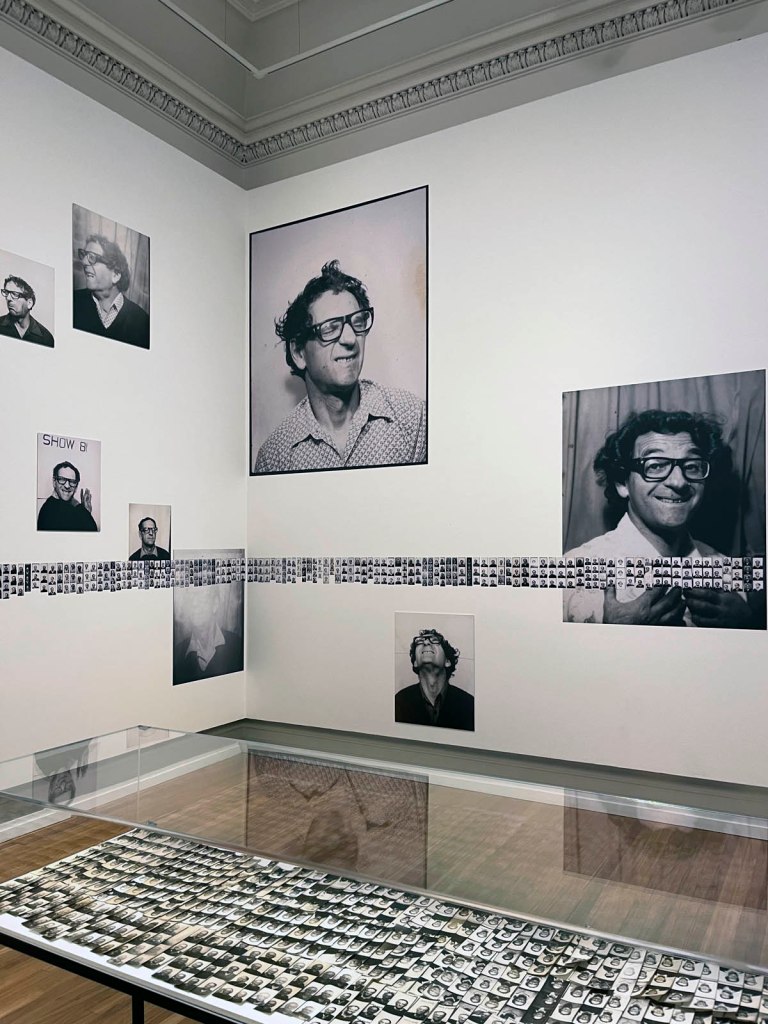
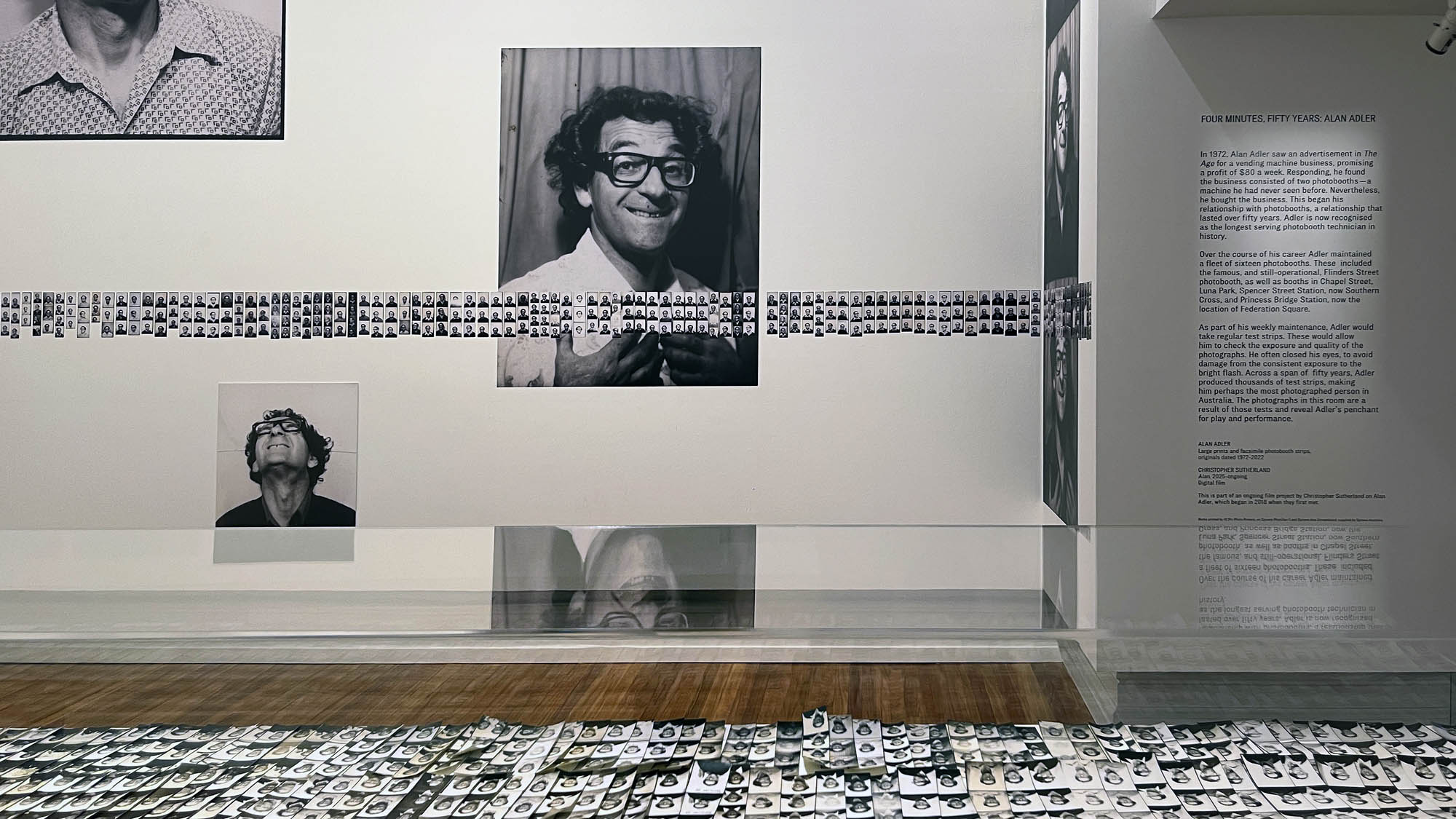
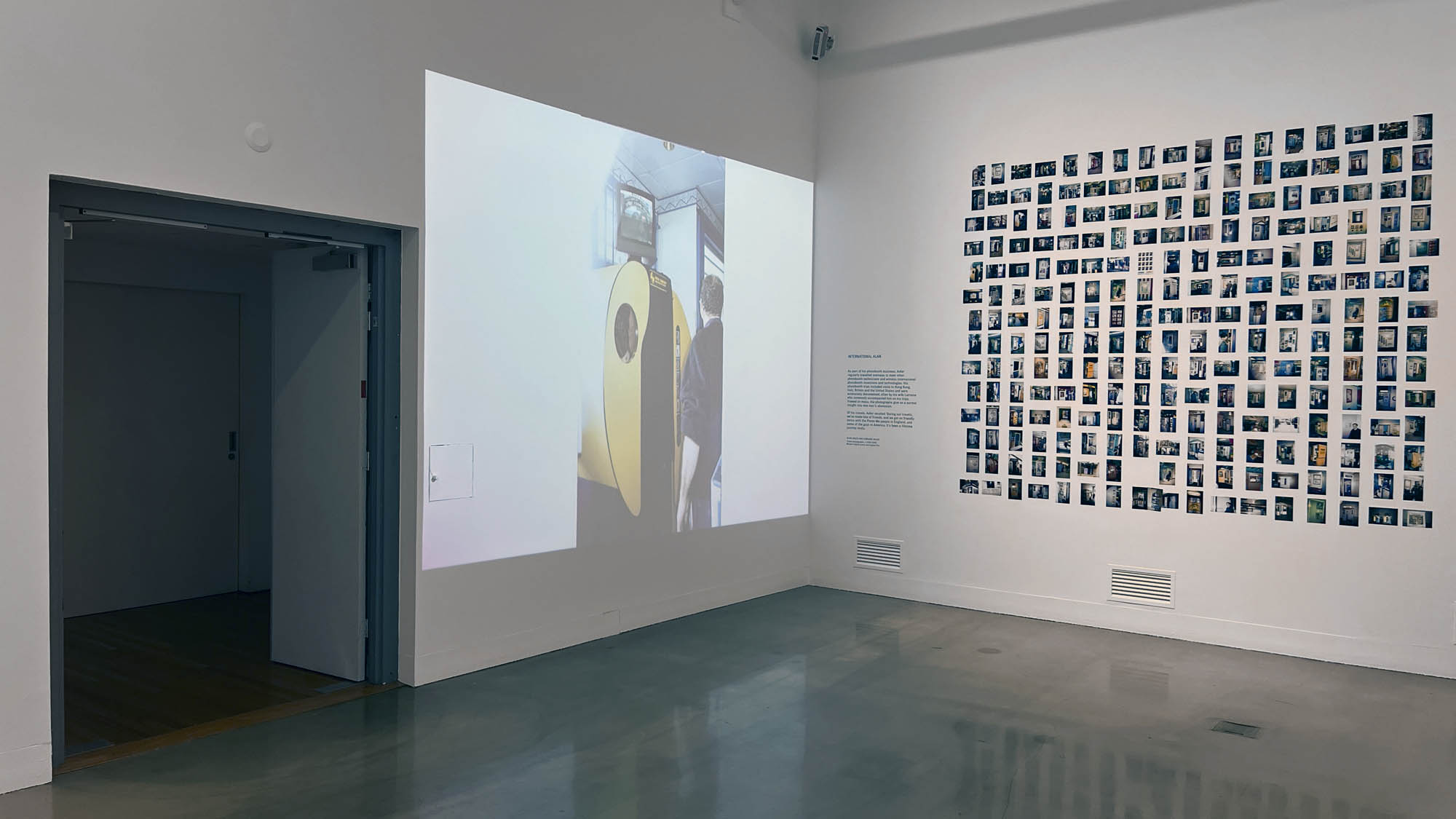
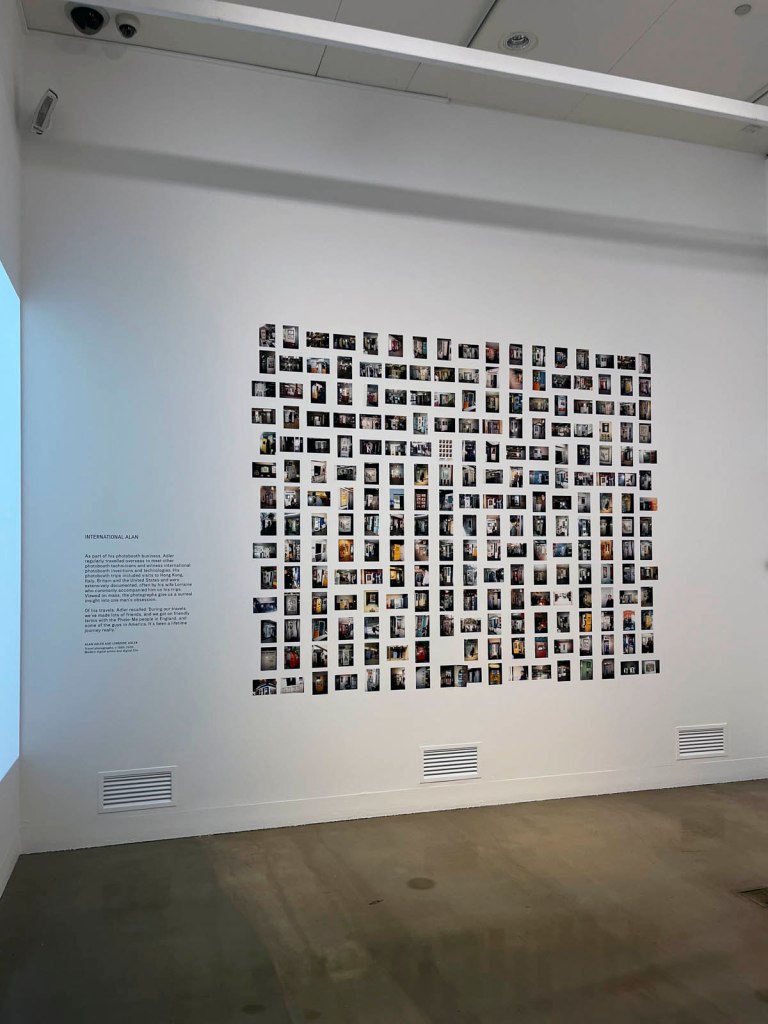
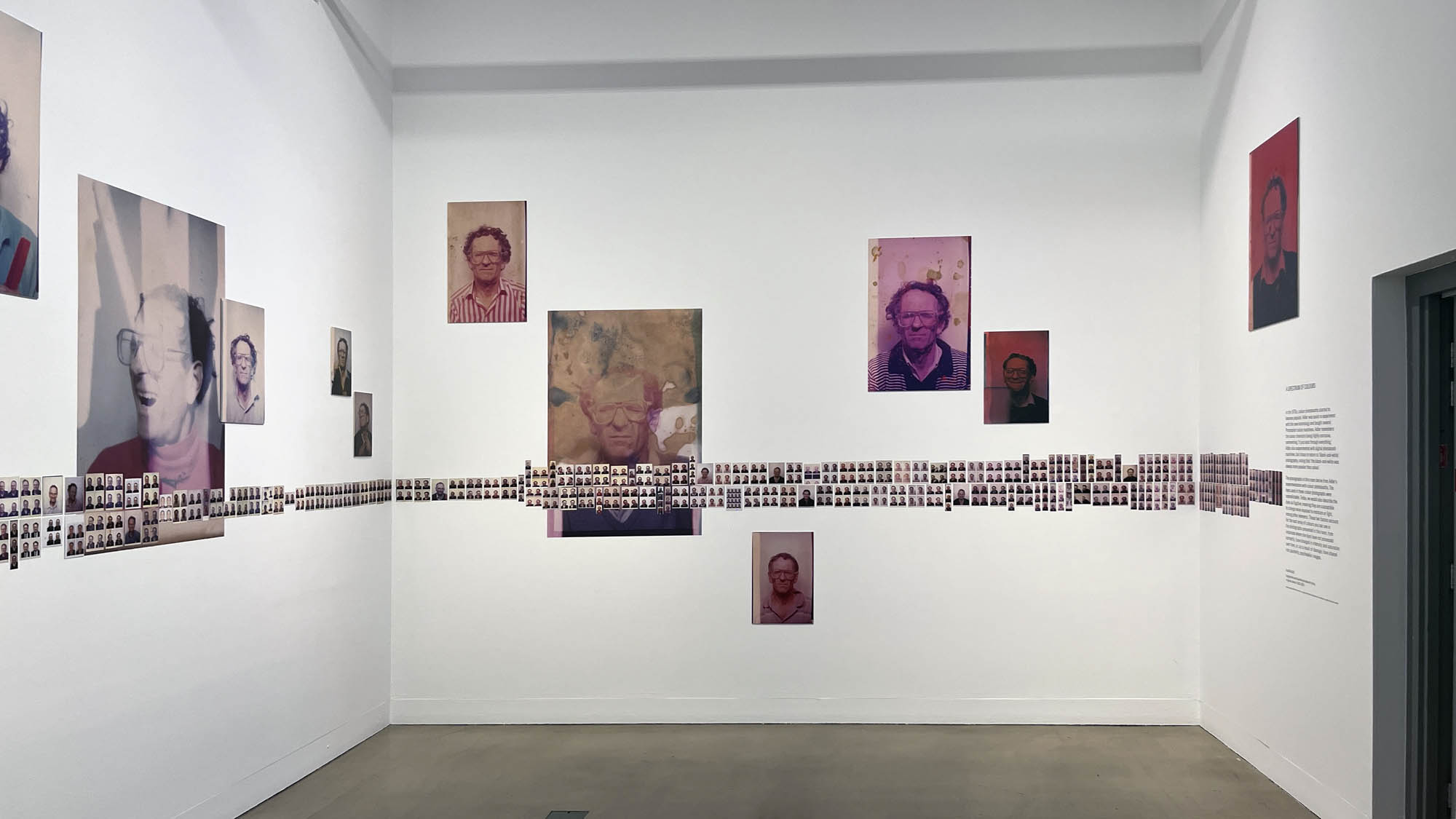
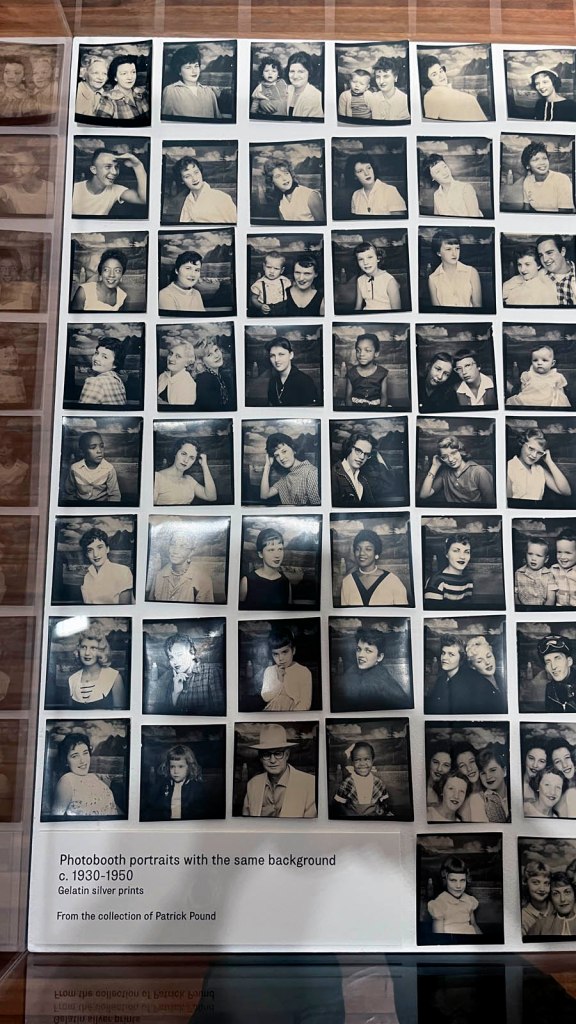
This “small archival display celebrating 100 years of the much-loved photobooth” (which occurred in 2025) – no installation photographs available – seems not a patch on one of the best photography exhibitions on Art Blart in 2025: Auto-Photo: A Life in Portraits at RMIT Gallery, Melbourne, June – August 2025 which introduced us to “Alan Adler (2932-2024), who while little known, was the oldest and longest serving photobooth technician in the world… For over 50 years, Adler maintained a fleet of photobooths across Melbourne / Narrm, most notably the site at Flinders Street Station.”
There are still some delightful, happy, joyful snapshots in this posting however.
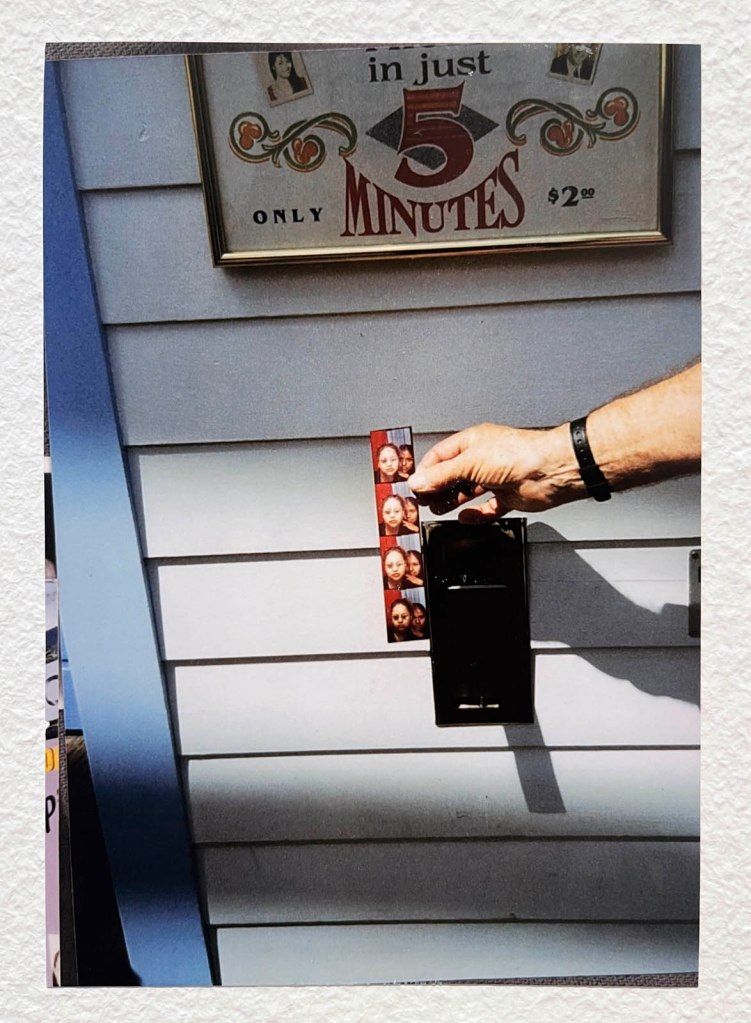
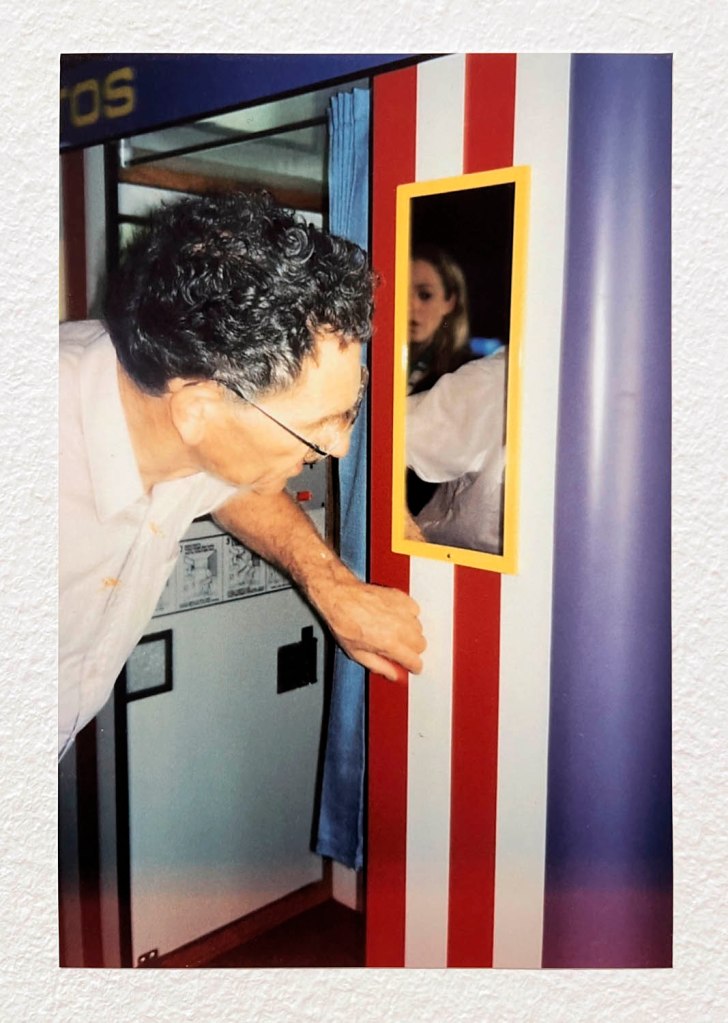
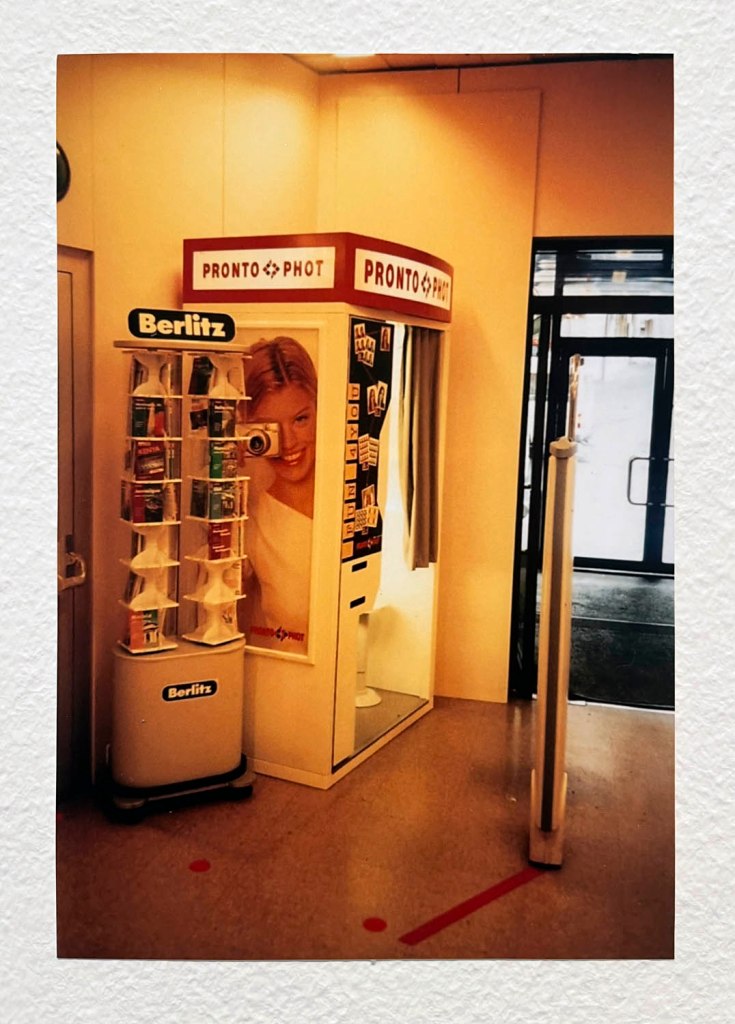
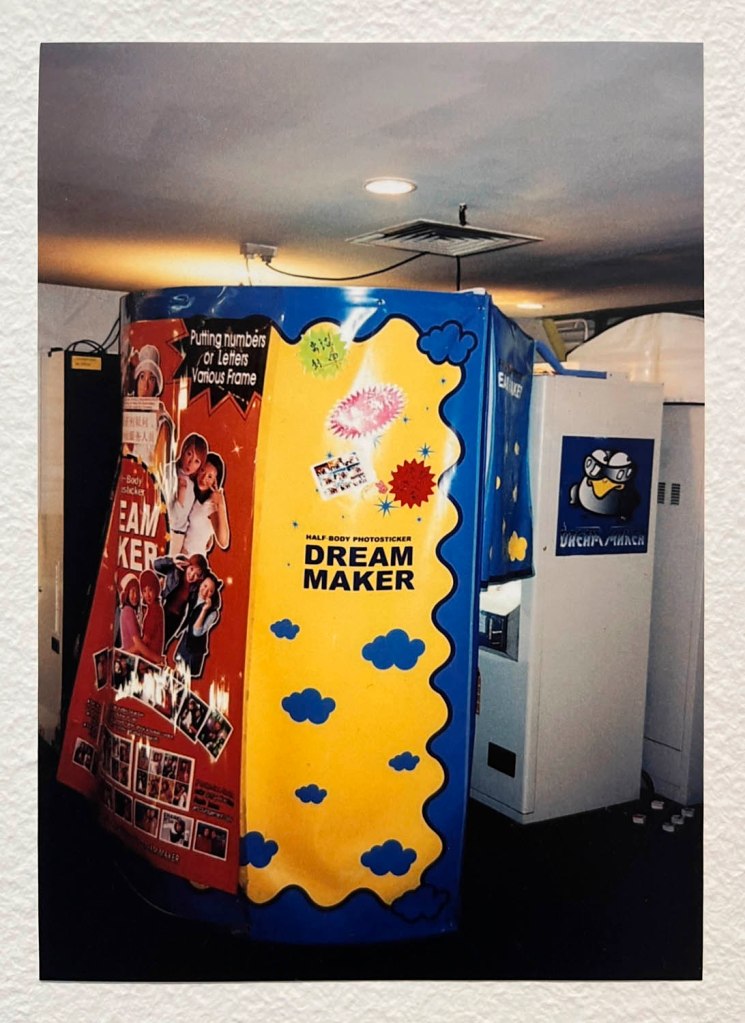
Pay the money, cross the threshold of the booth, draw the curtain, adjust the seat, comport yourself into whatever “pose” you choose, then perform for each flash of the Time Machine.
Captured in a space of privacy and experimentation these portraits of the self (your essential being at that moment in time), eventually, minutes later, reveal you to yourself.
Some conforming, some rebelling, some crossing the taboo of self-revealing.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to The Photographers’ Gallery for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“Practical at first – cheap, quick and accessible identity photos – the booth quickly became something else: a private stage. Behind the curtain, anyone could perform beyond the gaze of a photographer. Sitters experimented alone or packed in with friends, kissing, laughing, trying on disguises or staring back with deadpan seriousness. The Photomaton promised autonomy: pull the curtain, face the lens, decide how to appear. Some likened the ritual to a slot machine: drop a coin, wait for the surprise. Josepho’s invention, in hindsight, feels like the ancestor of the selfie: it put image-making directly into the hands of its subjects, a century before smartphones did the same. …
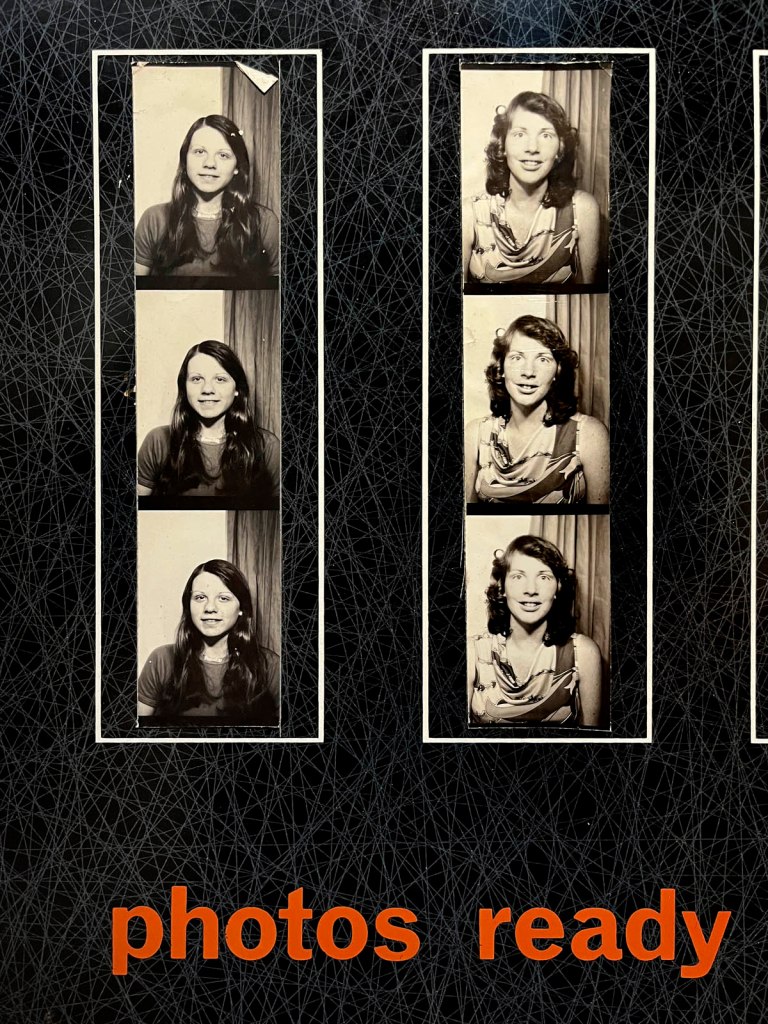
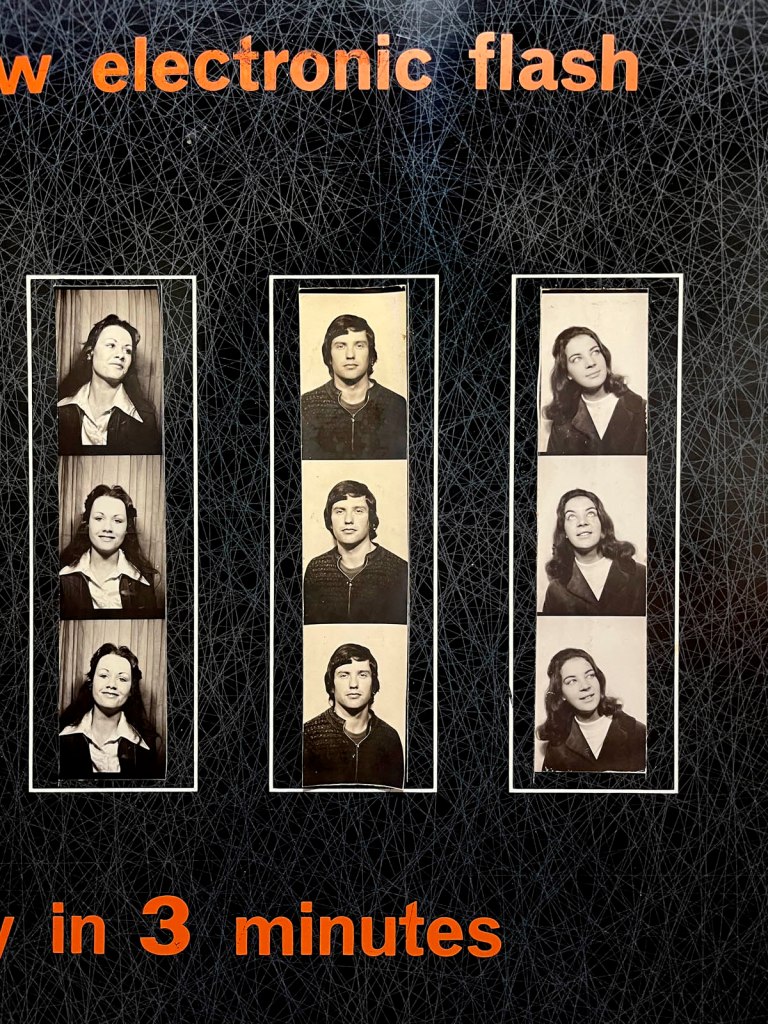
In our digital world, we’re used to photographs that are instant, endless and easily stored or deleted. By contrast, the analogue photobooth resists perfection. Control is never total: the flashes are blinding, the stool wobbles, the timing is merciless. Each strip bears the marks of chance – a blink, a smirk, a blur, a half-formed gesture. That unpredictability is its charm, giving the images a peculiar energy that no app filter can replicate.
Their resurgence taps into the wider appetite or the tactile and the ‘vintage’: objects that feel authentic precisely because they escape the seamlessness of the digital. The photobooth doesn’t have a photographer mediating or directing the sitter. It’s a space of agency and play, where friends cram together or someone experiments alone, producing an image that can be private or shared, that can be spontaneous or completely staged.
In contemporary culture, where self-presentation is curated and optimised online, the photobooth is a refreshing counterpoint. The strips are imperfect, uneditable and physical – small paper relics that capture a moment in time with all its messiness intact. That’s why they resonate now: they remind us that identity is not just polished images, but also the accidents, surprises and fleeting gestures that make us human.”
Taous Dahmani, curator, quoted in Ellis Tree. “The cooler, elder sibling of the selfie turns 100: Celebrating the centenary of the photobooth,” on the It’s Nice That website 10 October 2025 [Online] Cited 27/01/2026
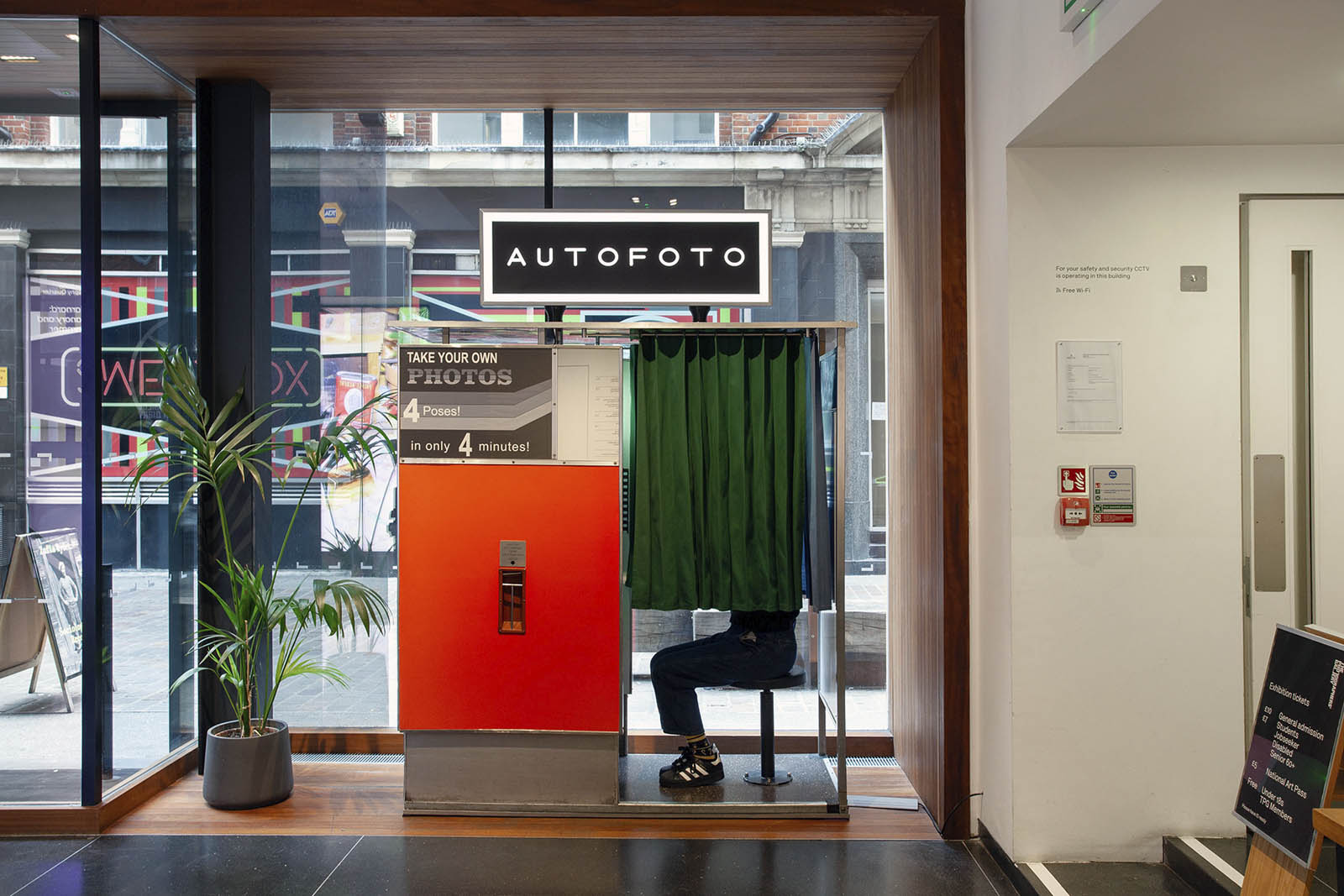
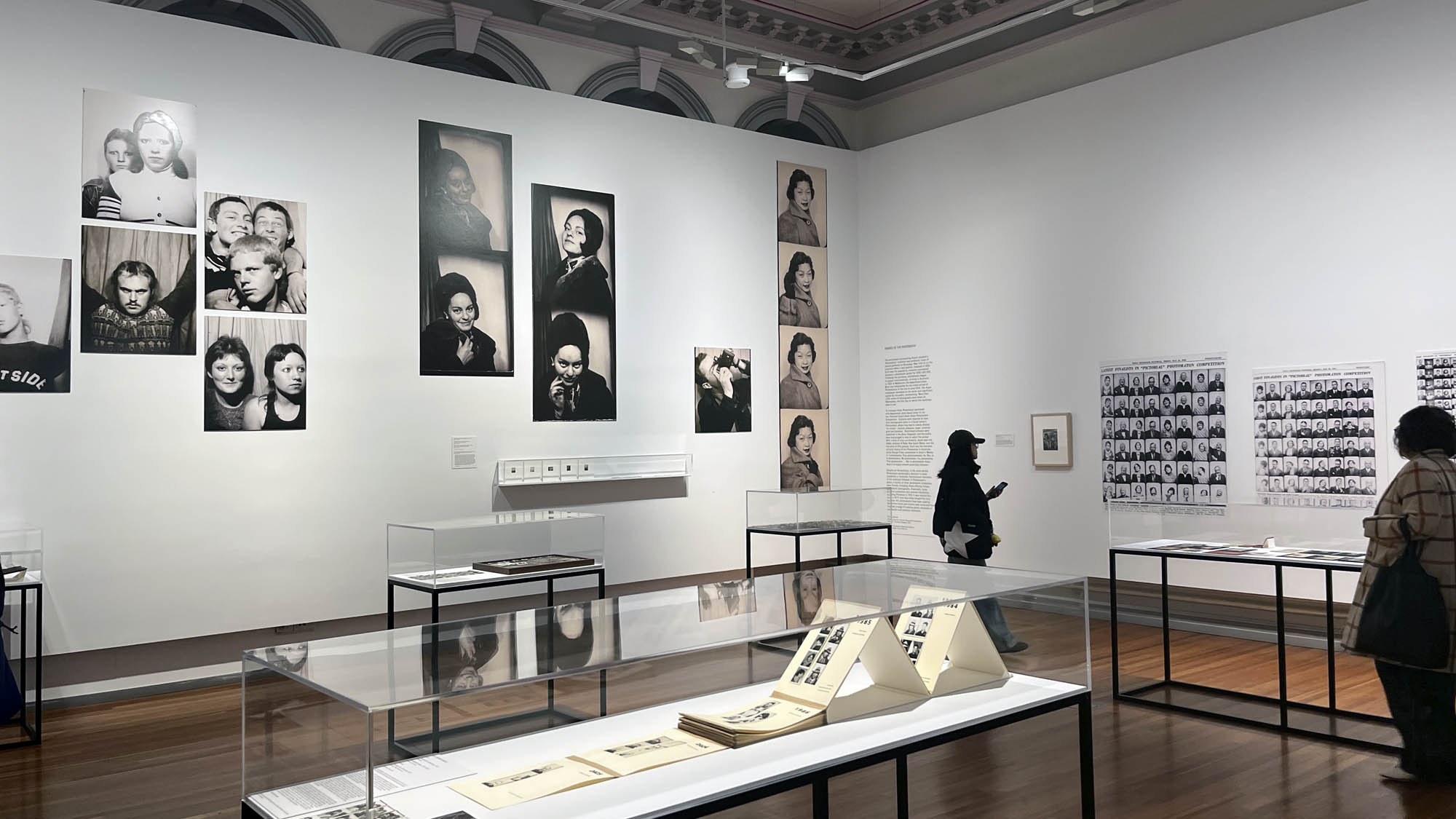
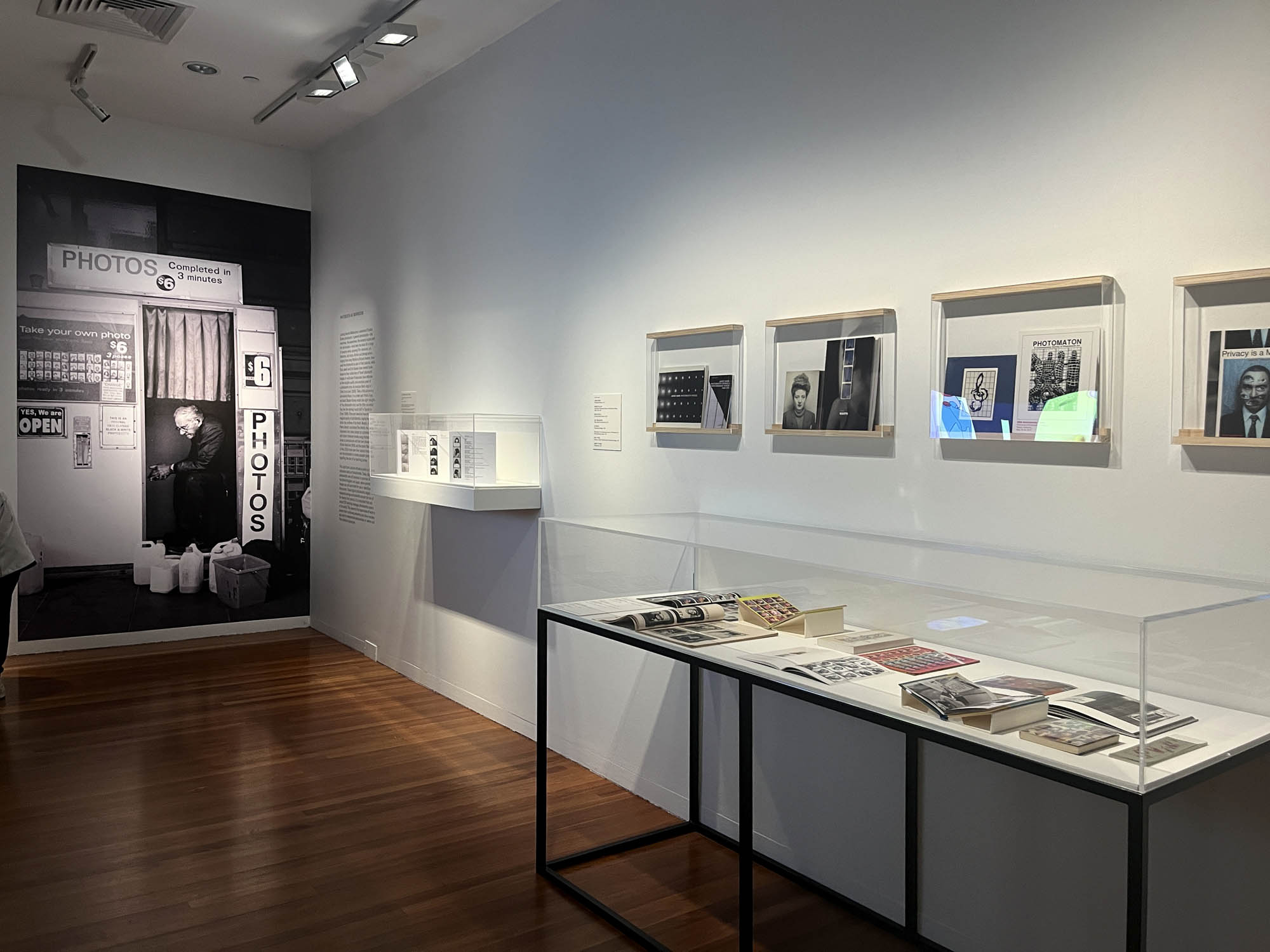
Installation view of the AUTOFOTO photobooth at the exhibition Strike a Pose! 100 Years of the Photobooth at The Photographers’ Gallery, London
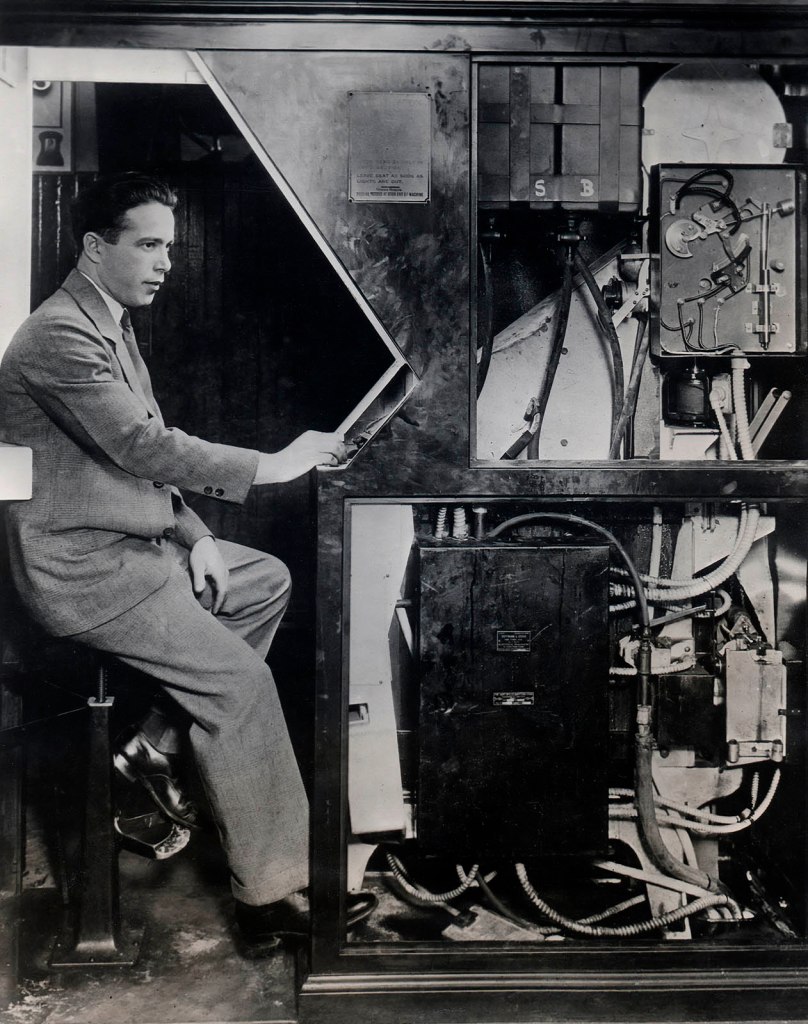

Anonymous photographer
Portrait of Anatol Josepho in his Photomaton
United States of America, 1927
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer

French Photomaton Advertising “6 photos in 8 minutes. Identity”
1927
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer

8 Poses Strip
USA, 1927
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer


8 Poses Strip (details)
USA, 1927
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer

“Always thinking of you”
United States of America, 1930s
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer
A special, small archival display celebrating 100 years of the much-loved photobooth.
2025 marks 100 years since the invention of the photobooth in New York. A game-changer for the world of photography, photobooths became an everyday sight in cities around the world.
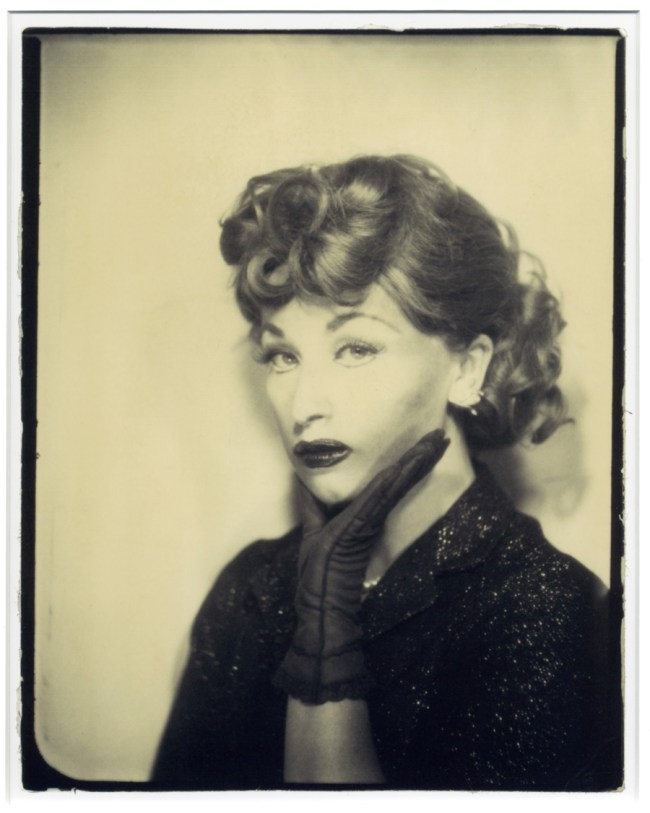
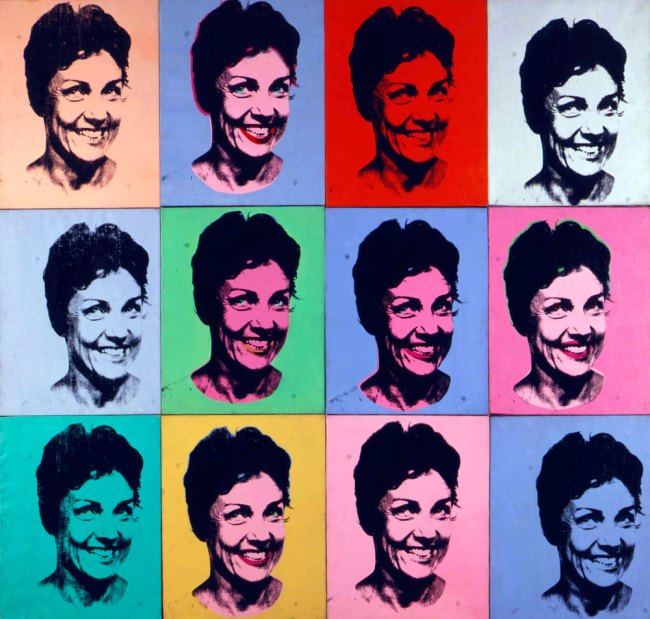
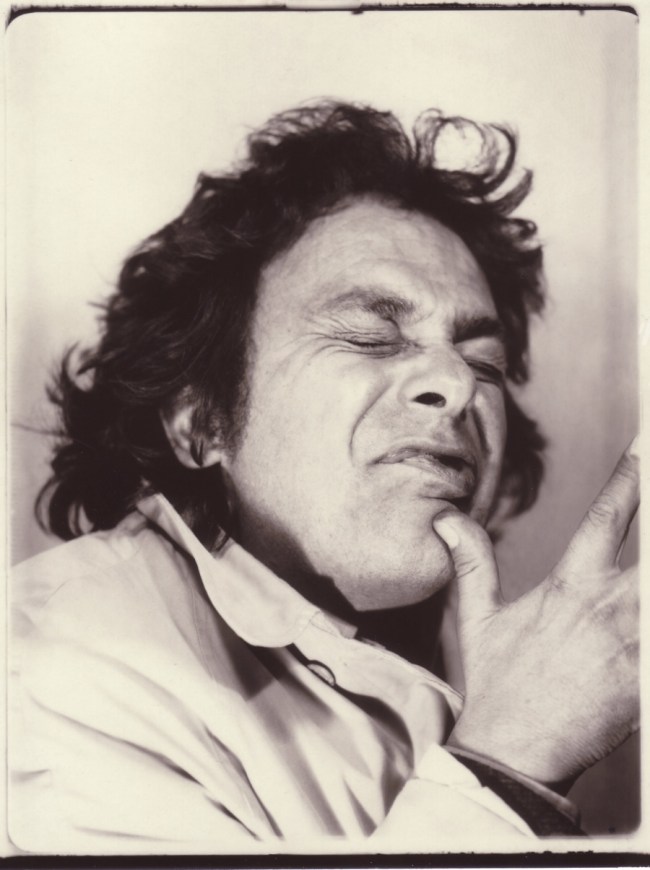
In the 1950s and 1960s, photobooths were a common feature at fairs, shopping centres and train stations. With no technical knowledge needed and no operator, anyone could step behind the curtain, alone or crammed in with friends, put their money in the slot and strike a pose. The booths were loved by everyone, from John Lennon and Yoko Ono, to John and Jacqueline Kennedy, and used by artist Andy Warhol for his famous series of self-portraits.
These popular coin-operated booths began to disappear with the rise of digital photography in the 1990s. Now, restored by dedicated experts, analogue booths are reappearing in cities across the world and enjoying a resurgence of interest and delight with modern-day fans.
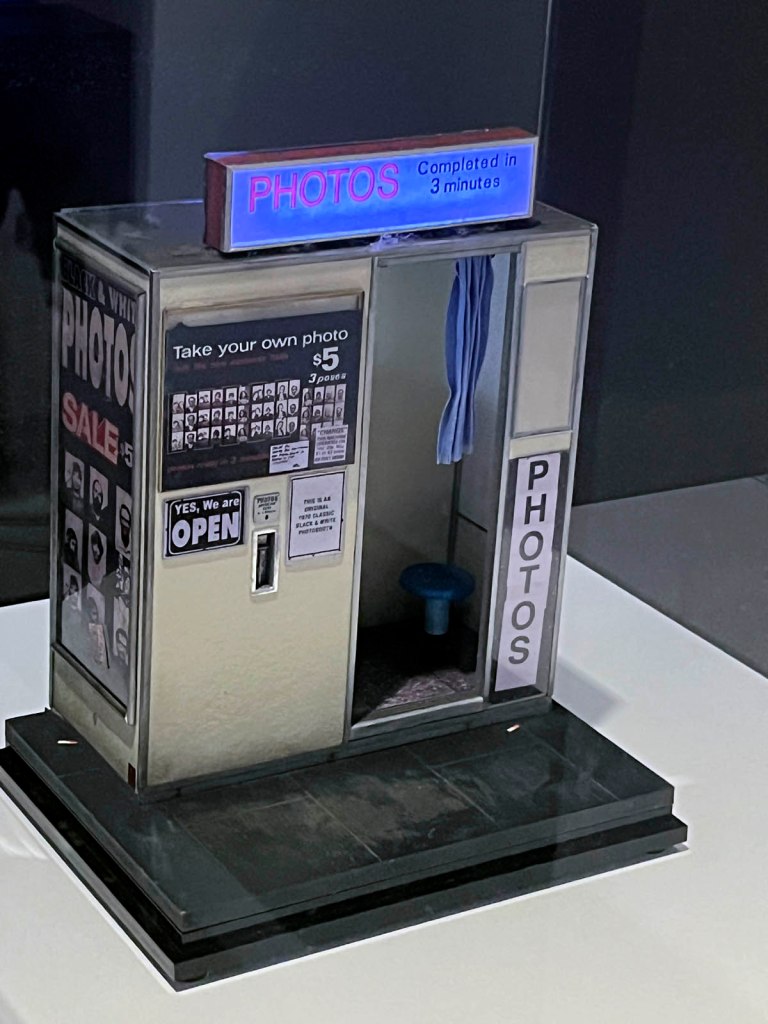
This autumn we’re celebrating the centenary by telling the story of the much-loved photobooth. Through a small archival display, Strike a Pose! 100 Years of the Photobooth will explore the history, imperfections and quirks of the booth. There’s also a 1960s analogue booth at the Gallery for everyone to create their own selfie souvenir and a live feed to see the unique mechanics of the booth in action.
Strike a Pose! 100 Years of the Photobooth features work from the collection of Raynal Pellicer and is part of a year-long programme of centenary celebrations, in partnership with AUTOFOTO.
Text from The Photographers’ Gallery website
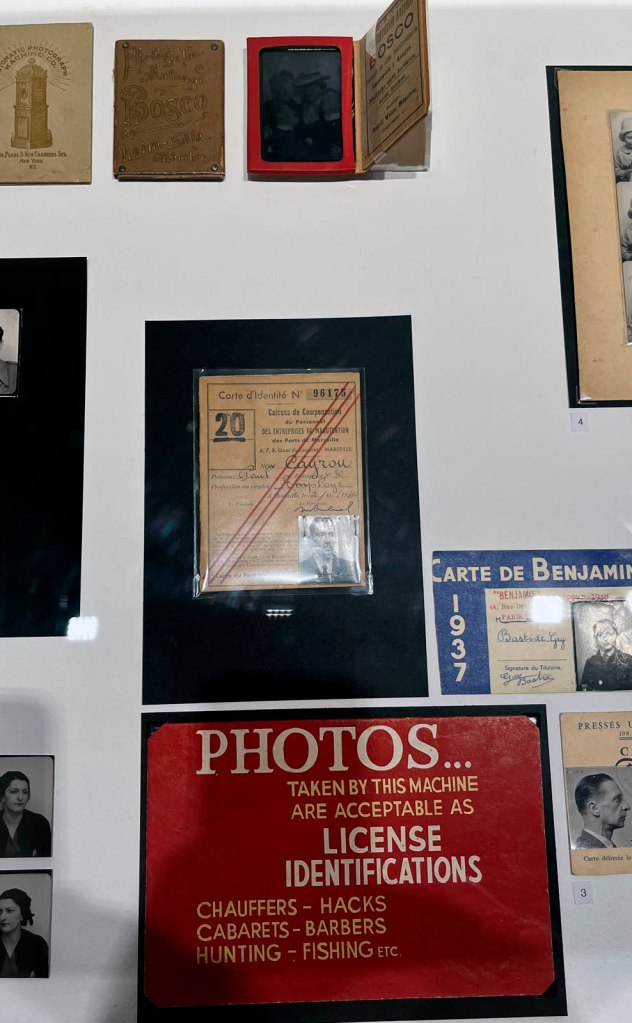
Photomaton Envelope
1940s
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer

Photomaton Pochette
France, c. 1930s-1950s
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer
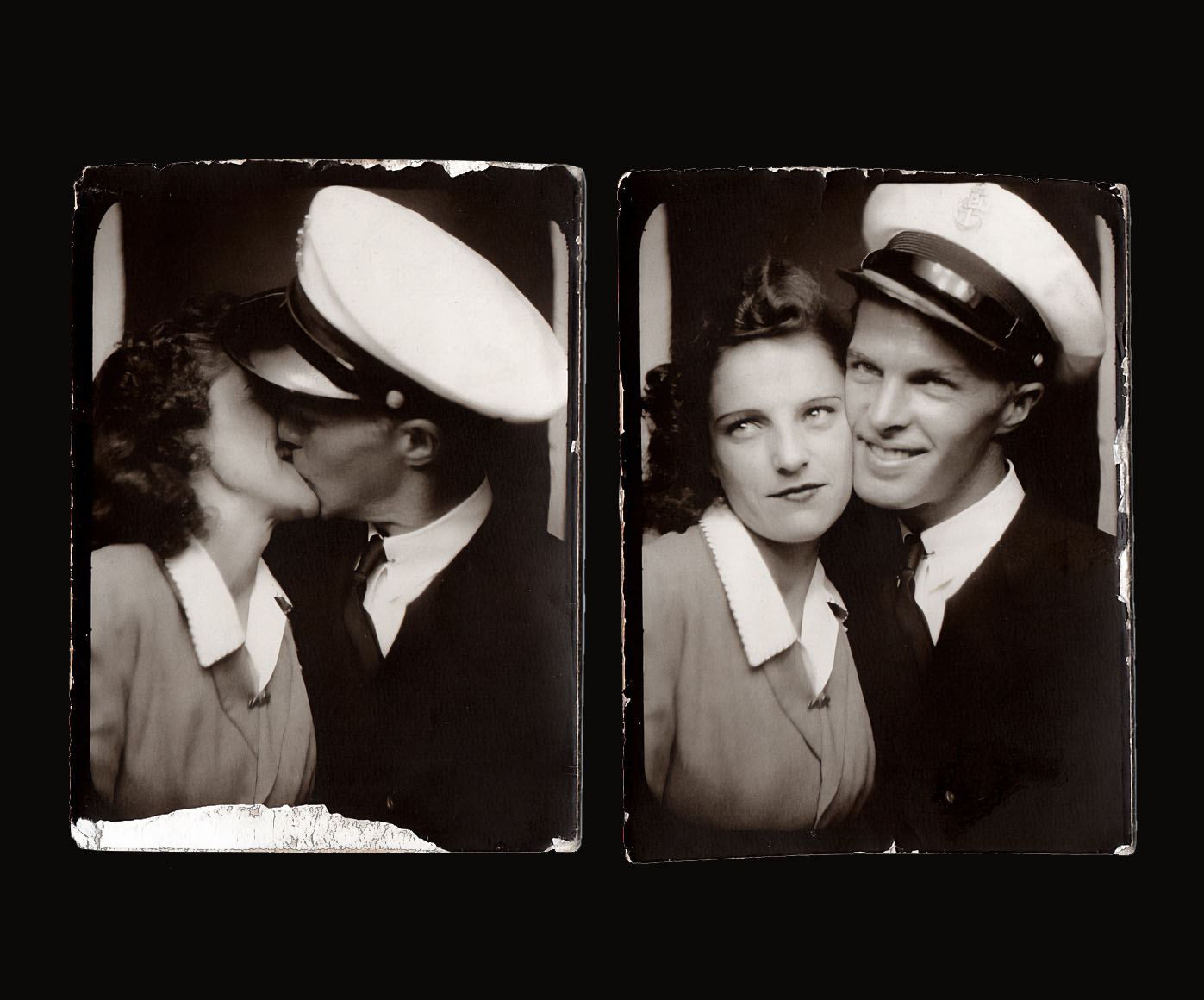

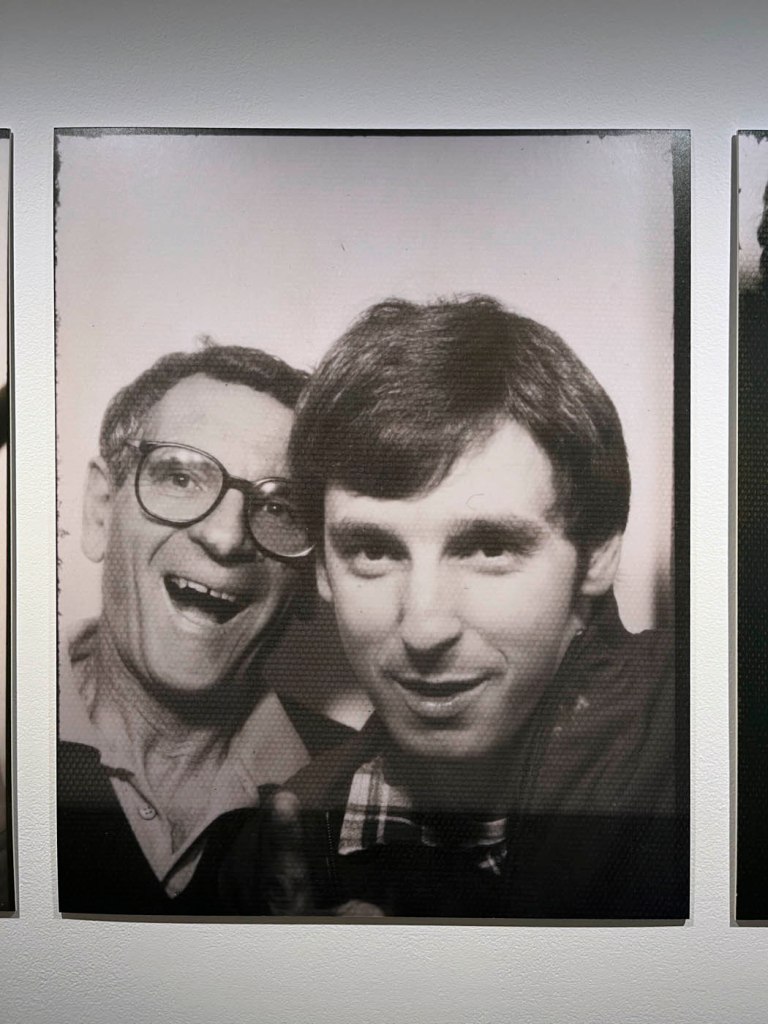
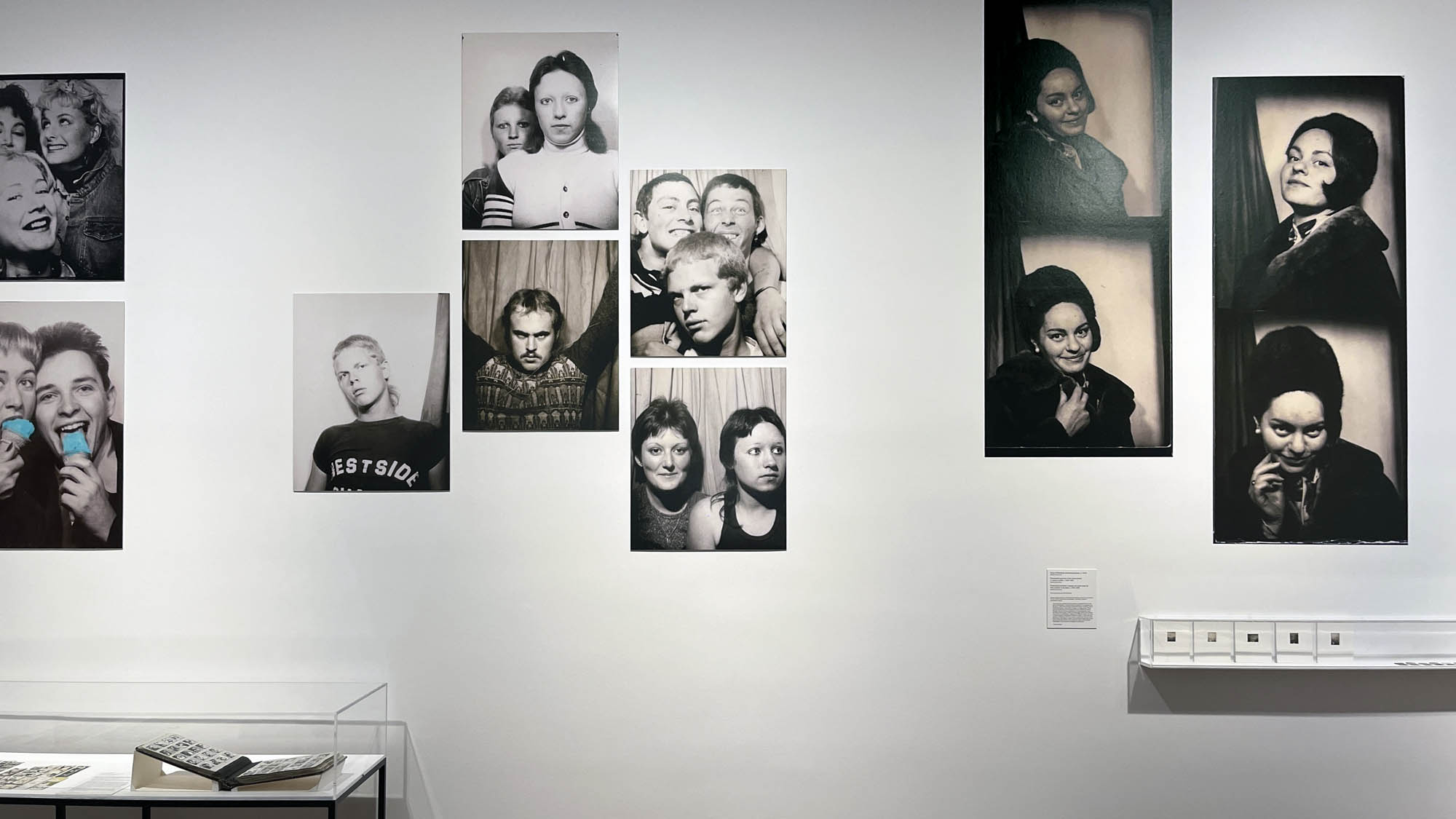
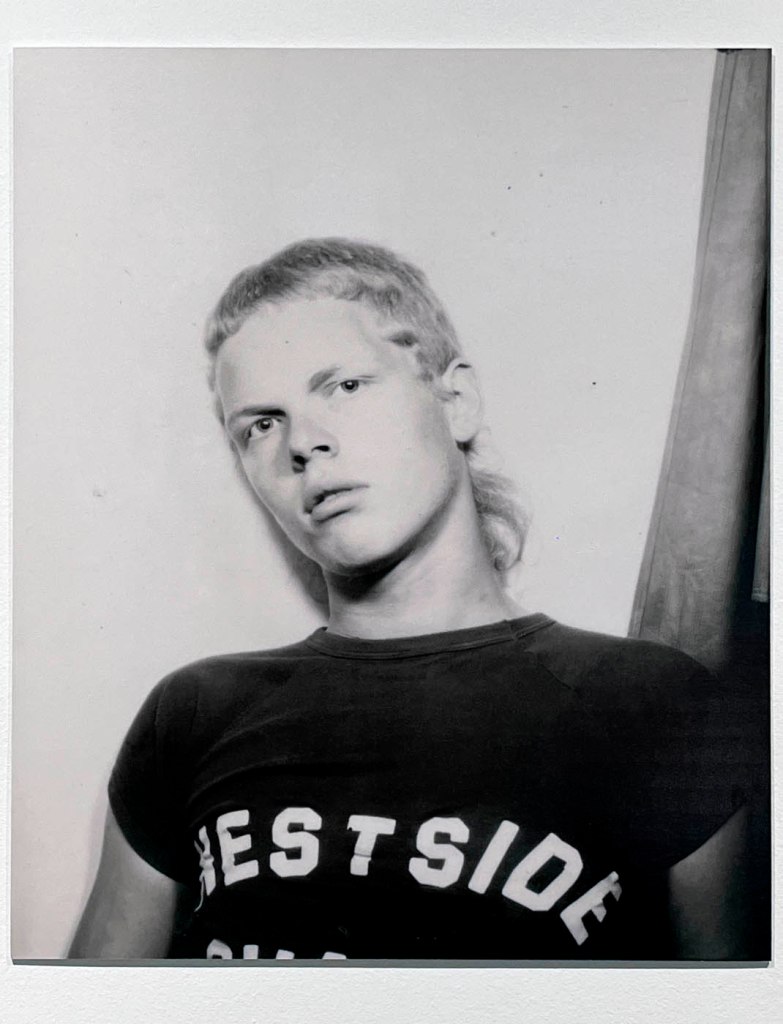
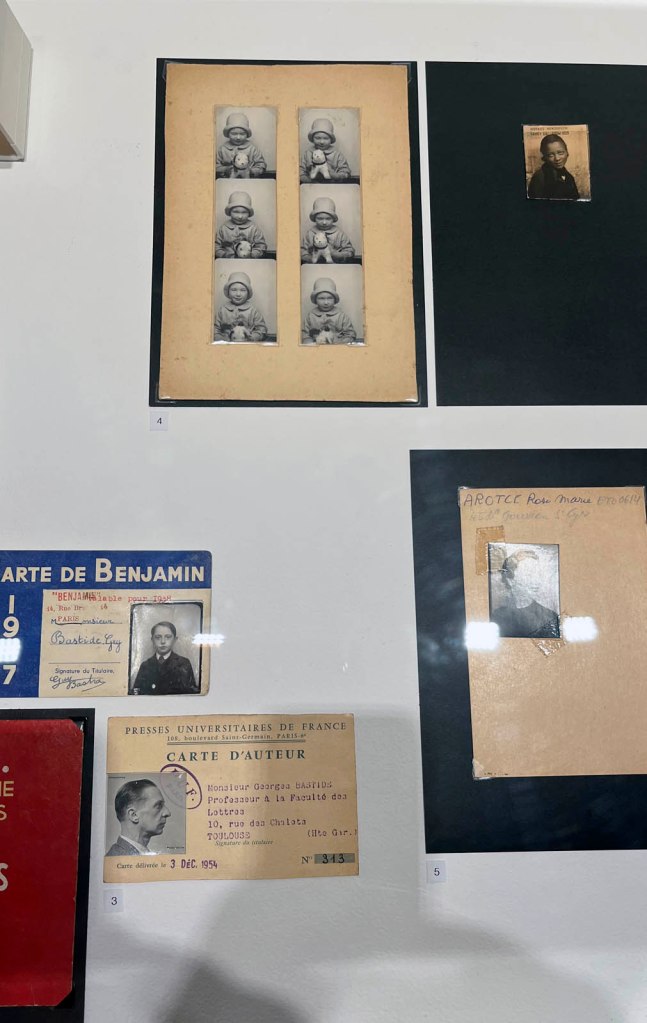
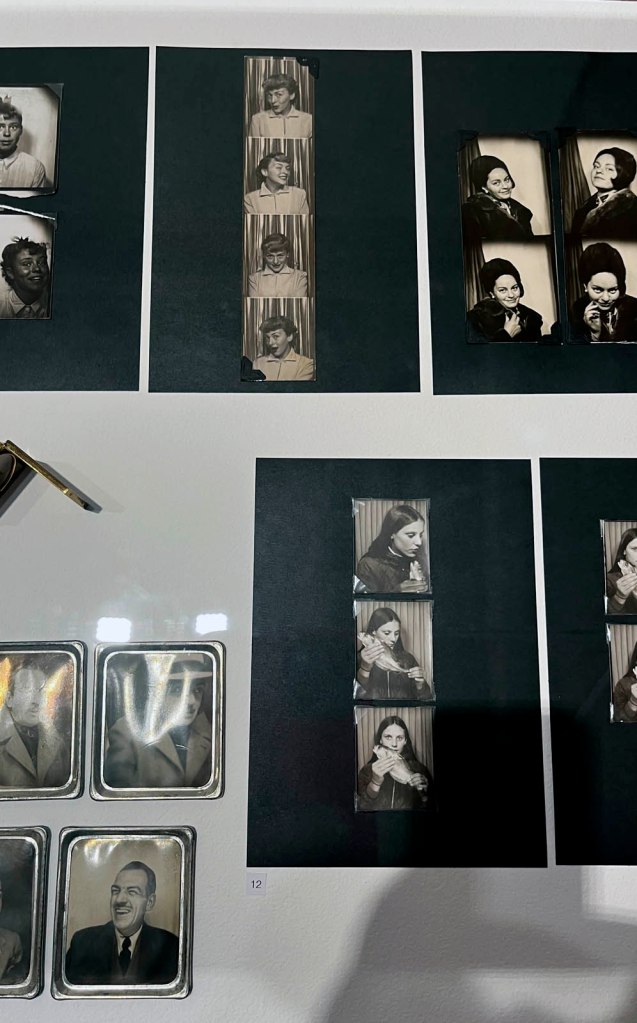
Couple
c. 1930s-1950s
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer
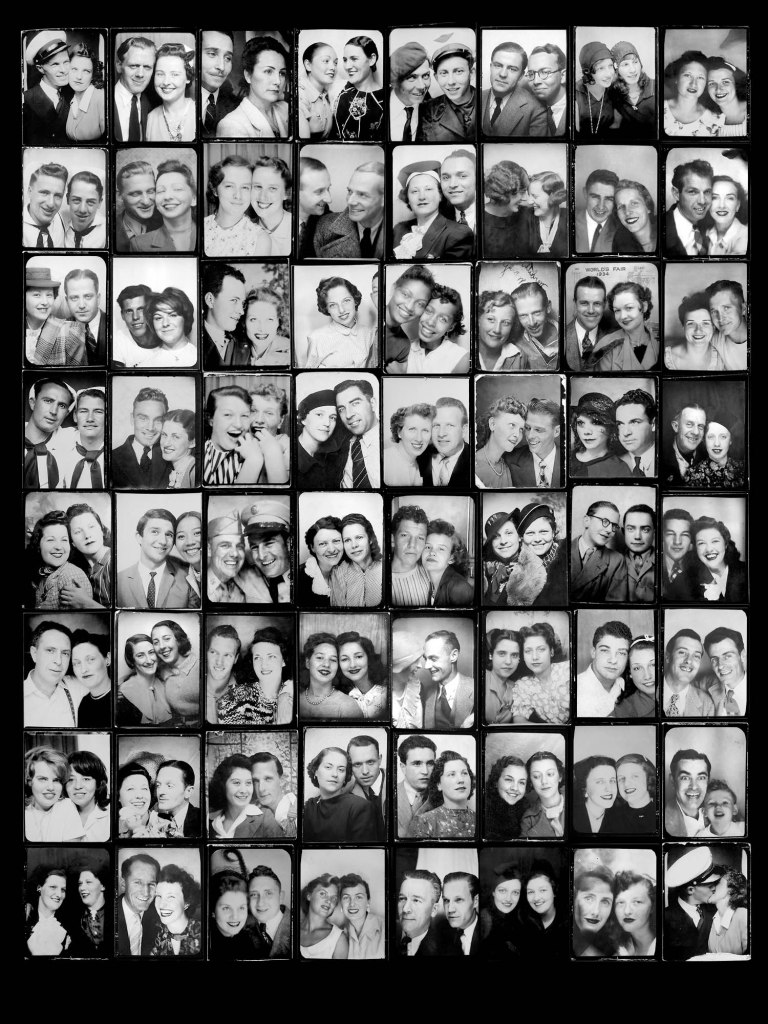

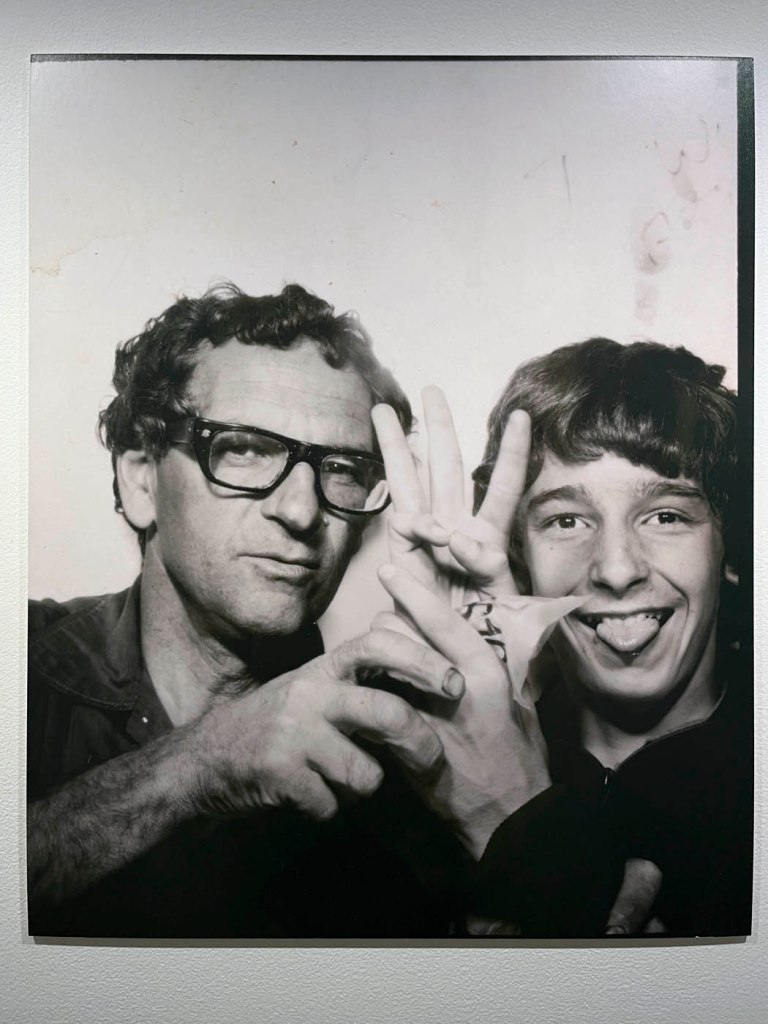
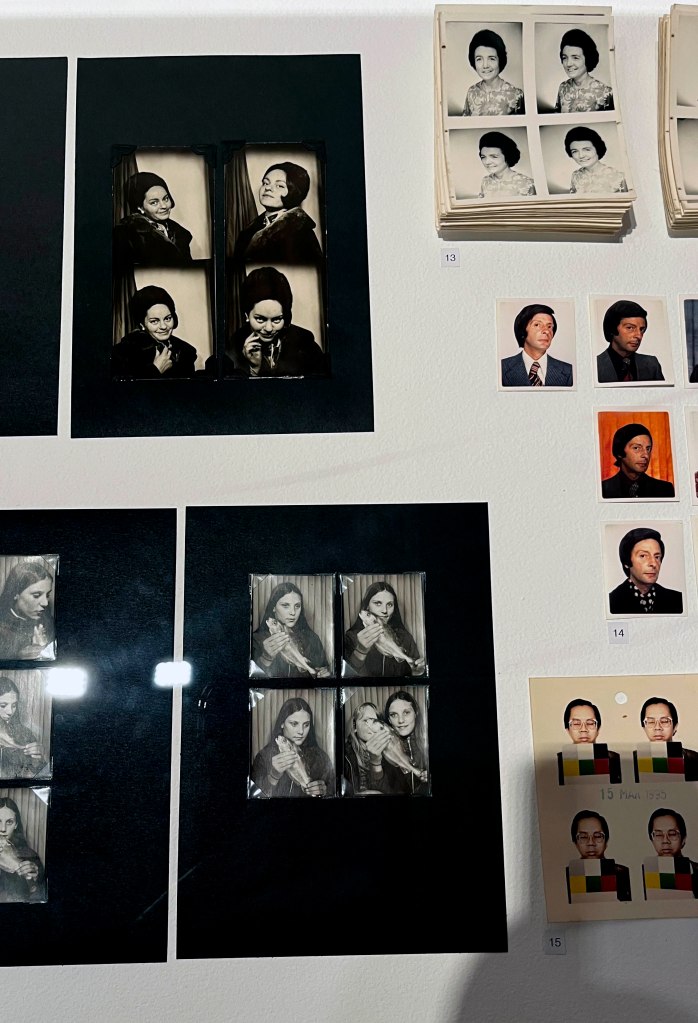
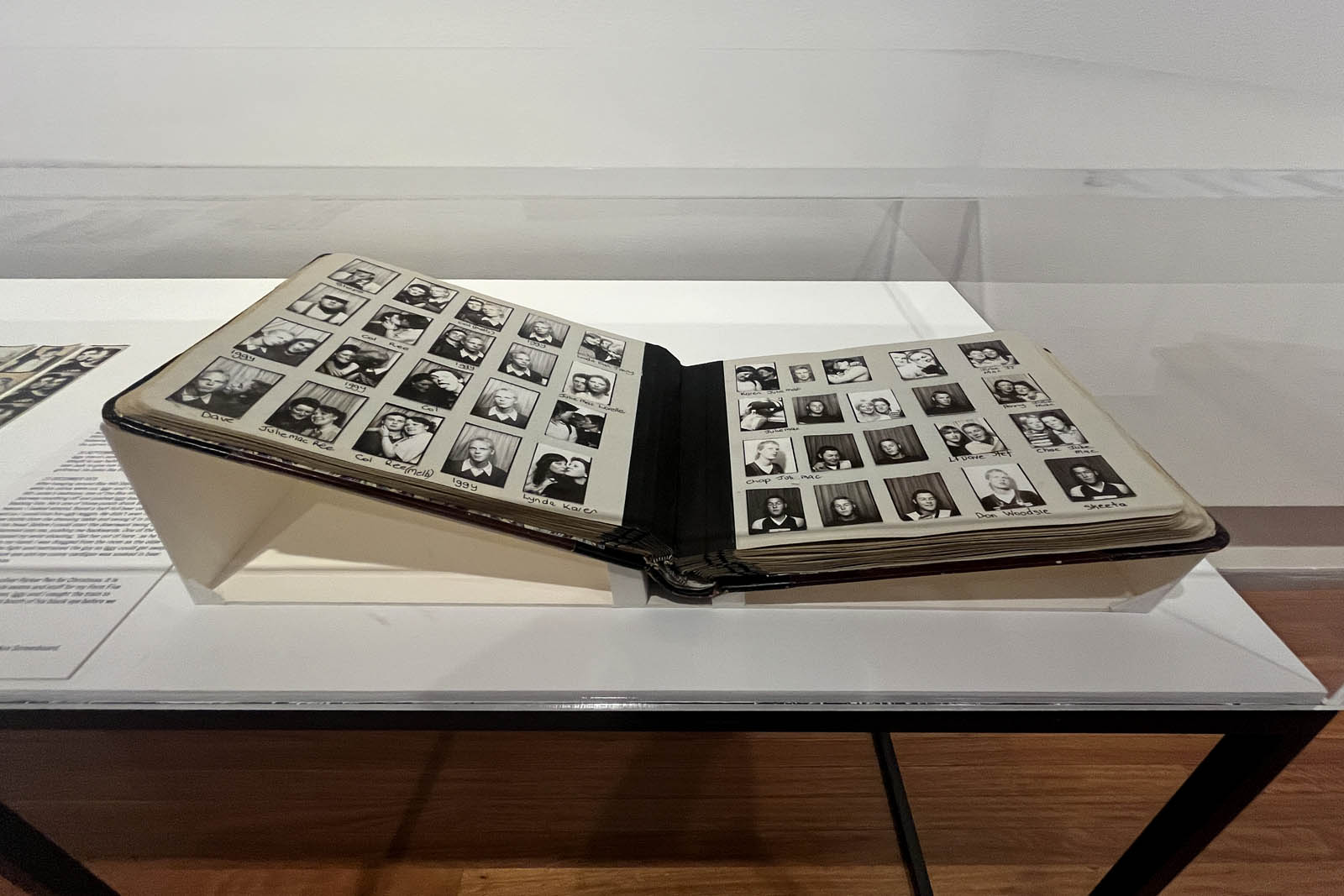
Couples
c. 1930s-1950s
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer
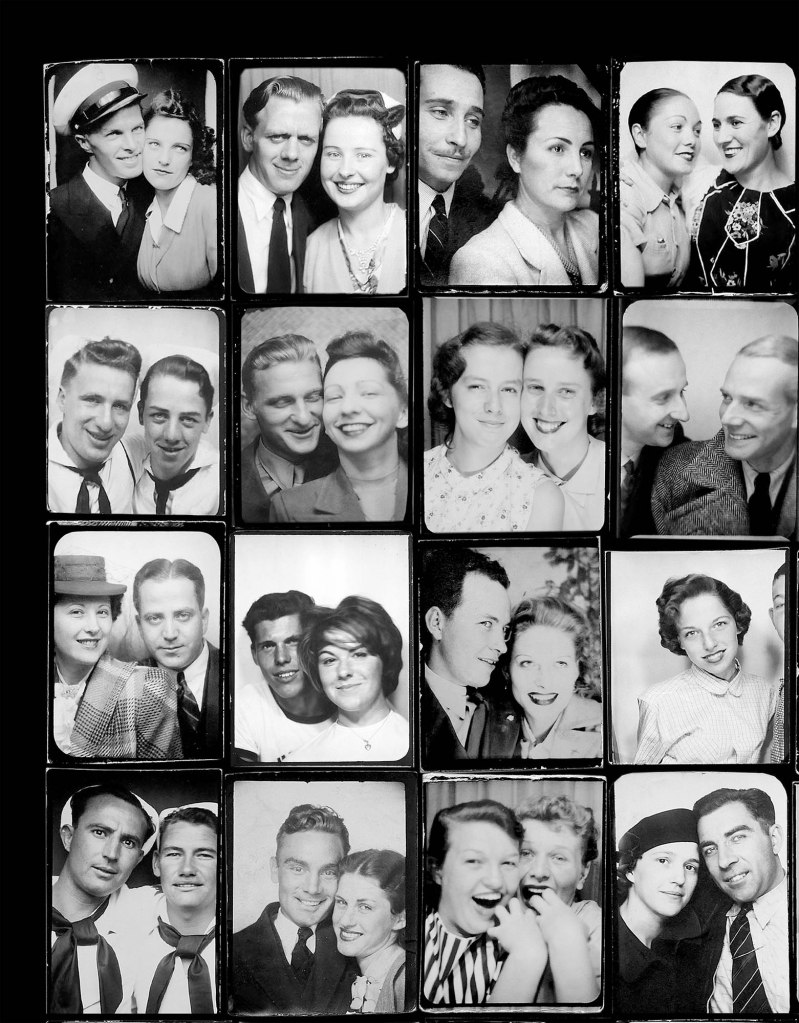
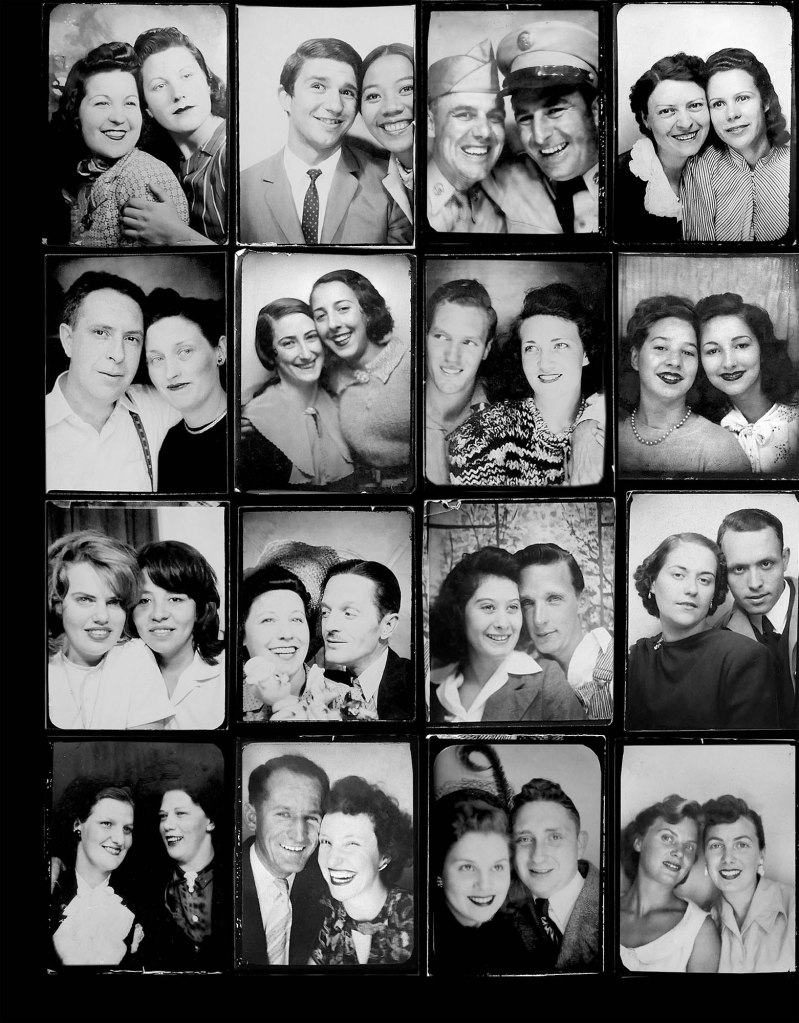
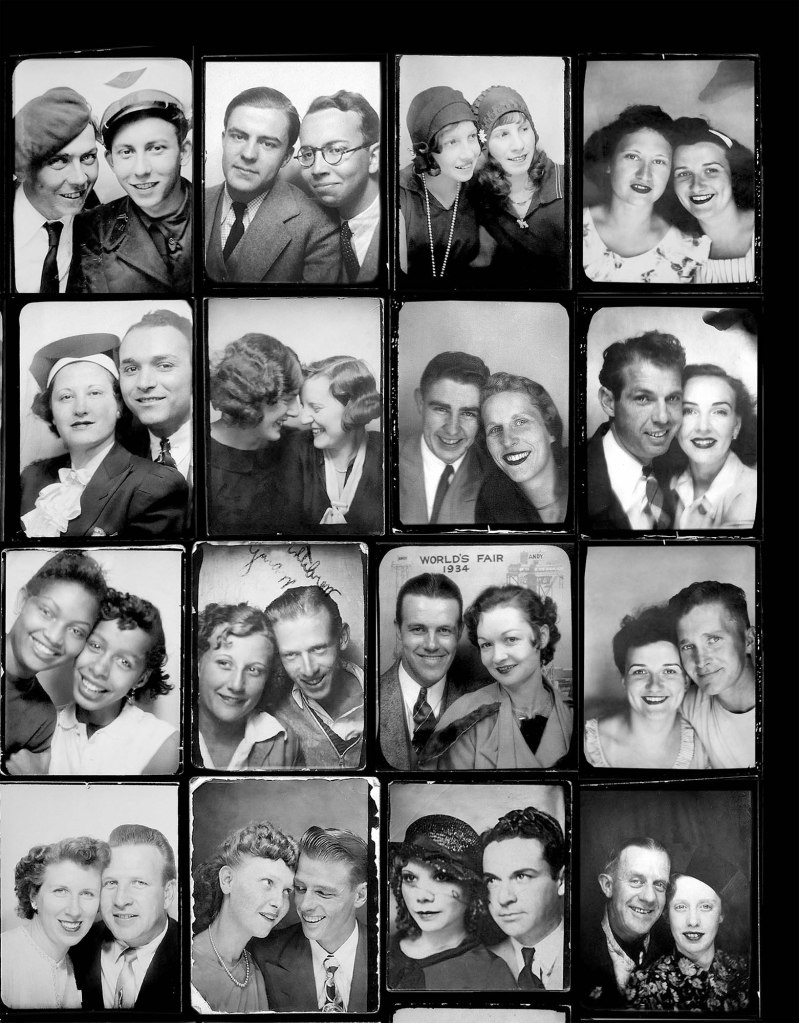
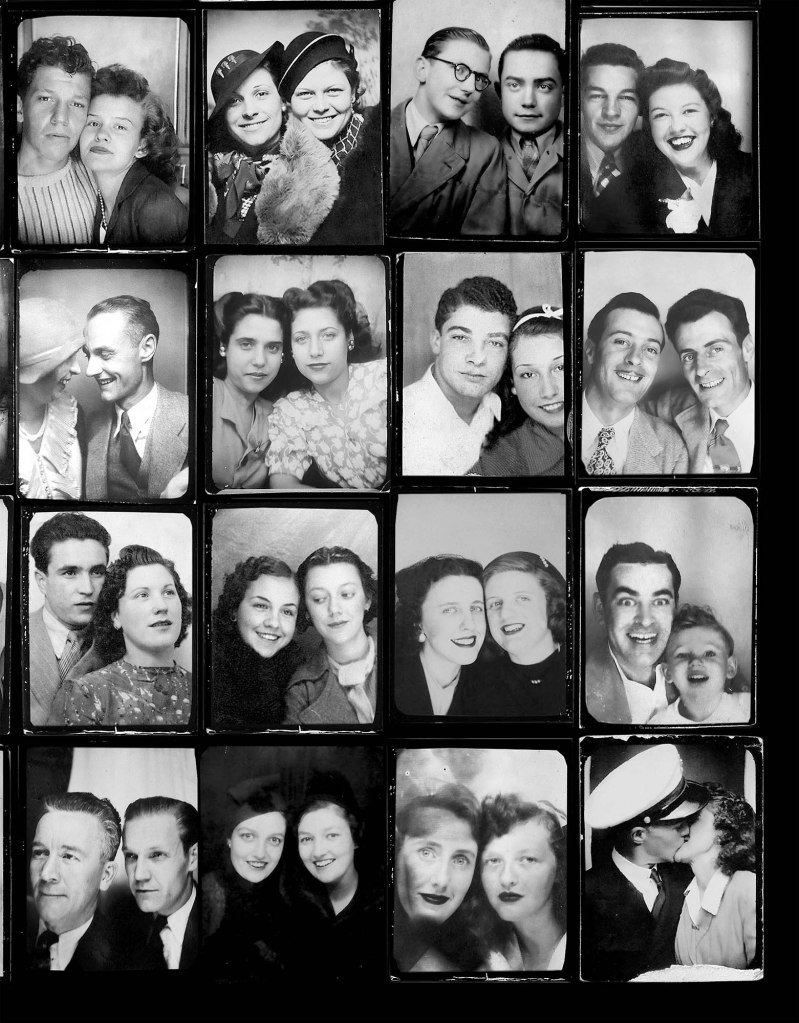




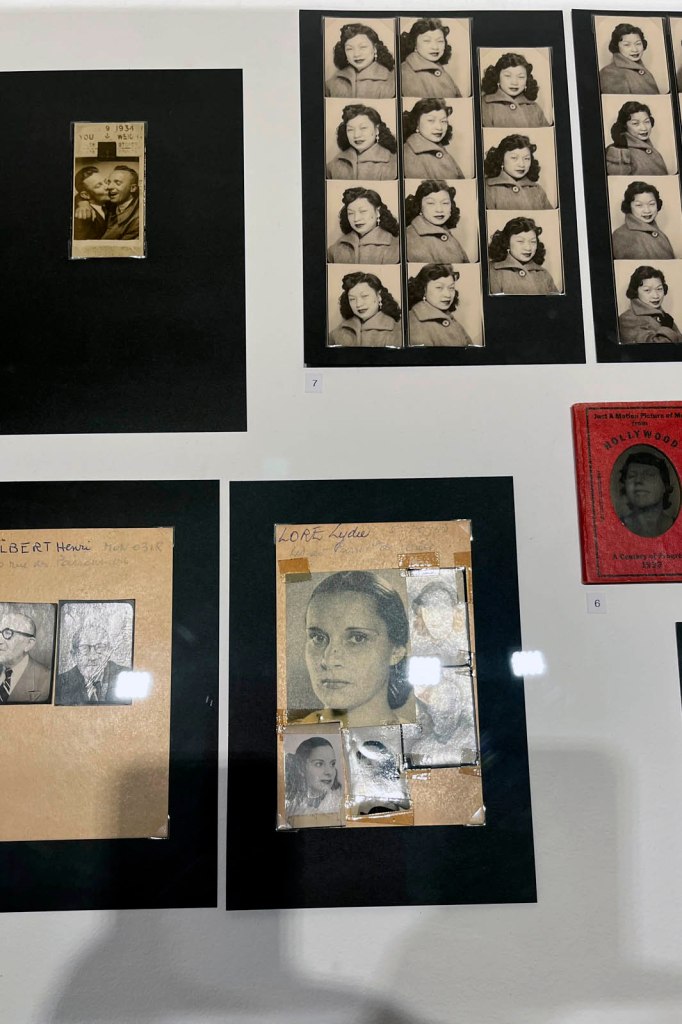
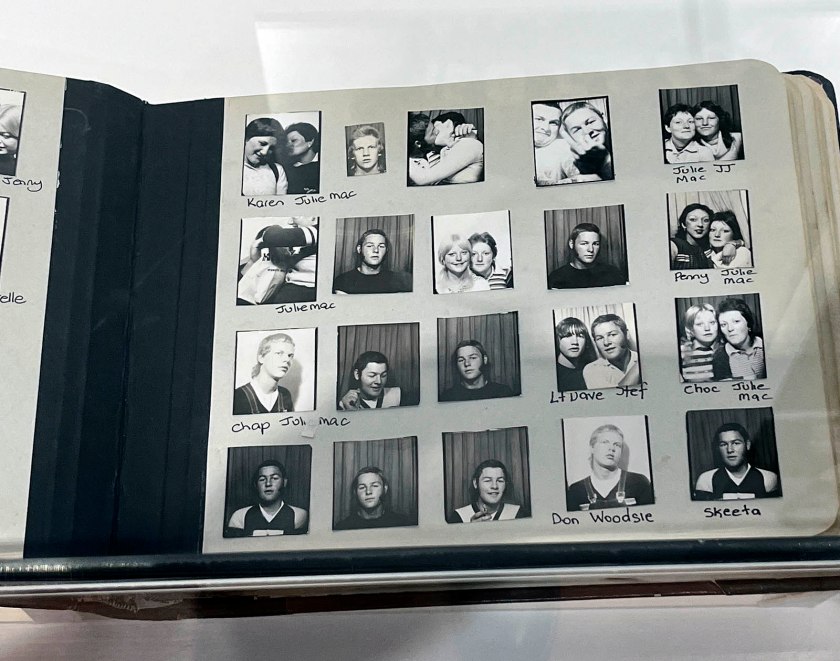
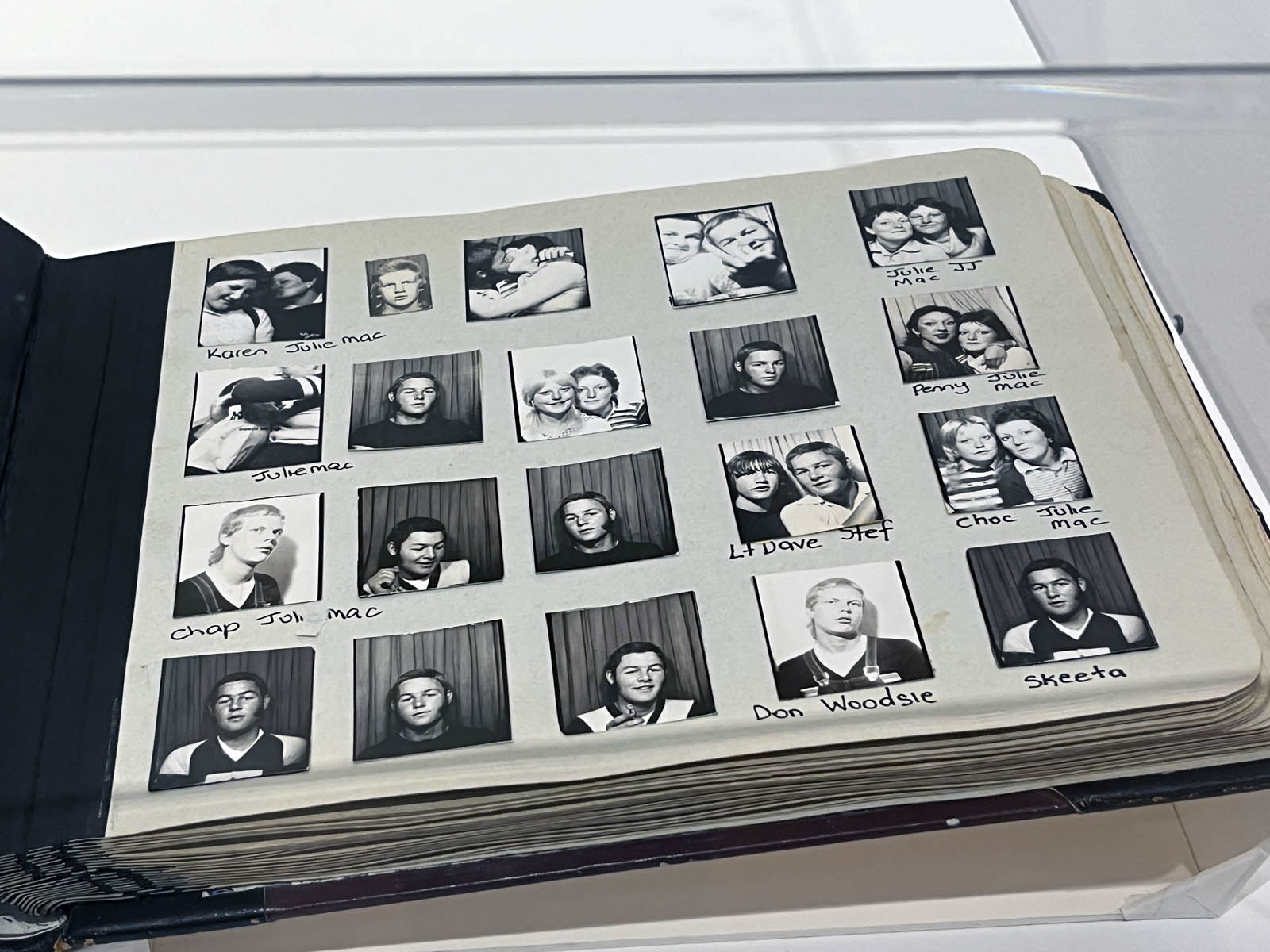
Couples (details)
c. 1930s-1950s
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer
This autumn The Photographers’ Gallery celebrates 100 years of the much-loved photobooth.
Through a special archival display, Strike a Pose! 100 Years of the Photobooth looks back on the history of the photobooth and explores its intimate charms, imperfections and quirks.
2025 marks the year-long celebration of the 100th anniversary of the invention of the analogue photobooth by Anatol Josepho. His first Photomaton appeared on Broadway in New York in 1925. The photobooth was a game-changer for the world of photography and quickly became an everyday sight in cities around the world.
A combined studio and photography lab in one place, booths offered the first affordable access to photography. With no technical knowledge needed and no operator, anyone could step behind the curtain, put their money in the slot and strike a pose.
After the success of the first booth, when over 7,500 New Yorkers used the booth in its first 5 days, global success quickly followed. The first photobooth launched in the UK in Selfridges, London, in 1928 and was an immediate hit.
In the 1950s and 1960s, photobooths were a common feature at fairs, shopping centres and train stations. These intimate inexpensive spaces gave everyone the freedom to control their own images. Behind the curtain, whether alone or crammed in with friends, the photobooth was a playground, beyond the gaze of a photographer. The booths were loved by everyone, from John Lennon and Yoko Ono, to John and Jacqueline Kennedy, and used by artist Andy Warhol for his famous series of self-portraits.
The coin-operated booths, once ever-present on high streets and stations, disappeared with the rise of digital photography in the 1990s. Now, restored by dedicated experts, analogue booths are reappearing in cities across the world and enjoying a resurgence of interest and delight with modern-day fans. Alongside the display of archive prints, vintage strips and materials, there’ll also be a booth at the Gallery for everyone to create their own selfie souvenir and a live feed to see the unique mechanics of the booth in action.
Strike a Pose! 100 Years of the Photobooth features work from the collection of Raynal Pellicer and is part of a year-long programme of centenary celebrations, in partnership with AUTOFOTO.
AUTOFOTO are analogue photobooth experts who have been rescuing and restoring original auto-photography machines for over a decade. Their restored machines can be found in locations across London and Barcelona. Through careful restoration and servicing, AUTOFOTO’s mission is to ensure the survival of these beautiful machines and photobooth photography for future generations.
Press release from The Photographers’ Gallery, London
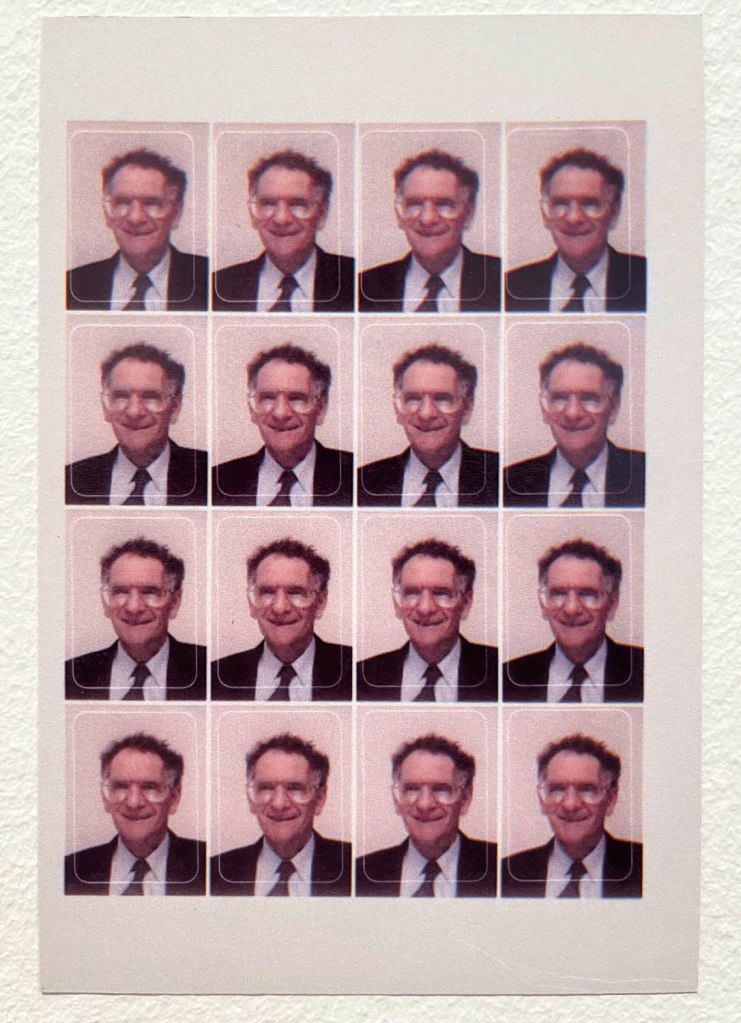
!['Untitled [Color Photobooth Portraits]' c. 1940s-1950s 'Untitled [Color Photobooth Portraits]' c. 1940s-1950s](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/untitled-color-photobooth-portraits.jpg?w=801)
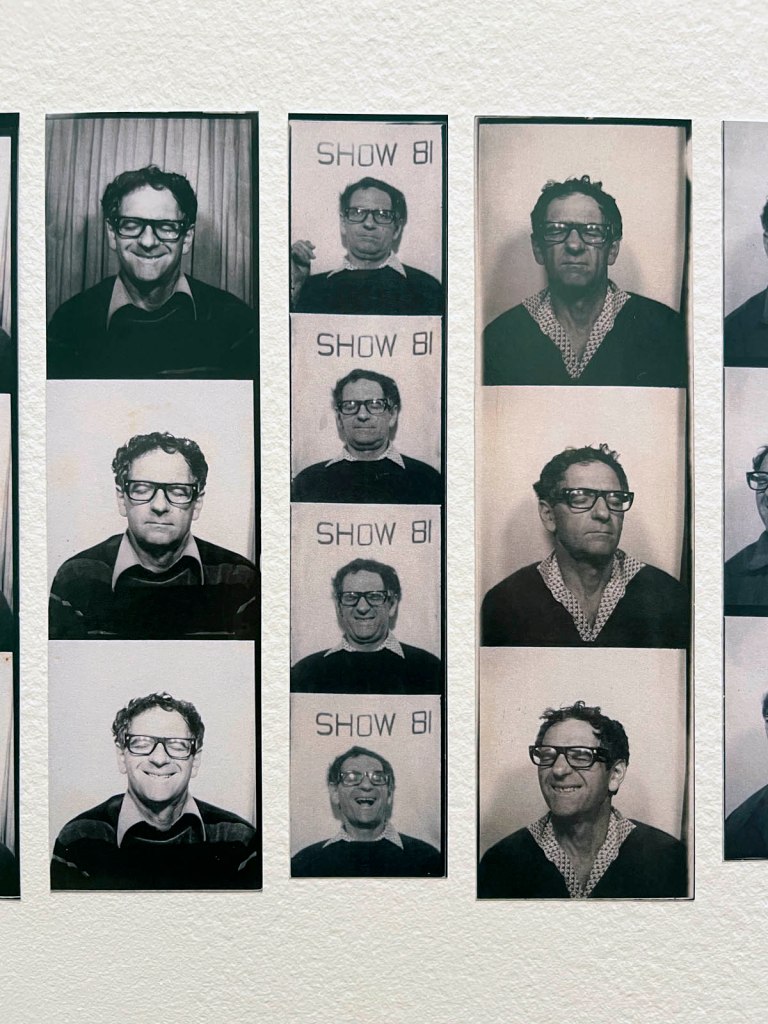
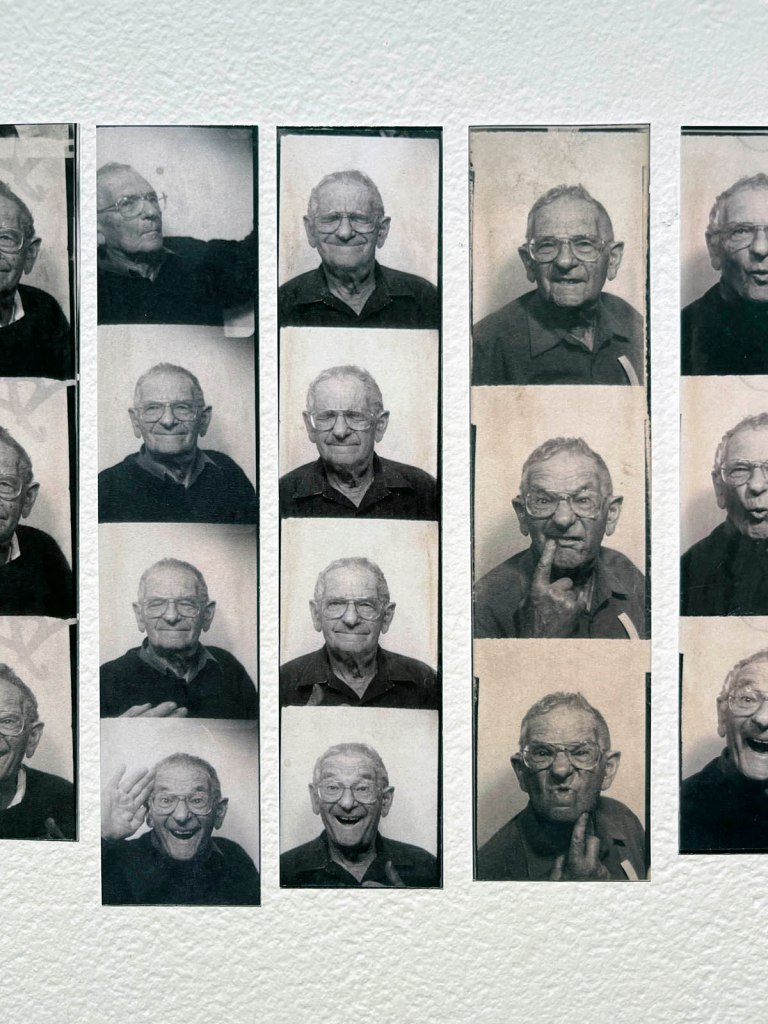
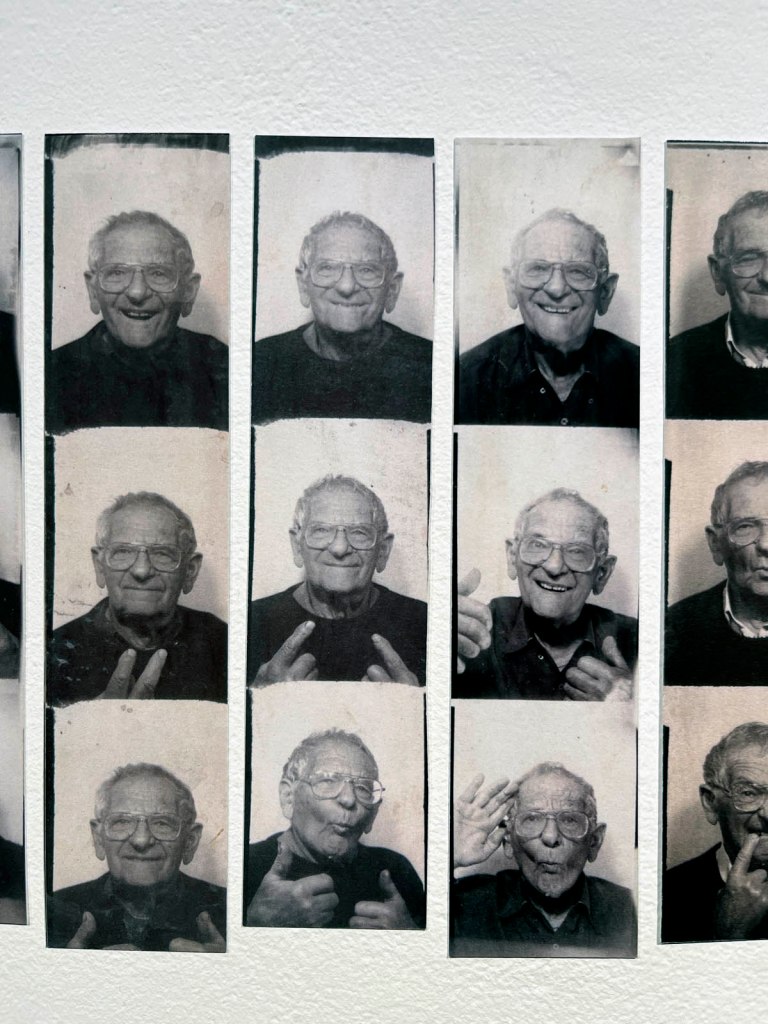
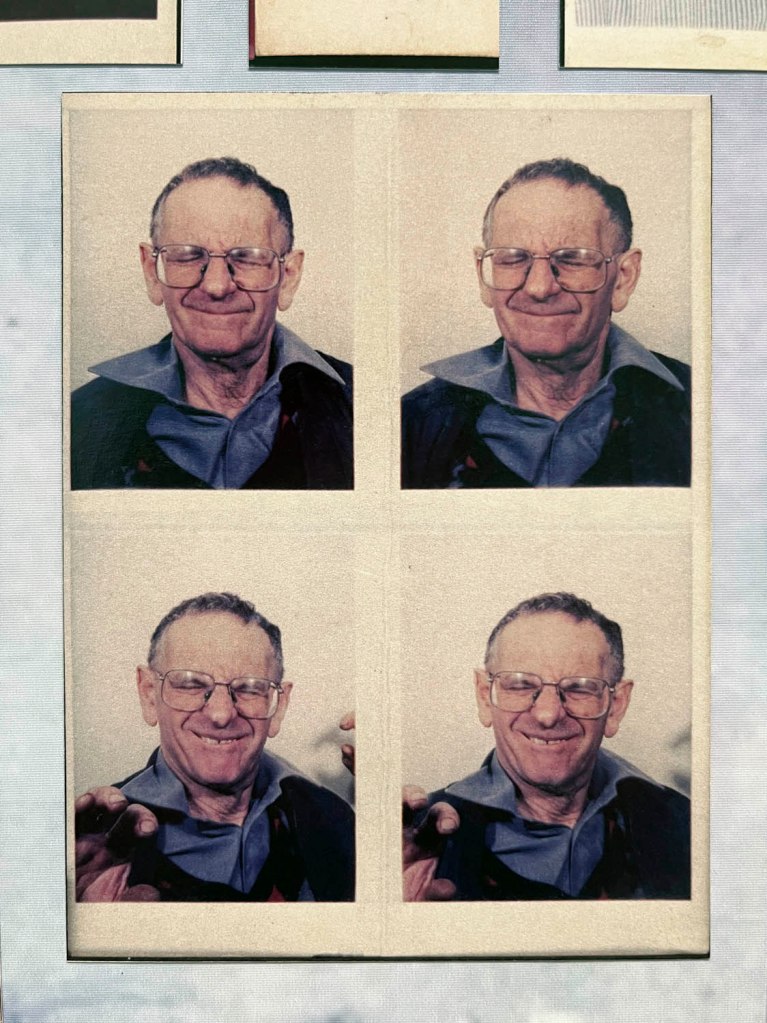
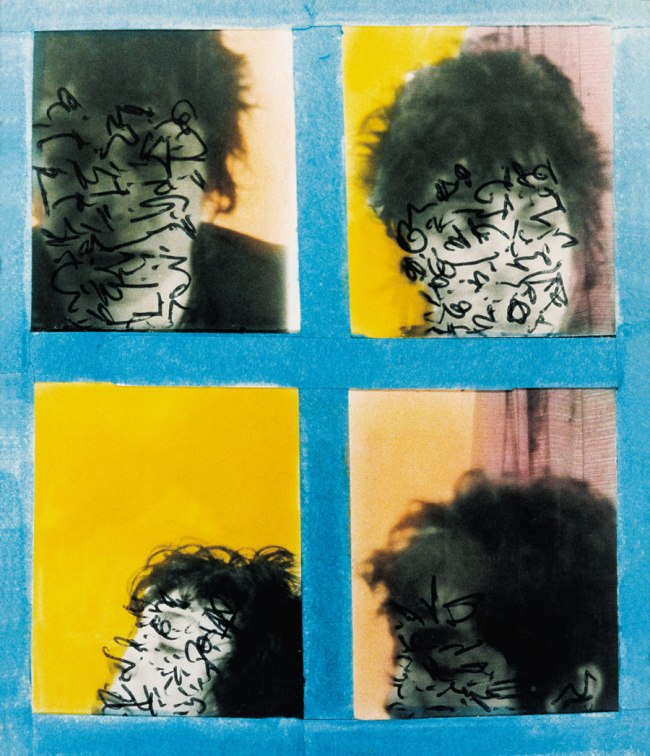
Untitled [Color Photobooth Portraits]
c. 1940s-1950s
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer
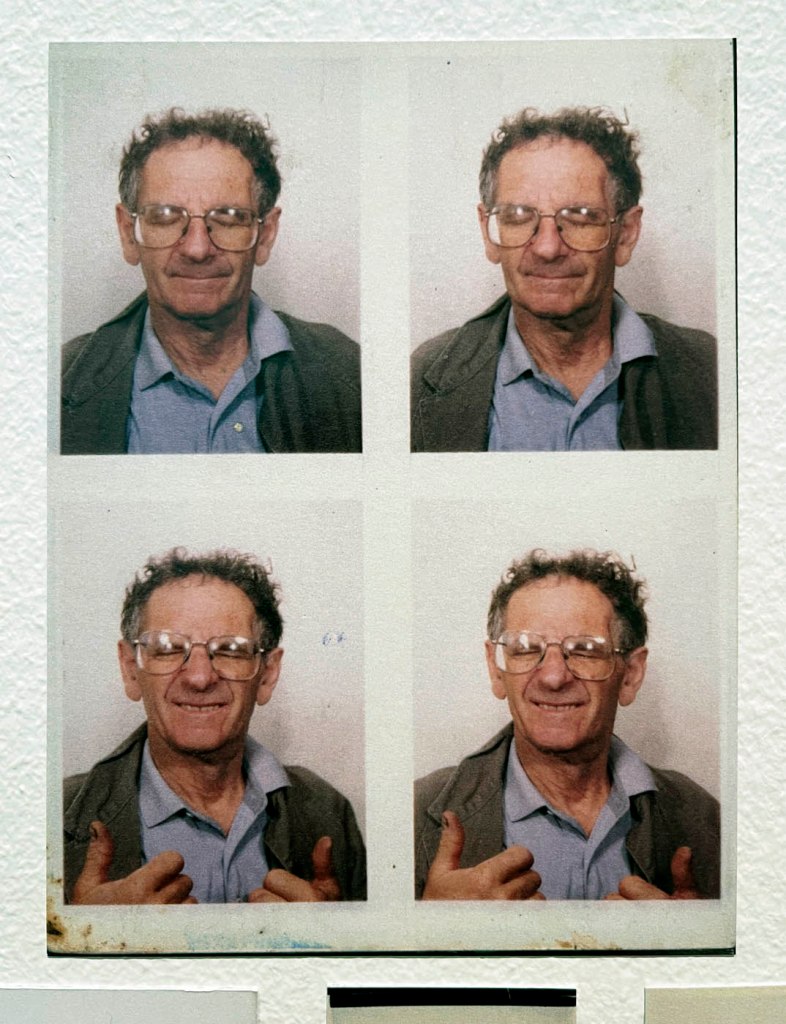
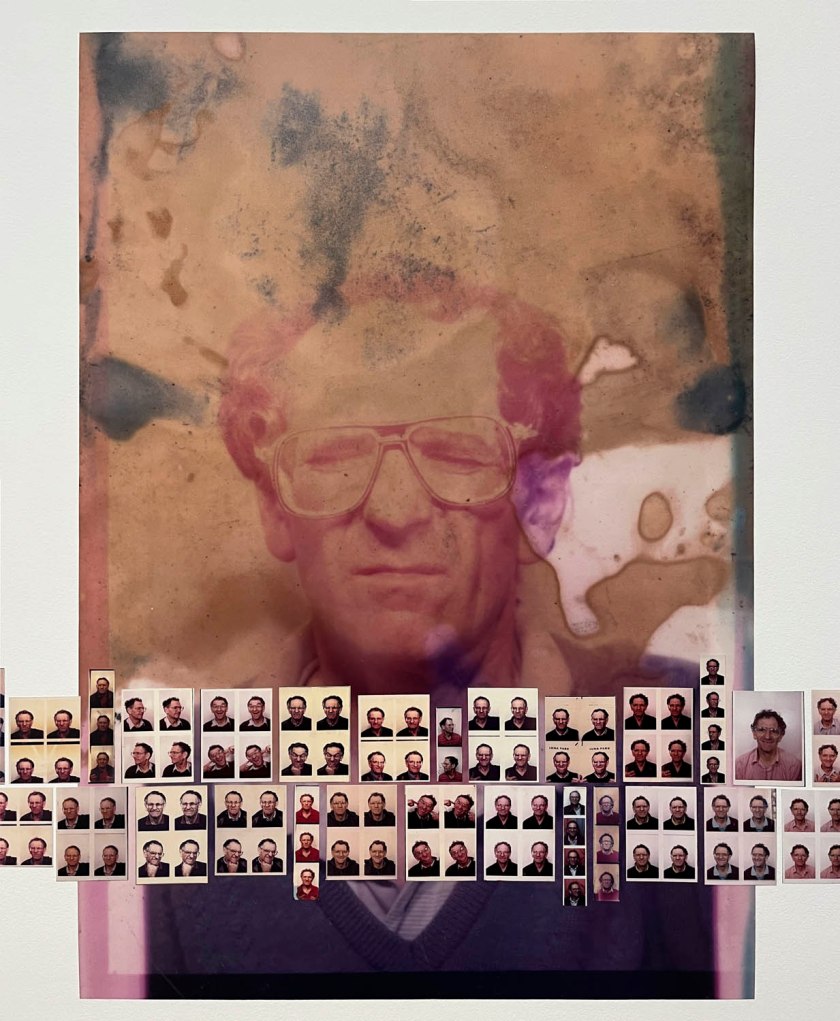
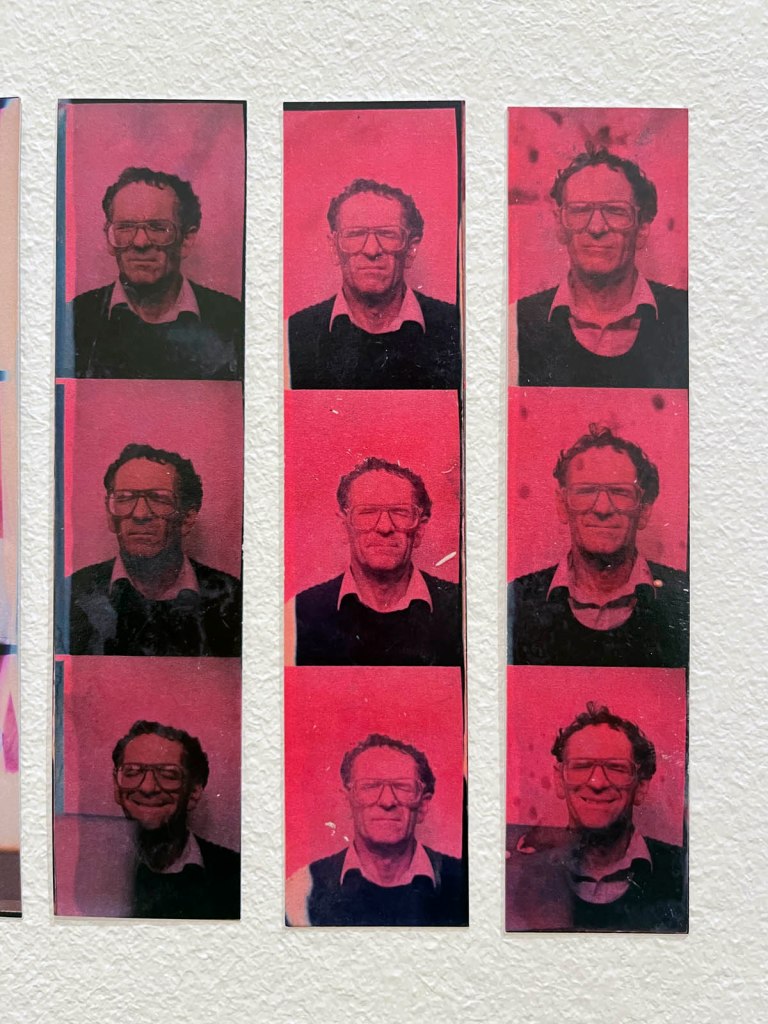
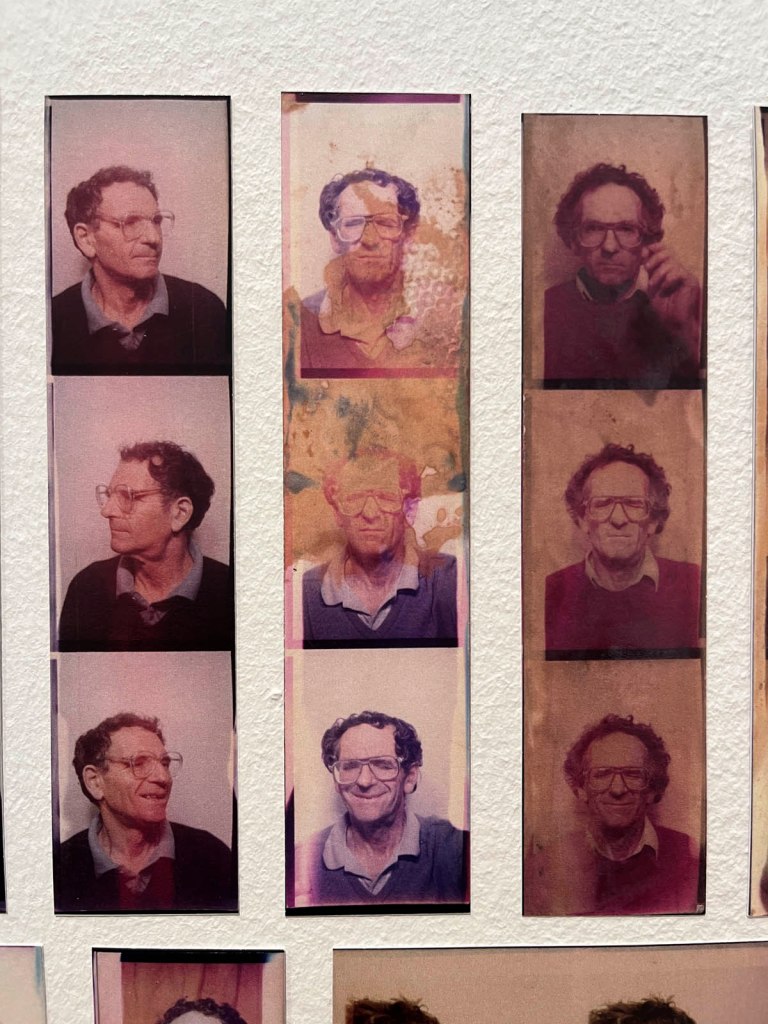
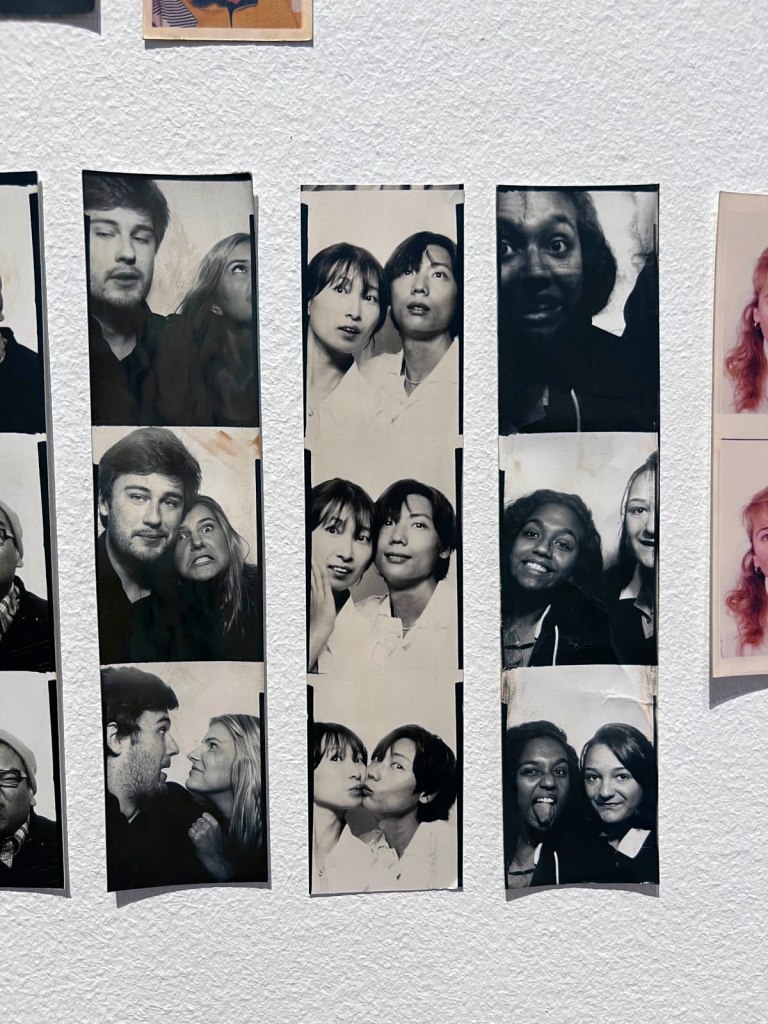
Untitled [Color Photobooth Portraits] (details)
c. 1940s-1950s
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer
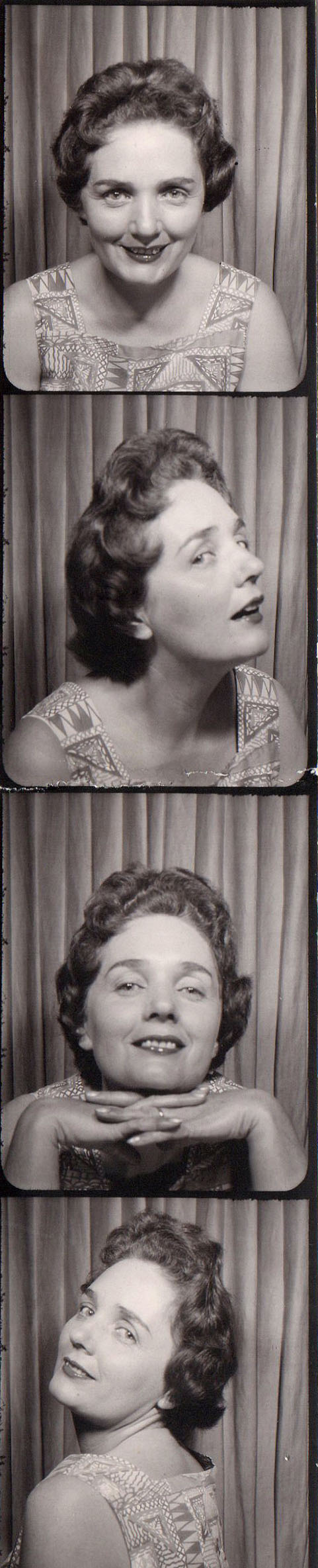

Strip
United States of America, 1950s
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer

“Couple”, Photomaton
Blackpool, England, 1950s
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer
“French Couple”, Six Strips
France, 1960s
Courtesy Raynal Pellicer
The Photographers’ Gallery
16-18 Ramillies Street
London
W1F 7LW
Opening hours:
Mon – Wed: 10.00 – 18.00
Thursday – Friday: 10.00 – 20.00
Saturday: 10.00 – 18.00
Sunday: 11.00 – 18.00

!['Untitled [Women Photobooth Portraits]' c. 1940s-1950s from the exhibition 'Strike a Pose! 100 Years of the Photobooth' at The Photographers' Gallery, London, October 2025 - February 2026 'Untitled [Women Photobooth Portraits]' c. 1940s-1950s from the exhibition 'Strike a Pose! 100 Years of the Photobooth' at The Photographers' Gallery, London, October 2025 - February 2026](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/women-photobooth-portraits.jpg)


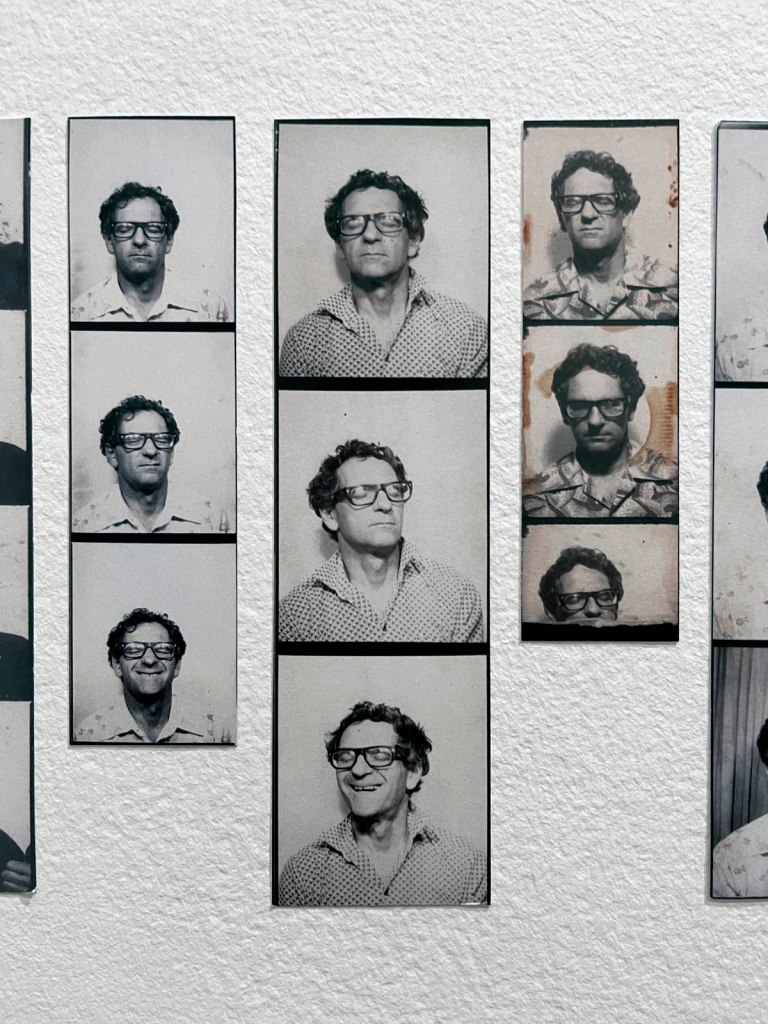
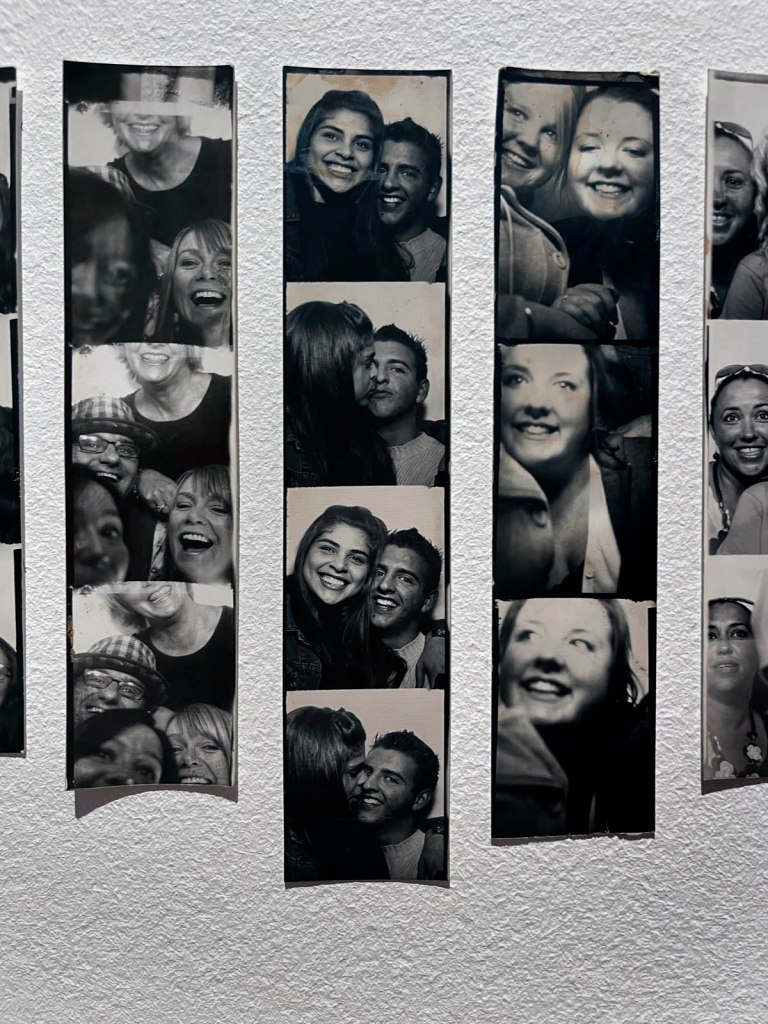
!['Untitled [Color Photobooth Portraits]' c. 1940s-1950s (detail) 'Untitled [Color Photobooth Portraits]' c. 1940s-1950s (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/untitled-color-photobooth-portraits-a.jpg)
!['Untitled [Color Photobooth Portraits]' c. 1940s-1950s (detail) 'Untitled [Color Photobooth Portraits]' c. 1940s-1950s (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/untitled-color-photobooth-portraits-b.jpg)






































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.