Exhibition dates: 26th April – 15th September 2024
Altstadt (Rupertinum)
Curator: Katharina Ehrl
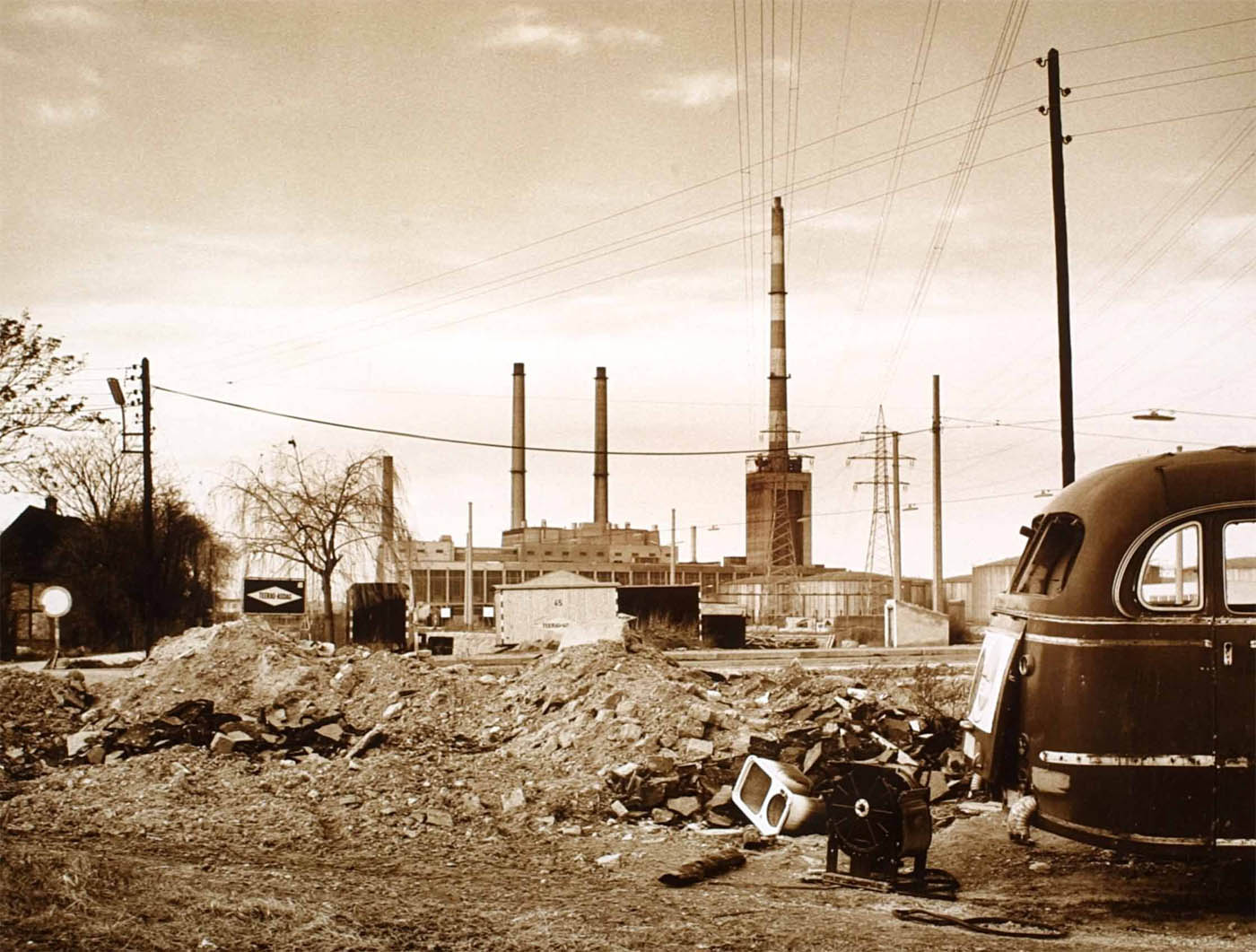
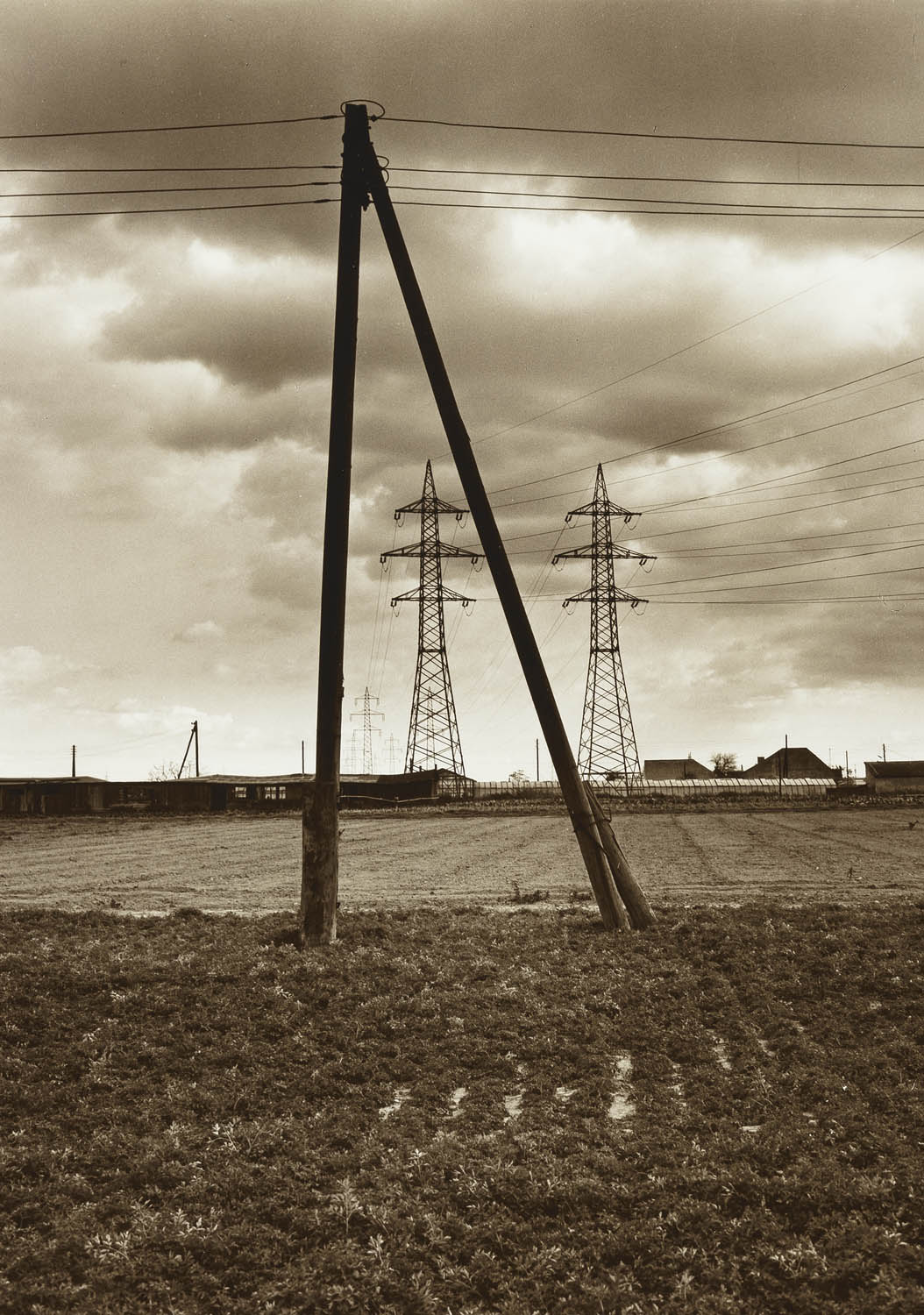
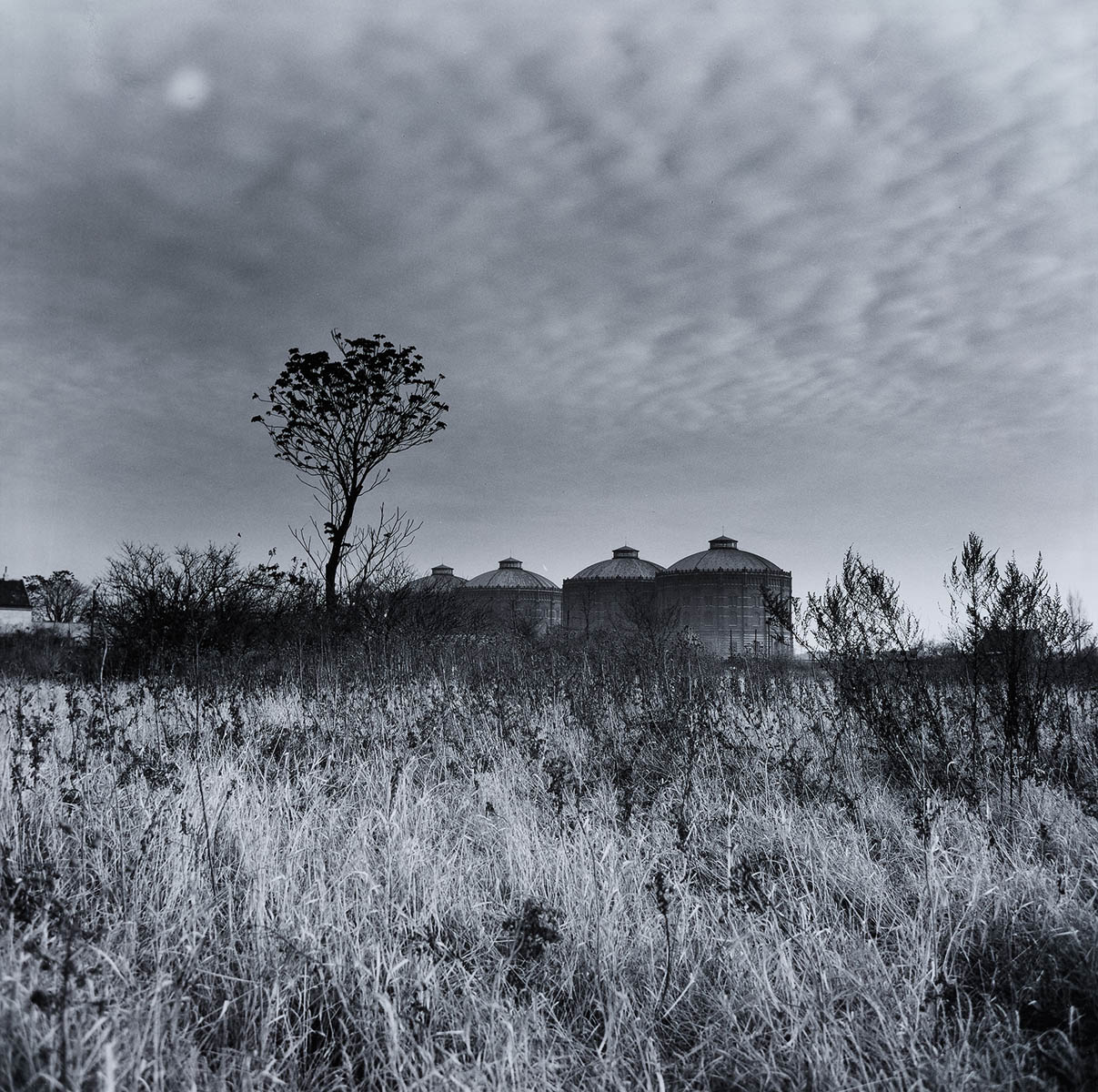
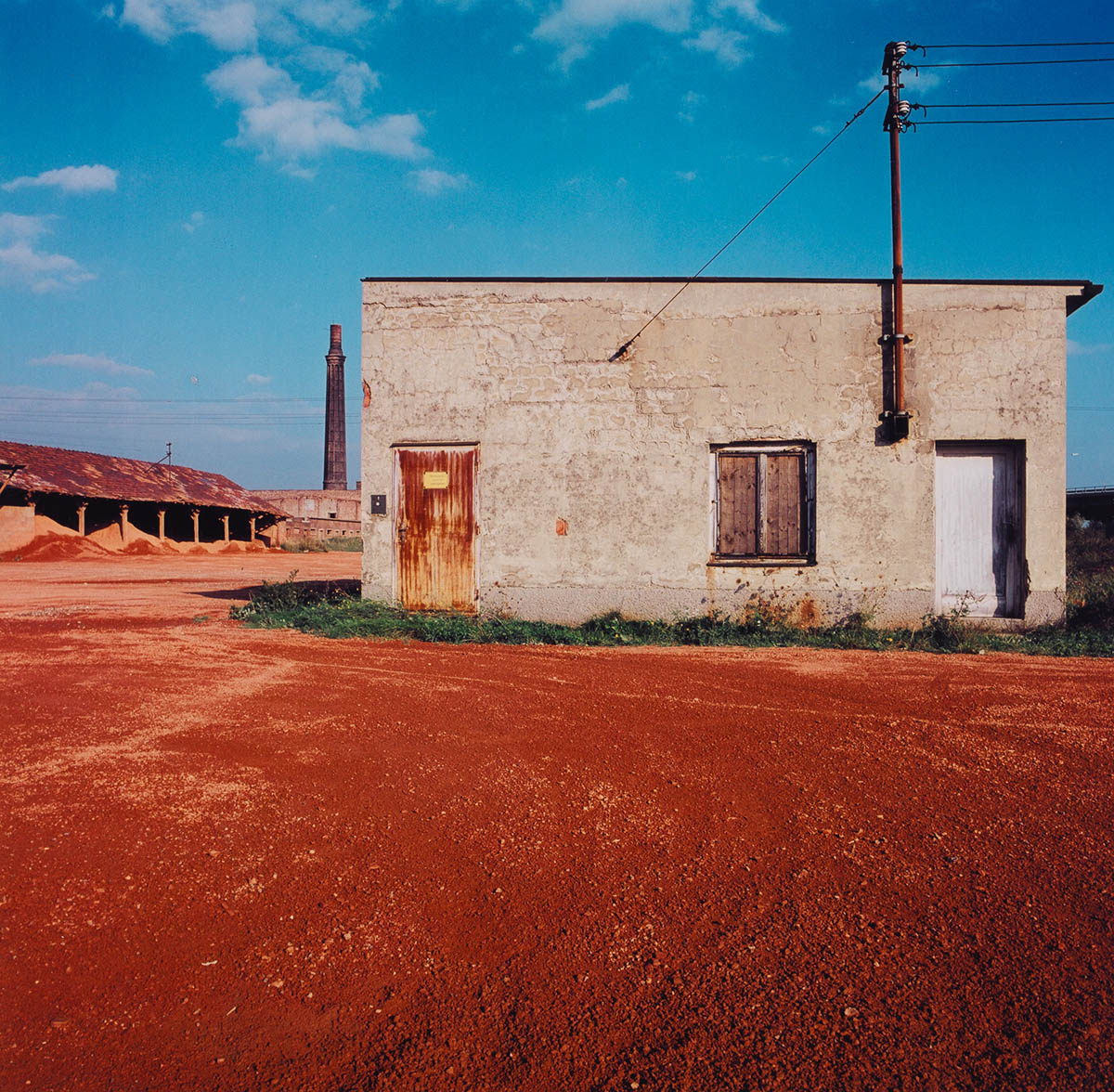
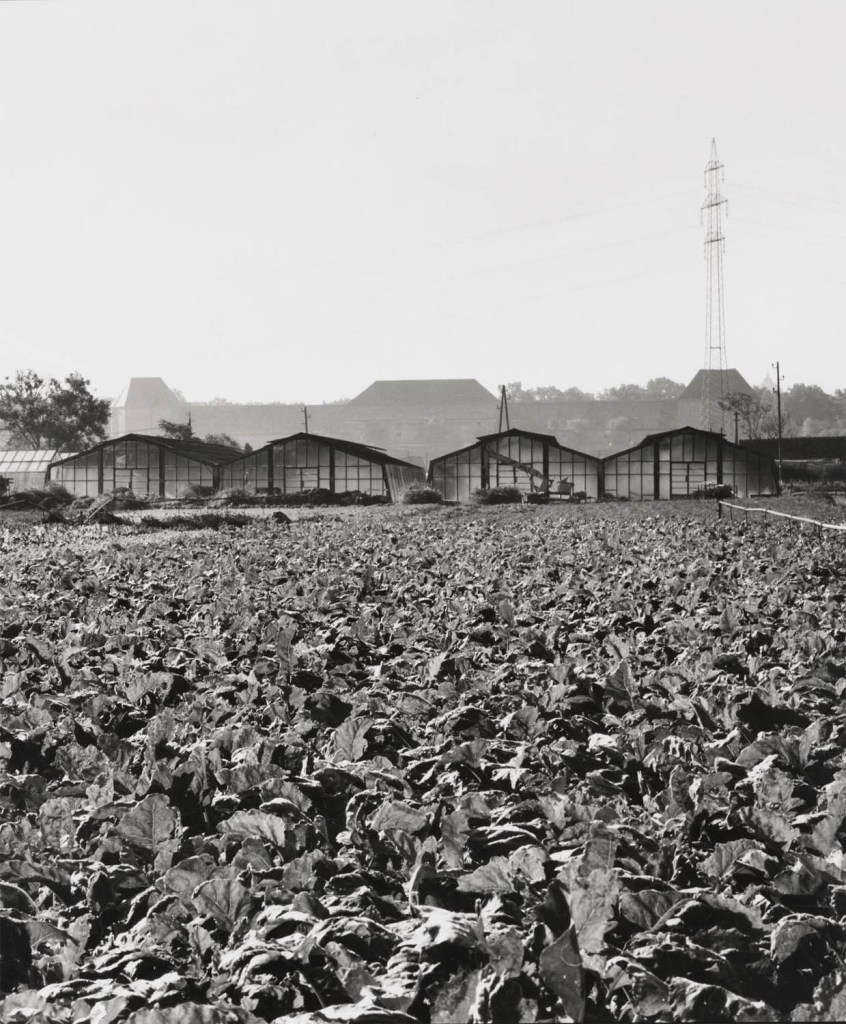
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
From the series Simmeringer Heide und Erdberger Mais, 1967-1976
Silver gelatine print on baryta paper, brown toned
Museum der Moderne Salzburg
© Bildrecht, Vienna 2024
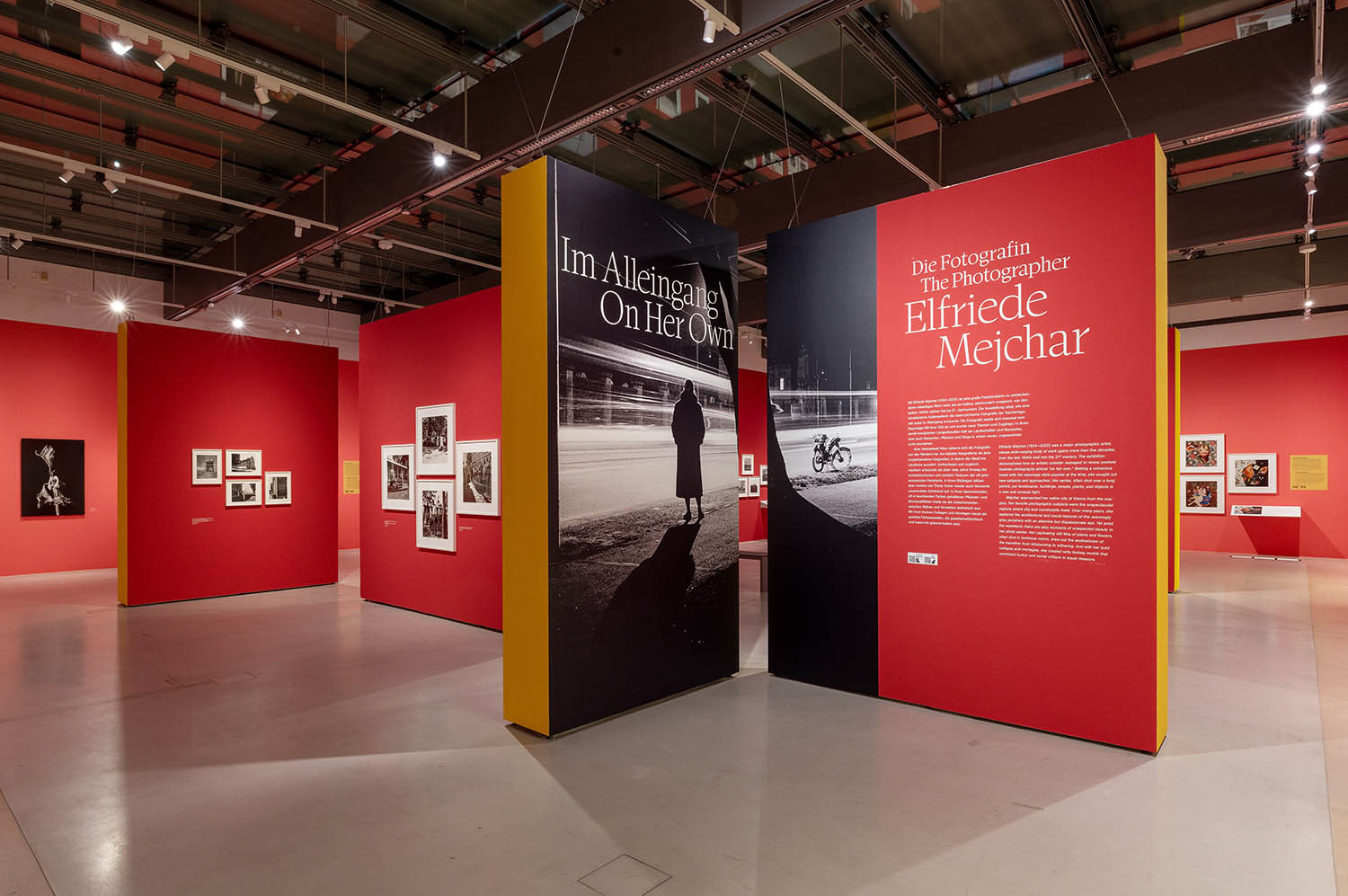
Deriving pleasure from the dérive
In recent weeks Art Blart has posted on social documentary photographers of the urbanscape: David Goldblatt documenting social conditions in South Africa under apartheid and Roger Mayne with his “mixture of reality and unreality” photographs of the communities of Southam Road and surrounds, London.
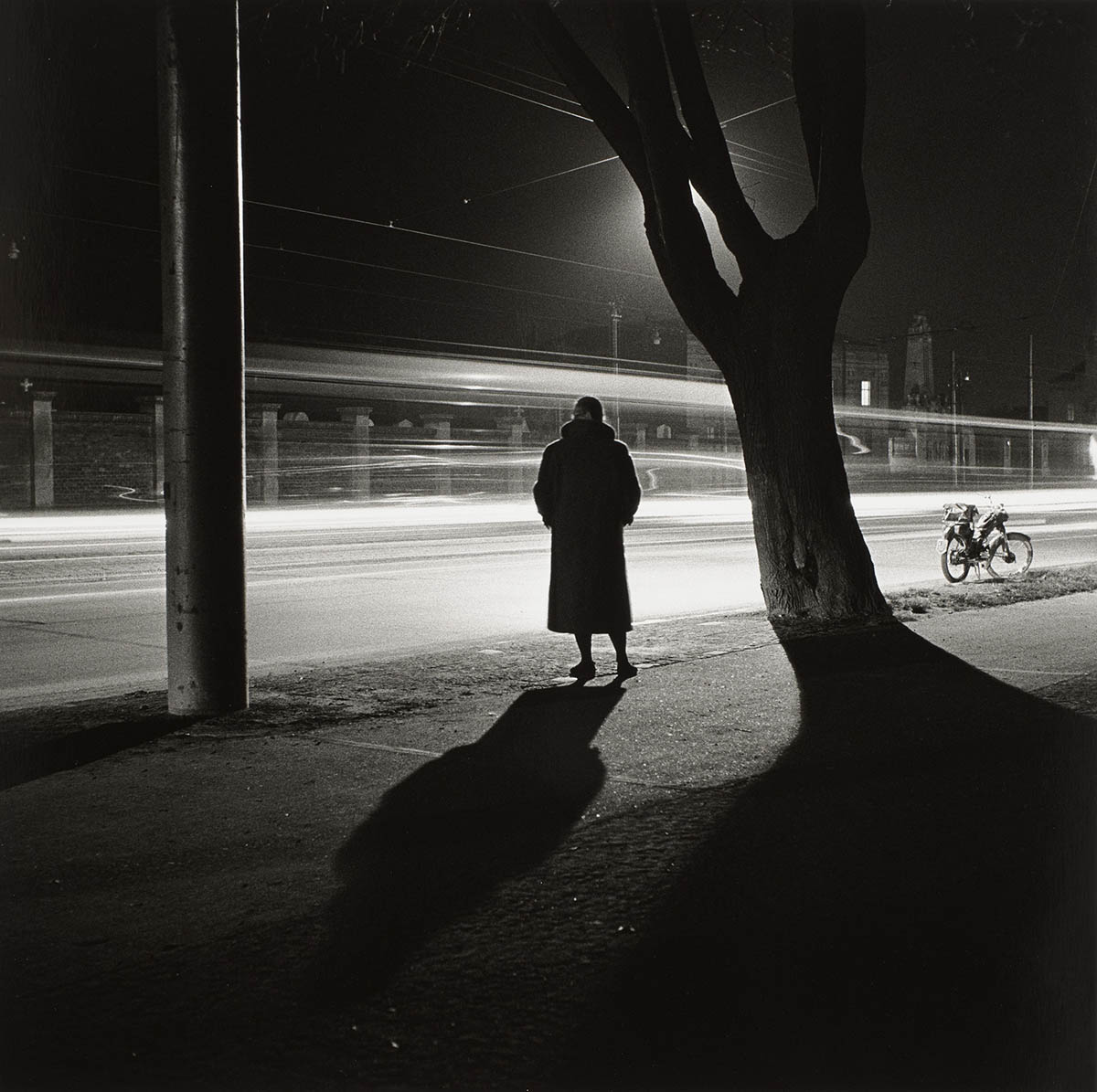
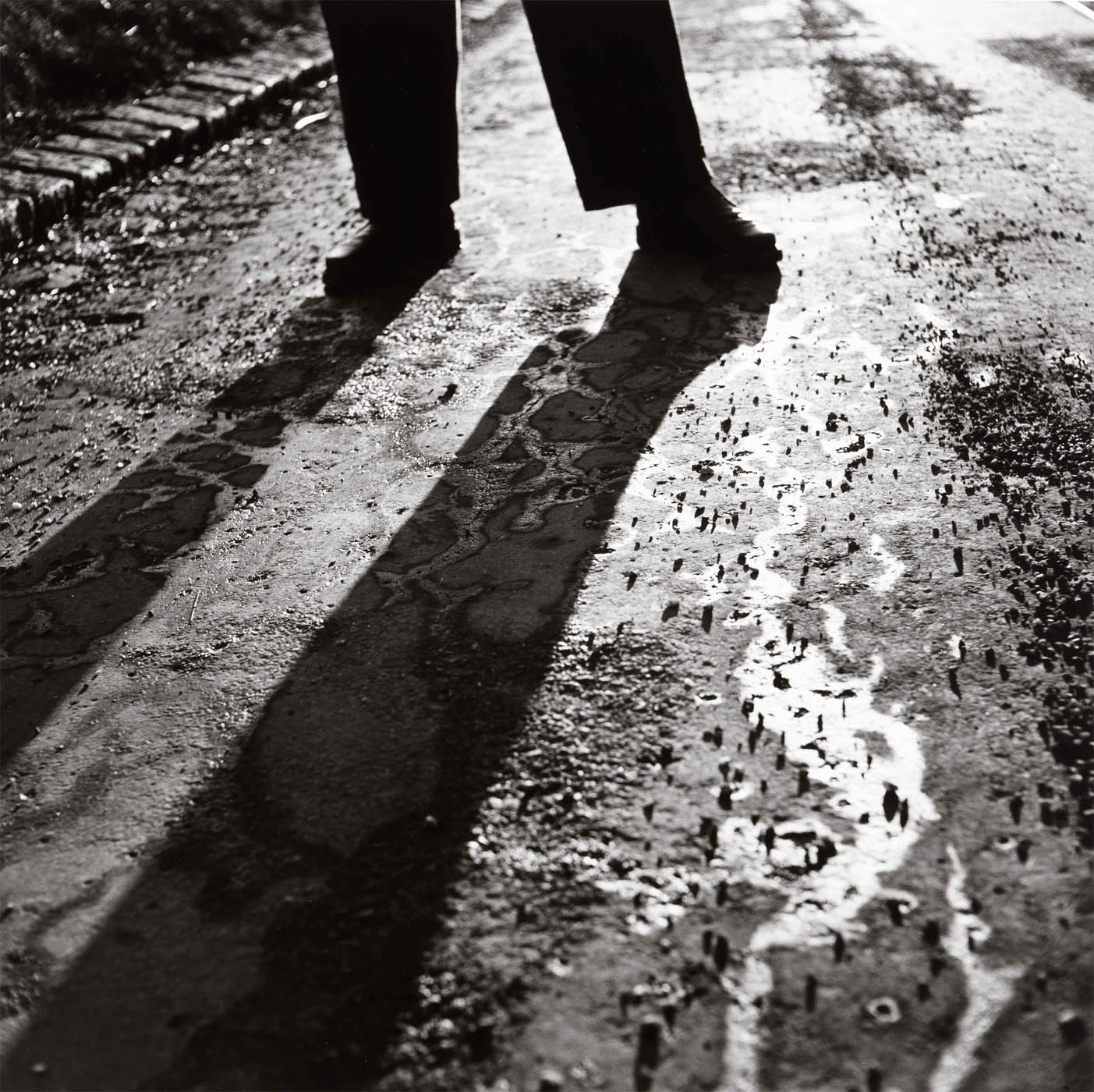
One could argue that both could be seen as a focused urban male flâneur (or flâneuse in the case of a female), who saunters around the city observing society – the serendipitous Mayne more so than the working in series focused Goldblatt. And here we have another photographer of the urbanscape until recently unknown to me, that of the magnificent Austrian photographer Elfriede Mejchar (1924-2020) who – according to the exhibition text – is another flâneur, “her flaneur-like practice underlying her earlier bodies of work.”
But Mejchar’s was a very concentrated photographic practice, one in which the photographer again and again “explored Vienna’s peripheral zones on the southeast edge of the city” to create photographic series often created over several years. Therefore, rather than being a wandering dilettante photographer, I believe that Mejchar was a focused conceptual artist who used Guy Debord’s “Theory of the Dérive” (1956)1 (or “drift”) to ground her photographic practice.
With its focused flow of acts, its gestures, its strolls, its encounters, one of the goals of the dérive includes studying the terrain of the city (psychogeography), the exploration of urban environments that emphasises interpersonal connections to places. The pyschogeography of the urbanscape.2
A quotation by Grant W. Ray is instructive in this regard:
“Debord’s Dérive is not simple a walk through the streets of the city, of chance encounters. Instead one must move rapidly and decisively through the urban space, with intention… They should be aware of their surroundings, of the “… ecological analysis of the absolute or relative character of fissures in the urban network, of the role of microclimates, of distinct neighborhoods with no relation to administrative boundaries, and above all of the dominating action of centers of attraction…” Thus the most talented photographers who’s oeuvre includes the investigation of the urbanscape. The walk itself, the interaction of operator, camera, and site breaks down the normal relationship we have with public urban spaces. Their activity alone is the Dérive.”3
Working decisively and with intention, at the edge of the city, in spaces with no boundaries, where there were few people, or using different typologies of the city such as hotel rooms in which she stayed during her everyday job, Mejchar focused on the pyschogeography of the urbanscape through her reflective, non-decisive moment photographs, capturing “the complexity of this desolate and yet, in her eyes, beautiful landscape” and the changes that were happening to the urbanscape.
“Elfriede Mejchar consciously broke away from the photographic mainstream and the reportage style that was popular at the time. Rather than searching for the so-called “decisive moment,” she approached her subjects in a strongly conceptual and serial manner. She focused not on the extraordinary but on the unspectacular and the commonplace, the everyday and the banal, repeatedly addressing these in new ways in her photographic series.” (Text from the Wien Museum website)
Working with the periphery, the borders between urban and rural spaces, the non-decisive moment, landscapes subjected to human interventions and photographs in series, Mejchar’s photographs are more than mere representation of these sites: they challenge the viewer to “instigate more than just chance encounters for the viewer looking at the photographs,” through an understanding of the “subtle variations of the daily social realities created and maintained through public works and layout.”4 “The photographers activity of finding these sites is the dérive, the photograph itself is the pyschogeography, the questioning.”4
With her training as a classical photographer in the manner of Sudek, Brassaï or Tudor-Hart (see the first two photographs in the posting On Her Own. The photographer Elfriede Mejchar) grounding her later objective conceptual photographs, Mejchar’s point of departure is the pleasure she derives from the focused dérive and the results of her activity (through the objective and precise eye of a topographer a la Bernd and Hiller Becher) – the questioning photographs – brought to the attention of the viewer.
Mejchar investigates “traces of civilisation that humans leave in nature or along the edges of the urban fabric” and in so doing brings peripheral things (and her ideas about them) to the centre of our attention, making them psychologically valuable for all of us. The artist derives pleasure from her measured dérive and investigation of the evanescent, posing important questions about seemingly mundane things before they pass out of sight, memory, and existence.
And in her pleasure, is ours.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
See another posting about the artist’s work: On Her Own. The photographer Elfriede Mejchar at Wien Museum MUSA, Vienna, 18th April – 1st September, 2024
1/ “Psychogeography describes the effect of a geographical location on the emotions and behaviour of individuals.
How do different places make us feel and behave? The term psychogeography was invented by the Marxist theorist Guy Debord in 1955 in order to explore this. Inspired by the French nineteenth century poet and writer Charles Baudelaire’s concept of the flâneur – an urban wanderer – Debord suggested playful and inventive ways of navigating the urban environment in order to examine its architecture and spaces.”
Anonymous. “Psychogeography,” on the Tate website Nd [Online] Cited 13/09/2024
2/ Guy Debord (November 1956). “Theory of the Dérive”. Les Lèvres Nues (9). Translated by Ken Knabb.
3/ Guy Debord, “Theory of the Dérive,” 1958 on the Bureau of Public Secrets website Nd quoted in Grant W. Ray. “Dérive,” on the Silverpoetics website 13 July 2009 [Online] Cited 20/08/2024
4/ Ibid.,
Many thankx to the Museum der Moderne Salzburg for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Poesie des Alltäglichen. Fotografien von Elfriede Mejchar / The poetry of the everyday
To mark the centenary of her birth, in 2024 three museums in Austria host exhibitions of works by the photographer Elfriede Mejchar (1924-2020, Vienna, AT). The Museum der Moderne Salzburg presents the artist as a portraitist. Curator Katharina Ehrl guides you through the exhibition in this short film.
In 2024, three museums host exhibitions of works by the Austrian photographer Elfriede Mejchar (1924-2020, Vienna, AT). The Museum der Moderne Salzburg is collaborating with the Landesgalerie Niederösterreich and the Wien Museum to honor the artist’s work at three different locations on the occasion of her 100th birthday, with each location offering a different focus.
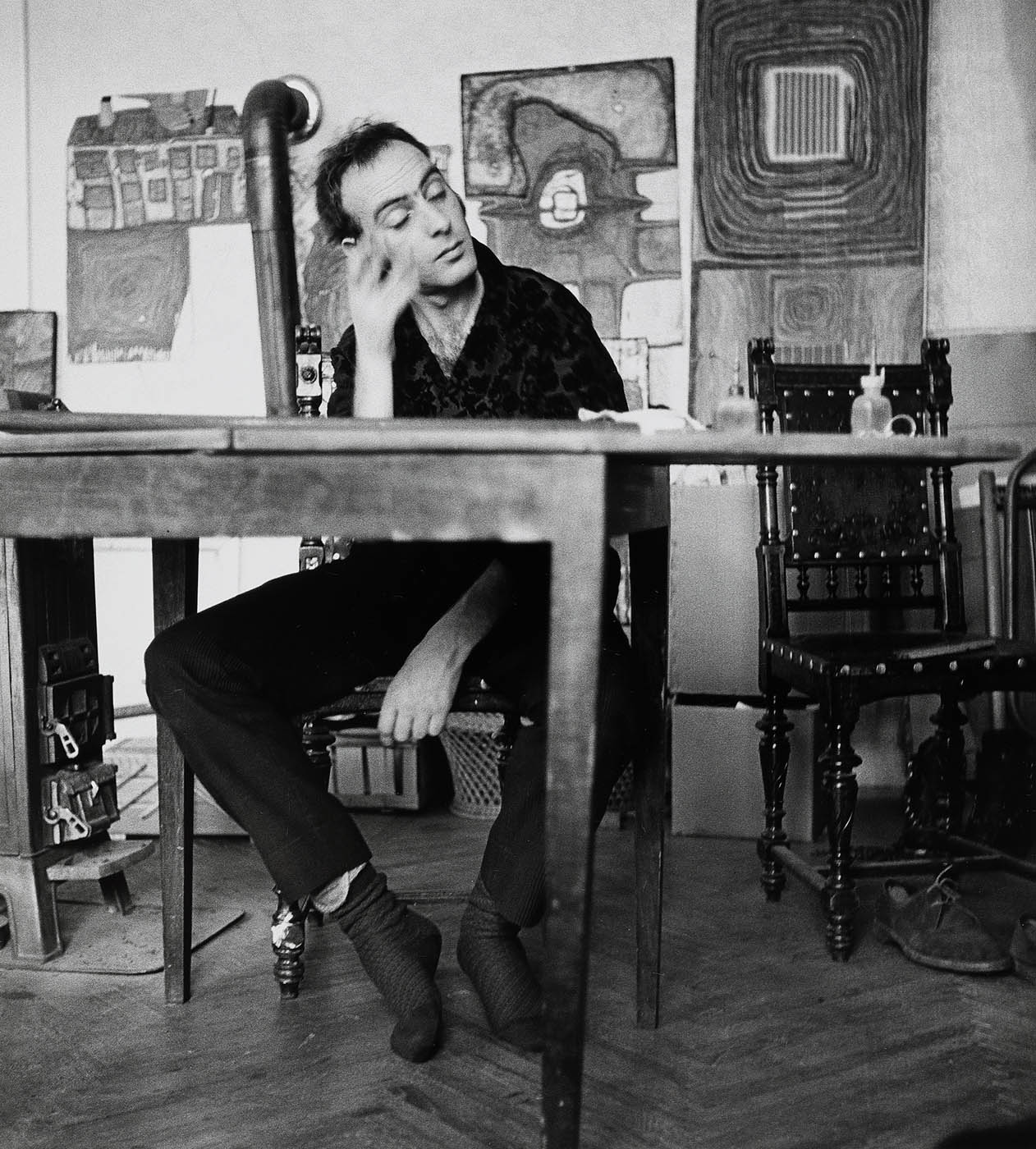
Salzburg’s contribution to this collaborative project will present the artist’s portraits. With her series of works entitled “Artists at work” (1954-1961), for example, Mejchar demonstrates impressively how she engages with the artistic personalities of Christa Hauer, Friedensreich Hundertwasser, Josef Mikl and Arnulf Rainer by mapping their working situation in their studios. But she also demonstrated the same precision of perception when encountering the inanimate objects in her surroundings, thereby giving landscapes, flowers and discarded furniture the appearance of animated portraits.
The photo collections at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg hold a total of 665 photographs by Mejchar. Otto Breicha, the first director of the Museum’s predecessor institution, was a long-time colleague of Mejchar who recognised the artistic value of her photographic work and helped to promote it. As early as 1982, one year before the official opening of the Rupertinum, a comprehensive collection of her work was added to the photographic collection that later grew through further purchases and donations and today constitutes a focal point of the Museum’s photographic holdings.
Text from the Museum der Moderne Salzburg website
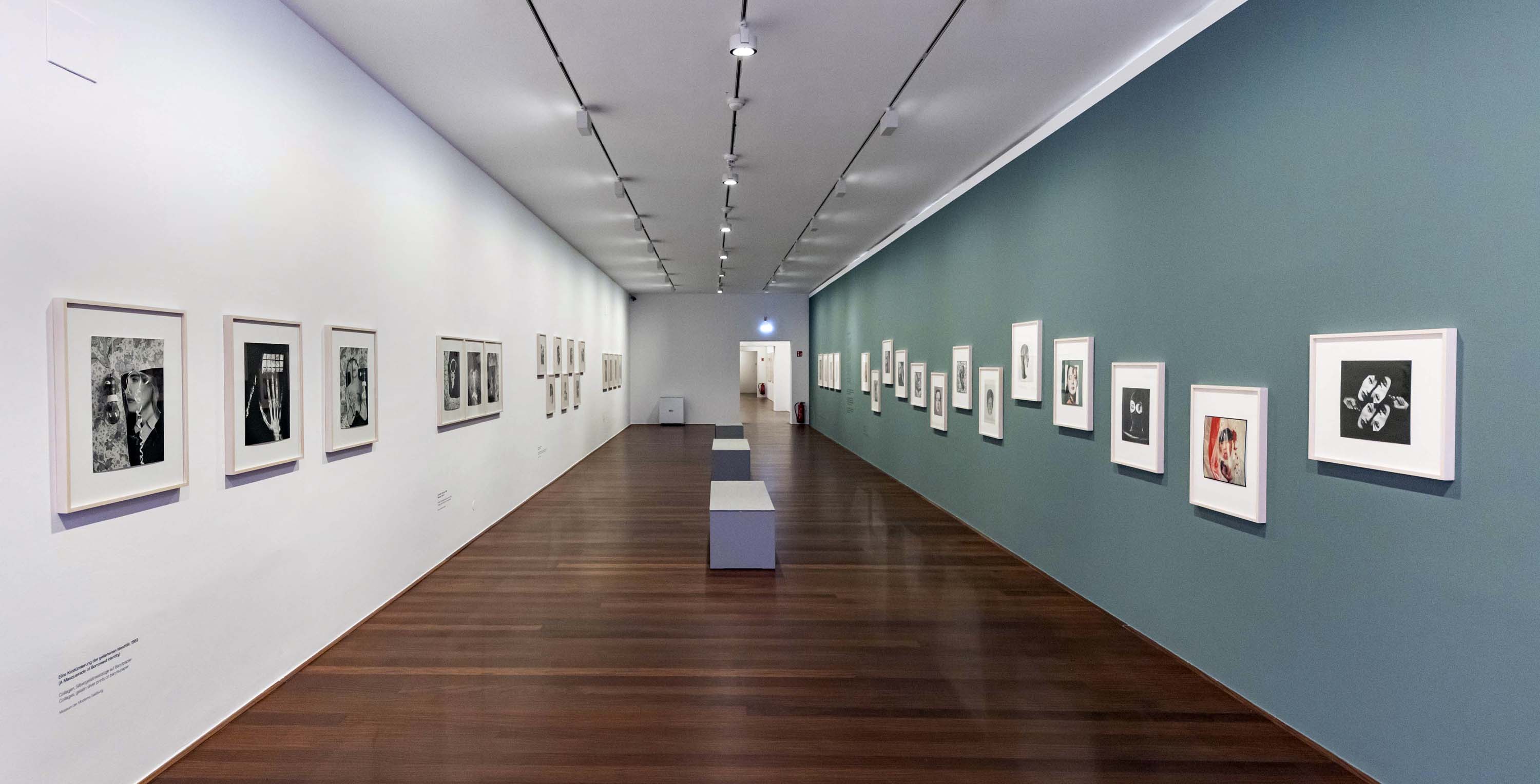
Installation view of the exhibition The Poetry of the Everyday. Photographs by Elfriede Mejchar, Museum der Moderne Salzburg 2024 showing at left, work from Mejchar’s series Eine Kostümierung der geliehenen Identität (A Masquerade of Borrowed Identity) (below); and at right, photographs from the series Nobody is Perfect (below)
© Museum der Moderne Salzburg
Photo: wildbild/Günter Freund
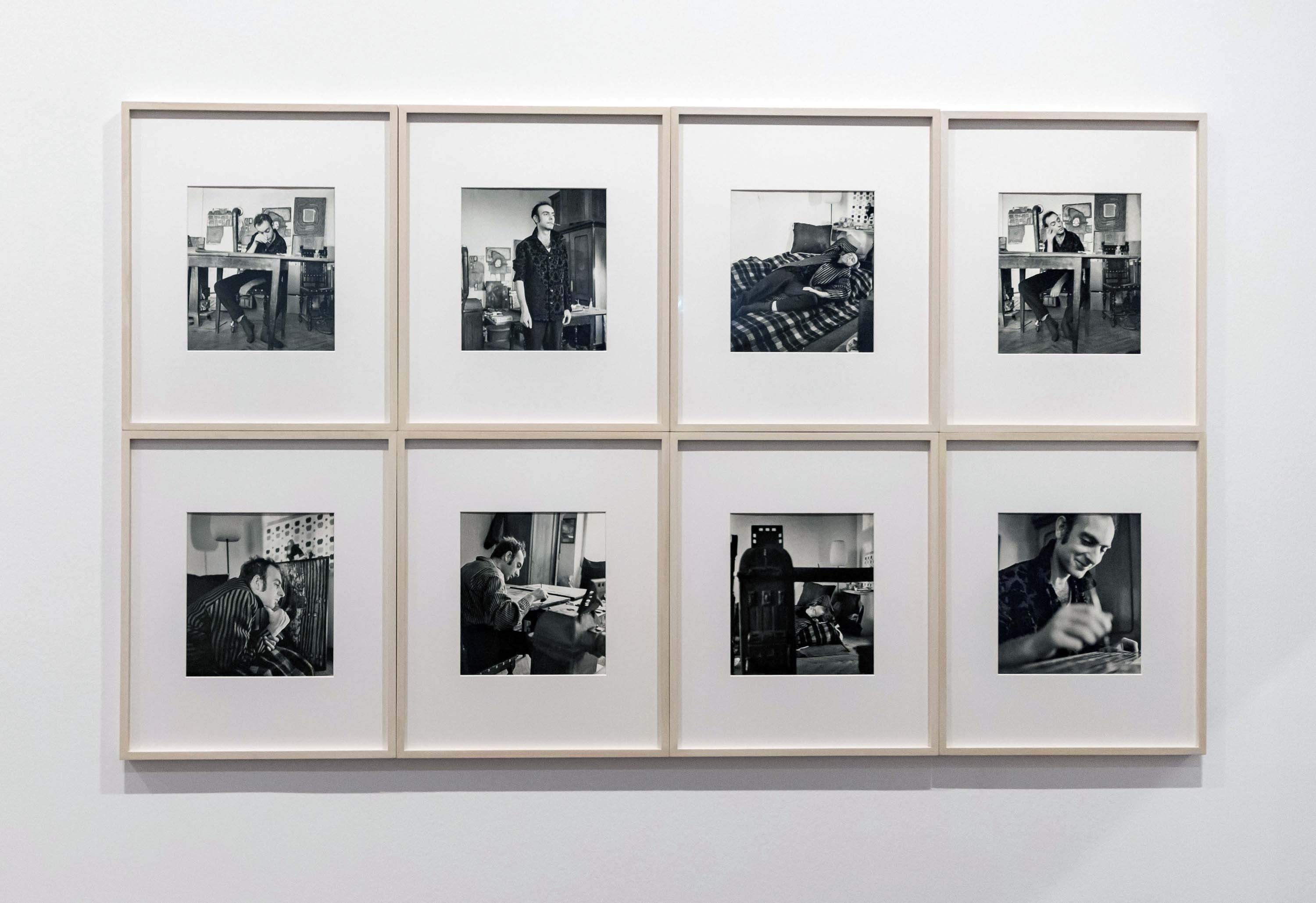
Installation view of the exhibition The Poetry of the Everyday. Photographs by Elfriede Mejchar, Museum der Moderne Salzburg 2024 showing work from Mejchar’s series Künstler bei der Arbeit, 1954-1961 (Artists at work, 1954-1961) (below)
© Museum der Moderne Salzburg
Photo: wildbild/Günter Freund
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
Arnulf Rainer
1954-1961
From the series Künstler bei der Arbeit, 1954-1961 (Artists at work, 1954-1961)
Silver gelatin print on baryta paper
Federal Photography Collection at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg
Arnulf Rainer (Austrian, b. 1929)
Arnulf Rainer (born 8 December 1929) is an Austrian painter noted for his abstract informal art.
Rainer was born in Baden, Austria. During his early years, Rainer was influenced by Surrealism. In 1950, he founded the Hundsgruppe (dog group) together with Ernst Fuchs, Arik Brauer, and Josef Mikl. After 1954, Rainer’s style evolved towards Destruction of Forms, with blackenings, overpaintings, and maskings of illustrations and photographs dominating his later work. He was close to the Vienna Actionism, featuring body art and painting under the influence of drugs. He painted extensively on the subject of Hiroshima such as it relates to the nuclear bombing of the Japanese city and the inherent political and physical fallout.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
Christa Hauer
1954-1961
From the series Künstler bei der Arbeit, 1954-1961 (Artists at work, 1954–1961)
Silver gelatin print on baryta paper
Federal Photography Collection at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg
Christa Hauer-Fruhmann (Austrian, 1925-2013)
Christa Hauer-Fruhmann (b. March 13, 1925 in Vienna; d. March 21, 2013 in St. Pölten) was an Austrian painter. …
She was initially under the artistic influence of her father and created representational works such as landscapes, portraits and nude drawings. At the end of her stay in the USA, around 1960, she turned to abstract painting, particularly action painting, color field painting and informal art. Later, cosmic forms and a turn to nature determined her works.
Text from the German Wikipedia website translated by Google Translate
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
Friedensreich Hundertwasser
1954-1961
From the series Künstler bei der Arbeit, 1954-1961 (Artists at work, 1954-1961)
Silver gelatin print on baryta paper
Federal Photography Collection at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg
Friedensreich Hundertwasser (Austrian, 1928-2000)
Friedensreich Hundertwasser Regentag Dunkelbunt (born Friedrich Stowasser, born December 15, 1928 in Vienna; died February 19, 2000 on board the Queen Elizabeth 2 off Brisbane) was an Austrian artist, who worked primarily as a painter, but also in the fields of architecture and environmental protection. …
Artistically, he was an opponent of the “straight line” and any kind of standardisation throughout his life. This is particularly evident in his work in the field of building design, which is characterised by imaginative liveliness and individuality, but above all by the inclusion of nature in architecture.
Text from the German Wikipedia website translated by Google Translate
Installation view of the exhibition The Poetry of the Everyday. Photographs by Elfriede Mejchar, Museum der Moderne Salzburg 2024 showing photographs from Mejchar’s series Porträts von Künstler-Photographen und Kunstvermittlern (Portraits of Artist Photographers and Art Educators) (below)
© Museum der Moderne Salzburg, photo: wildbild/Günter Freund
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
Aglaia Konrad
1988
From the series Porträts von Künstler-Photographen und Kunstvermittlern (Portraits of Artist Photographers and Art Educators)
Silver gelatin print on baryta paper
Federal Photography Collection at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg
Aglaia Konrad (Austrian, b. 1960)
Aglaia Konrad (born 1960) is an Austrian photographer and educator living in Brussels. …
Konrad’s photographs explore urban space in large cities. Konrad’s work has been to known to be distinctly international in that it highlights urban elements independent of cultural markers. Her work highlights the ubiquitous elements of urban life through methods like filming a city from the perspective of a moving car or compiling a series of aerial views of skyscrapers.
Text from the Wikipedia website
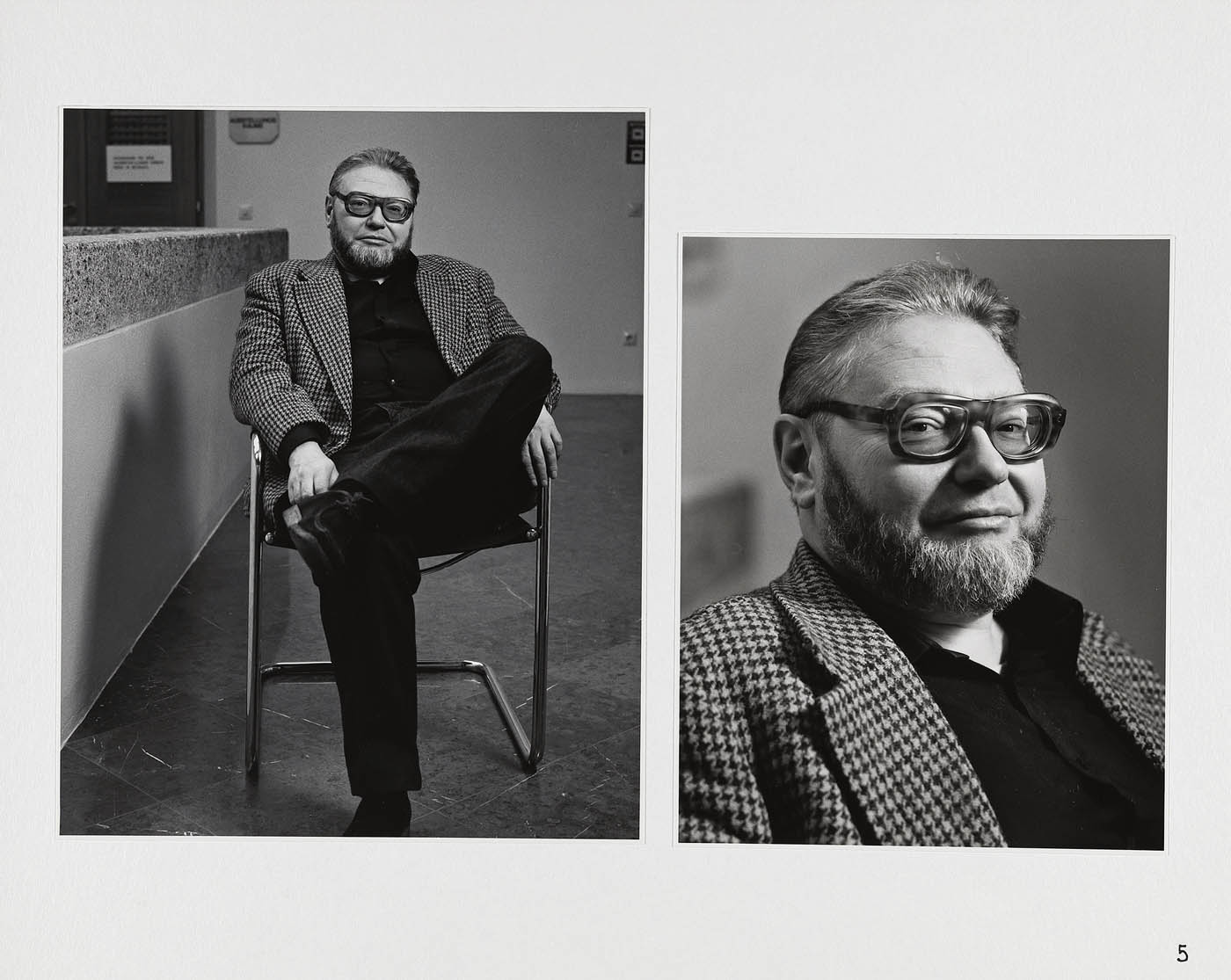
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
Prof. Dr. Otto Breicha
1988
From the series Porträts von Künstler-Photographen und Kunstvermittlern (Portraits of Artist Photographers and Art Educators)
Silver gelatin print on baryta paper
Federal Photography Collection at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg
Otto Breicha (Austrian, 1932-2003)
Otto Breicha (b. 26 July 1932 in Vienna; d, 28 December 2003 in Vienna) was an Austrian art historian, publicist and museum director. …
Breicha is considered an important integration figure in the Austrian art and literature scene of the 1960s. As director of the Rupertinum he collected works by Kurt Moldovan, Günter Brus, Fritz Wotruba and Gotthard Muhr, among others. He edited portfolios by Karl Anton Fleck, Gotthard Muhr, Peter Pongratz, Alois Riedl, Karl Rössing, Johannes Wanke, Max Weiler and many others.
Breicha built up an important photo collection in the Rupertinum. He also took photos of authors himself, especially during his time at the Austrian Society for Literature from 1962 to 1972.
Text from the German Wikipedia website translated by Google Translate
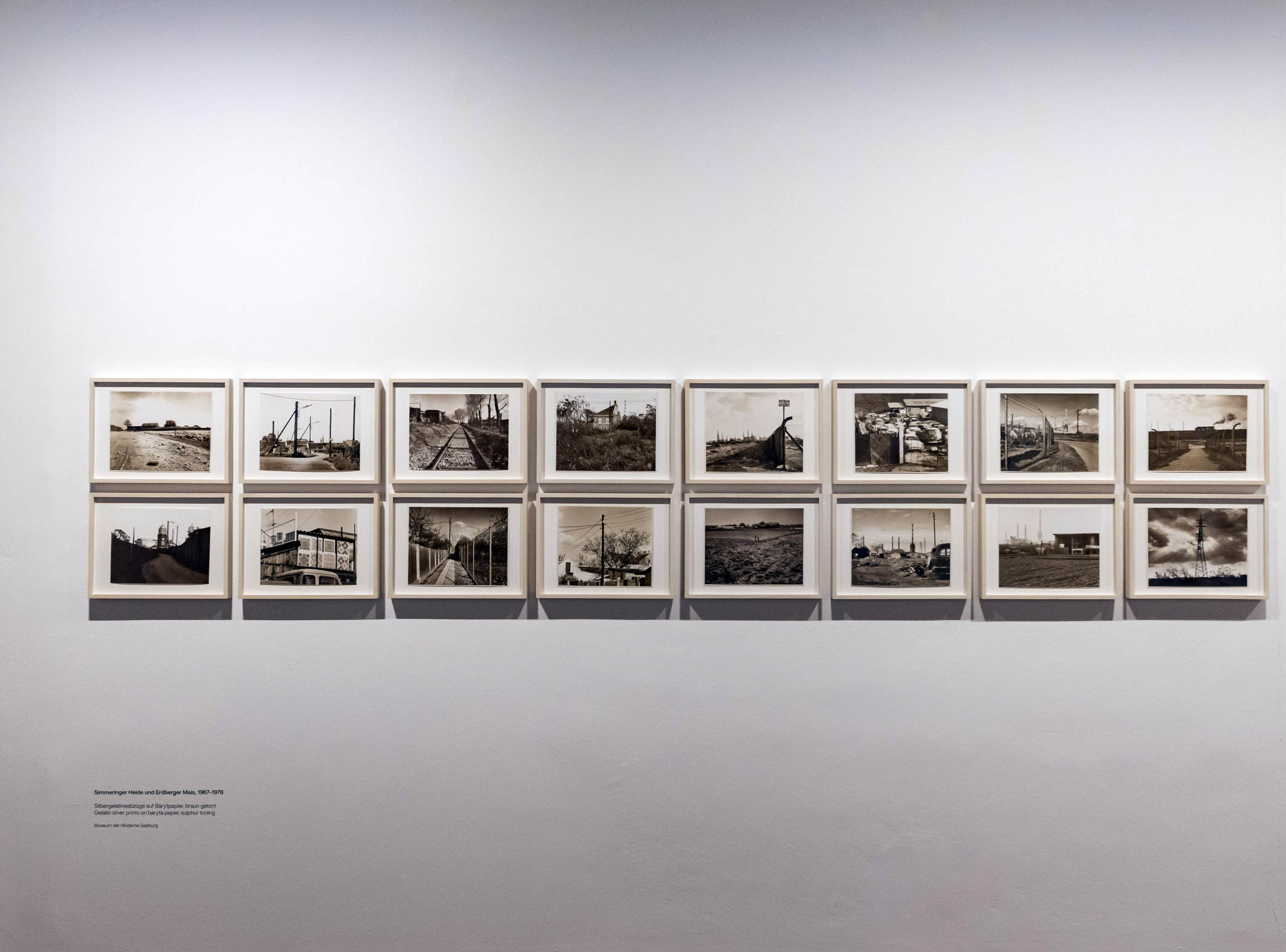
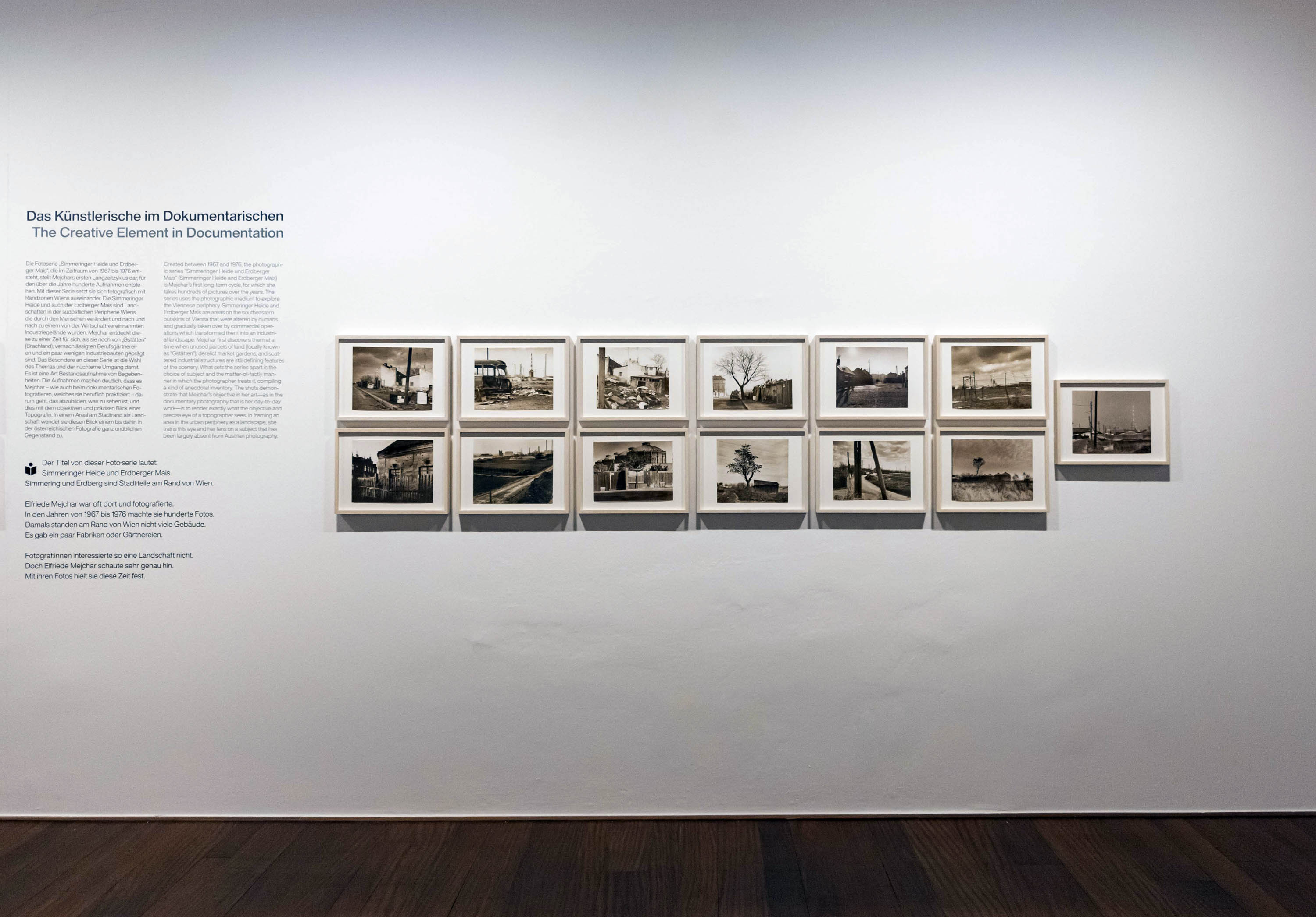
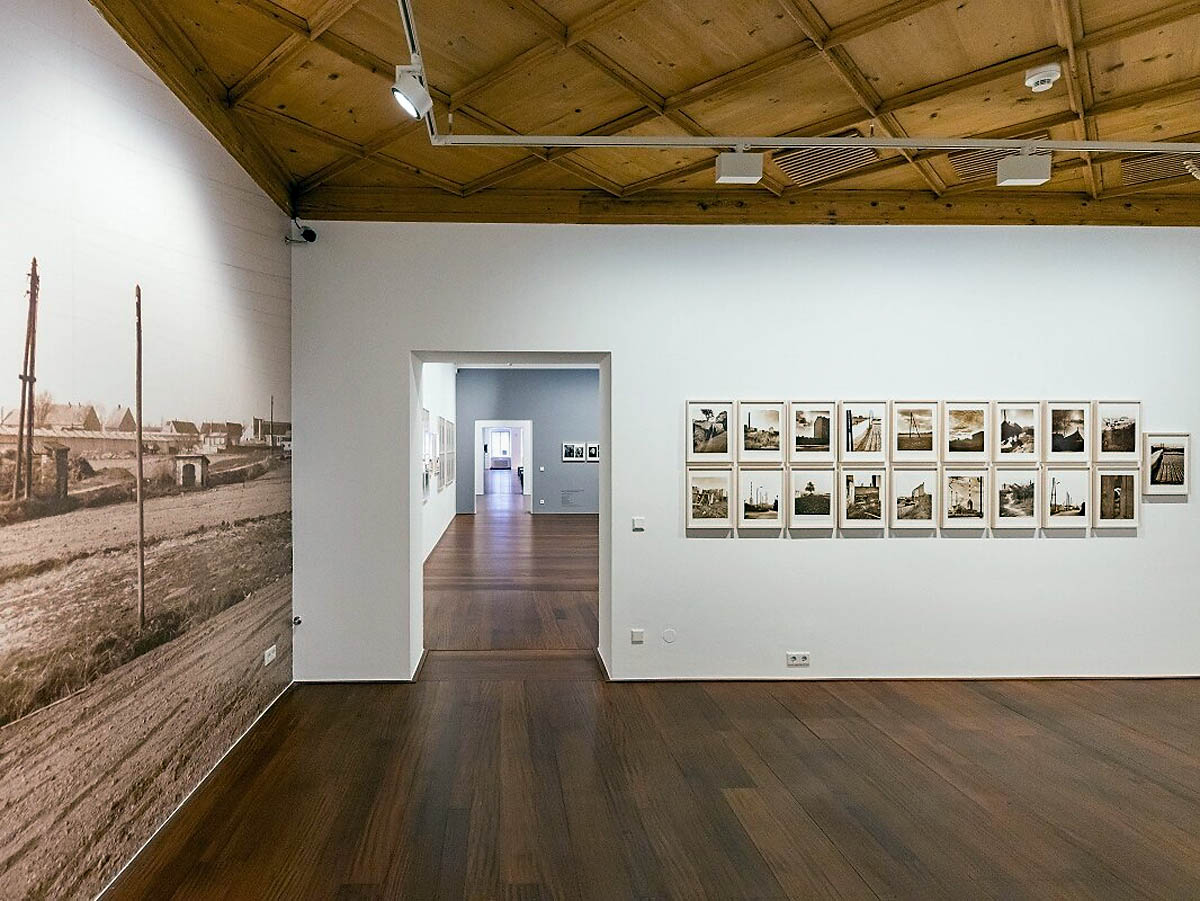
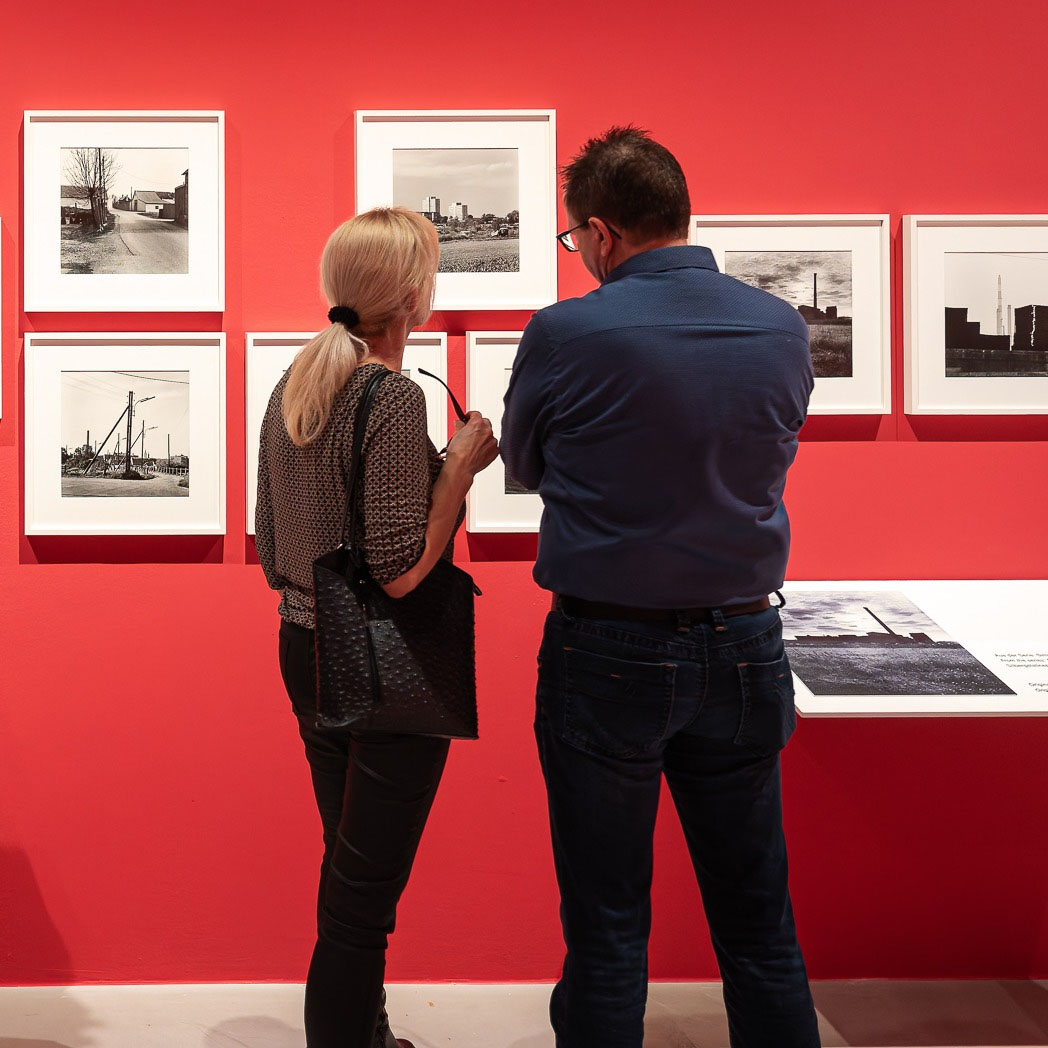
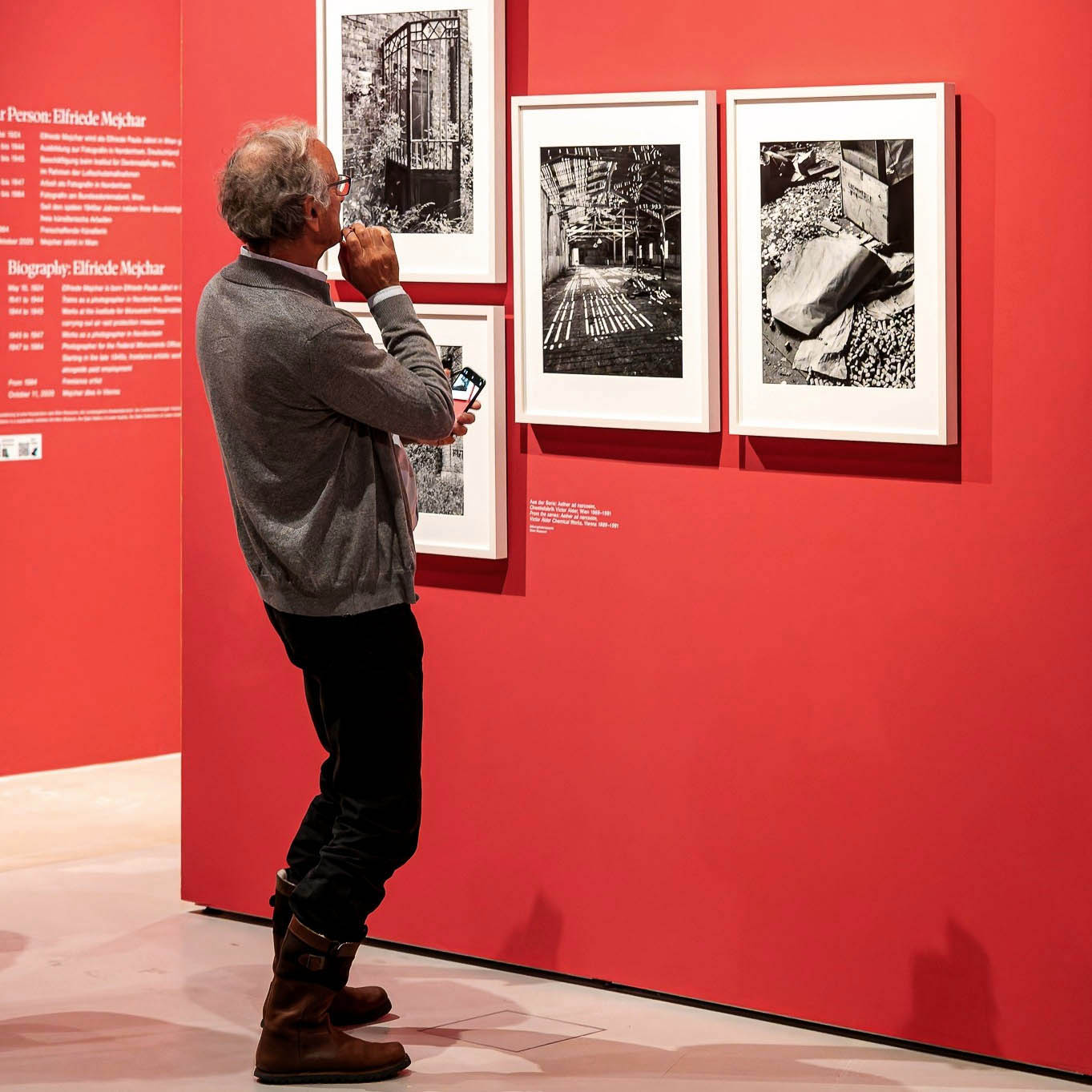
Installation view of the exhibition The Poetry of the Everyday. Photographs by Elfriede Mejchar, Museum der Moderne Salzburg 2024 showing photographs from Mejchar’s series Simmeringer Heide und Erdberger Mais, 1967-1976 (below)
© Museum der Moderne Salzburg, photo: wildbild/Günter Freund
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
From the series Simmeringer Heide und Erdberger Mais, 1967-1976
Silver gelatine print on baryta paper, brown toned
Museum der Moderne Salzburg
© Bildrecht, Vienna 2024
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
From the series Simmeringer Heide und Erdberger Mais, 1967-1976
Silver gelatine print on baryta paper, brown toned
Museum der Moderne Salzburg
© Bildrecht, Vienna 2024
The Creative Element in Documentation
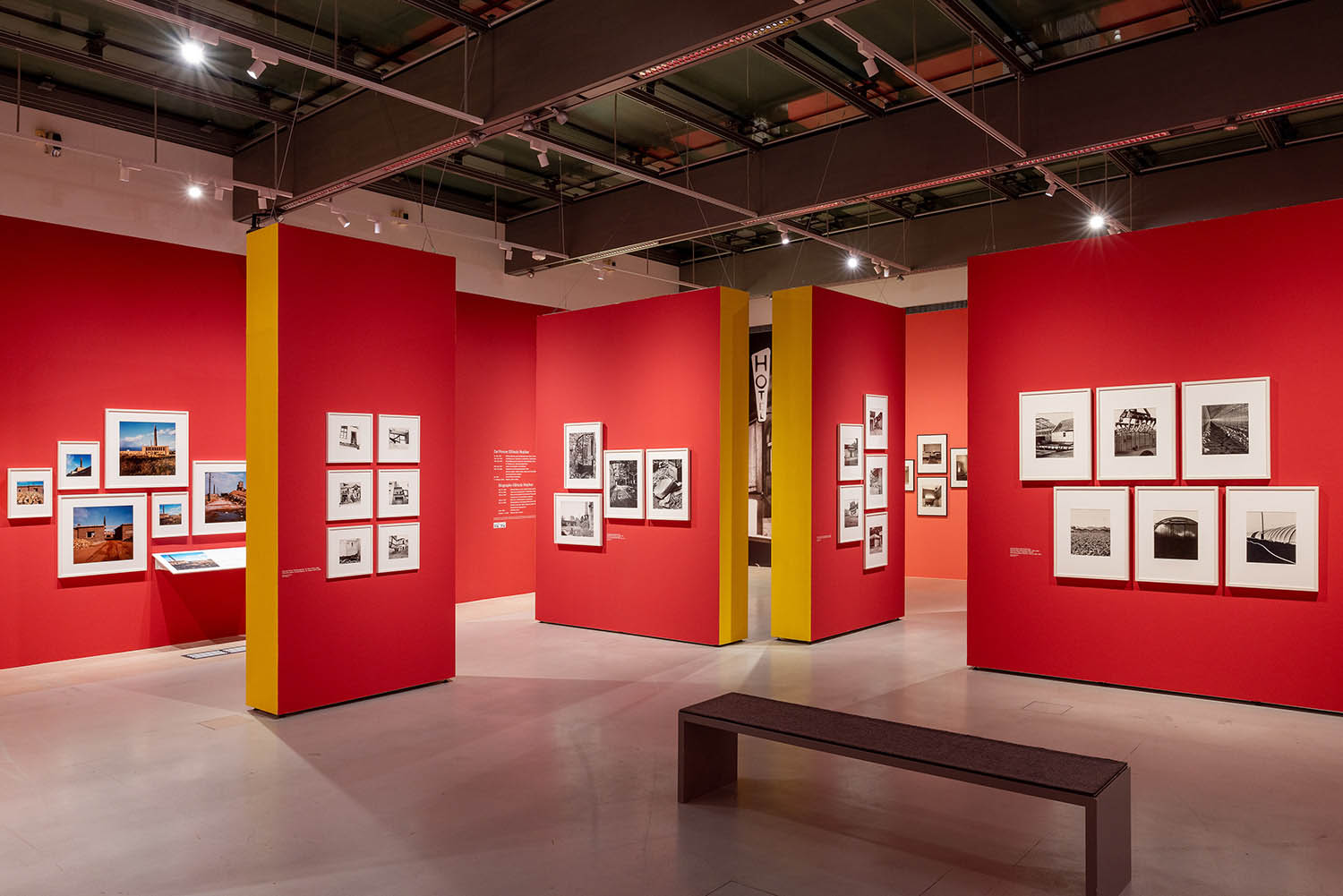
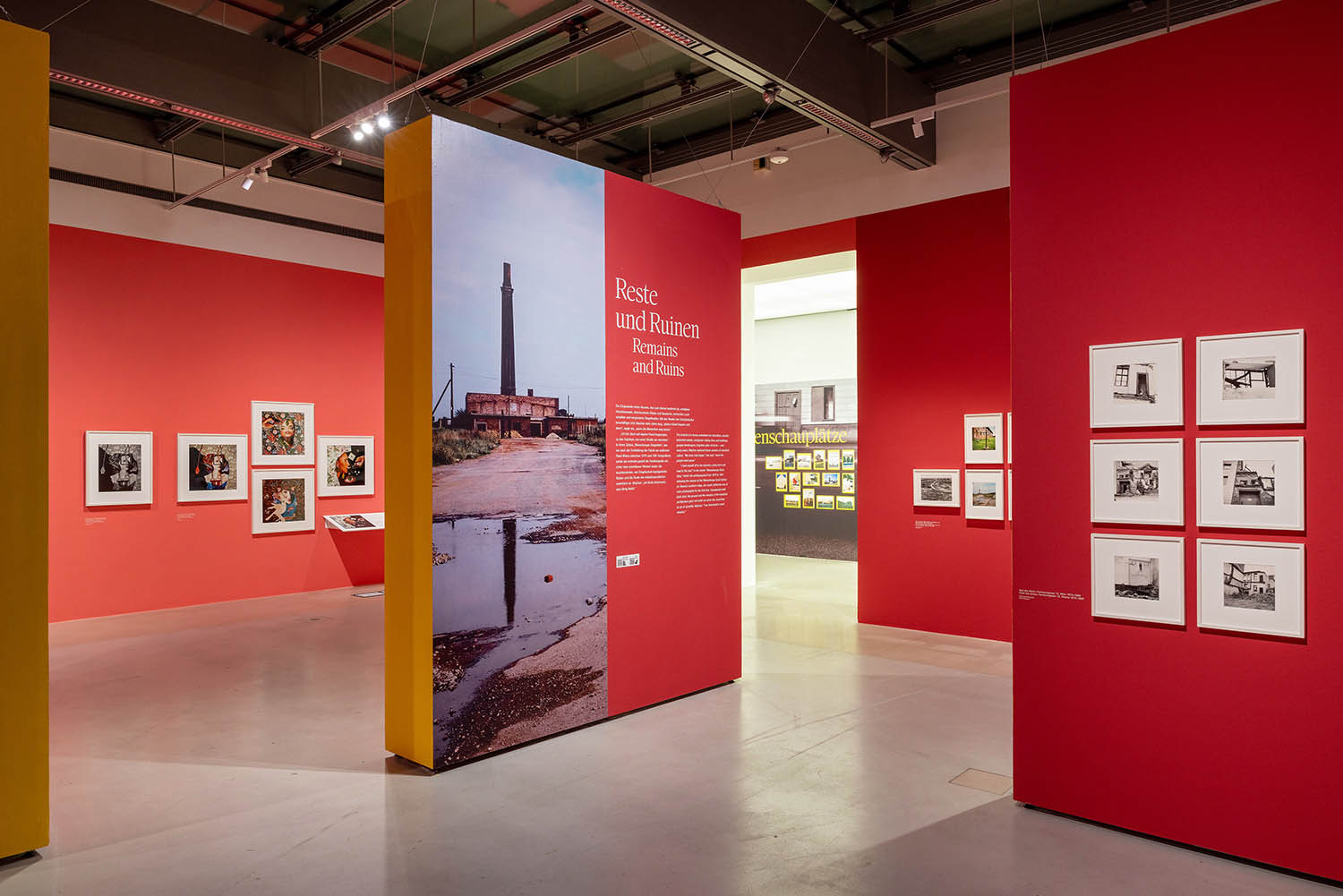
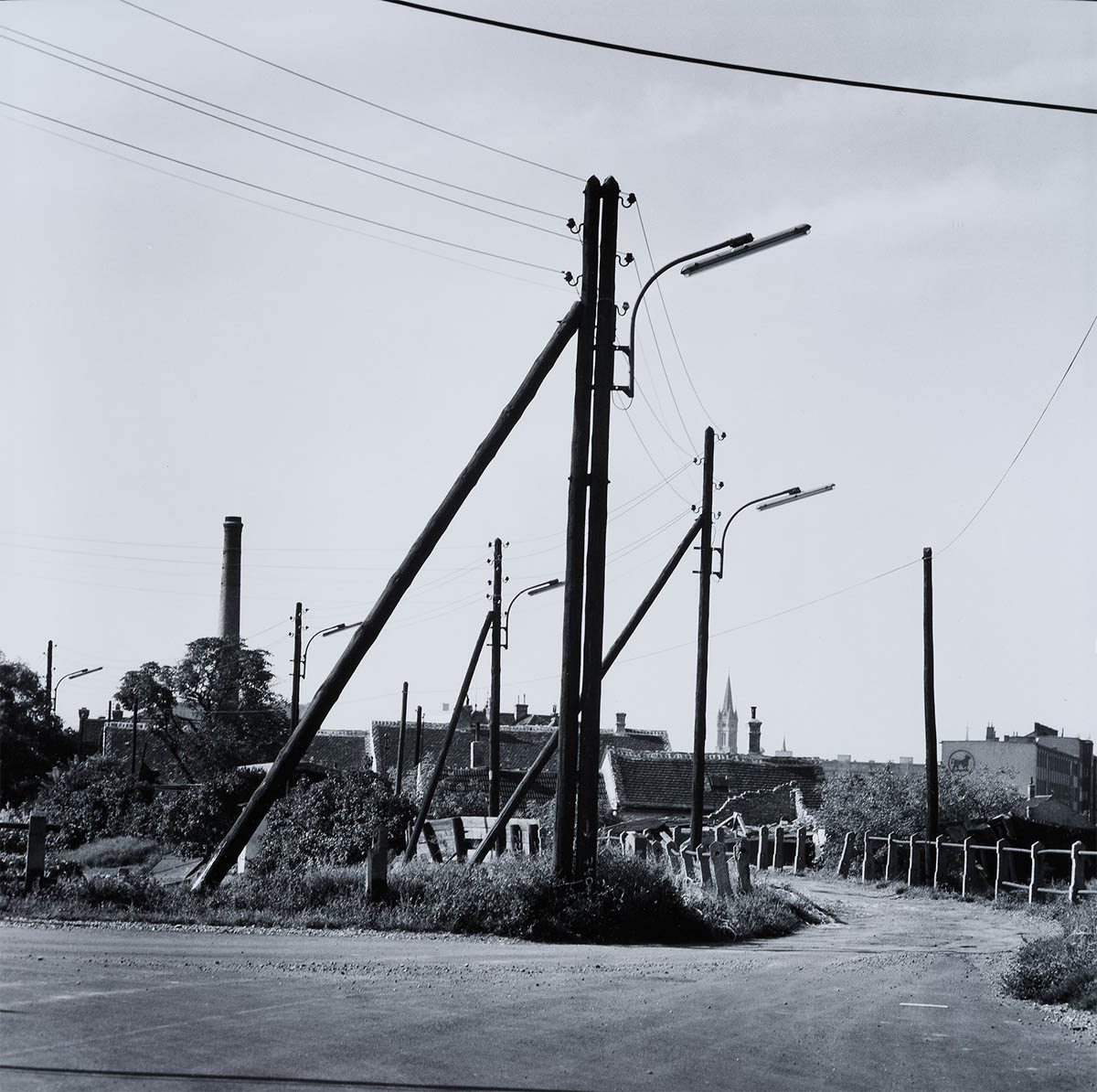
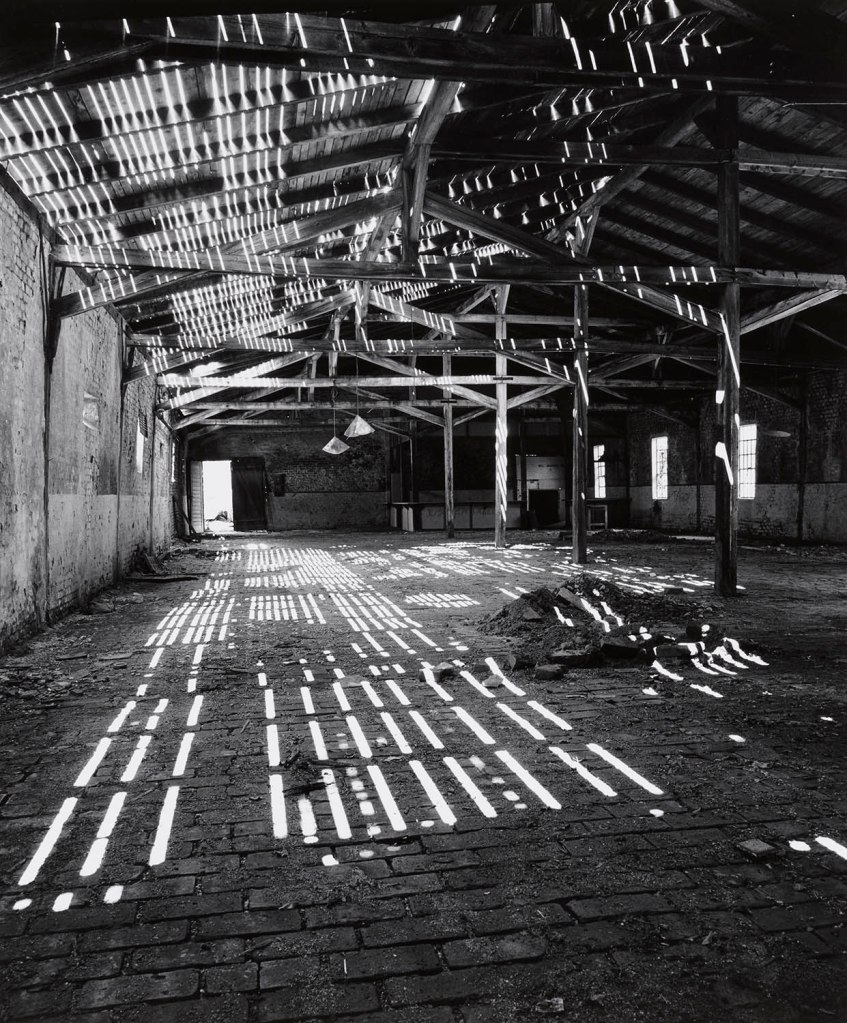
Created between 1967 and 1976, the photographic series “Simmeringer Heide und Erdberger Mais” (Simmeringer Heide and Erdberger Mais) is Mejchar’s first long-term cycle, for which she takes hundreds of pictures over the years. The series uses the photographic medium to explore the Viennese periphery. Simmeringer Heide and Erdberger Mais are areas on the southeastern outskirts of Vienna that were altered by humans and gradually taken over by commercial operations which transformed them into an industrial landscape. Mekchav first discovers them at a time when unused parcels of land (locally known as “Gstatten”), derelict market gardens, and scattered industrial structures are still defining features of the scenery. What sets the series apart is the choice of subject and the matter-of-fact manner in which the photographer treats it, compiling a kind of anecdotal inventory. The shots demonstrate that Mejchar’s objective in there art – as in the documentary photography that is her day-to-day work – is to render exactly what the objective and precise eye of a topographer sees. In framing an area in the urban periphery as a landscape, she trains this eye and her lens on a subject that has been largely absent from Austrian photography.
Wall text from the exhibition
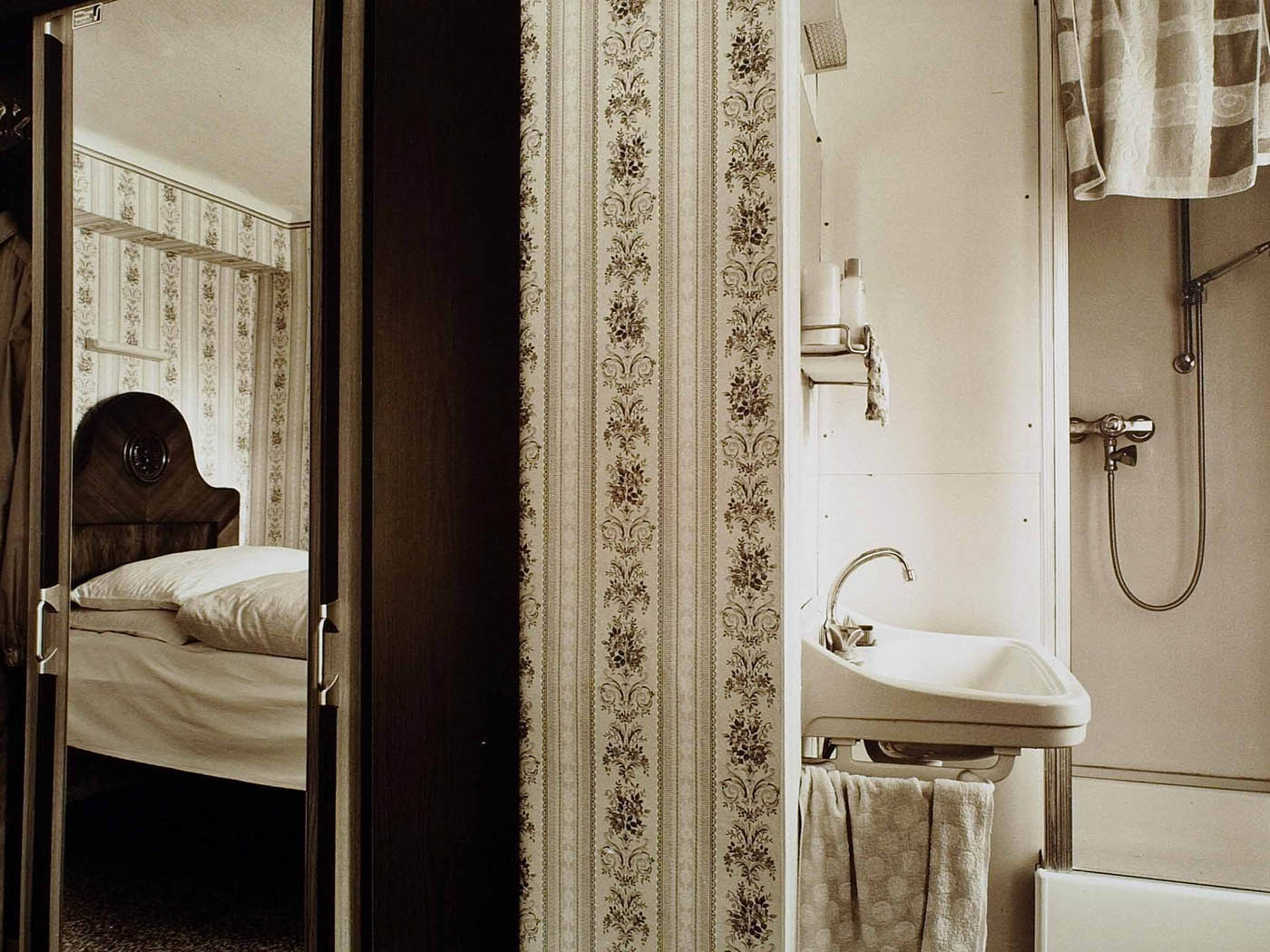
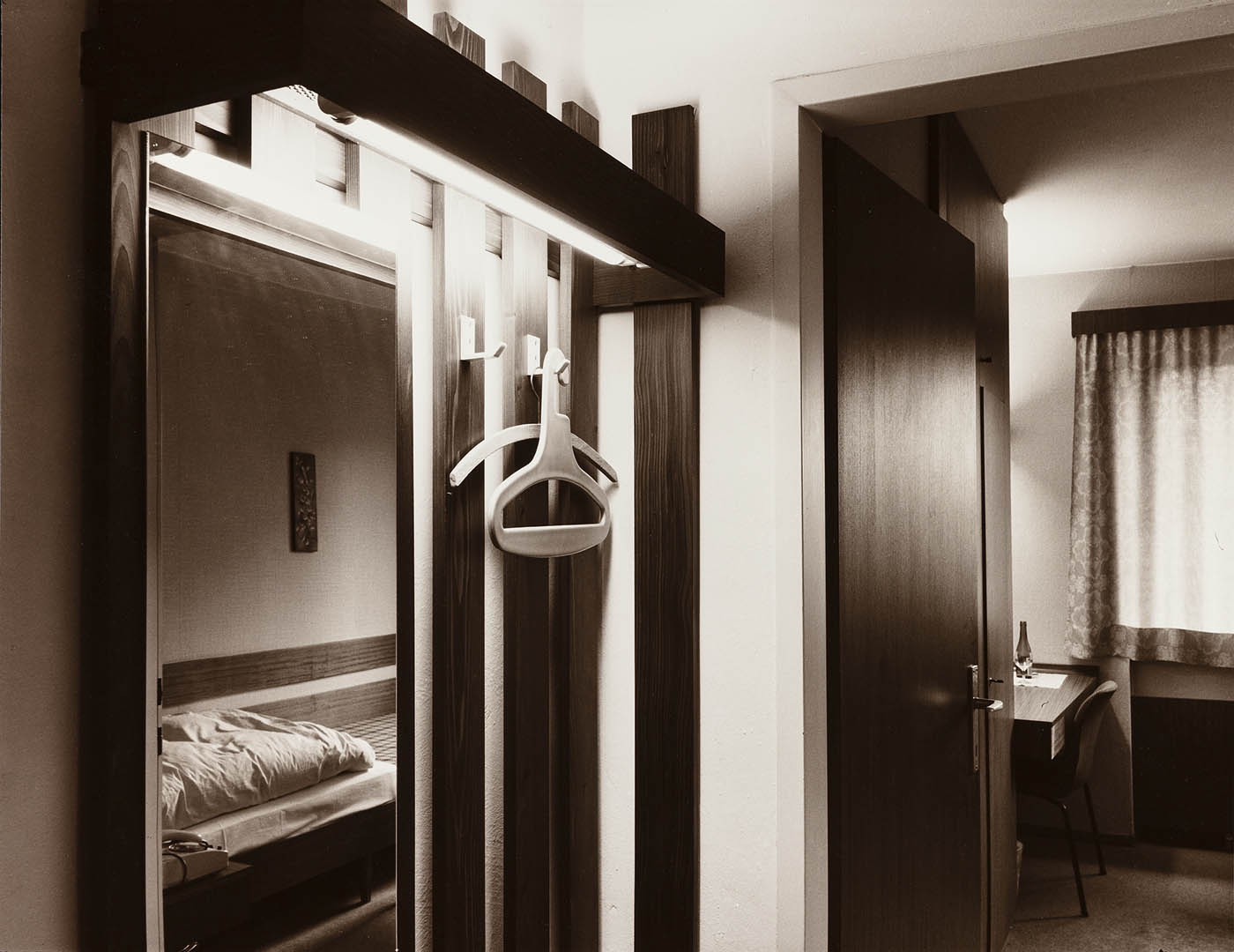
Installation view of the exhibition The Poetry of the Everyday. Photographs by Elfriede Mejchar, Museum der Moderne Salzburg 2024 showing work from Mejchar’s series Hotel (Fremdenzimmer), 1970-1986 (Hotel (Guest Room), 1970-1986) (below)
© Museum der Moderne Salzburg, photo: wildbild/Günter Freund
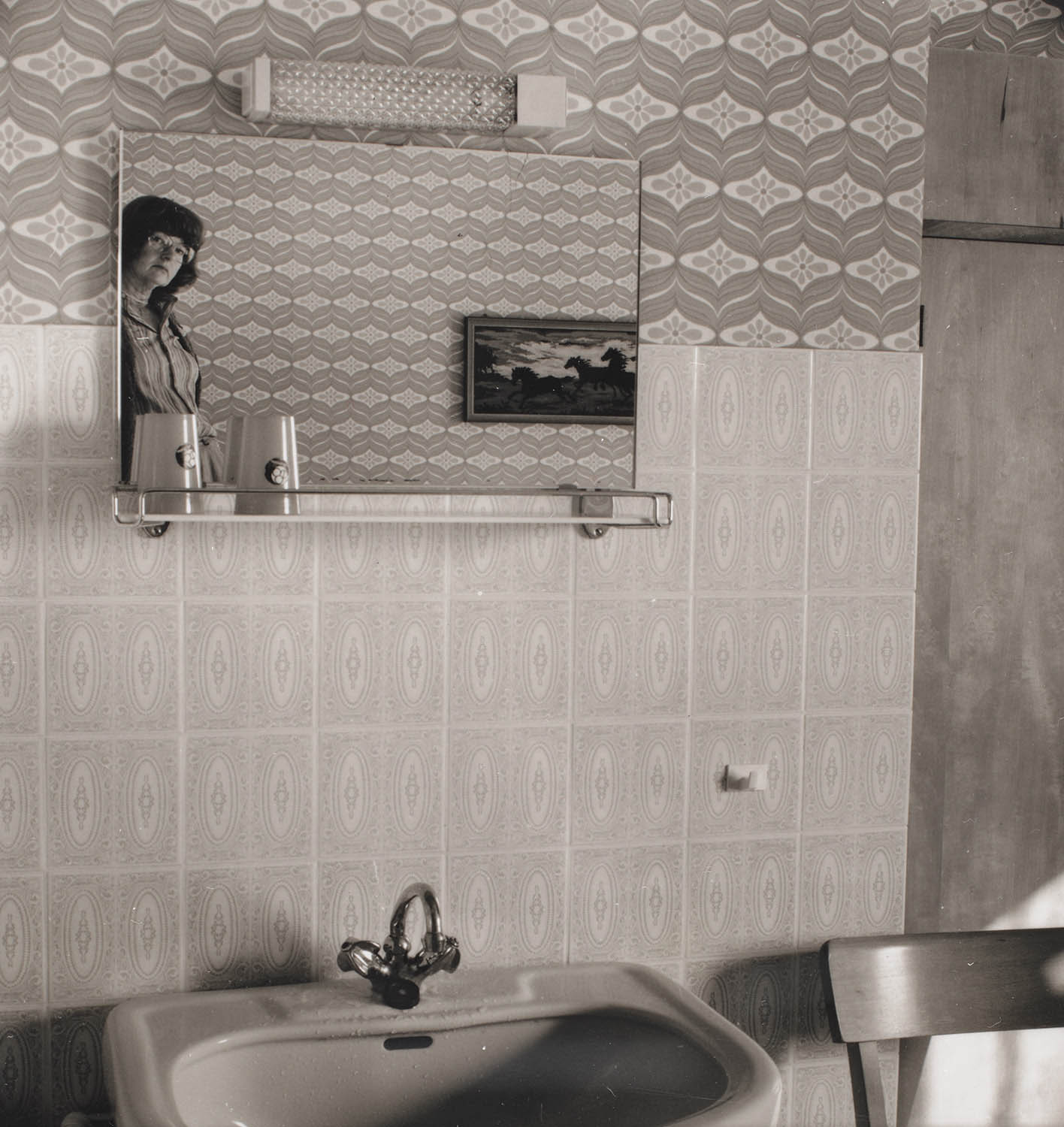
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
From the series Hotel (Fremdenzimmer), 1970-1986 (Hotel (Guest Room), 1970-1986)
Silver gelatin print on baryta paper, brown tones
Federal Photography Collection at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
From the series Hotel (Fremdenzimmer), 1970-1986 (Hotel (Guest Room), 1970-1986)
Silver gelatin print on baryta paper, brown tones
Federal Photography Collection at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg
© Bildrecht, Vienna, 2024
Photo: Andrew Phelps
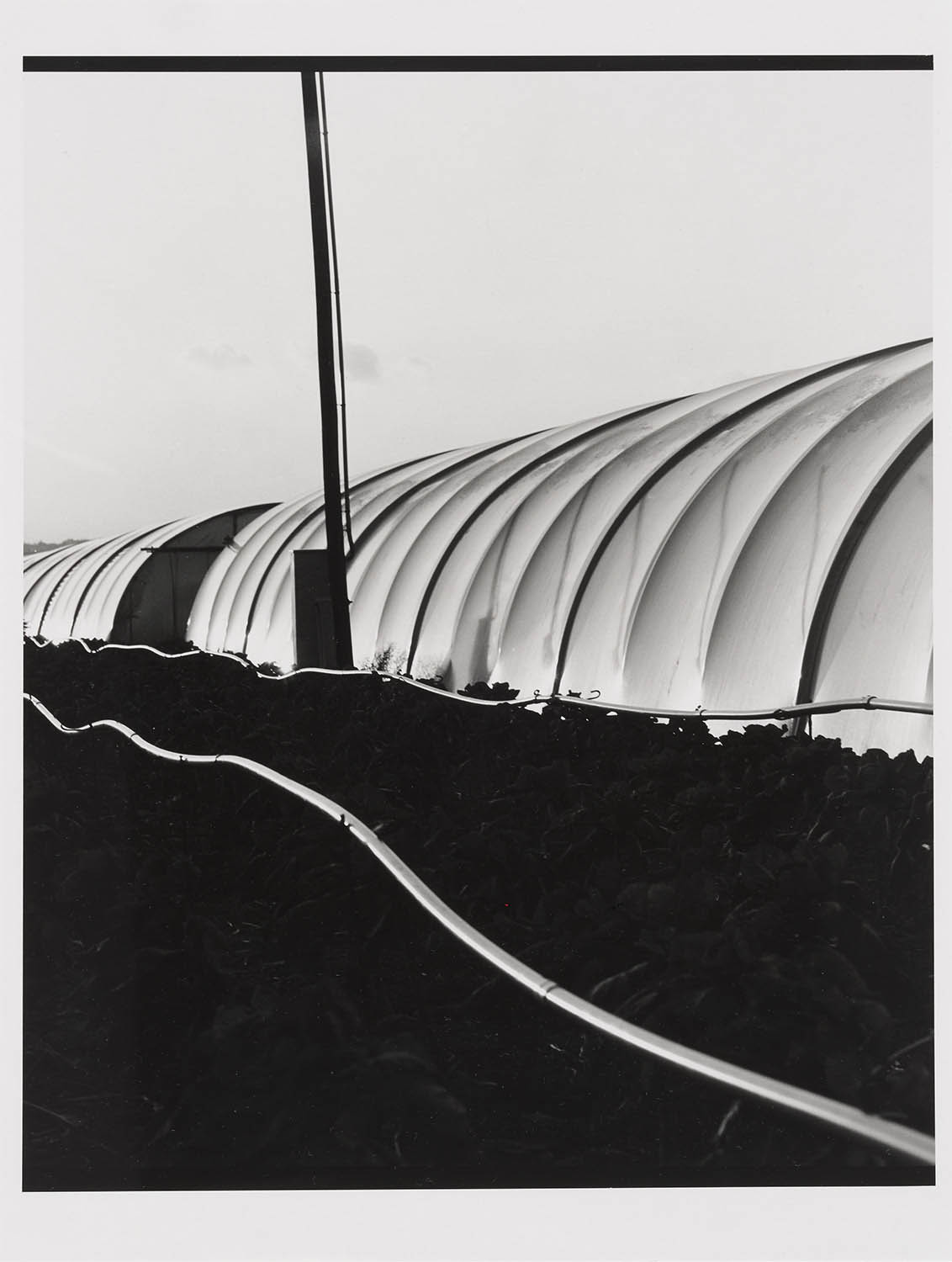
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
Flachsspinnerei in Stadl-Paura (Flax spinning mill in Stadl-Paura)
1986
© Elfriede Mejchar/Landessammlungen NÖ
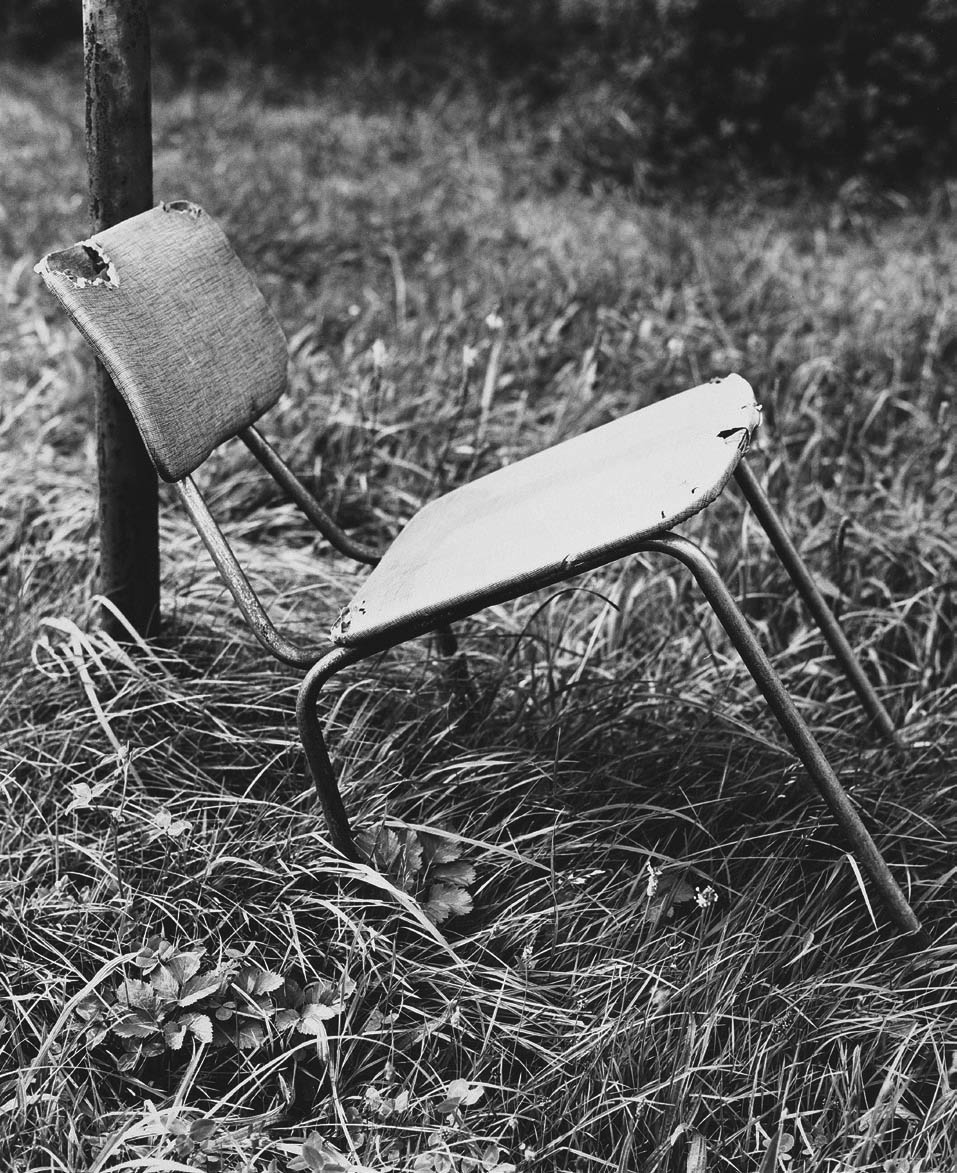
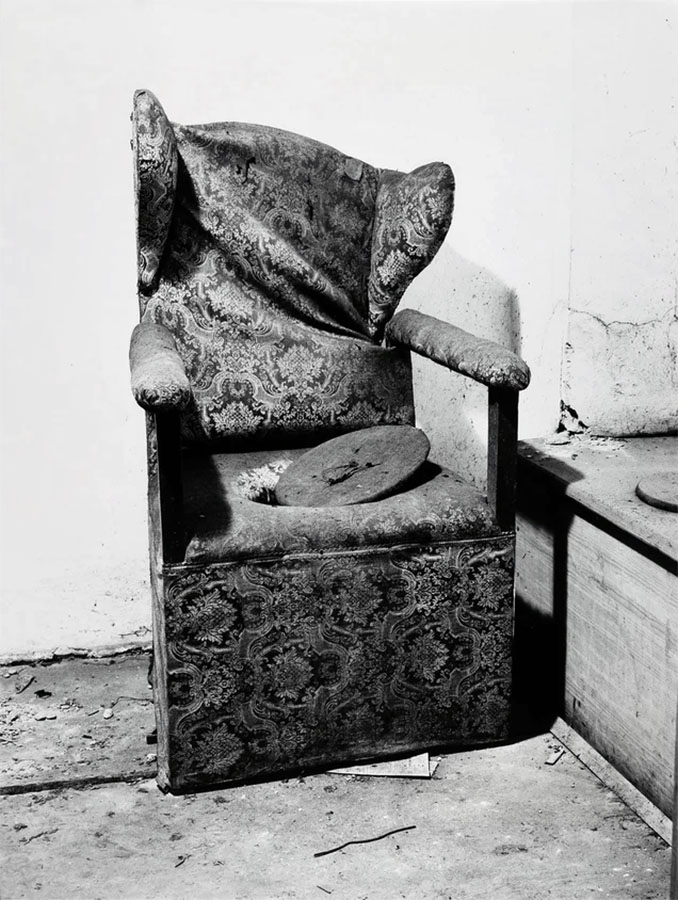
Installation view of the exhibition The Poetry of the Everyday. Photographs by Elfriede Mejchar, Museum der Moderne Salzburg 2024 showing work from Mejchar’s series Die Monatssesseln, 1986-1988 (The Armchairs of the Month, 1986-1988) (below)
© Museum der Moderne Salzburg, photo: wildbild/Günter Freund
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
From the series Die Monatssesseln, 1986-1988 (The Armchairs of the Month, 1986-1988)
Federal Photography Collection at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
From the series Die Monatssesseln, 1986-1988 (The Armchairs of the Month, 1986-1988)
Federal Photography Collection at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
From the series Oscillation (Salzburger Landesatelier) (Oscillation (Salzburg State Studio))
1988
Silver gelatin print on baryta paper
Federal Photography Collection at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg
Installation view of the exhibition The Poetry of the Everyday. Photographs by Elfriede Mejchar, Museum der Moderne Salzburg 2024 showing work from the Mejchar’s series Eine Kostümierung der geliehenen Identität (A Masquerade of Borrowed Identity) (below)
© Museum der Moderne Salzburg, photo: wildbild/Günter Freund
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
From the series Eine Kostümierung der geliehenen Identität (A Masquerade of Borrowed Identity)
1989
Gelatin silver print on baryta paper
Museum der Moderne Salzburg
© Bildrecht, Vienna, 2024
Photo: Andrew Phelps
Introduction
Elfriede Mejchar (1924-2020 Vienna, AT), the grande dame of Austrian photography, was in the employ of the Federal Monuments Office for almost forty years. Meanwhile, she also began her groundbreaking work on the outskirts of Vienna. Harnessing the photographic series as a documentary and investigative medium, she limned an imposing portrait of the urban landscape. Her work, which had a lasting influence on the evolution of photography in Austria, now also stands as an important documentary record of the country in the postwar period.
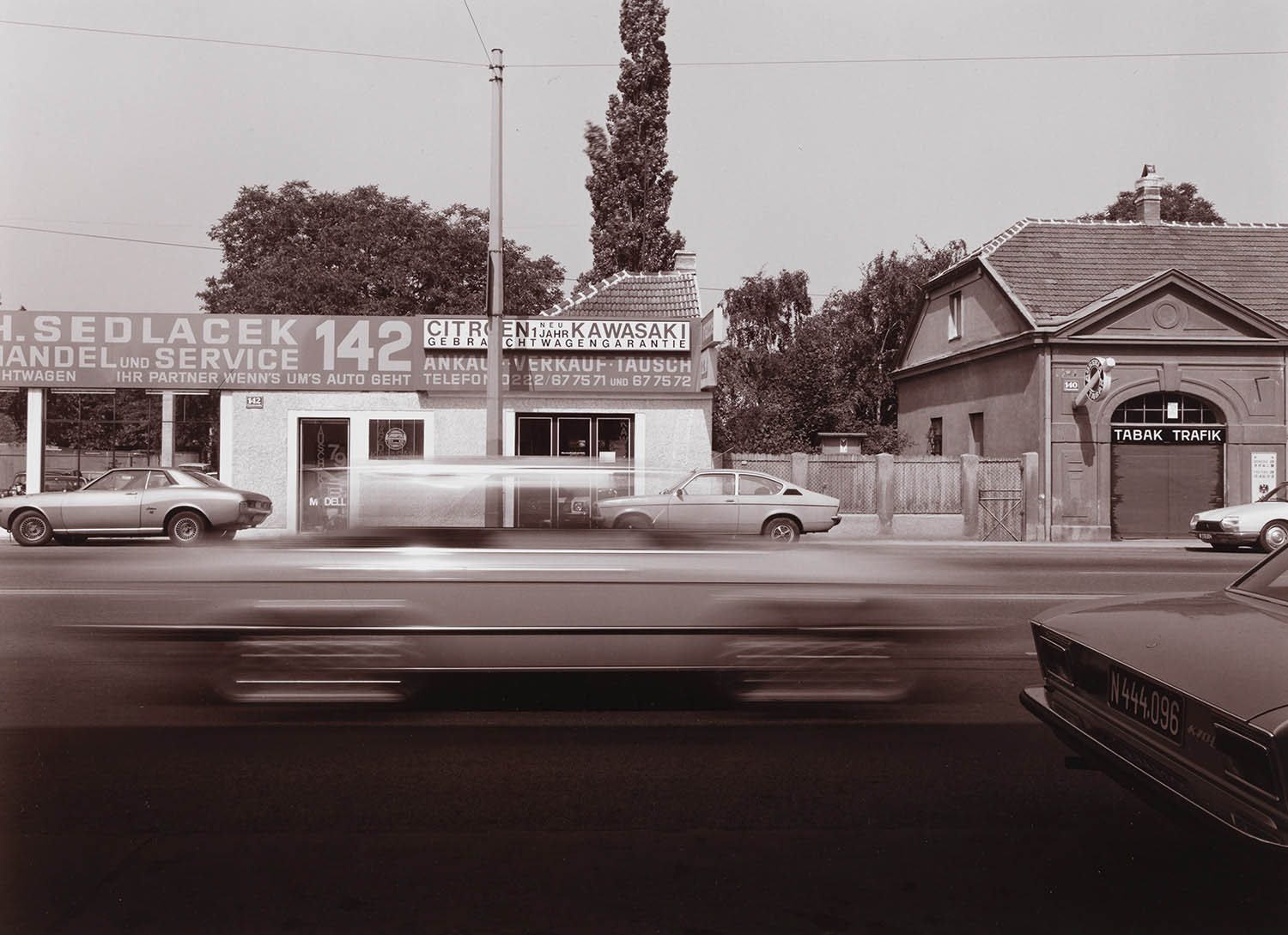
As a professional photographer, Mejchar traveled to various regions throughout Austria, including in Lower and Upper Austria and Styria, to capture buildings and cultural assets of art-historical significance in photographs. Yet she also used her official trips and her scant free time to pursue her own photographic interests, which focused on the small and seemingly trivial and the traces of civilisation that humans leave in nature or along the edges of the urban fabric and that receive little if any attention. It may seem that the documentary dimension is less important in the resulting works, that it is eclipsed by the narrative element. In fact, Mejchar fuses both, scrutinising her motifs with an attentive eye that picks up on the singular or peculiar and registers it without manipulation.
Elfriede Mejchar was not interested in the so-called “pivotal moment” and did not care for the conventional photojournalistic style of her time. Her work began when people had left, and she approached her themes from a very conceptual angle. Both the documentary series she created under the open sky and the object photographs, still lifes, and collages she made in her studio reflect this approach. She photographed the “evanescent before it evanesces”, in urban and rural landscapes and everyday scenes, capturing the changes that affected the particular scenery and its distinctive atmosphere.
The Creative Element in Documentation
Produced between 1967 and 1976, the photographic series “Simmeringer Heide and Erdberger Mais” is Mejchar’s first long-term cycle, for which she takes hundreds of pictures over the years. The series uses the photographic medium to explore the Viennese periphery. Simmeringer Heide and Erdberger Mais are areas on the southeastern outskirts of Vienna that were altered by humans and gradually taken over by commercial operations which transformed them into an industrial landscape. Mejchar first discovers them at a time when unused parcels of land (locally known as “Gstätten”), derelict market gardens, and scattered industrial structures are still defining features of the scenery. What sets the series apart is the choice of subject and the matter-of-factly manner in which the photographer treats it, compiling a kind of anecdotal inventory – empty lots, paths and roads, utility poles and a select few close-ups. The shots demonstrate that Mejchar’s objective in her art – as in the documentary photography that is her day-to-day work – is to render exactly what the objective and precise eye of a topographer sees. In framing an area in the urban periphery as a landscape, she trains this eye and her lens on a subject that has been largely absent from Austrian photography.
The use of a sulfur-based solution to tone the photographs – which is the cause of the brownish tinge – reflects a recurring concern in Mejchar’s photographs: existence in time and impermanence. In this instance, the technique’s purpose is not to alter the colour, but rather to make it more durable.
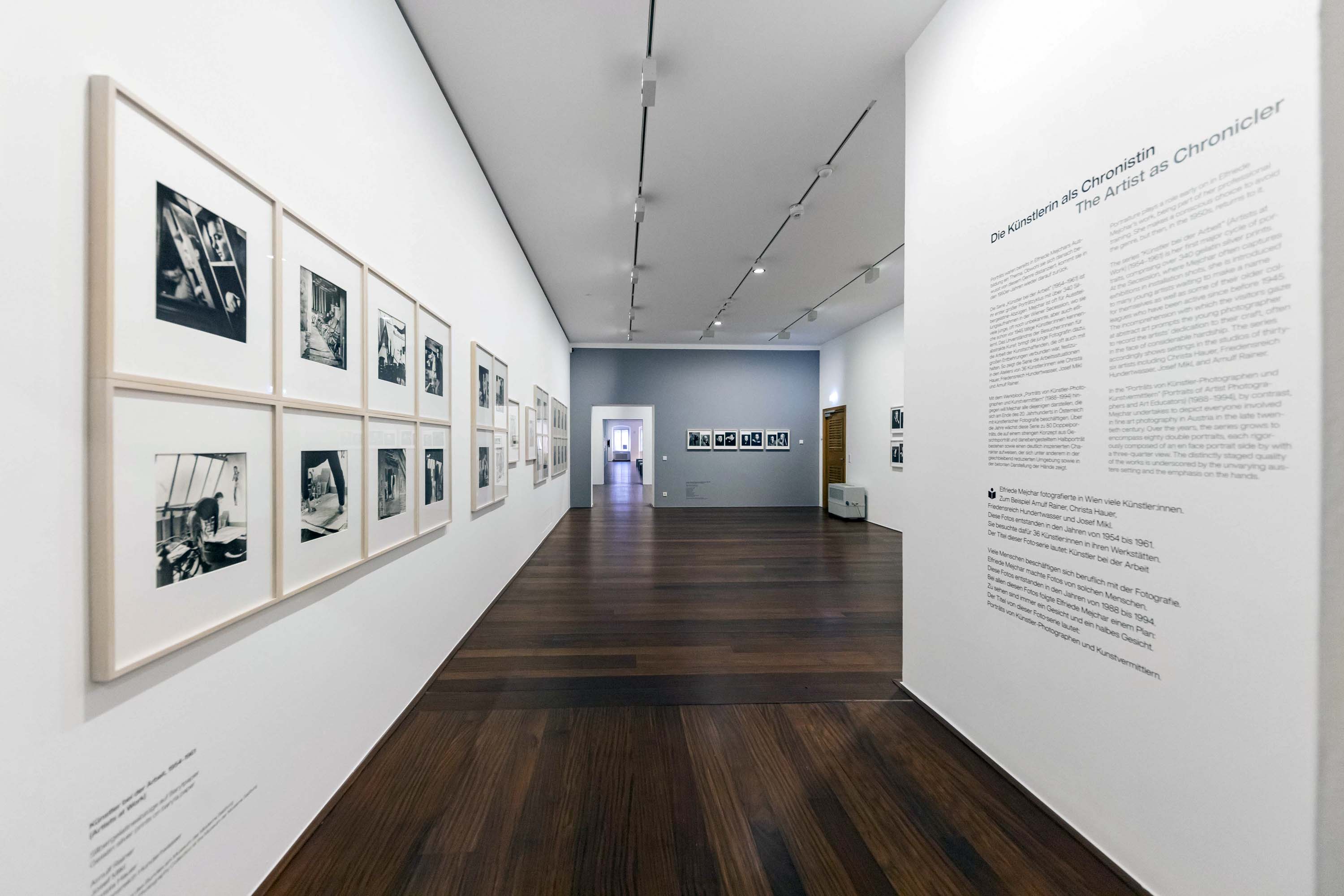
Installation view of the exhibition The Poetry of the Everyday. Photographs by Elfriede Mejchar, Museum der Moderne Salzburg 2024 showing at left, work from Mejchar’s series Künstler bei der Arbeit, 1954-1961 (Artists at work, 1954-1961); and at right, the wall text ‘The Artist as Chronicler’
© Museum der Moderne Salzburg, photo: wildbild/Günter Freund
The Artist as Chronicler
Portraiture plays a role early on in Elfriede Mejchar’s work; she receives her professional training in a portrait studio. She subsequently makes a conscious choice to avoid the genre, but then, in the 1950s, returns to it.
“Künstler bei der Arbeit”, 1954-1961 (Artists at Work)
The series “Künstler bei der Arbeit” (Artists at Work) is her first major cycle of portraits, comprising over 340 gelatin silver prints. Mejchar is often brought in to capture exhibitions in installation shots, especially at the Vienna Secession, where she is introduced to many young artists waiting to make a name for themselves as well as some of their older colleagues who have been active since before 1945. The incomprehension with which the visitors gaze at abstract art that does not represent anything with any accuracy prompts the young photographer to record the intensity and seriousness with which the artists dedicate themselves to their craft, often braving considerable hardship. The series accordingly focuses on visualising the real studio and workplace settings of thirty-six artists, including Christa Hauer, Friedensreich Hundertwasser, Josef Mikl, and Arnulf Rainer.
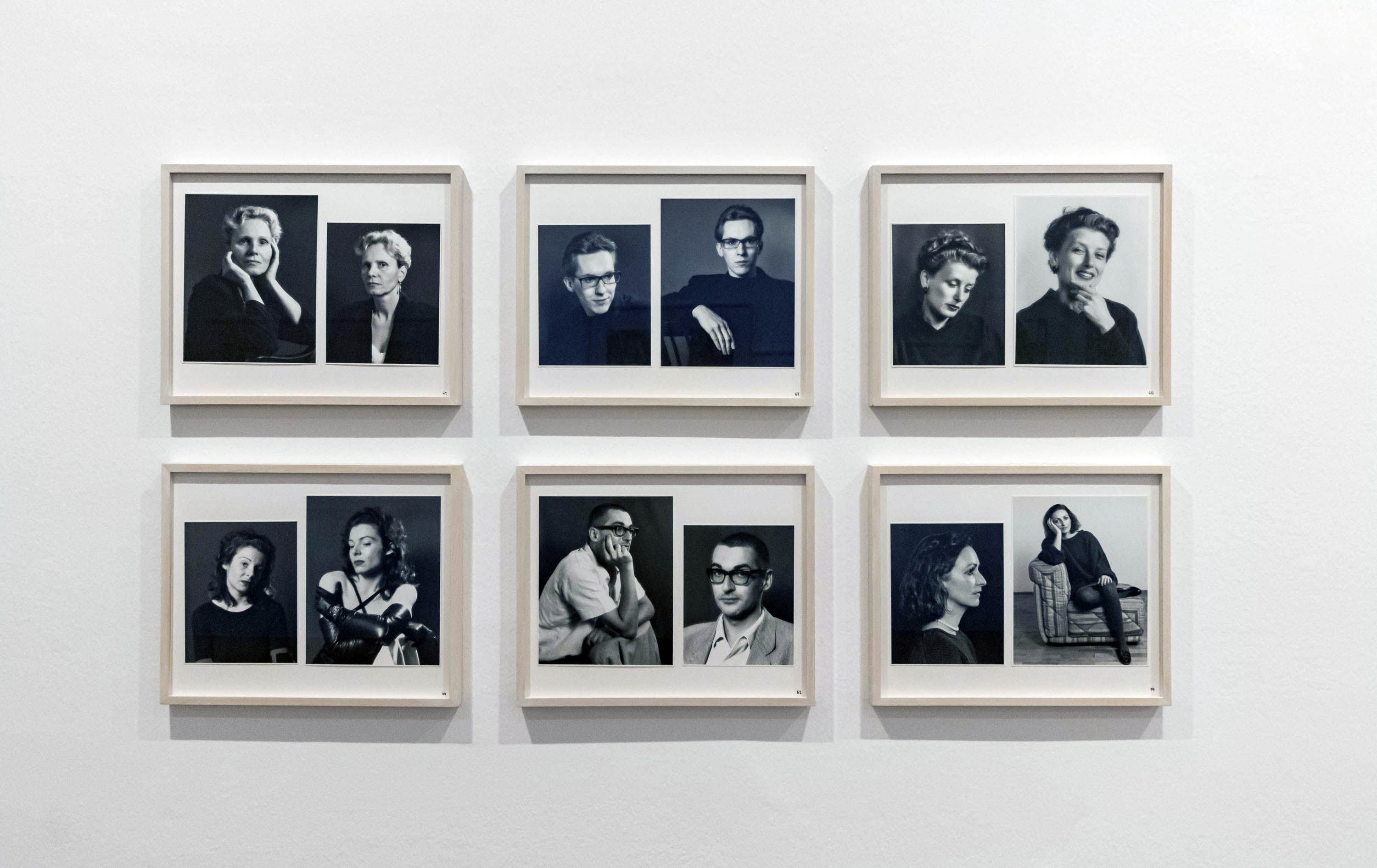
“Porträts von Künstler-Photographen und Kunstvermittlern”, 1988-1994 (Portraits of Artist Photographers and Art Educators)
In the body of work “Porträts von Künstler-Photographen und Kunstvermittlern” (Portraits of Artist Photographers and Art Educators), by contrast, Mejchar undertakes to depict everyone involved in fine art photography in Austria in the late twentieth century. Over the years, the series grows to comprise eighty double portraits, each composed, in accordance with a rigorous conception, of an en face portrait side by with a three-quarter view. The works have a distinctly staged quality, underscored by the unvarying austere setting and the emphasis on the hands, among other aspects. In this respect they recall Mejchar’s final examination, in which she had to realise a portrait both in profile and en face to demonstrate her command of photographic lighting designing and the handling of human sitters.
With these two projects, Mejchar becomes an important chronicler of the Austrian arts scene.
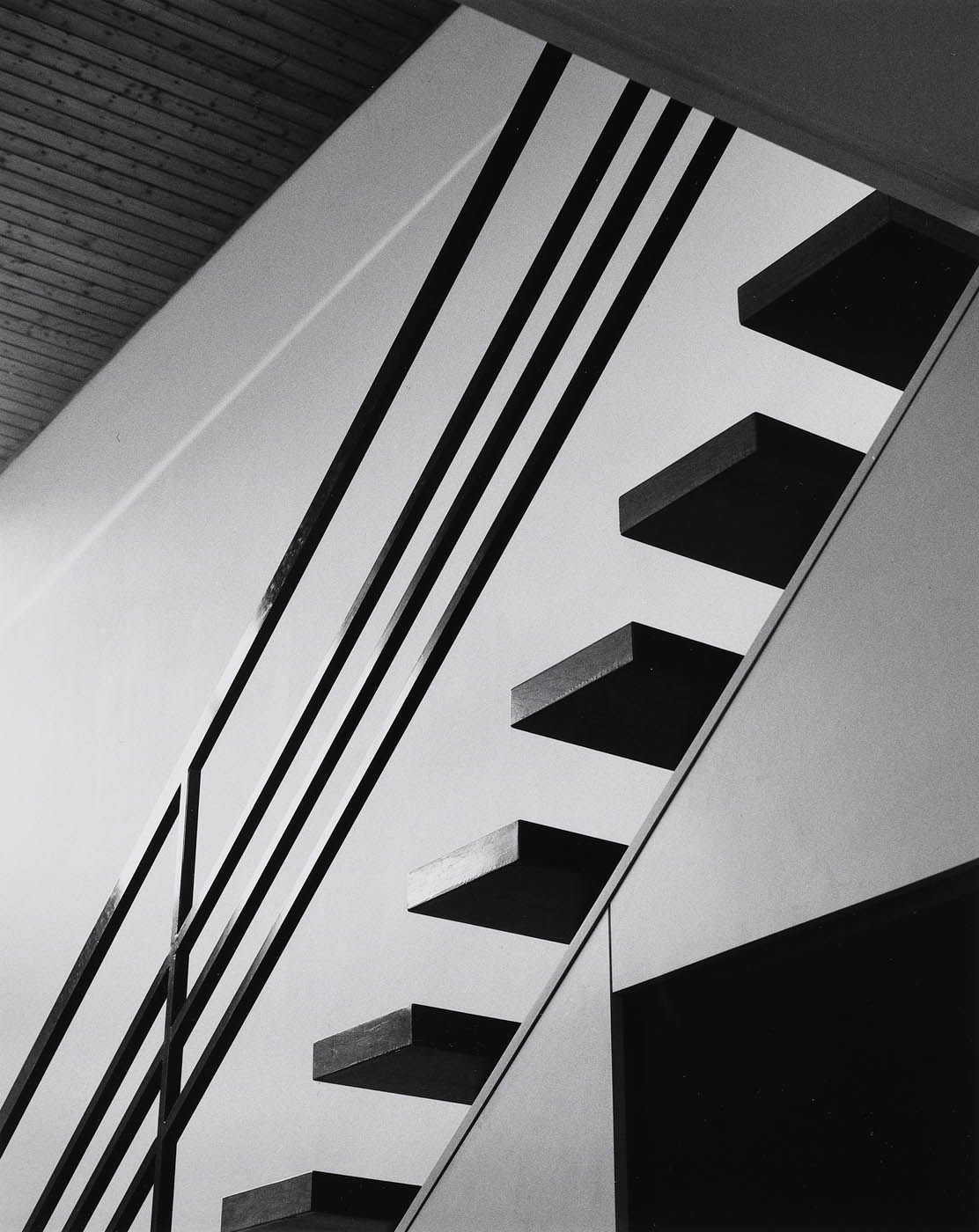
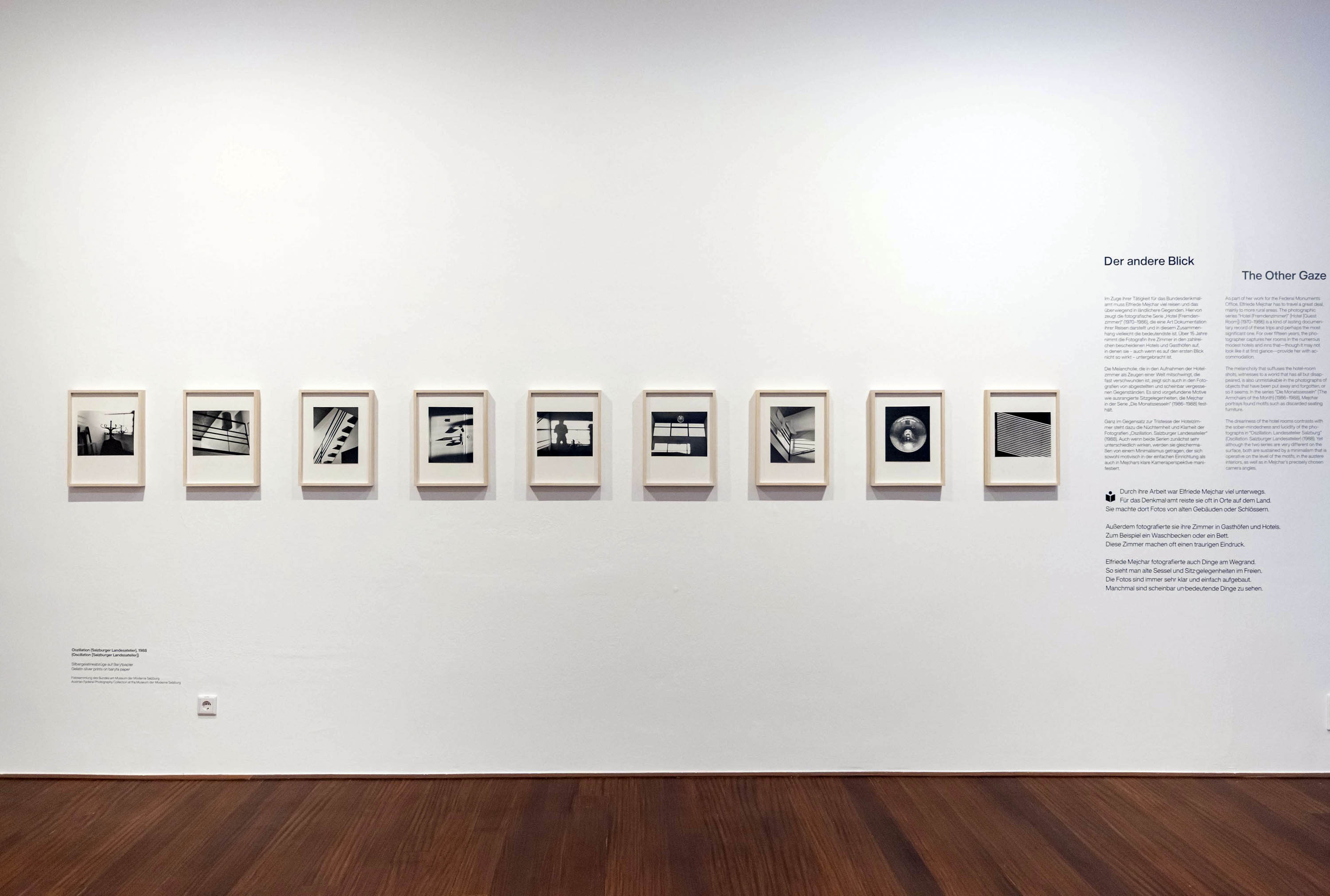
Installation view of the exhibition The Poetry of the Everyday. Photographs by Elfriede Mejchar, Museum der Moderne Salzburg 2024 showing at left, work from Mejchar’s series Oscillation (Salzburger Landesatelier) (Oscillation (Salzburg State Studio)) (above); and at right, the wall text ‘The Other Gaze’ (below)
© Museum der Moderne Salzburg, photo: wildbild/Günter Freund
The Other Gaze
“Hotel (Fremdenzimmer)”, 1970-1986 (Hotel (Guest Room))
As part of her work for the Federal Monuments Office, Elfriede Mejchar has to travel a great deal, mainly to more rural areas. The photographic series “Hotel (Fremdenzimmer)” (Hotel (Guest Room)) is a kind of lasting documentary record of these trips and perhaps the most significant one. Bed, table, chair, mirror, wardrobe, patterned wallpaper, and sometimes a washbasin: for over fifteen years, the photographer captures her rooms with their often spartan furnishings in the numerous modest hotels and inns that – though it may not look like it at first glance – provide her with accommodation. Here and there one does espy a toothbrush, a pair of shoes, a ruffled bedcover, all traces that reveal the ostensibly absent photographer’s presence. A certain melancholy suffuses these shots of hotel rooms as witnesses to a world that has all but disappeared
“Die Monatssesseln”, 1986-1988 (The Armchairs of the Month)
The same melancholy is also unmistakable in the photographs of objects that have outlived their usefulness and been discarded and, it seems, forgotten. In the series “Die Monatssesseln” (The Armchairs of the Month) Mejchar portrays found motifs such as discarded seating furniture. The series shows a wide variety of such items, from kitchen chairs to living-room armchairs and even car seats, that have become part of the natural or other scene where they were dumped. No less diverse than the pieces of furniture and their environments are the feelings they elicit; as Mejchar puts it, “a mess can be beautiful in its own way.”
“Oszillation (Salzburger Landesatelier)”, 1988
The dreariness of the hotel rooms contrasts with the sober-mindedness and lucidity of the photographs in “Oszillation (Salzburger Landesatelier)” (Oscillation (Salzburger Landesatelier)). Yet although the two series are very different on the surface, both are sustained by a minimalism that is operative on the level of the motifs, in the austere interiors, as well as in Mejchar’s precisely chosen camera angles. These photographs capture the rooms of the State of Salzburg’s studio residence for visiting artists, located, like the Salzburger Kunstverein, in the historic Künstlerhaus. Mejchar herself lives there for a while in 1988, a change of working environment that is reflected in her output from the period.
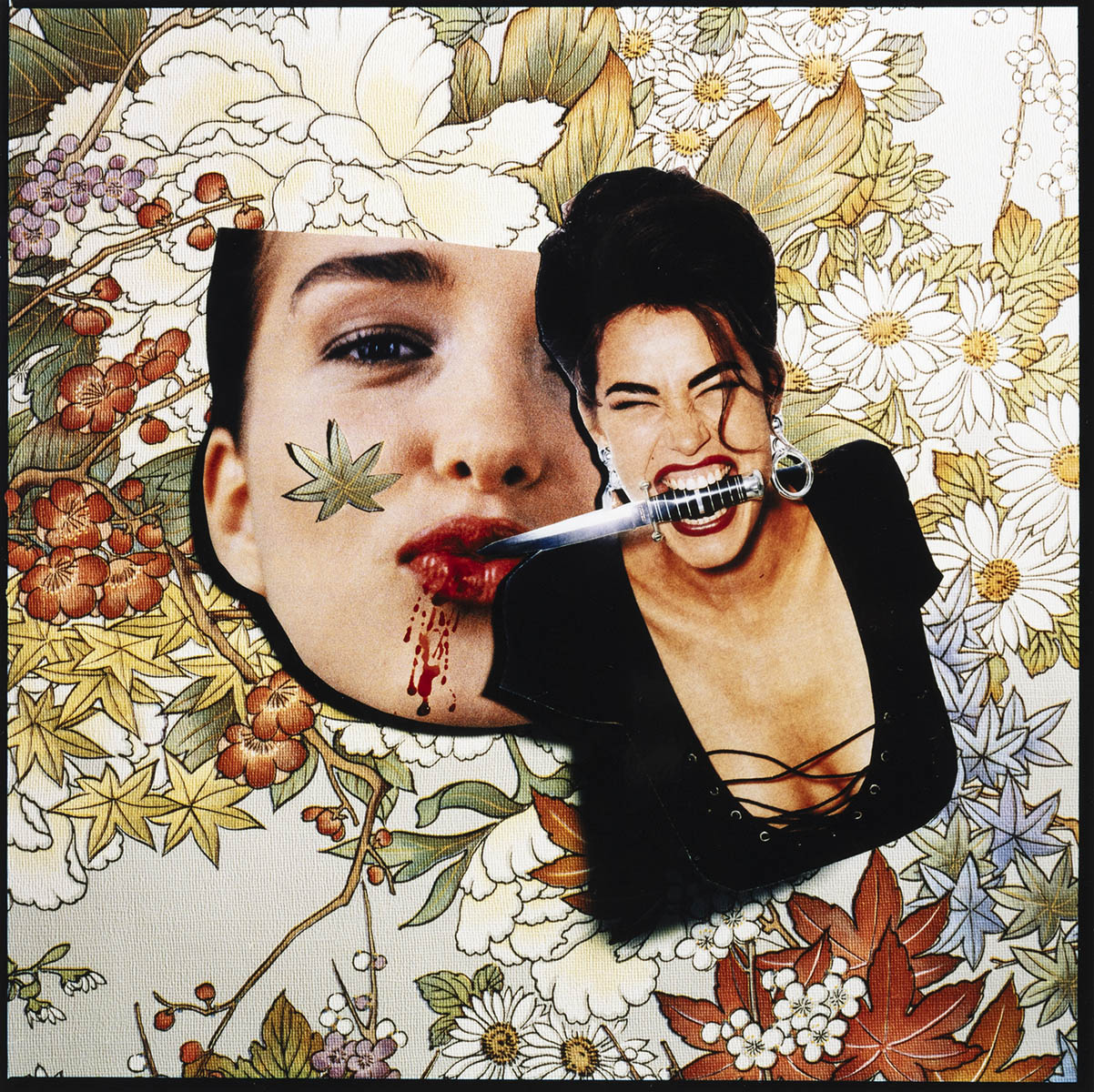
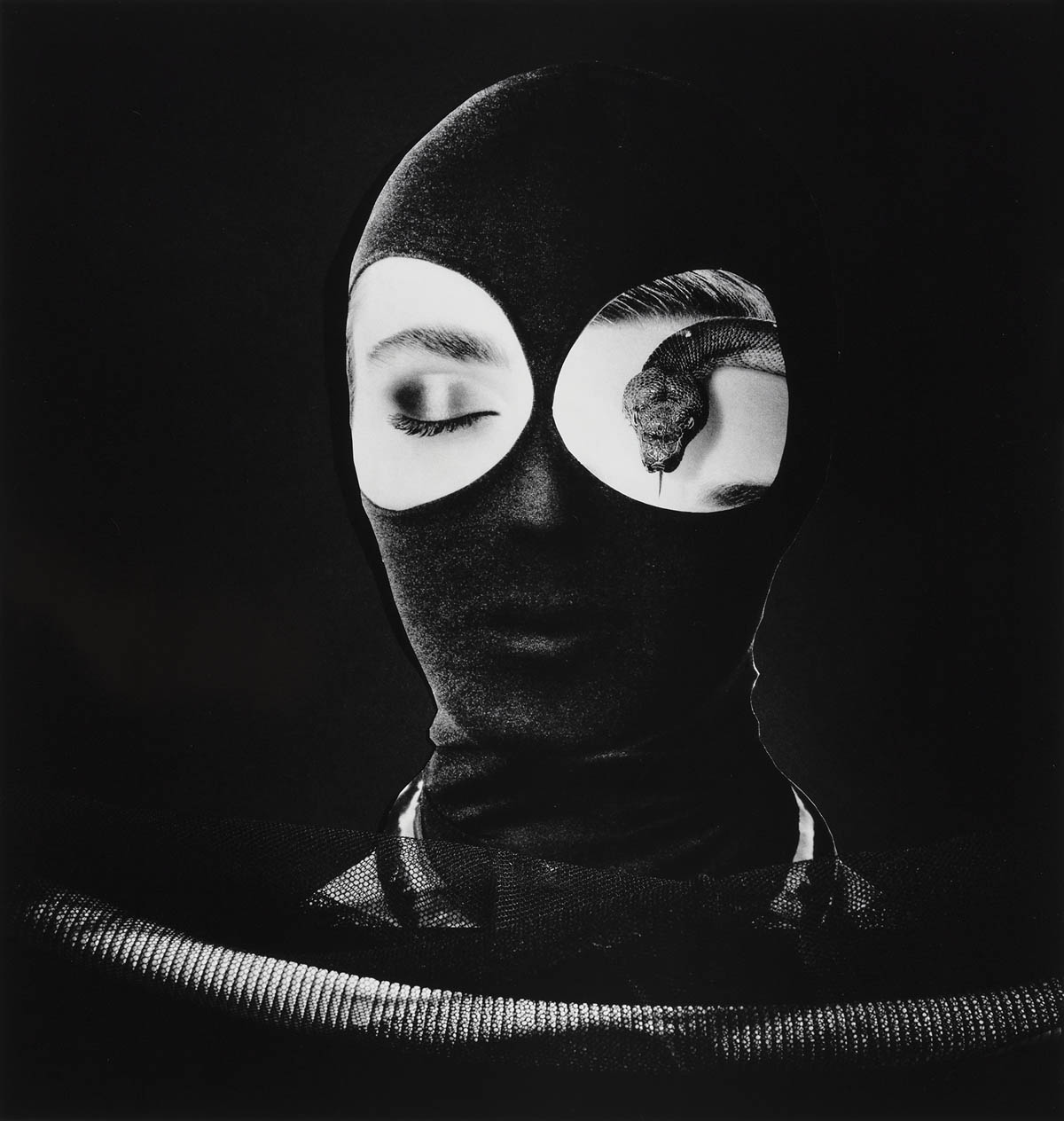
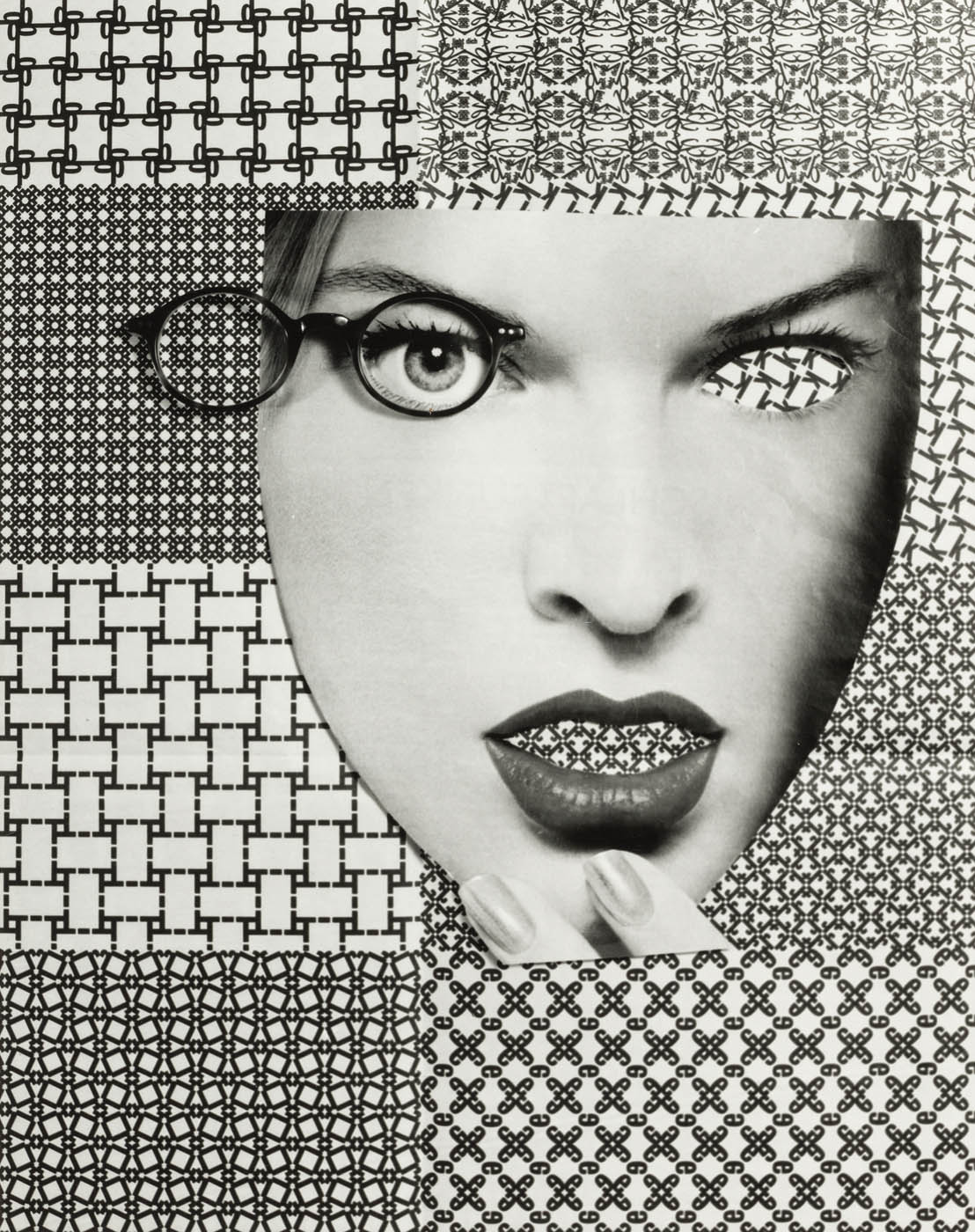
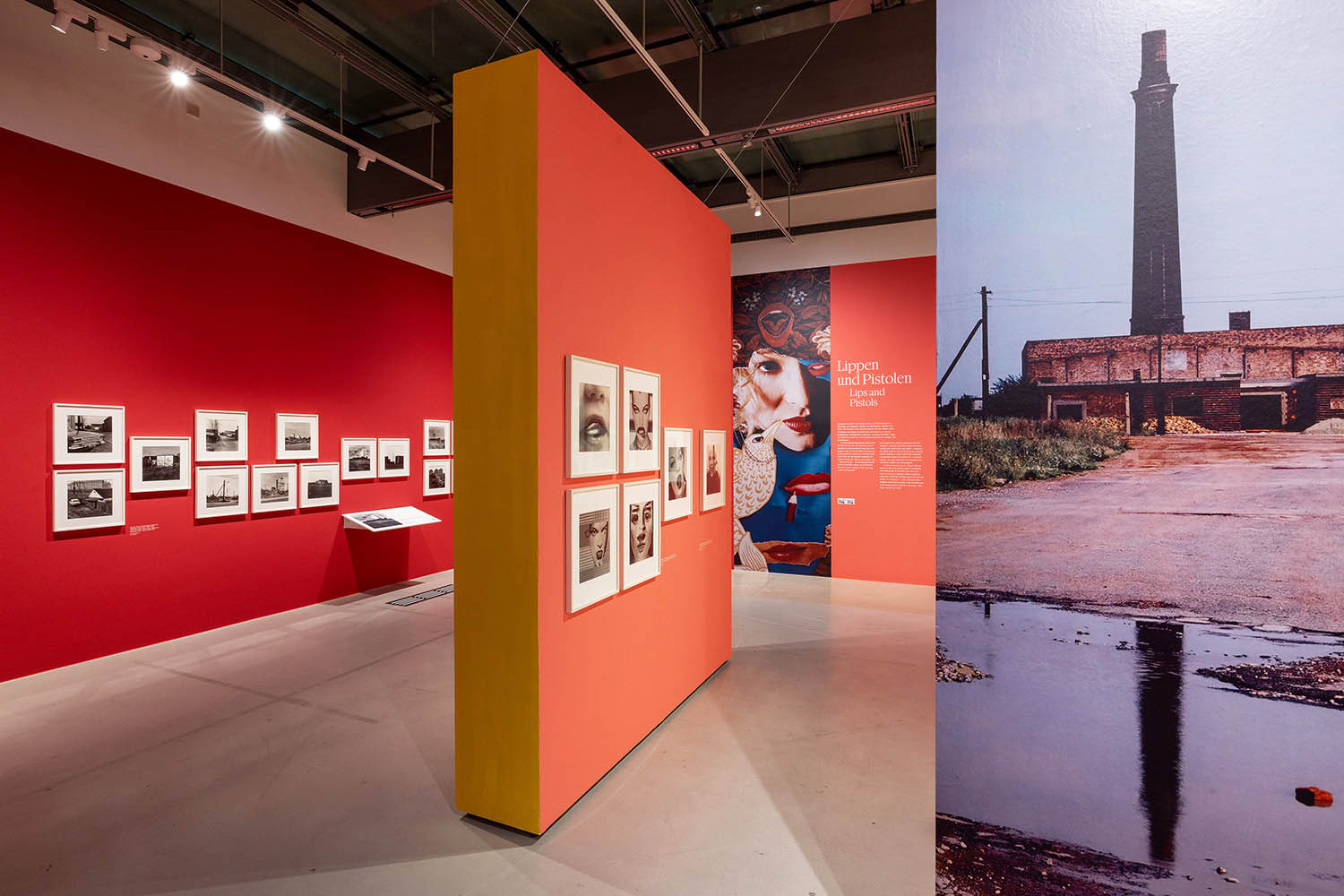
Nobody Is Perfect
In the late 1980s, Elfriede Mejchar branches out in a fresh creative direction. She has been retired for some years and feels free to take on new challenges. Setting aside the flaneur-like practice underlying her earlier bodies of work, she starts photographing in the studio.
Tapetenbild. Triptychon, 1988 (Wallcover Picture. Tryptic) “Eine Kostümierung der geliehenen Identität”, 1989 (A Costume for the borrowed Identity) “Tagebuch Jänner 1988”, 1988 (Diary January 1988) “Nobody Is Perfect”, 1996
Faces change shapes, snakes coil around heads, open and closed eyes alternate. For the collages in “Tagebücher Jänner 1988,” Mejchar reuses her own photographs; in other series, by contrast, she works with found images such as shots of female models from print advertisements or fuses figural representations with fabric and wallpaper patterns. The works are rapidly composed out of visual fragments that she often only loosely places side by side or in overlapping arrangements, dispelling their aura of perfection. “I build pictures for myself on the wall, from materials that are at hand in the public sphere, that are on public display, but I strip away the ideal of flawless beauty that is constantly rubbed in our faces by dismembering it or covering it up.” It is the temporary and easily mutable that fascinates Mejchar, qualities that had had no place in her professional work.
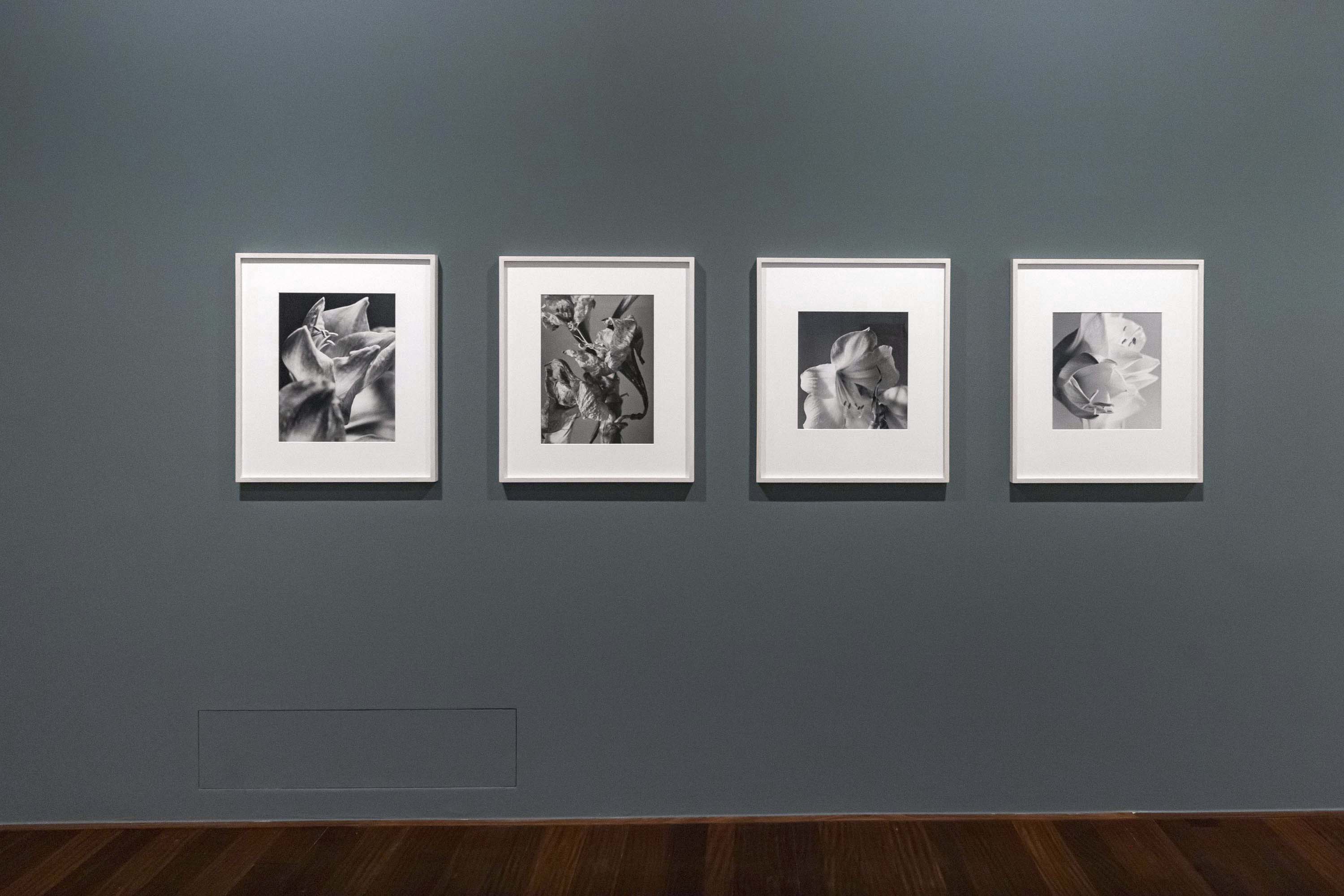
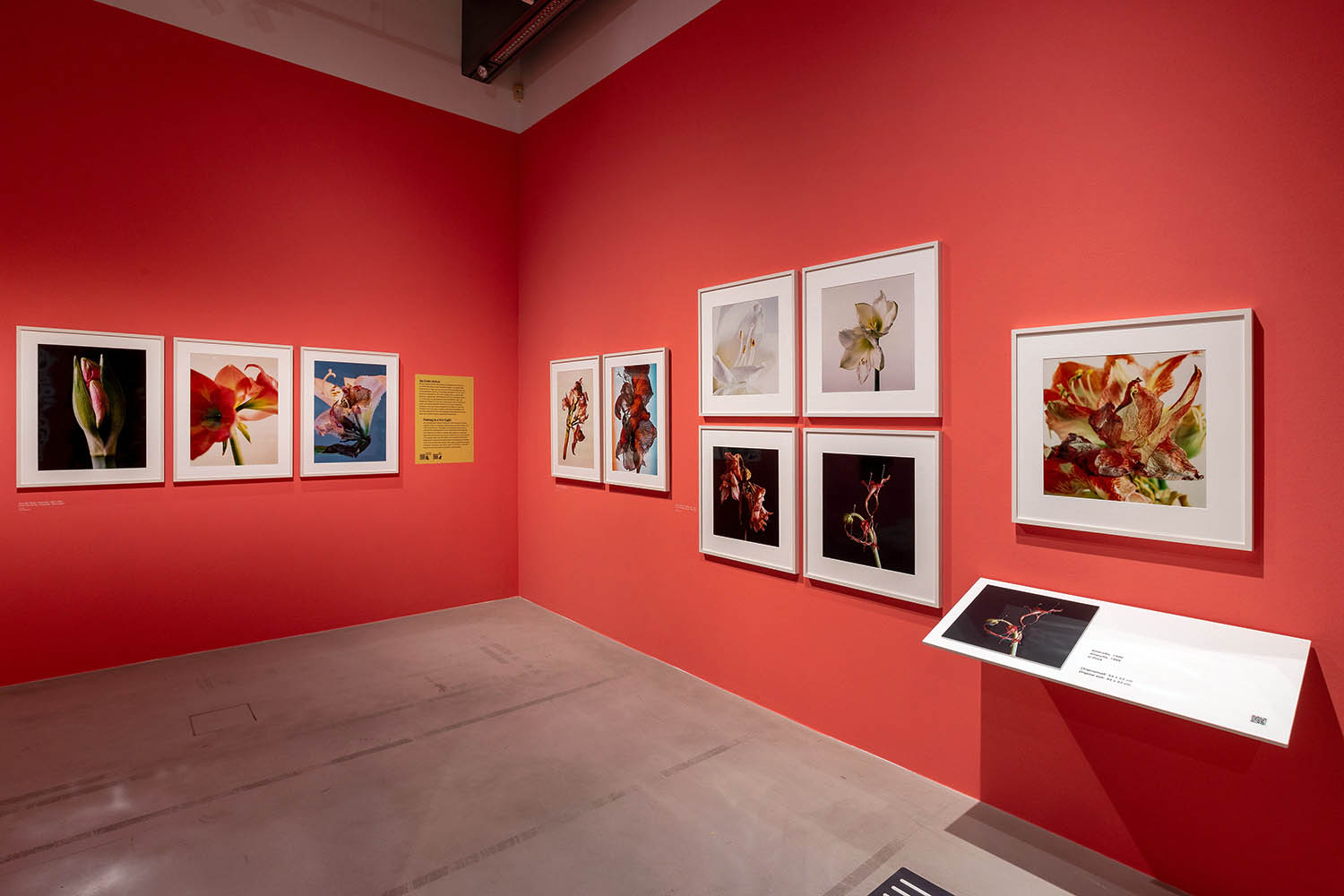
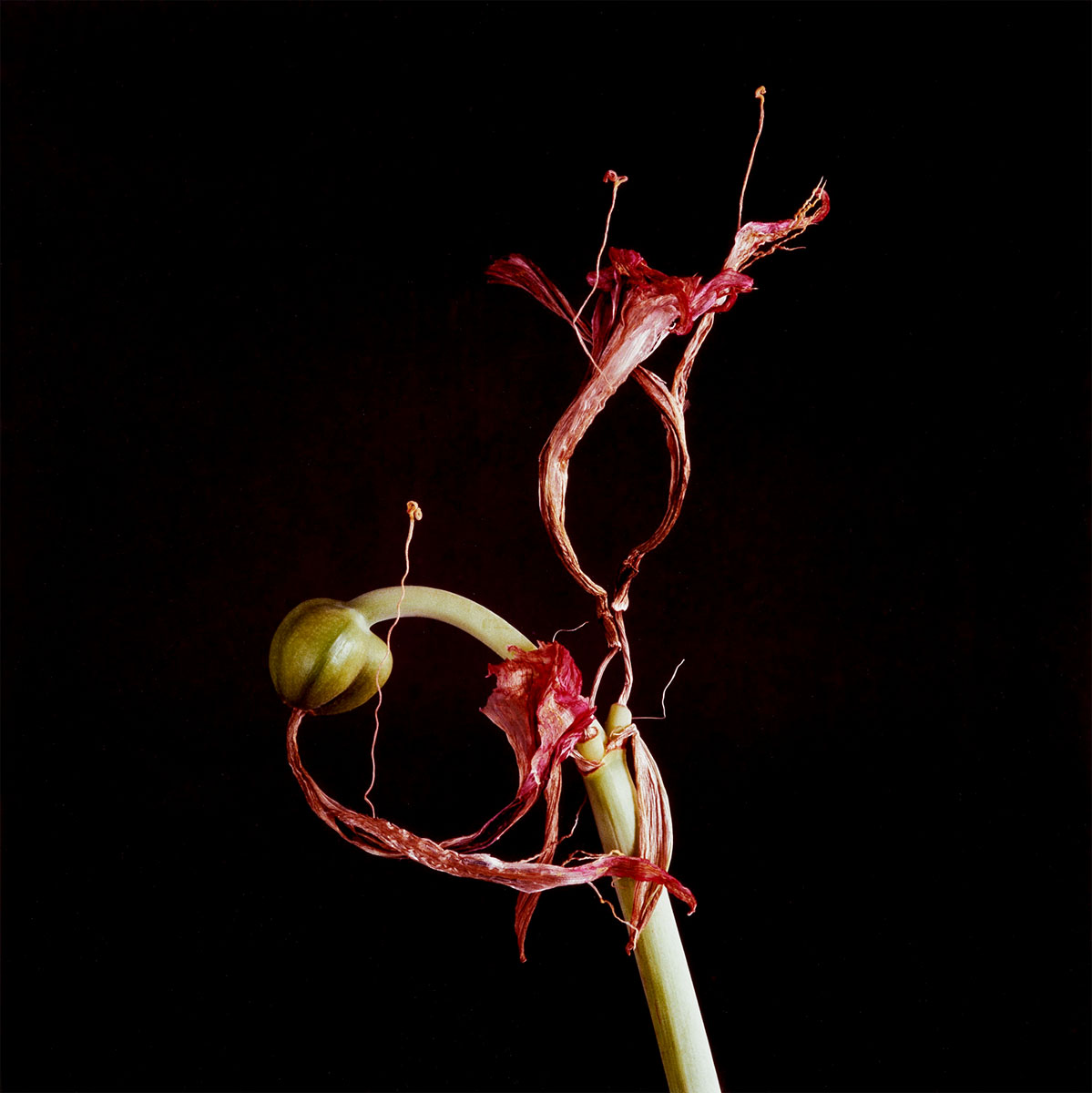
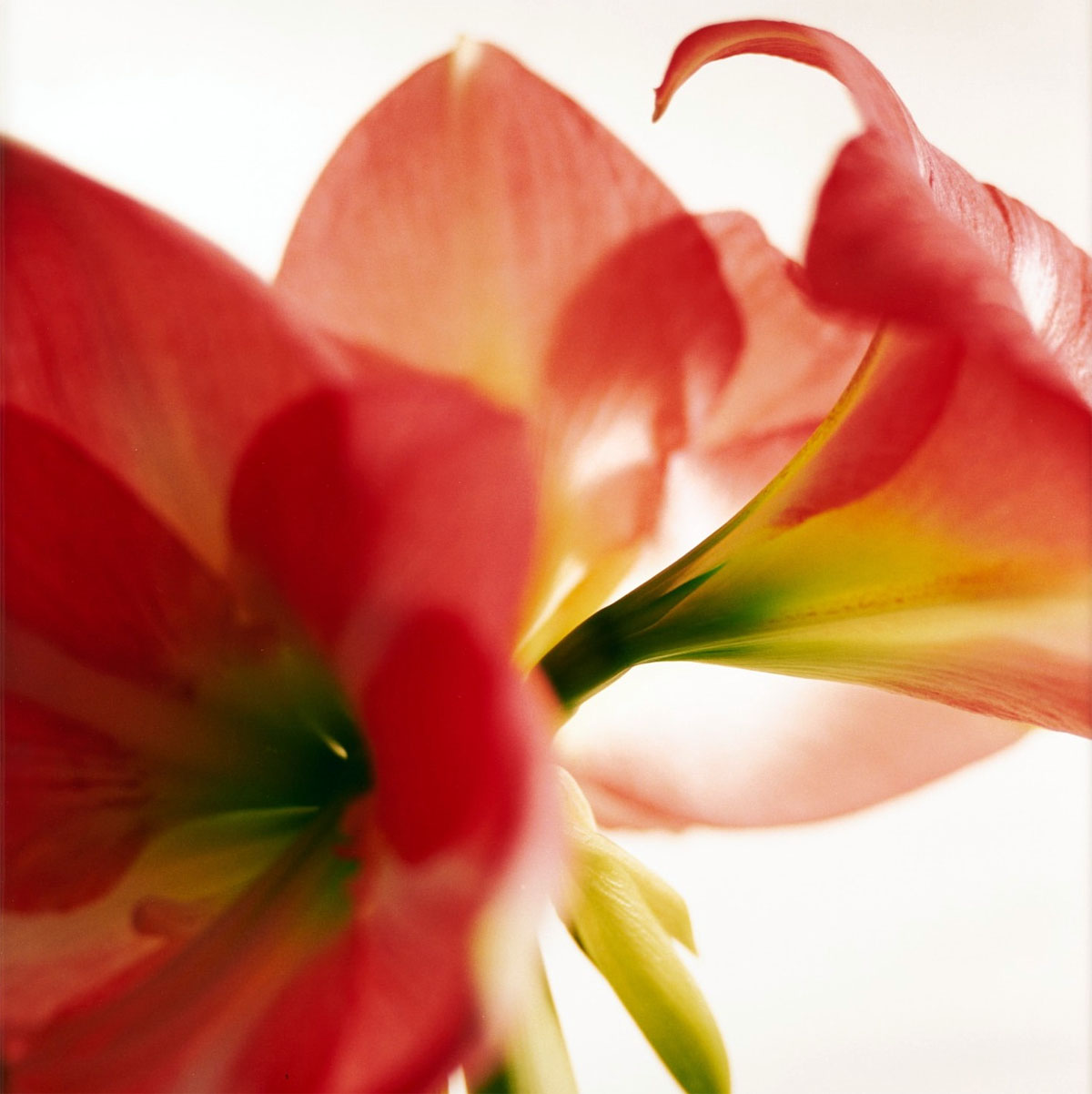
“Amaryllis”, 1994-1997
Pictures of flowers in fine art, whether painted or photographed, inevitably have a clichéd dimension. Mejchar photographs only a special selection of flowers such as amaryllises, lilies, and tulips that she grows in her own garden. In the studio, rather than recording the flowers with a romantic gesture, she captures their gradual transformations – full blossoms, some full of delicate life, some already wilting and recognisably perishable. Showing them between florescence and decay, in a kind of liminal instant, she revisits a theme that surfaces throughout her oeuvre: the capturing of a state of affairs at a defined point in time.
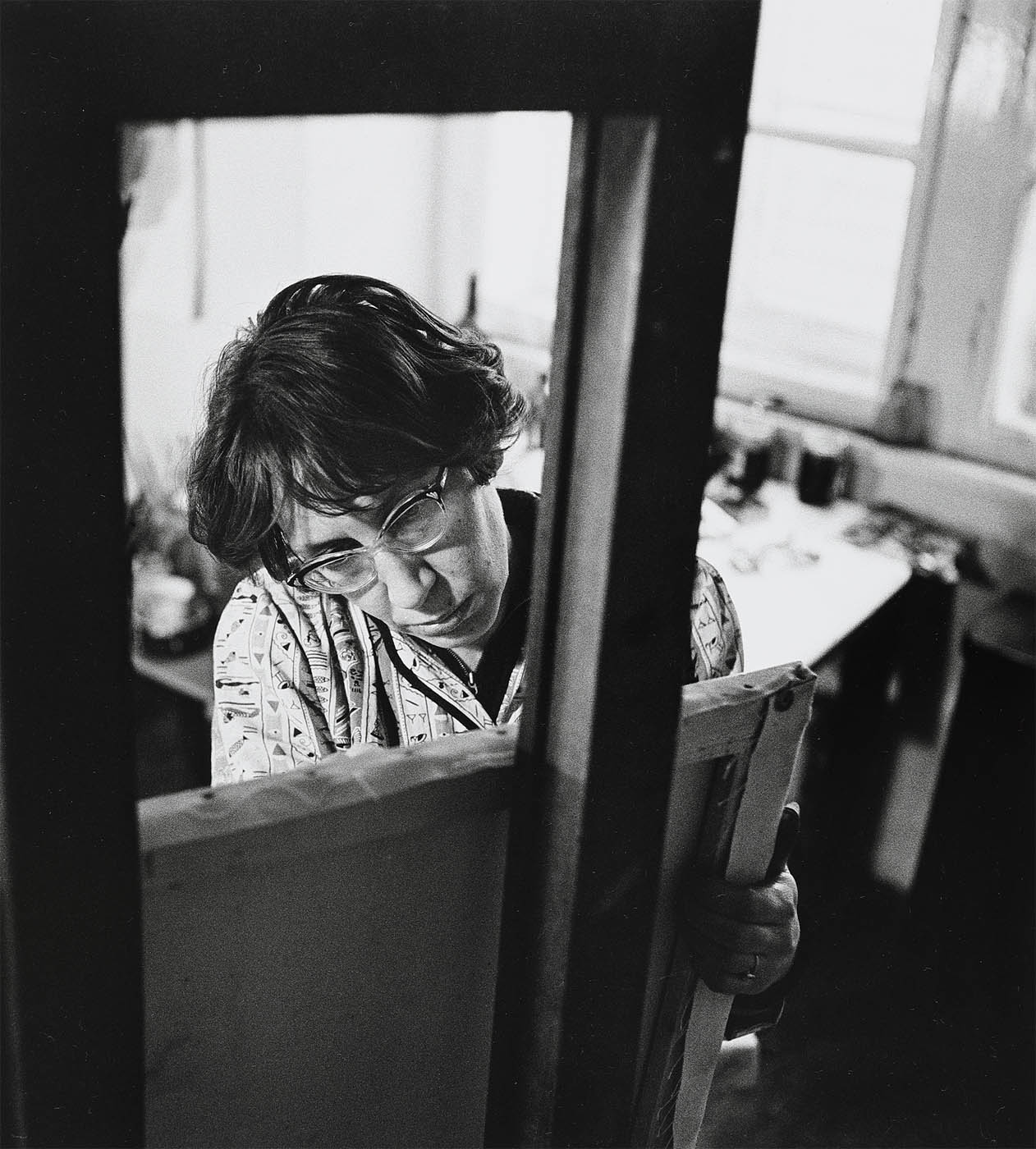
Installation view of the exhibition The Poetry of the Everyday. Photographs by Elfriede Mejchar, Museum der Moderne Salzburg 2024 showing the wall text Elfriede Mejchar: biographical note 1924-2020 Vienna, AT; and some photographs of Elfriede Mejchar working
© Museum der Moderne Salzburg, photo: wildbild/Günter Freund
Elfriede Mejchar: biographical note 1924-2020 Vienna, AT
Elfriede Mejchar is raised in Lower Austria. In 1939, she moves to Germany, where, from 1941 until 1944, she trains as a photographer with Ernst Ley in his small photography studio in Nordenham, completing her education with the official apprenticeship examination.
In light of the political developments, the young photographer and her mother to return to Vienna in 1944. She gets her first job when the Federal Monuments Office (BDA) hires her to document historic architecture with a view to potential bomb damage. She witnesses the turbulent final weeks of the war in Austria, then returns to northern Germany, before settling in Vienna in 1947. From then until her retirement in 1984, Mejchar works as a photographer for the Federal Monuments Office on a steady contract. She buys her first own camera in 1953, and in 1960 she earns a master’s certificate in photography as an external student at the Graphische Lehr- und Versuchsanstalt Wien. Busy with her daytime work for the BDA, she also starts pursuing her own photographic interests in the 1960s, although she does not publicly exhibit her output until 1976, when the Museum of the Twentieth Century in Vienna mounts the fifty-two-year-old photographer’s first solo exhibition. After retiring in 1984, she dedicates herself entirely to freelance and fine art photography.
Elfriede Mejchar does not win the public recognition she merits until old age; in 2002, she is awarded the Honorary Prize for Photography of the Federal Chancellor’s Office, followed in 2004 by the Honorary Prize for Fine Art Photography of the State of Lower Austria and the Prize of the City of Vienna for Fine Art.
Text from the exhibition
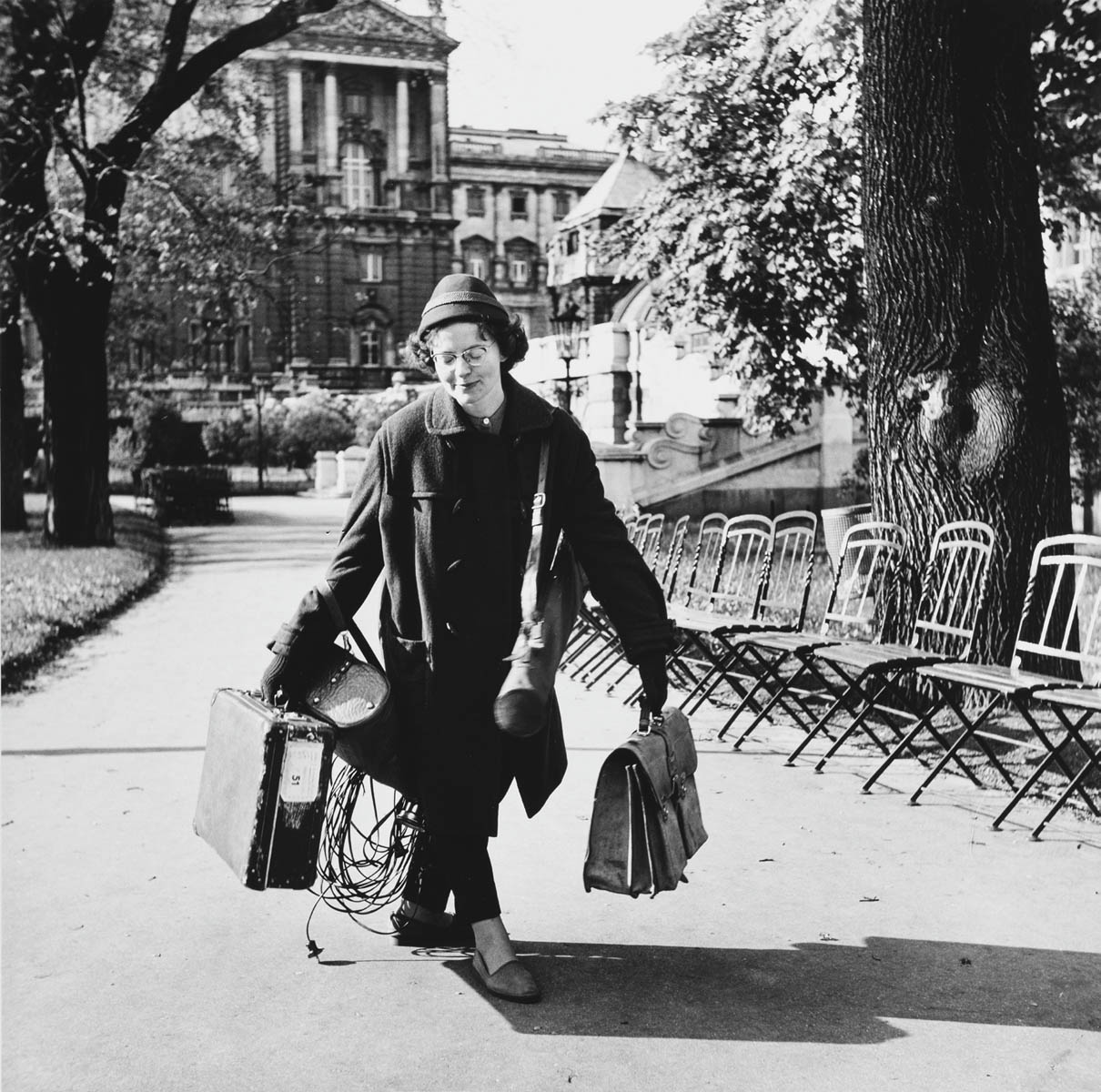
Anonymous photographer
Elfriede Mejchar
Nd
Gelatin silver print
Installation view of the exhibition The Poetry of the Everyday. Photographs by Elfriede Mejchar, Museum der Moderne Salzburg 2024 showing photographs of Mejchar’s flower series
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
Amaryllis
1997
© Elfriede Mejchar/Landessammlungen NÖ
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
From the series Nobody is perfect
1996
Chromogenic print
Federal Photography Collection at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg
© Bildrecht, Vienna, 2024
Photo: Andrew Phelps
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
From the series Nobody is perfect
1996
Chromogenic print
Federal Photography Collection at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg
© Bildrecht, Vienna, 2024
Photo: Andrew Phelps
Elfriede Mejchar (Austrian, 1924-2020)
From the series Nobody is perfect
2003
© Elfriede Mejchar/Landessammlungen NÖ
Museum der Moderne Salzburg
Altstadt (Rupertinum)
Wiener-Philharmoniker-Gasse 9
5020 Salzburg
Austria
Opening hours:
Daily 10am – 6pm






































































![James Coutts Crawford (New Zealand born Scotland, 1817-1889) 'Nurse Edgar [left] and Jessie Crawford' c. 1860 James Coutts Crawford (New Zealand born Scotland, 1817-1889) 'Nurse Edgar [left] and Jessie Crawford' c. 1860](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/crawford-nurse-edgar.jpg)

















![Henry Wright (New Zealand, 1844-1936) 'Rahui Te Kiri Tenetahi [right] and her daughter Ngāpeka Te Roa of Ngāti Manuhiri' 1893 Henry Wright (New Zealand, 1844-1936) 'Rahui Te Kiri Tenetahi [right] and her daughter Ngāpeka Te Roa of Ngāti Manuhiri' 1893](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/henry-wright-rahui-te-kiri-tenetahi-and-her-daughter.jpg)



















































![Mark Anthony (Marc Antoine Gaudin) (French, 1804-1880)(attributed) '[Staged scene featuring five women, their fingers pointing upwards]' England c. 1855-1865 Mark Anthony (Marc Antoine Gaudin) (French, 1804-1880)(attributed) '[Staged scene featuring five women, their fingers pointing upwards]' England c. 1855-1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/mark-anthony-staged-scene.jpg)
![Freeman Brothers, Sydney (Australian) '[Portrait of two girls in fancy dress]' c. 1855-1865 Freeman Brothers, Sydney (Australian) '[Portrait of two girls in fancy dress]' c. 1855-1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/hp2012.23.5-web.jpg)
![G.H. Nicholas, Sydney (Australian) '[Portrait of a child holding a stereoscope]' c. 1870 G.H. Nicholas, Sydney (Australian) '[Portrait of a child holding a stereoscope]' c. 1870](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/hp82.17.1-web.jpg)






![Lorna Studios, Glebe (Australian) '[Sunlight Soap Girl]' 1905-1915 Lorna Studios, Glebe (Australian) '[Sunlight Soap Girl]' 1905-1915](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/hp2023.8.1-web.jpg)
![George Henry Hawkins, Sydney (Australian) '[Four children in fancy dress featuring the products, Jelline and Silver Drop Flour]' 1910-1930 George Henry Hawkins, Sydney (Australian) '[Four children in fancy dress featuring the products, Jelline and Silver Drop Flour]' 1910-1930](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/hp88.21.165-web.jpg)
![George Henry Hawkins, Sydney (Australian) '[Lily dressed in costume as 'Victoria']' 1910-1930 George Henry Hawkins, Sydney (Australian) '[Lily dressed in costume as 'Victoria']' 1910-1930](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/hp88.21.767-web.jpg)
![J.G. Park, Leichhardt (Australian) '[Portrait of a young Jean Cunningham and Master Hurlstone in English court costumes]' c. 1914-1920s J.G. Park, Leichhardt (Australian) '[Portrait of a young Jean Cunningham and Master Hurlstone in English court costumes]' c. 1914-1920s](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/hp80.49.319-web.jpg)
![J.G. Park, Leichhardt (Australian) '[Portrait of Miss Orr in fancy dress as Britannia]' c. 1914-1920s J.G. Park, Leichhardt (Australian) '[Portrait of Miss Orr in fancy dress as Britannia]' c. 1914-1920s](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/hp80.49.696-web.jpg)
![J.G. Park, Leichhardt (Australian) '[Portrait of Miss Larsen wearing a Silver Star Starch costume]' c. 1914-1920s J.G. Park, Leichhardt (Australian) '[Portrait of Miss Larsen wearing a Silver Star Starch costume]' c. 1914-1920s](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/hp80.49.965-web.jpg)
![Oliver Emery, Sydney (Australian) '[Three boys posed outside against a makeshift backdrop]' c. 1914-1930 Oliver Emery, Sydney (Australian) '[Three boys posed outside against a makeshift backdrop]' c. 1914-1930](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/hp83.43.26-web.jpg)





![William Henry Fox Talbot (English, 1800-1877) '[A Stem of Delicate Leaves of an Umbrellifer]' probably 1843-1846 William Henry Fox Talbot (English, 1800-1877) '[A Stem of Delicate Leaves of an Umbrellifer]' probably 1843-1846](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/talbot-a-stem-of-delicate-leaves-of-an-umbrellifer.jpg)

![At left, Herbert Bell et al, '[Amateur World Tour Album, taken with early Kodak cameras, plus purchased travel photographs by various photographers]' (2 page spread); and at right, Stephanie Syjuco (American born Philippines, b. 1974) 'Herbaria' 2021 (detail) At left, Herbert Bell et al, '[Amateur World Tour Album, taken with early Kodak cameras, plus purchased travel photographs by various photographers]' (2 page spread); and at right, Stephanie Syjuco (American born Philippines, b. 1974) 'Herbaria' 2021 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/bell-and-syjuco-herbaria.jpg)
![Herbert Bell (English, 1856-1946) Frederick Nutt Broderick (English, about 1854-1913) Gustave Hermans (Belgian, 1856-1934) Anthony Horner (English, 1853-1923) Michael Horner (English, 1843-1869) C. W. J. Johnson (American, 1833-1903) Léon & Lévy (French, active 1864-1913 or 1920) Léopold Louis Mercier (French, b. 1866) Neurdein Frères (French, founded 1860s, dissolved 1918) Louis Parnard (French, 1840-1893) Alfred Pettitt (English, 1820-1880) Francis Godolphin Osborne Stuart (British born Scotland, 1843-1923) Unknown maker Valentine & Sons (Scottish, founded 1851, dissolved 1910) L. P. Vallée (Canadian, 1837-1905) York and Son J. Kühn (French, active Paris, France 1885 - early 20th century) '[Amateur World Tour Album, taken with early Kodak cameras, plus purchased travel photographs by various photographers]' (2 page spread) Herbert Bell (English, 1856-1946) Frederick Nutt Broderick (English, about 1854-1913) Gustave Hermans (Belgian, 1856-1934) Anthony Horner (English, 1853-1923) Michael Horner (English, 1843-1869) C. W. J. Johnson (American, 1833-1903) Léon & Lévy (French, active 1864-1913 or 1920) Léopold Louis Mercier (French, b. 1866) Neurdein Frères (French, founded 1860s, dissolved 1918) Louis Parnard (French, 1840-1893) Alfred Pettitt (English, 1820-1880) Francis Godolphin Osborne Stuart (British born Scotland, 1843-1923) Unknown maker Valentine & Sons (Scottish, founded 1851, dissolved 1910) L. P. Vallée (Canadian, 1837-1905) York and Son J. Kühn (French, active Paris, France 1885 - early 20th century) '[Amateur World Tour Album, taken with early Kodak cameras, plus purchased travel photographs by various photographers]' (2 page spread)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/amateur-world-tour-album.jpg)















![At left, William H. Mumler (American, 1832-1884) 'Mrs. Swan' 1869-1878; and at right, Khadija Saye (Gambian-British, b. 1992) 'Nak Bejjen' [Cow's Horn] 2017-2018 At left, William H. Mumler (American, 1832-1884) 'Mrs. Swan' 1869-1878; and at right, Khadija Saye (Gambian-British, b. 1992) 'Nak Bejjen' [Cow's Horn] 2017-2018](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/mumler-mrs.-swan-and-saye-nak-bejjen.jpg)

![Khadija Saye (Gambian-British, b. 1992) 'Nak Bejjen' [Cow's Horn] 2017-2018 Khadija Saye (Gambian-British, b. 1992) 'Nak Bejjen' [Cow's Horn] 2017-2018](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/saye-nak-bejjen.jpg)
![At left, Unknown maker (American) '[Seated Woman with "Spirit" of a Young Man]' about 1865-1875; and at right, Lieko Shiga (Japanese, b. 1980) 'Talking with Me' 2005 From the series 'Lilly' At left, Unknown maker (American) '[Seated Woman with "Spirit" of a Young Man]' about 1865-1875; and at right, Lieko Shiga (Japanese, b. 1980) 'Talking with Me' 2005 From the series 'Lilly'](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/seated-woman-and-shiga-talking-with-me.jpg)
![Unknown maker (American) '[Seated Woman with "Spirit" of a Young Man]' about 1865-1875 Unknown maker (American) '[Seated Woman with "Spirit" of a Young Man]' about 1865-1875](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/seated-woman-with-spirit.jpg)






![A.J. Russell (American, 1830-1902) 'Embankment No. 3 West of Granite Cannon [Wyoming]' April 1868 A.J. Russell (American, 1830-1902) 'Embankment No. 3 West of Granite Cannon [Wyoming]' April 1868](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/russell-embankment-no.-3-west-of-granite-cannon.jpg)
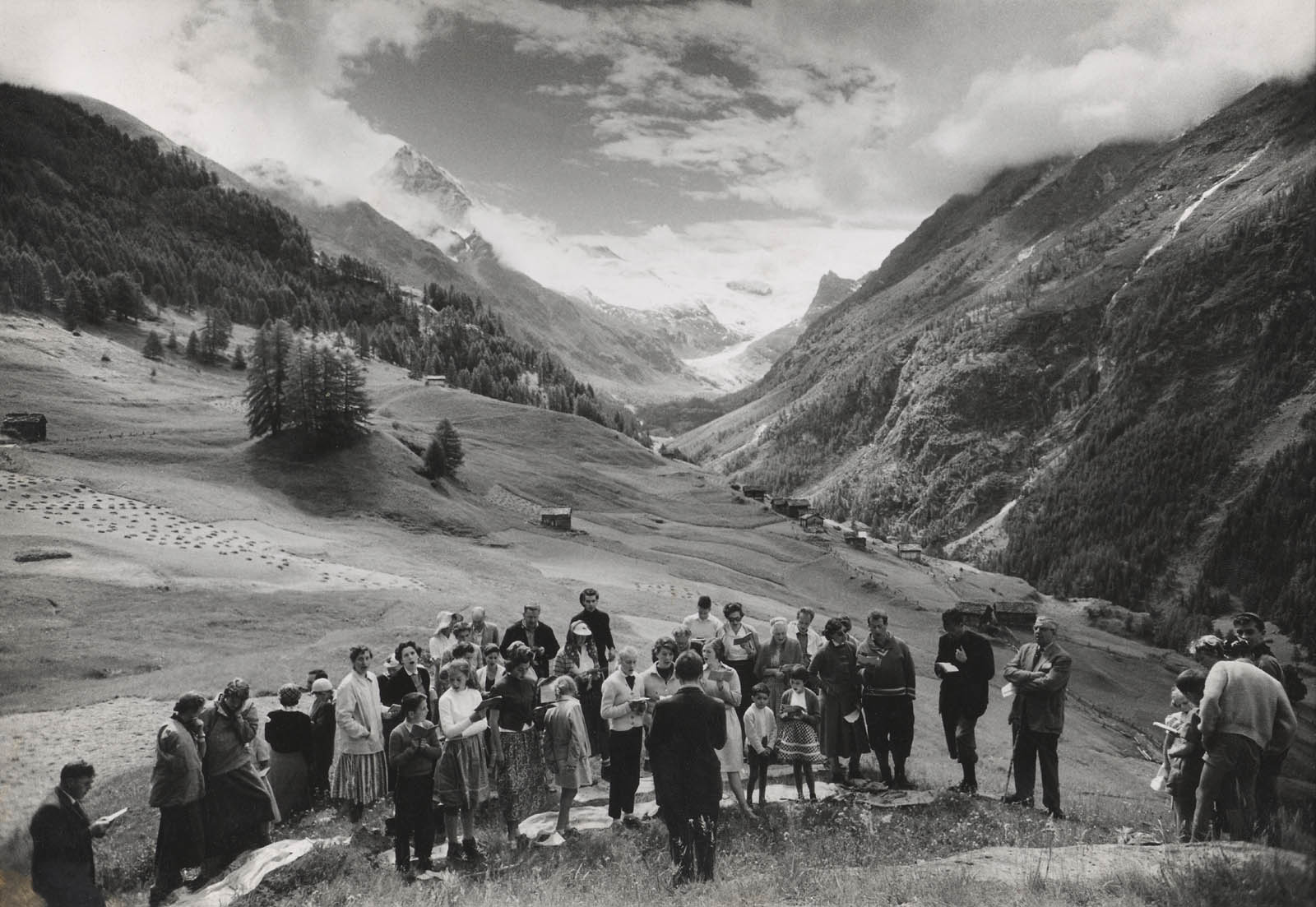
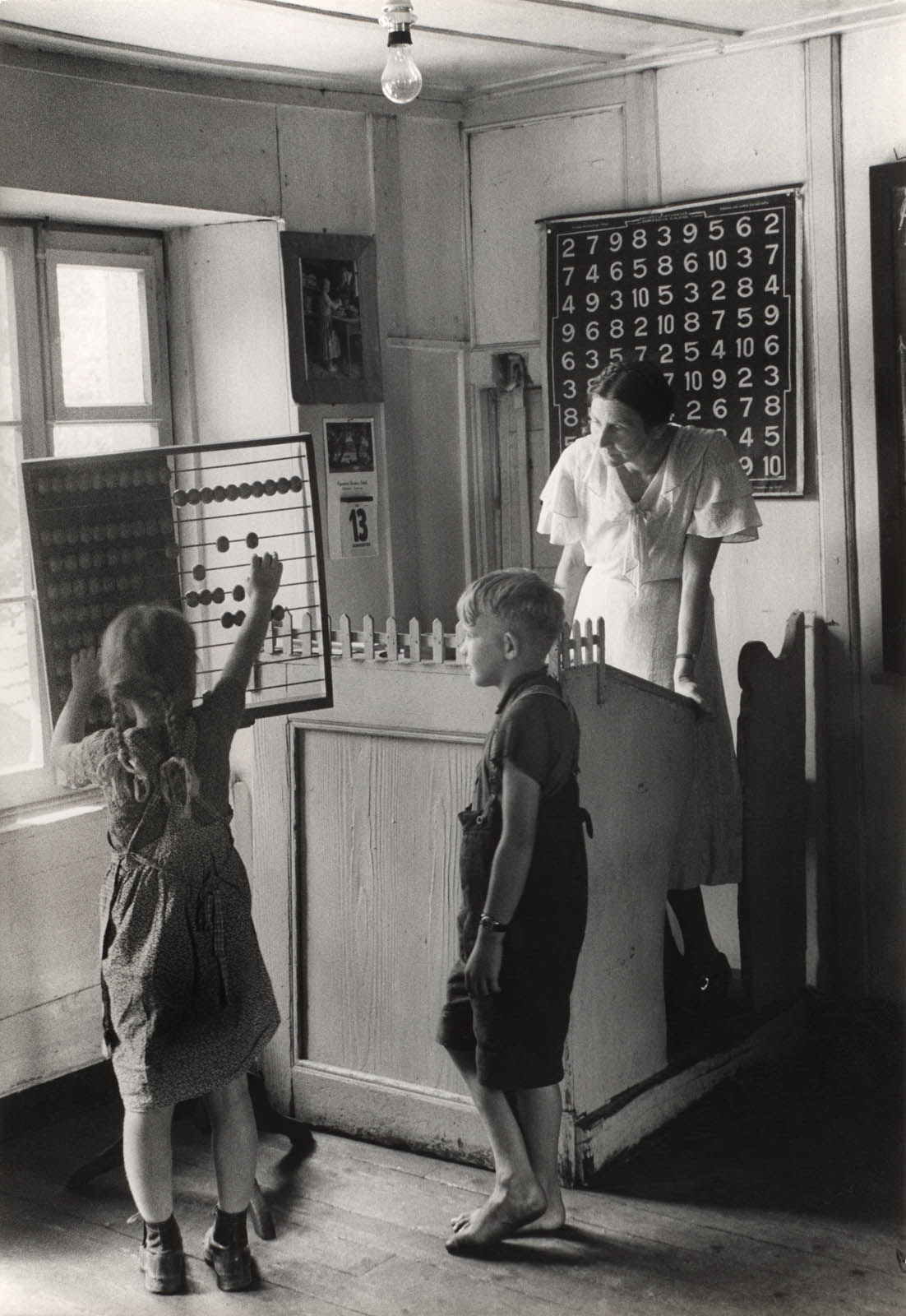
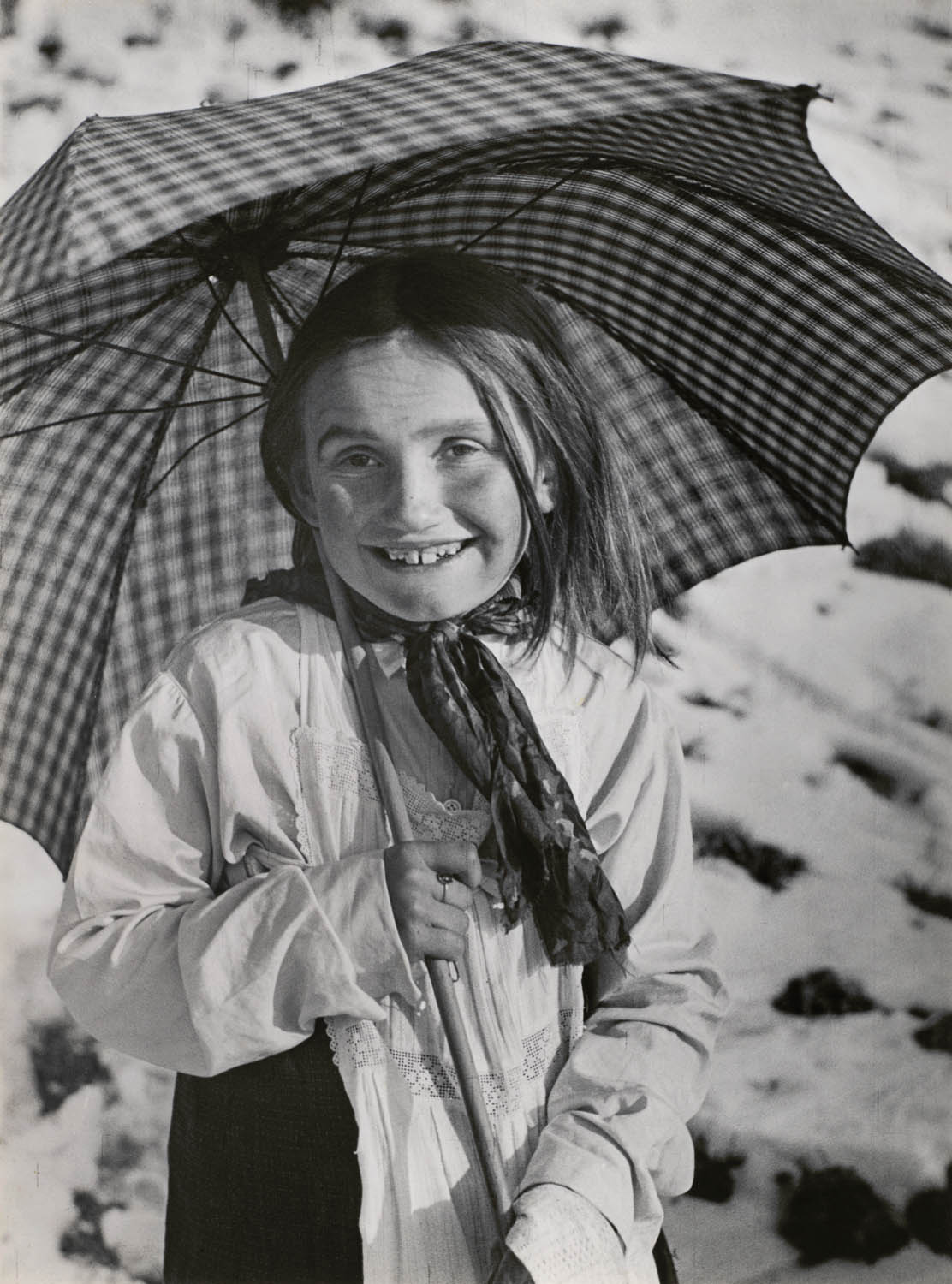
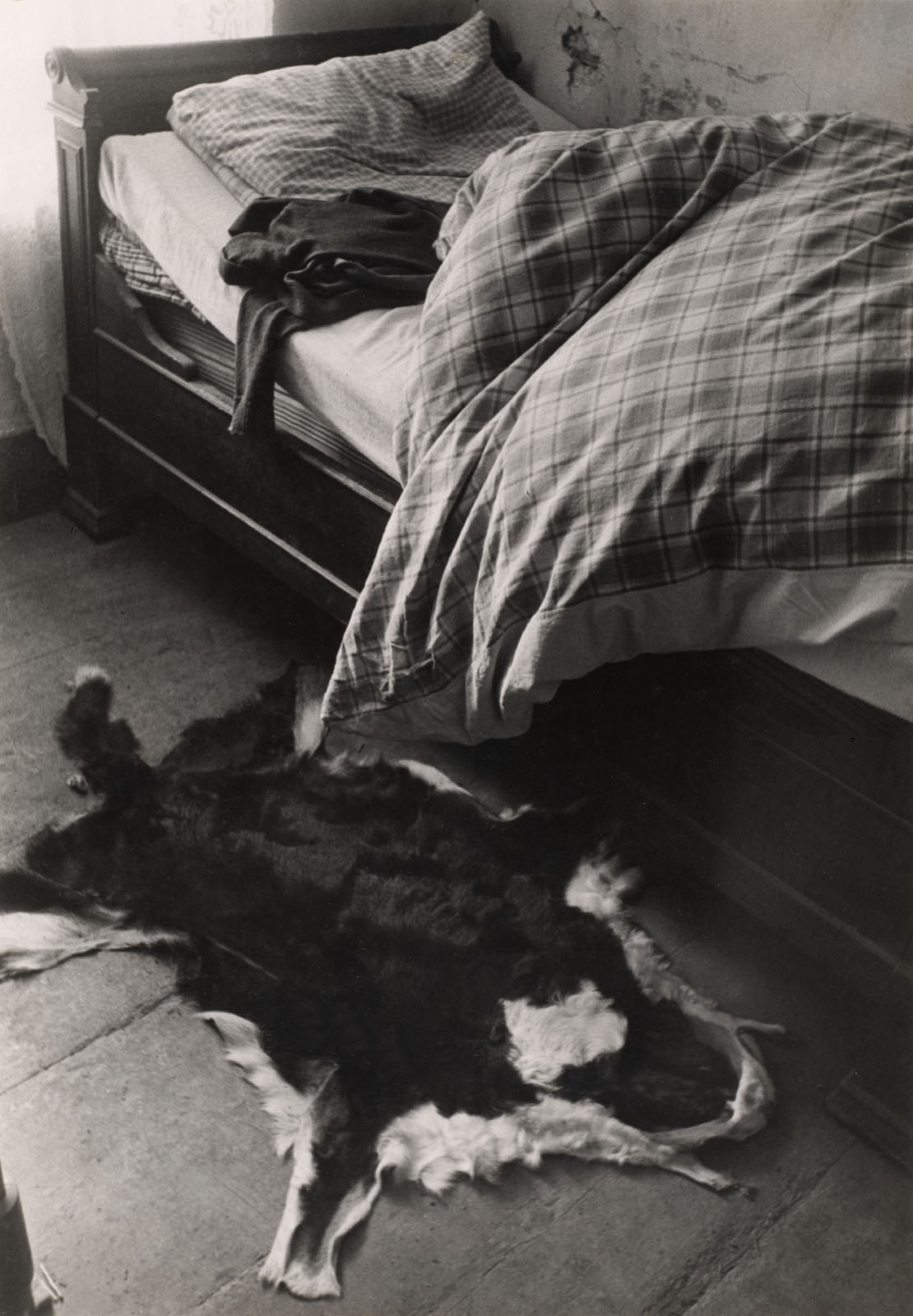






















































![Consuelo Kanaga (American, 1894-1978) '[Untitled] (Landscape Near Taos, New Mexico)' Nd Consuelo Kanaga (American, 1894-1978) '[Untitled] (Landscape Near Taos, New Mexico)' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/kanaga-landscape-untitled-near-taos-new-mexico.jpg)
![Consuelo Kanaga (American, 1894-1978) '[Untitled] (Landscape with Farmhouse)' Nd Consuelo Kanaga (American, 1894-1978) '[Untitled] (Landscape with Farmhouse)' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/kanaga-untitled-landscape-with-farmhouse.jpg)






















































You must be logged in to post a comment.