Exhibition dates: 7th February – 9th June, 2025
Curators: Mattie Boom and Hans Rooseboom
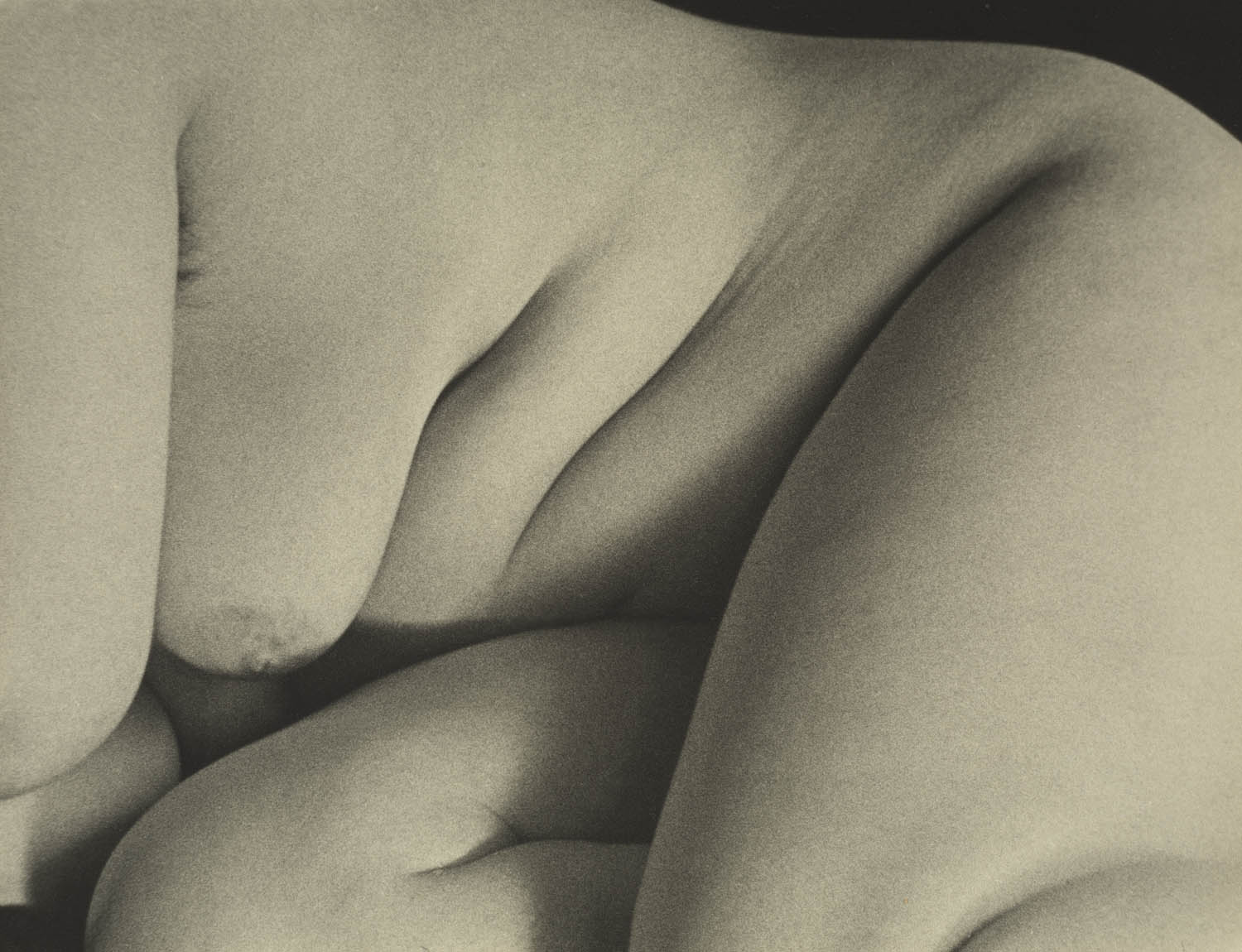
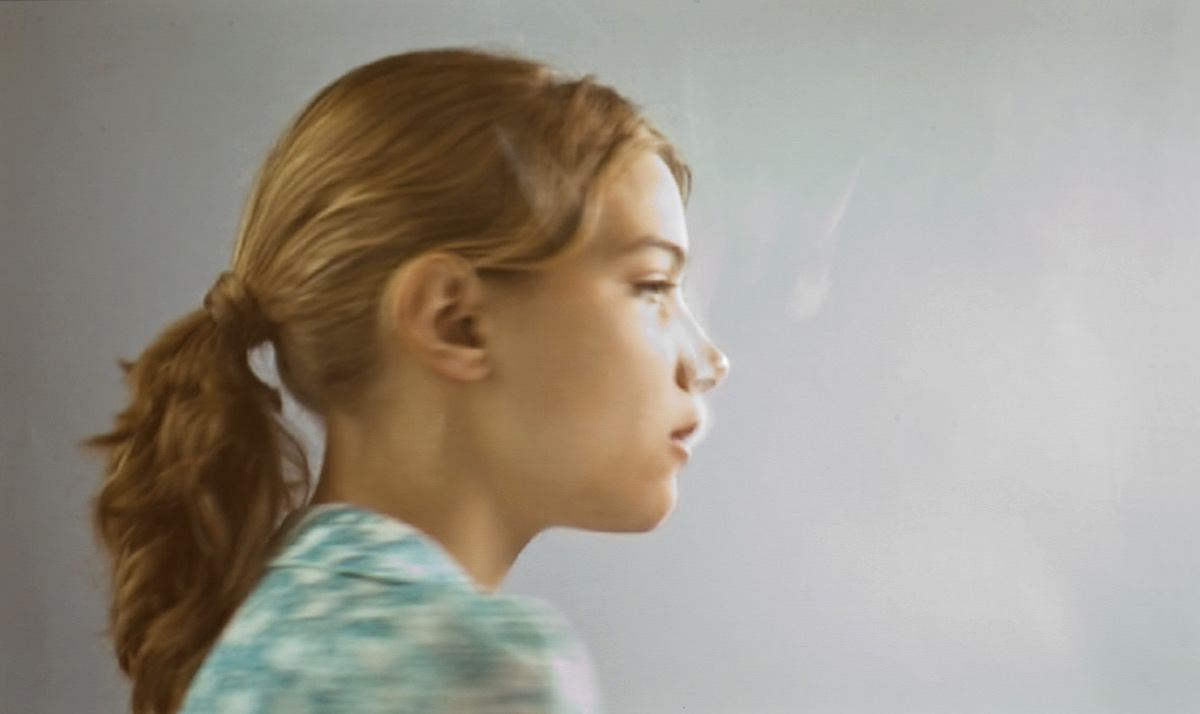
Amanda López (American, b. 1982)
Homegirls, San Francisco
2008
Inkjet print
320 x 435 mm
National Museum for American History, Washington (DC)
© Amanda López
Let’s get down to brass tacks.
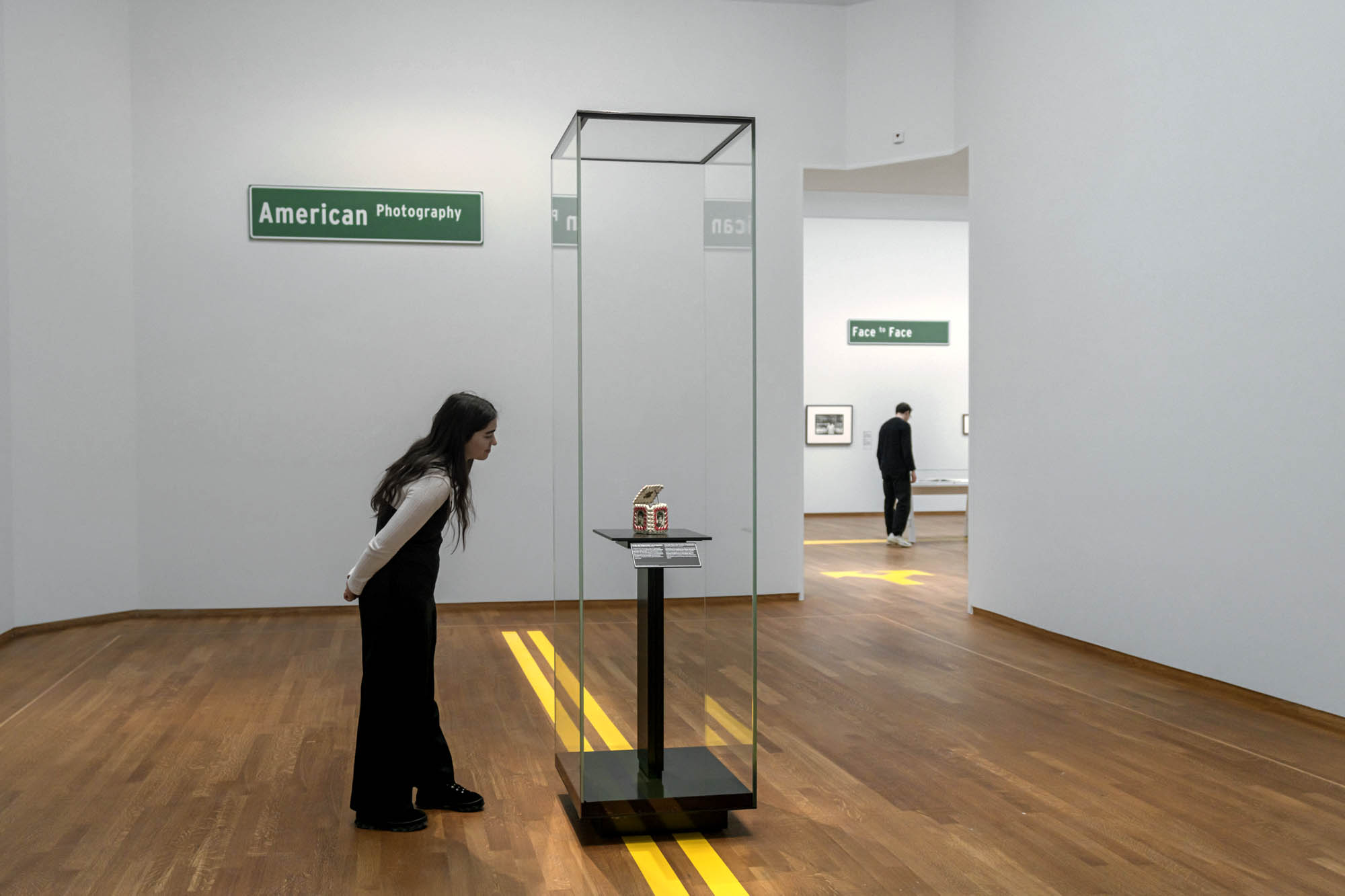
While I haven’t physically seen this exhibition – according to Rijksmuseum “the Netherlands’ first major survey exhibition of American photography… the first comprehensive survey of American photography in Europe … reflect[ing] the rich and multifaceted history of photography in the United States. The exhibition presents the country as seen through the eyes of American photographers, and shows how the medium has permeated every aspect of our lives: in art, news, advertising and everyday life” – you can glean a lot about an exhibition from the installation photographs.
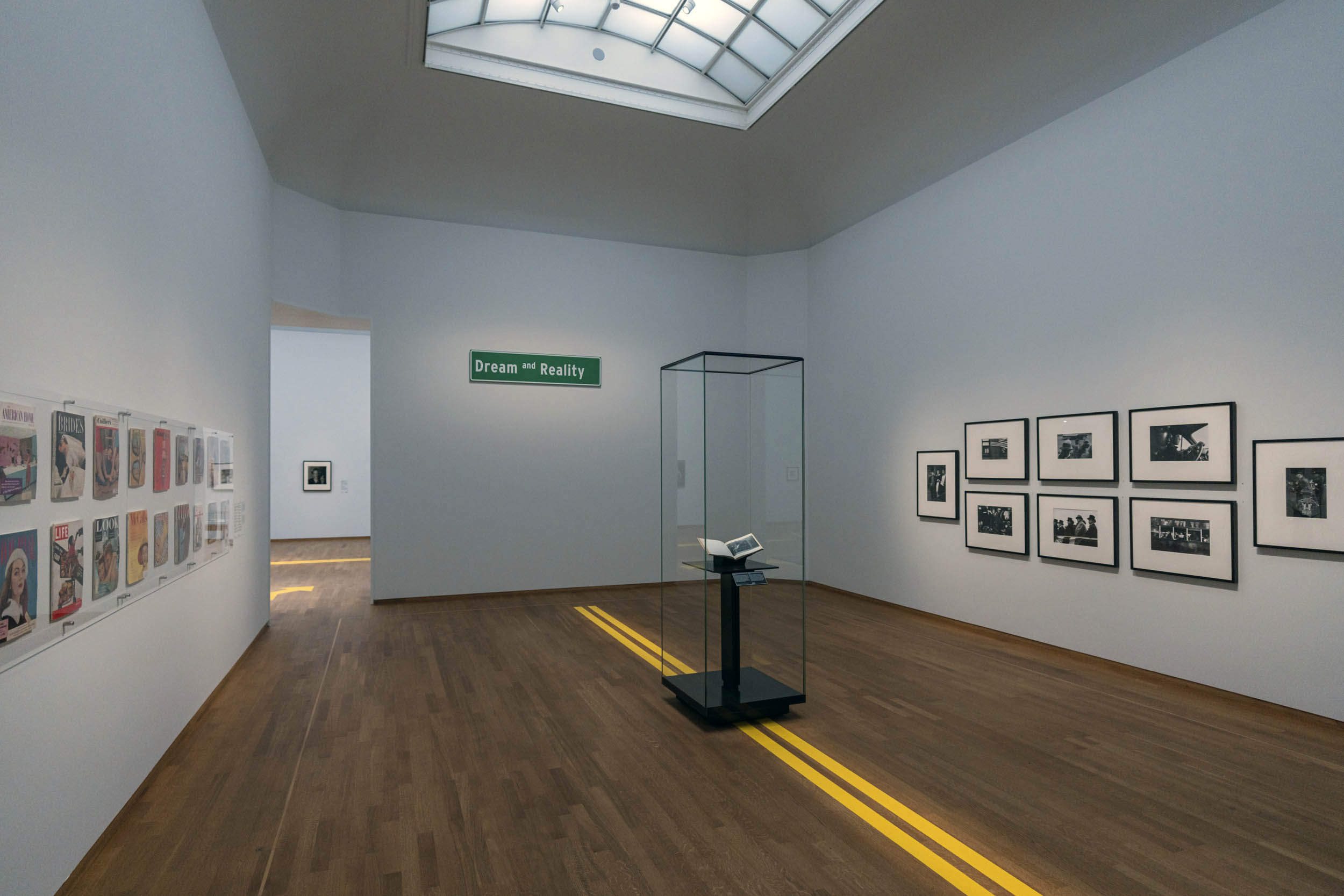
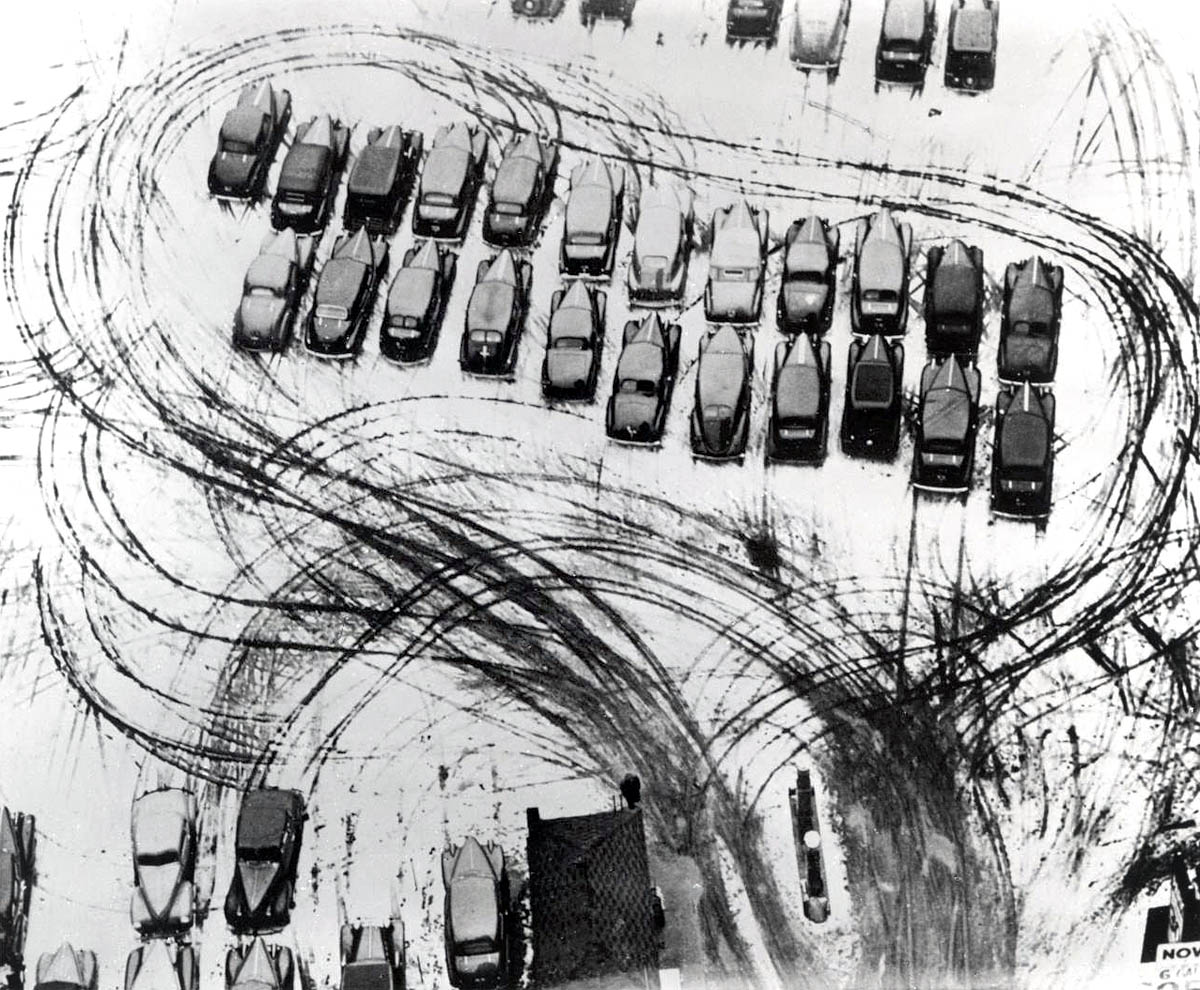
The feeling I get from the installation photographs is of a particularly meagre offering – gallery halls with minimal photographs, huge empty spaces (just look at the installation photograph Curio box made of cigarette packets with portraits of roommates, late 1960s below) – and to then consider this is supposed to be “the first comprehensive survey of American photography in Europe” and reflect the large photographic holdings of the Rijksmuseum. Really? You wouldn’t really know it from looking at “the show”.
Perhaps the problem stems from the rationale of the exhibition:
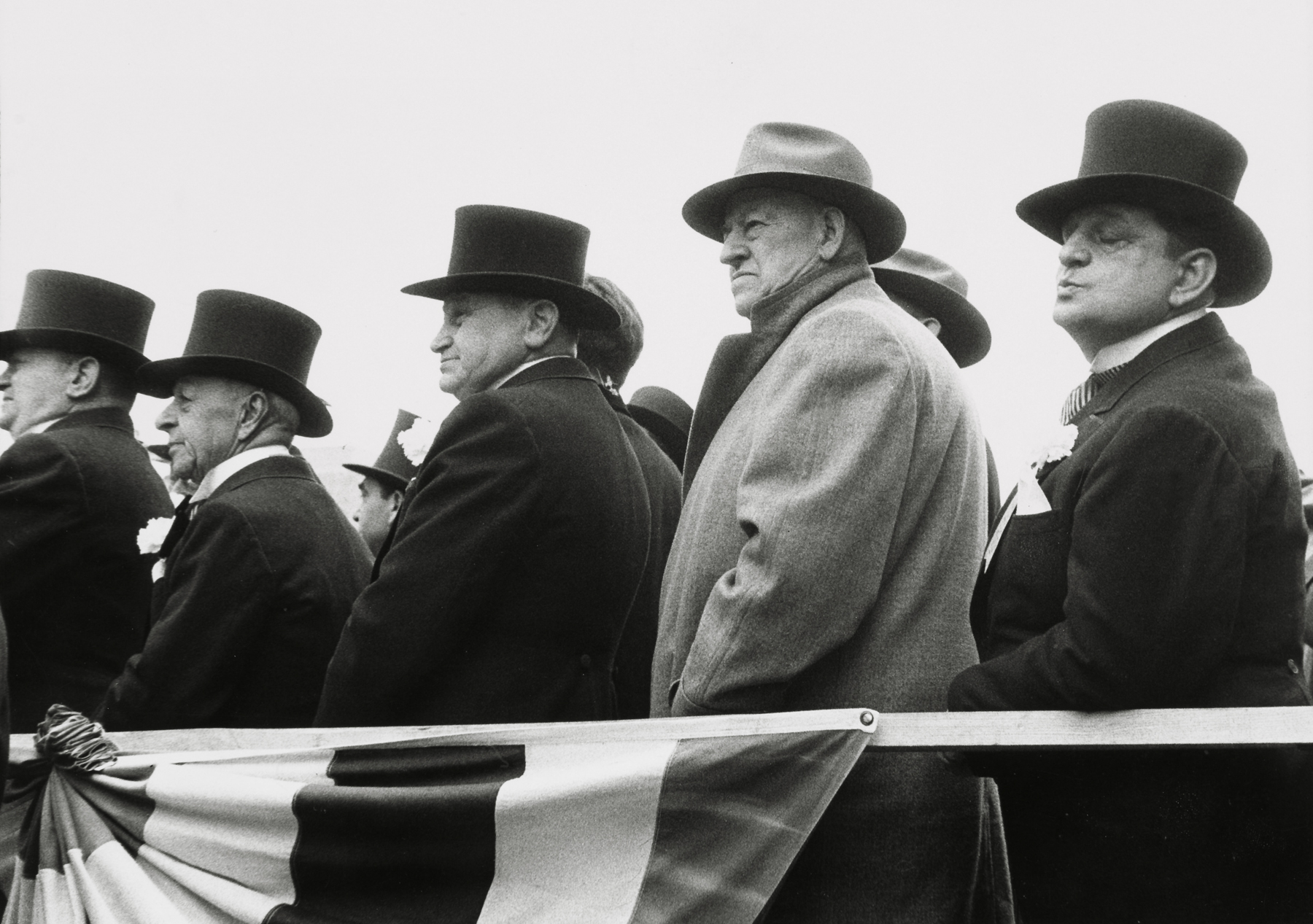
“There is no hierarchy to the selection. A sequence of rooms present numerous fields – portraiture, landscape, advertising work, art photography – like chapters in a novel. “We tried to find surprising images and things we’ve never seen before,” says Boom. The result is a broad mix, shaped with co-curator Hans Rooseboom, of anonymous photography, commercial work, news coverage, medical prints and propaganda, presented in tandem with masterpieces such as Robert Frank’s enigmatic picture of a woman watching a New Jersey parade in 1955, her face partially obscured by an unfurled Stars and Stripes.”1 (see below)
The phrase “a broad mix” says it all: a mishmash of anonymous photography, commercial work, fine art photography, the political power of photography, photographs on racism, war, etc., … taking on too much in one exhibition (the American landscape is largely absent from the walls), proclaiming to be a comprehensive survey of American photography. An impossible task.
“The exhibition has deliberately departed from a “top 100” approach, Rooseboom [one of the curators] adds, stating “that would have been too easy”.”2
Easy to say (and move away from) but not easy to do…
What I feel is lacking in this subjective selection (all exhibitions are subjective) is the focused “energy” present in American photography radiating from the wall – the energy that documents and imagines the growth of a nation and the passion of the artists that capture that energy.
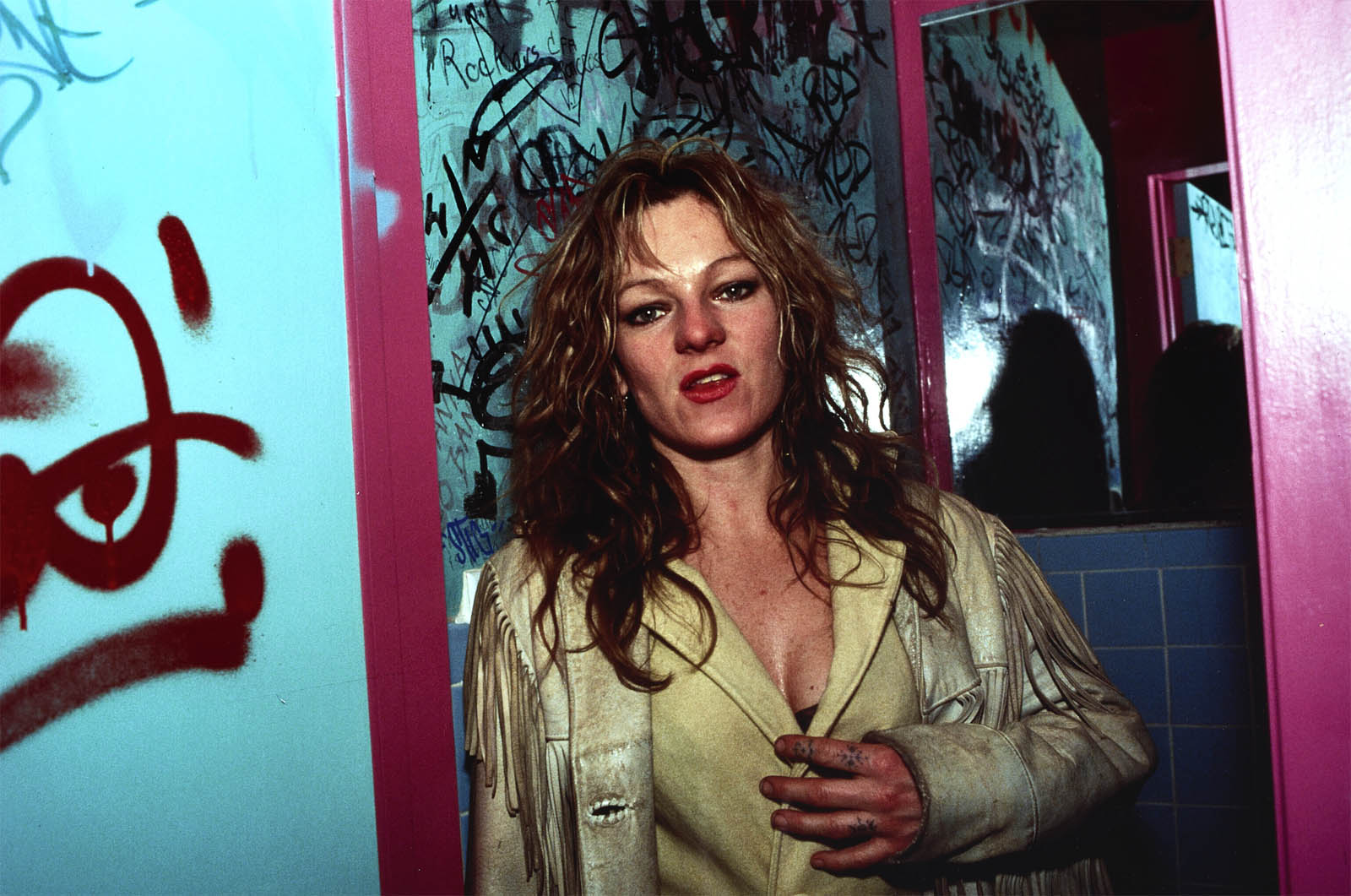
Where is, for example, the passion of Sally Mann’s photographs of the American South, the New York buildings of Berenice Abbott, George Dureau’s portraits of friends and amputees in New Orleans, the narrative stories of Duane Michals or the darkness / otherness that has always been present from the very start in American photography. In the selection in the posting, the photographs of Robert Frank (a foreigner, whose photographs of America were reviled when they were first published) and Nan Goldin (photographs of counter culture America) come closest to this alternate perspective, both outsiders from the main stream point of view.
Thus, while there are some interesting photographs in the exhibition it’s all too ho hum for me, perhaps a “vapour” of something almost brought into consciousness.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
1/ Christian House. “American Photography: unforgettable images of the beauty and brutality of a nation,” on The Guardian website Thu 13 Feb 2025 [Online] Cited 06/06/2025
2/ Deborah Nicholls-Lee. “Eight images that tell the story of America,” on the BBC website 12 February 2025 [Online] Cited 06/06/2025
Many thankx to the Rijksmuseum for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
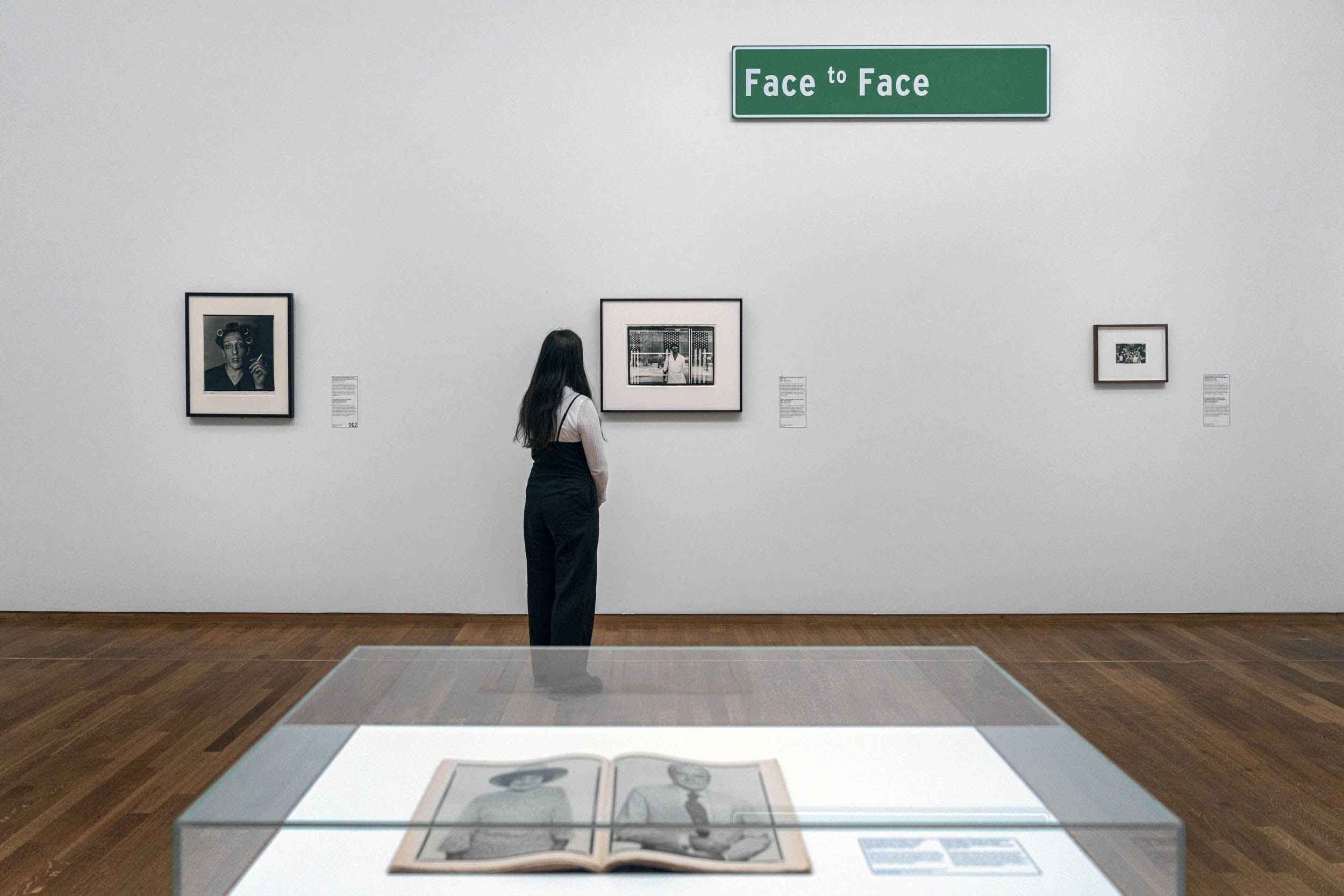
Installation view of the exhibition American Photography at Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam showing at right photographs by Robert Frank (below)
Photo: Rijksmuseum/Olivier Middendorp
Robert Frank (Swiss, 1924-2019)
City fathers – Hoboken, New Jersey
1955
Gelatin silver print
Robert Frank (Swiss, 1924-2019)
Parade – Hoboken, New Jersey
1955
Gelatin silver print
Robert Frank (Swiss, 1924-2019)
U.S. 91, Leaving Blackfoot, Idaho
1956
Gelatin silver print

Robert Frank (Swiss, 1924-2019)
New York City
1955
Gelatin silver print
Rijksmuseum moves you to The American Dream. To the real American. To unexpected recognition. The Rijksmuseum is staging the Netherlands’ first major survey exhibition of American photography.
The more than 200 works on display in American Photography reflect the rich and multifaceted history of photography in the United States. The exhibition presents the country as seen through the eyes of American photographers, and shows how the medium has permeated every aspect of our lives: in art, news, advertising and everyday life.
Over the past decades the Rijksmuseum has been assembling a collection of American photographic work. This is the first time we are exhibiting photographs from the collection, alongside loaned works from American, Dutch and other European collections. This show includes iconic photographs by the likes of Sally Mann, Robert Frank, Lisette Model, Nan Goldin, Richard Avedon, Andy Warhol, Paul Strand, Diane Arbus and James Van Der Zee, as well as surprising images by unknown and anonymous photographers.
Text from the Rijksmuseum website

Installation view of the exhibition American Photography at Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam showing in the bottom image at left, Sally Mann’s Jessie #34
(2004, below); at second left, Chuck Close’s Phil [Photo Maquette of Philip Glass] (1969, below); and at third right, László Moholy-Nagy’s Parking lot in Chicago, 1938 (1938, below)
Photo: Rijksmuseum/Olivier Middendorp
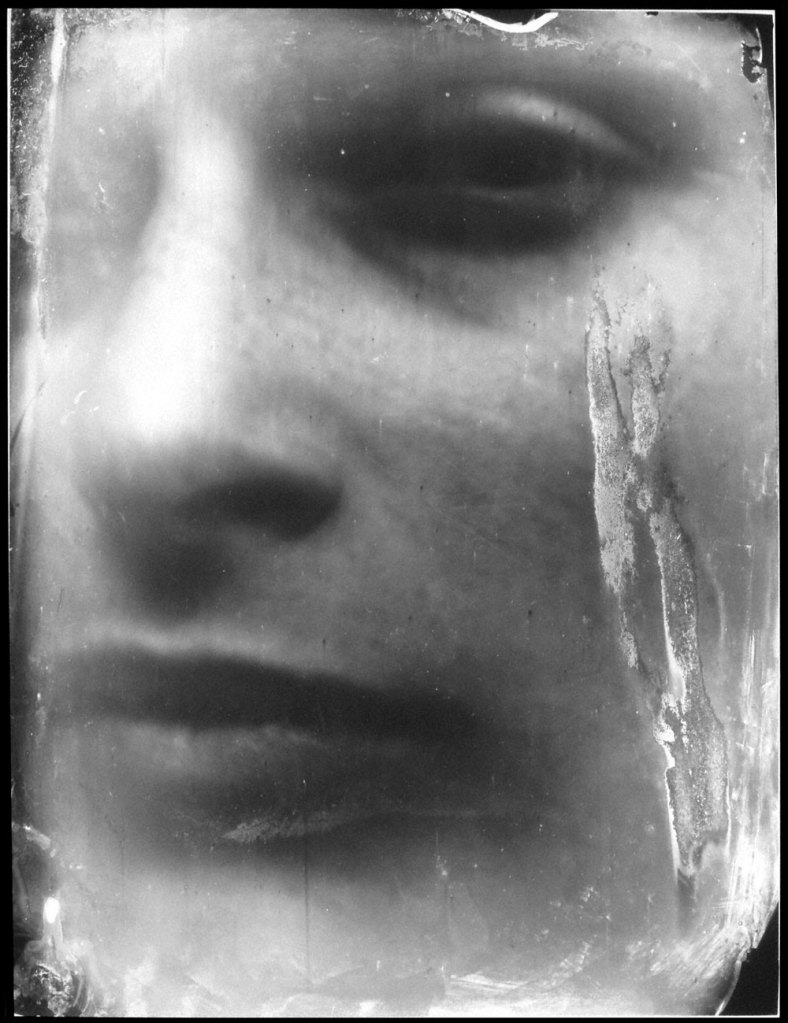

Sally Mann (American, b. 1951)
Jessie #34
2004
Gelatin Silver enlargement print from 8 x 10 in. collodion wet-plate negative, with Soluvar matte varnish mixed with diatomaceous earth
![Chuck Close (American, 1940-2021) 'Phil' [Photo Maquette of Philip Glass] 1969 Chuck Close (American, 1940-2021) 'Phil' [Photo Maquette of Philip Glass] 1969](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/chuck-close-photo-maquette-of-philip-glass.jpg?w=820)
Chuck Close (American, 1940-2021)
Phil [Photo Maquette of Philip Glass]
1969
16 x 12 inches (40.64 x 30.48cm)
Gelatin silver print mounted on mat board
© Chuck Close
László Moholy-Nagy (Hungarian, 1895-1946)
Parking lot in Chicago, 1938
1938
Gelatin silver photograph
23.8 × 33.8cm
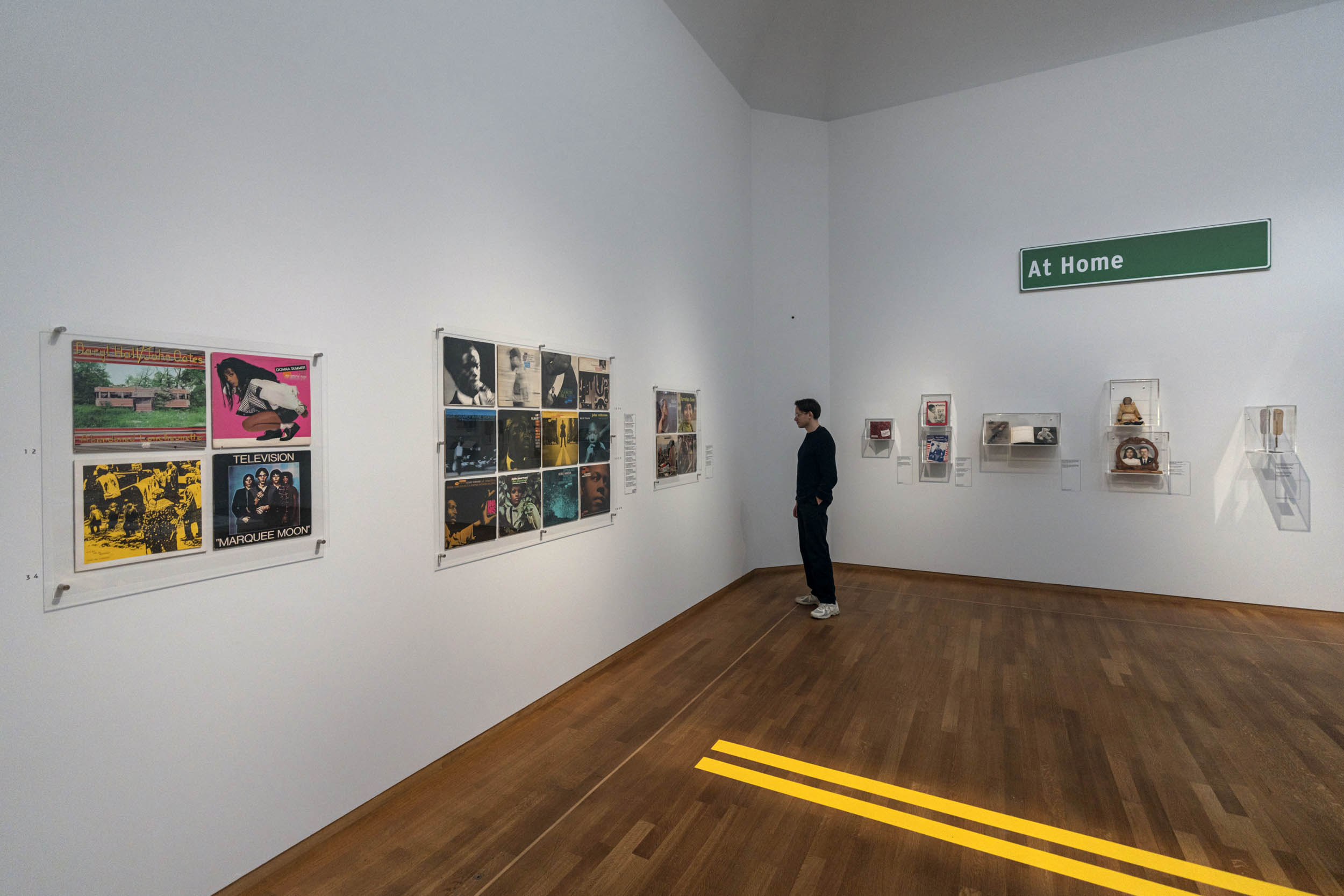
Installation view of the exhibition American Photography at Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam showing the work of Nan Goldin from The Ballad of Sexual Dependency (below)
Photo: Rijksmuseum/Olivier Middendorp
Nan Goldin (American, b. 1953)
Cookie with Me After Being Hit at the SPE Conference, Baltimore, MD, 1986
1986
Nan Goldin (American, b. 1953)
Cookie and Vittorio’s Wedding: The Ring, NYC, 1986
1986
Nan Goldin (American, b. 1953)
Cookie in the Bathroom at Hawaii 5.0, NYC, 1986
1986
The Rijksmuseum presents the first comprehensive survey of American photography in Europe. With more than 200 works spanning three centuries, American Photography will be an exploration of the rich and multifaceted history of photography in the United States, showing how the medium has permeated every aspect of our lives: in art, news, advertising and everyday life.
Over the past decade, the Rijksmuseum has built an extensive collection of American Photography. This exhibition is the first ever presentation of Rijksmuseum’s collection, which will be shown together with loans from over 30 collections in the United States, the Netherlands and other European countries. Works by icons including Sally Mann, Robert Frank, Lisette Model, Nan Goldin, Richard Avedon, Andy Warhol, Paul Strand, Diane Arbus and James Van Der Zee will be on view alongside eye-opening photographs by unknown and anonymous photographers.
The exhibition is possible by Rijksmuseum’s major partnership with Baker McKenzie. American Photography runs from 7 February to 9 June 2025. Concurrently with American Photography, Carrie Mae Weems’s 2021 series Painting the Town will be on show in the Rijksmuseum’s photography gallery.
American Photography will give picture of the country through the eyes of American photographers, showing the country in all its complexity. The exhibition takes themes such as the American dream, landscapes and portraiture to trace how photographers increasingly reflected on changes and events in their country. A major topic of the show is photography’s evolution as an art form, from 19th-century daguerreotypes of frost flowers on a window to the work of Paul Strand, Charles Sheeler, Sally Mann, Irving Penn, Dawoud Bey and Sarah Sense. Another important theme is how photography has grown to be a part of everyday life, which is demonstrated by family portraits, advertisements, postcards, gramophone record covers and more.
Press release from Rijksmuseum

Installation view of the exhibition American Photography at Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam showing in the bottom photograph at right, Jocelyn Lee’s Julia in Greenery (2005, below)
Photo: Rijksmuseum/Olivier Middendorp

Jocelyn Lee (American, b. 1962)
Julia in Greenery
2005
Archival Pigment Print
20 × 24 in | 50.8 × 61cm
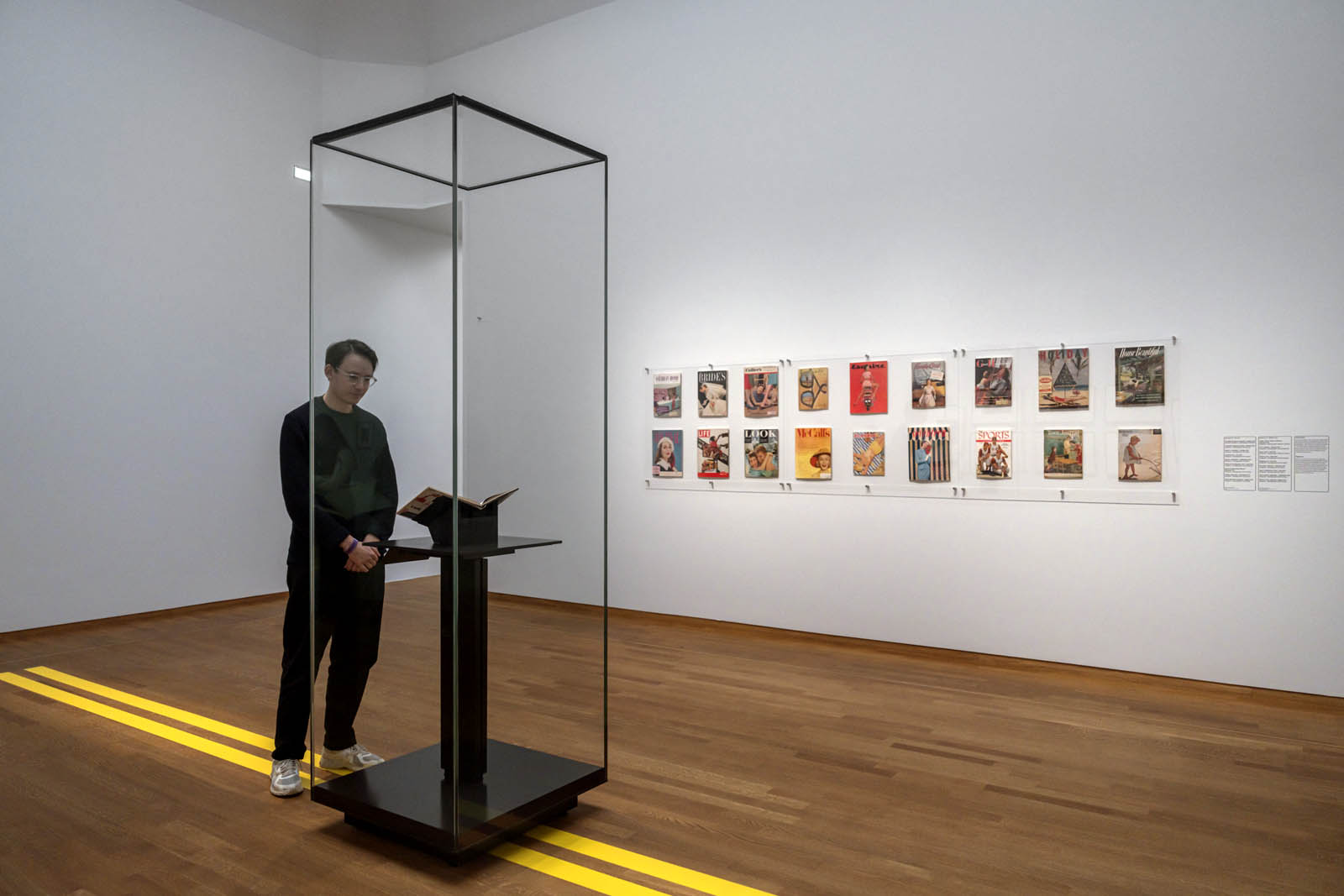
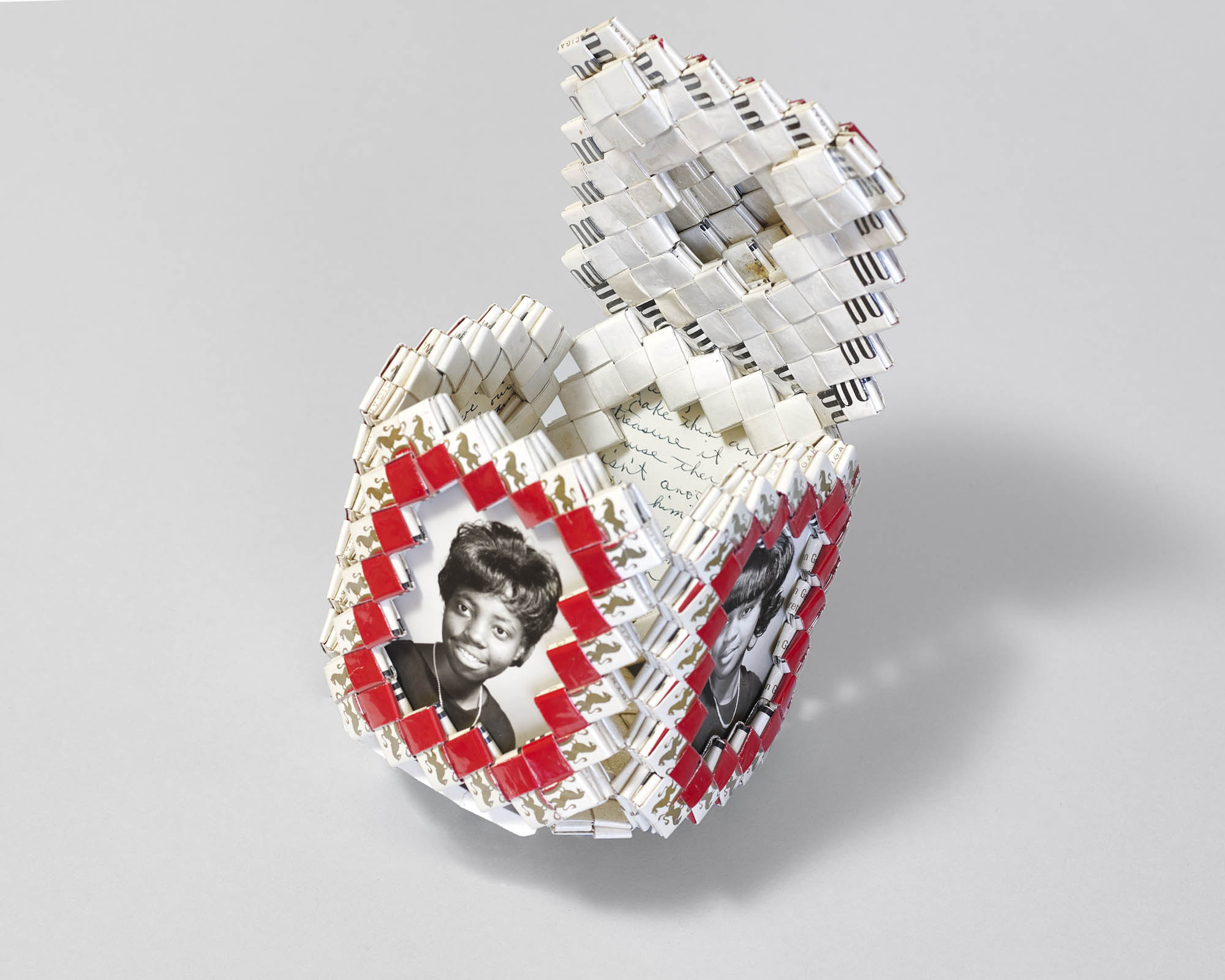
Installation view of the exhibition American Photography at Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam showing in the display case, Curio box made of cigarette packets with portraits of roommates, late 1960s (below)
Photo: Rijksmuseum/Olivier Middendorp
Curio box made of cigarette packets with portraits of roommates, late 1960s
Wood, handwoven cigarette packets, gelatin silver prints
140 x 110 x 195 mm
Collection of Daile Kaplan, Pop Photographica, New York
Photo: Andy Romer Photography, New York
Installation view of the exhibition American Photography at Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam showing at left, Diane Arbus’ A young man in curlers at home on West 20th St., N.Y.C. 1966 (1966, below); and at second left, Ming Smith’s America Seen Through Stars and Stripes, New York City (1976, below)
Photo: Rijksmuseum/Olivier Middendorp
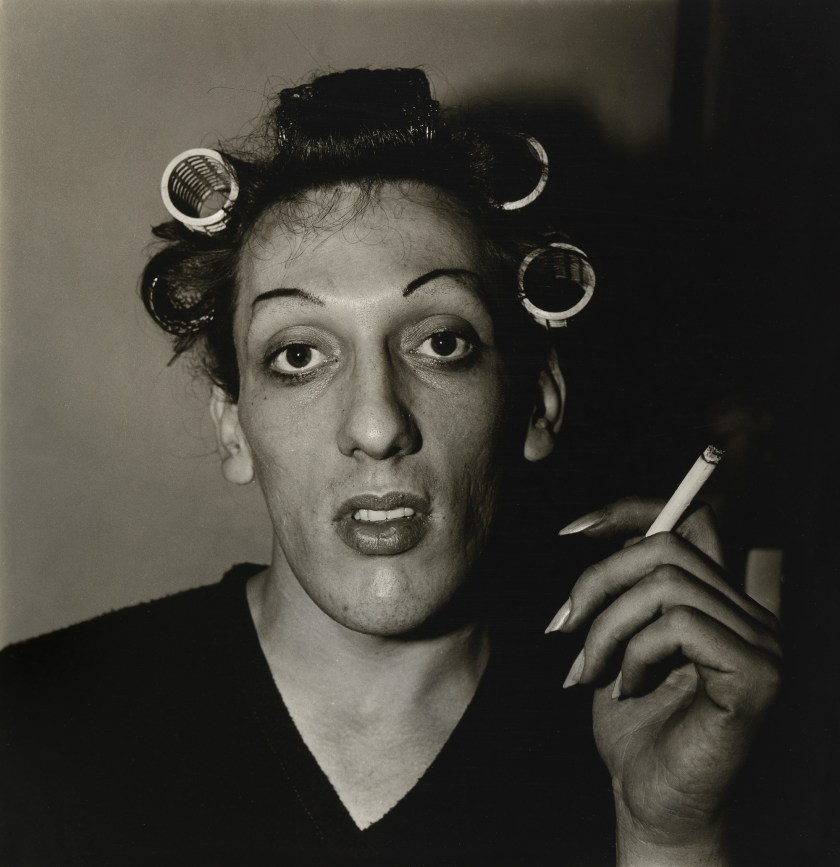

Diane Arbus (American, 1923-1971)
A young man in curlers at home on West 20th St., N.Y.C. 1966
1966
Gelatin silver print
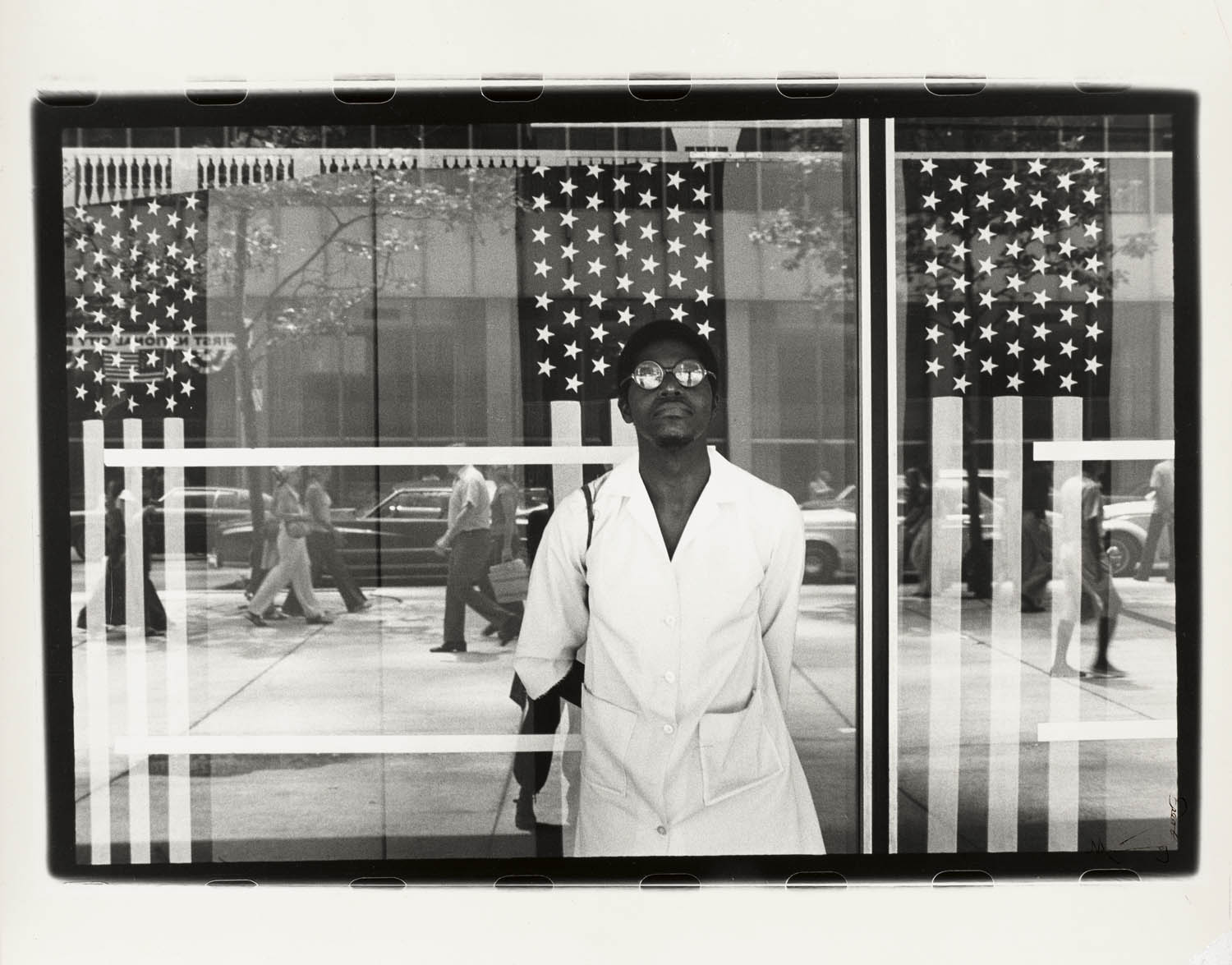
Ming Smith (American, b. 1951)
America Seen Through Stars and Stripes, New York City
1976
Gelatin silver print
318 x 470 mm
Virginia Museum of Fine Arts, Richmond (VA)
Adolph D. and Wiliams C. Williams Fund
In the post-war years, mass immigration to the US brought new ways of thinking. the US took over from Europe as a cultural trendsetter, and photography was eventually accepted as an art form. Playful approaches to photography emerged, moving beyond documenting people and places to provoking emotion and inviting deep questions. Ming Smith’s America Seen Through Stars and Stripes (1976), created on the bicentenary of the Declaration of Independence, turns again to the flag inviting America to reflect on its history. By placing a figure in mirrored sunglasses in front of a shop window, she creates a disorientating mesh of reflective surfaces. The grid structure suggests incarceration but – in combination with the round glasses and the stars on the flag – also creates an abstract composition reminiscent of modern art. “She’s a careful observer, playing with all these layers in the image,” says Boom.
Smith explores the artistic potential of photography, experimenting with double-exposure, shutter speed and collage. In one version of this image, she paints on bold red stripes, altering this snapshot of the US with marks that resemble blood or flames. Smith’s work builds on the civil rights movement that preceded it and features activists such as James Baldwin and Alvin Ailey. She was the first woman to join the African-American photography collective the Kamoinge Workshop and the first black woman to have her work acquired by the Museum of Modern Art (MoMA). Yet her demographic was largely overlooked by the art world. “I worked to capture black culture, the richness, the love. That was my incentive,” she told the Financial Times in 2019. “It wasn’t like I was going to make money from it, or fame – not even love, because there were no shows.”
Deborah Nicholls-Lee. “Eight images that tell the story of America,” on the BBC website 12 February 2025 [Online] Cited 06/06/2025

Henry Fitz Jnr (American, 1808-1863)
Self-portrait
1840
Daguerreotype
Smithsonian National Museum of American History, Washington (DC)
In 1840, using a self-made copper plate, Henry Fitz Jnr produced one of the world’s first selfies, his eyes gently closed to prevent any blinking from spoiling the result. In creating this striking blue image, he was doing more than record his appearance; he was also documenting America’s first essays into an art form that would tell its story in radical new ways.
Deborah Nicholls-Lee. “Eight images that tell the story of America,” on the BBC website 12 February 2025 [Online] Cited 06/06/2025

Thomas Martin Easterly (American, 1809-1882)
Chief Keokuk (Watchful Fox)
1847
Daguerreotype
Missouri History Museum
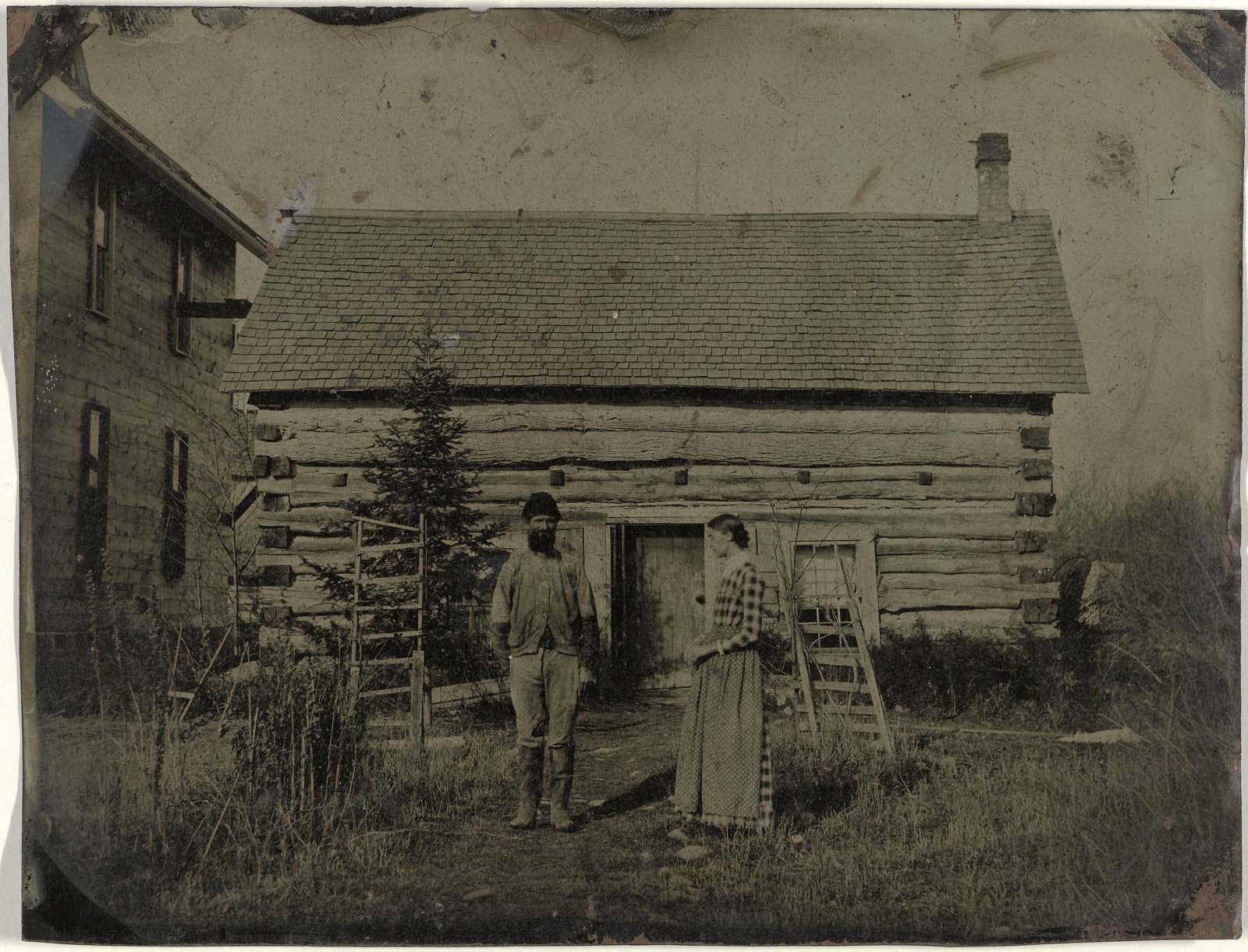
Anonymous photographer
View of a wooden house or barn with a man and a woman in front
c. 1870-1875
Tintype
164 x 215 mm
Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam
A 19th-Century tintype (an image made on a sheet of metal) featuring a man and woman in front of a rustic barn is a case in point. The image was probably sold on the spot by a travelling tin typist “for a modest price”, explains Rooseboom. “Many people had just arrived and were living in the countryside, no big city nearby, so this was the only possibility of having your portrait taken.” The man stands proud, looking at the camera, but the woman’s head is bowed and she is looking away. “Sometimes you can sense that people were simply not used to being photographed,” says Rooseboom. “Nowadays, we’ve seen in magazines and movies how to pose elegantly.” This may be the only time in their whole life that they would be photographed, and the result, adds Boom, “would hang on the wall of the house where they lived forever”.
Deborah Nicholls-Lee. “Eight images that tell the story of America,” on the BBC website 12 February 2025 [Online] Cited 06/06/2025
Detroit Photographic Company
Home of Rip Van
Nd
Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam

Bertha E. Jaques (American, 1863-1941)
Tree – in Governor Gleghorn’s Place Honolulu
1908
Cyanotype
248 x 152 mm
Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam, purchased with the support of Baker McKenzie

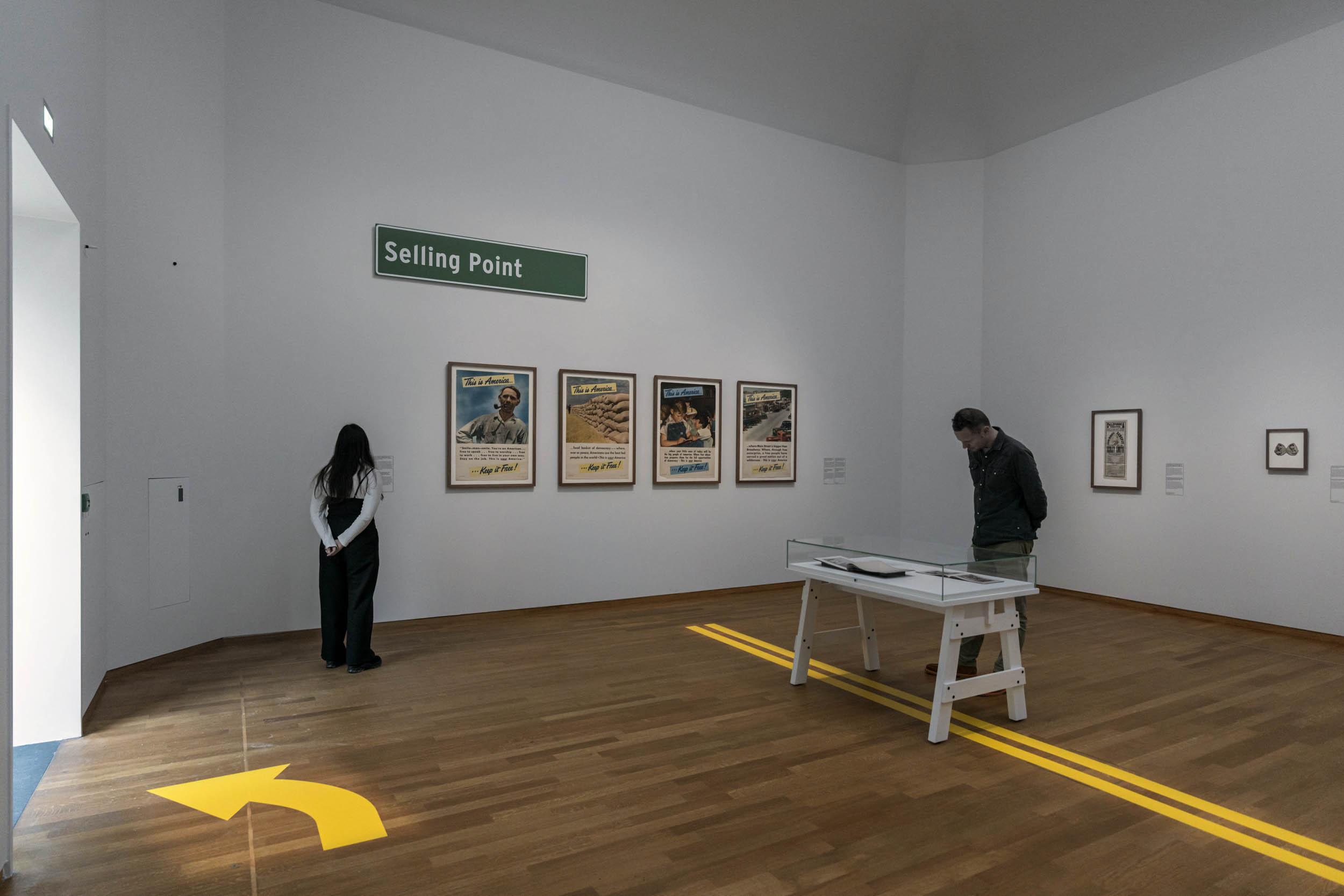
Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975) (photographer) (mentioned on object)
A free country? This is America … Keep it Free!
Nd
Sheldon-Claire Company
United News Company (publisher)
12,000 Employees of the Ford Motor Company, Detroit, Mich.
1913
Postcard, relief halftone and colour lithography
88 × 137 mm
Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam
… a 1913 postcard featuring 12,000 employees of the Ford Motor Company in Detroit may have been the “most expensive picture that was ever taken”, quipped a newspaper at the time, as the factory had to shut down for two hours to assemble the staff. The image, the company boasted, was “the largest specially posed group picture ever made” and illustrates a turning point where industry saw the value in investing large sums in promotional photography. Taken in the year when Ford introduced America’s first moving assembly line and the US had become the world’s largest economy, the photograph also depicts the mass production that would shape the country.
The image’s reappearance in Ford marketing also made it an early example of photoshopping. While the same tinted faces swarmed in the foreground, the number of employees cited in the caption increased exponentially, and a building to the left was cropped out in one version and acquired extra floors in another. “Apparently, many photographers and their publishers had no qualms about abandoning their medium’s potential for realism,” write Boom and Rooseboom in the exhibition catalogue.
Deborah Nicholls-Lee. “Eight images that tell the story of America,” on the BBC website 12 February 2025 [Online] Cited 06/06/2025
Schadde Brothers Studio
Display, sample or trade catalogue photograph for sweet manufacturer Brandle & Smith Co.,
c. 1915
Gelatin silver print with applied colour
288 x 240 mm
Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam
Charles Sheeler (American, 1883-1965)
Nude #3
1918-1919
Gelatin silver print
127 × 171 mm
Museum of Fine Arts, Boston

James Van Der Zee (American, 1886-1983)
Portrait of an Unknown Man, Harlem, New York City
1938
Gelatin silver print
244 x 203 mm
Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam
Purchased with the support of Baker McKenzie
© The James Van Der Zee Archive/The Metropolitan Museum of Art
… the New York portrait photographer James Van Der Zee was also embellishing his work, drawing jewellery on to his subjects and retouching their faces to erase dark lines and wrinkles. “I put my heart and soul into them and tried to see that every picture was better looking than the person,” he said. As a black photographer working from his Harlem studio at the height of the Harlem Renaissance, his work records a period when black migrants fleeing the segregationist South were forging a new life for themselves in the urban North. For the first time, African Americans and other minority groups could be photographed by someone inside their community, and represented in a way that uplifted them. Van Der Zee’s Portrait of an Unknown Man (1938), for example, is carefully posed to suggest confidence. The outfit is elegant and the buttonhole daisy adds a dandyish flourish. It’s an image that reflects the aspirations and upward mobility of African-American people and the pride Van Der Zee had in his culture.
Deborah Nicholls-Lee. “Eight images that tell the story of America,” on the BBC website 12 February 2025 [Online] Cited 06/06/2025
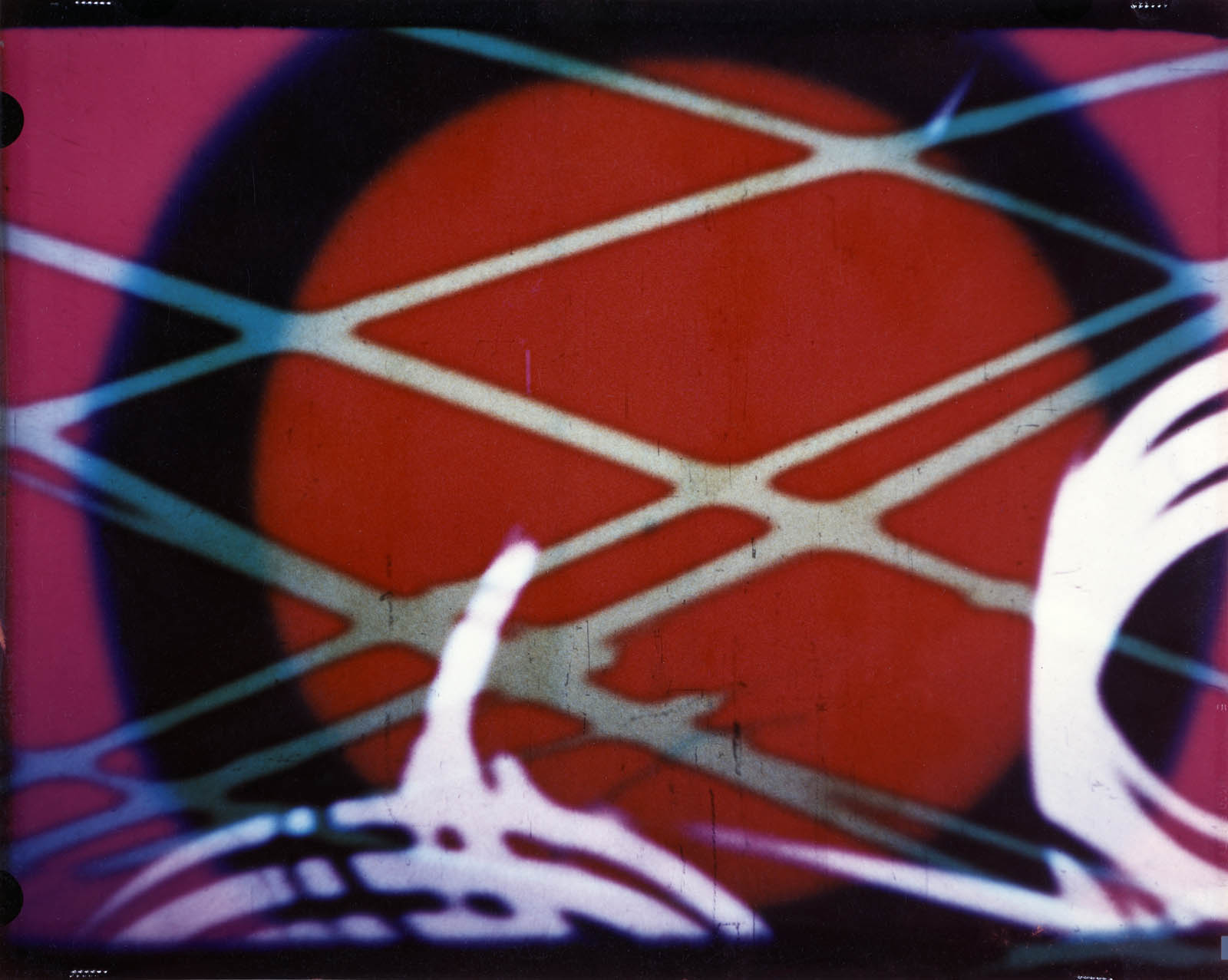
Hy Hirsh (American, 1911-1961)
Untitled (abstraction)
c. 1950
Chromogenic print, 251 x 200 mm
Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam
Purchased with the support of Baker McKenzie

Anonymous photographer
Family Standing beside their Car
c. 1957-1960
Chromogenic print (Kodak Instamatic)
76 x 76 mm
Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam

Irene Poon (American, b. 1941)
Virginia
1965
San Francisco Museum of Modern Art
Gift of Charles Wong
© Irene Poon Photography Archive, Department of Special Collections, Stanford University Libraries
It is the Chinese-American community that is the focus of the work of Irene Poon, who grew up in San Francisco’s Chinatown, where her parents, first-generation immigrants from Guanghzou, ran a herbalist store. A 1965 image features Poon’s sister Virginia in a local sweet shop, crowded out by Hershey’s and Nestlé bars. The letters “Nest” peep out from the densely packed shelves, reinforcing a sense that she is enclosed by this mass of graphic lettering. Beside her head a “Look” bar competes for attention, hinting at that other ever-expanding role for American photography: advertising − a sector in which the US was a forerunner. “Many of the 20th-Century artists started in advertising. It’s part of art history,” Boom says. “This whole field already existed, and the arts, and photography as an art form, draws from it.”
Deborah Nicholls-Lee. “Eight images that tell the story of America,” on the BBC website 12 February 2025 [Online] Cited 06/06/2025

Bruce Wrighton (American, 1950-1988)
Portrait of a woman, Binghampton, NY (‘Woolworth Shopper’)
1987
Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam
Purchased with the support of Baker McKenzie
© Estate of Bruce Wrighton, Courtesy Laurence Miller Gallery
Hulleah Tsinhnahjinnie (American, b. 1954)
This is not a commercial, this is my homeland
1998
Platinum lambda print
476 x 609 mm
Courtesy of the artist
The political power of photography is also seen in the work of Native American (Seminole-Muscogee-Navajo) photographer Hulleah Tsinhnahjinnie who uses the camera to correct misconceptions about Indigenous populations and to offer an alternative viewpoint on US history. “No longer is the camera held by an outsider looking in, the camera is held with brown hands opening familiar worlds,” she writes in a 1993 essay. “We document ourselves with a humanising eye, we create new visions with ease, and we can turn the camera and show how we see you.”
Tsinhnahjinnie’s captioning of a touristic image of Monument Valley, Arizona with This is not a commercial, this is my homeland highlights the commodification of American land, and uses what she calls “photographic sovereignty” to take us back to the very beginning and reclaim and retell the story of America. In combination with works such as Bryan Schutmaat’s Tonopah, Nevada (2012), which documents mining’s effect on the landscape of the American West, images like Tsinhnahjinnie’s tell a story of a beautiful land that means different things to different people: financial gain, security or a sacred space.
Deborah Nicholls-Lee. “Eight images that tell the story of America,” on the BBC website 12 February 2025 [Online] Cited 06/06/2025

Bryan Schutmaat (American, b. 1983)
Tonopah, Nevada
2012
Inkjet print
1017 x 1277 mm (printed 2021)
Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam
Purchased with the support of Baker McKenzie
Rijksmuseum
Museumstraat 1
1071 XX Amsterdam
Opening hours:
Open daily 9 – 17h


















































You must be logged in to post a comment.