Exhibition dates: 4th July – 27th September, 2009
All photographs are of work in the exhibition. Many thankx to the De La Warr Pavilion for allowing me to publish the photographs and art work in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
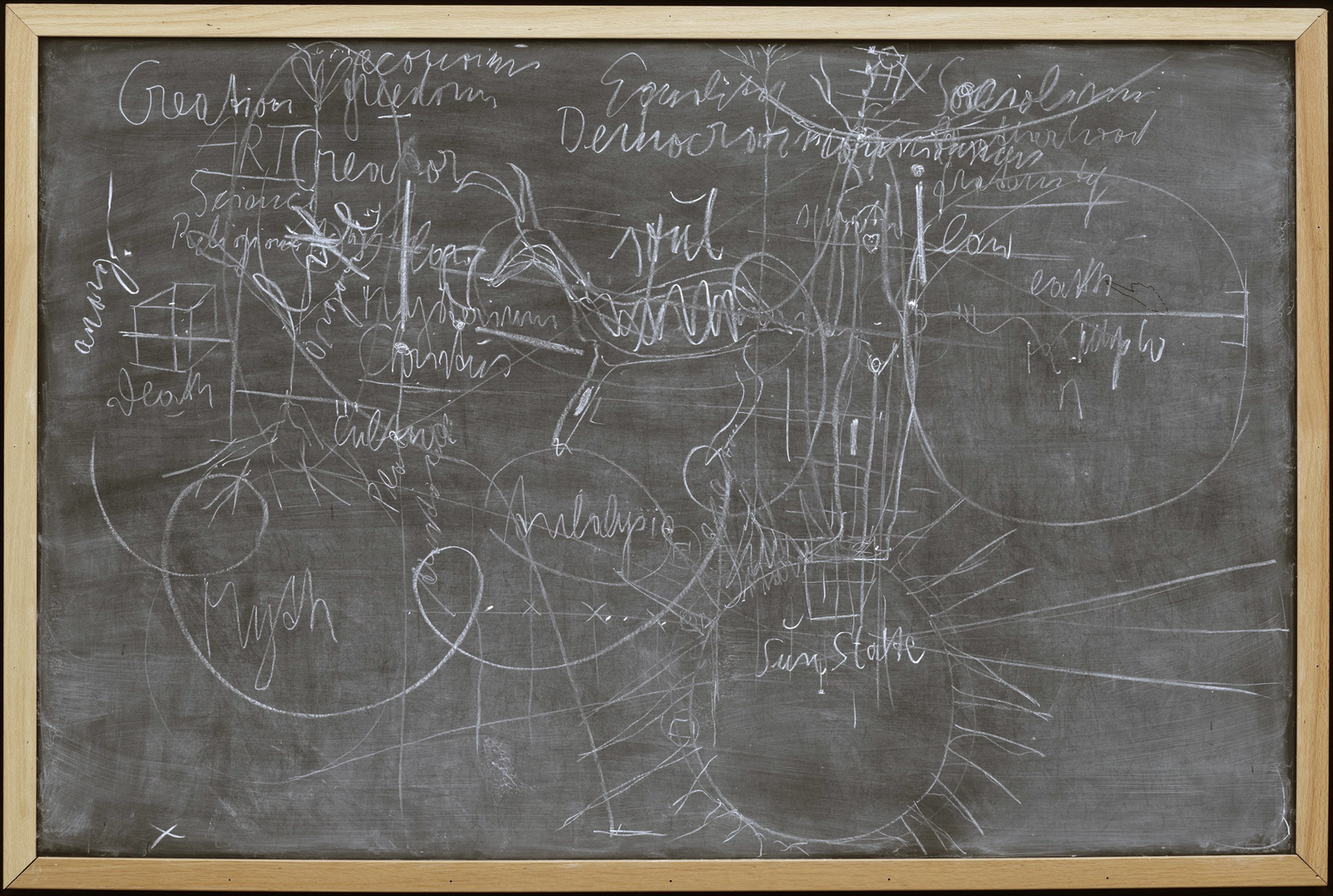
Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
Untitled (Sun State)
1974
Chalk and felt-tip pen on blackboard with wood frame
47 1/2 x 71 1/8″ (120.7 x 180.7cm)
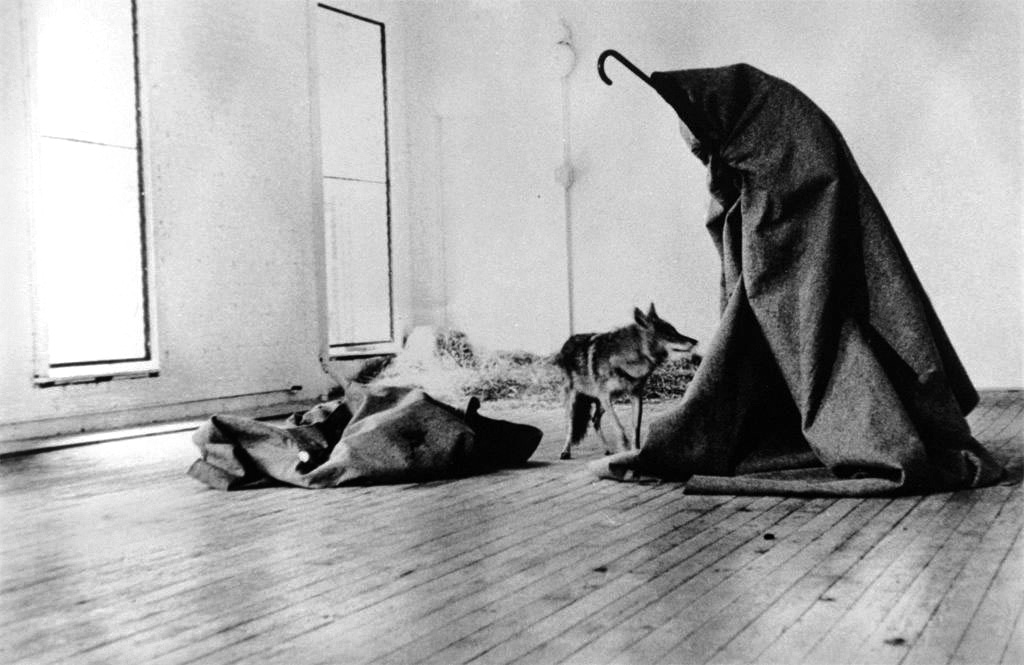

Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
I like America and America likes me action
1974
Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
Überwindet endlich die Parteiendiktatur – Poster, N070815SE_118_098 – Overcome Party Dictatorship Now
1971
Print on paper
278 x 395 mm
ARTIST ROOMS Tate and National Galleries of Scotland
Galleries of Scotland through The d’Offay Donation with assistance from the National Heritage Memorial Fund and the Art Fund 2008
German artist Joseph Beuys (1921-1986) is widely recognised as one of the most influential and extraordinary artists of the twentieth century. Artist, educator, political and social activist, Beuys’s philosophy proposed the healing power and social function of art, in which everyone can participate and benefit. The works in this exhibition provide an opportunity to experience this expanded concept of art as he understood it. Collectively, the exhibition presents the ‘constellation of ideas’ central to Beuys’s practice, revealing his ideas on zoology, ecology, homeopathy, economics, politics, social activism, teaching and learning. Beuys incorporated into his work various materials such as felt, fat and metal, selected because of their inherent properties such as insulation, conduction and protection which all have associations with Beuys’s ideas.
The exhibition is largely selected from the ARTIST ROOMS collection and brings together well-known sculptures, drawings, vitrines and a remarkable selection of posters recalling live actions and events. Works include Fat Chair (1964-1985) and, in Gallery 2, a single major work Scala Napoletana (1985) is shown for the first time in the UK. In addition nearly twenty notable multiples are included within the exhibition selected from National Galleries of Scotland. The multiple was a form of communication for Beuys – a means by which he could share and distribute his ideas beyond the confines of the artworld.
Text from the De La Warr Pavilion website [Online] Cited 23/07/2009. No longer available online
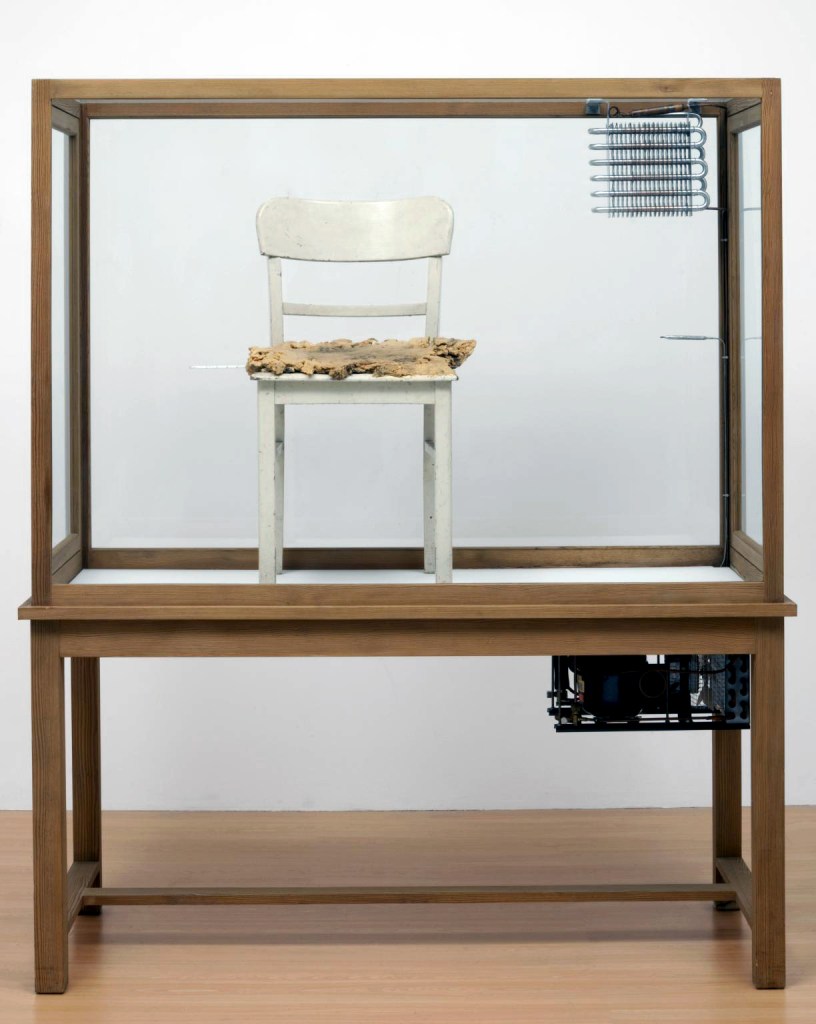

Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
Fettstuhl (Fat Chair)
1964-1985
Wood, glass, metal, fabric, paint, fat and thermometer
1830 x 1550 x 640 mm
ARTIST ROOMS Tate and National Galleries of Scotland
Galleries of Scotland through The d’Offay Donation with assistance from the National Heritage Memorial Fund and the Art Fund 2008
![Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986) 'Entwurf für ein Filzenvironment [Model for a Felt Environment]' 1964 Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986) 'Entwurf für ein Filzenvironment [Model for a Felt Environment]' 1964](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/07/beuys-filzenvironment-web.jpg?w=1024)
Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
Entwurf für ein Filzenvironment (Model for a Felt Environment)
1964
Wood, glass, felt, oil paint and lead
1840 x 1680 x 840 mm
ARTIST ROOMS Tate and National Galleries of Scotland
Galleries of Scotland through The d’Offay Donation with assistance from the National Heritage Memorial Fund and the Art Fund 2008
The neat rolls of grey felt on painted wood inside this vitrine are intended as a model for an ‘environment’. Felt insulates and absorbs, representing protection but also a sense of constriction, like being suffocated. The same type of felt rolls are seen in the ‘environment’ Plight (1958/1985), now in the Pompidou Centre, in which the walls and ceiling are covered with felt to create a stifling atmosphere. Beuys used felt in an infamous ‘action’ performed the same year this model was made. The Chief saw the artist being wrapped in a felt blanket, fighting claustrophobia to lie practically still, as if in a coffin, for a nine-hour period.
![Joseph Beuys. 'Fettecke (Prozess) [Fat Corner (Process)]' 1968](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/07/beuys-fettecke-web.jpg)
Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
Fettecke (Prozess) (Fat Corner (Process))
1968
Wood, glass, 2 cardboard boxes and fat
1835 x 1680 x 840 mm
ARTIST ROOMS Tate and National Galleries of Scotland
Galleries of Scotland through The d’Offay Donation with assistance from the National Heritage Memorial Fund and the Art Fund 2008
Looking inside the two boxes in this vitrine, we can see that in one, the fat has been neatly shaped into the corner to make a wedge. In the other, the shape of the fat has a disturbing biological look to it, like inner organs which have been unceremoniously dumped in a heap. Beuys used triangles of fat in both his sculptures and ‘actions’. From around 1963, he would use wedges of fat or felt to mark the boundaries of a space when performing an ‘action’.
Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
Langhaus (Vitrine)
1953-1962
Wood, glass, felt, oil paint and paper
1830 x 1545 x 640 mm
ARTIST ROOMS Tate and National Galleries of Scotland
Galleries of Scotland through The d’Offay Donation with assistance from the National Heritage Memorial Fund and the Art Fund 2008
Langhaus can be variously translated as ‘nave’ such as one finds in a church, or ‘longhouse’, such as the dwelling house for one or several families found in early north European regions or, still today, in tribal communities in the Amazon region or the South Seas. The block of wood has a small piece of felt attached to the top, suggesting, according to Beuys’s usual iconography, the idea of protection, a connotation strengthened by the length of felt also lying in the vitrine. The walking stick lying alongside the felt is a traditional Beuysian symbol for leadership and protection, much as a shepherd looks after his flock.
Beuys is recognised as one of the most influential artists of the late twentieth century. Adopting the roles of political and social activist and educator, his philosophy proposed the healing power and social function of art for all.
From the 1950s onwards, many of his works are made from a distinctive group of materials, in particular felt, fat and copper. These were chosen for their insulating, conductive, protective, transmitting and transforming properties. Animals of all kinds appear in his work, but he was particularly drawn to stags, bees and hares. A childhood interest in the natural sciences remained with him throughout his life, fuelling a desire to explore themes and experiment with the properties of materials.
Beuys produced a vast body of work that includes performance, drawing, print-making, sculpture and installation. His complex, interlocking themes cover science, myth, history, medicine and energy. Beuys’ own image and life story is inextricably linked to his work through his persona of the Shaman, shepherd or stag-leader.
This group of works covers forty years of Beuys’s career. Included are nature-based drawings of the 1950s, images and scores recording 1960s ‘actions’ and later installations, in addition to sculptures and vitrines. The collection brings together drawings with sculpture from the 1960s like the iconic Fat Chair, and images relating to Actions and installations like Coyote and Show Your Wound. It culminates with the sculpture Scala Napoletana which was made only a few months before the artist’s death, and relates to the theme of communication with the beyond.”
Text from the National Galleries of Scotland website [Online] Cited 23/07/2009. No longer available online

Joseph Beuys with Rose for Direct Democracy
1973

Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
Schwangere und Schwan (Pregnant Woman with Swan)
1959
Oil paint and watercolour on paper
276 x 214 mm
ARTIST ROOMS Tate and National Galleries of Scotland
Galleries of Scotland through The d’Offay Donation with assistance from the National Heritage Memorial Fund and the Art Fund 2008
The tiny swan in this painting looks as if it is swimming serenely inside the woman, replacing the foetus inside her pregnant body. The drawing combines male and female elements, with the phallic nature of the swan’s neck. Beuys had been fascinated with swans since childhood. A sculpture of a large golden swan sat on top of the tower of Schwanenburg castle (Swan Castle) in his home town of Cleves, and was visible from his bedroom window while he was growing up. With his interest in language, the artist would also have delighted in the similarity between the German words for pregnant woman (Schwangere) and swan (Schwan).
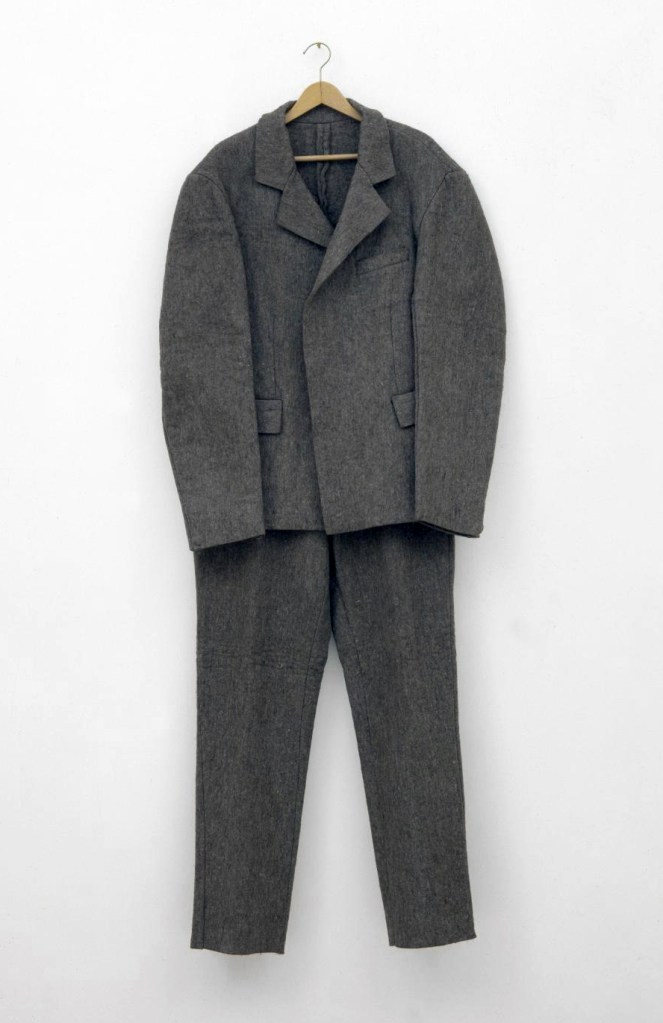

Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
Felt Suit
1970
Felt and wood
1660 x 660 x 260 mm
ARTIST ROOMS Tate and National Galleries of Scotland
Galleries of Scotland through The d’Offay Donation with assistance from the National Heritage Memorial Fund and the Art Fund 2008
Beuys began producing works in multiples in the 1960s, partly as a way to combat the elitism of the art world. This is probably his most famous multiple. It has its origins in the performance Action the Dead Mouse/Isolation Unit of 1970, where Beuys wore a felt suit with lengthened arms and legs, like the one seen here. He described the suit as an extension of the sculptures he made with felt, where the material’s insulating properties were integral to the meaning of the work. Beuys intended this concept of warmth to extend beyond the material to encompass what he described as ‘spiritual warmth or the beginning of an evolution’.
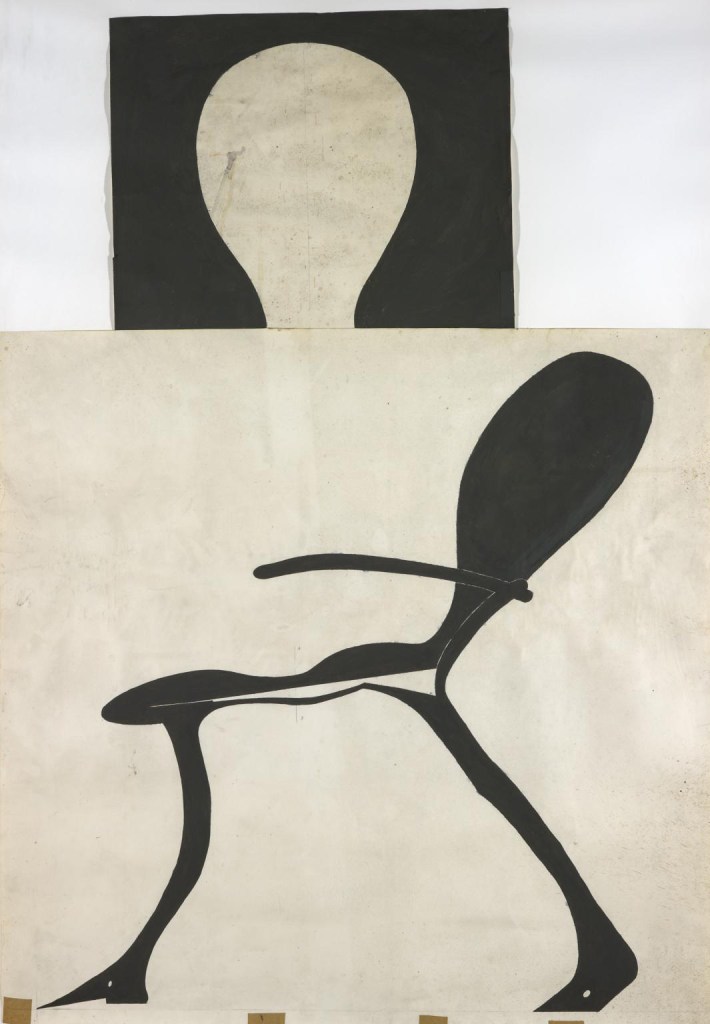

Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
Stark beleuchteter Hirschstuhl (Brightly-Lit Stag Chair)
1957-1971
2 works on paper, oil paint, graphite and masking tape
1390 x 963 mm
ARTIST ROOMS Tate and National Galleries of Scotland
Galleries of Scotland through The d’Offay Donation with assistance from the National Heritage Memorial Fund and the Art Fund 2008
Although Beuys began this collage in 1957, it was not finished until 1971. The chair is similar to the subject of the artist’s 1972 sculpture Backrest for a fine-limbed person (Hare-type) of the 20th Century A.D. This is a cast iron impression of a child’s plaster corset, made as a multiple. However, the striding feet of the chair in this collage give it a human aspect, making it seem almost confident and self-possessed. The curved back of the chair is echoed in the lightbulb shape at the top of the image. The stag, in Beuys’s bestiary, guided the soul in its journey to the afterlife.
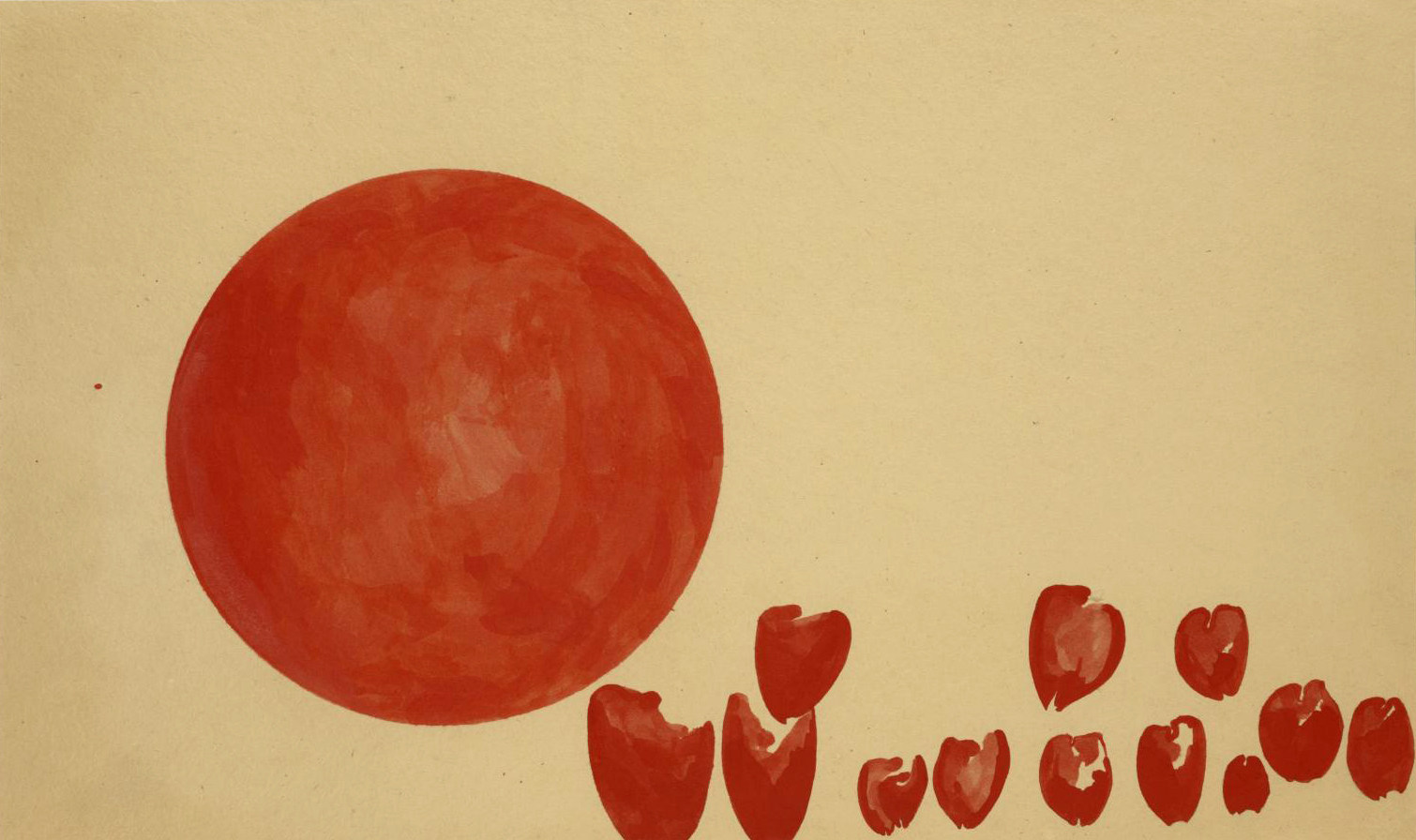

Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
Passage der Zukunftplanetoiden (Hearts of the Revolutionaries: Passage of the Planets of the Future)
1955
Watercolour on card
295 x 490 mm
ARTIST ROOMS Tate and National Galleries of Scotland
Galleries of Scotland through The d’Offay Donation with assistance from the National Heritage Memorial Fund and the Art Fund 2008
The choice of red for this painting would seem like an obvious one, reflecting both the heart and the virtues of honour and courage of the revolutionary in the title of the piece. Red also represents socialism, a belief of Beuys which became central to his later work. However, the colour red is used sparingly and symbolically in the artist’s work, and here it makes a bold statement on life, vitality and the future. The inclusion of the round shape to represent a planet brings an astronomical element into the work.
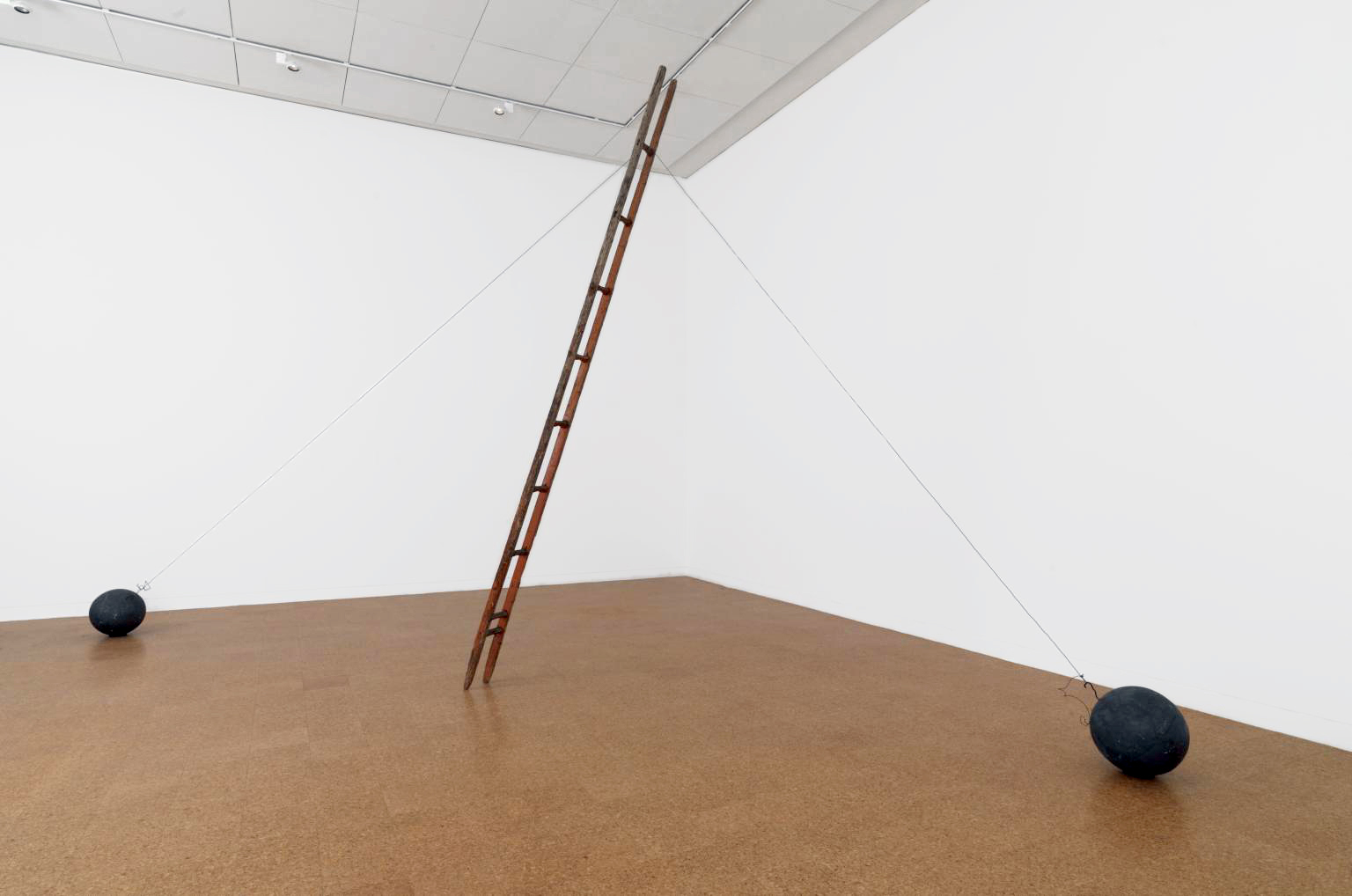

Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
Scala Napoletana
1985
Overall dimensions variable: 11000 x 10000 x 6000mm (room size at Bexhill)
Ladder: 4510 x 250 x 80mm, Lead spheres: 500mm diameter each
ARTIST ROOMS Tate and National Galleries of Scotland
Galleries of Scotland through The d’Offay Donation with assistance from the National Heritage Memorial Fund and the Art Fund 2008
Much of the work Beuys made in his last few years includes objects or themes which suggest death. This sculpture was originally inspired by a ladder the artist found while recovering from illness on the island of Capri in Autumn 1985, which he hung with two stones. When he visited Amalfi at Christmas in the same year, he purchased a ladder (Scala Libera) from a landlord which he used to make this sculpture. Held in suspension, it appears as if the pair of lead weights are preventing this heavy wooden ladder from soaring into the air. This is one of the last sculptures Beuys made. He died in January 1986.
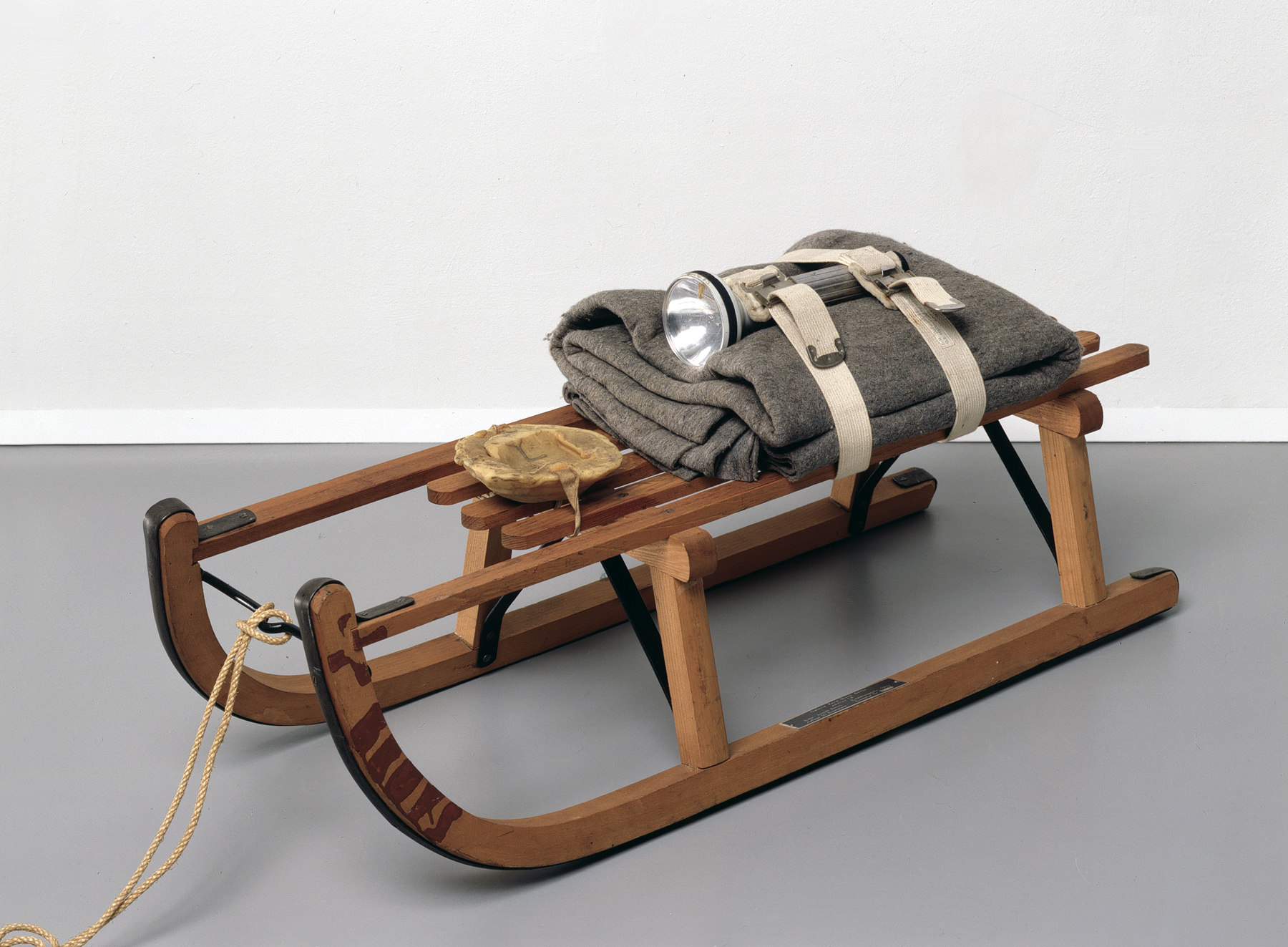

Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
Sled
1969
The materials used in the making of this work relate to Beuys’s experience of being rescued by nomadic Tartars when his plane was shot down during the Second World War. Fat was rubbed into his body and he was wrapped in felt to keep him warm. The sled looks as if it has been prepared for an expedition or in response to an emergency, with a survival kit strapped to it. The flashlight represents the sense of orientation, the felt is protective, and the fat is for food.

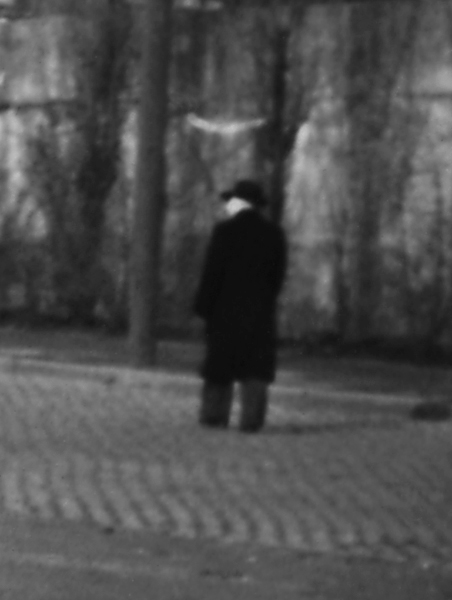
Joseph Beuys (German, 1921-1986)
Ohne Titel (Untitled)
1970
Gelatin silver print on canvas
2330 x 2275 mm
ARTIST ROOMS Tate and National Galleries of Scotland
Galleries of Scotland through The d’Offay Donation with assistance from the National Heritage Memorial Fund and the Art Fund 2008
Wearing his unmistakeable felt trilby hat, with his fishing vest poking through a luxuriant fur-lined jacket, this large image (over two metres square) shows Beuys at his most iconic. The clothes he wears here were part of his artist’s ‘uniform’, chosen for comfort and practicality (the multi-pocketed vest was particularly useful) but also as a way to create his image. Fittingly, he is depicted with one of his most distinctive sculptures. In the foreground is The Pack (1969), a group of twenty-four sledges. Each one has its own survival kit including fat for sustenance, felt for warmth and a torch for navigation, making the artist’s signature materials part of this image too.
Text under images from the National Galleries of Scotland website [Online] Cited 23/07/2009. No longer available online
De La Warr Pavilion
Bexhill-on-Sea,
East Sussex, TN40 1DP
Opening hours:
10am – 5pm, seven days a week














You must be logged in to post a comment.