Exhibition dates: 24th November 2012 – 3rd February 2013
Many thankx to the Museum de Moderne Salzburg for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Osvaldo Salas (Cuban, 1914-1992)
Che fumano (Che smoking)
1964
Gelatine-Silberprint, Vintage
40 x 50cm
From the Skrein Photo Collection
Perfecto Romero (Cuban, b. 1936)
Miliz Campesinos (Military peasants)
1961
Gelatine-Silberprint, Vintage
30 x 40cm
From the Skrein Photo Collection
Osvaldo Salas (Cuban, 1914-1992)
Camilo beim Einzug in Havanna, 8.1.1959 (Camilo moving into Havana, 8.1.1959) (Camilo Cienfuegos)
1959
Gelatine-Silberprint, Vintage
40 x 50cm
From the Skrein Photo Collection
Alberto Korda (Cuban, 1928-2001)
1. Mai 1960, Volksverteidigungsarmee (1. May 1960, People’s Defence Force)
1960
s/w Fotografie
From the Skrein Photo Collection
© VBK, Wien, 2012
René Burri (Swiss, 1933-2014)
Che Guevara
1963
Kontaktbogen, Gelatine-Silberprint
22 x 34cm
From the Skrein Photo Collection
Raúl Corrales (Cuban, 1925-2006)
La Cabelleria (The Cavalry)
1961
Cuban President Fulgencio Batista, who seized power in a military coup in 1952, ran a corrupt and dictatorial regime. This gave rise to the Cuban revolutionary movement that still continues today: In 1953 Fidel Castro and his loyal followers organised an armed attack on the Moncada Barracks, which was brutally quashed by the Batista regime.
M-26-7 is a reference to this failed attack which marks the beginning of the Cuban Revolution and became a symbol of the revolution for Castro’s followers. On 26th of July 1953 the protagonists of the revolution were arrested, Fidel and Raul Castro were sentenced to many years in prison and numerous combatants were executed. In 1955 Batista released Castro from prison, who went into exile in Mexico, where Che Guevara, an Argentine-born physician, joined his movement. In 1956 they returned to Cuba from Mexico with 82 fighters; they landed in the Granma Province, south of Havana which also became a synonym of the revolution, like the Sierra Maestra Mountains.
This is where the Skrein Collection begins: the preparation of the guerilla war, the recruitment of new fighters, including Camilo Cienfuegos, who formed the triumvirate of the revolution with Che Guevara and Fidel Castro, or Celia Sánchez, one of the first women of the revolutionary movement. The activities of the revolutionists attracted many followers and enjoyed strong support among the population until victory was finally achieved with the Castro‘s triumphal entry in Havanna in 1959. This was followed by a phase of consolidation, during which Castro, Guevara and other revolutionaries assumed political offices and were appointed as ministers. After the Bay of Pigs disaster in 1961, the USA imposed a total embargo on Cuba, thus contributing to the isolation of the Caribbean island and its political leadership.
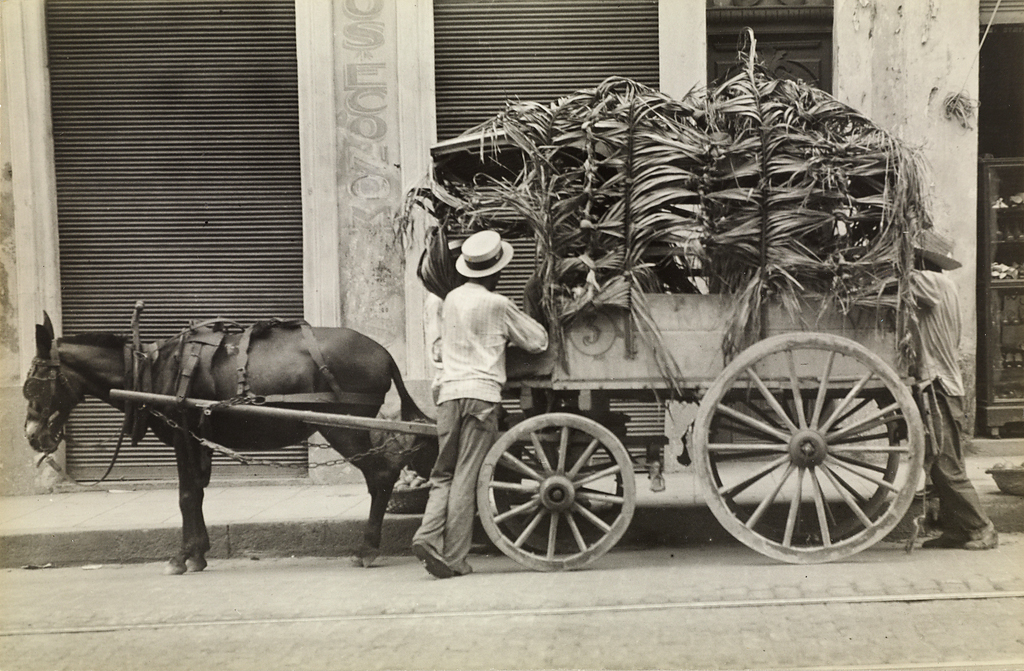
The photographs from the Skrein Photo Collection cover the period from the end of the Batista-Regime to the Cuban Missile Crisis. Both Cuban and foreign photographers were involved into political events as reporters, sympathisers, journalists and adventurers and spread the revolutionary ideology. Leading European photographers travelled into this troubled country in the midst of social upheavals and turned the leaders of the revolution into icons and symbols of a dissatisfied youth on the eve of the global 1968 movement world wide.
Austrian photographer Christian Skrein (b. 1945, Vienna) began his career as an art, commercial and fashion photographer. He later became an enthusiastic and expert collector of photography and compiled comprehensive archives of snapshot photography and international press and art photography. For over 15 years now, he has focused on photographs of the Cuban Revolution and its protagonists. Today, his collection comprises more than 4,500 items, including several icons of the history of photography as well as numerous less spectacular photographs which document the political situation and social life in Cuba from the 1950s to the 1970s.
In 2011 the Getty Museum in Los Angeles selected a set of 60 photographs from the Skrein Collection for its first exhibition on the Cuban Revolution: the onslaught of visitors testified to the huge interest in this historical period and its profound and far-reaching impact on global politics and in the role of photography as mediator of pictures that create identity. The presentation of 150 photographs at the Museum der Moderne Salzburg offers visitors insights into this extensive specialised collection, but also shows the importance of photography and media for events and personalities. No other political event of this period was photographically documented as much as the Cuban Revolution; the pictures of its heroes were reproduced many thousands of times. The world famous photograph of Che Guevara by Alberto Korda is the most often reproduced photograph in the world, owing to a large-scale ideological and PR campaign initiated in 1967 by Italian publisher Giangiacomo Feltrinelli.
The myth of revolution – image pictures and iconic reception
Che Guevara was recognised as media star already during the revolution; his portrait adorned the walls of every government authority and factory building, every office and tobacco factory – he was omnipresent, an icon and role model and a crucial propaganda instrument of the political movement. The charismatic, eternally young revolutionary adorned public and private rooms as poster, photograph and icon, and the people identified themselves with their leader on a never-before-seen scale. Che united the revolution with the idea of social upheaval and personified a socialist future, a new man and a new country.
After the successful revolution the photographs of its heroes became a synonym of the new society; they were revered and distributed all over the country like pictures of saints. While the early iconic pictures of the revolution were made by Cuban photographers, who were part of the revolutionary movement, the Western world began to take notice of developments in Cuba in 1959. Leading European photographers travelled into this troubled country in the midst of social upheavals and turned the leaders of the revolution into icons and symbols of a dissatisfied youth on the eve of the global 1968 movement. Particularly the word famous portrait of Che Guevara as “guerrillero heroico” with beret and red star, photographed by Alberto Korda, is still regarded as an epitome of revolution and rebellion today and considered the most famous portrait of a person worldwide.
The photographic language of the revolution
Few photographs exist from the early years of the revolutionary movement against the Batista regime, and most of them were made by amateur photographers and travellers. They resemble the documentary photographic style of the 1930s which was popular in the United States and Europe at that time. Event photography, like the picture of Fidel Castro’s release from prison in 1955, retrospectively achieved iconic status and became the initial image of the revolution widely distributed in numerous reproductions, details and enlargements. The guerrilla fights in the Sierra Maestra are only documented in small incidental photographs made by sympathisers and fellow guerrillas with their own cameras.
Professional photographers discovered the “faces of the revolution” and their protagonists only in 1959. From then on countless portraits of Che Guevara, Fidel and Raúl Castro and their combatants were created. This is also the reason why so few photographs exist of Camilo Cienfuegos, who died in 1959, and of the authentic event of the triumphant entry into Havana on 8 January 1959, which were replaced by pictures of Fidel Castro’s famous speech. Photographers developed a photographic language with an epic style which was situated between documentation and homage and supported the political scope of the revolution. A photograph by Raúl Corrales became famous under the name “La Cabelleria”, even though the occasion (illegal entry into the premises of the American Fruit company) was not primarily heroic. The image created the identity of event and ideology and thus became a political statement.
The style of the photographers – from Alberto Korda to Liborio Noval and Osvaldo Salas, from Corrales to Tirso and Mayito – was characterised by a pictorial dramaturgy that was suitable for the media: strong contrasts, little internal drawing, silhouette-like figures against a discreet background – in other words the criteria of good news photography as it has been practiced since the 1940s. In addition, the photographers sympathising with and involved in the revolution had a feel and understanding for pathos and staging and paid attention to small details and scenes on the fringe of large events.
Press release from the Museum de Moderne Rupertinum website
Alberto Korda (Cuban, 1928-2001)
Siegesfeier nach der Schlacht in der Schweinebucht, Fidel Castro mit aufgemalter Flagge
(Victory celebration after the Battle in the Bay of Pigs, Fidel Castro with painted flag)
1961
Gelatine-Silberprint, Vintage, Deckfarben
40 x 30cm
From the Skrein Photo Collection
© VBK, Wien, 2012
Carlos Morales
Siegreiche Revolution, 8.1.1959 (Victorious Revolution, 8.1.1959)
1959
Gelatine-Silberprint, Vintage
28 x 20cm
From the Skrein Photo Collection
Venancio Diaz (Cuban, 1916-2003)
Volksparade anlässlich “La Coubre” (People’s parade dedicated to “Coubre”)
1960
Gelatine-Silberprint, Vintage
27 x 15cm
From the Skrein Photo Collection
Anonymous photographer
Fidel Castro
c. 1970
Vintage silver gelatin print
33.5 x 28cm
From the Skrein Photo Collection
Alberto Korda (Cuban, 1928-2001)
Che Guevara
1960
s/w Fotografie
From the Skrein Photo Collection
© VBK, Wien, 2012
Museum de Moderne Salzburg
Mönchsberg 32
5020 Salzburg, Austria
Opening hours:
Tuesday – Sunday: 10.00am – 6.00pm
Wednesday: 10.00am – 8.00pm
Monday: closed

![Osvaldo Salas (Cuban, 1914-1992) 'Che fumano' [Che smoking] 1964 Osvaldo Salas (Cuban, 1914-1992) 'Che fumano' [Che smoking] 1964](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/mdm-rupertinum_bilder-revolution_salas_che-fumano-web.jpg)
























You must be logged in to post a comment.