Exhibition dates: 16th April – 25th August 2019
Curator of the exhibition: István Virágvölgyi
Co-curator: Miklós Tamási
Curatorial assistant: Mária Madár
The catalog is a richly illustrated catalog in Hungarian and English.
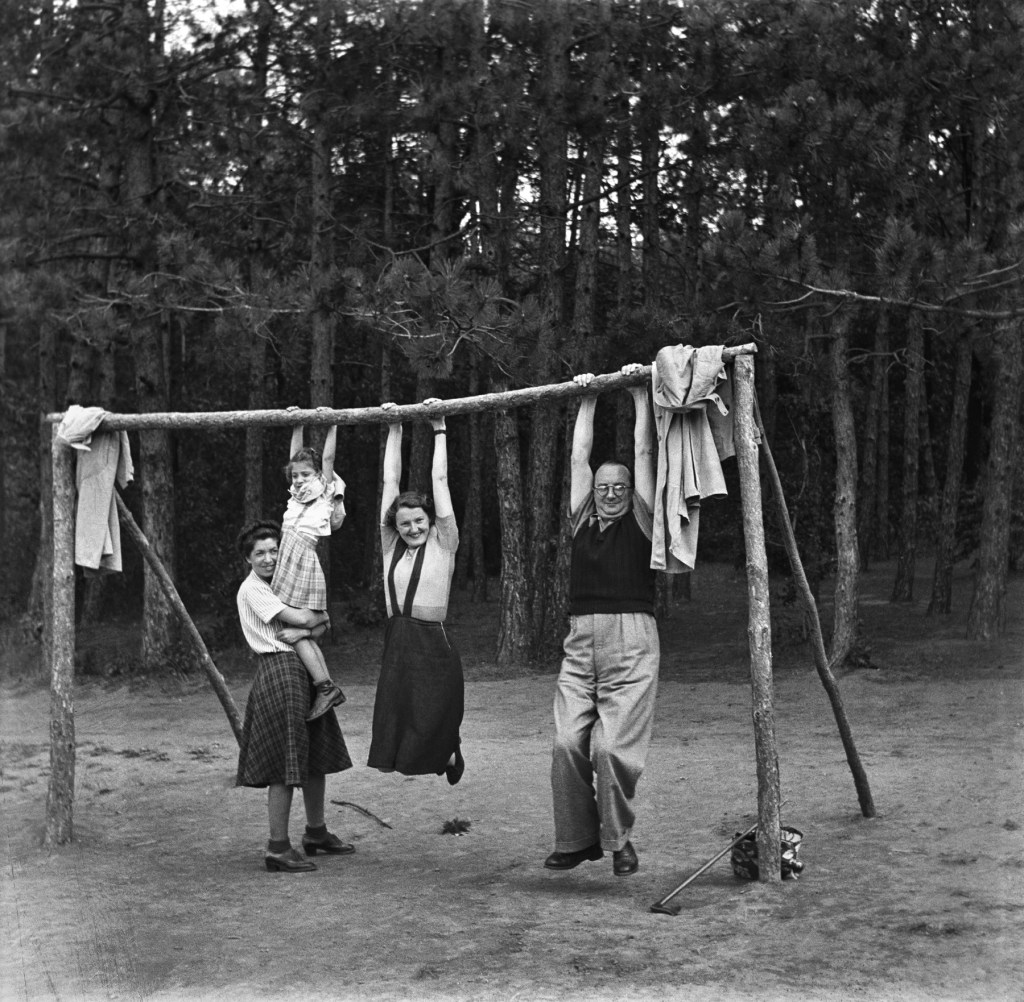

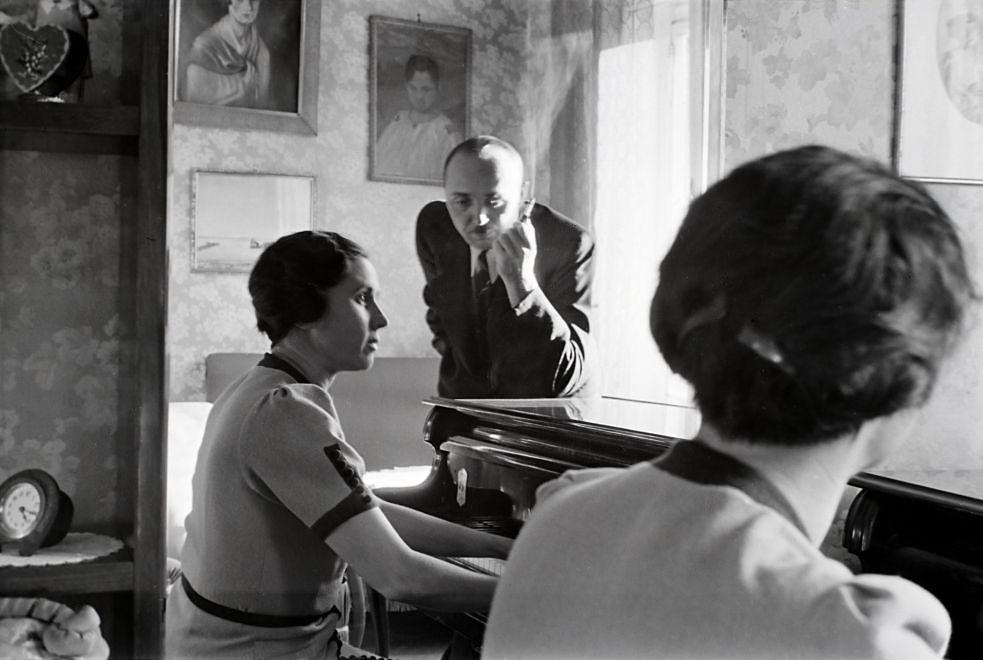
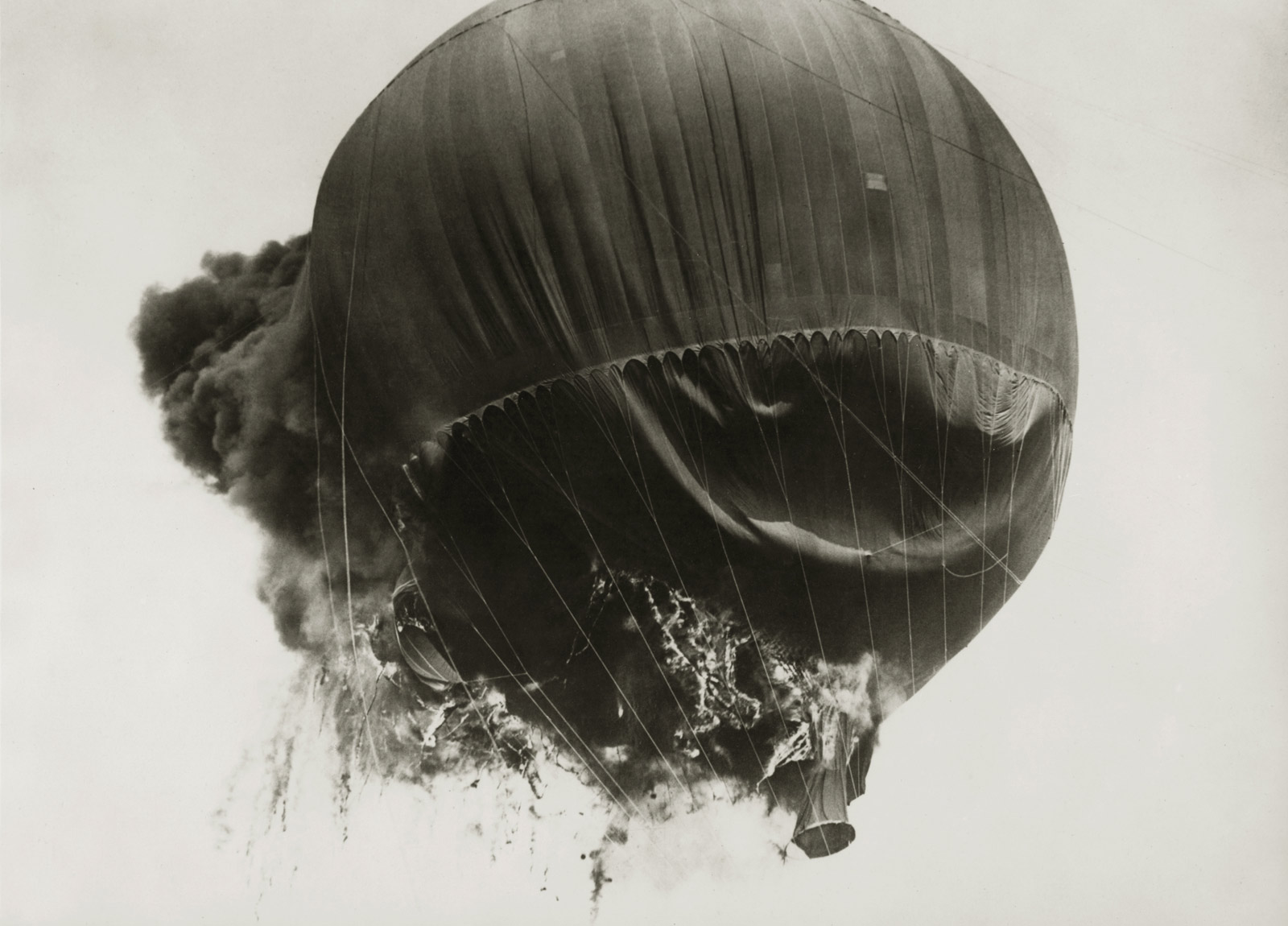
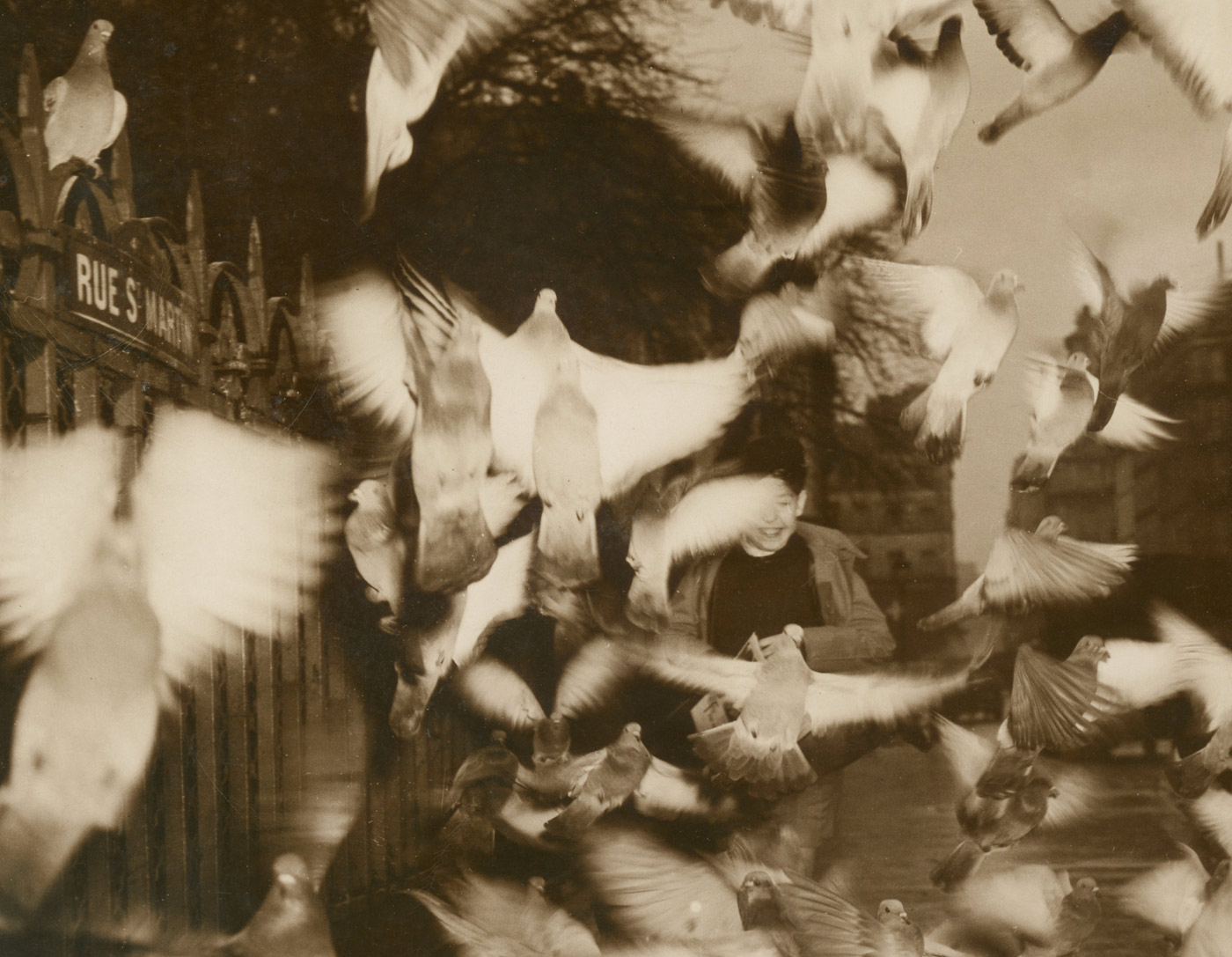
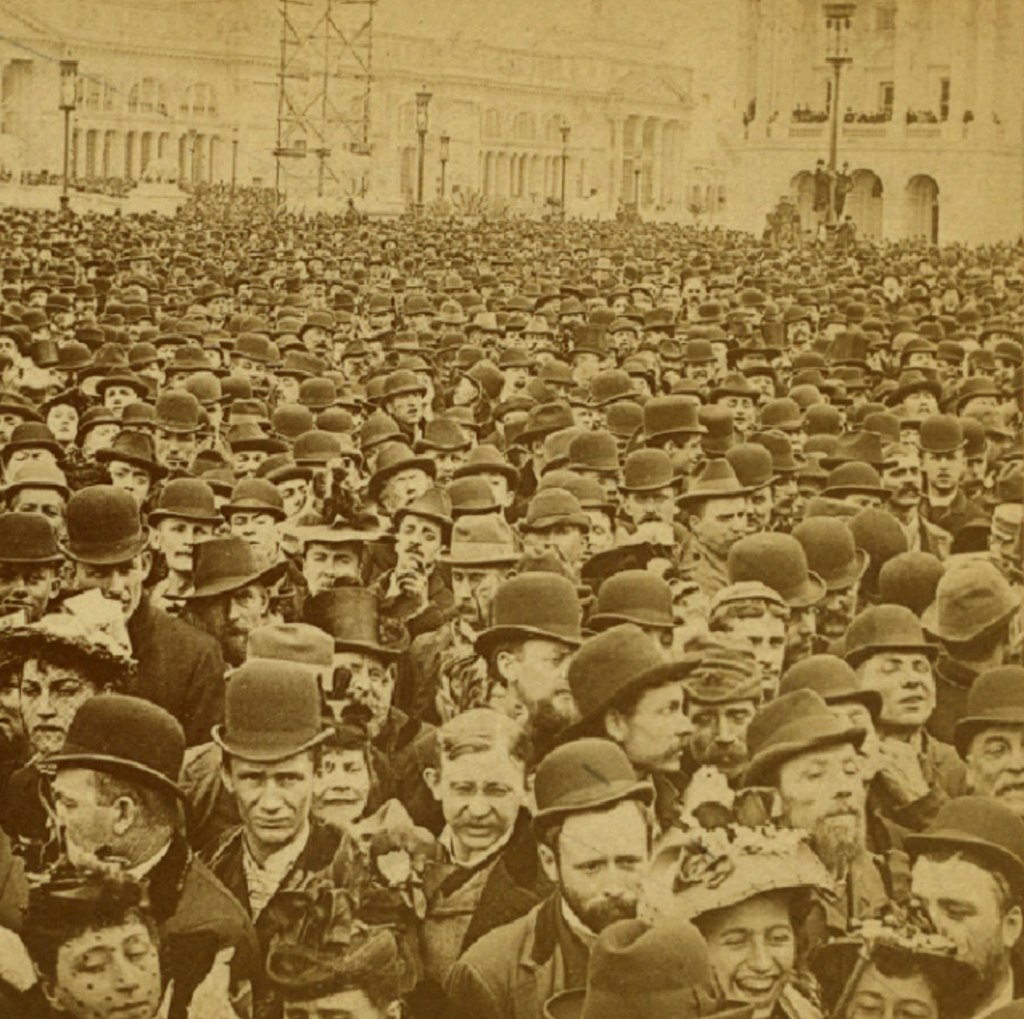
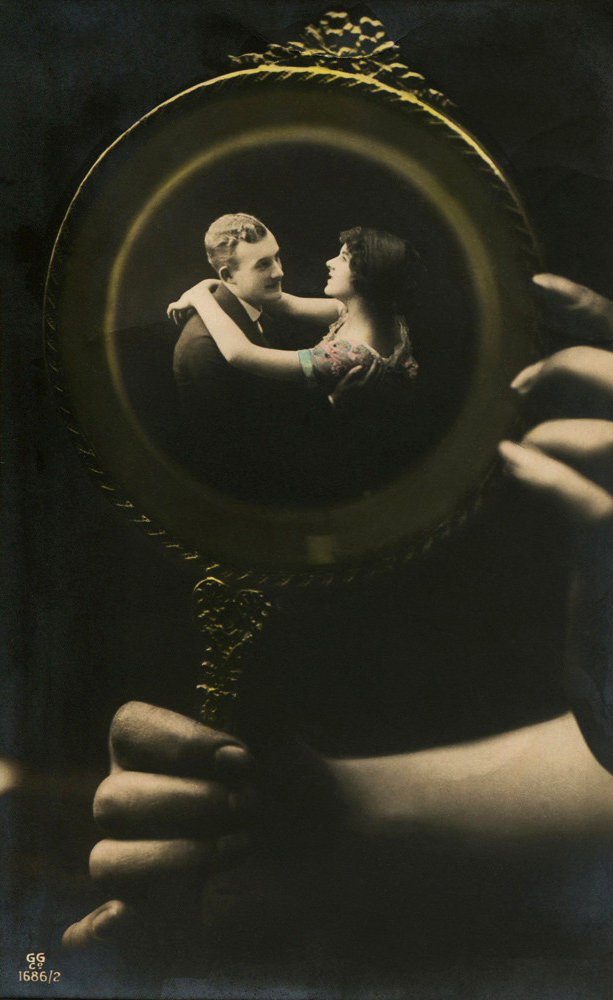
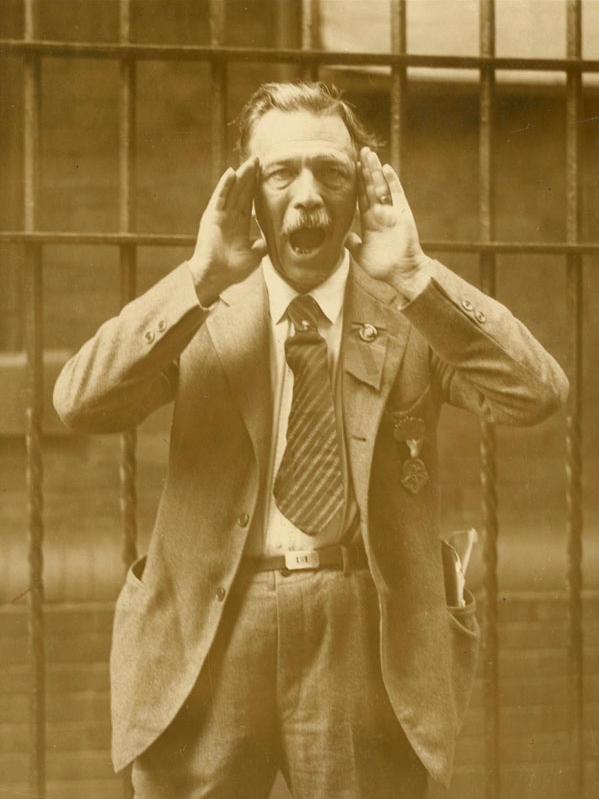
Unknown photographer
Untitled
1948
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
In seeking to understand the past, present and future of a people and a country, the importance of analysing the pictures stored within a historical photographic archive cannot be underestimated. The photographs in an archive such as the Hungarian Fortepan digital photo archive are a form of cultural memory, a collective consciousness, in pictures, of the numerous lifelines of the people of that country, its history, it triumphs, its trials and tribulations. Jean-Paul Sartre observes, “Time … is everywhere a self-transcendence and a referring of the before to the after and of the after to the before…” Photographs do this very well, as the future beyond the click of the shutter, becomes past time; that very time is then transcended back into present time, the past into the present embracing the future, when someone looks at an “old” photograph. The old is young again.
The Fortepan digital photo archive usually de/pics anonymous people taken by unknown photographers in sometimes known, sometimes unknown settings. It represents “Hungary’s 20th century history, the images focusing on the lives of ordinary people and their experiences, as conveyed by private photographers.” These vernacular photographs act as a tabula rasa,1 a touchstone for hidden stories and histories. The prima materia, the base material of chaos, forms a clean slate (tabula rasa) on which is written the order of the image. Out of light emerges darkness, the inversion that is the negative, which is then made positive again during printing. The etching of light onto the negative builds up a story first seen in the mind’s eye – that knowledge then decoded (or not) through experience and perception: how do you interpret a photograph? What language does it speak? Do you understand what it is saying? The before to the after and the after to the before…
And then we see. Images of happy human beings hanging from a crossbar; a young boy with amputation looking quizzically at the camera while a doctor and nurses pose stiffly, sullenly; and the horrors of war and an uprising that failed. The bits and pieces of lives and people and places and things and events and wars and death and youth and happiness and fun. A palimpsest. The past presently emerging, the present being constantly overwritten, the future embedded in the past. We are but a speck, an infinitesimal speck in the cosmos, not even a micron of a grain of sand in the fluidity of space/time.
“Even our experience of time and space, argues Jameson, has been transformed under postmodernism. Time has collapsed into a perpetual present, in which everything from the past has been severed from its historical context in order to circulate anew in the present, devoid of its original meanings but contributing to the cluttered texture of our commodified surroundings. The result, he writes, is historical amnesia, a lack of knowledge about the past that, in its pathological form, resembles the schizophrenic’s inability to remember anything and consequent inability to sustain a coherent identity.”2
What the photographs of the Fortepan archive let us achieve is to compile an incomplete, an in/coherent but valid identity from a certain perspective (and that is very important). As with any system of classification, it all depends who is looking and from what point of view. They also let us meditate on our brief existence in order to say, we were/are/will be here. And it mattered.
I look forward to hopefully meeting my friends Tamás Németh and Miklós Tamási when I am in Budapest soon.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
1/ Tabula rasa is the theory that individuals are born without built-in mental content and that therefore all knowledge comes from experience or perception.
2/ Jameson, Frederic. Postmodernism, or, The Cultural Logic of Late Capitalism. Duke University Press, Durham, N.C., 1991, p. 419 quoted in Springer, Claudia. Electronic Eros: Bodies and Desire in the Postindustrial Age. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1996, p. 40
Many thankx to the Hungarian National Gallery, Tamás Németh, Ákos Szepessy and the Fortepan digital photo archives for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“Time … is everywhere a self-transcendence and a referring of the before to the after and of the after to the before … If time is considered by itself, it immediately dissolves into an absolute multiplicity of instants which considered separately lose all temporal nature and are reduced pure and simply to the total a-temporality of the this.”
Satre, Jean-Paul. Being and Nothingness. (trans. Hazel Barnes). London: Methuen, 1966, p. 215.
“Fortepan is a collective effort at “codebreaking” the assembled scanned negatives, to decipher what is there before us in the image. Fortepan has become a public resource of the Hungarian audio-visual culture.”
“In a word, Fortepan perhaps helps to make the 20th century, with all its turns and twists, a little more understandable, bearable and emotionally fathomable.”
Miklós Tamási, Founder of Fortepan
“The archive is one that is free, high resolution, and operates based on Creative Commons 3. This means that it can be used free of charge even for commercial purposes. Even in such cases, people don’t owe us anything.”
András Török, Cultural Manager of Fortepan
FORTEPAN ADOMANYOZÓK, FELHASZNÁLÓK
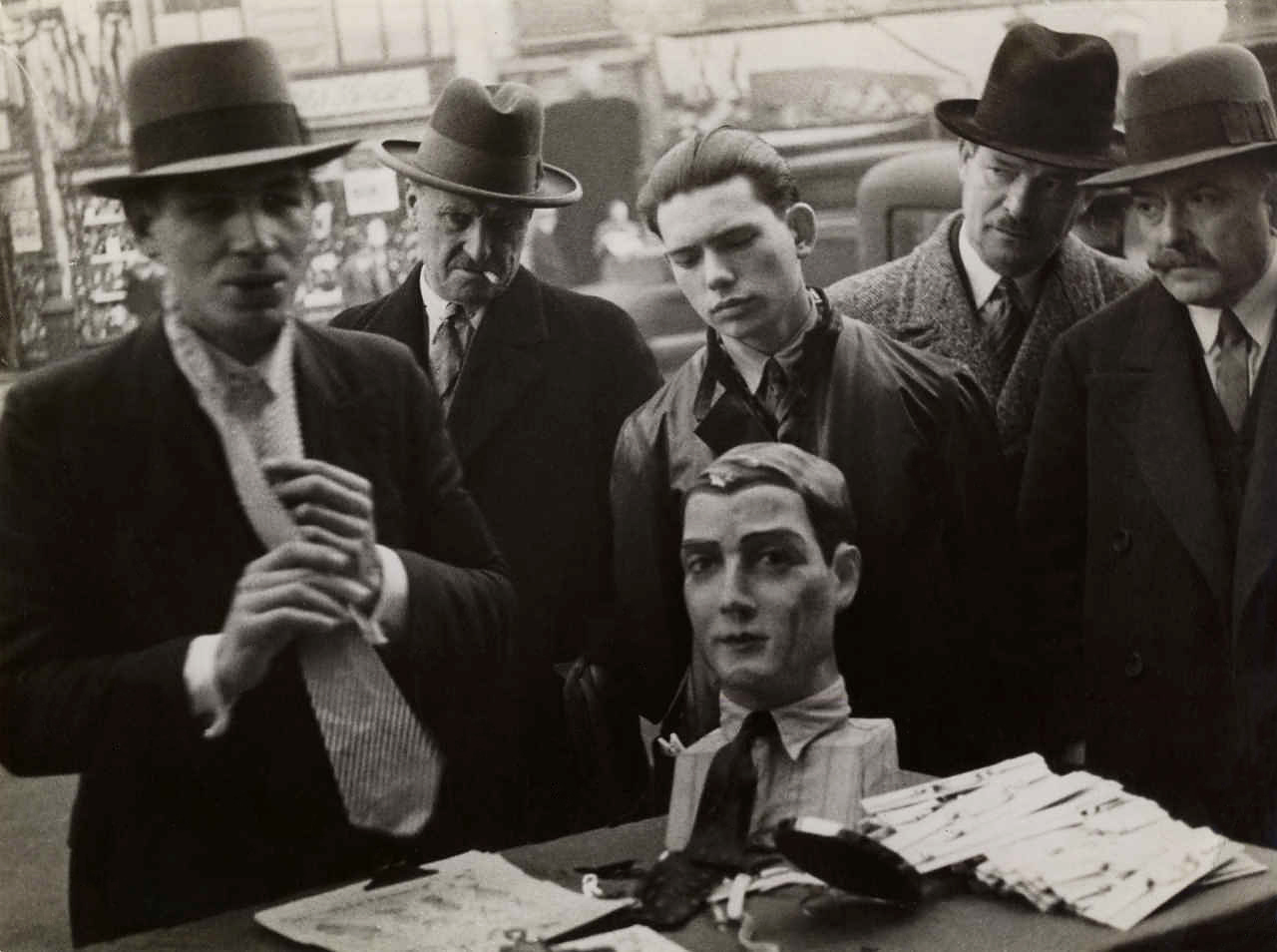
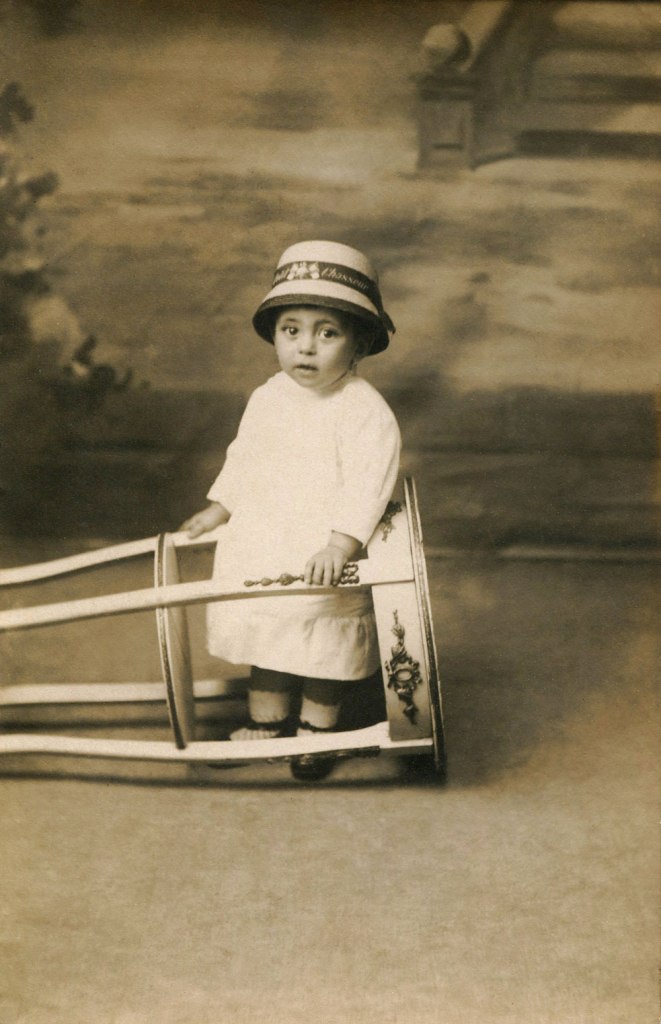
Unknown photographer
Untitled (amputation)
1916
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Unknown photographer
Hungary, Slovakia, Esztergom the Castle Hill and the Basilica from the Maria-Valeria Bridge
1900
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Unknown photographer
Hungary, Balaton, Siofok
1920
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Unknown photographer
Hungary, Rácalmás opposite the Catholic Church (demolished in 1969)
1920
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
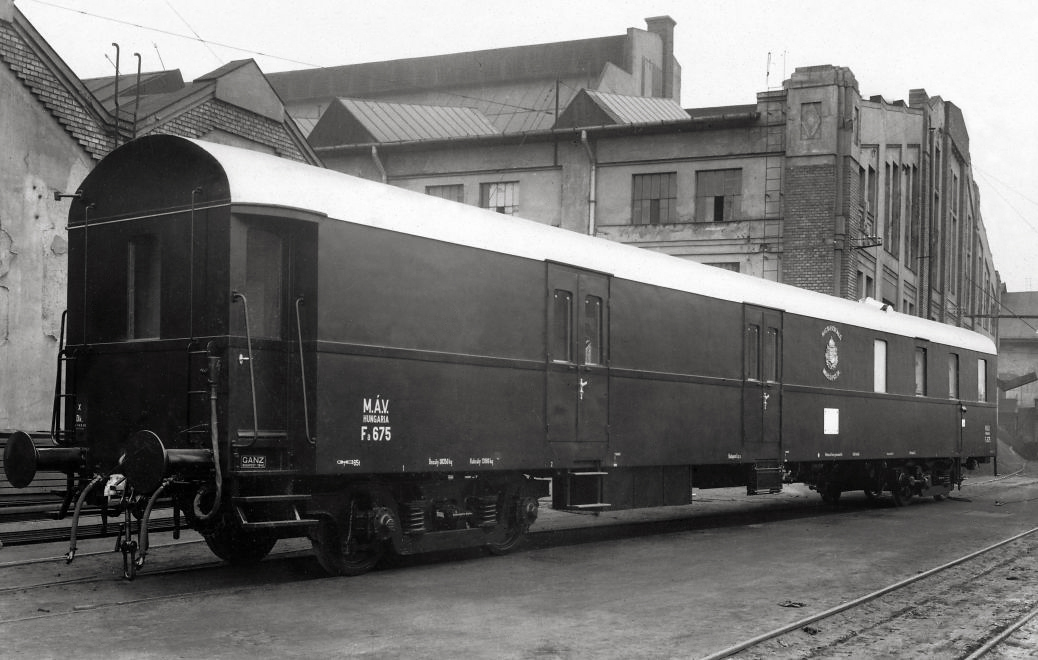
Unknown photographer
Hungary, Budapest III., Óbuda Óbuda Shipyard, Danube branch next to Hajógyári Island, BL floating crane and two DDSG barge
1920
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
From the material of the popular Fortepan digital photo archive, a selection of more than three hundred pieces at the Hungarian National Gallery is presented. The exhibited pictures are closely related to Hungary’s 20th century history. The age in which they were made is manifested in many different ways in these images, but the emphasis is on the view and life events of the average person through the private photographs that provide the backbone of the collection.
Representing Hungary’s 20th century history, the images focus on the lives of ordinary people and their experiences, as conveyed by private photographers.
The founders of the collection, two high school classmates Miklós Tamási and Ákos Szepessy, began to collect the photographs in the digital Fortepan archives back in the 1980s. They launched an online site with 5,000 digitised images in 2010. Today the collection numbers 110,000 photos.
Each photograph in the exhibition tells a story. In some cases these stories can be reconstructed, but in most others the people in the pictures are no longer known, and neither are the circumstances in which the photo was taken, allowing visitors to use their imagination and invent their own stories linked to the images.
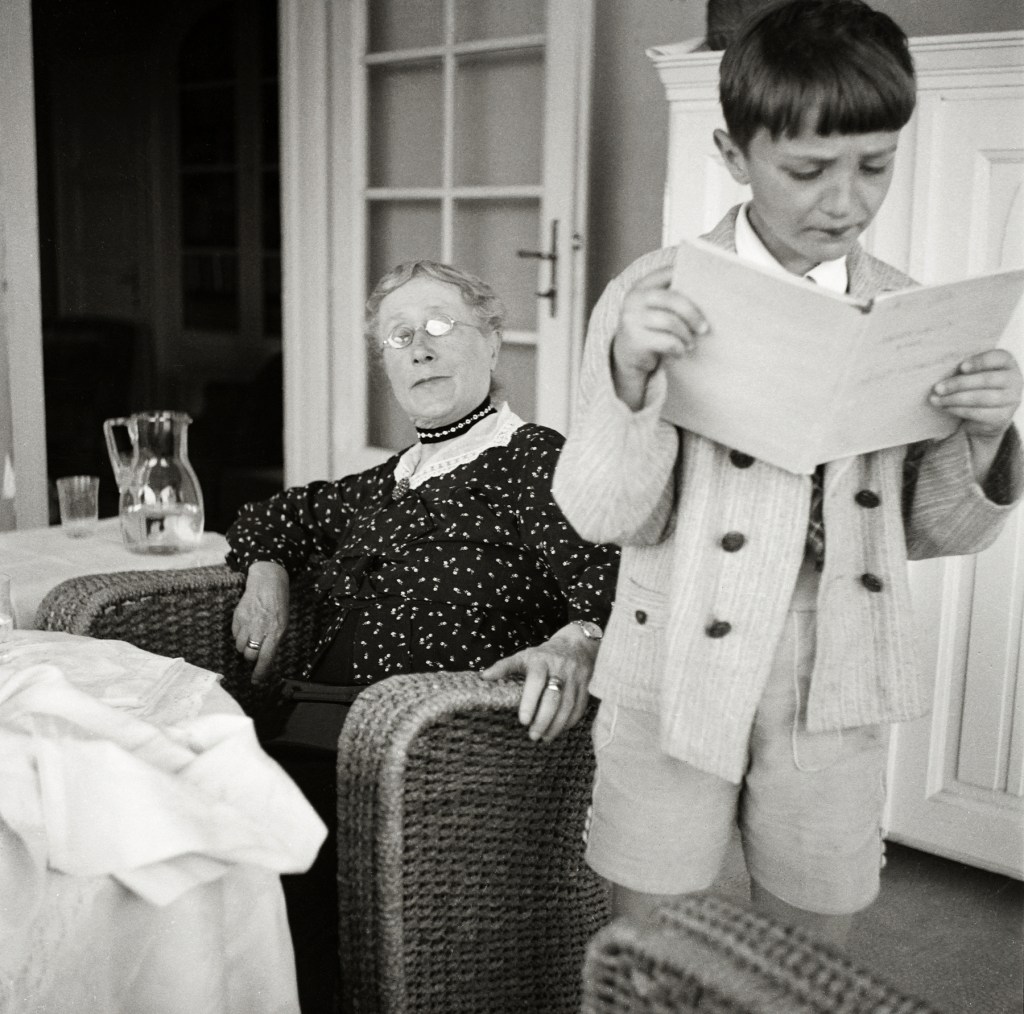

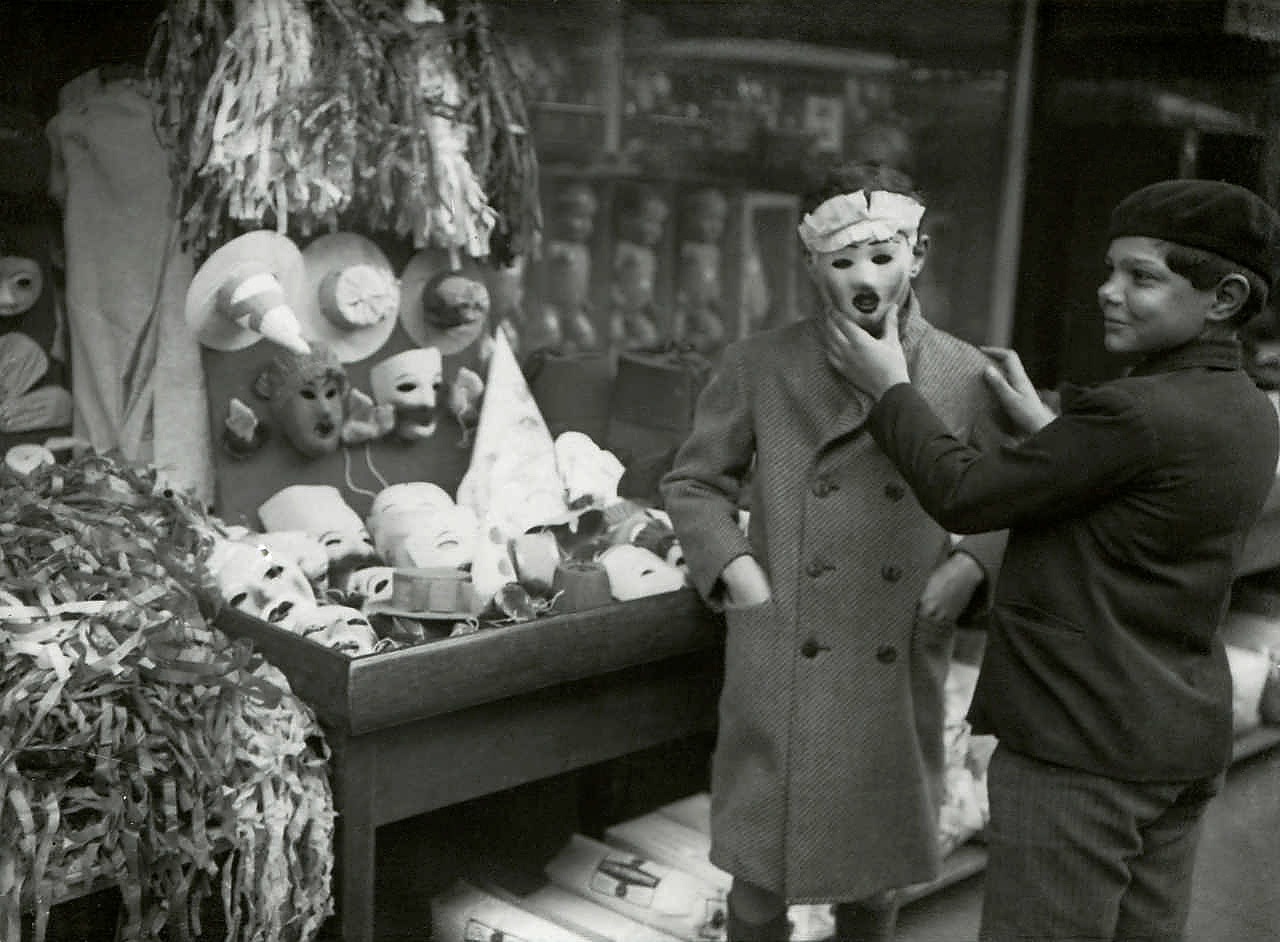
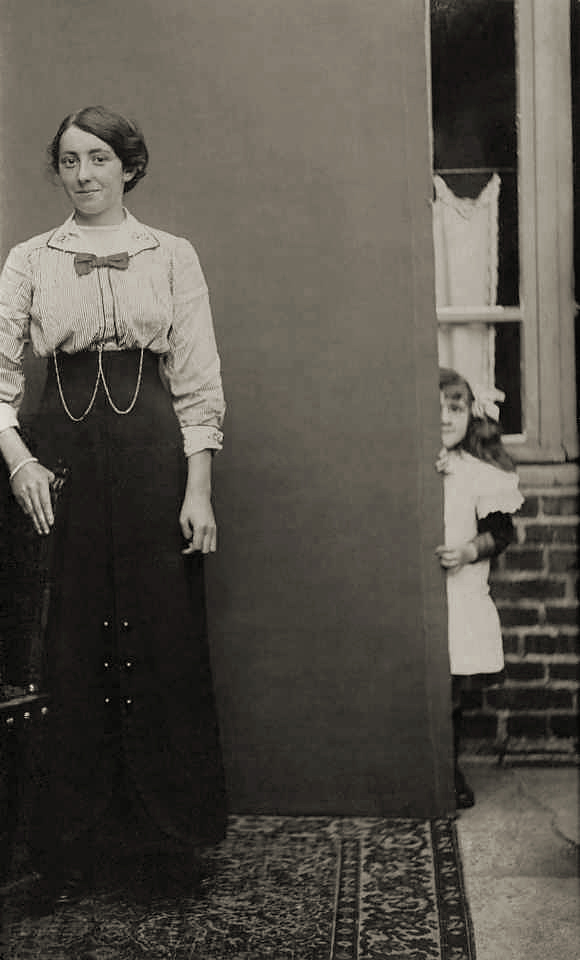
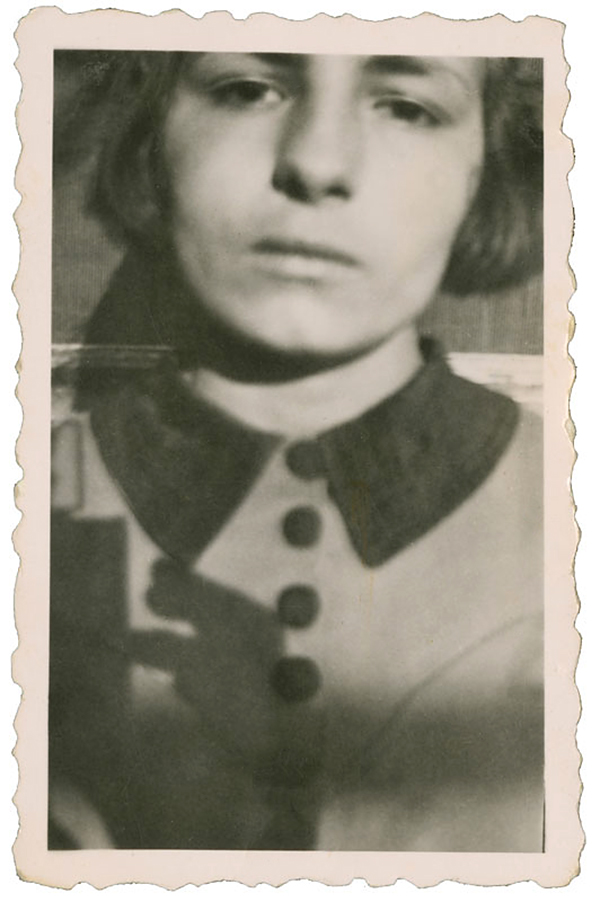
Unknown photographer
Untitled (woman and boy)
1935
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Unknown photographer
Romania, Transylvania, Strait of Békés
1935
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Unknown photographer
Slovakia, Three Revuca highway between Veľký Šturec pass and village, opposite Čierny Kameň
1935
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Unknown photographer
Hungary, Szentes St. Imre street, opposite number 5
1936
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Unknown photographer
Hungary, Budapest VIII. Tavaszmező utca 1, Gartner Károly, writer of sipotei Golgotha
1942
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Gartner Károly (author) Gyula Komjáti (graphics). A Sipotei Golgotha: Romániai Rabmagyarok Története (A Sipotei Golgotha: The history of the Romanian prisoners of Hungarians). G. Z. Hartrampf I, 1932
The name of Șipotele, even for those interested in history, is mostly unknown. One of the most inhumane prisoners of war prisons in the First World War was established near this Romanian settlement, and most of the prisoners were Hungarian. Șipotele was located near the Romanian-Russian border at the time, eight kilometres from the Prut River and 40 kilometers south of lași.

Gartner Károly (Hungarian born Transylvania, 1908-1972) (author)
Gyula Komjáti (Hungarian, 1894-1958) (graphics)
G. Z. Hartrampf I (publisher)
A Sipotei Golgotha: Romániai Rabmagyarok Története
Golgotha Sipotei: The history of the Romanian prisoners of Hungarians
1932
Book cover
Gartner Károly (1908-1972) was born in Transylvania and married Irén Weigand, an officer of the Waterworks in Székesfehérvár, in 1936. Károly Gartner was mentioned in his thirties and forties as a result of his reminiscences of Golgotha, which depicts the death of fourteen thousand Hungarian prisoners of war from the experiences of the First World War. Together with his wife he also wrote a Hungarian song titled Cherry Blossom, was former director of the Phoenix Chocolate Shop, was the national director of the Bethlen István National Unity Party, and from 1938 he was the head of the Municipal Food Plant in Budapest.
Gyula Komjáti (1894-1958) was a Hungarian graphic artist, painter and teacher. He studied at Olgyai Viktors at the College of Fine Arts in Budapest. He was captured in World War I; it has become known through the graphics and etchings of the Sipotei prison camp. In 1926 he won the Ernst Prize and the Zichy Prize. Between 1927 and 1929 he spent a longer time in London with a state scholarship. He also captured World War II in drawings. From 1953 he was a teacher at the Budapest School of Fine Arts and Applied Arts.
Gyula Komjáti (Hungarian, 1894-1958)
Csendélet Sipotén
1917
Drawing for the book Golgotha Sipotei
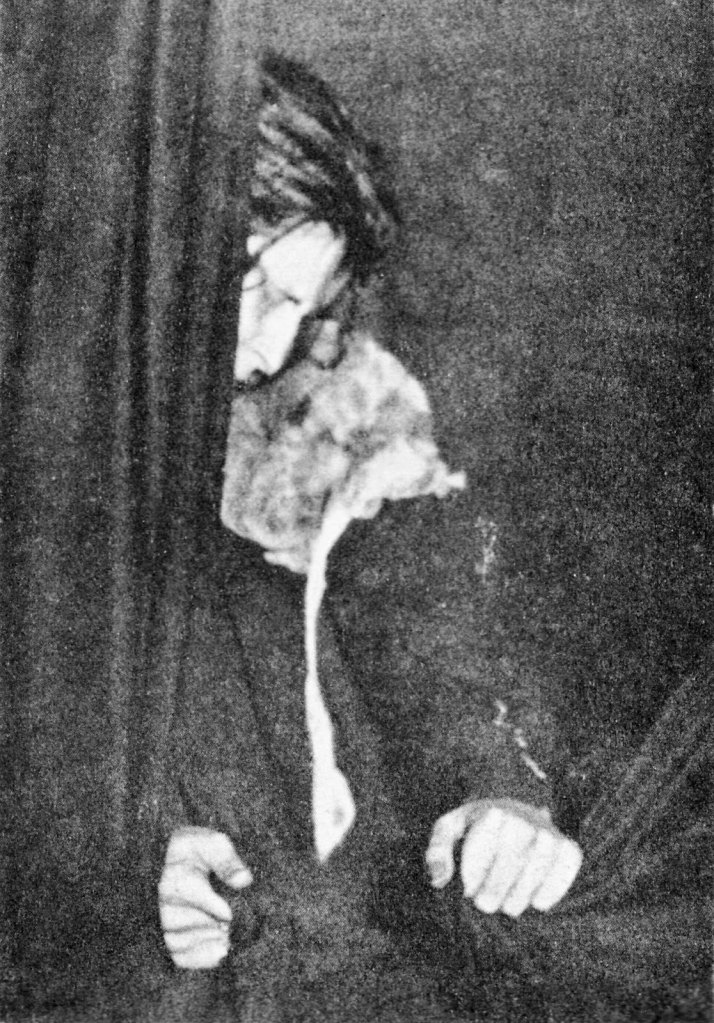
Unknown photographer
Untitled
1942
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Unknown photographer
Hungary, Budapest XIV., City Park, Budapest International Fair showing captured Soviet I-15 Csajka fighter wreck
1942
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Polikarpov I-15
The Polikarpov I-15 (Russian: И-15) was a Soviet biplane fighter aircraft of the 1930s. Nicknamed Chaika (Russian: Чайка, “Seagull”) because of its gulled upper wings, it was operated in large numbers by the Soviet Air Force, and together with the Polikarpov I-16 monoplane, was one of the standard fighters of the Spanish Republicans during the Spanish Civil War, where it was called Chato (snub-nose).
More than 1,000 I-15bis fighters were still in Soviet use during the German invasion when the biplane was employed in the ground attack role. By late 1942, all I-15s and I-15bis’ were relegated to second line duties.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Kogo
Polikarpov I-15bis ‘Bort 19’ (Aviarestoration)
2005
CC 2.0
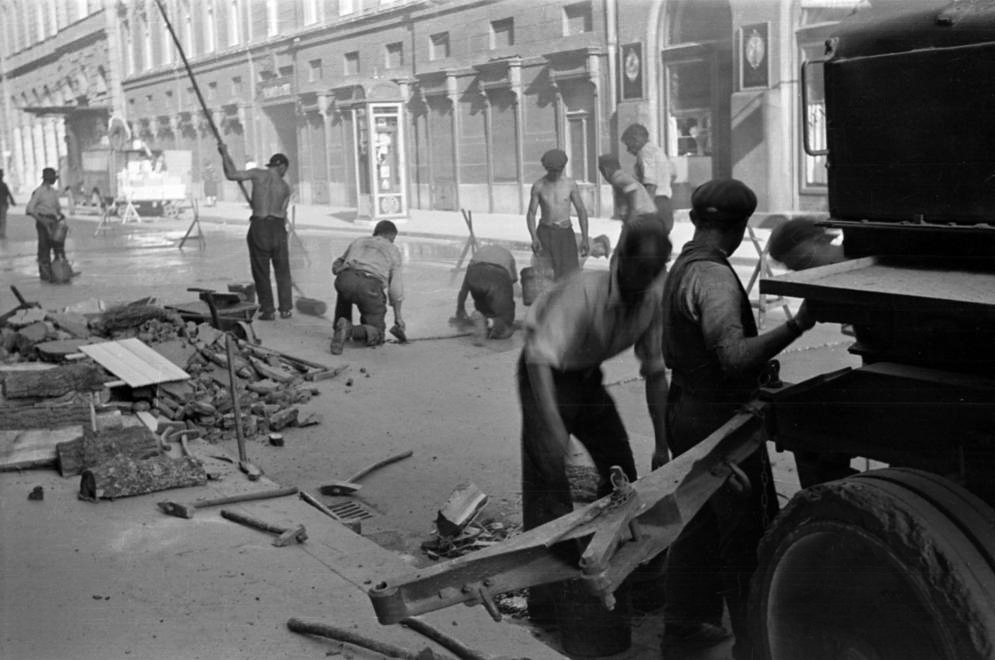
Unknown photographer
Untitled
1943
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
More than 110,000 photographs of Fortepan’s digital collection were collected by two high school classmates, Miklós Tamási and Ákos Szepessy in the 1980s. After the regular, but possibly collecting, amateur photos and negatives appearing on the out of stock markets, they launched their Internet site in 2010 with the publication of 5,000 digitised photos. Soon, many private individuals and public institutions have joined the donating circle of 600 people, whose images are expanding monthly with the archive.
The two most important features of Fortepan’s archive (named after the most popular amateur film by amateur photographers of the former Vác Forte) are free and common. Shared because it is made up of our pictures and is about our world. Shared because it is based on volunteers. Shared because anyone can help identify individual locations and people. Free because it is freely available to anyone without any restrictions, and images can be used without royalty.
It belongs to all the photos in the exhibition, it was a story. In the fortunate case, this story can be recalled, but in most cases it is no longer known what the individuals in the photos are, the history of the individual images – so the visitor’s imagination is left to see the story behind the photo. Today’s background stories provide an insight into the misery of the world champion, who is modelled on the figure on the back of the old twenty-pound banknote, or the rescue of a burnt photo archive. In addition to this, the exhibition is strongly summoned by the ruined Budapest destroyed during World War II; visitors can walk through an imaginary capital street with pictures taken over decades and in different places, placed in the position of Fortepan editors and picking pictures of a legacy; or read into the many readers’ letters written to Fortepan.
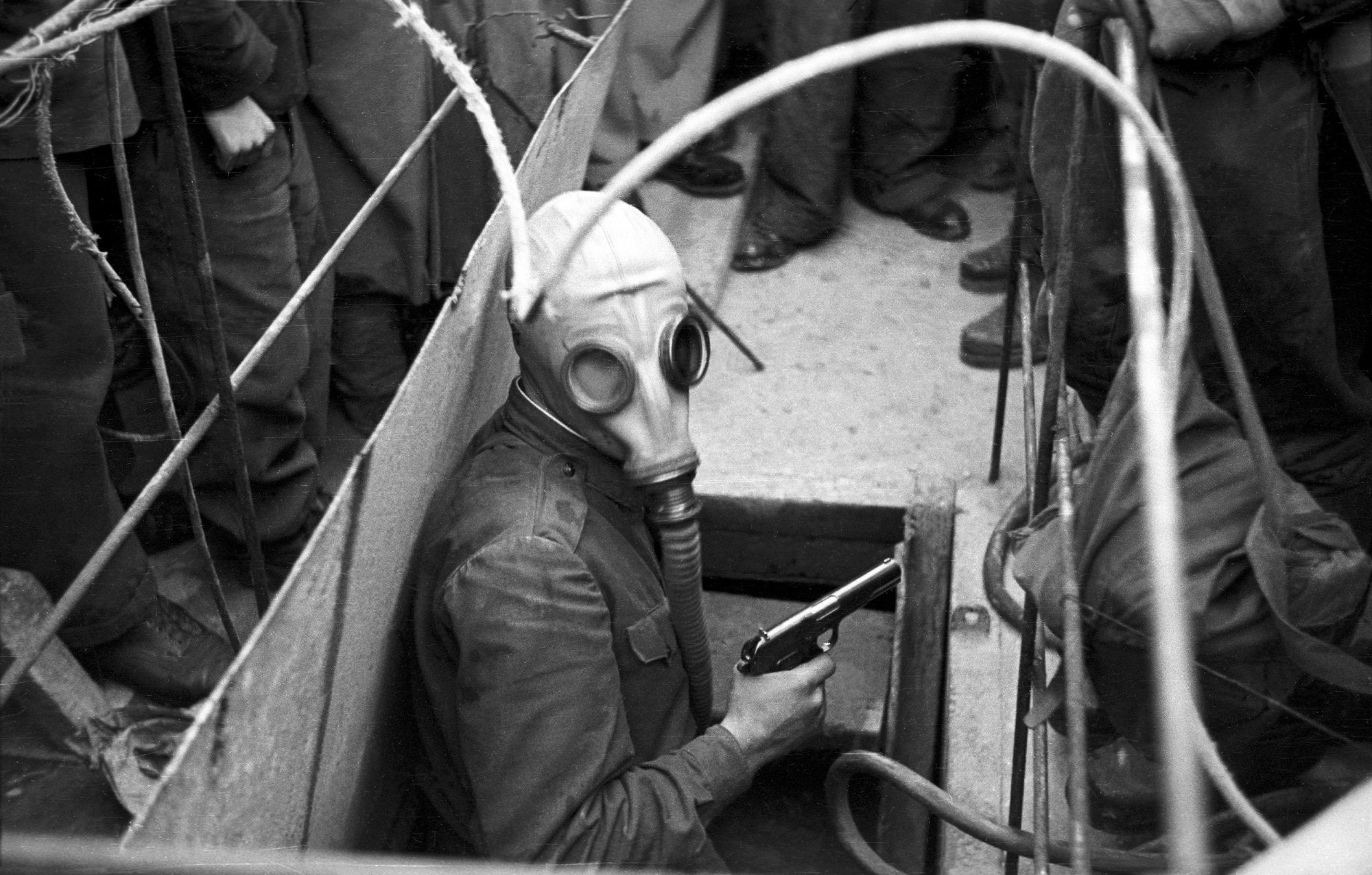
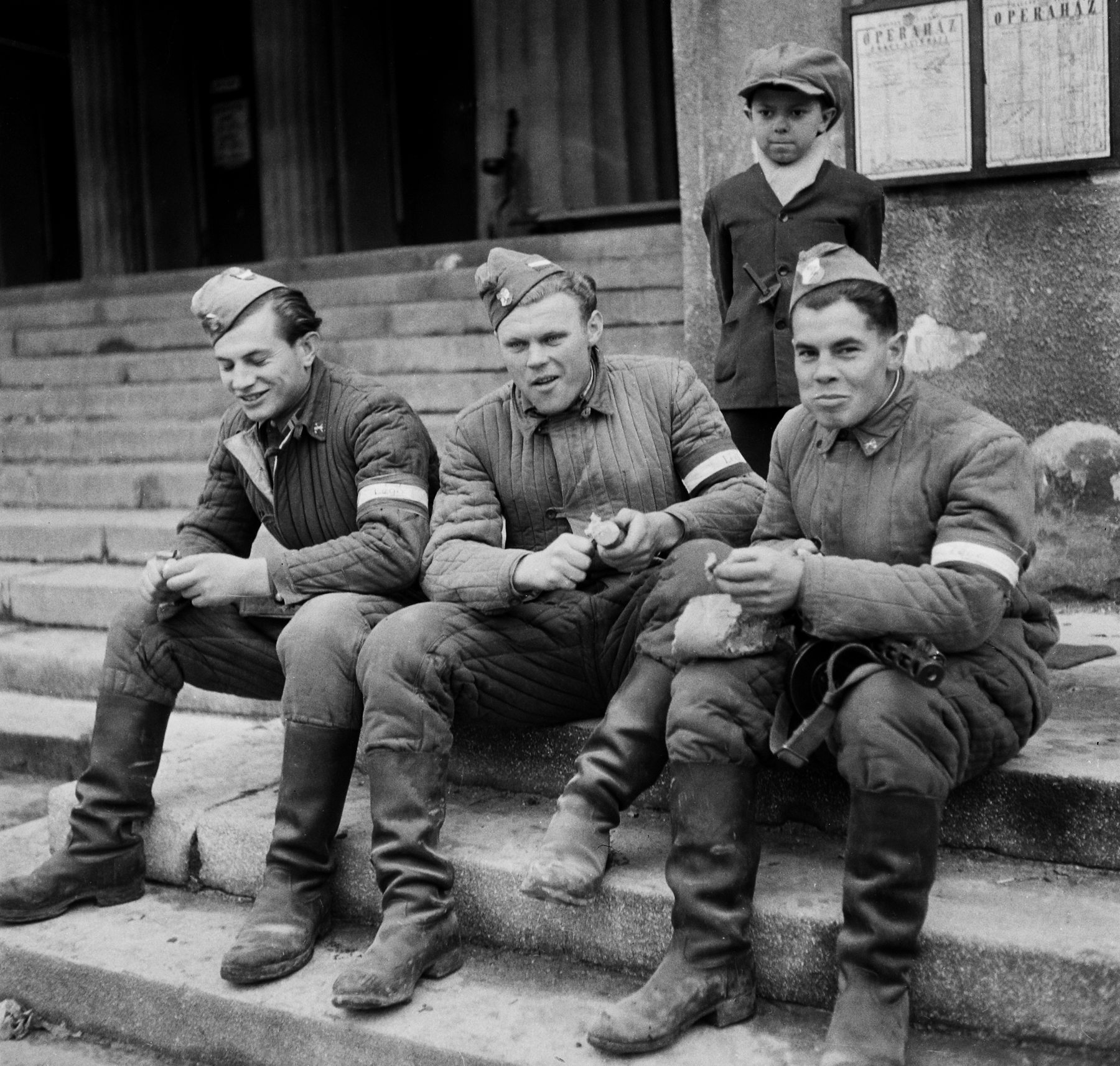
In the exhibition, as well as in a large, common family photo album, along the paths of human life, photographs taken before the 1990s are followed by a total of about 200 pieces. For the first time in this exhibition, the main characters are children, then young people, adults and finally the elderly. In addition, we present more than 150 photos, of which sixteen well-described stories are drawn. Including the 2 World War II fronts – as a war correspondent saw; the idyll of rural life with the eyes of a photographic painter; barely photographed history of the Hungarian Holocaust; life in Transylvania during the dictatorship of the 1980s or everyday life of a First World War Prisoner in Siberia. The pictures of Budapest, destroyed by war, or youth sports with the defence content of the Cold War years form a separate story. But there is more unity in the last years of the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy, pictures of the Stalin statue in 1956, photographs of the rebellious youth of the 1970s and 1980s, or banned photos of commuters from 1964. The sixteen stories, with their associated photos and their complementary items, appear in a separate installation at the exhibition.
In our centuries-old common history, the exhibition updates our memory of the memories that are directly and directly linked to us, just as Zsuzsa Rakovszky puts it in his poem Fortepan: “Every past is my past”.
Text from the Hungarian National Gallery website [Online] Cited 29/06/2019
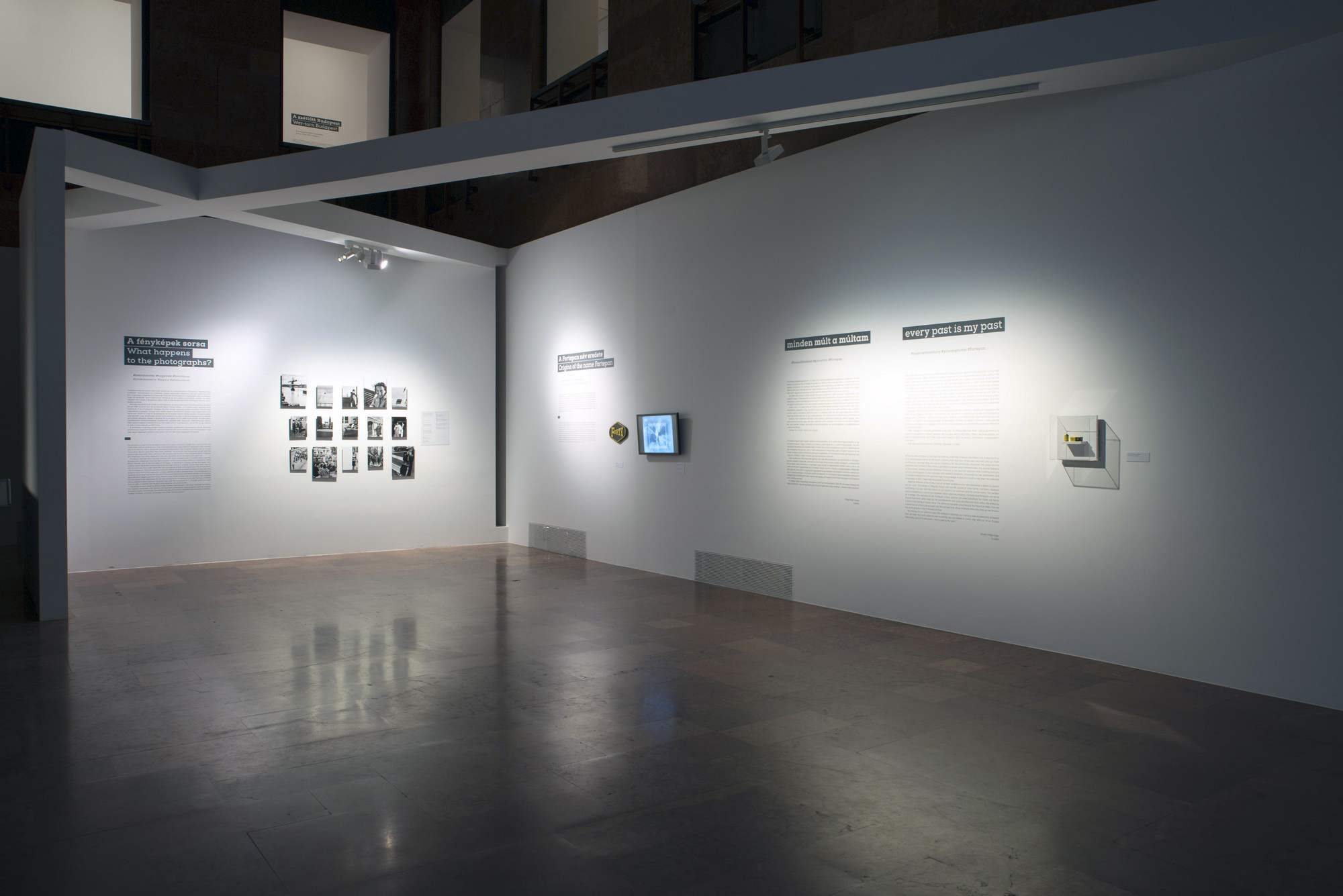
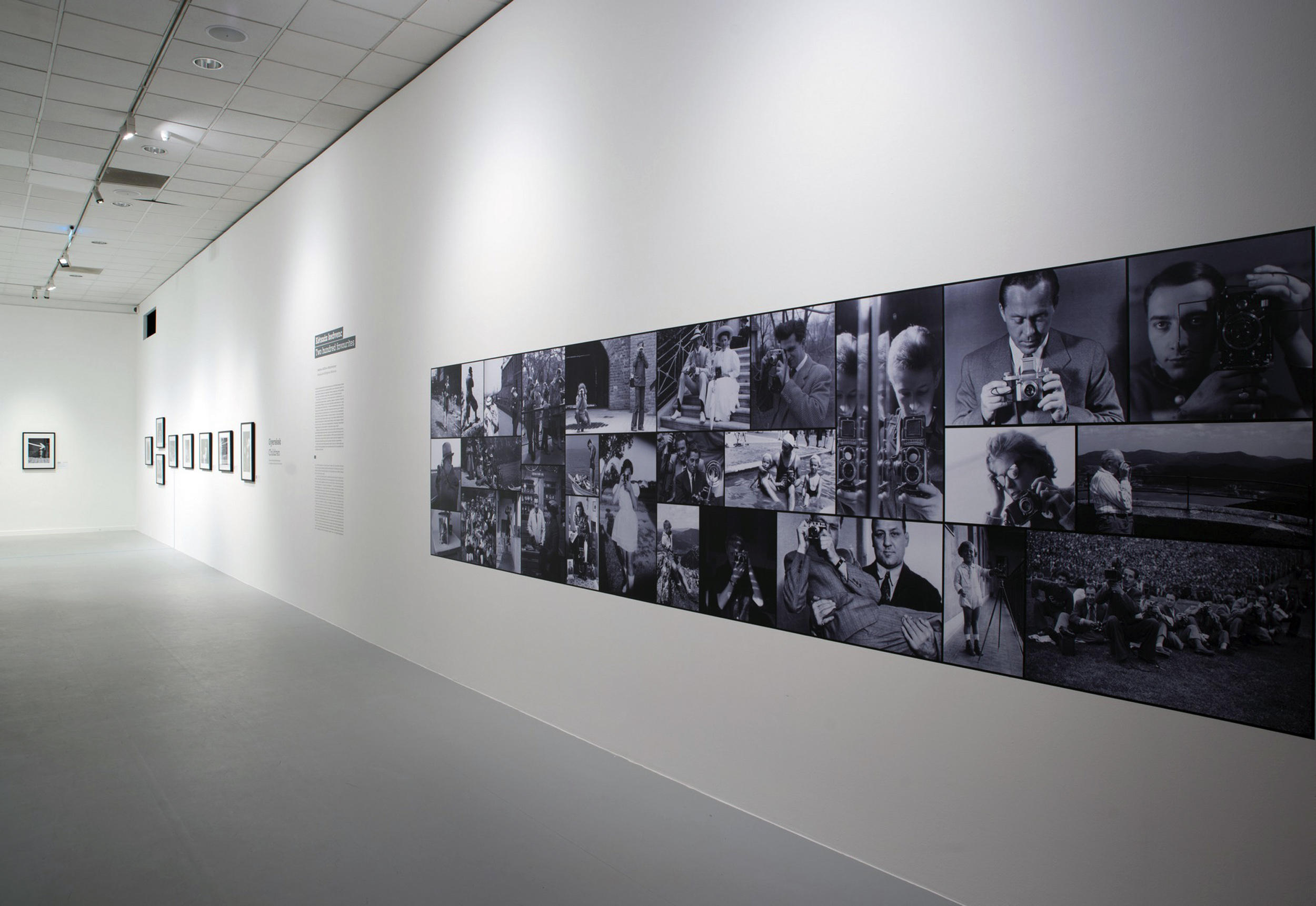
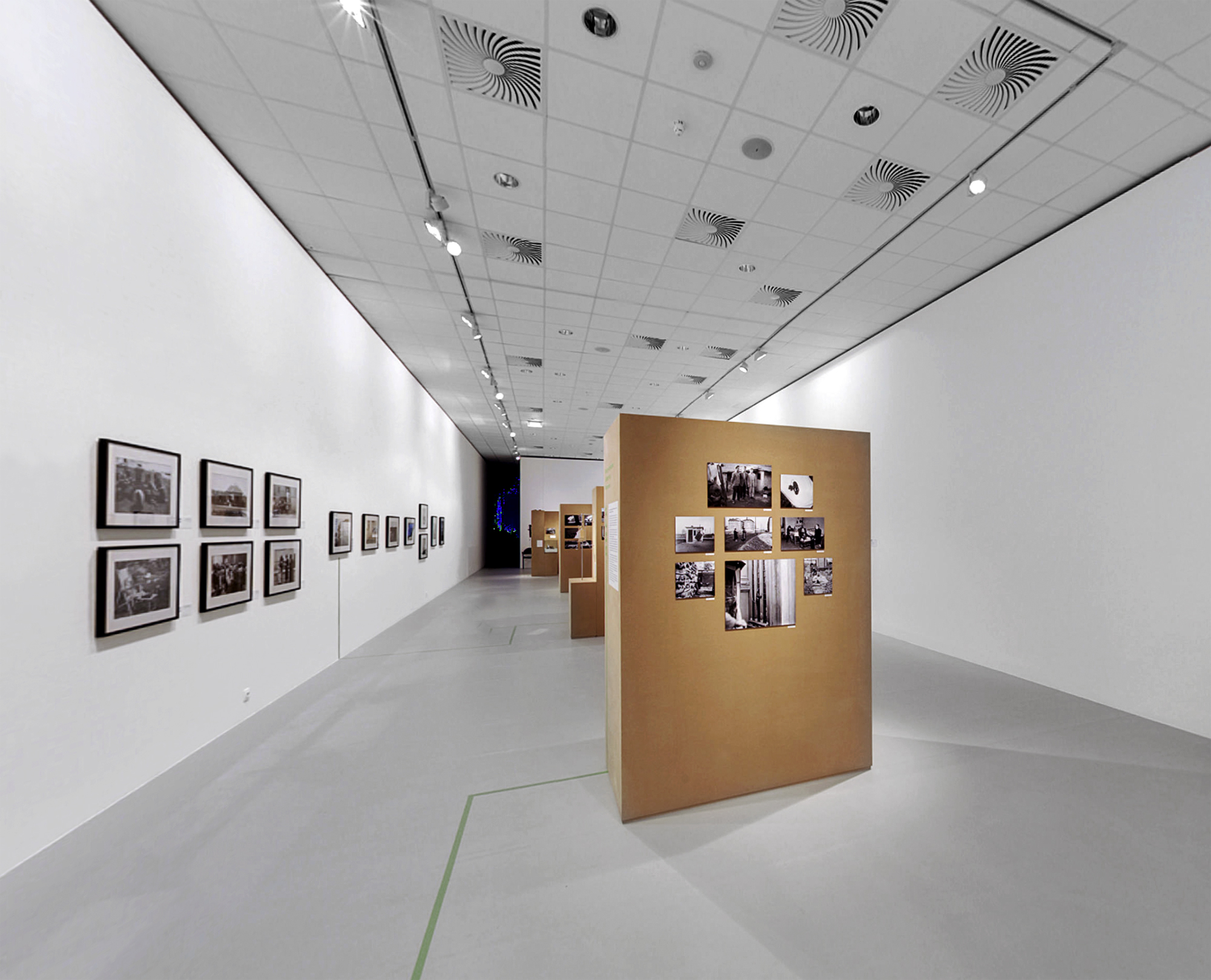
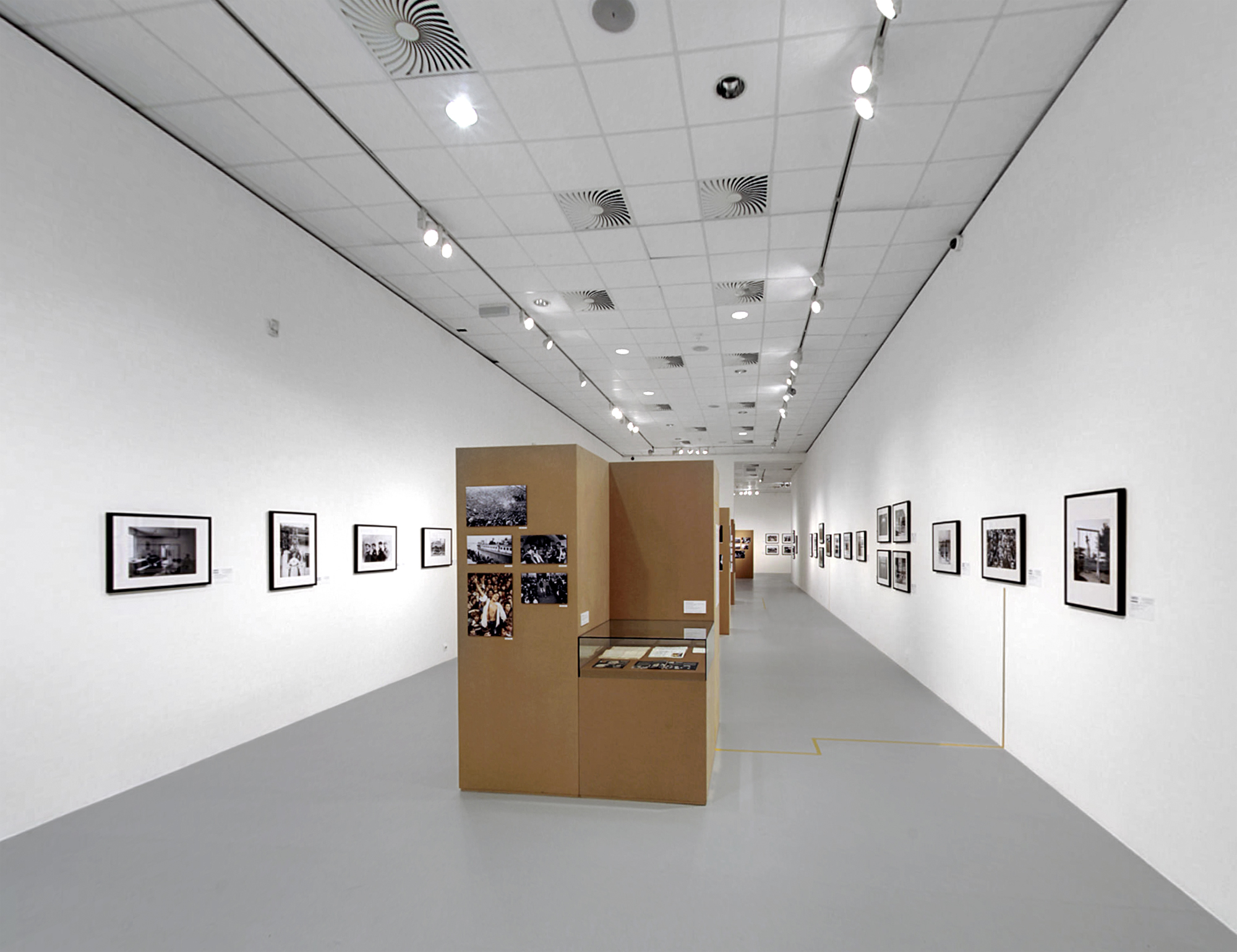
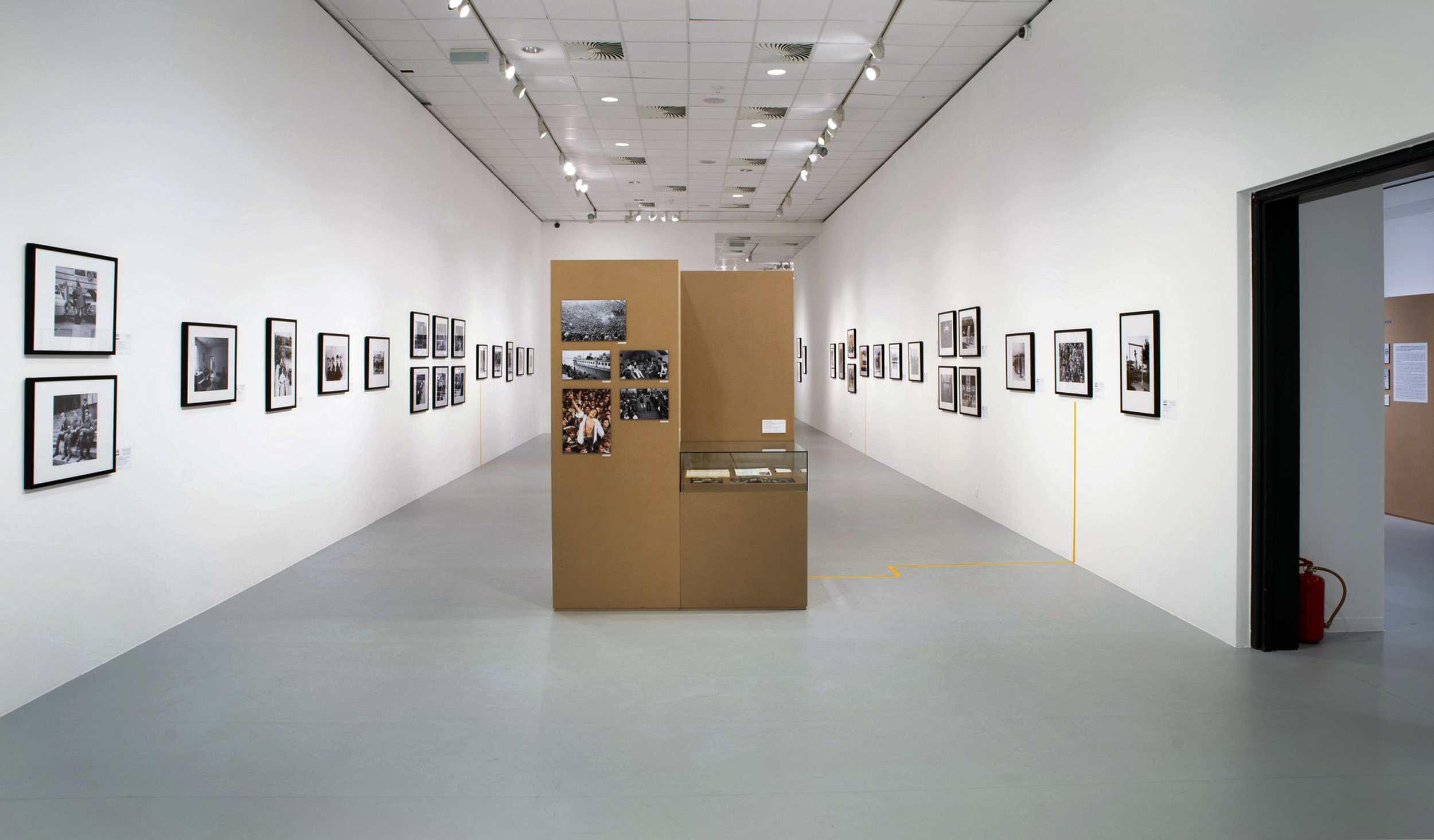
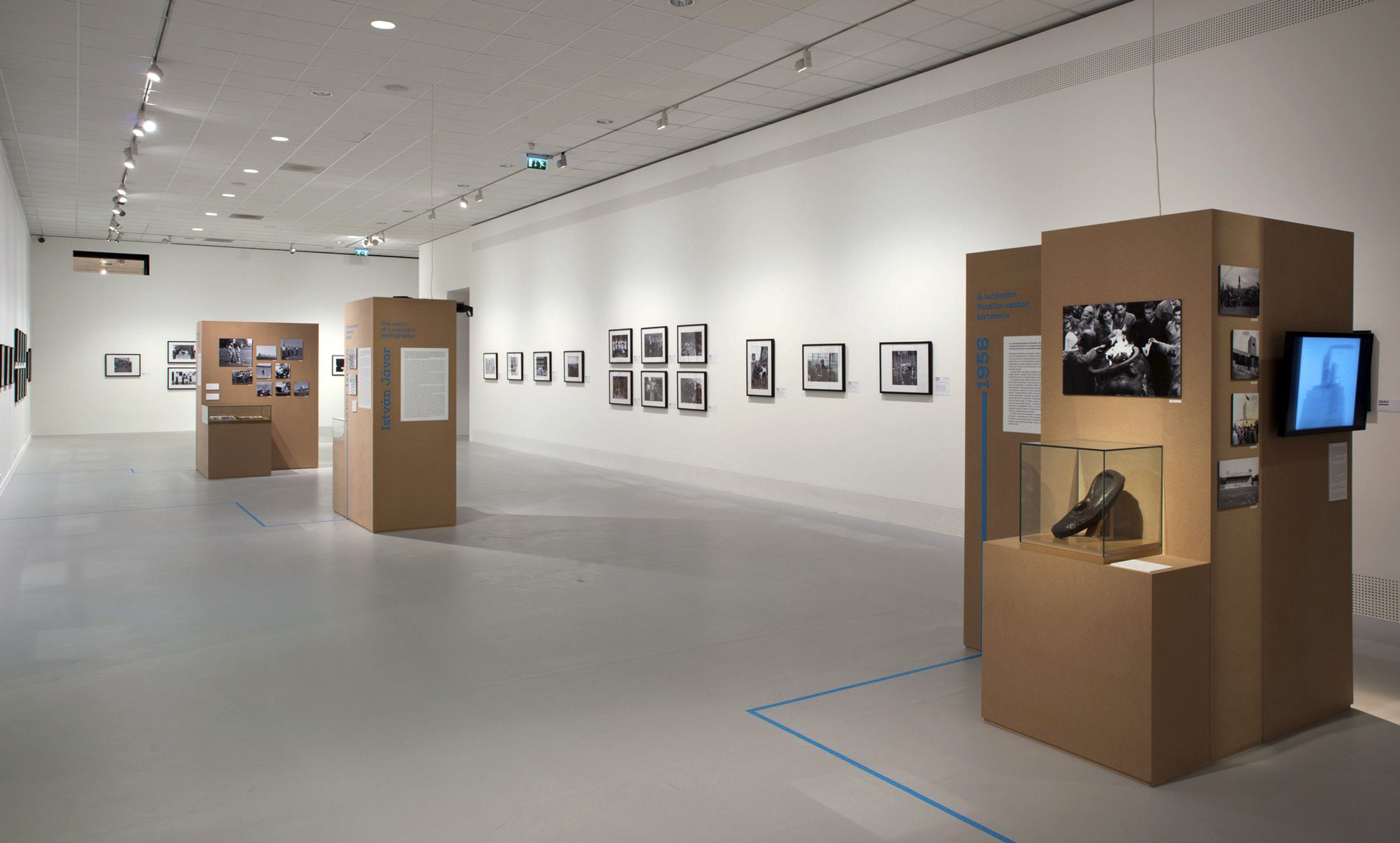
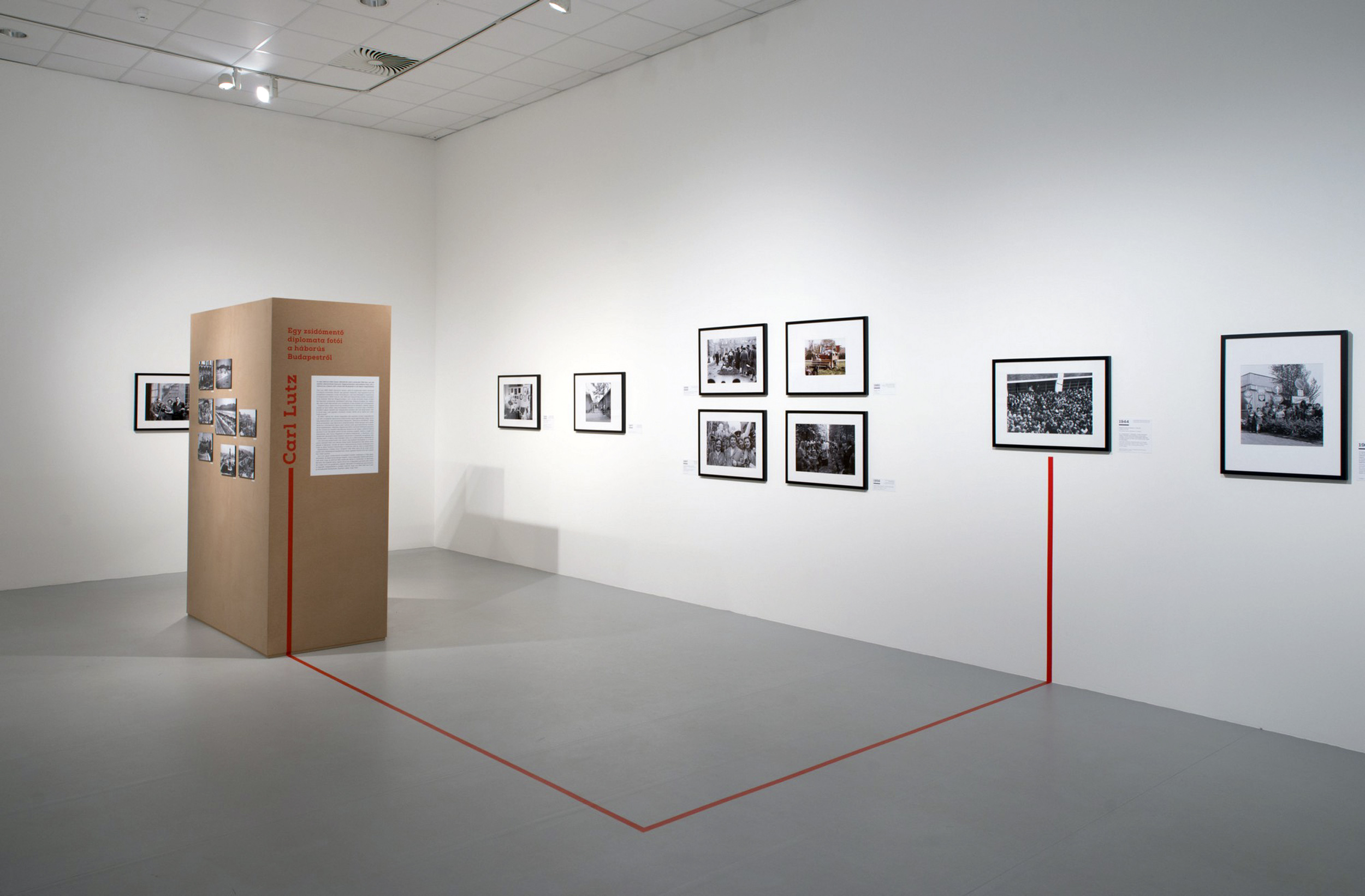
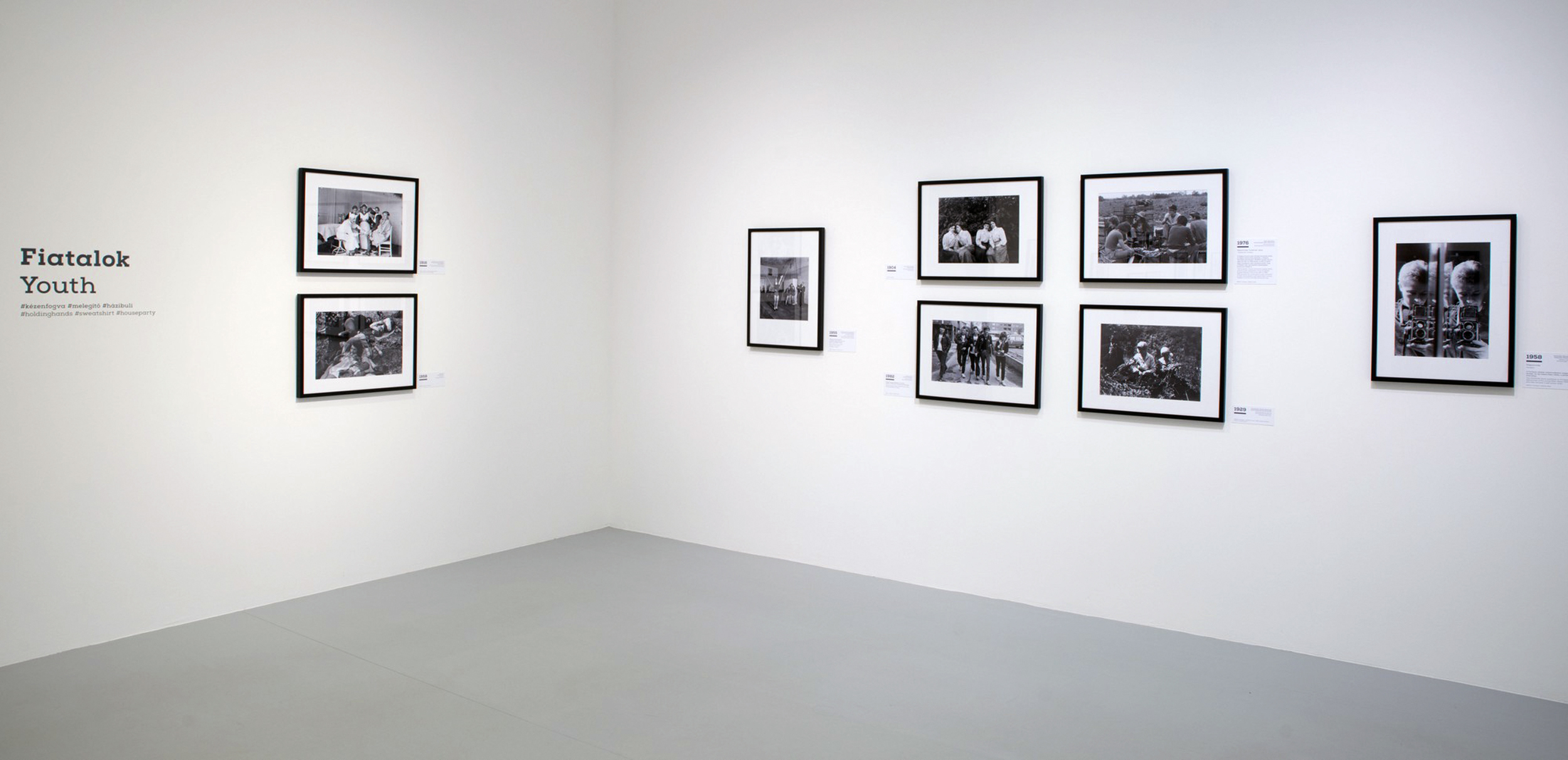
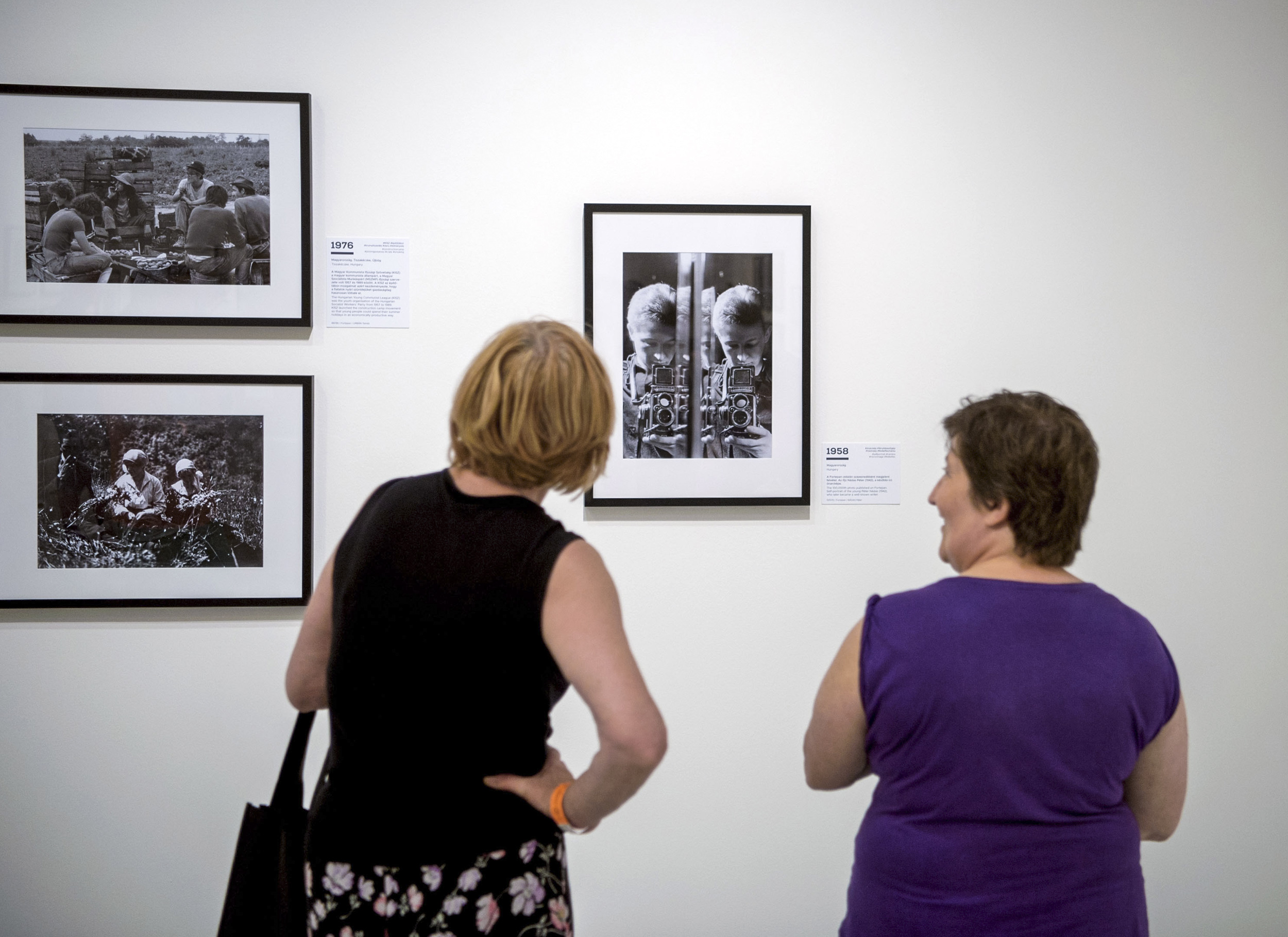
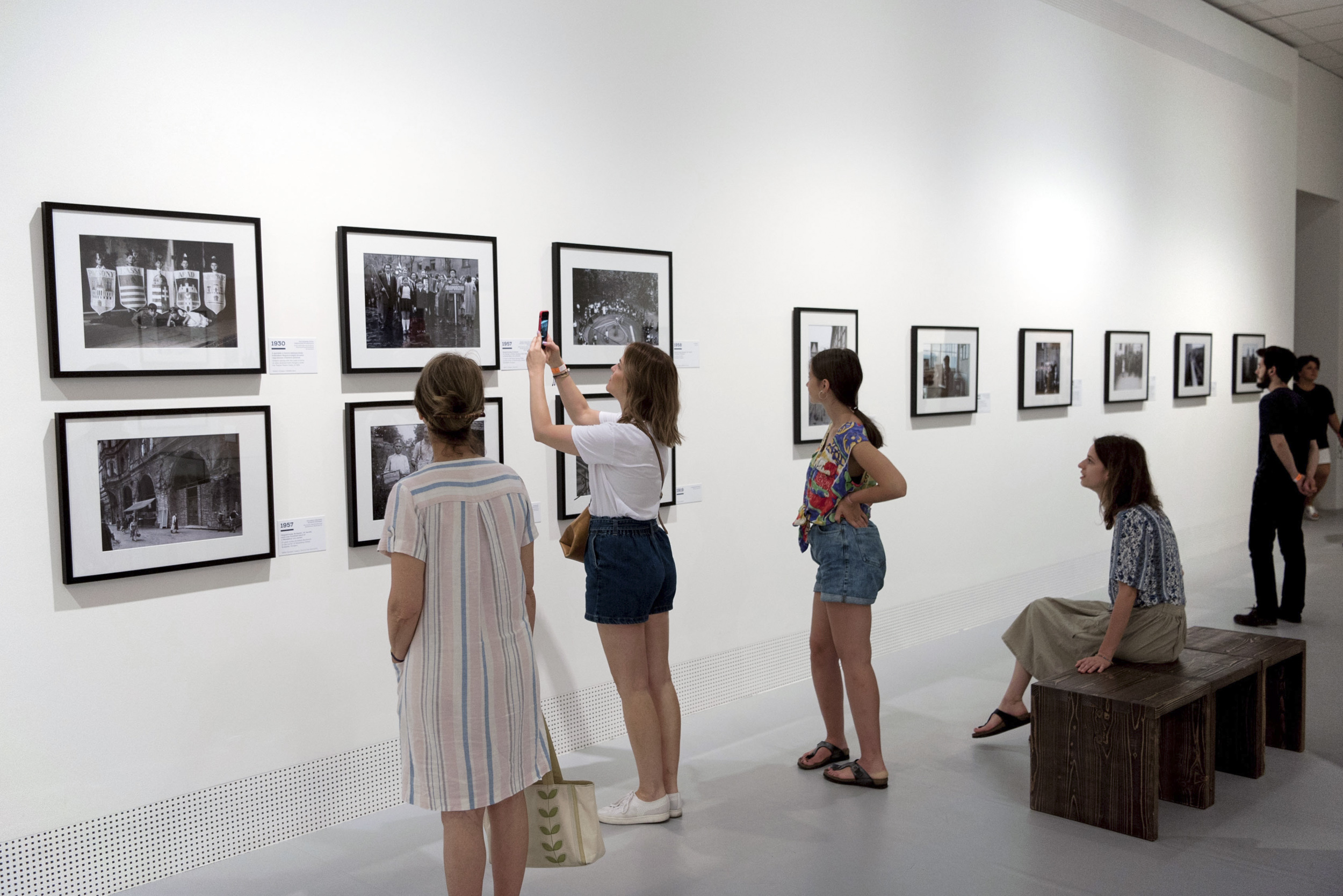
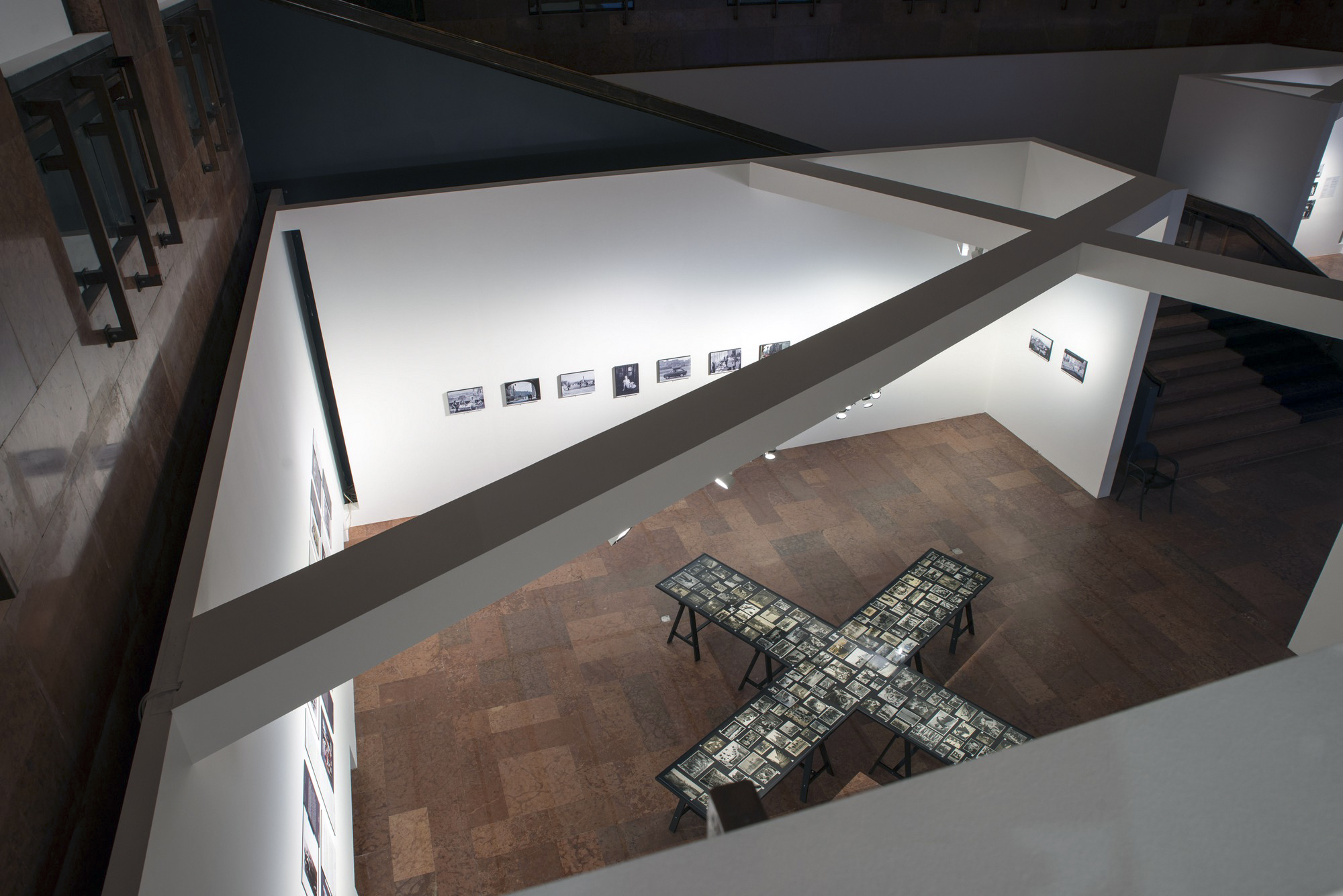
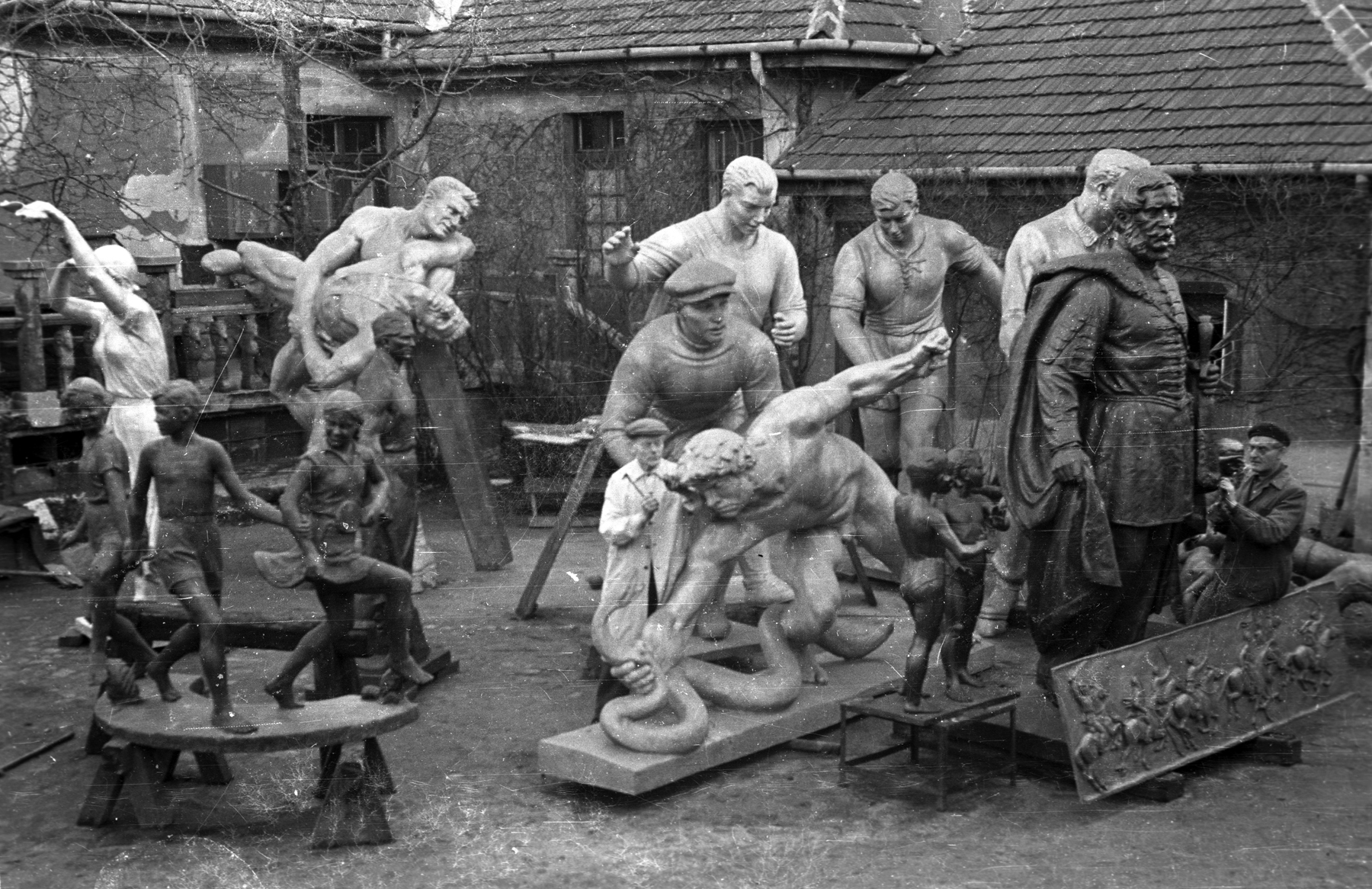
Installation views of the exhibition Every Past Is My Past at the Hungarian National Gallery (MNG), Budapest
About Fortepan
Fortepan is a copyright-free and community-based photo archive with over 100,000 photographs available for anyone to browse and download in high-resolution, free of charge. The images are free to share with the appropriate credit given as FORTEPAN / NAME OF DONOR. Please do provide the full credit at all times as it is a tribute to the selfless contribution of the donor.
This website was launched in 2010 by Ákos Szepessy and Miklós Tamási and it initially contained photographs found randomly in the streets of Budapest. The archive has expanded since then through donations from families, amateur and professional photographers, along with public collections. The images on the website are selected by editors. The descriptions attached to the images are compiled and edited by volunteers, utilising information contributed at the Fortepan Forum. We gladly offer to process your photographs and negatives as well, you can contact us at fortepan@gmail.com.
Fortepan’s collaborators are: László Gál, Luca Jávor, László Lajtai, Pál Négyesi, Tamás Németh, András Pálfi, Zsolt Pálinkás, Gábor Péter, Dávid Sándor, Gyula Simon, Miklós Tamási, András Török, János Varga, János F. Varga. Fortepan’s work is supported by Arcanum, Blinken OSA Archivum, Archive of Modern Conflict and Forum Hungaricum Nonprofit Kft. Administrative management is provided by Summa Artium Nonprofit Kft.
Text from the Fortepan website
Unknown photographer
Hungary, Uzsa (at that time part of the Lesenceistvánd settlement), Liget utca
1950
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Unknown photographer
Hungary on 8126 from Söréd and Csákberény towards Csákberény. To the right is the Bodajk-Gánt railway
1950s
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Unknown photographer
Hungary, Budapest VII. Elizabeth (Lenin) road from New York Palace to Blaha Lujza Square
1956
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Unknown photographer
Hungary, Budapest V. South of Kossuth Lajos Square, underground construction area
1956
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Unknown photographer
Hungary, Budapest VIII. II. Pope John Paul (Republic) Square, main entrance of the Erkel Theater
1956
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
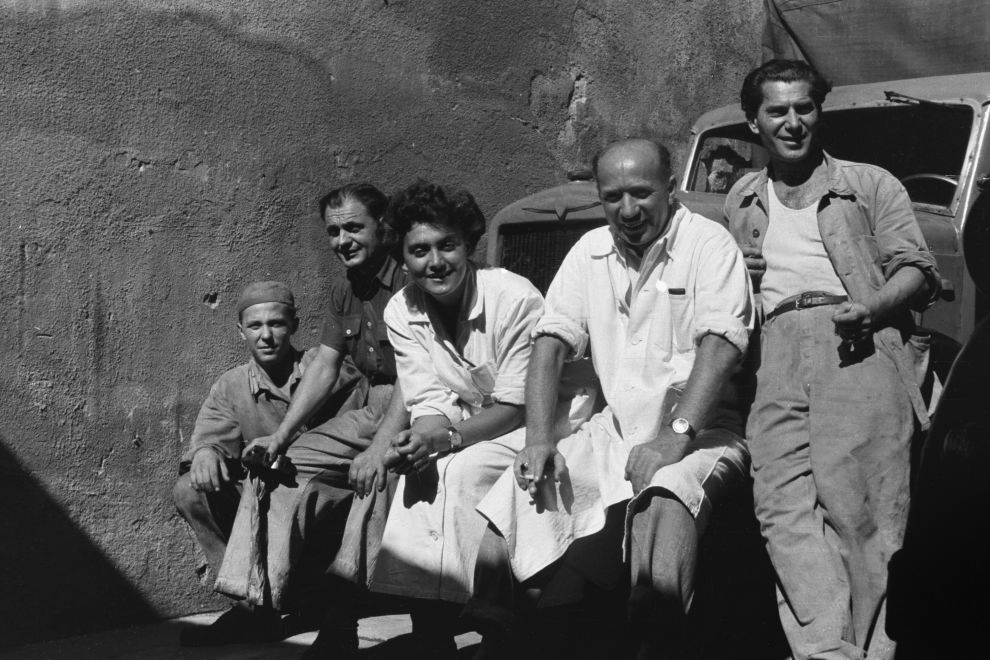
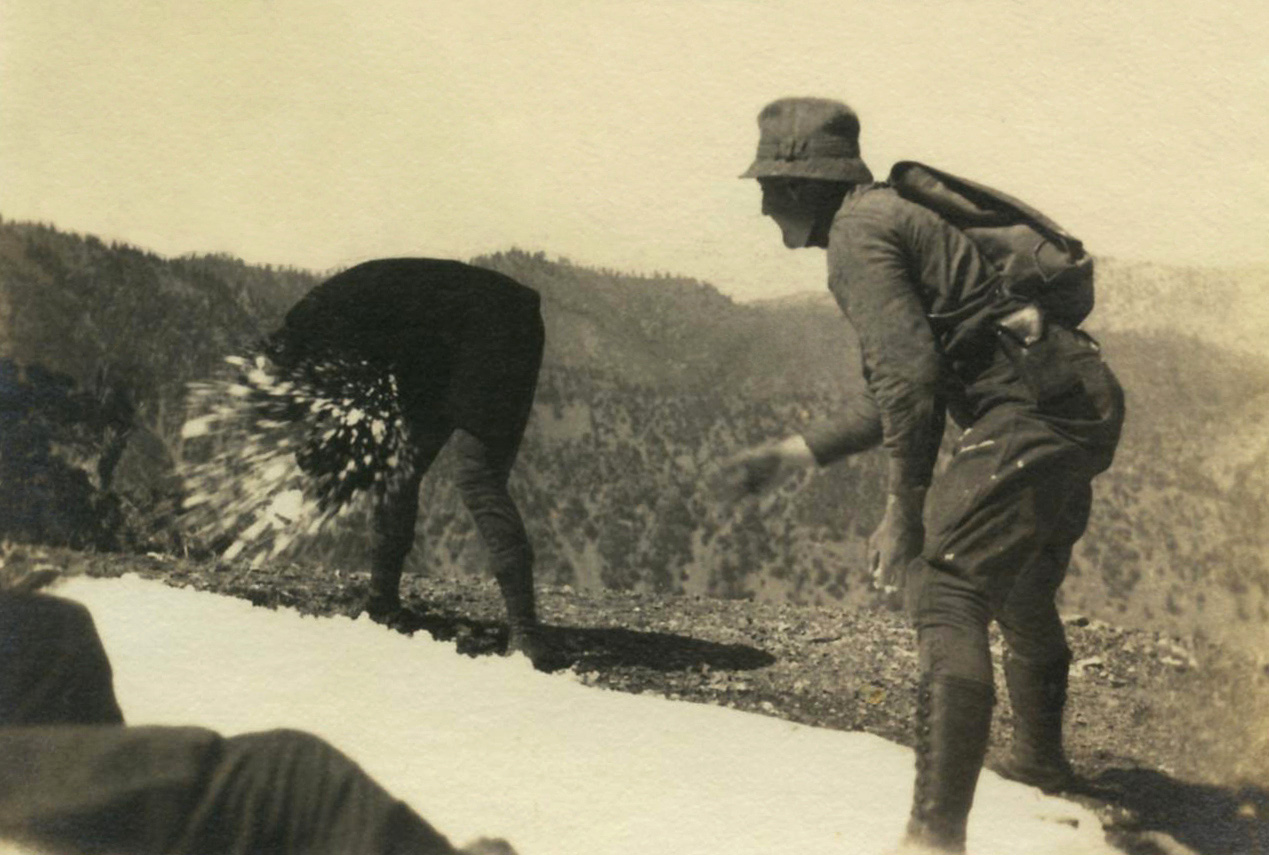
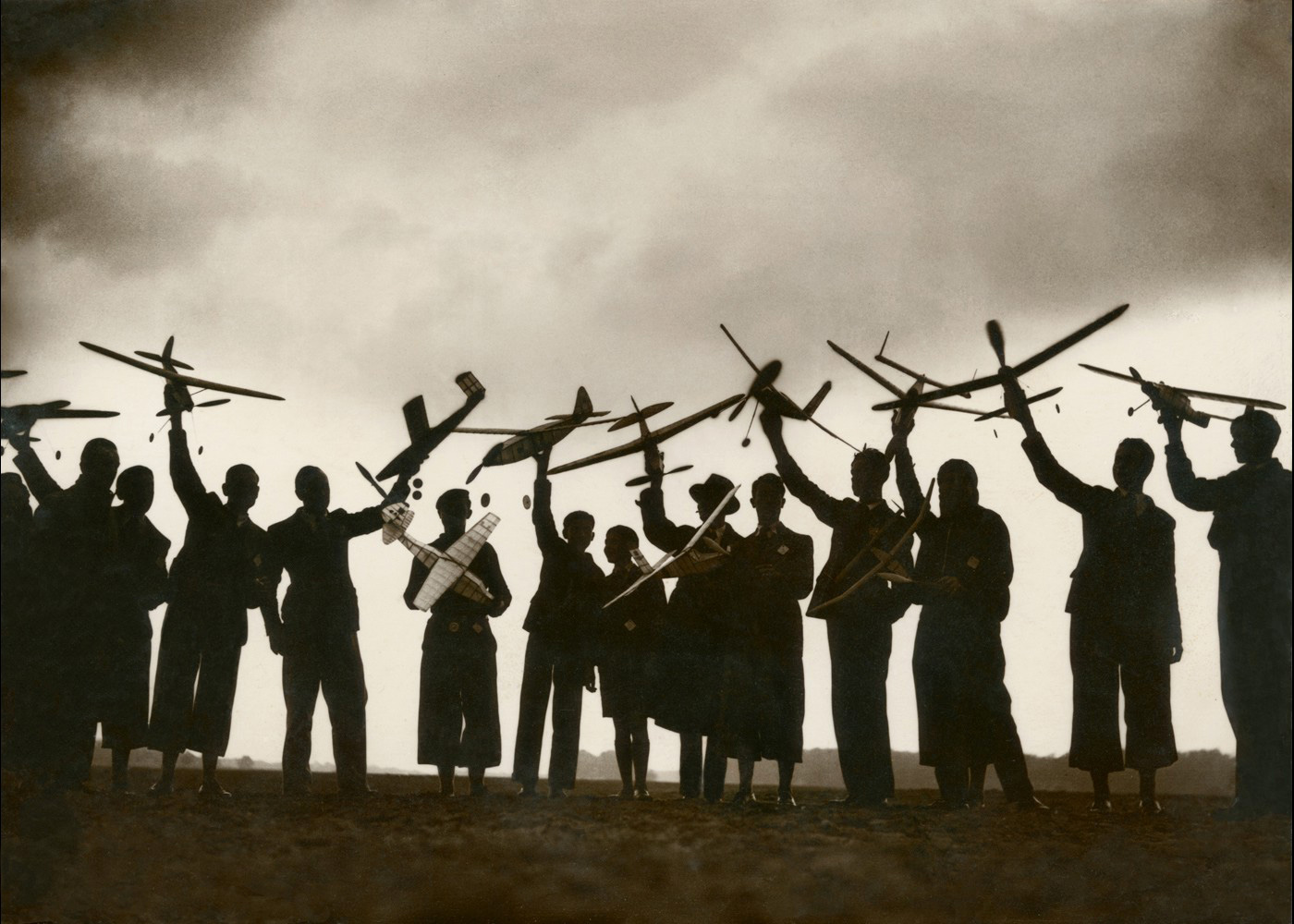
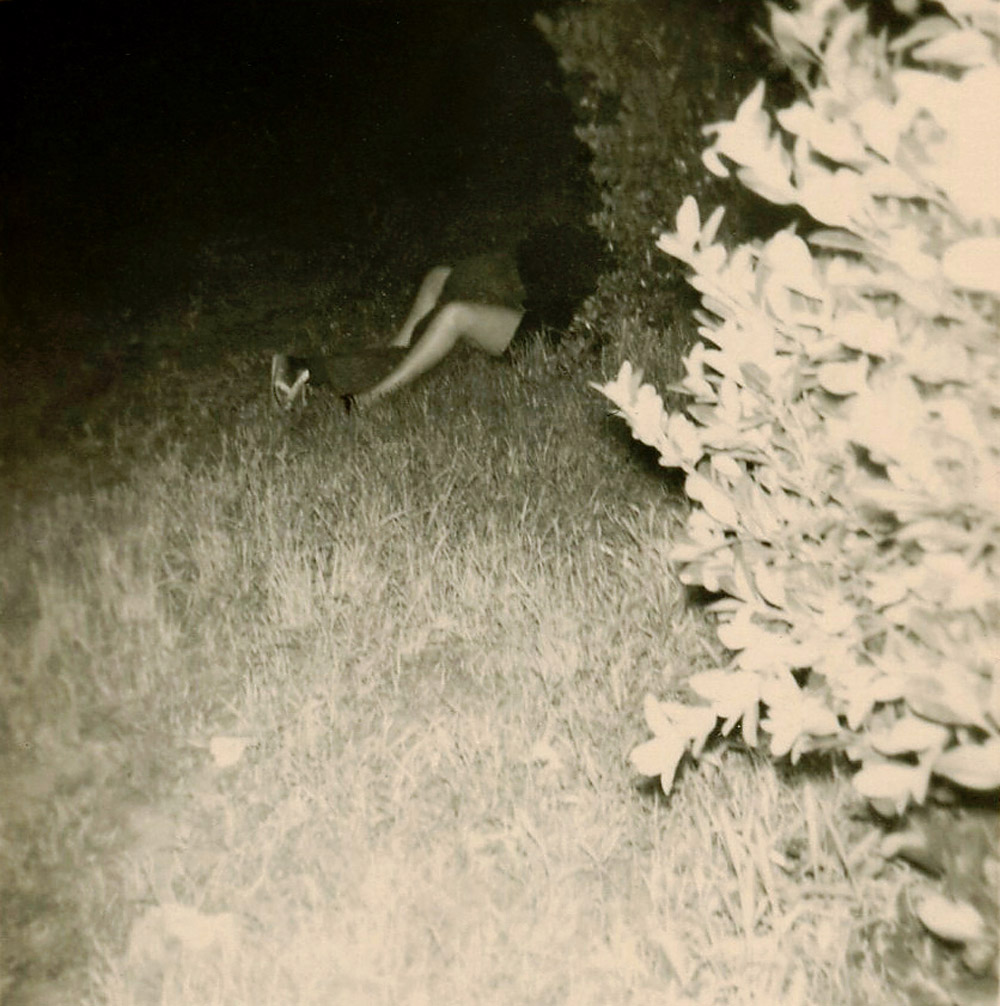
Unknown photographer
Untitled
1957
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
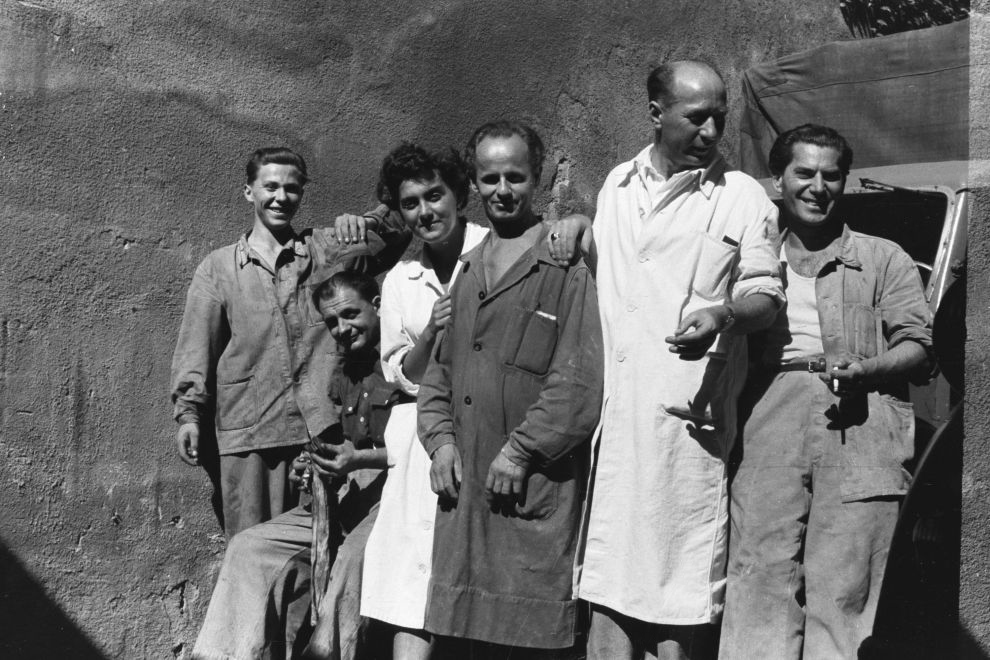
Unknown photographer
Untitled
1957
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
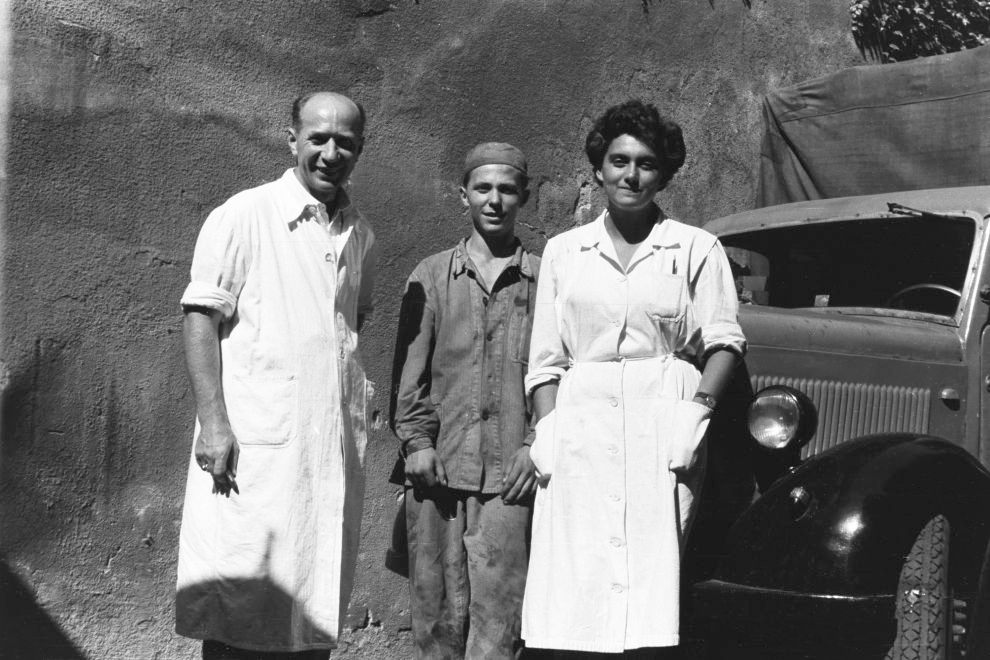
Unknown photographer
Untitled
1957
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
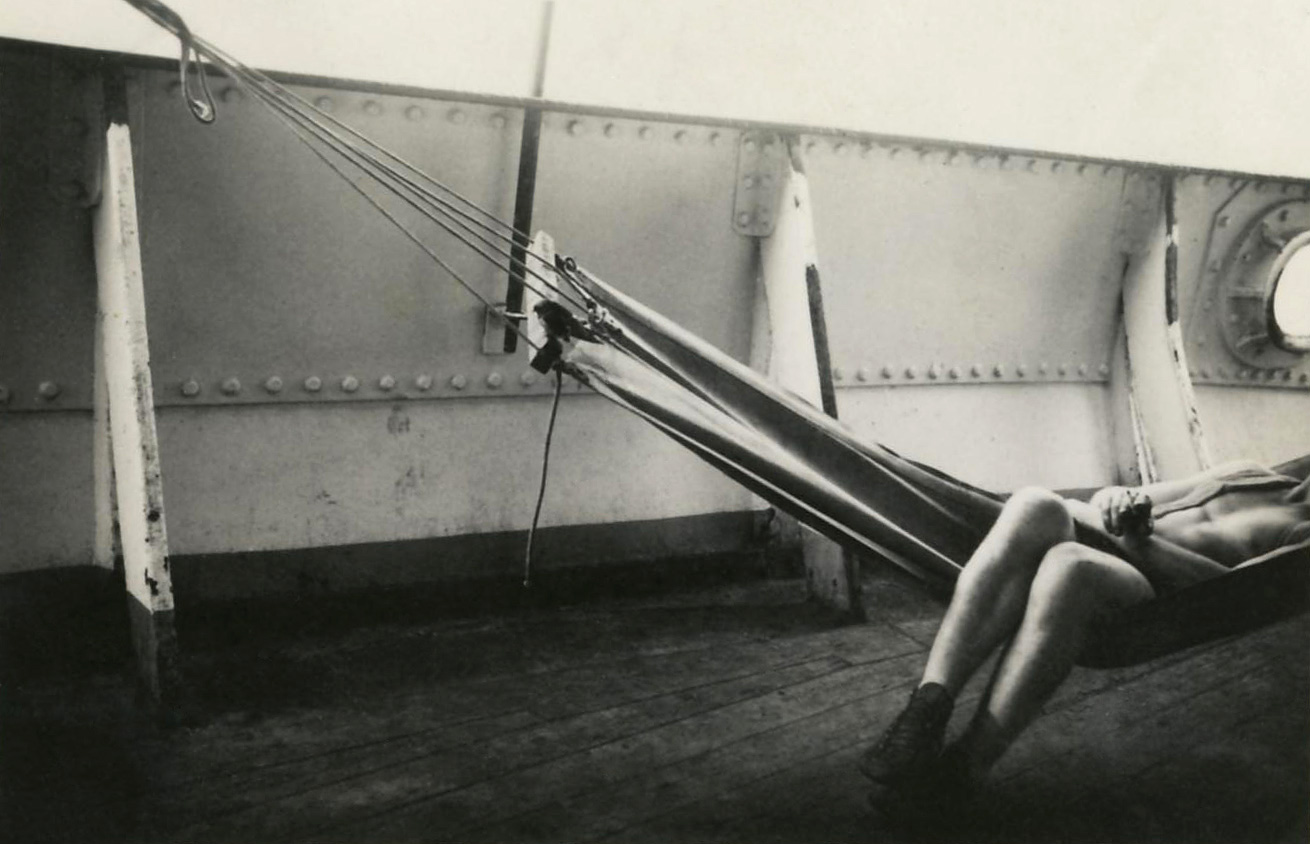
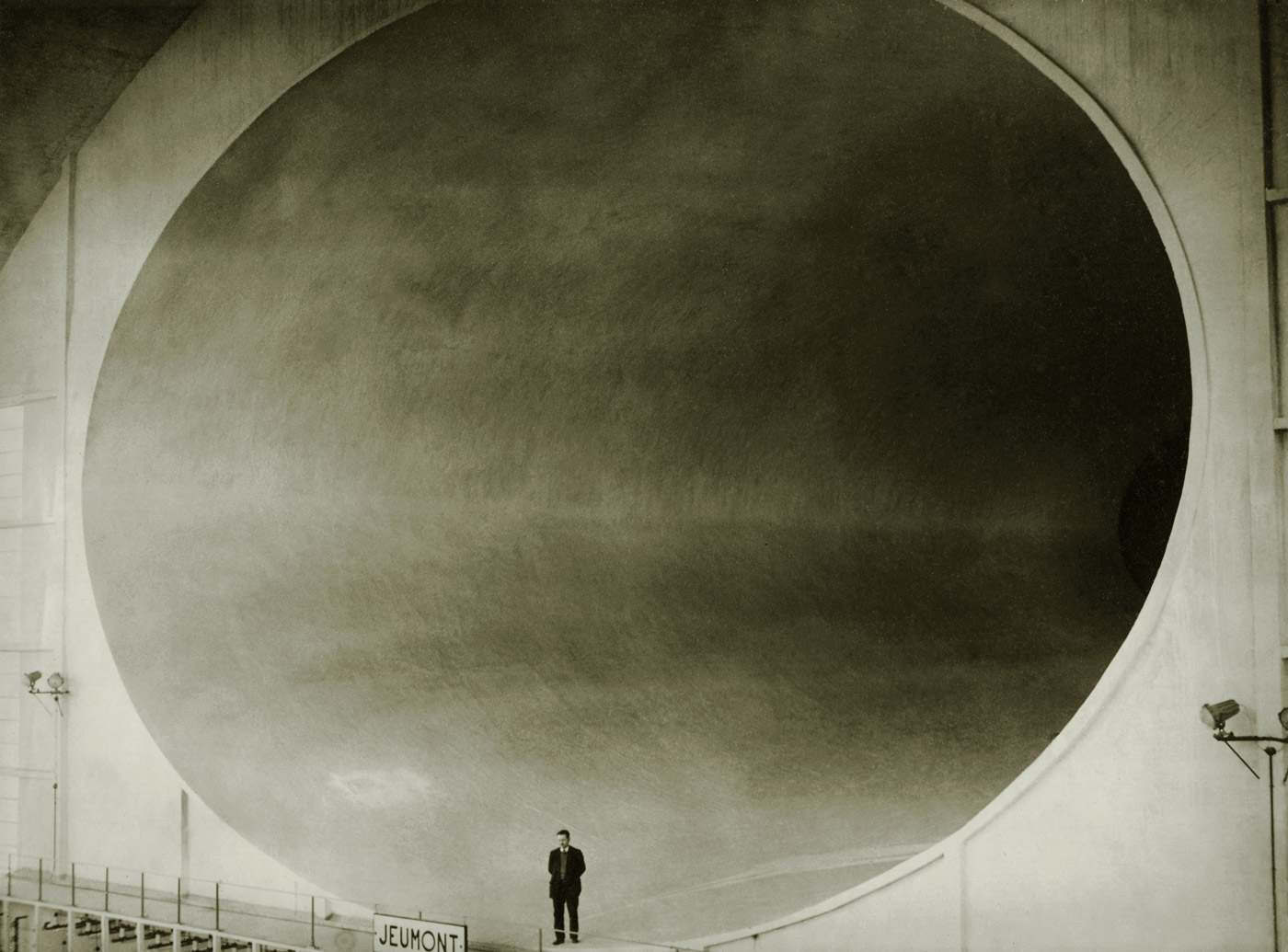
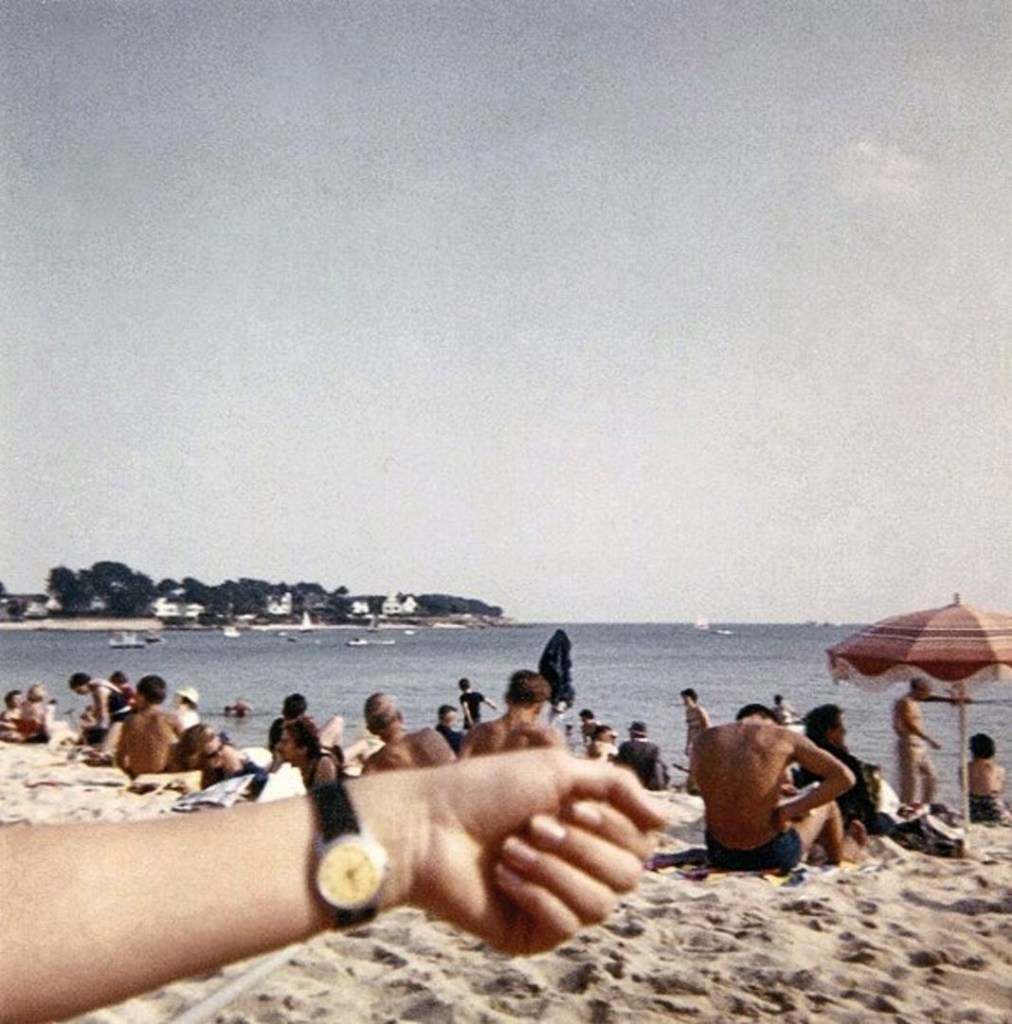
Unknown photographer
Untitled
1969
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
Unknown photographer
Untitled
1969
Fortepan / Capital of Budapest Archives
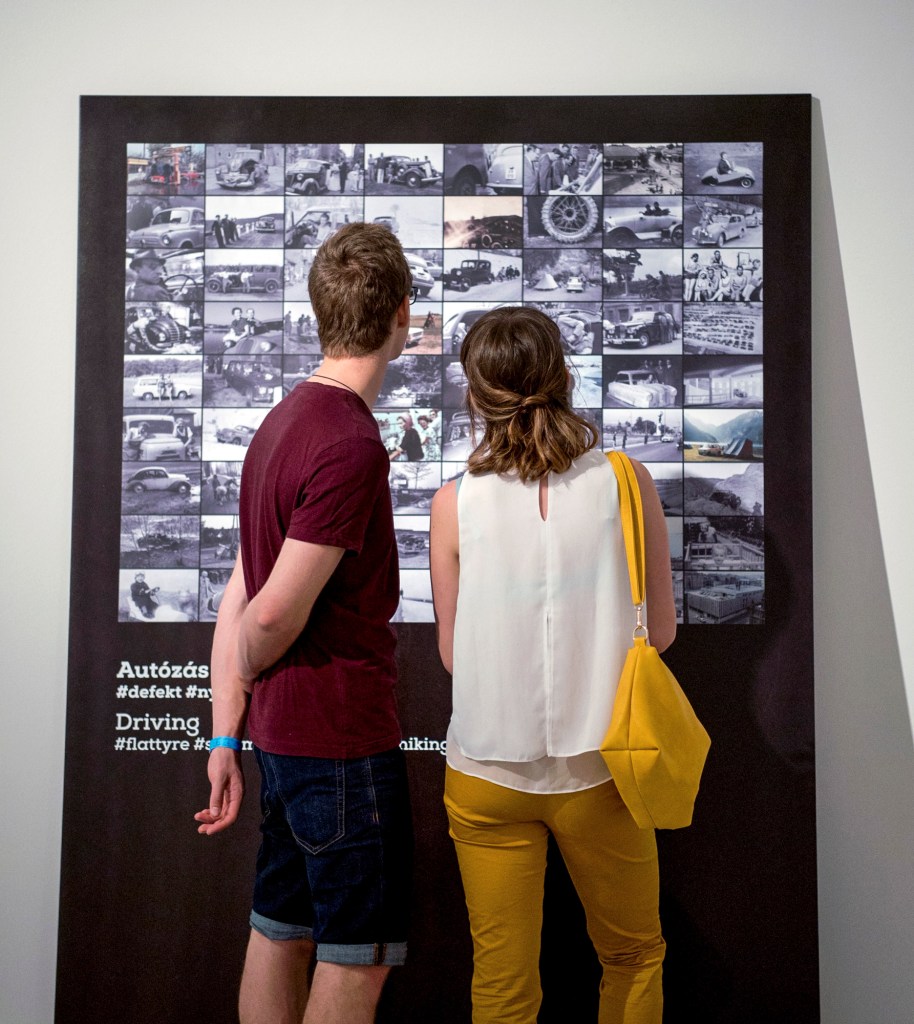


Installation views of the exhibition Every Past Is My Past at the Hungarian National Gallery (MNG), Budapest
Hungarian National Gallery
1014 Budapest, Szent György Square 2
Central Telephone: +361 201 9082
Opening hours
Tuesday to Sunday 10.00 to 18.00
Monday closed
















































































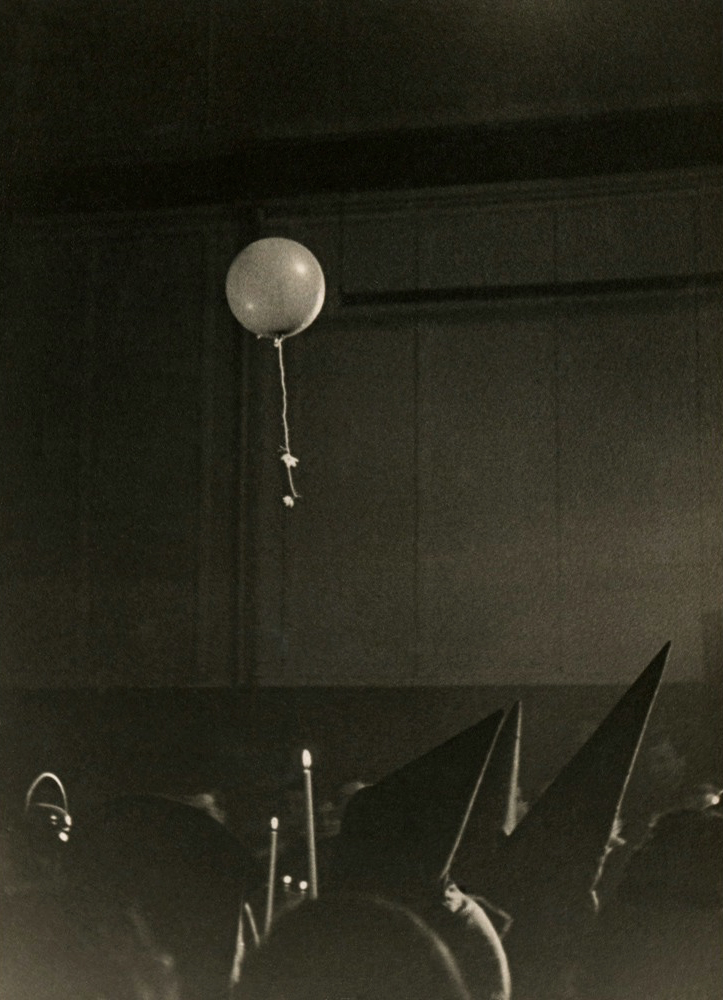

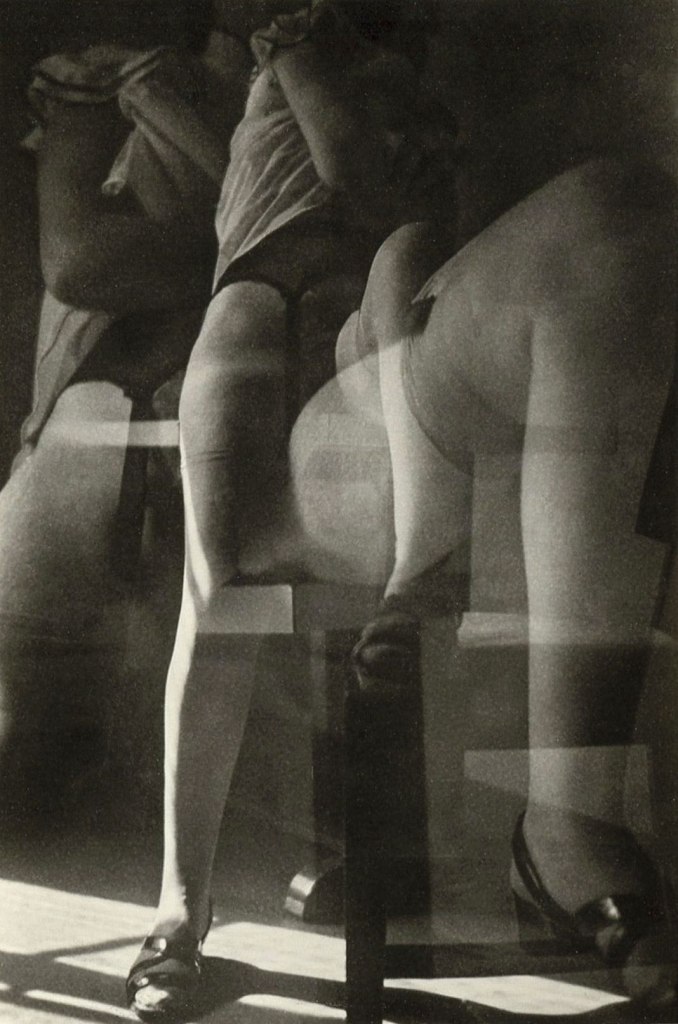






You must be logged in to post a comment.