Exhibition dates: 2nd September – 26th October 2011
Foam Paul Huf Award 2011
Raphaël Dallaporta (French, b. 1980)
Fragile, Blood 1
2010
© Raphaël Dallaporta
Antipersonnel. The positive pleasure of inflicting cruelty at an ambiguous physical and ethical distance. Use limited only by the imagination of the user. Detonated remotely using a laptop computer. 10 million times. US$3 each.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to Foam for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Raphaël Dallaporta (French, b. 1980)
Domestic Slavery, Angha
2006
© Raphaël Dallaporta
Domestic Slavery, 2006
Cold, distant images of building facades are associated with text. The narratives are written by Ondine Millot to describe the events that took place at the exact address of the buildings in the photographs. The spectator comes to understand that the series deals with an often undocumented consequence of human trafficking: modern slavery.
The images force us to come to terms with the upsetting reality that is hidden behind the ordinary facades. Raphaël Dallaporta denounces unbearable situations where one human being reduces another to the status of thing, and gives it depth through the distance of the photographs and his refusal to sensationalise.
Text from the Musée Nicéphore Niépce website [Online] Cited 29/03/2020
Raphaël Dallaporta (French, b. 1980)
Domestic Slavery, Henriette
2006
© Raphaël Dallaporta
Raphaël Dallaporta (French, b. 1980)
Ruins (Season 1), The Balkh-AB gorges, Afghanistan
2011
© Raphaël Dallaporta
Ruin, Season 1, 2011
In the autumn of 2010, Raphaël Dallaporta took part in an archaeological mission in the Bactriane region in Afghanistan, scene of Alexander the Great’s mythical conquest. Using a drone he designed himself, he took aerial photographs of endangered or heretofore unknown archaeological sites in a country at war. The remote controlled device was timed to take photos of unrivalled precision every five seconds. The way the images are put together with their voluntarily asymmetrical contours depict these inaccessible monuments and places at their best. The most cutting-edge technology reveals the artist’s themes – destruction, the precariousness of things. It brings to light that which was and is no longer. Is this not the very definition of all photography?
Text from the Musée Nicéphore Niépce website [Online] Cited 29/03/2020
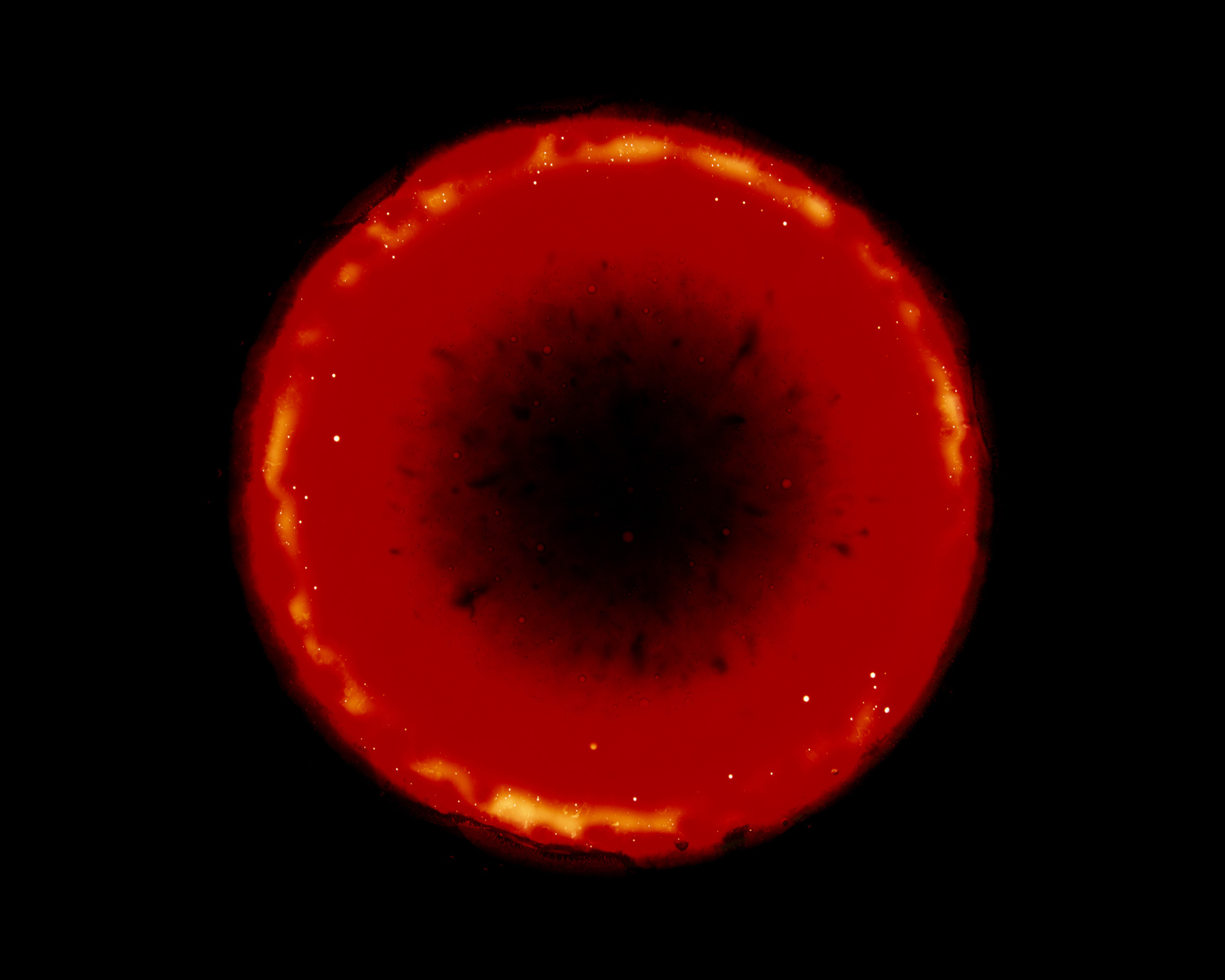
Raphaël Dallaporta (French, b. 1980)
Fragile, “Four Moods”, Black Bile
2010
© Raphaël Dallaporta
Fragile, 2010
Raphaël Dallaporta photographs organs, like the encyclopaedic colour plates for an anatomy class. The legend, again, explains the origins of these silent images. The organ represented is not the issue; the reason for its presence on the slab is the issue. The apparent neutrality of the shot, according to a strict protocol (frontal shot, on a black background enabling the strong lighting of the “subject”), isolates each fragment of the body as a clue that enables to determine the cause of death. These relics of flesh and bone have a real role to play. But the way they are shot lends them a metaphysical and philosophical dimension that reminds us of life’s ephemeral nature and human vulnerability.
Text from the Musée Nicéphore Niépce website [Online] Cited 29/03/2020
Raphaël Dallaporta (French, b. 1980)
Fragile, Cardiopulmonary system
2010
© Raphaël Dallaporta
Undetermined circumstances
The body of the subject whose presumed identity is …, aged 92, was found in a ditch around 10.05am by a walker whose attention had been attracted by his dog.
The autopsy that we carried out on the body showed the presence of a state of extremely advanced putrefaction with partial skeletonisation, consistent with a death dating back one month in an outdoor environment; it is not possible to be more precise. There is no immediately detectable cause of death. No lesions suggesting recent detectable violence were observed. As for identification, the deceased is an adult male, wearing a pacemaker and an old surgical scar on the abdominal wall.
Raphaël Dallaporta (French, b. 1980)
Fragile, Pacemaker
2010
© Raphaël Dallaporta
French photographer Raphaël Dallaporta (b. 1980) received the Foam Paul Huf Award earlier this year from an international jury. The prize is organised by Foam and is awarded annually to up and coming international photographers below the age of 35. A major aspect of the award is an exhibition. Observation appears at Foam from 2 September to 26 October. Characteristic of the show’s four series is the clinical, perceptive style of photography. Dallaporta’s photos possess an inner tension that stems from the beauty of the object and the serious tone of the subject. The photographer works intensively with specialists in fields relating to his series. Jury chair François Hébel (director of Les Rencontres d’Arles international photography festival) comments on Dallaporta’s work that ‘He combines involvement with a highly analytical approach to social perversities. His uncompromising, conceptual and extremely creative approach mark him as an authentic artist who stands out in the young generation of photographers.’
The landmines in the Antipersonnel series have an exquisite beauty: small, with pleasant colours and an attractive form. Elegantly photographed, simply framed and persuasively presented, their aesthetic quality is what first attracts attention. Until we realise the full purpose of their existence: pure cruelty.
Fragile features frontal and objective shots of organs and limbs taken from corpses. Dallaporta worked with a team of forensic surgeons for this series. While the physicians were looking for causes of death, Dallaporta recorded the body parts they examined and the instruments they used. The power of this work comes from the combination of apparently neutral images and texts relating to human pain.
Dallaporta also worked with experts when making Ruins. He travelled with a team of French archaeologists to Afghanistan. Using a drone – a small remote-controlled helicopter – he took numerous photos of the war-ravaged landscape. In combination, these form a single large aerial picture that also shows traces of ancient civilisations. Past and present come together in this series of almost scientific photos.
In Domestic Slavery, Dallaporta (pictures) and Ondine Millot (text) tackle the tragic reality of this phenomenon: people, many unregistered migrants, held against their will in places where their voice cannot be heard. While their names have been altered, the stories are true. Dallaporta’s clinical, unsentimental pictures of the buildings in which these modern-day slaves are kept testify to the banality of day-to-day inhumanity.
Text from the Foam website
Antipersonnel, 2004
Unknown objects seem to emerge from the darkness. The legend quickly informs us that they are anti-personnel mines. Raphaël Dallaporta deals with the object reproduced to scale and lets us imagine the consequences of its existence. There are no bloody reportage images to illustrate the mutilations caused by these devices. The photographer presents us with contemporary still life that appear inoffensive but that tend to be aestheticised by photographic techniques all the better to erase the actual use of the object.
Text from the Musée Nicéphore Niépce website [Online] Cited 29/03/2020
Raphaël Dallaporta (French, b. 1980)
Antipersonnel, Blast Mine Type 72B China
2004
© Raphaël Dallaporta
Type 72 blast mines are said to make up 100 million of China’s 110 million antipersonnel landmine stockpiles (Chinese officials claim this figure is exaggerated). Manufactured by China North Industries Corporation (NORINCO), Type-72s are reportedly priced at US$3 each. The Type-72B includes an anti-handling mechanism that makes it impossible to neutralise – if the mine is moved more than 8º from the horizontal, it will explode, amputating the limb that activated it.
Raphaël Dallaporta (French, b. 1980)
Antipersonnel, Submunition BLU-3/B USA
2004
© Raphaël Dallaporta
On release from a CBU-2C.A bomb this 785 g submunition – known as the “Pineapple” – is stabilised and slowed in its descent by six fins. Each CBU-2C/A contains 409 BLU-3/Bs, of which nearly 25 percent do not explode on impact. d: 73mm W: 785g
Raphaël Dallaporta (French, b. 1980)
Antipersonnel, Bounding Fragmentation Mine M-16, USA
2004
© Raphaël Dallaporta
When detonated the M-16 antipersonnel bounding fragmentation mine is shot up approximately 1.5m in the air and explodes within 0.5 seconds, creating a lethal radius of 10m. Nicknamed the “Bouncing Betty,” each mine is supplied with four tripwires (two olive-green, two sand-coloured) and a wrench. In September 2002 (the most recent statistics available) the USA had 465,330 M16s in stock.
Raphaël Dallaporta (French, b. 1980)
Antipersonnel, Directional Fragmentation Mine M-18/A1, USA
2004
© Raphaël Dallaporta
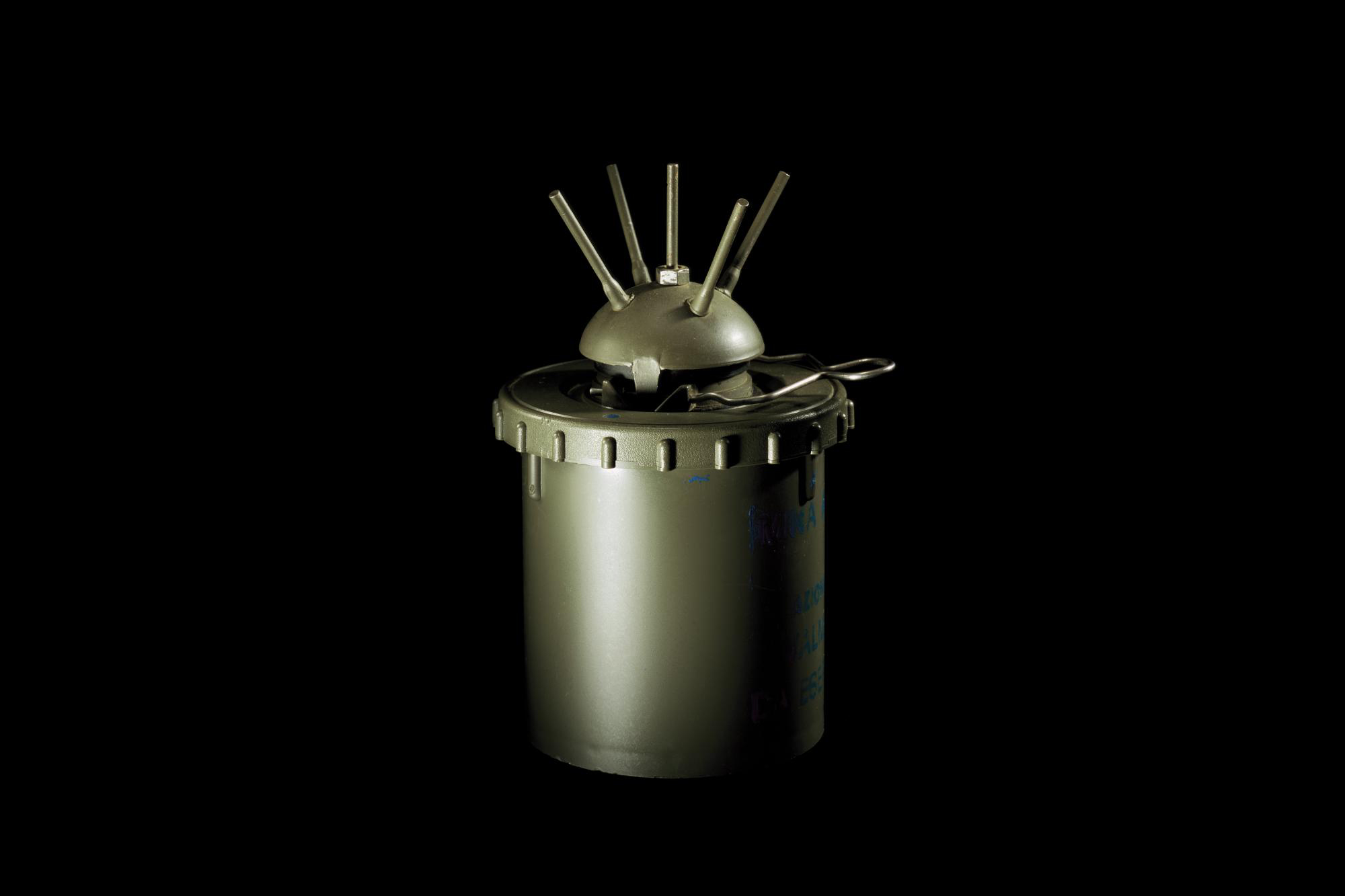
A “Claymore” directional fragmentation mine releases 700 steel balls when detonated by a hand-turned dynamo, a tripwire or, when used with the “Matrix” system, remotely using a laptop computer. (Multiple Claymores can also be linked together using a detonator cord.) A 1996 Department of the Army filed manual states that, “the number of ways in which the Claymore may be employed is limited only by the imagination of the user.” In September 2002 (the most recent available statistics), Claymores made up 403,096 of the 10,404,148 landmines stockpiled by the USA.
Raphaël Dallaporta (French, b. 1980)
Antipersonnel Bounding Fragmentation Mine, V-69, Italy
2004
© Raphaël Dallaporta
Antipersonnel Bounding Fragmentation Mine, V-69, Italy. The V-69 can be set off by footfall pressure or through a tripwire. When detonated the fuse sets off propellant gases that fire the mine’s inner body 45cm above the ground. This explodes sending out more than 1,000 pieces of chopped steel. Between 1982 and 1985, its manufacturer Valsella sold around 9 million V-69s to Iraq. The mine was given a nickname by Iraqi minelayers: the “Broom”. 120mm, 3.2kg.
Foam
Keizersgracht 609
1017 DS Amsterdam
The Netherlands
Phone: + 31 20 5516500
Opening hours:
Mon – Wed 10am – 6pm
Thu & Fri 10am – 9pm
Sat & Sun 10am – 6pm






















You must be logged in to post a comment.