Exhibition dates: 23rd June – 22nd September 2013
Daniel Douke (American, b. 1943)
Ace
1979
Acrylic on masonite
8 x 8 x 12 1/4 in.
Courtesy Minnesota Museum of American Art, Saint Paul
Life (like).
“For the French theorist Jean Baudrillard, this consciousness of construction finds its most powerful expression in the concept of hyperreality. To appreciate Baudrillard’s view, recall the treatment of literary deconstruction… Deconstruction theorists propose that words gain their meaning through their reference to other words; literary works gain their significance by the way they are related to other writings. Thus language does not derive its character from reality, but from other language. Now consider the media – newspapers, television, the movies, radio. For Baudrillard, media portrayals of the world are not driven by the way the world “is,” but by the steadily emerging histories of portrayal itself. As these histories unfold, each new lamination is influenced by the preceding, accounts are layered upon accounts, and reality is transformed into hyperreality. For example, Baudrillard asks, what is the reality of the “Holocaust”? One cannot deny that certain events took place, but as time goes on these events become subject to myriad re-presentations. Diaries become subject to redefinition by television and movies; biographies influence the writing of historical novels; narrated history is transformed into plays, and each “telling” lays the experiential groundwork for subsequent retellings. Realities accumulate, accentuate, interpenetrate, and ultimately create the world of hyperreality – itself in continuous evolution into the future. We feel we possess an intimate acquaintance of the events in themselves; they are sharply etched in our consciousness. For Baudrillard, however, this consciousness moves increasingly toward hyperreality.
And thus the culture opens to the possibility of selves as artifacts of hyperreality. As political events, health and illness, and world history slip from the realm of the concrete into the domain of representation, so a commitment to obdurate selves becomes increasingly difficult to maintain. What, after all, is the reality of our motives, intentions, thoughts, attitudes, and the like? …
As we find, the current texts of the self are built upon those of preceding eras, and they in turn upon more distant forms of discourse. In the end we have no way of “getting down to the self as it is.” And thus we edge toward the more unsettling question: On what grounds can we assume that beneath the layers of accumulated understandings there is, in fact, an obdurate “self” to be located? The object of understanding has been absorbed into the world of representations.”
Gergen, Kenneth. The Saturated Self: Dilemmas of Identity in Contemporary Life. New York: Harper Collins, 1991, pp. 121-122.
Many thankx to The Blanton Museum of Art for allowing me to publish the artwork in this posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the art.
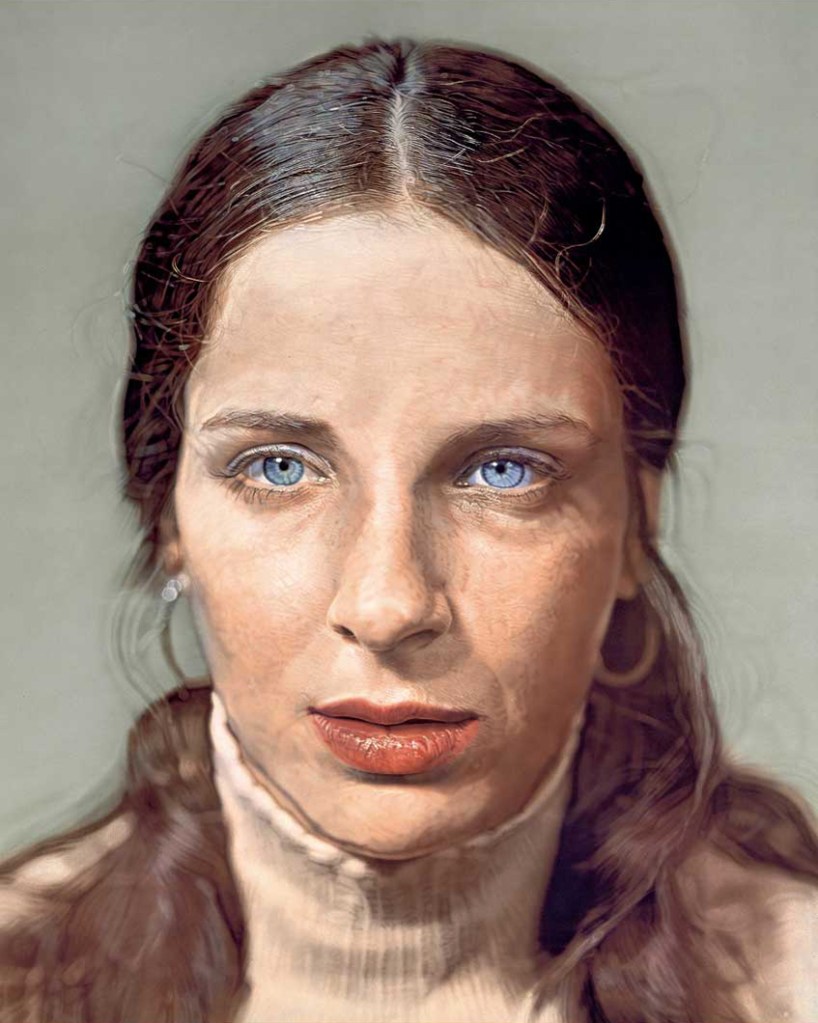
Evan Penny (South African, b. 1953)
(Old) No One – in Particular #6, Series 2
2005
Silicone, pigment, hair, aluminium
40 x 32 x 7 1/2 in.
© Evan Penny
Courtesy Sperone Westwater, New York
Vija Celmins (Latvian American, b. 1938)
Eraser
1967
Acrylic on balsa wood
6 5/8 x 20 x 3 1/8 in.
Collection Orange County Museum of Art, Newport Beach, CA
Gift of Avco Financial Services, Newport Beach
Maurizio Cattelan (Italian, b. 1960)
Untitled
2001
Stainless steel, composition wood, electric motor, electric light, electric bell, computer
23 1/2 x 33 5/8 x 18 5/8 in.
Courtesy the artist and Marian Goodman Gallery, New York
Keith Edmier (American, b. 1967)
Bremen Towne
2008
Installation dimensions variable
Courtesy of the artist and Friedrich Petzel Gallery
Bremen Towne was an idea I’d been thinking about prior to [my 2008] show at Bard College. It had been floating in my head for a number of years based on the sales brochure of my parents’ home I had obtained around 1999 off of eBay. It was just one of these things I had around… I didn’t really have the idea of constructing this house back then… As it turned out, the interior dimensions of my parents’ home from the original blueprints fit directly into one of the galleries at the museum. At that point I started considering it more as an art object, or as a sculpture more than an installation… The main visual references were family photographs, mostly taken during critical events or holidays or birthday parties. My process involved going through the photo album – everything. They were all pictures of people posing, so I started looking at the spaces [in the background]… I ended up buying the whole decade of both Sears and JCPenney catalogues up until that time, the early ’70s. Through that I was able to identify some products based on visual descriptions or in the family photographs… I initially went to a place that has all kinds of wallpapers and floorings from other periods, used a lot for movies and things like that. I heard they had thousands of wallpapers. It turned out I couldn’t find the exact wallpaper that was in the house. I guess at that point I started thinking it was more interesting for me to remake it, and to remake it more or less new. I wanted to represent the time element, the moment before the day of the family moving into the new house. It wasn’t supposed to look lived in.
I think I was initially interested in doing that to have some kind of separation from taking a real object that was loaded with personal history or some sentimental thing. It was a way of moving from a subjective to an objective position… [I was interested] in just thinking about the whole interior of the house itself as a cast, or this negative space. I thought about how the house is essentially the space that shapes us, that shapes oneself… I think that my reason to make it, or to make almost anything, went beyond just the visual aspects of it, or the idea of re-creating an illusion of the thing. I’ve always been more interested in a certain level of representation or pictorial literalness… I like words or descriptions like “actual” or “actual scale.” I like the idea of “what is real?”
Keith Edmier
Siri Engberg. “Unconventionally Real: Nine Artists Discuss Their Work in Lifelike,” on the Walker Art Center website Mar 1, 2012 [Online] Cited 20/12/2020
The exhibition Lifelike, on view at the Blanton Museum of Art at The University of Texas at Austin June 23 to September 22, 2013, invites a close examination of artworks based on commonplace objects and situations, which are startlingly realistic, but often made of unusual materials in unexpected sizes.
Organized by the Walker Art Center in Minneapolis, this international, multigenerational group exhibition features 75 works from the 1960s to the present by leading figures in contemporary art, such as Andy Warhol, Gerhard Richter, James Casebere, Vija Celmins, Keith Edmier, Robert Gober, Ron Mueck, Mungo Thomson, and Ai Weiwei, and illuminates artists’ enduring fascination with realism.
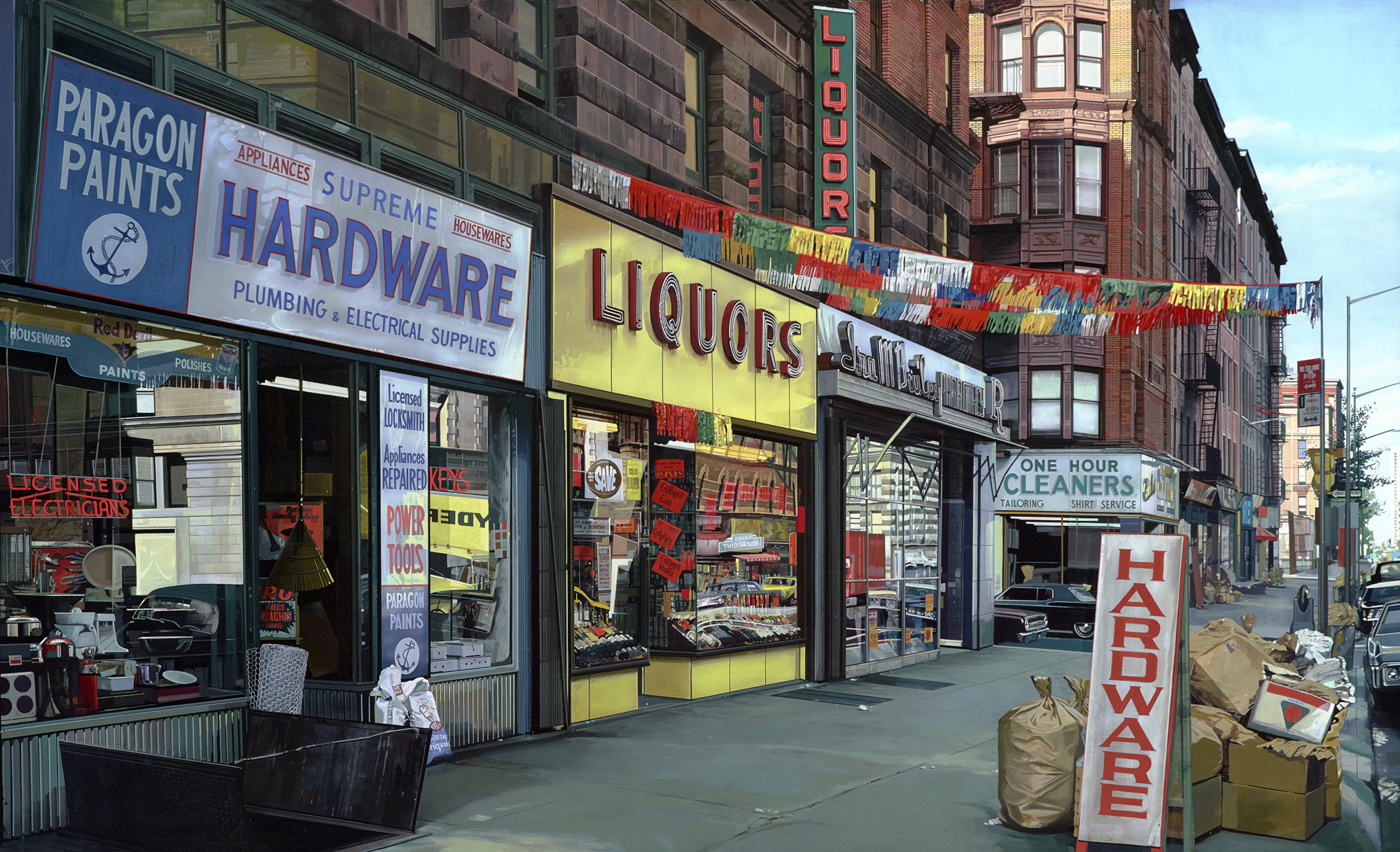
Avoiding the flashiness embraced by 1960s Pop Artists and the slick urban scenes introduced at that time by the Photorealists, the contemporary artists in Lifelike investigate often overlooked items and moments as subject matter: a paper bag, an eraser, an apple core, a waiting roo, an afternoon nap. Favouring a handmade, labour intensive practice rather than technological enhancements, the works in the exhibition – including painting, sculpture, photography, drawing and video – transform the seemingly ordinary into something beguiling, loaded with narrative and metaphor.
The exhibition explores the many ways artists have pursued realism through a range of media. Some artists featured, such as Vija Celmins, Chuck Close, and Peter Rostovsky, paint from photographs, creating works that exhibit an astonishing degree of likeness and detail. Others work in sculpture often fashioning objects from materials that belie the pedestrian nature of the subject – Ai Weiwei’s jar of hundreds of sunflower seeds, hand painted on to cast porcelain, or Tom Friedman’s bee, made out of clay, plastic, and paint. In photography, artists including James Casebere and Isaac Layman play with the hyperreal, through fabricated scenes or clever layering of images. In video, artists including Thomas Demand and Jeon Joonho create moving images that at first seem familiar, but deceive us through sly use of animation.
Conspicuously absent in most of the works in Lifelike is a reliance on technological intervention. Instead, in seemingly inverse proportion to the ease of producing goods for the marketplace, many artists are slowing and complicating their own working methods, remaking banal things into objects of fixation and desire: Catherine Murphy’s details of textured fabric on the seat of a chair, or Ron Mueck’s strikingly “real” sculpture – down to the last hair and pore – of human subjects. Frequently these artists work from photographs, but just as often, their inspiration is the observed world, and the notion that a tangible, perhaps ephemeral object or moment can somehow be brought back to life æ reinterpreted through the artist’s hand as re-made readymades.
To address the nuances of this subject, the exhibition presents several key conceptual sections:
Common Objects gathers a group of late 1960s and early 1970s works that borrowed strategies from Pop, but rejected that movement’s brand-name emphasis in favour of conceptual, more process-oriented approaches to subject matter.
Another section presents the notion of The Uncanny, which features work by a generation of artists in the 1980s and 1990s who inflected realism with a psychologically-laden, surreal sensibility, such as Robert Gober’s child-sized chair and flower-covered box of tissues, resting mysteriously atop a floor drain; or Charles Ray’s disarming photograph of himself as a mannequin.
A third section entitled Realism into Abstraction presents a range of works by artists such as Peter Rostovsky, Catherine Murphy and Tauba Auerbach, in which lushly painted surfaces such as velvet curtains, the seat of a chair, and other ordinary items are cropped in such a way that they resemble abstract paintings, their original sources difficult to discern.
Handmade Sleight of Hand, the fourth section, presents work by artists who make objects that are indistinguishable from their real-life counterparts, but made with the traditional techniques of painting, sculpture, or drawing. Highlights include Jud Nelson’s trash bag carved from Carrara marble and Susan Collis’s checkered plastic shopping bag painstakingly rendered in ballpoint pen on paper.
A fifth section, Special Effects: The Real as Spectacle, presents artists making work that engages an instant response – be it astonishment, fear, confusion, or delight – through their surprising size or unusual installation.
Press release from The Blanton Museum of Art website
Peter Rostovsky (Russian, b. 1970)
Curtain
2010
Oil on linen
72 x 48 in.
Courtesy of the artist
What does it mean in Warholian fashion to “want to be a machine,” to long for a kind of inhumanity that has to be constantly performed and repeated? Is this not a radical disavowal of an all too human vulnerability? Can we not read in the mechanical appeals of photorealism a kind of excessive sentimentality, a naïve expressionism that uses the camera and the photograph as a shield against trauma?
And likewise in expressionism’s hyperbolic restatement of its humanity, is there not a silent concession to its opposite, a founding anxiety about inauthenticity, a mortal dread regarding the total triumph of simulation and technology?
However, it is important to stress that these are unfulfilled desires. No photorealist painting completely fools the viewer into the fact that it is machine-made; it entertains the fantasy, much like electronic music. And each autonomous artwork is only a temporary escape, a utopian space, “an orchid in the land of technology,” to borrow a phrase that Walter Benjamin applied to the illusion of reality in film.
What these two positions in fact represent are two negative theologies that stand as sentinels, forever pointing to and away from a traumatically unresolved subject position – a position of the never sufficiently technological, and the never completely human. They are both Romantic positions and should be read as such: as positions of longing and disavowal, not of identity.
Why would this be important to emphasise? Because it answers the familiar question asked to every painter painting photographs. It’s not about the ends, it’s about the means. It’s about the performance of painting that re-states the position, not the photo-like product that it yields. In other words, it’s about trying and failing to be a machine. Therein resides the futility and poetic nature of the practice. The failure marks the fragility and evanescence of the subject negatively, knowing that the alternative is to misname, to misrepresent, to conjure the opposite. This poetic is more latent, and seldom acknowledged in art that aspires toward indifference and inhumanity, but I hope that I have shown that every tin man has a heart, just like every photorealist hides an abstract painter.
Peter Rostovsky
Siri Engberg. “Unconventionally Real: Nine Artists Discuss Their Work in Lifelike,” on the Walker Art Center website Mar 1, 2012 [Online] Cited 20/12/2020
Matt Johnson (American, b. 1978)
American Spirit
2010
Paper, plastic, foam, paint, and magnets
1 x 3 1/2 x 2 1/4 in.
Edition of 3
Courtesy of the artist and Blum & Poe, Los Angeles
Photo credit: Joshua White
© Matt Johnson
Ron Mueck (Australian, b. 1958)
Untitled (Seated Woman)
1999
Silicone, acrylic, polyurethane foam and fabric
25 1/4 x 17 x 16 1/2 in.
Collection of the Modern Art Museum of Fort Worth
Alex Hay (American, b. 1930)
Paper Bag
1968
Fiberglass, epoxy, paint, and paper
59 1/4 x 29 x 18 in.
Whitney Museum of American Art, New York
© Alex Hay
Courtesy of the artist and Peter Freeman, Inc., New York Photograph by Jerry L. Thompson
Jonathan Seliger (American, b. 1955)
Heartland
2010
Enamel on bronze
103 x 29 x 29 in.
Courtesy of the artist and Jack Shainman Gallery, NY
Yoshihiro Suda (Japanese, b. 1969)
Weeds
2008
Painted on wood
Size varied according to site
© Yoshihiro Suda
Courtesy of Gallery Koyanagi, Tokyo
The Blanton Museum of Art
200 E. Martin Luther King Jr. Blvd.
Austin, TX 78712
Opening hours:
Wednesday – Saturday 10am – 5pm
Sunday 1pm – 5pm
Closed Mondays and Tuesdays





































You must be logged in to post a comment.