Exhibition dates: 3rd December, 2016 – 12th March, 2017
Curators: Roxana Marcoci, Senior Curator, Department of Photography, and Sarah Suzuki, Curator, Department of Drawings and Prints; with Hillary Reder, Curatorial Assistant, Department of Drawings and Prints.

Various artists with Natalia Goncharova, Mikhail Larionov, Nikolai Rogovin, Vladimir Tatlin
Mirskontsa (Worldbackwards)
1912
My apologies to readers of Art Blart, but my postings will be short of comment in the next month or so as I try to take as much rest as possible. I have bad hands which is preventing me from using the keyboard. At the moment I am using dictation software to do the writing for me. I will keep the blog going as much as possible because it is my form of therapy for my mental health.
Which brings me to this posting, another slice of the brilliance of the European inter-war avant-garde, this time from Russia. Design, intense colouration (or lack of it), and complexity of form are hallmarks of this “new, militant art.” Photomontage, form and propaganda go hand in hand with this New Vision. The photograph and the cinema were social and essential elements of this new world order.
Perspective shifted. Pictorial planes fractured. Points of view pictured the unusual: from below, from above, with few vanishing points contained within the image or photomontage. Films had no sound and often no story and no actors. They were experimental intersections of man, machinery, and the world. Art was exciting and revolutionary. For me, Aleksandr Rodchenko is the star of the show. You only have to look at images such as Mother, Pioneer with Bugle, Pioneer girl, and the two photographs titled Dive (1934, below) – both with a sense of weightlessness and perspectival difference – to understand the genius of this artist.
It is indeed a telling indictment that such creativity, in both Russia and Germany (and by default, the rest of Europe), was snuffed out by two dictators who imposed on art a (usually masculine) utopian purity which stifled any hint of militant subversion and originality.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Museum of Modern Art for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
We are breaking with the past, because we cannot accept its hypotheses. We ourselves are creating our own hypotheses anew and only upon them … can we build our new life and new world view.
Lyubov Popova
Russian Avant-Garde | HOW TO SEE the art movement with MoMA curator Roxana Marcoci
For the hundredth anniversary of the 1917 Russian Revolution, MoMA curator Roxana Marcoci explains how artists such as Malevich, Rodchenko, and Vertov attempted to revolutionise Russian society through new means of artistic production – and how the styles developed by the Russian Avant-Garde still affect how we look at art today.

Natalia Goncharova (Russian, 1881-1962)
Rayonism, Blue-Green Forest
1913
Oil on canvas
21 1/2 x 19 1/2″ (54.6 x 49.5cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. The Riklis Collection of McCrory Corporation
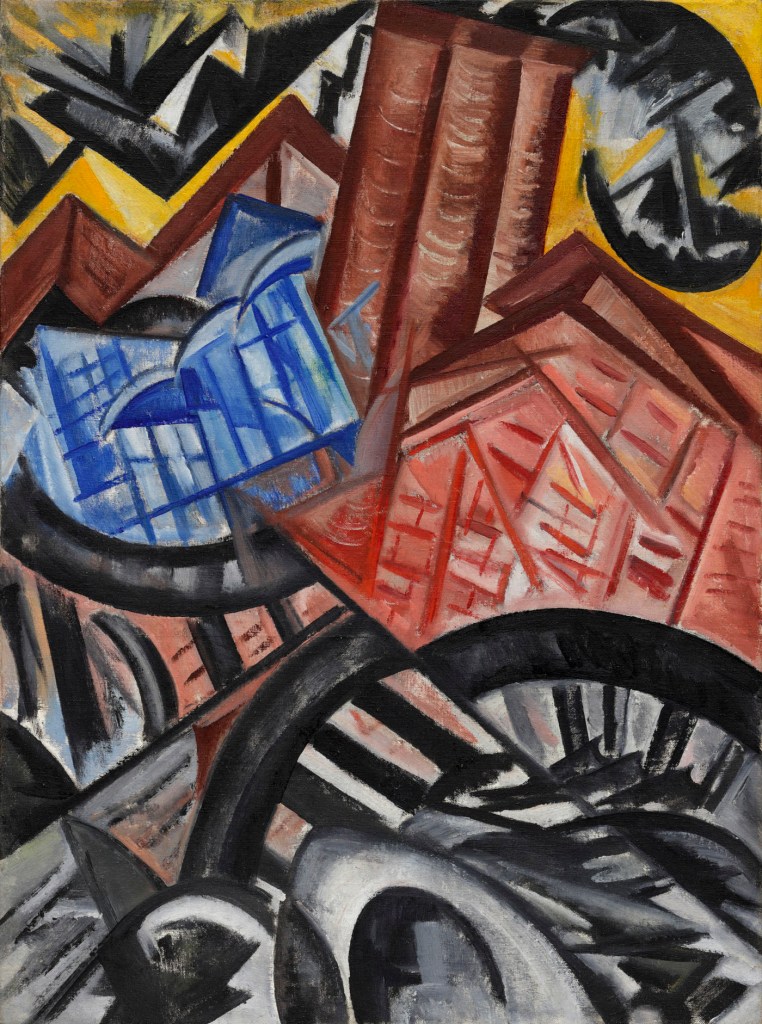

Olga Rozanova (Russian, 1886-1918)
The Factory and the Bridge
1913
Oil on canvas
32 3/4 x 24 1/4″ (83.2 x 61.6cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. The Riklis Collection of McCrory Corporation

Kazimir Malevich (Russian born Ukraine, 1878-1935)
Suprematist Composition: Airplane Flying
1915
Oil on canvas
22 7/8 x 19″ (58.1 x 48.3cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Acquisition confirmed in 1999 by agreement with the Estate of Kazimir Malevich and made possible with funds from the Mrs. John Hay Whitney Bequest (by exchange)
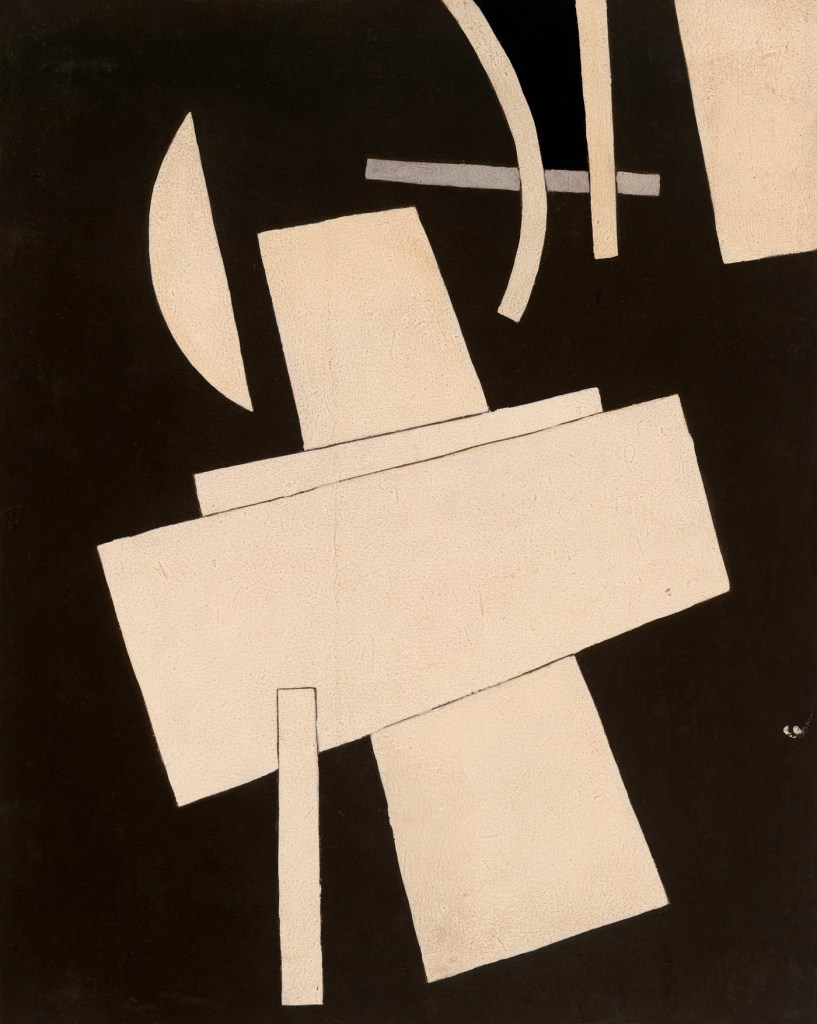
Lyubov Popova (Russian, 1889-1924)
Untitled
c. 1916-1917
Gouache on board
19 1/2 x 15 1/2″ (49.5 x 39.5cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. The Riklis Collection of McCrory Corporation
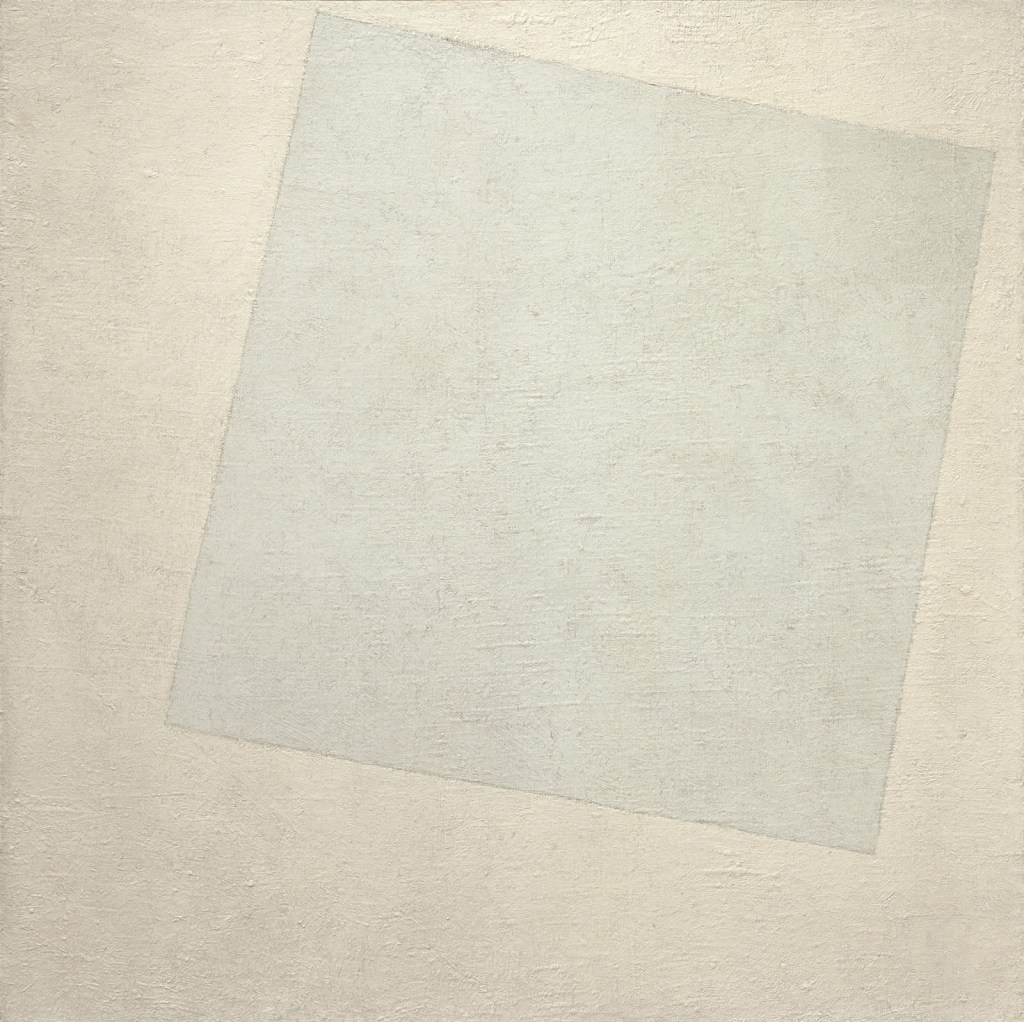
Kazimir Malevich (Ukrainian, 1878-1935)
Suprematist Composition: White on White
1918
Oil on canvas
31 1/4 x 31 1/4″ (79.4 x 79.4cm)
1935 Acquisition confirmed in 1999 by agreement with the Estate of Kazimir Malevich and made possible with funds from the Mrs. John Hay Whitney Bequest (by exchange)

Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Non-Objective Painting no. 80 (Black on Black)
1918
Oil on canvas
32 1/4 x 31 1/4″ (81.9 x 79.4cm)
Gift of the artist, through Jay Leyda
This work belongs to a series of eight black paintings Rodchenko made in direct response to a group of white paintings of the same year by the older and more established artist Kazimir Malevich. Malevich relied on a severely reduced palette of whites to suggest a floating form in an infinite spatial expanse; Rodchenko moved toward eliminating colour completely in order to focus instead on the material quality of the paintings surface. “Where the black works are winning is in the fact that they have no colour, they are strong through painting …,” declared artist Varvara Stepanova, Rodchenko’s wife. “Nothing besides painting exists.” Both series were first shown in Moscow in April 1919, in the 10th State Exhibition: Non-Objective Art and Suprematism. The black works were received with enthusiasm and helped establish Rodchenko as a leader of the Russian avant-garde.
MoMA gallery label 2015
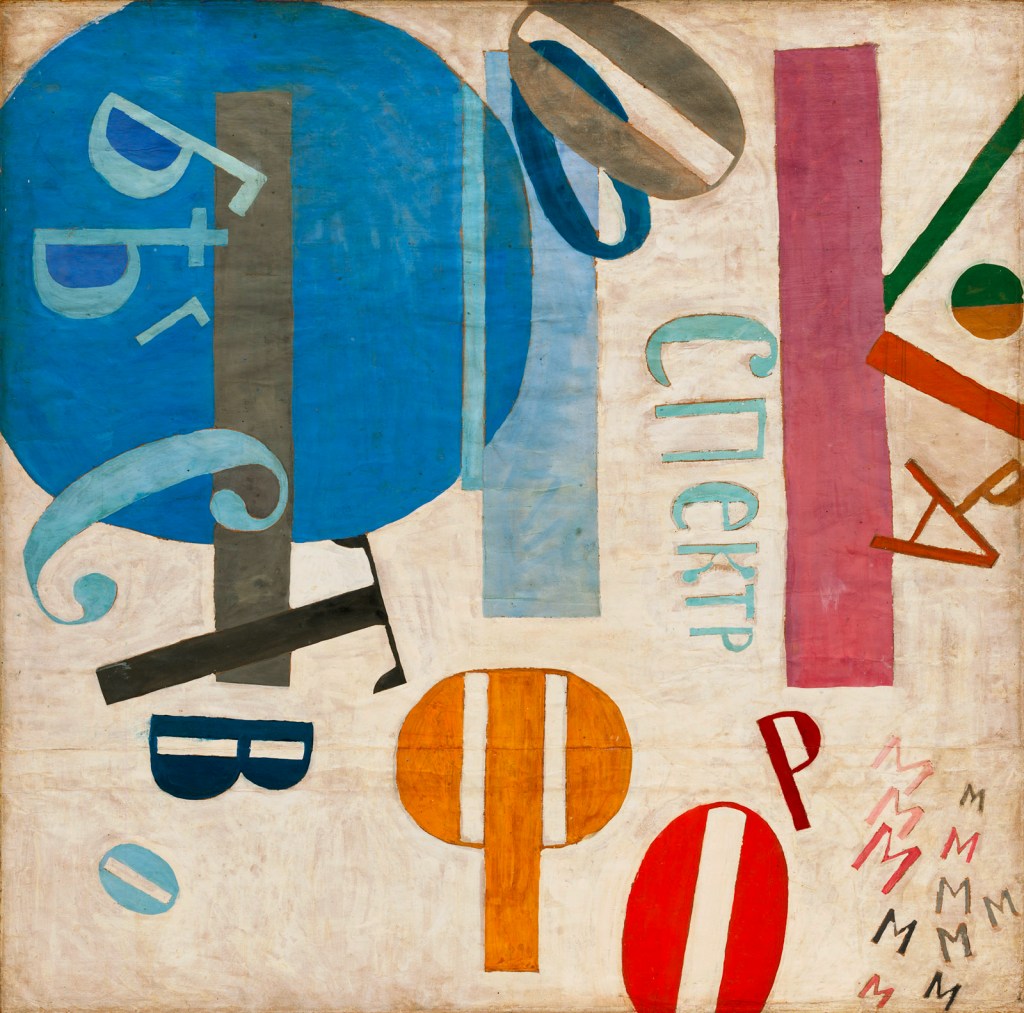

Jean Pougny (Ivan Puni) (Russian born Finland, 1892-1956)
Flight of Forms
1919
Gouache and pencil on paper
51 1/8 x 51 1/2″ (129.7 x 130.8cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Abby Aldrich Rockefeller Fund
© 2016 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / ADAGP, Paris
A new art was needed, armed by technology and chemistry, an art that stood side by side with socialist industry, a new, militant art, which could organise the will of the masses.
Gustav Klutsis
In the first decades after the 1917 Revolution, a central focus of the nascent Soviet Union was the modernisation of its vast territories. Through a series of comprehensive economic development plans, the socialist state attempted to institute rapid industrialisation, collectivise agriculture, achieve nationwide literacy, and update the infrastructure of towns and cities. Artists, often working in official capacities, captured these aspirations in a variety of projects, many of which were propagandistic.
Some turned to agitational photomontage, in which photographs and images culled from mass media were spliced together to create ideologically charged designs for posters, book covers, advertisements, and postcards. Artists also made illustrations for children’s books that feature didactic tales aimed at rallying the next generation of Soviet citizens. Architects were tasked with reconceiving domestic and civic spaces in order to advance a communal way of life, reflected in studies for buildings and triumphant photographs of construction. While much of this work celebrates Soviet might and ingenuity, Joseph Stalin’s repressive regime began to reign in the activities of artists and other cultural producers in the 1920s, terminating this period of utopian innovation in the early 1930s with the declaration of Socialist Realism as the official Soviet style.
El Lissitzky (Russian, 1890-1941)
Proun 1 D
1920
One from a portfolio of eleven lithographs
Composition: 8 7/16 x 10 9/16″ (21.5 x 26.9cm)
Sheet: 13 1/2 x 17 5/8″ (34.3 x 44.7cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Vincent d’Aquila and Harry Soviak Bequest, by exchange, Committee on Prints and Illustrated Books Fund, Orentreich Family Foundation, Sue and Edgar Wachenheim III Endowment, Mrs. Sash A. Spencer, Sue and Edgar Wachenheim III, Peter H. Friedland, Maud I. Welles, Deborah Wye Endowment Fund, Riva Castlemen Endowment Fund, Lily Auchincloss Fund, Monroe Wheeler Fund, and John M. Shapiro
© 2016 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn
El Lissitzky (Russian, 1890-1941)
Proun 19D
1920 or 1921
Gesso, oil, varnish, crayon, coloured papers, sandpaper, graph paper, cardboard, metallic paint, and metal foil on plywood
38 3/8 x 38 1/4″ (97.5 x 97.2cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Katherine S. Dreier Bequest
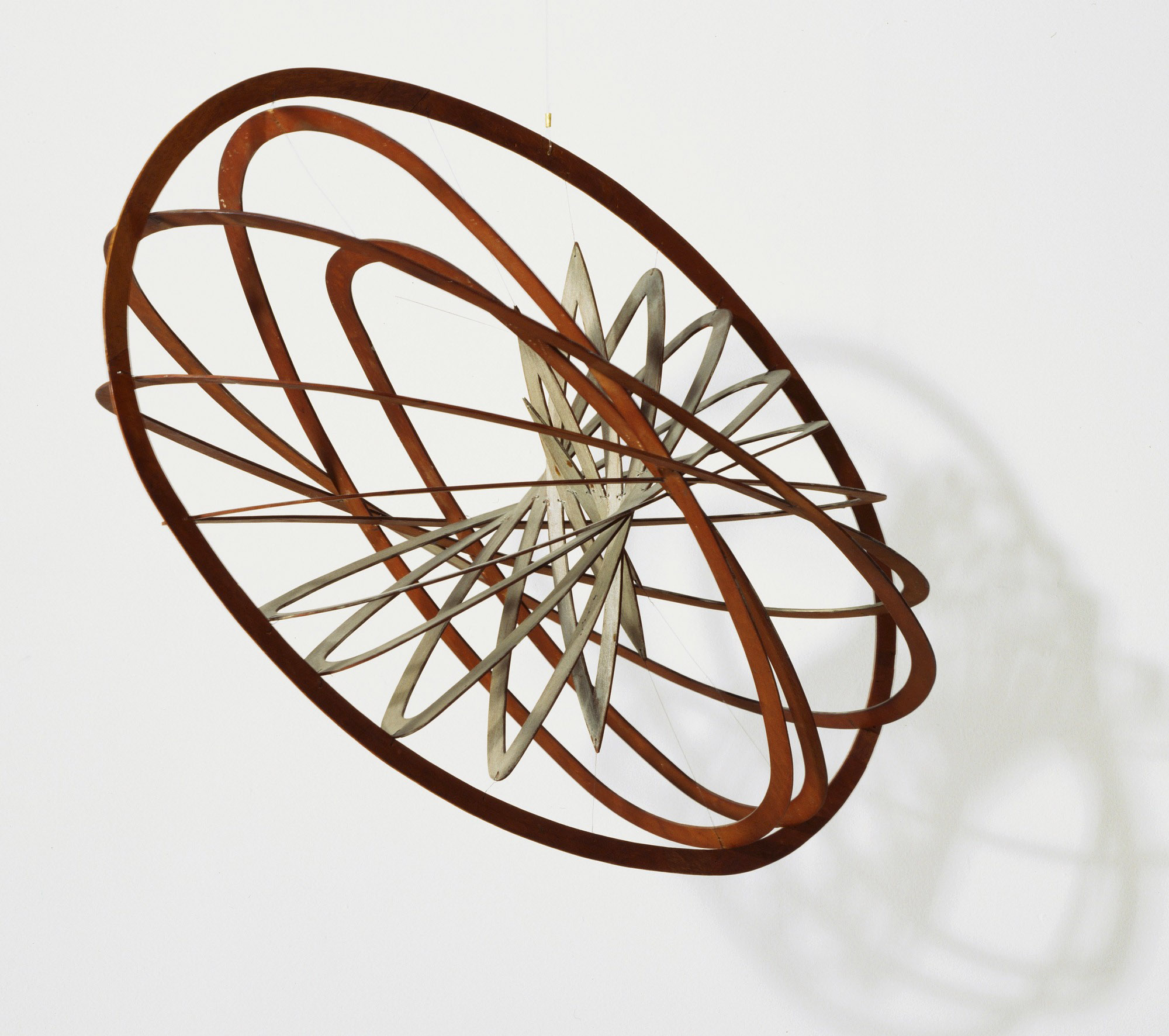
Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Spatial Construction no. 12
c. 1920
Plywood, open construction partially painted with aluminium paint, and wire
24 x 33 x 18 1/2″ (61 x 83.7 x 47cm)
Acquisition made possible through the extraordinary efforts of George and Zinaida Costakis, and through the Nate B. and Frances Spingold, Matthew H. and Erna Futter, and Enid A. Haupt Funds
The nesting ovals that compose this construction were measured out on a single sheet of aluminium-painted plywood, precisely cut, then rotated and suspended to make a three-dimensional object suggestive of planetary orbits. It was made at a time of both civic turmoil and great possibility in Russia, when Rodchenko and his fellow Constructivist artists sought to apply aesthetic ideals to everyday materials. They hoped their approach to art would help create a new language for the Communist state. Reflecting back on this time, Rodchenko said, “We created a new understanding of beauty, and enlarged the concept of art.”
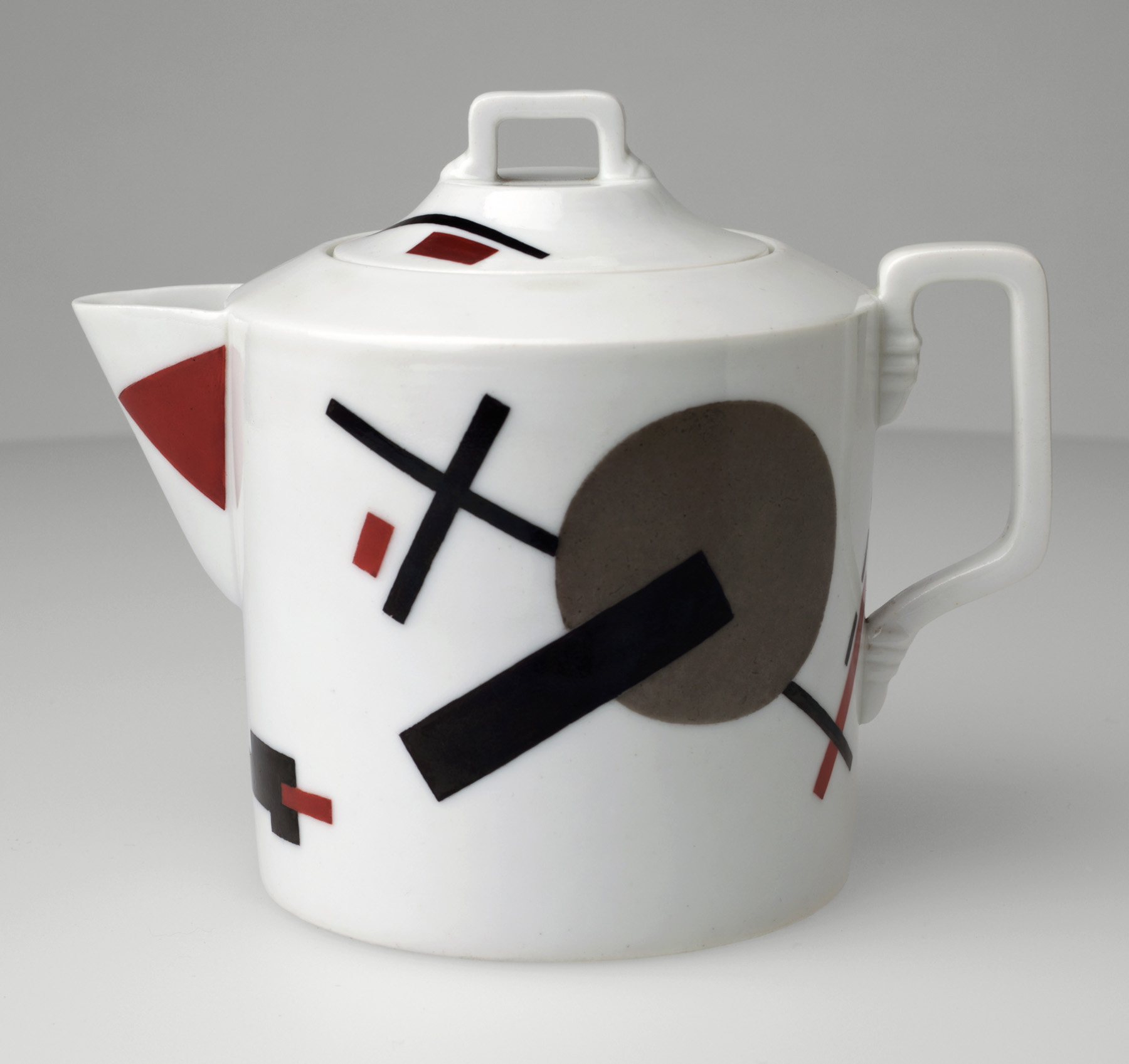
Nikolai Suetin (Russian, 1897-1954)
Teapot
c. 1923
Porcelain with overglaze painted decoration
5 1/2 x 4 1/2″ (14 x 11.4cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Estée and Joseph Lauder Design Fund
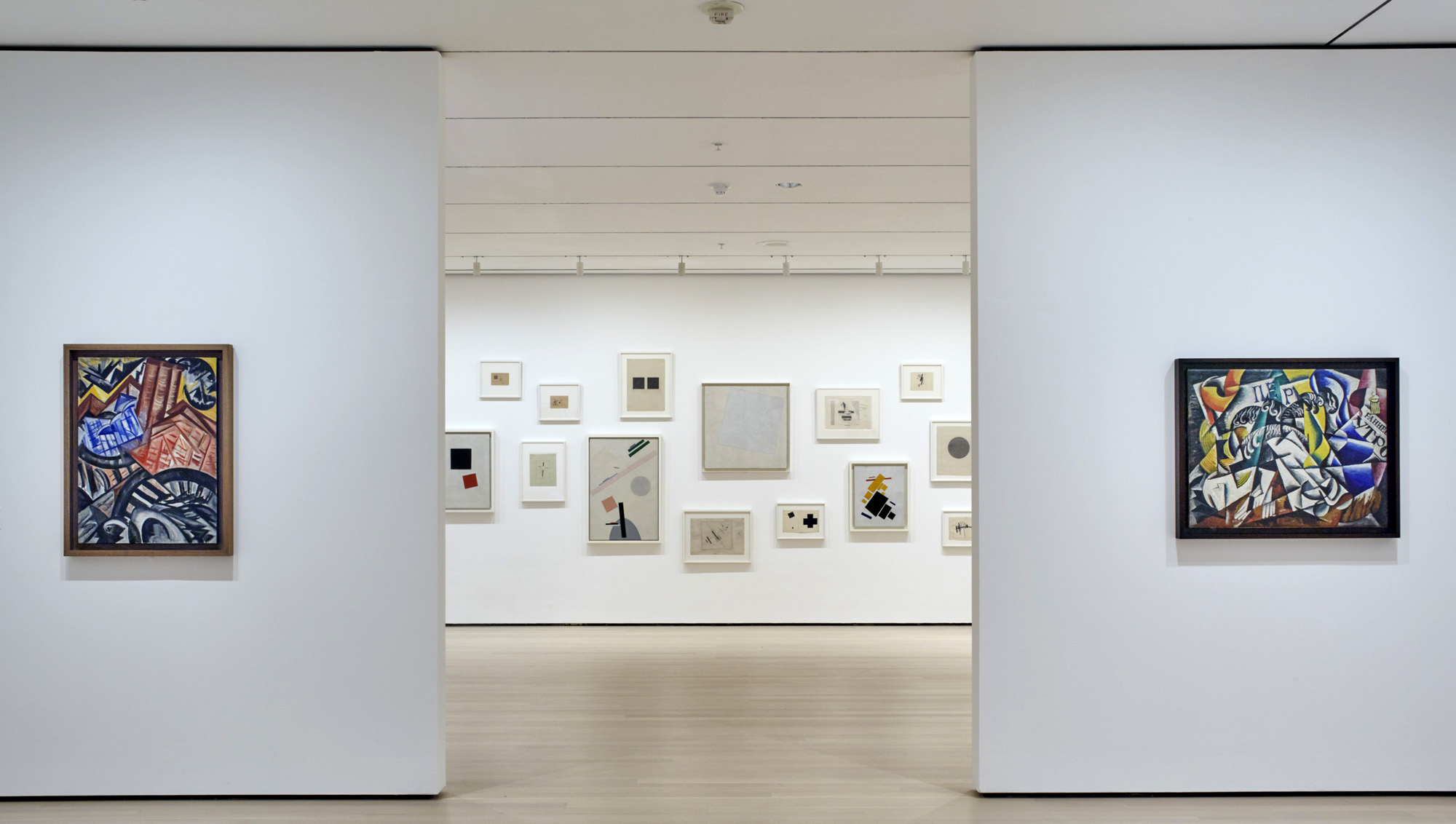
Installation views of A Revolutionary Impulse: The Rise of the Russian Avant-Garde. The Museum of Modern Art, New York, December 3, 2016 – March 12, 2017
© 2016 The Museum of Modern Art
Photo: Robert Gerhardt
The Museum of Modern Art presents A Revolutionary Impulse: The Rise of the Russian Avant-Garde, an exhibition that brings together 260 works from MoMA’s collection, tracing the arc of a period of artistic innovation between 1912 and 1935. The exhibition will be on view December 3, 2016 – March 12, 2017. Planned in anticipation of the centennial year of the 1917 Russian Revolution, the exhibition highlights breakthrough developments in the conception of Suprematism and Constructivism, as well as in avant-garde poetry, theatre, photography, and film, by such figures as Alexandra Exter, Natalia Goncharova, El Lissitzky, Kazimir Malevich, Vladimir Mayakovsky, Lyubov Popova, Alexandr Rodchenko, Olga Rozanova, Vladimir and Georgii Stenberg, and Dziga Vertov, among others. The exhibition features a rich cross-section of works across several mediums – opening with displays of pioneering non-objective paintings, prints, and drawings from the years leading up to and immediately following the Revolution, followed by a suite of galleries featuring photography, film, graphic design, and utilitarian objects, a transition that reflects the shift of avant-garde production in the 1920s. Made in response to changing social and political conditions, these works probe and suggest the myriad ways that a revolution can manifest itself in an object. A Revolutionary Impulse: The Rise of the Russian Avant-Garde is organised by Roxana Marcoci, Senior Curator, Department of Photography, and Sarah Suzuki, Curator, Department of Drawings and Prints; with Hillary Reder, Curatorial Assistant, Department of Drawings and Prints.
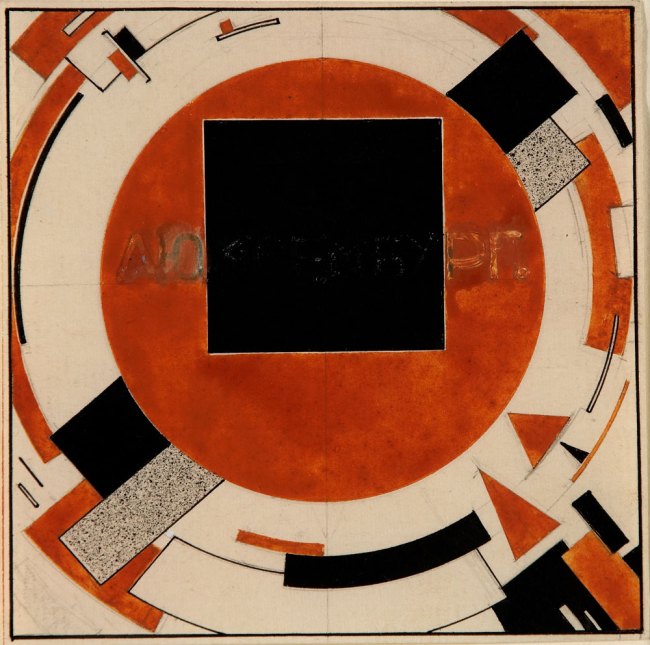
A series of works by artists including Natalia Goncharova and her husband and artistic collaborator Mikhail Larionov open the exhibition. Goncharova and Larionov sought to combine Western European developments such as Cubism and Futurism with a distinctly Russian character, drawing on history, folklore, and religious motifs for inspiration. One outgrowth of their efforts was Rayonism, an abstract style that derived its name from the use of dynamic rays of contrasting colour, exemplified in Goncharova’s Rayonism, Blue-Green Forest (1913). A hallmark of this period was a fertile collaboration between painters and poets that resulted in illustrated books, also on view in the exhibition. These collaborations rejected fine-art book traditions in favour of small, distinctly handmade volumes, such as the rare book Worldbackwards (1912), shown in an astonishing four variations, each with a unique, collaged cover.
Radical new efforts in painting and poetry are also featured, such as an unpublished, uncut sheet from poets Aleksei Kruchenykh and Velimir Khlebnikov’s Te li le (1914), with images by Olga Rozanova. The sheet features a poetic language conceived in 1913 by the pair called Zaum (“transrational,” “beyonsense,” or “transreason”), which frees letters and words from specific meanings, instead emphasising their aural and visual qualities. Painters likewise sought to push their medium to its limits, dismissing the strictures of realism and rationality in favour of advancing new abstract forms. The Last Futurist Exhibition of Paintings 0.10 (zeroten), held in Petrograd (now St. Petersburg) in December 1915, highlighted two new models of abstraction. One, developed by Vladimir Tatlin, focused on a group of nonrepresentational Counter-Reliefs (“reliefs with a particular pronounced tension”). An example can be found in the exhibition in the exceedingly rare Brochure for Tatlin’s counter-reliefs exhibited at 0.10 (1915). The other, proposed by Kazimir Malevich, unveiled a radically new mode of abstract painting that abandoned reference to the outside world in favour of coloured geometric shapes floating against white backgrounds. Because this new style claimed supremacy over the forms of nature, Malevich called it Suprematism. The exhibition includes Malevich’s Suprematist Composition: Airplane Flying (1915), which was featured in 0.10, and Suprematist Composition: White on White (1918), which ranks among the most iconoclastic paintings of its day.
While Suprematism’s focus on pure form had a spiritual bent, the adherents of Constructivism privileged the creation of utilitarian objects with orderly, geometric designs. In 1918, Rodchenko made Non-Objective Painting no. 80 (Black on Black), one of a series of eight black paintings he conceived in direct response to the group of white paintings by Malevich. By eliminating colour almost completely, Rodchenko underscored the material quality of the painting’s surface. Around this time, he also produced a series of “spatial constructions” focused on kineticism, marking a significant leap from his exploration of the painted surface to three-dimensional objects. 5 x 5 = 25: An Exhibition of Painting (1921), a brochure for an exhibition of the same title, typed by Varvara Stepanova, features contributions from Rodchenko, Lyubov Popova, Alexandra Exter, and Aleksandr Vesnin. Held in Moscow at the All-Russian Union of Poets in September 1921, the exhibition featured five works by each of the five participants, and was the Constructivist group’s last presentation of painting.
Between 1919 and 1927 El Lissitzky produced a large body of paintings, prints, and drawings that he referred to as Proun, an acronym for “Project for the Affirmation of the New” in Russian. A particular highlight is the portfolio Proun (1920), made during Lissitzky’s short but prolific period working at the art school in Vitebsk, alongside Malevich. Lissitzky asserted Proun is “the station on the way to the construction of a new form,” and in these lithographs, he arranges geometric forms in dynamic, overlapping relationships to create imagined spaces. It will be the first time this rare portfolio, acquired in 2013, will be on view. New developments in theatre are surveyed through the example of Alexandra Exter, an artist deeply engaged with theatrical design and production, including several examples of her innovative set designs and costumes for the science-fiction film Aelita (1924). These are shown alongside prints from Lissitzky’s portfolio Victory Over the Sun, which he made after seeing a 1920 restaging of the seminal Cubo-Futurist opera of the same name, and features characters from the production transformed into “electromechanical” figurines.
As the 1920s progressed, photography and film surpassed painting and sculpture as the chosen medium for the avant-garde, moving works from the studio to the public sphere. The exhibition includes an in-depth look at Soviet avant-garde cinema, in a gallery that features clips from seminal films by Alexander Dovzhenko, Sergei Eisenstein, Vsevolod Pudovkin, and Dziga Vertov, highlighting a variety of strategies in montage, including disjunctive cutting, extreme close-ups, unusual angles, and image superimposition. At this time, Lissitzky began to describe his work as fotopis (painting with photographs), a neologism that first appeared in the title of a maquette for a mural version of Record (1926), a photomontage included in the show. After turning away from painting, Rodchenko also found new means to build networks of communication – in photographs and book design. He collaborated with the progressive writers Nikolai Aseev, Osip Brik, Vladimir Mayakovsky, and Sergei Tret’iakov on covers and layouts for the journal Novyi LEF (1927-1928), a complete run of which is on view. Eschewing the conventional belly-button view in his photographs, Rodchenko’s pictures of this era – such as Mother (1924), Assembling for a Demonstration (1928-1930), and Pioneer Girl (1930) – favour dynamic camera angles. Advocating for a cinematic, fractured representation of his subjects, Rodchenko also tried his hand at film, designing inter-titles for Dziga Vertov’s Kino-Pravda newsreel series.
The ideology of the Revolution touched all aspects of daily life, from economy to education. The most significant artists of the day, in accordance with state orders, were soon applying avant-garde tactics to create propagandistic work that would be easily comprehensible to the Soviet public at large. The final gallery of the exhibition contains this kind of material, including children’s books created by Vladimir Lebedev and Samuil Marshak, whose book designs balanced sophistication and accessibility, drawing on Cubism and Suprematism, with stories that nourished the intellectual and visual imagination. Also on view are film posters, by the brothers Vladimir and Georgii Stenberg, which feature radical uses of typography and colour, underscoring the relationship between graphic arts and the burgeoning Soviet cinema. The Constructivist architect Iakov Chernikov applied his ideas to imagine a future reflecting the avant-garde culture of the new Soviet Union. His Architectural Fantasies: 101 Compositions in Color, 101 Architectural Miniatures (1933) featured here, however, never had a chance to materialise. Joseph Stalin’s repressive regime effectively put an end to Constructivism and other avant-garde activities in the cultural sphere by the mid-1930s.
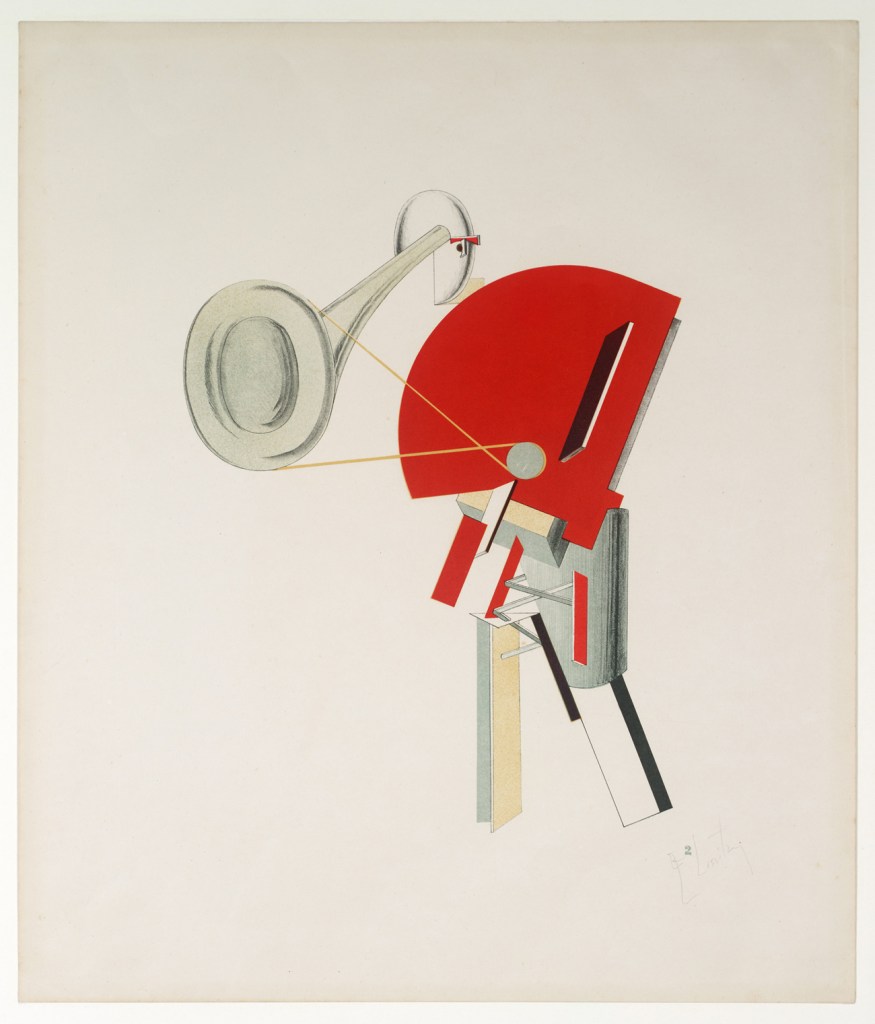

El Lissitzky (Russian, 1890-1941)
Announcer (Ansager) from Figurines: The Three-Dimensional Design of the Electro-Mechanical Show “Victory over the Sun” (Figurinen, die plastische Gestaltung der elektro-mechanischen Schau “Sieg über die Sonne”)
1920-1921, published 1923
One from a portfolio of ten lithographs
Composition (irreg.): 13 3/4 x 11 7/8″ (35 x 30.2cm)
Sheet: 21 x 18″ (53.3 x 45.7cm)
Purchase

El Lissitzky (Russian, 1890-1941)
The Globetrotter from Figurines: Plastic Representations of the Electro-Mechanical Production Entitled “Victory over the Sun” (Figurinen, die plastische Gestaltung der elektro-mechanischen Schau “Sieg über die Sonne”)
1920-1921, published 1923
One from a portfolio of ten lithographs
Composition (irreg.): 14 3/16 x 10 1/4″ (36 x 26cm)
Sheet: 21 x 17 7/8″ (53.3 x 45.4cm)
Purchase

Alexandra Exter (Russian-French, 1882-1949)
Construction
1922-1923
Oil on canvas
35 1/8 x 35 3/8″ (89.2 x 89.9cm)
The Riklis Collection of McCrory Corporation
Aleksandra Aleksandrovna Ekster (née Grigorovich) (Russian: Алекса́ндра Алекса́ндровна Эксте́р, Ukrainian: Олекса́ндра Олекса́ндрівна Е́кстер; 18 January 1882 – 17 March 1949), also known as Alexandra Exter, was a Russian and French painter and designer.
As a young woman, her studio in Kiev attracted all the city’s creative luminaries, and she became a figure of the Paris salons, mixing with Picasso, Braque and others. She is identified with the Russian/Ukrainian avant-garde, as a Cubo-futurist, Constructivist, and influencer of the Art Deco movement.
Read a fuller biography on the Wikipedia website

Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Pro eto. Ei i mne (About This. To Her and to Me)
“Pro eto” by Vladimir Mayakovsky
1923
Book with letterpress cover and illustrations
Overall (closed): 9 1/16 x 6 1/8 x 1/8″ (23 x 15.5 x 0.3cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Gift of The Judith Rothschild Foundation
Yakov Protozanov
Aelita Queen of Mars NTSC
1924
A mysterious radio message is beamed around the world, and among the engineers who receive it are Los, the hero, and his colleague Spiridonov. Los is an individualist dreamer. Aelita is the daughter of Tuskub, the ruler of a totalitarian state on Mars in which the working class are put into cold storage when they are not needed.

Alexandra Exter (Russian-French, 1882-1949)
“Guardian of Energy” (costume design for the film “Aelita” by Yakov Protozanov)
1924
Ink, gouache, and pencil on paper
21 1/4 x 14 1/4″ (54 x 36.2cm)
The J. M. Kaplan Fund, Inc.

Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Mother
1924
Gelatin silver print
8 7/8 x 6 1/2″ (22.5 x 16.5cm)
Gift of the Rodchenko family
© 2017 Aleksandr Rodchenko/Licensed by VAGA, New York, NY
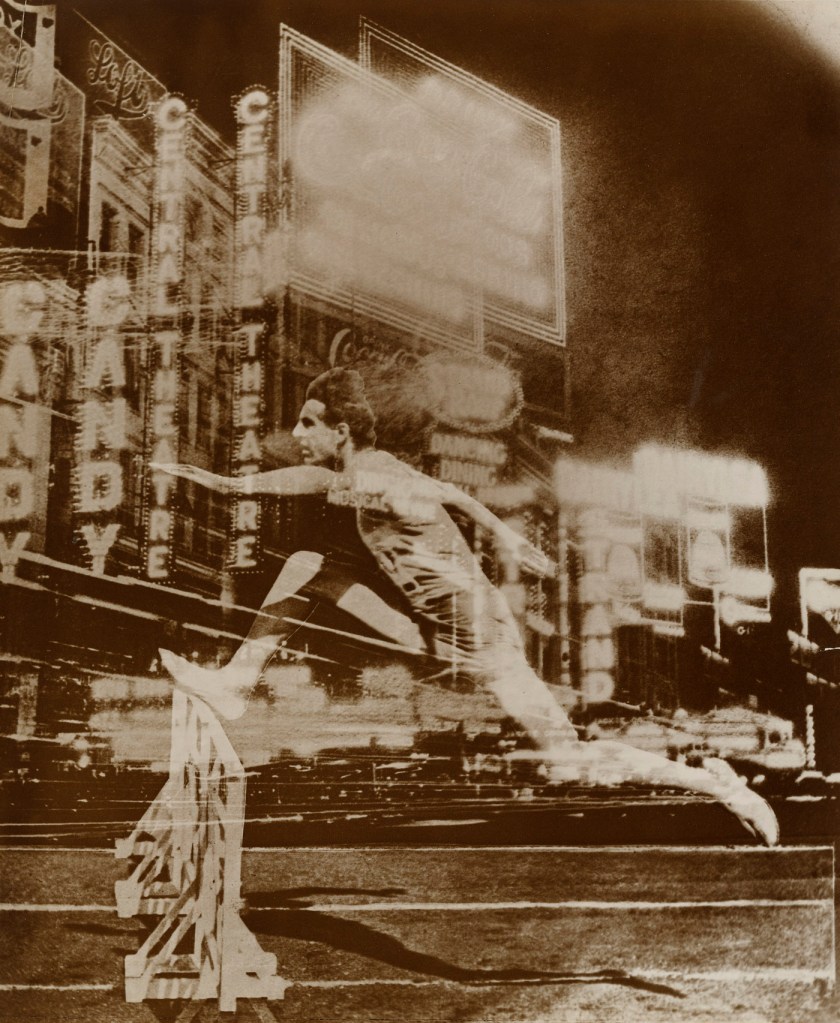

El Lissitzky (Russian, 1890-1941)
Record
1926
Gelatin silver print
10 1/2 x 8 13/16″ (26.7 x 22.4cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Thomas Walther
© 2016 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn
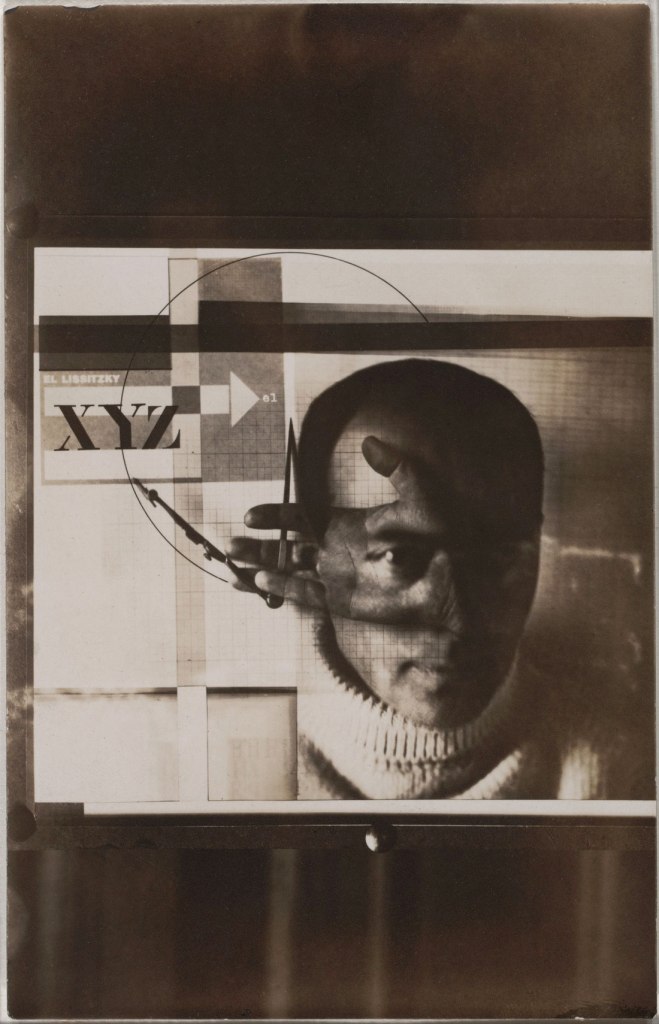

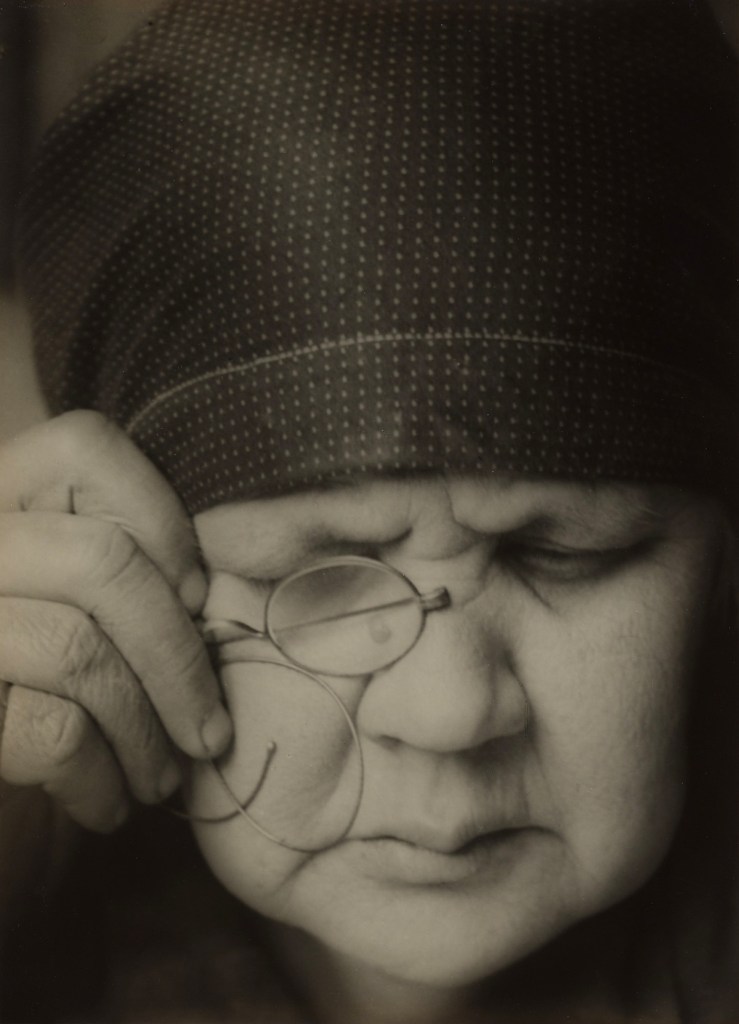
El Lissitzky (Russian, 1890-1941)
Self-Portrait
1924
Gelatin silver print
5 1/2 x 3 1/2″ (13.9 x 8.9cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Shirley C. Burden, by exchange
The essence of New Vision photography is pointedly expressed in this picture, commonly known as The Constructor, which puts the act of seeing at centre stage. Lissitzky’s hand, holding a compass, is superimposed on a shot of his head that explicitly highlights his eye: insight, it expresses, is passed through the eye and transmitted to the hand, and through it to the tools of production. Devised from six different exposures, the picture merges Lissitzky’s personae as photographer (eye) and constructor of images (hand) into a single likeness. Contesting the idea that straight photography provides a single, unmediated truth, Lissitzky held instead that montage, with its layering of one meaning over another, impels the viewer to reconsider the world. It thus marks a conceptual shift in the understanding of what a picture can be.
Gallery label from The Shaping of New Visions: Photography, Film, Photobook, April 16, 2012 – April 29, 2013
The (painted) picture fell apart together with the old world which it had created for itself. The new world will not need little pictures. If it needs a mirror, it has the photograph and the cinema.
El Lissitzky
By the mid-1920s, leading figures of the Soviet vanguard extolled photography, theatre, and film as quintessential mediums of the future. Eager to answer Lenin’s call to build a new Soviet mass culture in the wake of the Revolution, artists embraced performative and lens-based mediums for their democratising potential. They also seized the opportunity presented by stage and costume design to realise Constructivist principles in real space.
Film, one of the most experimental mediums of these years, wielded a profound influence on Soviet visual culture, particularly graphic design and photography, as well as on international cinema. Dziga Vertov redefined still and motion-picture photography with the concept of kino-glaz (cine-eye), according to which the camera lens creates a novel perception of the world. Aleksandr Rodchenko was likewise inspired by photography’s ability to energise audiences with its thrilling images of a transformed reality, which he shaped with distinctive strategies: unconventional camera angles, radical foreshortening, and close-ups. Rodchenko’s commitment to mass communication is also manifest in his engagement with the illustrated press, exemplified by his cover and layout designs for the avant-garde journal Novyi Lef.

Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Cover design for Novyi LEF: Journal of the Left Front of the Arts, no. 1
1928
Letterpress
Page: 9 1/16 x 6″ (23 x 15.2cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Gift of The Judith Rothschild Foundation

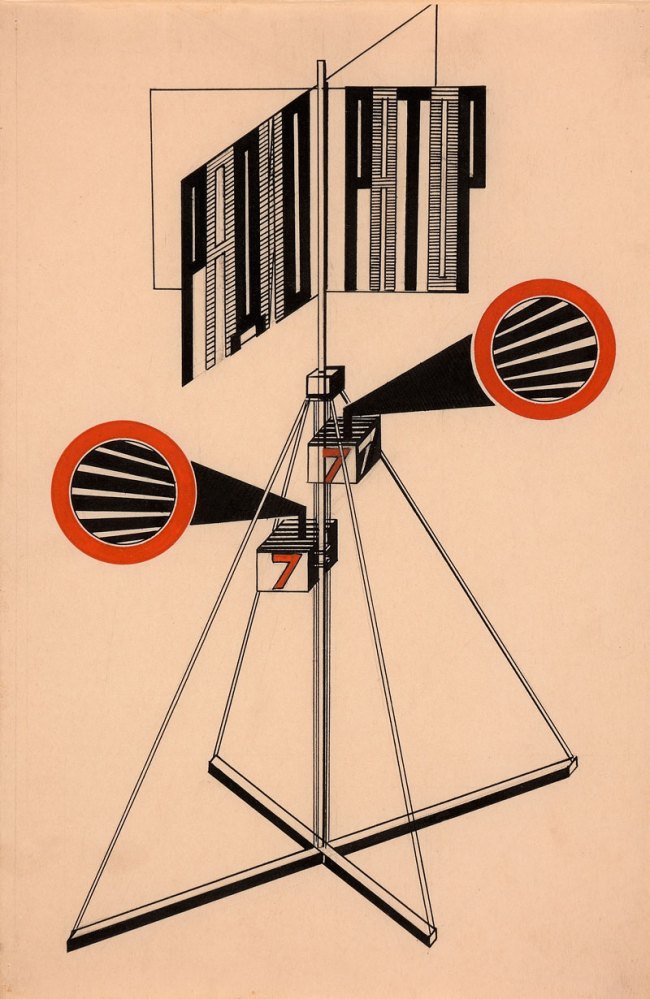
Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Novyi LEF. Zhurnal levogo fronta iskusstv (New LEF: Journal of the Left Front of the Arts), no. 7
1927
Journal with letterpress cover and illustrations
Page: 8 15/16 x 5 15/16″ (22.7 x 15.1cm)
Publisher: Gosudarstvennoe izdatel’stvo, Moscow
Gift of The Judith Rothschild Foundation
Sergei Eisenstein (Russian, 1898-1948)
Battleship Potemkin
1925
35mm film (black and white and hand-coloured, silent)
75 min.
Acquired from Reichsfilmarchiv
Vsevolod Pudovkin (Russian, 1893-1953)
Mat (Mother)
1926
35mm film (black and white, silent)
90 min.
Acquired from N.I.S., Soyuzintorkino, Moscow 1985
Mother (1926) (film based on Maxim Gorky’s famous novel)
In this film, the mother of Pavel Vlasov is drawn into the revolutionary conflict when her husband and son find themselves on opposite sides during a worker’s strike. After her husband dies during the failed strike, she betrays her son’s ideology in order to try, in vain, to save his life. He is arrested, tried in what amounts to a judicial farce, and sentenced to heavy labor in a prison camp. During his incarceration, his mother aligns herself with him and his ideology and joins the revolutionaries. In the climax of the movie, the mother and hundreds of others march to the prison in order to free the prisoners, who are aware of the plan and have planned their escape. Ultimately, the troops of the Tsar suppress the uprising, killing both mother and son in the final scenes.
Esther Shub (Ukrainian, 1894-1959)
The Fall of the Romanov Dynasty
1927
35mm film (black and white, silent)

Gustav Klutsis (Russian born Latvia, 1895-1938)
Memorial to Fallen Leaders
1927
Cover with lithographed photomontage illustrations on front and back
13 1/2 x 10 1/4″ (34.3 x 26cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Gift of The Judith Rothschild Foundation
© 2016 / Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York

Vladimir Stenberg (Russian, 1899-1982) and Georgii Stenberg (Russian, 1900-1933)
Symphony of a Big City
1928
Lithograph
41 x 27 1/4″ (104 x 69cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Marshall Cogan Purchase Fund
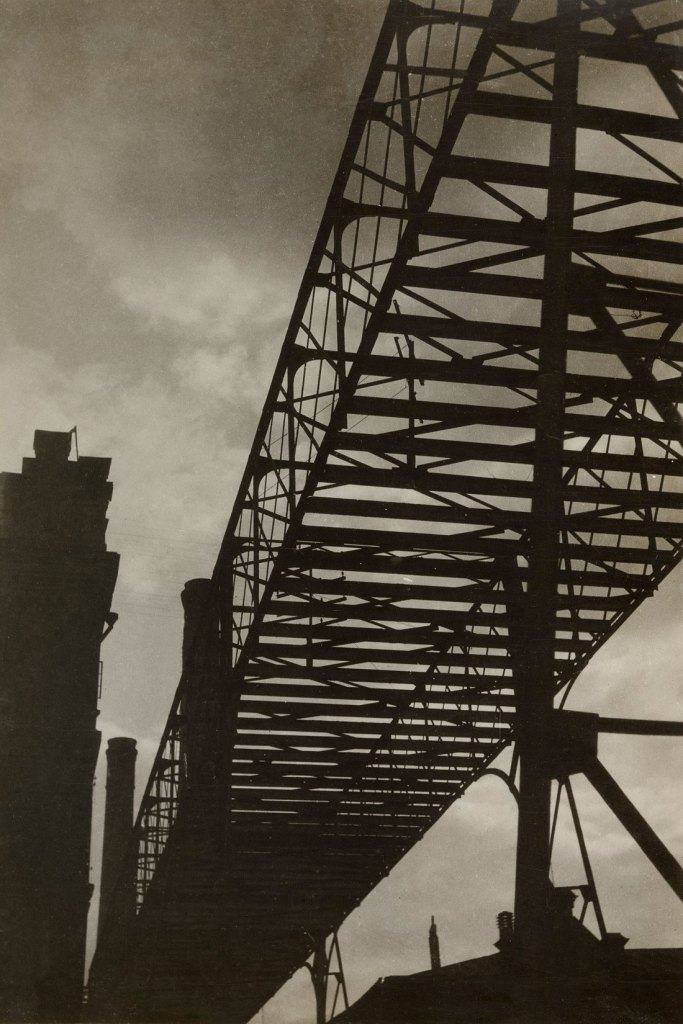

Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Untitled
1927
Gelatin silver print
8 11/16 x 5 13/16″ (22.1 x 14.8cm)
Gift of the Rodchenko family
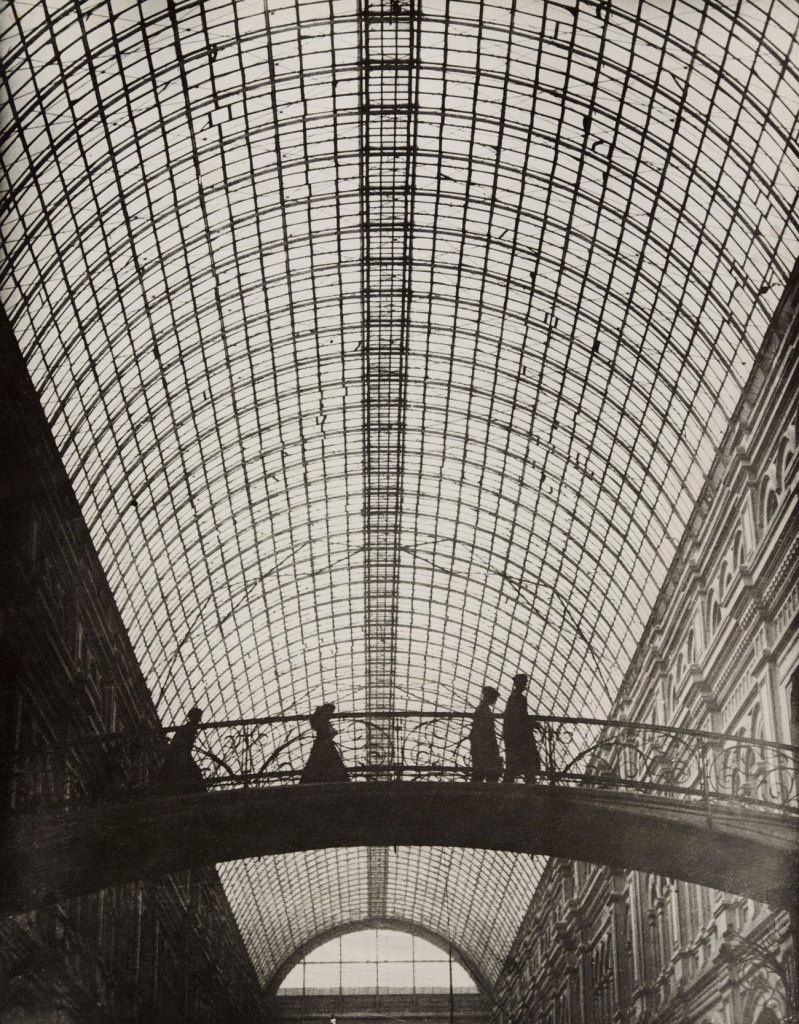

Semyon Fridlyand (Russian, 1905-1964)
In the Gallery
1927
Gelatin silver print
8 9/16 x 6 5/8″ (21.7 x 16.8cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Harold Edgerton, by exchange
Semyon Fridlyand (Russian, 1905-1964)
Semyon Fridlyand (1905-1964) was a socially-grounded photographer with a remarkably gifted eye for colour. His career would begin at Ogonyok when at age 20, he was invited to work as a photo laboratory assistant; and would conclude with Ogonyok, where he would eventually serve as its director.
Fridlyand began taking photographs after his early darkroom training at the Ogonyok magazine’s photography lab. By the 1930s, Fridlyand had become embedded in Moscow’s milieu of photojournalists. In 1930 he joined Soyuzfoto, a state-sponsored photographer’s union that helped disseminate its members’ photographs throughout the world. Through Soyuzfoto, many of his photographs were published in the internationally-distributed periodical USSR in Construction, that featured innovative graphic design by El Lissitzky, Varvara Stepanova, among others. In 1933, Fridlyand also began working for the newspaper Pravda home to the period’s most prominent photojournalists such as Arkady Shaikhet and Boris Ignatovich.
Fridlyand was both an artists and a voice for Soviet photojournalism. He and his colleagues Arkady Shaikhet, Yakov Khalip, and Max Alpert founded the Revolutionary Society of Proletarian Photographers (ROPF), dedicated to producing accessible photographs of Soviet life and labor for a wide proletarian audience. In the 1931 article “About Creative Methods” for the magazine Proletarskoe Foto, Fridlyand acknowledges how the ruling class influences the appearance of people’s everyday surroundings through their control of artistic taste and commerce. His response was a fresh photographic style that truthfully reflected the realities of the proletarian subject. His photographs for ROPF for his reason are focused on proletarian workers, and their labor on farms and in factories. Fridlyand’s subject-focused approach differed from that of his colleagues in the October organisation, who radically experimented with form and composition, and have been historically associated with Constructivism. Nevertheless members from both organisations explored formalist techniques such as worms-eye view, and unusual lighting and perspective.
Fridlyand began his explorations of colour photography in the 1940s. Using German-made Agfa colour film, he created thousands of photographs of Soviet life and recreation on diverse subject matter. In some of these photographs he continued to explore themes of labor and industry that were popular in the 1930s. In others, he captured stunning landscapes of the Caucasus, and the intricately painted folk designs around ceramic figurines. In his larger series, he captured life in the 1950s on a Kalinin Soviet Cruiser, and an idyllic summer in the sea-side town of Vladivostok. Many of these photographs were published in the popular illustrated weekly Ogonyok, where he served as director. Ogonyok continues to publish today. Fridlyand passed away in 1964 at age 59.
Anonymous text. “Semyon Fridlyand,” on the Nailya Alexander Gallery website [Online] Cited 03/12/2021
Dziga Vertov (Russian, 1895-1954)
The Man with the Movie Camera
1929
35mm film (black and white, silent)
Acquired on exchange with Gosfilmofund
Man with a Movie Camera is an experimental 1929 silent documentary film, with no story and no actors by Soviet-Russian director Dziga Vertov, edited by his wife Elizaveta Svilova. Vertov’s feature film, produced by the film studio VUFKU, presents urban life in the Soviet cities of Kiev, Kharkov, Moscow and Odessa. From dawn to dusk Soviet citizens are shown at work and at play, and interacting with the machinery of modern life. To the extent that it can be said to have “characters,” they are the cameramen of the title, the film editor, and the modern Soviet Union they discover and present in the film.
This film is famous for the range of cinematic techniques Vertov invents, deploys or develops, such as double exposure, fast motion, slow motion, freeze frames, jump cuts, split screens, Dutch angles, extreme close-ups, tracking shots, footage played backwards, stop motion animations and self-reflexive visuals (at one point it features a split-screen tracking shot; the sides have opposite Dutch angles).
In the British Film Institute’s 2012 Sight & Sound poll, film critics voted Man with a Movie Camera the 8th best film ever made. In 2014 Sight & Sound also named it the best documentary of all time.
Dziga Vertov (Russian, 1895-1954)
The Man with the Movie Camera
1929
35mm film (black and white, silent)
Acquired on exchange with Gosfilmofund
Alexander Dovzhenko (Russian, born Russia (Chernigov province) 1894-1956)
Zemlya (Earth)
1930
35mm film (black and white, silent)
62 min.
Acquired from Gosfilmofond
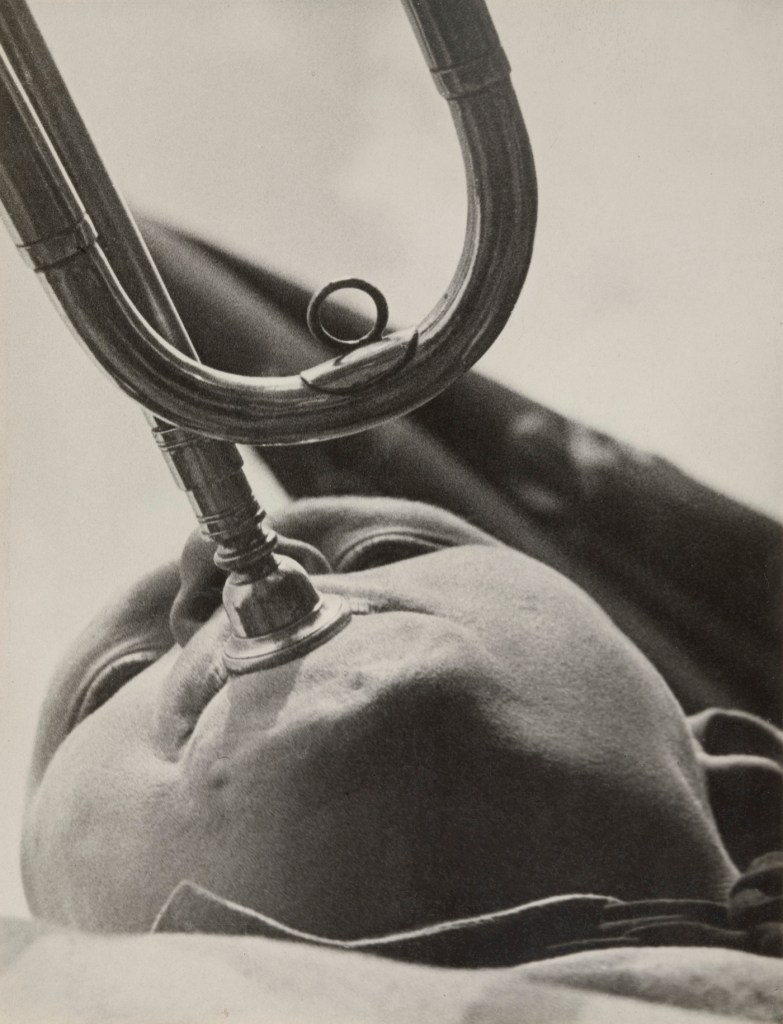
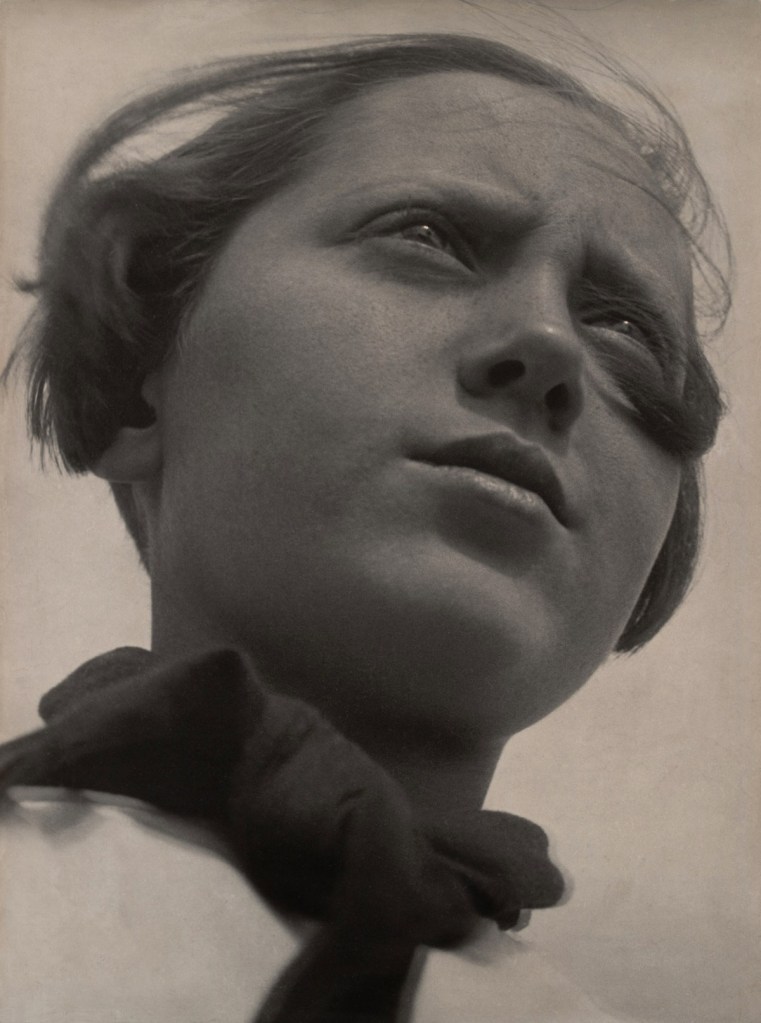
Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Pioneer with a Bugle
1930
Gelatin silver print
9 1/4 x 7 1/16″ (23.5 x 18cm)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Gift of the Rodchenko Family

Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Pioneer Girl
1930
Gelatin silver print
19 1/2 x 14 9/16″ (49.6 x 37cm)
Gift of Alex Lachmann and friends of the Rodchenko family
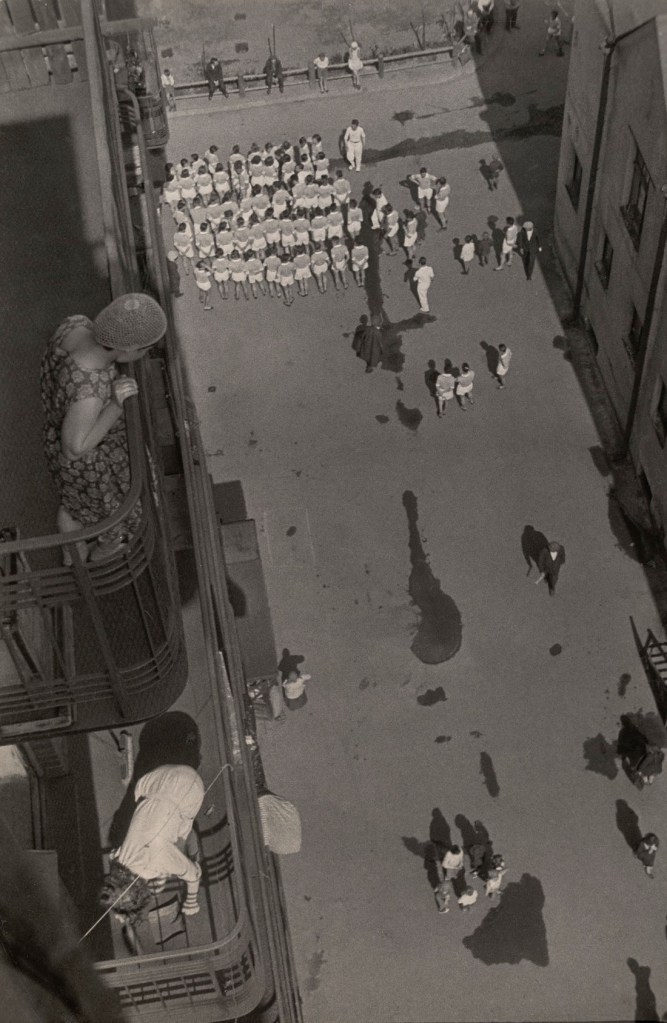

Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Assembling for a Demonstration
1928-30
Gelatin silver print
19 1/2 x 13 7/8″ (49.5 x 35.3cm)
Mr. and Mrs. John Spencer Fund
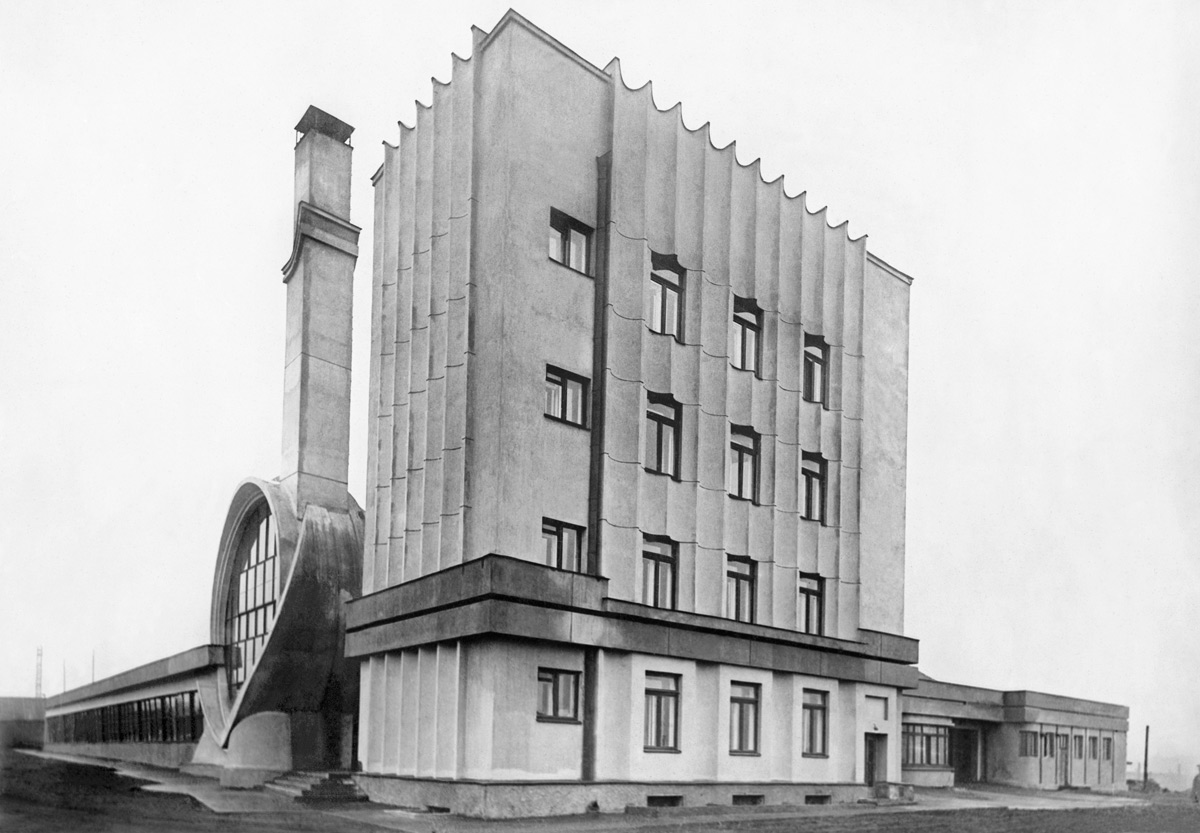
Iakov Chernikhov (Russian, 1889-1951)
Arkhitekturnye Fantazii
before 1933
Letterpress
12 x 8 7/8″ (30.5 x 22.5cm)
Arthur A. Cohen Purchase Fund
Yakov Georgievich Chernikhov (Яков Георгиевич Чернихов) (5 (17) December 1889 in Pavlograd, Yekaterinoslav Governorate, Russian Empire (now Pavlohrad, Ukraine) – 9 May 1951 in Moscow, Soviet Union) was a constructivist architect and graphic designer. His books on architectural design published in Leningrad between 1927 and 1933 are amongst the most innovative texts (and illustrations) of their time.
In his introduction to Architectural Fantasies: 101 Compositions, Iakov Chernikov’s sixth and final volume on design theory, he defended the significance of visionary paper architecture: “Not without reason, however, have great thinkers of all times accorded vast importance to fantasy, as being the forerunner of any kind of progress. To look one-sidedly at the idea of fantasy and not to consider its positive role in all fields of culture and art-this is to make a great mistake.” For Chernikov the fantasy drawing offered the architect an effective means of liberating himself from convention and imagining a future reflecting the avant-garde culture of the new Soviet Union.
As a Constructivist, and like contemporaries such as Kasimir Malevich and El Lissitzky, Chernikov was possessed by the powers of abstraction and geometry. This is reflected in the phrase Combination of curvilinear and rectilinear forms along principles of design, the rather perfunctory subtitle for Complex Architectural Invention (composition no. 49 from Architectural Fantasies): this is a formal composition based on line (curved or straight), plane, surface, body, and volume. The excitement and brilliance of Chernikov’s fantasy lie in his dynamic handling of diagonal lines, ellipses, and bright colours, presented in a dizzying axonometric view. The imagery, unabashedly industrial in character yet devoid of any context or program, is remarkably fresh and pregnant with possibility.
In producing his Architectural Fantasies Chernikov was interested not only in self-discovery but in inspiring his viewers. The seeds of his fantasies, however, never had a chance to germinate in the Soviet Union: Stalin’s repressive regime, which effectively put an end to Constructivism in the 1930s, favoured a banal architecture based on monumental classicism and Social Realism. The potential of Architectural Fantasies lay dormant until Chernikov and other Constructivist architects were “rediscovered” in the 1980s, inspiring a new generation of architects worldwide in a movement that was labeled “deconstructivist.”
Publication excerpt from Matilda McQuaid, ed., Envisioning Architecture: Drawings from The Museum of Modern Art, New York: The Museum of Modern Art, 2002, pp. 78-79
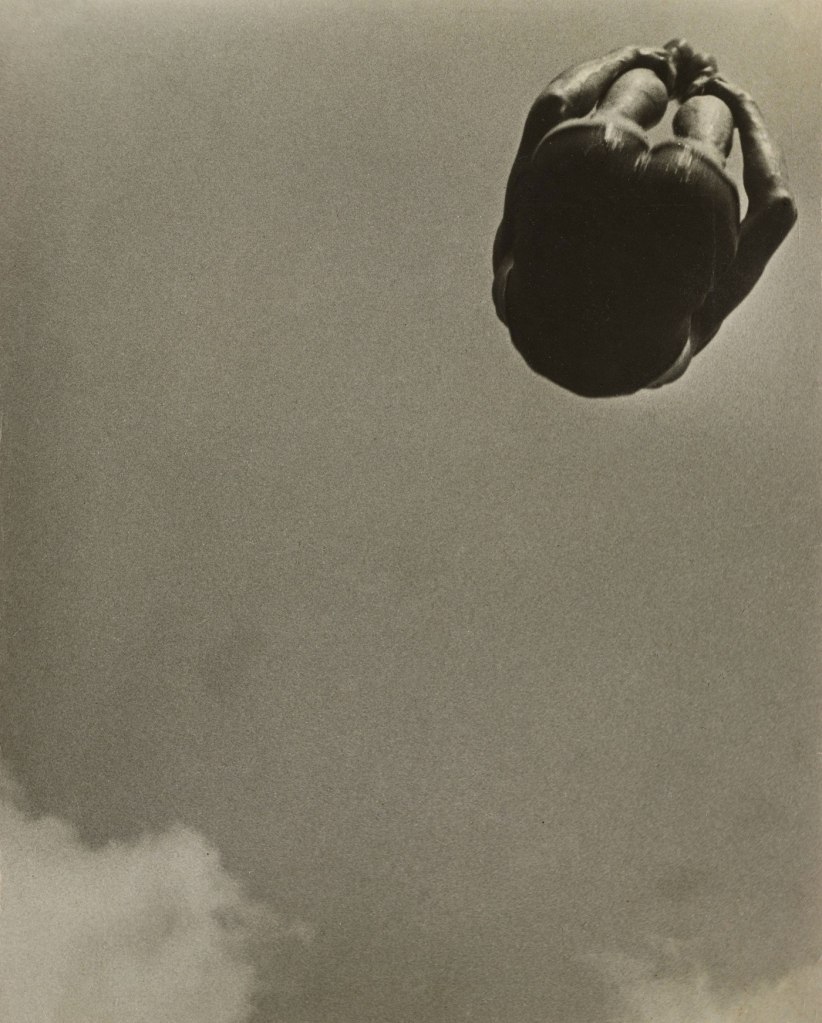

Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Dive
1934
Gelatin silver print
11 3/4 x 9 5/16″ (29.9 x 23.6cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Shirley C. Burden, by exchange
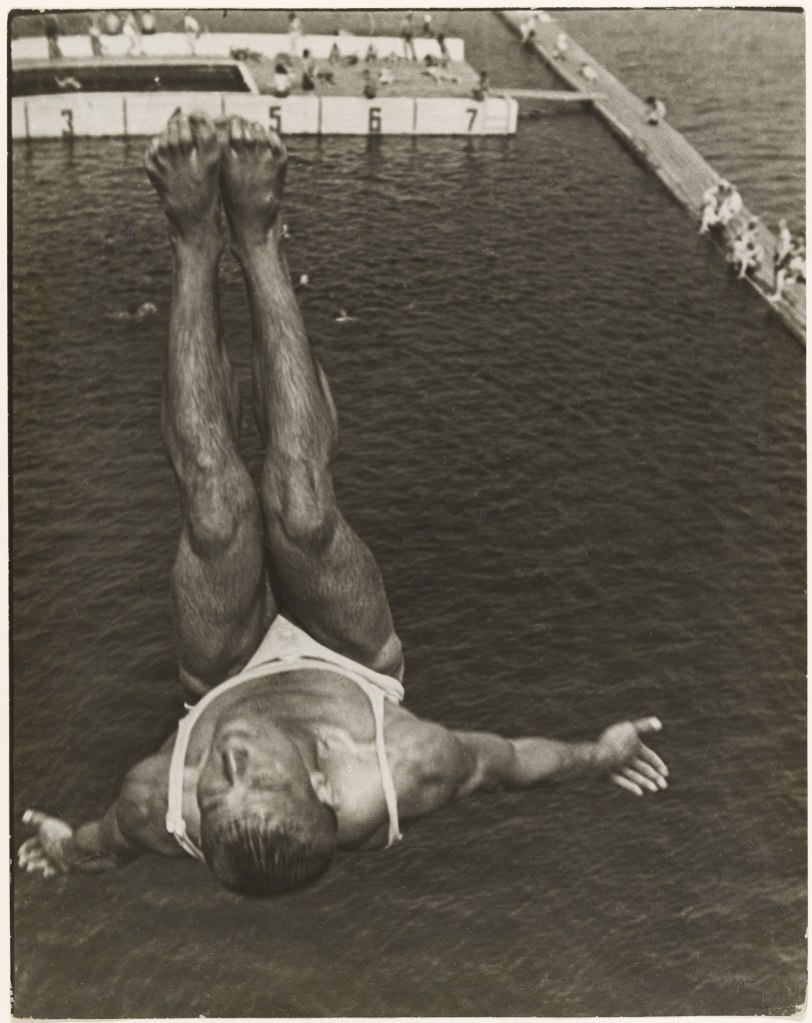

Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Dive
1934
Gelatin silver print
11 11/16 x 9 3/8″ (29.7 x 23.8cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Shirley C. Burden, by exchange
The Museum of Modern Art
11 West 53 Street
New York, NY 10019
Phone: (212) 708-9400
Opening hours:
10.30am – 5.30pm
Open seven days a week























You must be logged in to post a comment.