Exhibition dates: 3rd May – 28th July, 2024
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
Annie
1864
Albumen print
25.5cm x 21.3cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
Julia Margaret Cameron made this portrait of Annie Philpot, the daughter of a family staying on the Isle of Wight, within a month of receiving her first camera. She inscribed some prints of it ‘My first success’. She later recounted, ‘I was in a transport of delight. I ran all over the house to search for gifts for the child. I felt as if she entirely had made the picture.’
Text from the V&A website
“Nothing is scared but beauty.”1
Since the establishment of Art Blart in November 2008, Julia Margaret Cameron appears in a select and esteemed group of photographic artists who each have over 6 postings in the archive: Eugène Atget, William Eggleston, Walker Evans, Robert Frank, Dorothea Lange, Robert Mapplethorpe, László Moholy-Nagy and August Sander.
I am always ecstatic when I see Cameron’s work. Nobody has ever taken portraits like JMC before or since.
As I have written on JMC in earlier exhibitions:
“When you think about it, here is one the world’s top ten photographers of all time – a woman, taking photographs within the first twenty five years of the birth of commercial photography, using rudimentary technology and chemicals – whose photographs are still up there with the greatest ever taken. Still recognisable as her own and no one else’s after all these years. That is a staggering achievement – and tells you something about the talent, tenacity and perspicacity of the women… that she possessed and illuminated such a penetrating discernment – a clarity of vision and intellect which provides a deep understanding and insight into the human condition.”2
“As with any genius (a person who possesses exceptional intellectual or creative power) who goes against the grain, full recognition did not come until later. But when it does arrive, it is undeniable. As soon as you see a JMC photograph… you know it is by her, it could be by no one else. Her “signature” – closely framed portraits and illustrative allegories based on religious and literary works; far-away looks, soft focus and lighting, low depth of field; strong men (“great thro’ genius”) and beautiful, sensual, heroic women (“great thro’ love”) – is her genius.
There is something so magical about how JMC can frame a face, emerging from darkness, side profile, filling the frame, top lit. Soft out of focus hair with one point of focus in the image. Beautiful light. Just the most sensitive capturing of a human being, I don’t know what it is… a glimpse into another world, a ghostly world of the spirit, the soul of the living seen before they are dead.
Love and emotion. Beauty, beautiful, beatified.”3
Dr Marcus Bunyan
1/ “The line runs from Winckelmann’s Thoughts on the Imitation of Greek Works of Art in Painting and Sculpture, first published in 1755, to the end of the 19th century and beyond; see Walter Pater’s “Winckelmann,” written in 1867 and published in The Renaissance.
Margaret Walters. “The Classical Nude,” in Margaret Walters. The Nude Male: A New Perspective. New York & London: Paddington Press, 1978, p. 34. Footnote 2.
2/ Marcus Bunyan on the exhibition Julia Margaret Cameron: from the Victoria and Albert Museum, London at the Art Gallery of New South Wales (AGNSW), Sydney on Art Blart 24th October 2015
3/ Marcus Bunyan on the exhibition Victorian Giants: The Birth of Art Photography at the National Portrait Gallery, London on Art Blart 13th May 2018
Julia Margaret Cameron exhibitions on Art Blart
~ Exhibition: ‘Francesca Woodman and Julia Margaret Cameron: Portraits to Dream In’ at the National Portrait Gallery, London, March – June 2024
~ Exhibition: ‘Victorian Giants: The Birth of Art Photography’ at the National Portrait Gallery, London Part 1, March – May 2018
~ Exhibition: ‘Julia Margaret Cameron’ at the Victoria and Albert Museum, London, November 2015 – February 2016
~ Exhibition: ‘Julia Margaret Cameron: from the Victoria and Albert Museum, London’ at the Art Gallery of New South Wales (AGNSW), Sydney Part 2, August – October 2015
~ Exhibition: ‘Julia Margaret Cameron: from the Victoria and Albert Museum, London’ at the Art Gallery of New South Wales (AGNSW), Sydney Part 1, August – October 2015
~ Exhibition: ‘Julia Margaret Cameron’ at The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, August 2013 – January 2014
Many thankx to the Milwaukee Art Museum for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“I longed to arrest all beauty that came before me, and at length the longing has been satisfied.”
Julia Margaret Cameron
One of the most influential photographers in the medium’s history, Julia Margaret Cameron made portraits of transcendent beauty in close-up, soft-focus photographs. Arresting Beauty: Julia Margaret Cameron – a major traveling exhibition the Milwaukee Art Museum partnered with the Victoria and Albert Museum, London, to bring to the Midwest – highlights the renowned photographer’s pioneering style.
Cameron (English b. India, 1815-1879) received her first camera at the age of 48, making her career even more impressive for its brevity. Her portraits depict family and friends; contemporary scientists, scholars, and artists; and scenes staging allegorical, biblical, historical, and literary stories. For over a decade, she produced thousands of photographs and built a career, selling and exhibiting her work internationally. Her distinct style set her apart, and her legacy positions her as an artist who broke ground for future photographers.
The Museum’s unique presentation of this celebratory exhibition features more than 90 objects and includes works of art from its collection to provide historical context for the art that influenced, and was influenced by, Cameron.
A V&A Exhibition – Touring the World
Text from the Milwaukee Art Museum website
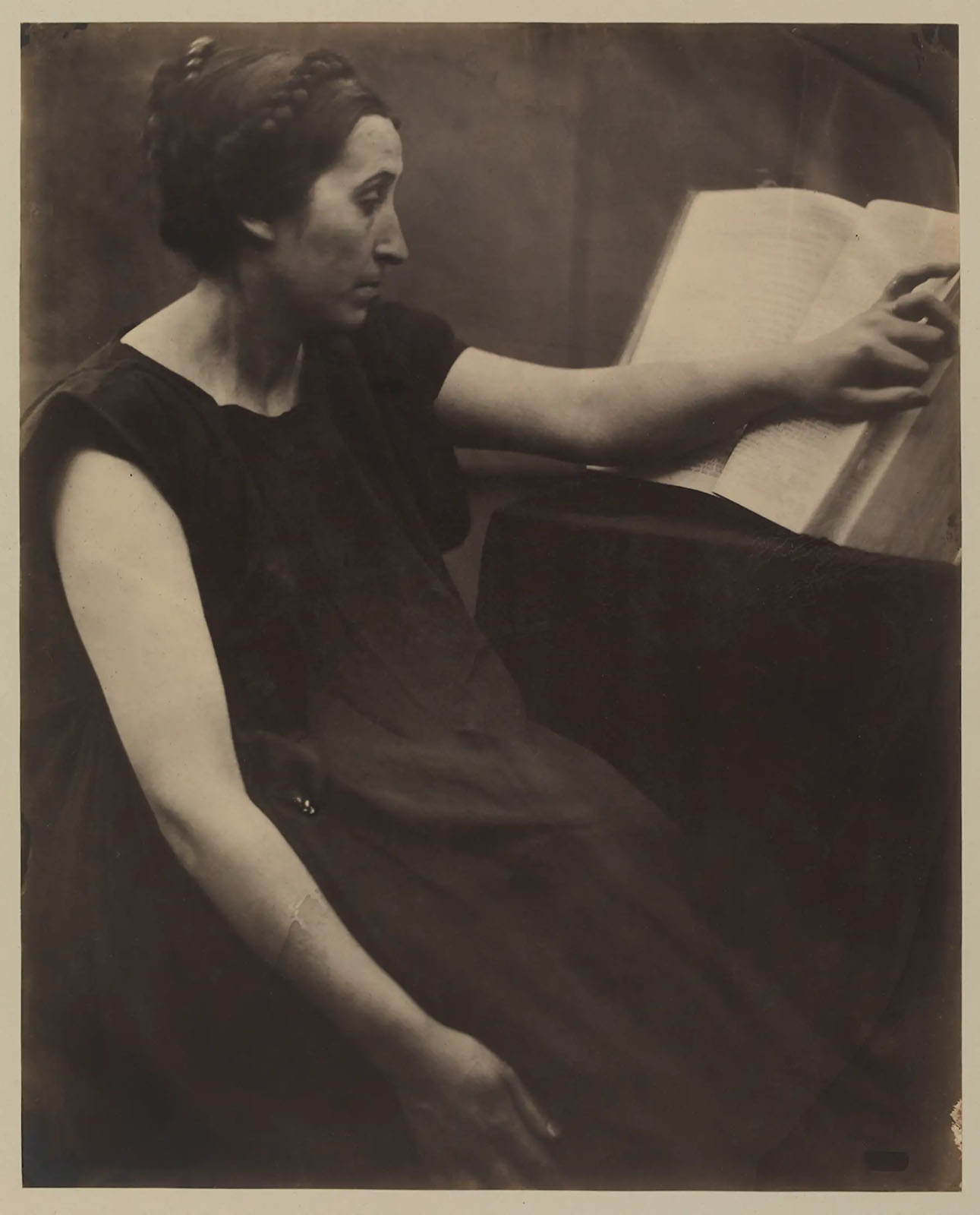
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
A Sibyl after the manner of Michelangelo
1864
Albumen print
28.5cm x 22.5cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
Just as she modelled her Madonna photographs on Renaissance art, Julia Margaret Cameron looked to painting and sculpture as inspiration for her allegorical and narrative subjects. Some works are photographic interpretations of specific paintings by artists such as Raphael and Michelangelo. Others aspired more generally to create ‘Pictorial Effect’.
This depiction of a sibyl, a prophetess from classical mythology, is based on Michelangelo’s fresco of the Erythraean Sibyl on the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel in Rome (1508-1510). The model’s braided hair, bare arms and profile pose with a large book are all copied from Michelangelo’s version. Cameron’s good friend and neighbour Tennyson had prints of the Sistine Chapel frescoes decorating his home.
Cameron’s friend and mentor, the painter G.F. Watts, wrote to Cameron, ‘Please do not send me valuable mounted copies … send me any … defective unmounted impressions, I shall be able to judge just as well & shall be just as much charmed with success & shall not feel that I am taking money from you.’ This photograph is one of approximately 67 in the V&A’s collection that was recently discovered to have belonged to him. Many are unique, which suggests that Cameron was not fully satisfied with them. Some may seem ‘defective’ but others are enhanced by their flaws. All of them contribute to our understanding of Cameron’s working process and the photographs that did meet her standards.
Text from the V&A website
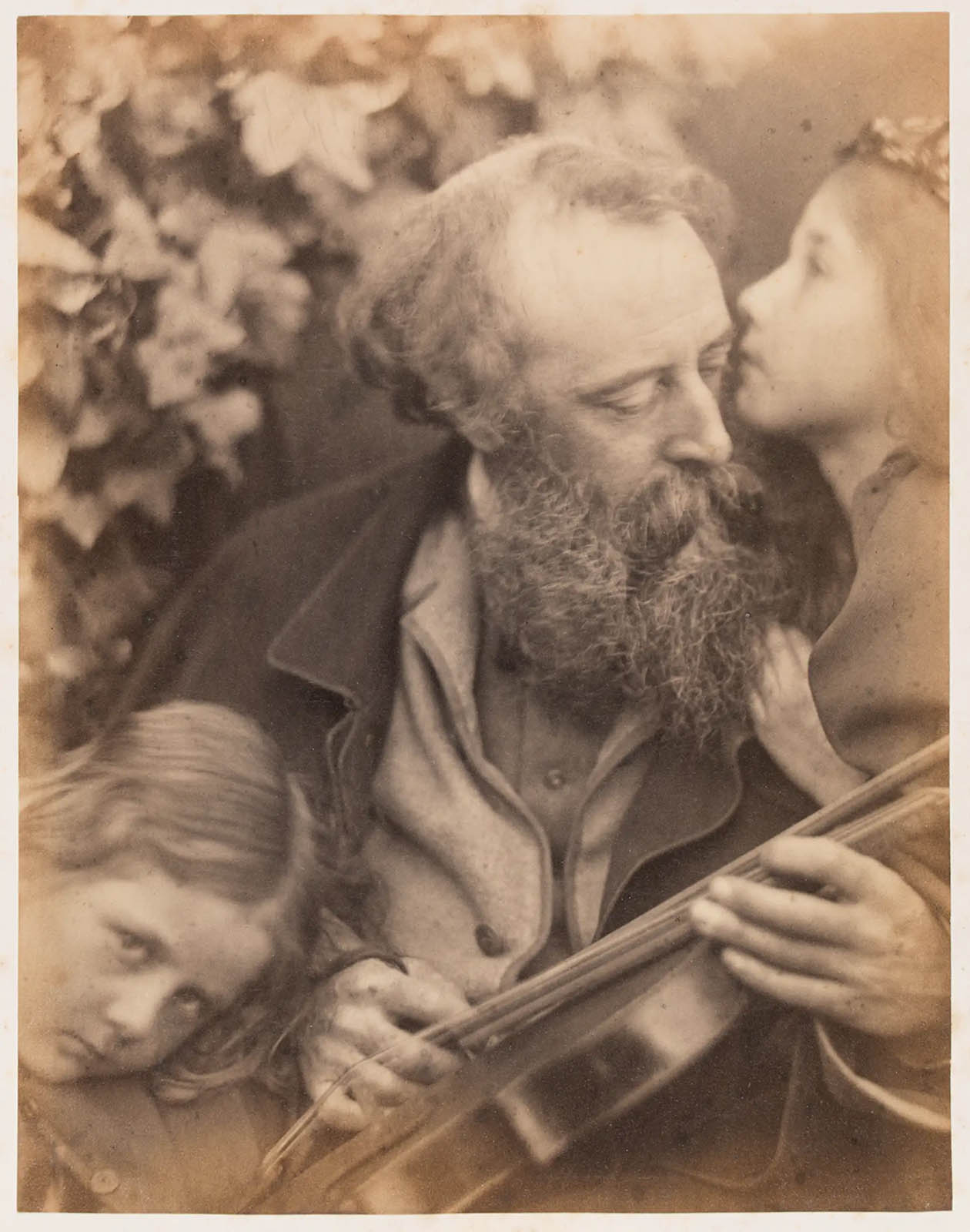
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
The Whisper of the Muse
1865
Albumen print
25.5cm x 21.3cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
Julia Margaret Cameron looked to painting and sculpture as inspiration for her allegorical and narrative subjects. Some works are photographic interpretations of specific paintings by artists such as Raphael and Michelangelo. Others aspired more generally to create ‘Pictorial Effect’.
Cameron’s harshest critics attacked her for using the supposedly truthful medium of photography to depict imaginary subject matter. Some suggested that at best her photographs could serve as studies for painters. The South Kensington Museum mainly acquired ‘Madonnas’ and ‘Fancy Subjects’, and exhibited them as pictures in their own right.
Cameron considered her close friend, the painter and sculptor G. F. Watts, to be her chief artistic advisor. She wrote of this period, ‘Mr. Watts gave me such encouragement that I felt as if I had wings to fly with.’ Here she transforms him into a musician, perhaps to symbolise the arts in general, rather than showing him specifically as a painter. Kate Keown, the girl on the right, whispers inspiration.
Text from the V&A website
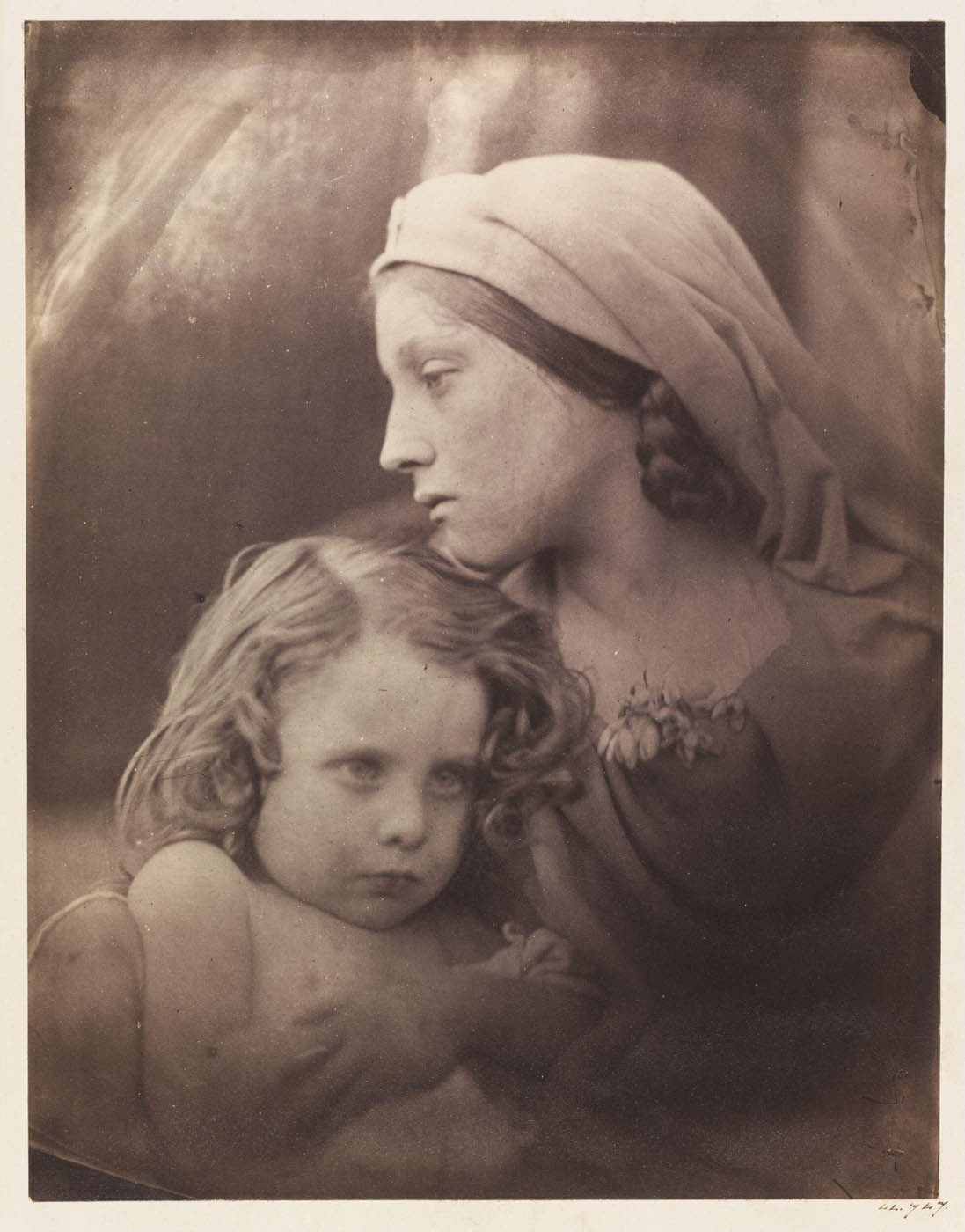
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
La Madonna Aspettante
1865
Albumen print from wet collodion negative
25.5 x 21.3cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
Many of the photographs purchased by the South Kensington Museum (now the Victoria and Albert Museum) from Julia Margaret Cameron were ‘Madonna Groups’ depicting the Virgin Mary and the infant Christ. Her housemaid Mary Hillier posed as the Virgin Mary so often she became known locally as ‘Mary Madonna’.
Like many of her contemporaries, Cameron was a devout Christian. As a mother of six, the motif of the Madonna and child held particular significance for her. In aspiring to make ‘High Art’, Cameron aimed to make photographs that could be uplifting and morally instructive.
Text from the V&A website
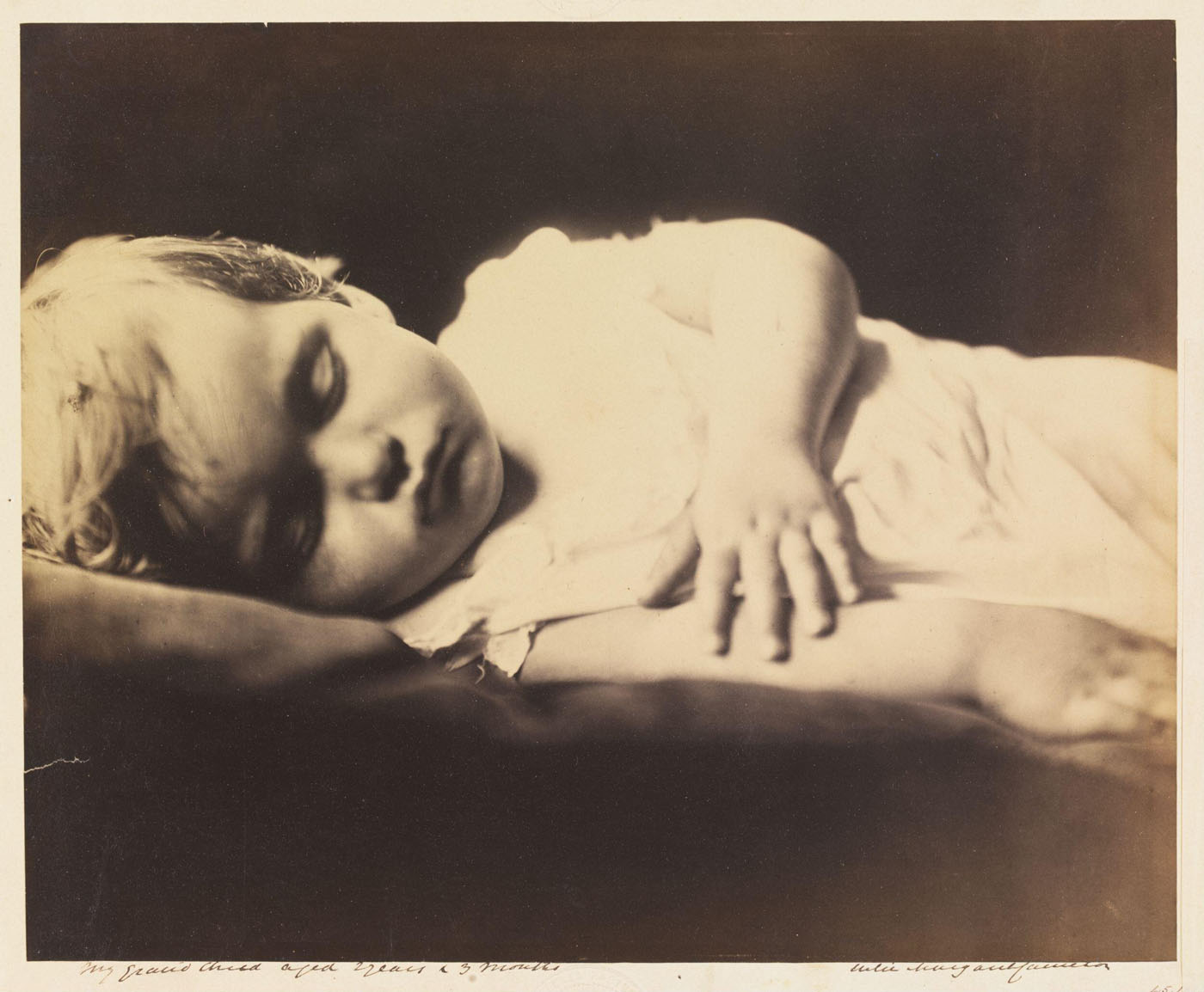
Julia Margaret Cameron (British, 1815-1879)
My grand child aged 2 years & three months
1865
Albumen print from wet collodion negative
25.5 x 21.3cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
Julia Margaret Cameron’s earliest photographic subjects were family and friends, many of whom were eminent literary figures. These early portraits reveal how she experimented with dramatic lighting and close-up compositions, features that would become her signature style.
Cameron made numerous studies of her grandson, both as himself and in the guise of the Christ child. He features in eight of the photographs the South Kensington Museum acquired in 1865.
Text from the V&A website
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
The Mountain Nymph Sweet Liberty
1866
Albumen print
25.5cm x 21.3cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
Christabel
1866
Albumen print from wet collodion negative
25.5 x 21.3cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
In the poem by Samuel Taylor Coleridge, Christabel is a virtuous maiden who is put under a spell by an evil sorceress. Cameron wrote of photographs such as this, ‘When coming to something which, to my eye, was very beautiful, I stopped there instead of screwing on the lens to the more definite focus which all other photographers insist upon’.
Text from the V&A website
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
Beatrice
March 1866
Albumen print from wet collodion negative
35.3 x 28.1cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
In late 1865, Julia Margaret Cameron began using a larger camera. It held a 15 x 12 inch glass negative, rather than the 12 x 10 inch negative of her first camera. Early the next year she wrote to Henry Cole with great enthusiasm – but little modesty – about the new turn she had taken in her work.
Cameron initiated a series of large-scale, closeup heads that fulfilled her photographic vision. She saw them as a rejection of ‘mere conventional topographic photography – map-making and skeleton rendering of feature and form’ in favour of a less precise but more emotionally penetrating form of portraiture. Cameron also continued to make narrative and allegorical tableaux, which were larger and bolder than her previous efforts.
Cameron based the model’s pose, drapery and sad expression on a painting attributed to Guido Reni that was famous at the time. The subject is the 16th-century Italian noblewoman Beatrice Cenci, executed for arranging the murder of her abusive father. One review admired Cameron’s soft rendering of ‘the pensive sweetness of the expression of the original picture’ while another mocked her for claiming to have photographed a historical figure ‘from the life’.
Text from the V&A website
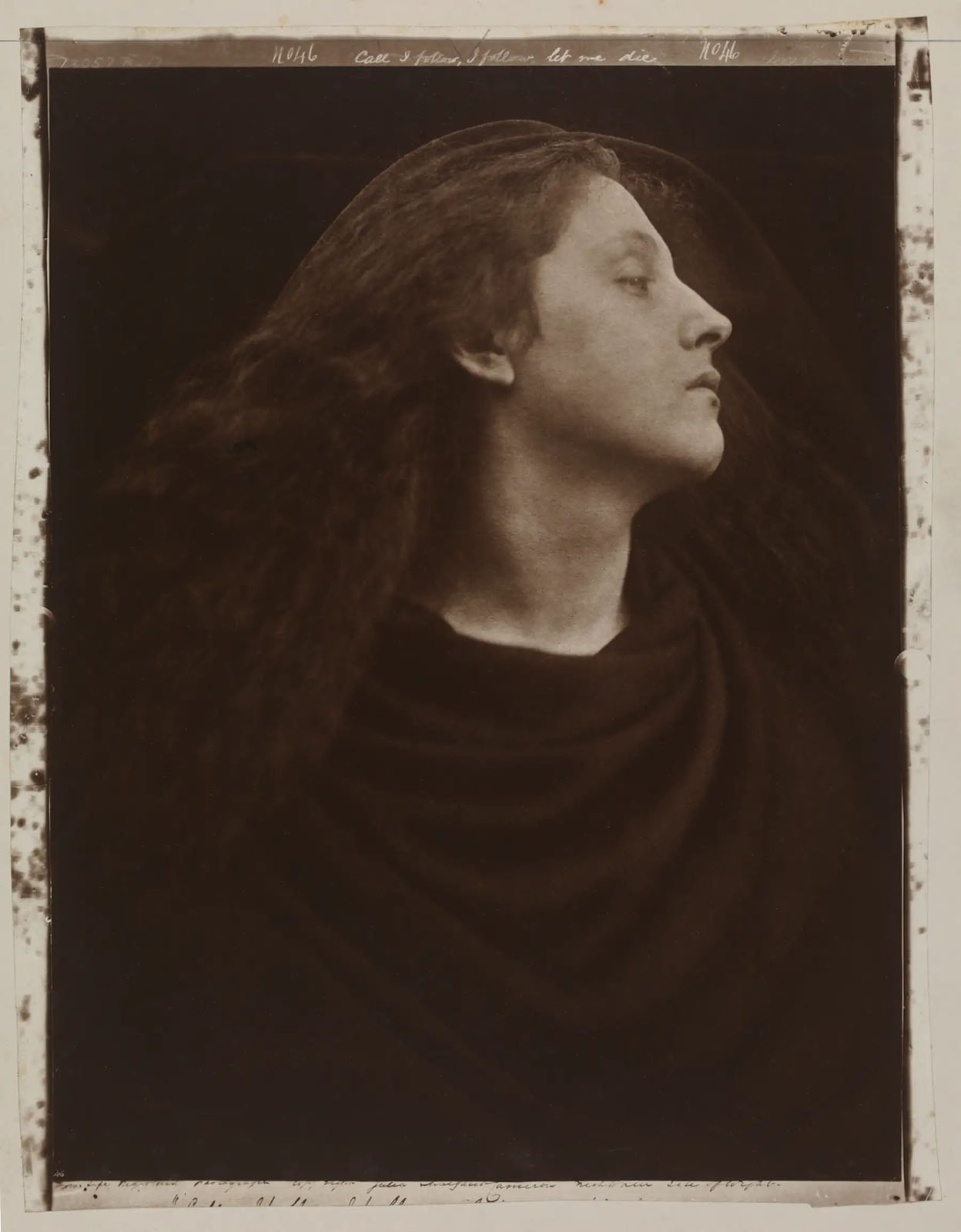
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
Call I Follow, I Follow, Let Me Die
1867
Carbon print
35.1cm x 26.7cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
In late 1865, Julia Margaret Cameron began using a larger camera. It held a 15 x 12 inch glass negative, rather than the 12 x 10 inch negative of her first camera. Early the next year she wrote to Henry Cole with great enthusiasm – but little modesty – about the new turn she had taken in her work.
Cameron initiated a series of large-scale, closeup heads that fulfilled her photographic vision. She saw them as a rejection of ‘mere conventional topographic photography – map-making and skeleton rendering of feature and form’ in favour of a less precise but more emotionally penetrating form of portraiture. Cameron also continued to make narrative and allegorical tableaux, which were larger and bolder than her previous efforts.
In this image, Cameron concentrates upon the head of her maid Mary Hillier by using a darkened background and draping her in simple dark cloth. The lack of surrounding detail or context obscures references to narrative, identity or historical context. The flowing hair, lightly parted lips and exposed neck suggest sensuality. The title, taken from a line in the poem ‘Lancelot and Elaine’ from Alfred Tennyson’s ‘Idylls of the King’, transforms the subject into a tragic heroine.
Text from the V&A website
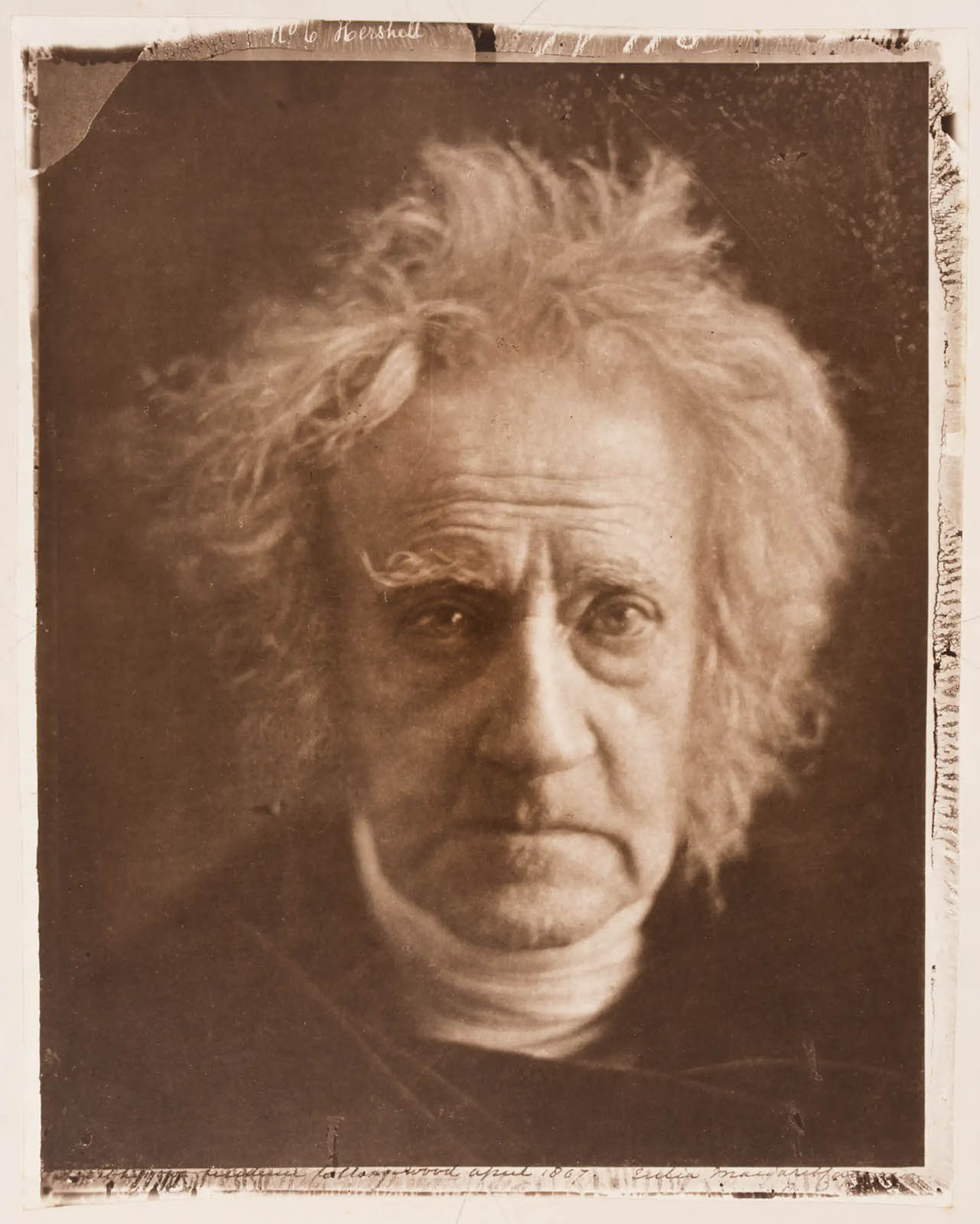
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
Sir John Herschel
1867
Albumen print
25.5cm x 21.3cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
When Julia Margaret Cameron photographed her intellectual heroes, such as Tennyson, her aim was to record ‘the greatness of the inner as well as the features of the outer man’. Another motive was to earn money from prints, since her family’s finances were precarious. Within her first year as a photographer she began exhibiting and selling through the London gallery Colnaghi’s. She used autographs to increase the value of some portraits.
In March 1868 Cameron used two rooms at the South Kensington Museum as a portrait studio. Her letter of thanks makes clear her commercial aspirations, mentioning photographs she had sold and asking for help securing more sitters, including, she wrote hopefully, any ‘Royal sitters you may obtain for me’.
Sir John Herschel was an eminent scientist who made important contributions to astronomy and photography. Cameron wrote of this sitting, ‘When I have such men before my camera my whole soul has endeavoured to do its duty towards them in recording faithfully the greatness of the inner as well as the features of the outer man. The photograph thus taken has been almost the embodiment of a prayer.’
Text from the V&A website
Milwaukee Art Museum Presents Major Exhibition of Renowned Photographer Julia Margaret Cameron’s Pioneering Portraits
The only Midwestern presentation of the internationally touring exhibition Arresting Beauty: Julia Margaret Cameron showcases the 19th-century artist’s explorations of transcendent beauty through portraiture.
The Milwaukee Art Museum partners with the Victoria and Albert Museum, London, to present Arresting Beauty: Julia Margaret Cameron, an exhibition illuminating the transcendent beauty of the renowned photographer’s pioneering style. Featuring more than 90 works, including photographs, paintings, and archival objects, the exhibition will be on view May 3 – July 28, 2024, in the Museum’s Herzfeld Center for Photography and Media Arts.
“We are honoured to bring this significant selection of Julia Margaret Cameron’s photographs from the V&A’s collection to the Milwaukee Art Museum,” said Marcelle Polednik, PhD, Donna and Donald Baumgartner Director. “As the only Midwest venue for Arresting Beauty, our visitors will have a unique opportunity to view these rare and groundbreaking prints that will likely not be brought back together again in our generation.”
Julia Margaret Cameron (English born India, 1815-1879) is distinguished as one of the most innovative and influential photographers in the medium’s history. In 1863, at 48 years old, she received her first camera as a gift from one of her children. Cameron refined her artistic practice, creating a distinct style that set her apart from other photographers: close-up, soft-focus portraits often with scratches and smudges she thought enhanced the images’ beauty. Though her style was criticised and considered aesthetically radical for her time, Cameron’s legacy positions her as an artist who broke ground for future photographers. For over a decade, she made photographs from her home in Freshwater on the Isle of Wight and her studio at the South Kensington Museum (now the V&A) in London. She is best known for sensitive, spiritual portraits of her contemporaries and scenes staging allegorical, biblical, historical, and literary stories. Sitters for Cameron’s photographs include Charles Darwin and Alfred Tennyson, as well as her family members, friends, neighbours, and domestic workers.
“Julia Margaret Cameron found beauty in the everyday – both in the people around her and in the photographic ‘mistakes’ she made,” said Kristen Gaylord, Herzfeld Curator of Photography and Media Arts at the Milwaukee Art Museum. “Her artistic pursuit of such beauty left an enduring impact on the field, and I’m thrilled we can bring this major internationally touring exhibition to our community.”
Arresting Beauty travels from Jeu de Paume, Paris, to the Milwaukee Art Museum and comprises three sections: Cameron’s early photography experiments, her portraits of her contemporaries, and her allegorical compositions and artistic tableaux.
Exhibition highlights include:
~ Annie, 1864, a portrait of Cameron’s neighbour, deemed by the artist as her “first success”;
~ The Whisper of the Muse, 1865, an early allegorical photograph featuring artist George Watts as a musician with two local girls as muses;
~ John Frederick William Herschel, 1867, a striking portrait of the prominent scientist and photographic inventor who was a friend of Cameron’s;
~ The Rosebud Garden of Girls, 1868, a composition featuring five women surrounded by flowers, its title inspired by a line from one of Alfred Tennyson’s poems.
Accompanying Cameron’s prints are archival treasures, such as rarely exhibited, handwritten pages from her influential memoir Annals of My Glass House; her camera lens; and a photograph of Cameron taken by her son, Henry Herschel Hay Cameron. To provide historical context for the art that influenced, and was influenced by, Cameron, the Milwaukee Art Museum will present pieces from its collection alongside those from the V&A, including its own photograph by Julia Margaret Cameron, three paintings from its European collection, and three prints never before exhibited.
Arresting Beauty: Julia Margaret Cameron was organised by Lisa Springer, Curator of Photography Touring Exhibitions, and Marta Weiss, Senior Curator of Photography, Victoria and Albert Museum, London. The Milwaukee Art Museum presentation was organised by Kristen Gaylord, Herzfeld Curator of Photography and Media Arts.
Press release from the Milwaukee Art Museum
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
The Rosebud Garden of Girls
1868
Albumen print
25.5cm x 21.3cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
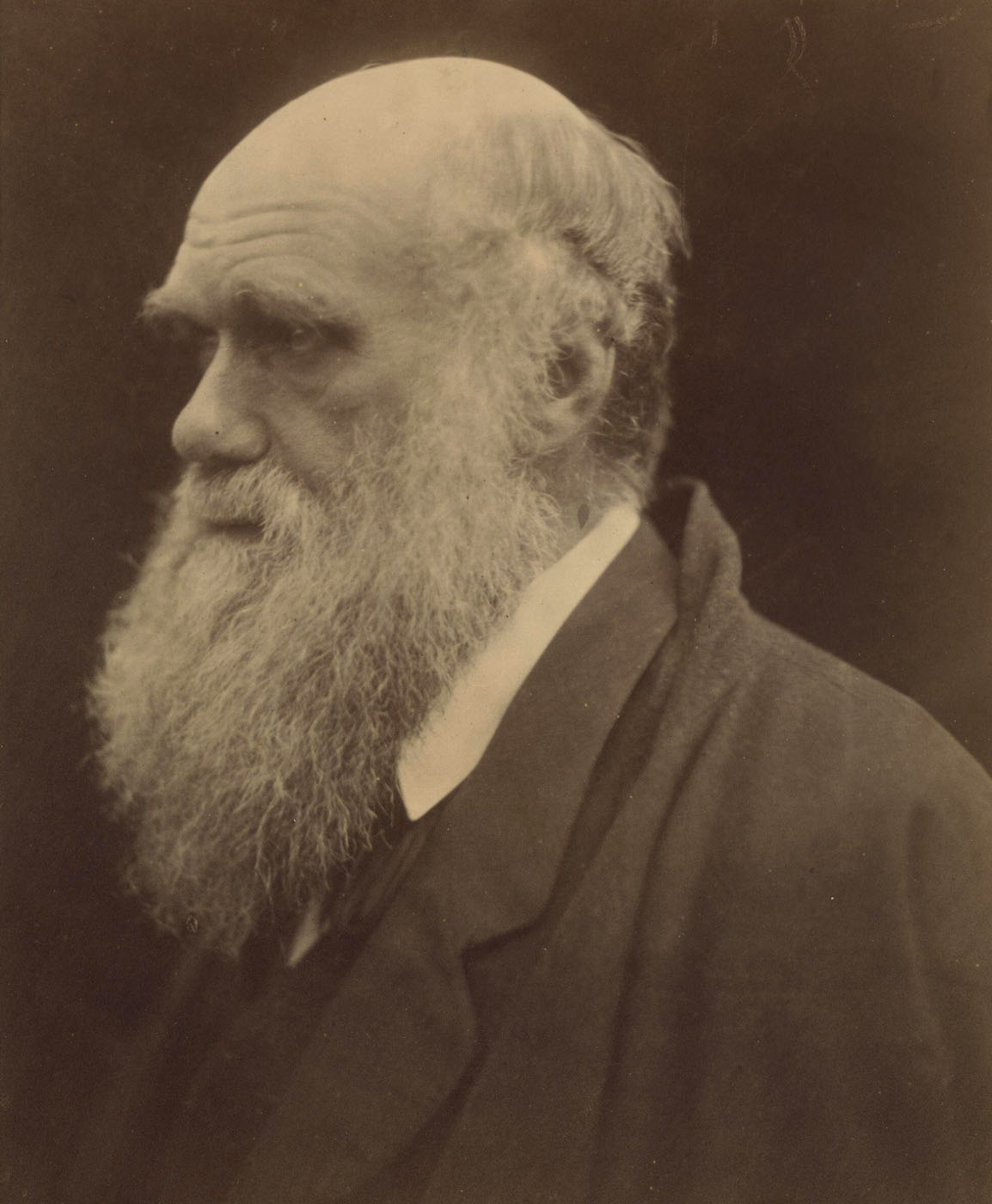
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
Charles Darwin
1868 (photographed), 1875 (printed)
Albumen print from wet collodion negative
25.5 x 21.3cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
When Julia Margaret Cameron photographed her intellectual heroes such as Alfred Tennyson, Sir John Herschel and Henry Taylor, her aim was to record ‘the greatness of the inner as well as the features of the outer man.’ Another motive was to earn money from prints of the photographs, since her family’s finances were precarious. Within her first year as a photographer she began exhibiting and selling through the London gallery Colnaghi’s. She used autographs to increase the value of some portraits.
The naturalist Charles Darwin and his family rented a cottage on the Isle of Wight from the Camerons in the summer of 1868. By 27 July, Colnaghi’s was advertising, ‘We are glad to observe her gallery of great men enriched by a very fine portrait of Charles Darwin’. Due to the sitter’s celebrity, Cameron later had this portrait reprinted as a more stable carbon print.
Text from the V&A website
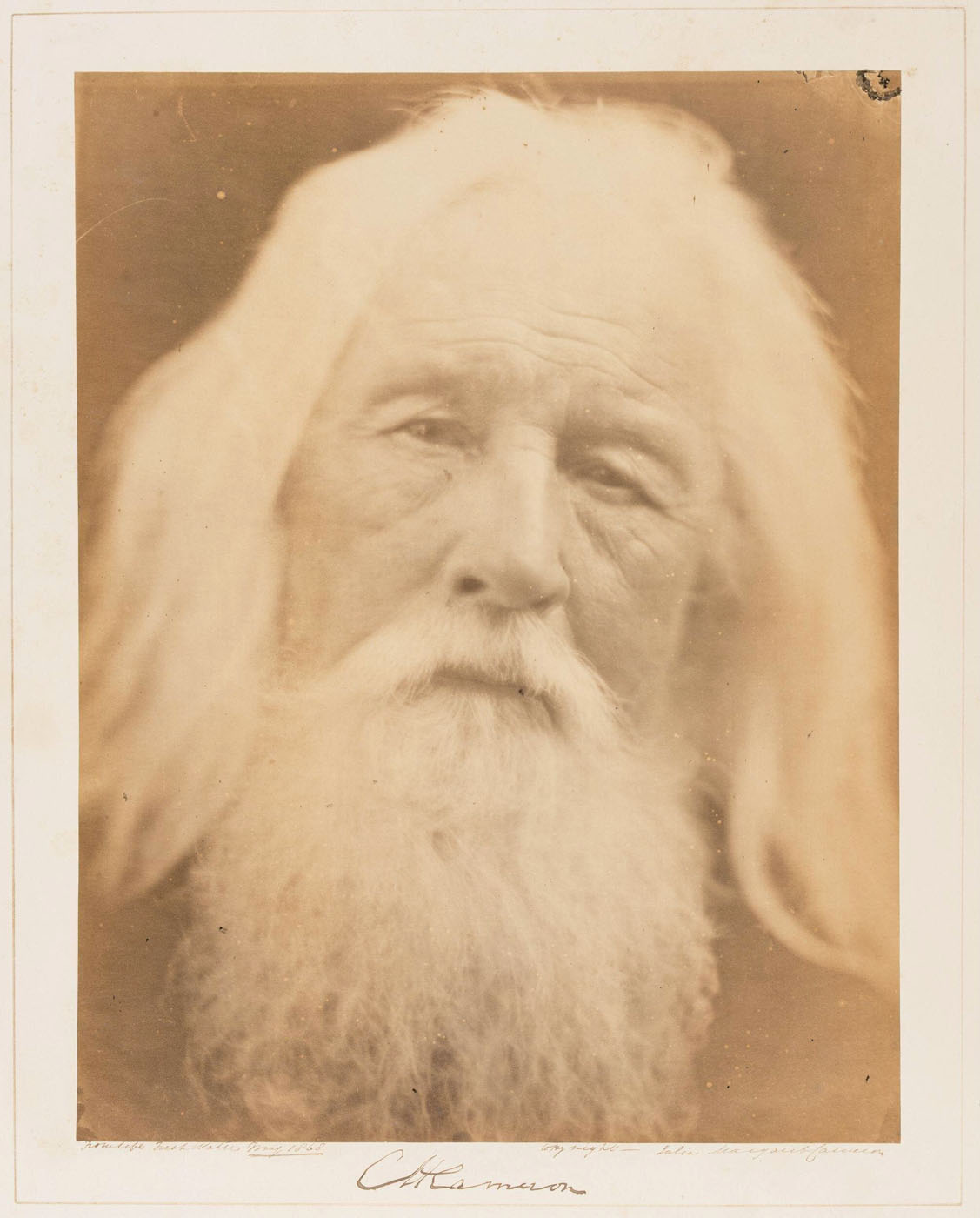
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
Charles Hay Cameron
May 1868
Albumen print from wet collodion negative
25.5 x 21.3cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
Her husband, Charles Hay Cameron, a retired reformer of Indian law and education, frequently posed for Cameron. Cameron’s husband, Charles, was two decades older than Julia.
Text from the V&A website
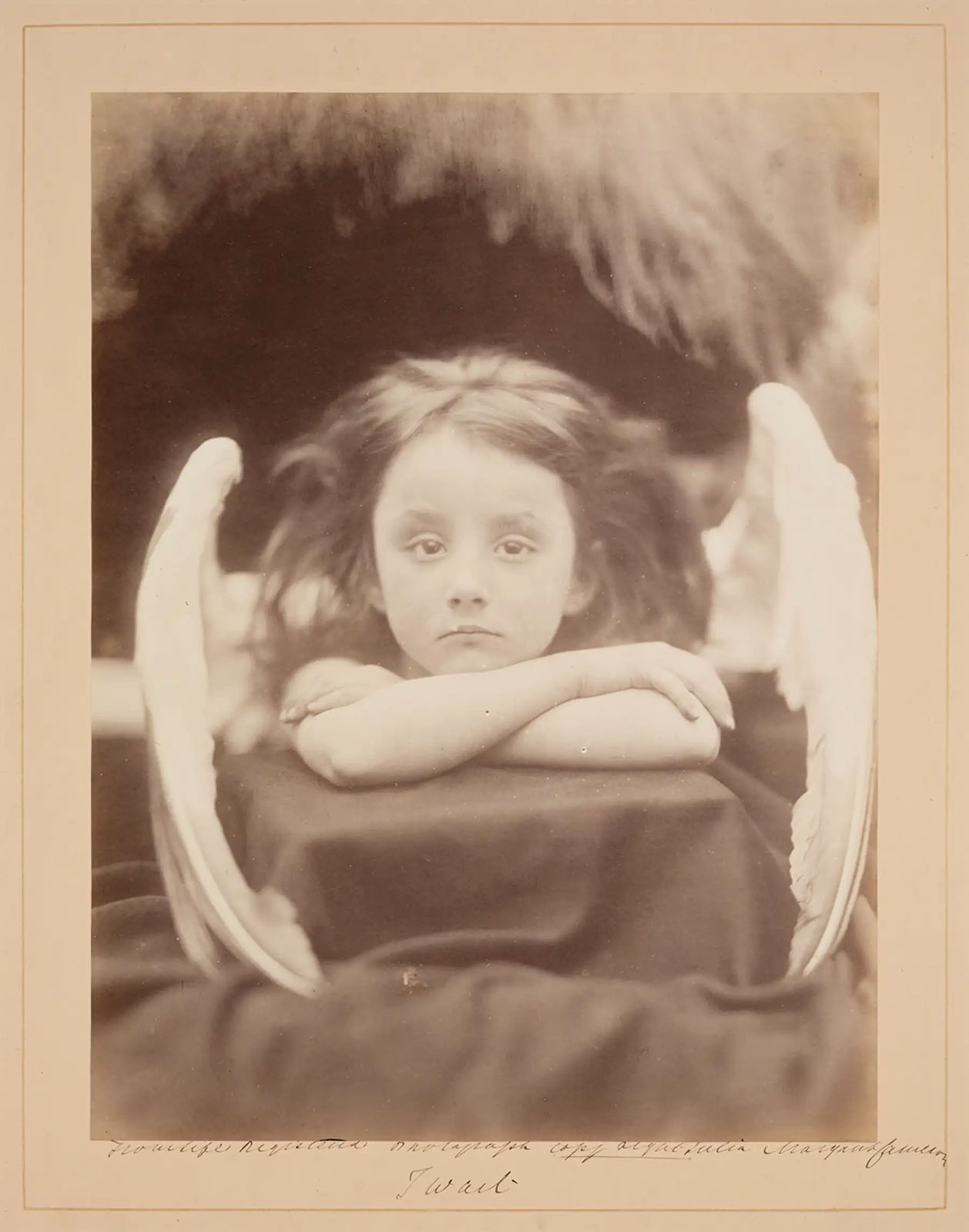
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
I Wait
1872
Albumen print
25.5cm x 21.3cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
St. Agnes
1872
Albumen print
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
Mary Hillier
1873
Albumen print
25.5cm x 21.3cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
In this image, Cameron concentrates upon the head of her maid Mary Hillier by using a darkened background and draping her in simple dark cloth. The lack of surrounding detail or context obscures references to narrative, identity or historical context. The flowing hair, lightly parted lips and exposed neck suggest sensuality.
Text from the V&A website
Julia Margaret Cameron (British born India, 1815-1879)
A Group of Kalutara Peasants
1878
Albumen print
25.5cm x 21.3cm
© The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A, acquired with the generous assistance of the National Lottery Heritage Fund and Art Fund
Milwaukee Art Museum
700 N Art Museum Dr, Milwaukee,
WI 53202, United States
Opening hours:
Monday – Tuesday: Closed
Wednesday: 10am – 5pm
Thursday: 10am – 8pm
Friday – Sunday: 10am – 5pm























































You must be logged in to post a comment.