Exhibition dates: 18th November, 2016 – 7th January, 2017
Curator: Juergen Teller
PLEASE NOTE: SINCE THIS POSTING, I ACKNOWLEDGE THAT THE ALISON JACQUES GALLERY, LONDON HAS UPDATED THEIR WEBSITE TO INCLUDE A MORE REPRESENTATIVE SELECTION OF MAPPLETHORPE’S IMAGES – INCLUDING SOME OF MAPPLETHORPE’S PHOTOGRAPHIC INVESTIGATION INTO THE SEXUAL BODY AND MORE WORKS FROM THE EXHIBITION – IN ALL THEIR GLORY! PLEASE SEE THE IMAGES ON THEIR WEBSITE AND REMEMBER, IF YOU DON’T LIKE, DON’T LOOK.

Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Pods
1985
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation
Used by permission Courtesy Alison Jacques Gallery, London
Nothing SALACIOUS
to see here
According to a tartly written denigration of Mapplethorpe in particular and more generally of photography as art by Guardian critic Jonathan Jones, “Cocks abound. Huge ones. Right at the centre of the main room, just so you don’t miss this basic Mapplethorpian theme, is a giant blow up of a man whose penis would be impressive even in a much smaller print. “Hey, don’t you get it?” Teller in effect is yelling. “This guy was all about cocks!””
Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks.
Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks.
Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks.
Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks.
Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks.
Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks.
Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks.
Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks.
Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks.
Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks.
Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks.
Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks. Cocks.
There, I’ve said it… because I can’t show it.
I’d really LOVE to refute this man’s drivel about Mapplethorpe’s work: “Teller succeeds brilliantly in making Mapplethorpe raw and immediate. Yet he also exposes him as very silly. For if Mapplethorpe was just wildly and naughtily picturing everything in life, willy nilly (but mostly willy), why the heavy monochrome aesthetic?”
But I can’t.
Why not?
Because of the
un/solicitous
(caring in a discriminatory way, as though to protect an image or reputation)
and
innocuous
set of press images that I can officially use to illustrate such a daring and radical rethinking of Mapplethorpe’s work by Juergen Teller.
Not the fault of the gallery at all, they have been marvellous sending me the images.
But they were authorised by The Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation for press sharing.
And there’s the rub.
LIKE RUBBING TWO COCKS TOGETHER.
The paradox of Mapplethorpe’s work: erect genitalia, orifices and violent sex acts teamed with corn, kittens and frogs can be seen in the flesh – but oh, NO!
We can’t have them being seen online
Cocks forbidden
How can you then judge, from a distance, what the effect of Teller’s pairings are; what delightful nuances of meaning are elicited, are illicit, in those very pairings, if we can’t see them? We can’t. Jones observes that, “Teller strips away that respectability and restores the shock to Robert Mapplethorpe … [revealing] hilarious double entendres in the way Mapplethorpe photographed nature.”
How can we understand the exhibition and the shock of these images … and then critique negative reviews like Jones’ if The Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation continues the sanitisation of his work online.
No comment is possible.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to Alison Jacques Gallery for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“Every picture is so strongly composed, and you feel that he really wanted to make that photograph. Not everything is erotic, but he has an interest in life, people, animals and landscapes, and his interest always comes through. I think life is what life is. It has day and night, sunny and grey, and he sees similar characteristics in different things. He cared enormously about how things looked. It all has this same intensity. Within all of that there’s a lot of sensitivity and romanticism in his work too, and a lot of clarity.”
Juergen Teller
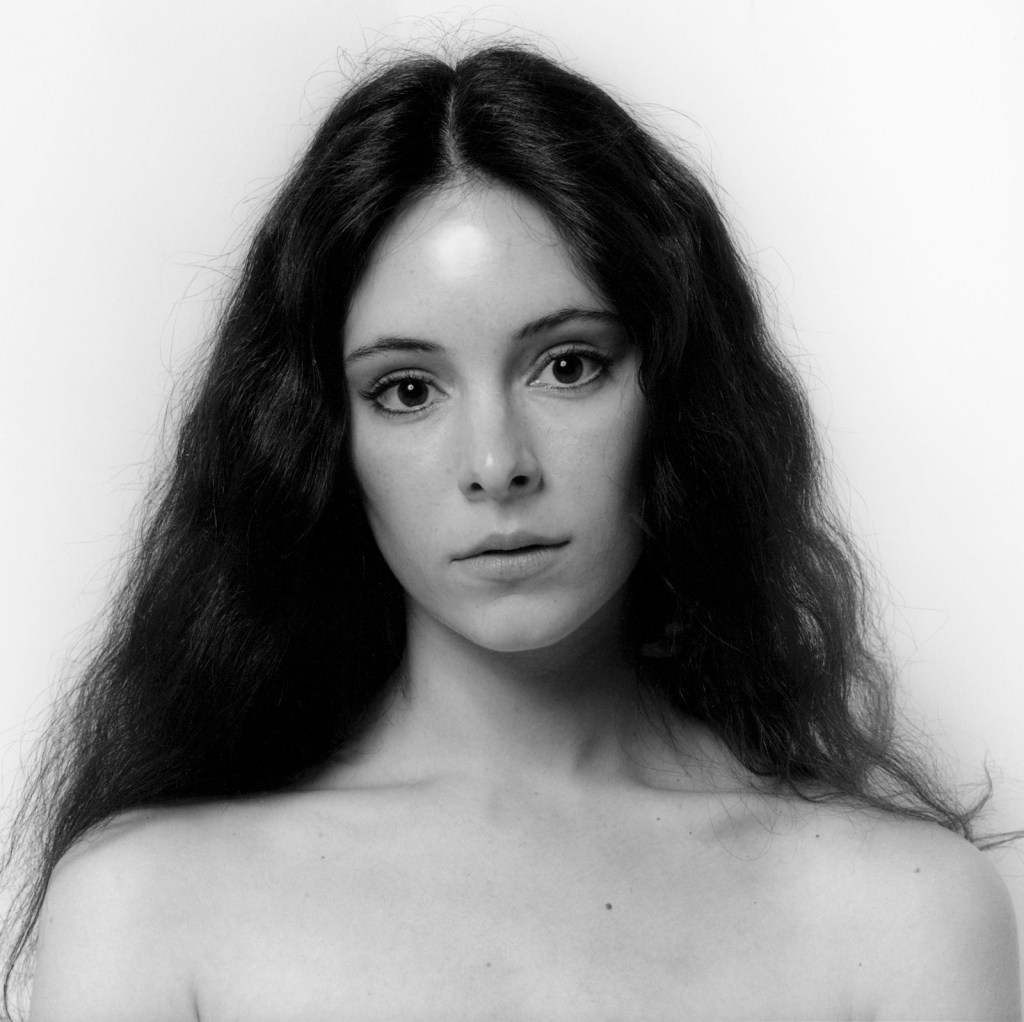

Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Madeline Stowe
1982
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation. Used by permission
Courtesy Alison Jacques Gallery, London
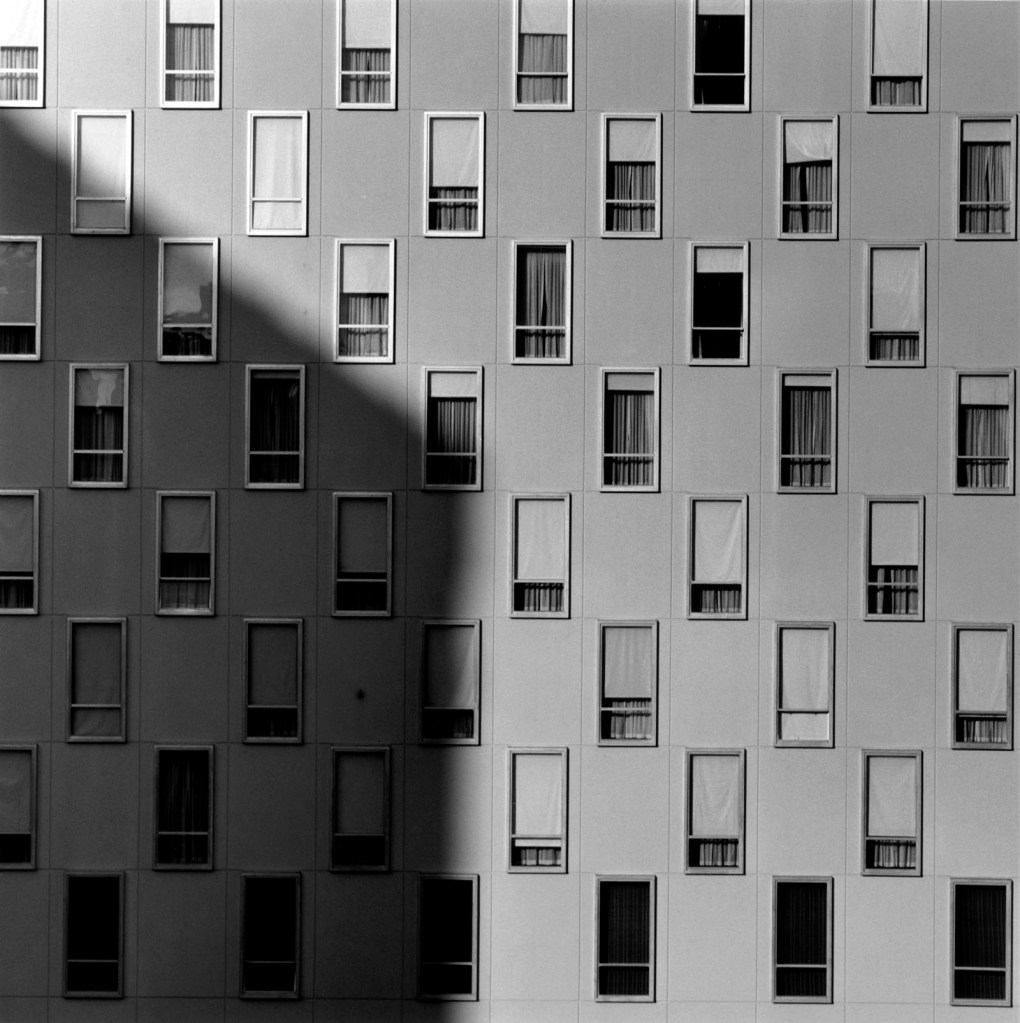

Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Apartment Window
1977
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation
Used by permission Courtesy Alison Jacques Gallery, London
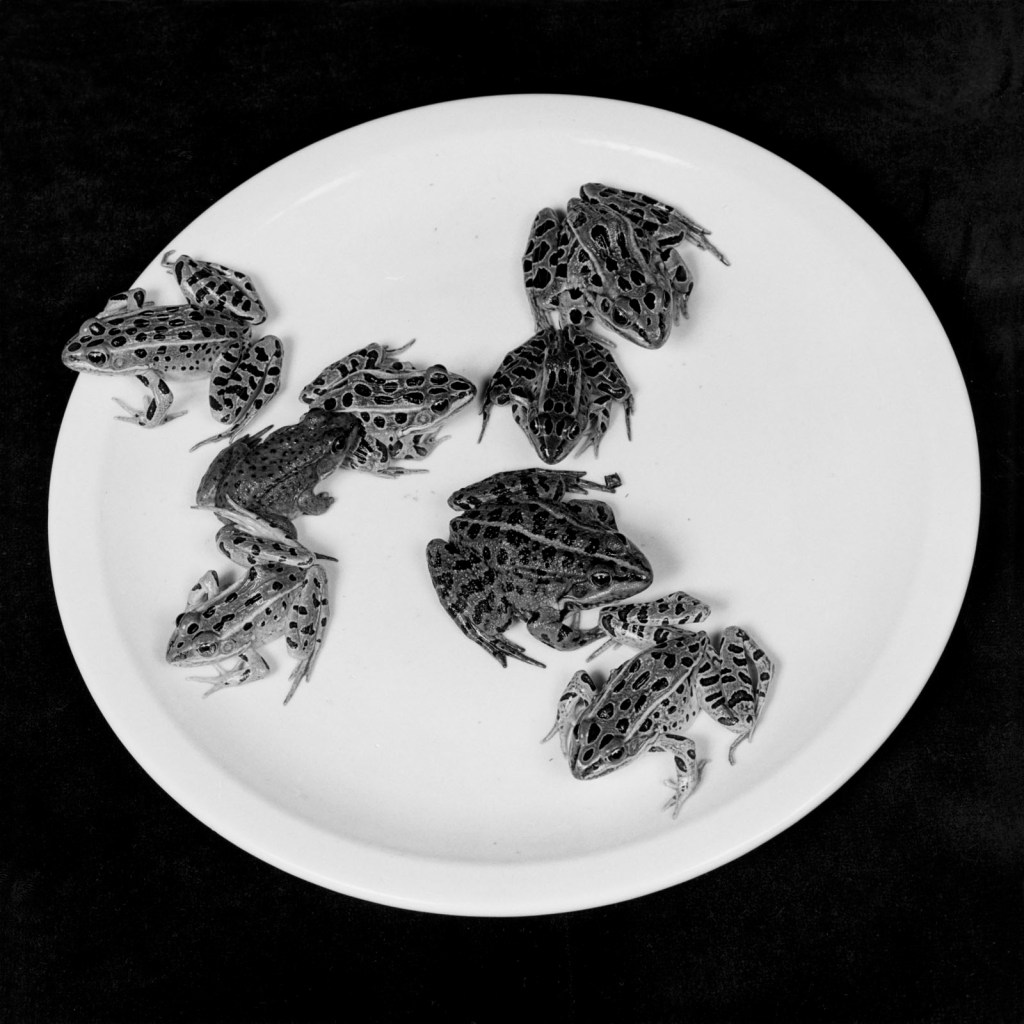

Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Frogs
1984
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation
Used by permission Courtesy Alison Jacques Gallery, London
To coincide with what would have been the 70th birthday of the iconic American photographer Robert Mapplethorpe, Alison Jacques has invited acclaimed UK-based, German-born photographer Juergen Teller to curate an exhibition of Mapplethorpe’s work. Teller worked in collaboration with The Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation in New York to make his selection.
Considered one of the most important photographers of the 20th century, Robert Mapplethorpe is currently the subject of a major touring retrospective The Perfect Medium, which opened at the J. Paul Getty Museum and Los Angeles County Museum of Art (LACMA), Los Angeles in 2016. The exhibition is currently on view at the Montreal Museum of Fine Arts, Canada (until 22 January 2017) and will travel to the Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia (October 2017 – February 2018). Mapplethorpe is also the subject of a recently released, Emmy nominated, HBO documentary Look at the Pictures (2016).
Juergen Teller is one of a few artists who, since Mapplethorpe, has been able to operate successfully both in the art world and the world of commercial fashion photography. Alison Jacques, who has represented Robert Mapplethorpe in the UK since 1999, said: “Provocative and subversive, making images which are the antithesis of conventional fashion photography, Juergen Teller was the only choice to curate this special exhibition of Robert’s work. There are obvious parallels between these two artists and I believe Juergen’s eye will bring a new reading of Robert’s work.”
With the permission of The Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation, Teller has enlarged two images, each over 4 metres in scale, which, pasted directly onto the gallery’s walls will provide a backdrop to the entire show. One wall will show Mapplethorpe’s first partner David Croland wearing a gag and the other features the model Marty Gibson from Mapplethorpe’s later work posing nude on a beach. Teller’s selection of 48 images exposes works within Mapplethorpe’s archive that have rarely been exhibited before and span Mapplethorpe’s entire career, ranging from the unique Polaroids of the early 1970s to his iconic medium of silver gelatin photographs from the mid-70s through to the late 80s.
Still life features as a prominent theme with unusual subjects including a spoon full of coffee, a set of antique silverware, two coconuts, a television set, and prickly unopened seedpods on a plate. Teller has also chosen a number of images depicting animals, a subject matter that Mapplethorpe is not famously associated with, including a hanging bat, plate of frogs, reclining dog, kitten on a sofa, and horses. Human subjects include some of Mapplethorpe’s key female muses such as Lisa Lyon, but also lesser-known personalities including Cookie Mueller, Lisa Marie Smith and Susan Sarandon’s daughter, Eva Amurri, as a small child. Well-known people in Mapplethorpe’s life are represented including Patti Smith, David Croland and Sam Wagstaff. Teller has also responded to his own German heritage and selected lesser-known portraits of German figures of the time, such as Hans Gert and the photojournalist Gisele Freund. The image of Gert was the first that Tom Baril worked on for Mapplethorpe from his Bond Street Darkroom. Baril continued to be Mapplethorpe’s exclusive printer for over 15 years.
Sexually-explicit images also feature in the exhibition but by interrelating these to a more romantic view of Mapplethorpe’s work, Teller has brought out the essential mission of Mapplethorpe’s work: a life-long quest for perfection of form whatever the subject matter may be.
Short biographies
Robert Mapplethorpe (b. New York, USA, 1946; d. Boston, USA, 1989) mounted over 50 solo exhibitions during his lifetime, including numerous museum shows in the USA, Europe and Japan. Since his death he has continued to be the subject of major institutional exhibitions. In recent years the Tate, in conjunction with other UK museums, acquired 64 works by Mapplethorpe through the Artists Rooms Art Fund and The d’Offay Donation, which culminated in an exhibition at Tate Modern in 2014.
Juergen Teller (b. 1964, Erlangen, Germany) moved to London in 1986, two years after graduating from Munich’s Bayerische Staatslehranstalt für Photographie. Since the late 1980s, his photographic works have gained critical acclaim and been featured in an array of influential international publications such as Vogue, W Magazine, I-D and Purple. With his unique photographic sensibility, Teller manages to strike a rare balance between creativity and commercialism, blurring the boundaries of art and advertising, and creating world-class images for collaborators such as Marc Jacobs, Céline, Yves Saint Laurent and Vivienne Westwood. Teller’s solo exhibition Woo! at the ICA in London in 2013 was the most well-attended exhibition in the ICA’s history, and in 2016 he had a major solo museum exhibition in Germany, Enjoy Your Life at Kunsthalle Bonn.
Press release from Alison Jacques Gallery
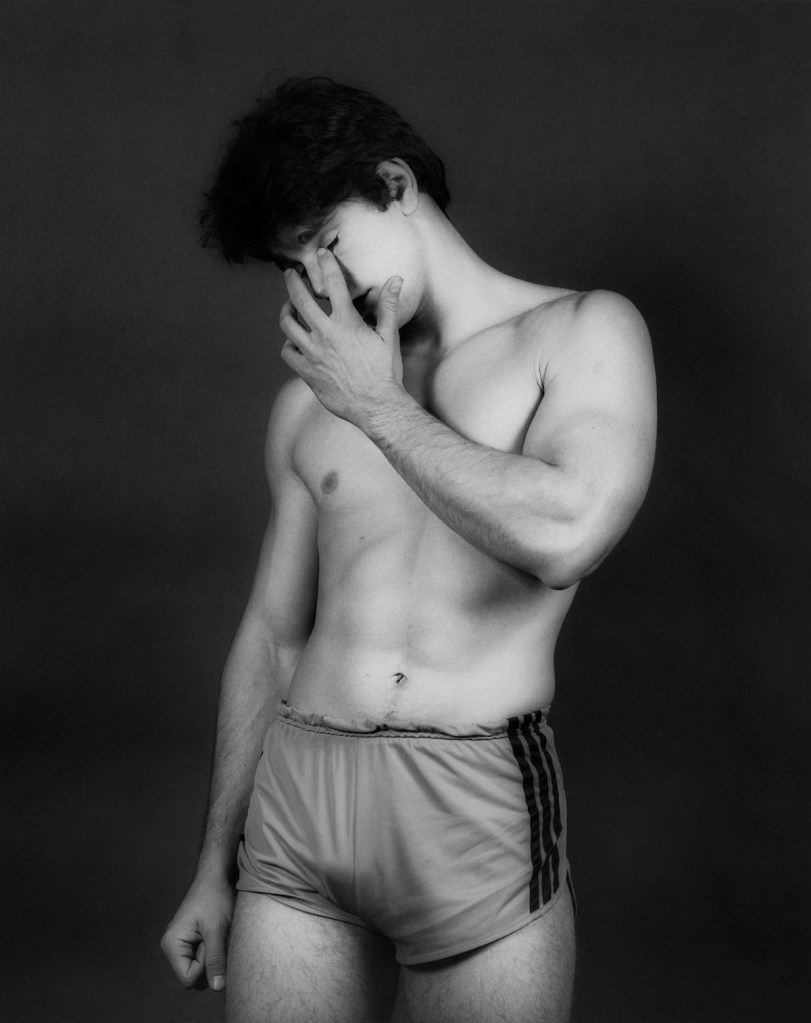

Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Arthur Diovanni
1982
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation
Used by permission Courtesy Alison Jacques Gallery, London
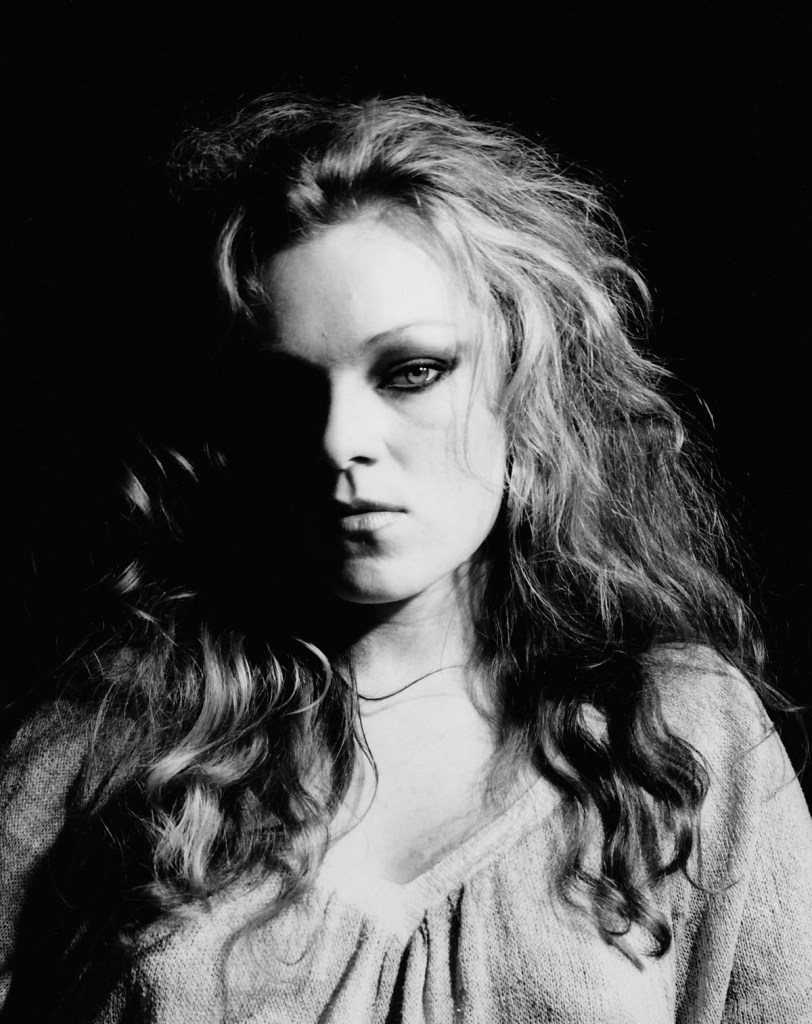

Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Cookie Mueller
1978
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation
Used by permission Courtesy Alison Jacques Gallery, London
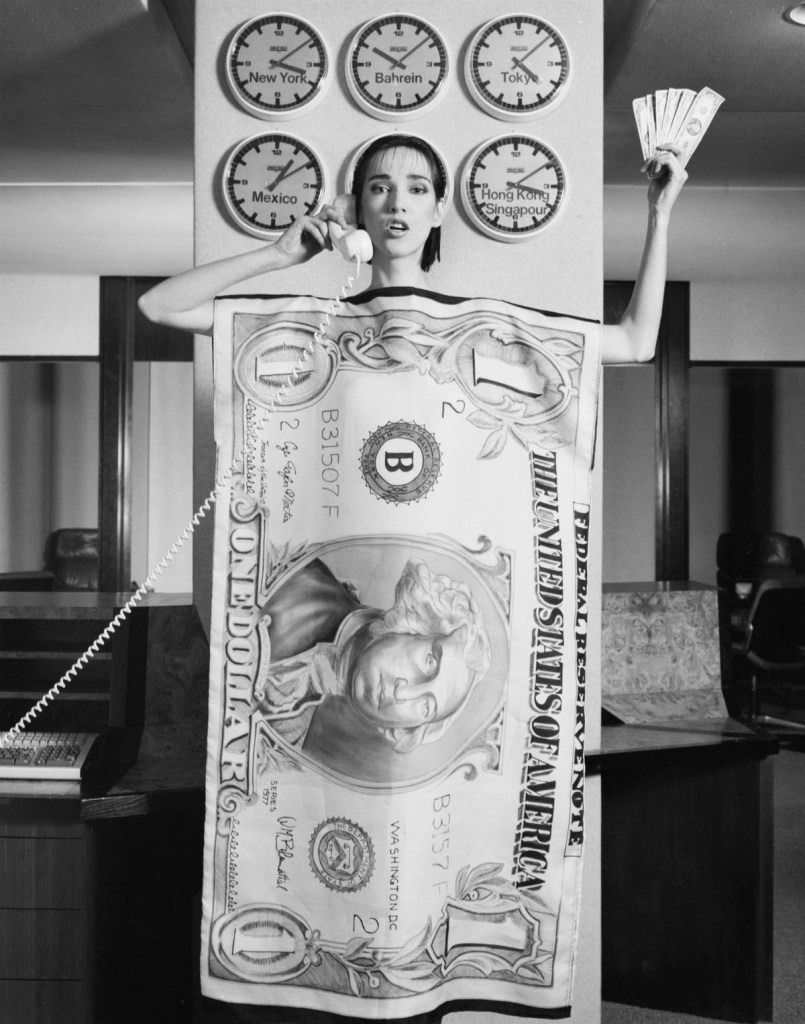

Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Paris Fashion Dovanna
1984
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation
Used by permission Courtesy Alison Jacques Gallery, London
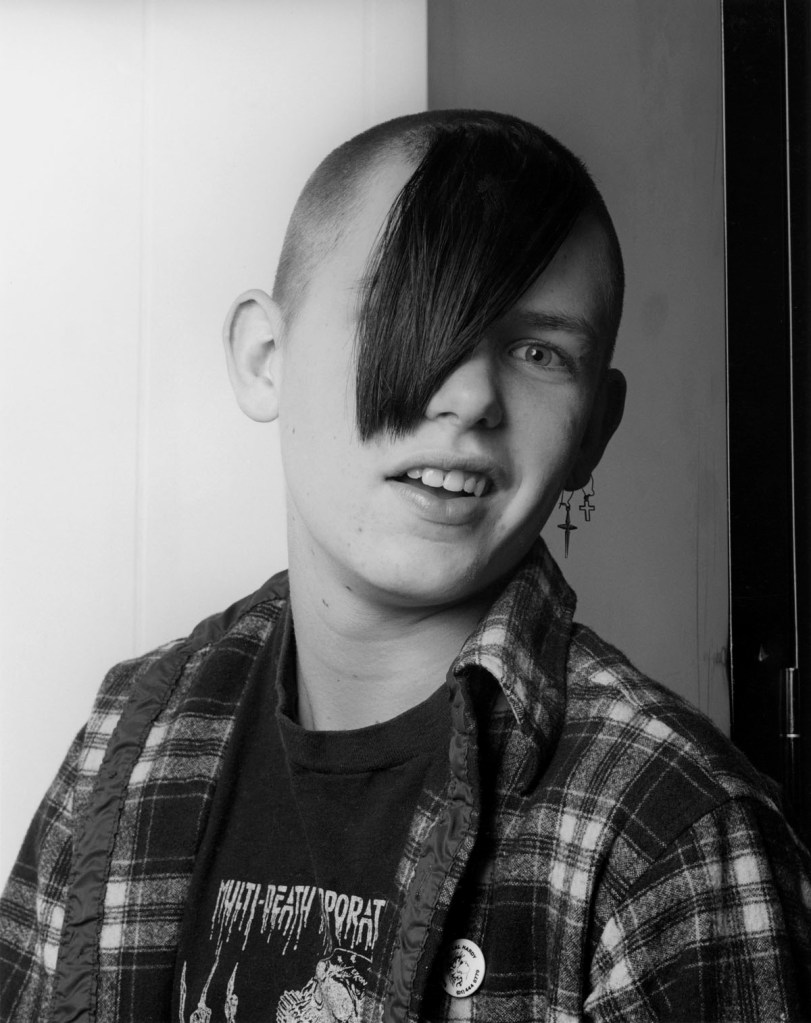

Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Tattoo Artists’ Son
1984
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation
Used by permission Courtesy Alison Jacques Gallery, London
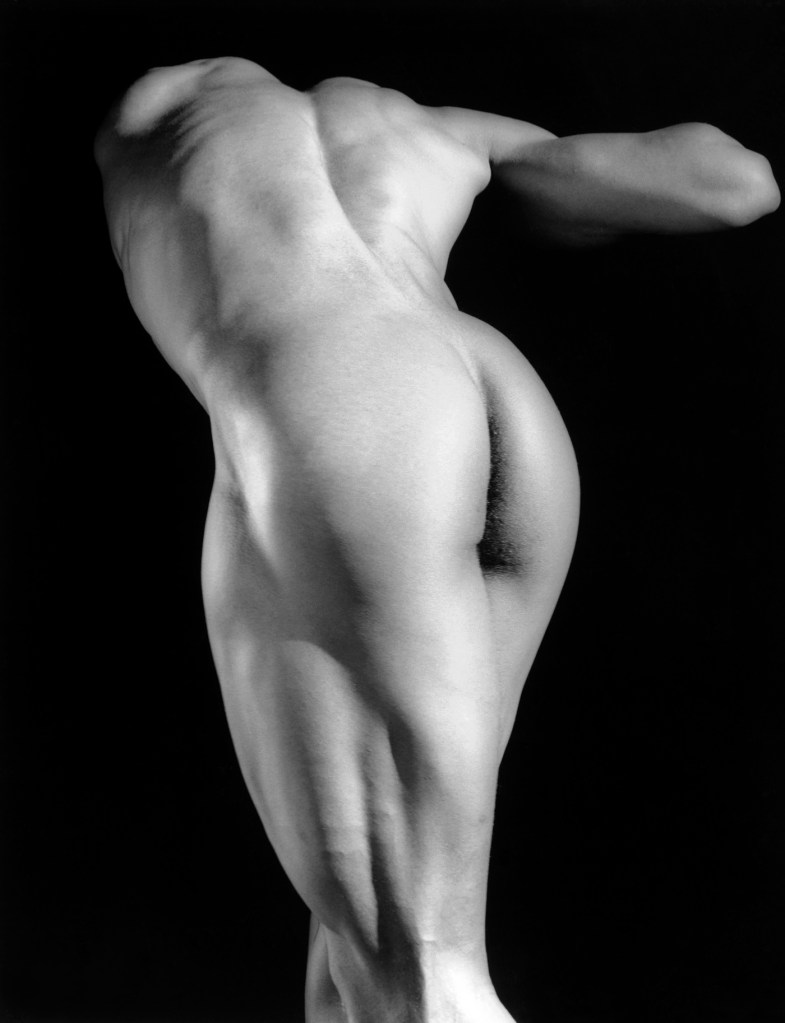

Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Michael Reed
1987
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation
Used by permission Courtesy Alison Jacques Gallery, London
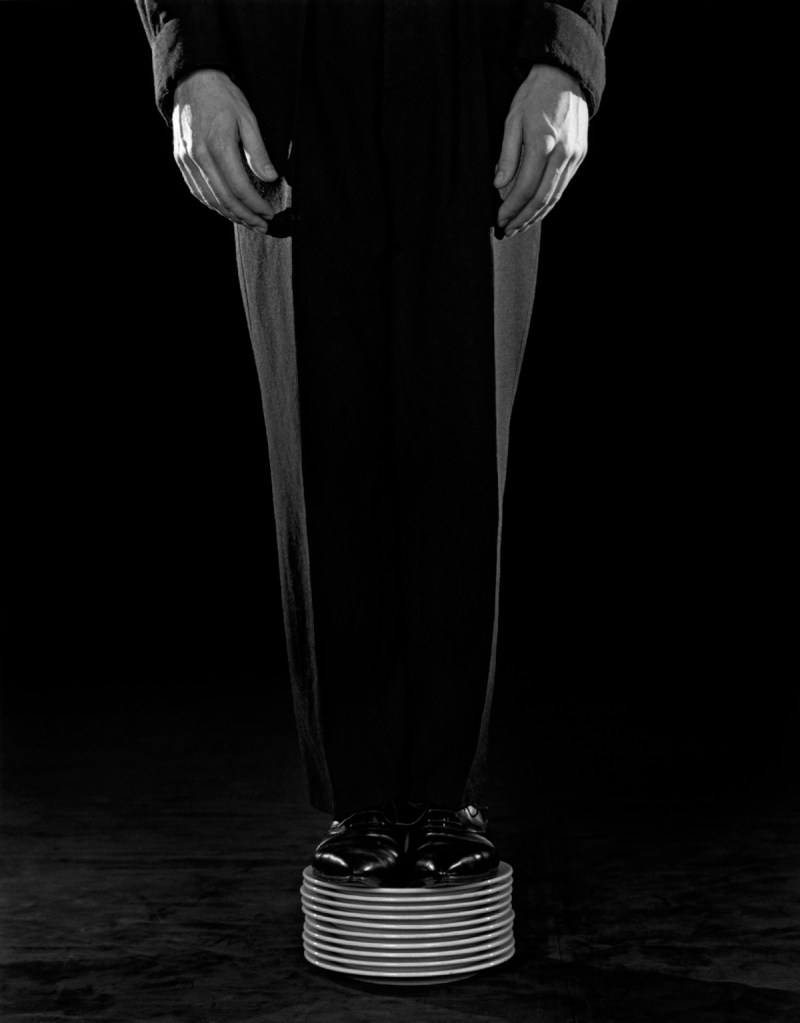

Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Shoes on Plates
1984
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation
Used by permission Courtesy Alison Jacques Gallery, London
Alison Jacques Gallery
Orwell House, 16-18 Berners Street
London W1T 3LN
Phone: +44 (0)20 7631 4720
Opening hours:
Tuesday – Saturday 11am – 6pm
Closed Sunday and Monday



















You must be logged in to post a comment.