Exhibition dates: 21st July, 2024 – 5th January, 2025
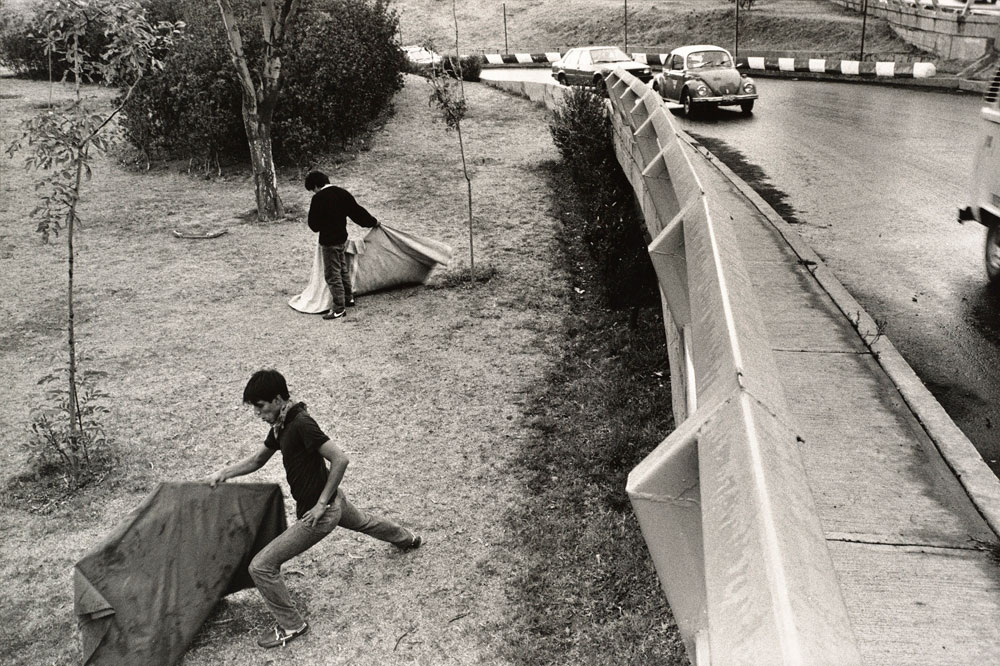
Miguel Fernández de Castro (Mexican, b. 1986)
Grammar of Gates / Gramática de las puertas
2019
Courtesy of the artist
© Miguel Fernández de Castro
I wrote this philosophical text as a flow of consciousness, a layered exposition of my thoughts on space, photography, identity and belonging. I hope I have done the subject justice… in freedom.
within, bridge and fissure
The struggle for identity, for culture, for nation is a struggle inscribed in space. So observes Wendy Garden.1
The spaces that bodies move in, through and over are fluid spaces, permeable spaces, fragmentary and transitory spaces. They are also spaces of displacement and distance which form a kind of ‘alienation’ which derives from the Latin alienare: to render foreign, other.2
Thus the “border” between one and the other – that fluid penumbra (a peripheral or indeterminate area or group), that oscillation of energy across the line – must be constructed to be legible and fixed by those that seek to control such spaces, through the imposition of a coded representation of space itself.3 The border wall between Mexico and America is one such imposition of a coded representation of space which, seeks to control an/other. It is a “direct translation of ideology and temporality into material and spatial culture”3 which masks as much as it represents, through a selective representation of history and memory.
Through systems of surveillance (e.g. CCTV, aerial surveillance, phone taps) and control (e.g. police, government, the judiciary), in which one reinforces the other in a never ending circle, and in the of naming of the ‘other’ (Foucault) – those with privilege embedded and thus emboldened within colonial and imperial systems seek to confirm hegemonic structures of power: for example, who can travel where, who has access adequate to health care, who is seen as an ill/legal alien. “Although Foucault rarely alludes to it in a clear-cut manner, what he describes in Discipline and Punish is the formation of the discursive regime of surveillance which is a central element in the expression of the modern state.”4
But we can counter this narrative.
In his influential book Thirdspace (Blackwell, 1996), the American postmodern political geographer and urban theorist Edward Soja (1940-2015) proposes the concept of First, Second and Thirdspace to demarcate the various spatial dimensions. Firstspace “is the ‘real’, the concrete materiality of spatial forms of the world, while Secondspace interprets this reality through imagined representations of spatiality.”5 Much early photographic practice is rooted in Firstspace, in the passive representation of an undeniable truth, the veracity of the image and its representation of the referent: this existed because it was captured by the camera.
Thirdspace on the other hand, “contains both real and imagined spaces simultaneously. Thirdspace permits an intermingling of the knowable and the unknowable, the real and the imagined by the experiences, events and political choices that are shaped by the interplay between centres and peripheries (Soja, Thirdspace 1996: 31). According to Soja, Thirdspace is a place where issues of race, class and gender can be addressed simultaneously without privileging one over the other. It is a space which enables an-‘other’ way of understanding and acting to change the spatiality of human life (Soja, Thirdspace 1996: 10). Photographic space, as a Thirdspace, is a site from which to contest the dominant ideologies of Firstspace. This has important ramifications for ‘others,’ especially those disenfranchised by colonialism.”6
Thus photographic Thirdspace as an amorphous space of both the real and imagined is the vibration of energy – doubled – the real and imagined spaces of everyday life, and the real and imagined spaces of photography through which we can contest the contexts of becoming, belonging.
These Thirdspaces of the real and imagined are not spaces of universalising totality which then would be constitutive of history or memory, but in-between spaces in which differences, memories and histories are not denied or negated, hidden, forgotten or repressed. It is not the segregation of black and white, either/or, but the grey areas in-between that interest me: those fluid zones of difference – think Tarkovsky’s film Stalker 1979, in which a guide helps a writer and a professor to infiltrate a restricted area, the Zone.
“The Thirdspace – in which “everything comes together… subjectivity and objectivity, the abstract and the concrete, the real and the imagined, the knowable and the unimaginable, the repetitive and the differential, structure and agency, mind and body, consciousness and the unconscious, the disciplined and the trans-disciplinary, everyday life and unending history”a – allows that none of these couples, such as the phenomenal and the noumenal, can be divided by an either/or attitude. “This… does not mean differences are denied, instead, it most of all means the inevitable reciprocity of any pair of definitions. In such a case both leave a mark on the other. It is a question of both-and – how each of the pair influences the other”b.”7
Both leave a mark on each other. And it is in this marking that social and political relations can be reconfigured, “in such a way as to suspect, neutralise, or invert the set of relations that they happen to designate, mirror or reflect.”8 Thus, the physical aspects as well as the attitudes and habitual practices of ‘space’, the arrangements of space and the socialisation of space, “is an order that is itself always undergoing change from within through the actions and innovations of social agents. In short, all ‘space’ is social space ….”9
Following, we can say that social and spatial relationships are dialectically inter-reactive, interdependent (Soja).
“Social and spatial relationships are dialectically inter-reactive and interdependent. Cultural landscapes reflect social relations and institutions, and they shape subsequent social relations. While elites create spatial inequalities and homogeneity simultaneously through their hegemony, non-elites create counter-hegemonic landscapes which reflect their own values. Behavioural resistance to the dominant culture leads to distinctive cultural landscapes: for example, cultural resistance by Maori.
Indeed, dominant ideologies such as those which are religious, political, economic, ethnic or racial, continually define or redefine ‘deviance’ or ‘otherness’ to maintain their power and landscapes of dominance. Space and place are key factors in the definition of deviance and of order and propriety.”10
But as Wael Salah Fahmi insightfully observes, we must not fall into the idea that juxtapositions of social space are just alternating choices of “either/or” or acts of simple resistance: “But “juxtaposition” might imply alternating choices, an “either/or.” Perhaps instead we might think of Lefebvre’s image of interpenetrating spaces, one violating another, yet rising up from within the very “fundament” of the space that wishes to ignore its existence. Here, perhaps, is a spatial dialectic that does not fall into a binary opposition of simple resistance.”11
Spaces that rise up from within each other!
Change that emanates from within through the actions and innovations of social agents… human beings, artists!
Here, the thoughts of that glorious Cuban-American interdisciplinary artist, writer, and curator Coco Fusco (b. 1960) – quoted by Jean Fisher – whose work explores gender, identity, race, and power through performance, video, interactive installations, and critical writing are particularly cogent.
“Two imperatives are set in motion: to alter the perceptions of those with privileged access to hegemonic structures of power, and to change the sense of disempowerment of those deprived of political agency. “What is more fundamentally at stake than freedom,” Fusco argues, “is power – the power to choose, the power to determine value, and the right of the more powerful to consume without guilt”: entitlements that Eurocentric cultures have assumed for themselves at the expense of others. These aims are advanced through an exploration of the relationship between the politics and practices of cultural difference and social inequity, in which intellectual, experiential, and artistic alliances are built across nationalistic and geographical boundaries …””12
As Wael Salah Fahmi notes, “spaces constantly juxtapose themselves one against the other” – in real life, in art, in photography. The media saturated world of the “total flow” of images is resistant to interpretation, yet in real life – and in this exhibition – the juxta/position (mapping of space), juxta/posing (posing for the camera) of one space against another, “of image to image calls to attention a line of conflict, either fissure or bridge.”13
The images in this posting draw our attention to fissures (George Rodriguez, Susan Meiselas, Ada Trillo) and bridges (Graciela Iturbide, Ronald Rael and Virginia San Fratello with Colectivo Chopeke). They also possess a multivalent narrative, allowing the work to be accessible to different interpretations, meanings, and values: a new door or path opens up on the basis of very diverse needs and objectives. These images, untraceable gifts from photography itself, are marks of candour and authenticity, both descriptions of a stable object and the fleeting glance (Firstspace and Thirdspace) interacting upon each other. They are an investigation into our fluid identity and shifting place in our worlds.14
In spatial dialectics and in the nuances of contradictions we proceed onwards, paying no heed to the dangers which lie ahead, journeying on to fulfil our desires: to be seen, to be heard, in our difference and uniqueness, enacting change from within.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Word count: 1,435
PS. My friend and Melbourne artist Elizabeth Gertsakis insightfully observes, “The philosophical arguments resonate with the vacillation of the photograph meanings/non-meanings. Spaces that implode from within to further generate the unknown which even in definition become dispersed. The photography around the border/wall is beautiful as well as tortuous as well as unspoken.”
Well said Liz 🙂
Footnotes
1/ Wendy Garden. “Photographic Space and the Indian Portrait Studio,” in On Space Issue Seven, Winter 2007
2/ Rob Shields. Lefebvre, Love and Struggle. London: Routledge, 1999, pp. 40-41.
3/ Ibid., pp. 79-80.
4/ Jon Stratton. The Desirable Body. Manchester: Manchester University Press, 1996, p. 19
5/ Garden, Op cit.,
6/ Garden, Op cit.,
7/ A: Edward W. Soja. Thirdspace. Malden (Mass.): Blackwell, 1996, p. 57; B: Mika Hannula. “Third space – a merry-go-round of opportunity,” on the Kiasma Magazine website No. 12, Vol. 4, 2001 [Online] Cited 01/05/2016. No longer available online quoted in Marcus Bunyan. “Thirdspace,” on the Marcus Bunyan website 2021 [Online] Cited 29/11/2024
8/ Michel Foucault. “Of Other Spaces,” in Diacritics Spring 1986, p. 24
9/ Shields, Op cit., pp. 154-155
10/Alexander Trapeznik. “Introduction,” from Public History Review, Vol. 13, 2006, p. 2
11/ Wael Salah Fahmi. “Reading of Post Modern Public Spaces As Layers Of Virtual Images and Real Events,” from The 37th International Planning Congress “HONEY, I SHRUNK THE SPACE” Planning in the Information Age. Utrecht, The Netherlands, 16-20 September, 2001
12/ Jean Fisher. “Witness for the Prosecution: The Writings of Coco Fusco,” in Coco Fusco. The Bodies That Were Not Ours. London: Routledge, 2001, pp. 226-227
13/ Wael Salah Fahmi, op cit.,
14/ Marcus Bunyan. “Thirdspace,” on the Marcus Bunyan website 2021 [Online] Cited 29/11/2024
Many thankx to the Cleveland Museum of Art for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“And do you know what “the world” is to me? Shall I show it to you in my mirror? This world: a monster of energy, without beginning, without end; a firm, iron magnitude of force that does not grow bigger or smaller, that does not expend itself but only transforms itself; as a whole, of unalterable size, a household without expenses or losses, but likewise without increase or income; enclosed by “nothingness” as by a boundary; not something blurry or wasted, not something endlessly extended, but set in a definite space as a definite force, and not a space that might be “empty” here or there, but rather a force throughout, as a play of forces and waves of forces, at the same time one and many, increasing here and at the same time decreasing there […]”
Frederick Nietzsche, The Will to Power
“Edward Soja employs the concept of First, Second and Thirdspace to demarcate the various spatial dimensions. For Soja Firstspace is the ‘real’, the concrete materiality of spatial forms of the world, while Secondspace interprets this reality through imagined representations of spatiality (Soja 1996: 6). Much early photography participated in perpetuating the belief that photographic space was a Firstspace. The camera lens merely passively and objectively recorded all that was placed before it. However even in the nineteenth century, many practitioners acknowledged the ability of photographs to lie or distort reality.
For Soja, Thirdspace contains both real and imagined spaces simultaneously. Thirdspace permits an intermingling of the knowable and the unknowable, the real and the imagined by the experiences, events and political choices that are shaped by the interplay between centres and peripheries (Soja, Thirdspace 1996: 31). According to Soja, Thirdspace is a place where issues of race, class and gender can be addressed simultaneously without privileging one over the other. It is a space which enables an-‘other’ way of understanding and acting to change the spatiality of human life (Soja, Thirdspace 1996: 10). Photographic space, as a Thirdspace, is a site from which to contest the dominant ideologies of Firstspace. This has important ramifications for ‘others,’ especially those disenfranchised by colonialism. It may account for the rise of photography as the preferred medium for many artists today interested in issues of identity and the colonial gaze. …
Photographic space can create a spatial reality which allows those who access it to contest, enlarge or in someway recreate their experiences of Firstspace. It never attempts to close off subjectivity or pin identity down, but rather allows fluid and transitory experiments with other ways of being that can then be carried over and inform experiences of Firstspace.”
Wendy Garden. “Photographic Space and the Indian Portrait Studio,” in On Space Issue Seven, Winter 2007
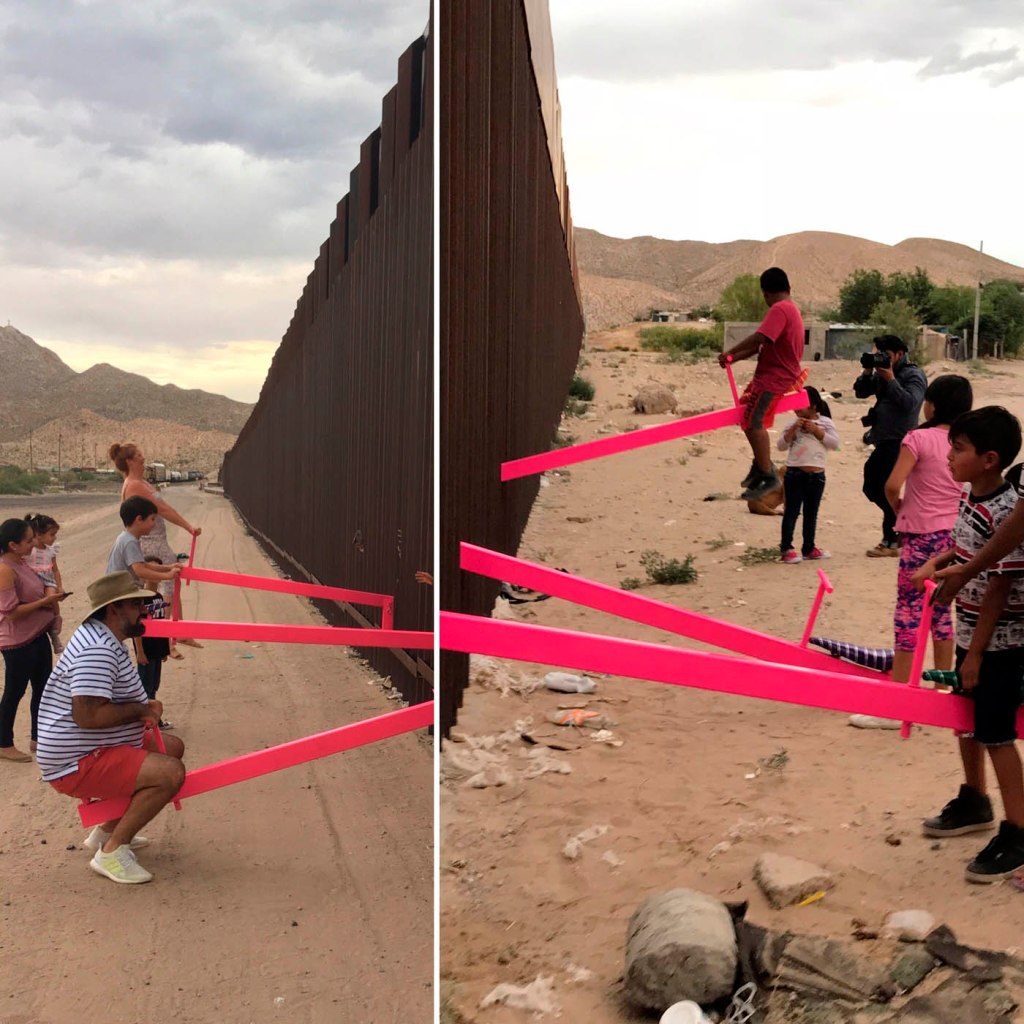

Ronald Rael (American, b. 1971) and Virginia San Fratello (American, b. 1971) with Colectivo Chopeke
Teeter-Totter Wall
2019
Single-channel video with sound; 4:13 minutes
Courtesy Rael San Fratello/Ronald Rael & Virginia San Fratello
© Ronald Rael & Virginia San Fratello
Photo: Ronald Rael
About the exhibition
Picturing the Border presents photographs of the US-Mexico borderlands from the 1970s to the present taken by both border residents and outsiders. They range in subject matter from intimate domestic portraits, narratives of migration, and proof of political demonstrations to images of border crossings and clashes between migrants and the US Border Patrol. The earliest images in this exhibition form an origin story for the topicality of the US-Mexico border at present, and demonstrate that the issues of the border have been a critical point of inquiry for artists since the 1970s. Many serve as counter-narratives to the derogatory narratives of migration and Latino/as in the US that tend to circulate in the mass media.
Capitalising on the prevalent issues of the border today, Picturing the Border aims to spark vital conversations of what constitutes citizenship, as well as complex negotiations of personal identity as it relates to the border. The exhibition shows through these images that Latinx, Chicano/a, and Mexican photographers have significantly rethought what defines citizenship, nationality, family, migration, and the border beyond traditional frameworks for decades.
Text from the Cleveland Museum of Art website
George Rodriguez (American, b. 1937)
Los Angeles police arrest a Chicano student protester in the neighbourhood of Boyle Heights
1970
Gelatin silver print
Susan Meiselas (American, b. 1948)
7.30am Arrest of undocumented worker by U.S. Border Patrol in downtown San Diego, CA
1989
From the series Crossings
Gelatin silver print
44.5 x 73.7cm
Courtesy of and © Susan Meiselas/Magnum Photos
Photojournalism from the US-Mexico border currently emphasises stark, divisive images: walls, fences, surveillance devices, border patrols, “coyotes,” and crossing migrants. Yet some of the most compelling artwork dealing with this region attests to several generations of cross-border familial relationships, personal identities that carry markers of both countries, and hybrid cultures that meld influences from the United States, Mexico, and farther south in Latin America. This more complex work demonstrates how border residents have resisted being defined by the border and its conflicts, concentrating instead on a deterritorialised notion of home, along with a sense of self that often transcends both nationalism and gender politics.
The photographs and video works included in Picturing the Border offer a more nuanced portrayal of life in the borderlands. The exhibition positions the US-Mexico border as a cultural framework and highlights how Latinx photographers – many of whom are border residents themselves – have instead formulated alternative photographic vocabularies with regard to place, identity, and race. Photographs range in subject matter from intimate domestic portraits, extended family gatherings, and political demonstrations to images of border crossings and clashes between migrants and the US border patrol. The earliest images in this exhibition form an origin story for the topicality of the US-Mexico border at the present moment and demonstrate that the issues of the border have been a critical point of inquiry for artists since the 1970s.
The exhibition is accompanied by an important scholarly publication that brings new insights to the subject of Latinx photography and the history of the US-Mexico border. Picturing the Border has also brought about the opportunity to grow our permanent collection in this area, precipitating recent acquisitions by Laura Aguilar and the donation of an important work by Ada Trillo, who has witnessed firsthand the perils of the unbelievably extensive journey migrants have taken from Central America to the United States.
Although Cleveland is far from the southern border, stories of global migration are woven throughout the CMA’s encyclopeadic collection as well as throughout the community in Northeast Ohio. Picturing the Border puts faces on stories and brings to life the various threads that stitch together an ever-growing understanding of, and empathy for, the migrant experience.
Nadiah Rivera Fellah, Associate Curator of Contemporary Art. “Picturing the Border,” on the Cleveland Museum of Art website June 1, 2024 [Online] Cited 19/07/2024
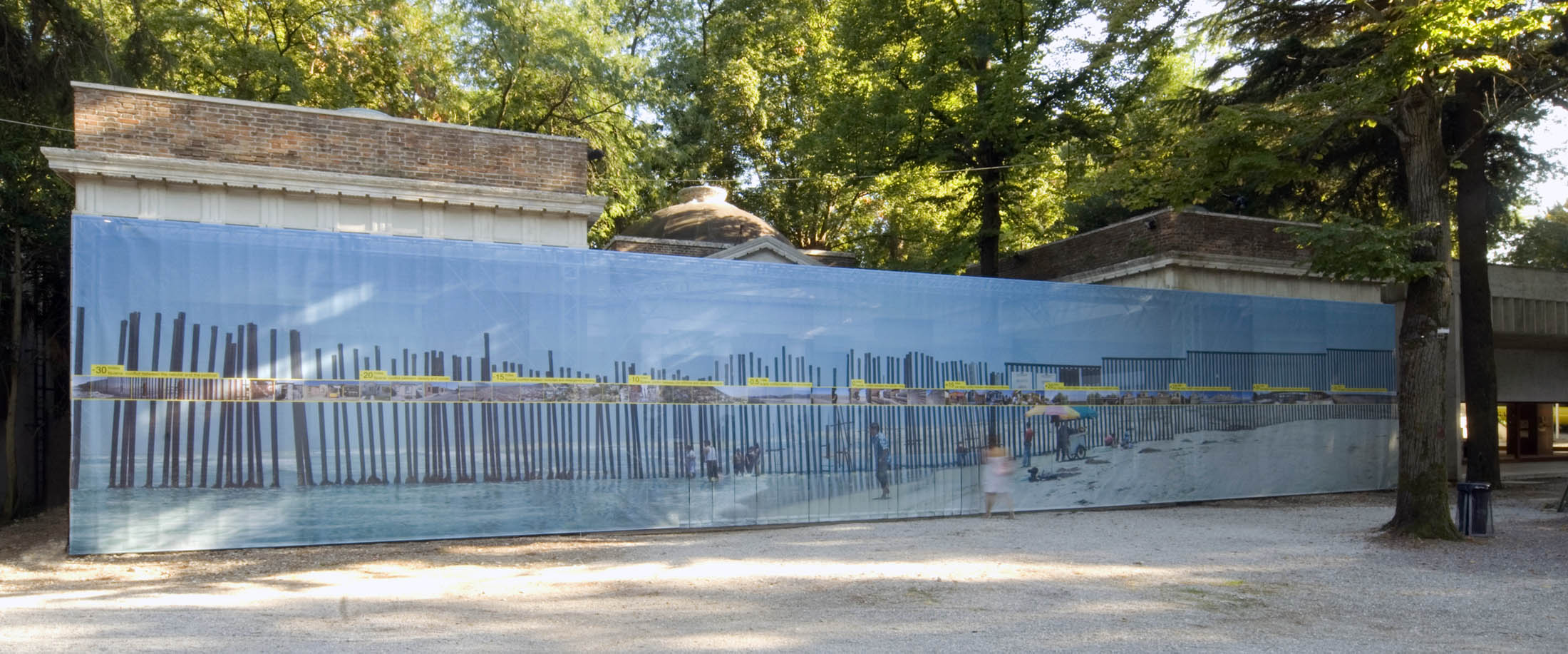
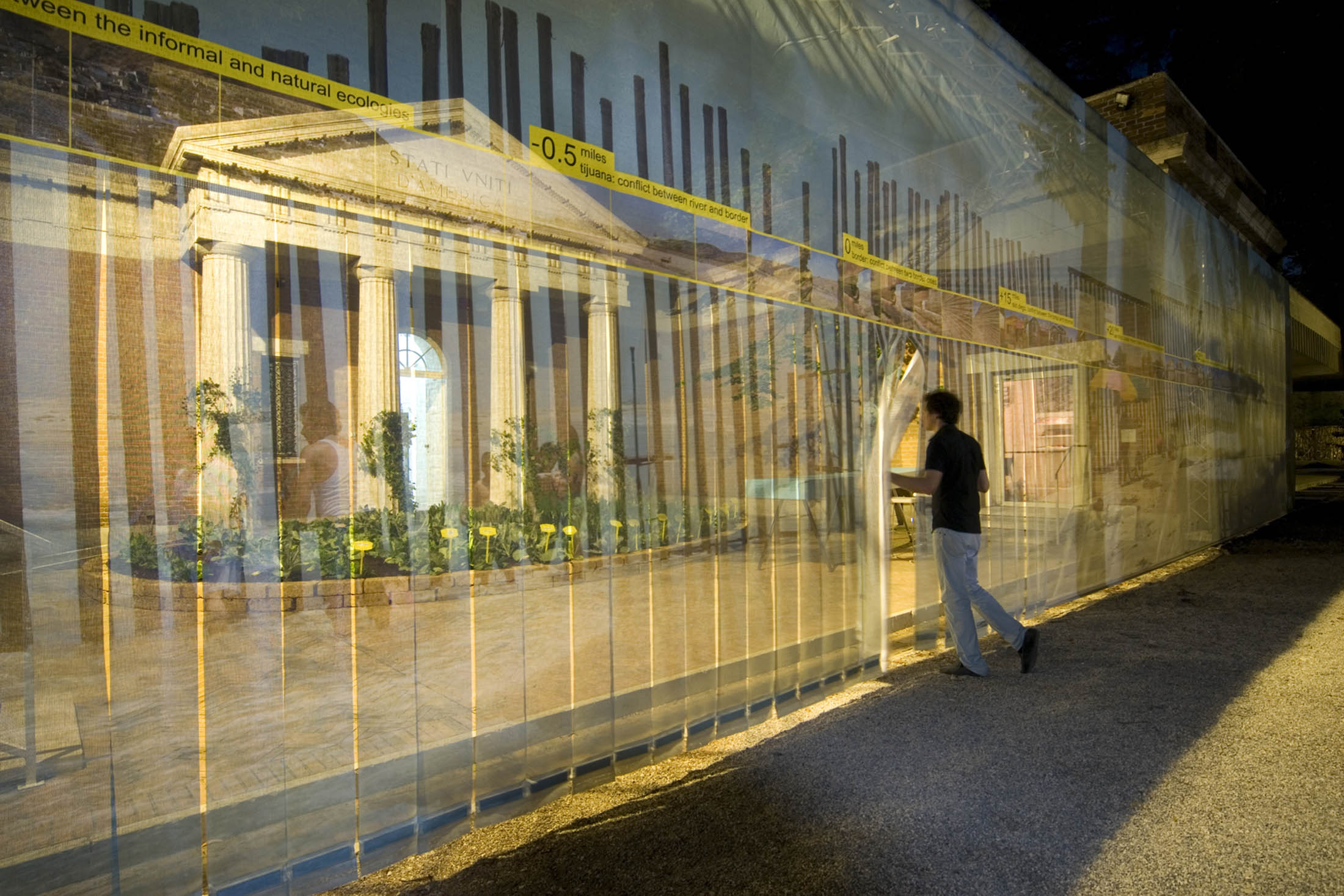
Teddy Cruz (American born Guatemala, b. 1962) and Fonna Forman (American, b. 1968)
Installation view of Radicalizing the Local: 60_Miles of Trans-Border Urban Conflict
2008
Commissioned by the US Pavilion for the Venice Architecture Biennale of 2008
Prints from a digital file; dimensions variable
© Teddy Cruz + Fonna Forman
Image courtesy the Cleveland Museum of Art
Featuring more than four dozen photographs, Picturing the Border aims to spark vital conversations of what constitutes citizenship, as well as complex negotiations of personal identity as it relates to the border. Through these images the exhibition shows that Latinx, Chicano/a, and Mexican photographers have significantly rethought what defines citizenship, nationality, family, migration, and the border beyond traditional frameworks for decades.
Opening on July 21, 2024, in the Mark Schwartz and Bettina Katz Photography Gallery, this free exhibition will be on view through January 5, 2025. From intimate domestic portraits, narratives of migration, and political demonstrations to images of border crossings and clashes between migrants and the US Border Patrol, this one-of-a-kind exhibition presents photographs taken by both border residents and outsiders, many of whom are Latinx, Chicano/a, and Mexican, and tells the story of the US-Mexico borderlands from the 1970s to the present.
“Borders have long been spaces of contention,” says Nadiah Rivera Fellah, curator of contemporary art. “The mainstream media in the United States tends to present nationalistic narratives about imminent threats at the border. This reductive and divisive narrative does not often portray the identities, languages, cultures, and social ties among communities. The photographs featured in this exhibition tell a different story that can serve as a counter-narrative and timely new perspective on life in this region.”
The earliest images in Picturing the Border form an origin story for the topicality of the US-Mexico border at present and demonstrate that the issues of the border have been a critical point of inquiry for artists since the 1970s. In addition, they showcase artists who were ahead of their time in presenting ideas about spaces and exclusion as they relate to issues of the borderlands and Latinx identities in the United States.
Exhibition catalogue
A beautifully illustrated 134-page exhibition catalogue accompanies Picturing the Border by Nadiah Rivera Fellah, curator of contemporary art, with contributions from Natalie Scenters-Zapico.
The US-Mexico border has undergone dramatic changes over the past six decades, becoming increasingly industrialised, urbanised, and militarised, especially in the aftermath of 9/11 and the War on Terror. Mainstream and conservative news coverage has often reinforced or exacerbated such developments, characterising the border as out of control and describing migrants in derogatory terms, in the process fuelling xenophobic sentiment.
A foil to this reductive and dehumanising narrative, this presentation of Latinx photography offers more nuanced portrayals of life in the borderlands. Ranging from the 1970s to the 2020s, images by Louis Carlos Bernal, Graciela Iturbide, and Laura Aguilar, as well as emerging artists such as Ada Trillo, Guadalupe Rosales, and Miguel Fernández de Castro display alternative photographic vocabularies regarding place, identity, and race. With subject matter spanning from intimate domestic portraits and youth counterculture to border crossings and clashes involving the US Border Patrol, this richly illustrated volume also features scholarly essays and new work by fronteriza poet Natalie Scenters-Zapico, providing new insights on this fraught and misunderstood region.
Press release from the Cleveland Museum of Art
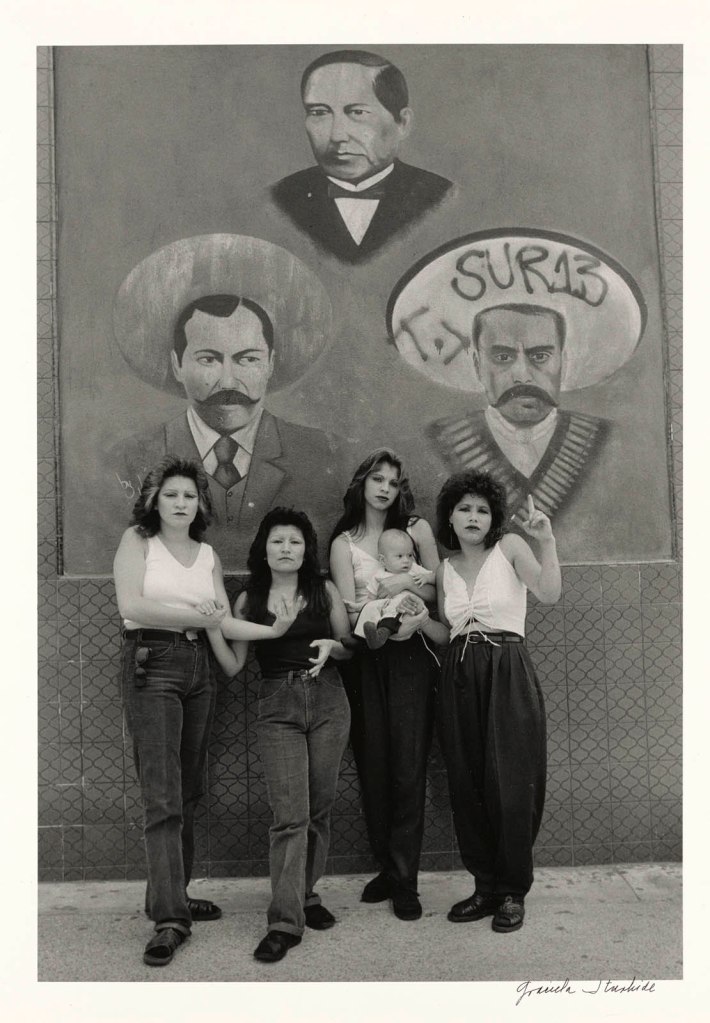

Graciela Iturbide (Mexican, b. 1942)
Cholos, White Fence, East Los Angeles
1986
Gelatin silver print
Framed: 57.5 x 42.2cm (22 5/8 x 16 5/8 in.)
Sheet: 35.2 x 27.7cm (13 7/8 x 10 7/8 in.)
Image: 32 x 21.9cm (12 5/8 x 8 5/8 in.)
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles, Gift of Leslie and Judith Schreyer and Gabri Schreyer-Hoffman in honour of Virginia Heckert
© Graciela Iturbide
Graciela Iturbide’s Cholo/as series from 1986 Los Angeles is perhaps the best encapsulation of the show’s thesis. The women in Cholos, White Fence, East Los Angeles told Iturbide that they wanted to be photographed under a mural of some mariachis. In fact, these were images of Emiliano Zapata, Benito Juárez and Pancho Villa. We might as well admire their freedom from context. After all, isn’t America all about freedom?
Dan Duray. “One Fine Show: ‘Picturing the Border’ at the Cleveland Museum of Art,” on the Observer website 09/06/2024 [Online] Cited 01/11/2024
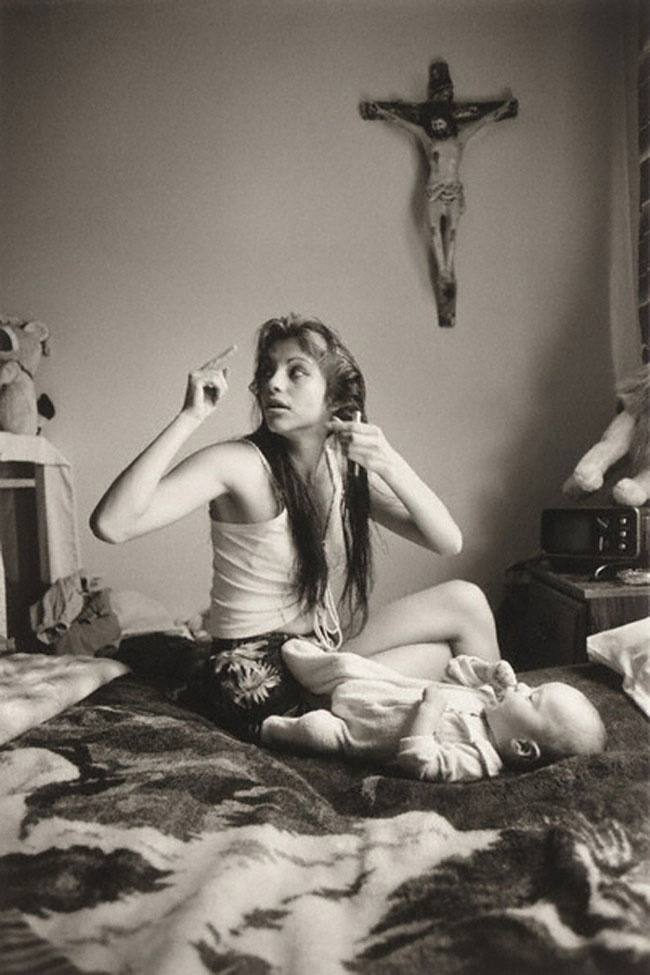

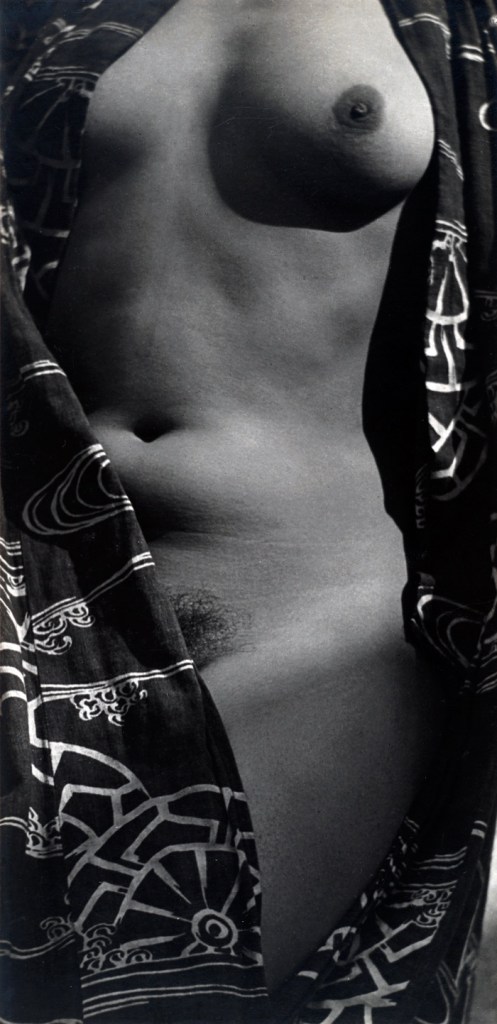
Graciela Iturbide (Mexican, b. 1942)
Rosario y Boo Boo en su casa, Los Angeles (Rosario and Boo Boo in their home, Los Angeles)
1986
Gelatin silver print
“Without the camera you see the world one way, with it, you see the world another way. Through the lens you are composing, dreaming even, with that reality, as if through the camera you are synthesising who you are… So you make your own image, interpreting.”
Graciela Iturbide
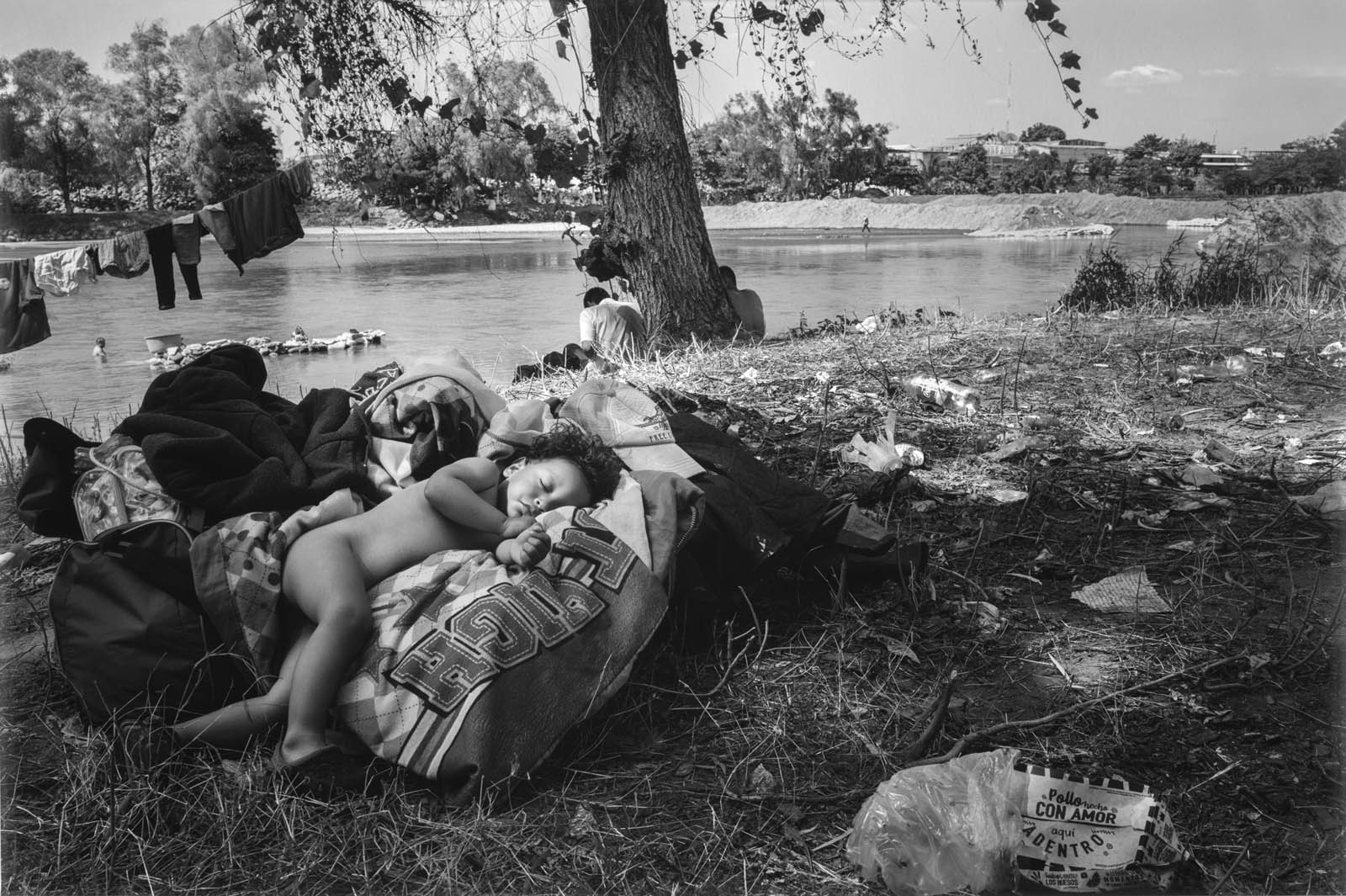
Ada Trillo (Mexican American, b. 1976)
Sleeping by the River, Tecun-Uman Guatemala
2020
Digital print
Framed: 54.4 x 79.7cm (21 7/16 x 31 3/8 in.)
Image: 50.8 x 76.2cm (20 x 30 in.)
The Cleveland Museum of Art, Gift of the Artist
© Ada Trillo
As Los Angeles is located over 100 miles north of Mexico, Iturbide’s work demonstrates that while the border is a physical space, its communities defy any single geographical boundary.
This argument echoes in photos made over 1,500 miles away by photographer Ada Trillo, who grew up on the liminal lands between El Paso, Texas, and Ciudad Juárez, Mexico. In her photobook on view in the exhibition, titled La Caravana del Diablo (2022), the artist documents three journeys: two alongside migrant people in caravans attempting to cross into Mexico on their way to the US border and a third aboard La Bestia, the infamous freight train that hundreds of thousands of Central American migrants ride each year to the north of Mexico – risking injury and death in the process. Trillo’s works are primarily populated by people from Honduras, El Salvador, and Guatemala, representing deep friendships the artist formed over days and weeks of gruelling travel. …
Trillo’s works, like those of other artists in the exhibition, capture how the border forces migrants and other communities to weave their stories within a maddening architecture of violence that is both systematic and capricious. “Many of the photographers in this show were inspired by one another,” Rivera Fellah explained. “And many have used their politically engaged photographic practices as a counter-narrative to derogatory images of the border that have circulated in the media since the 1970s and 1980s.”
Kayla Aletha Welch. “Photography Show Aims to Upend Xenophobic Border Narratives,” on the Hyperallergic website July 18, 2024 [Online] Cited 01/11/2024
Ada Trillo – La Caravana del Diablo
Hardcover/Sewn bound
192 pages/30.5 x 24.8cm
Language: English
ISBN: 978-94-91525-93-3
November 2021
Every day, thousands of people leave in processions from Guatemala, Honduras and El Salvador via Mexico for America because of flaring violence, murder (on women) and poor economic conditions in their own country. A journey covering hundreds of kilometres, often on foot, full of fear of being arrested and sent back. Some people even ‘disappear’. Under the Trump administration, despite fierce opposition, ‘The Wall’ was built to keep these immigrants out of ‘The Northern Triangle’, making their passage into America even more perilous.
Photographer Ada Trillo considers it her mission to portray this distressing situation. In ‘La Caravana del Diablo’ she doesn’t look away but confronts us. Ada shows that each of these thousands of migrants is a human being. A human being with a family, with fear, hope and dreams.
Text from the Houston Centre for Photography website
More than three thousand kilometers of border have unified the United States and Mexico since the mid-nineteenth century. Some 8,000,000 people live, sometimes in suspense, on both shores of a division as arbitrary as it is controversial. A dividing line that has changed throughout history, affecting those who have remained on one side or the other.
This same space, mythical, liminal, polemic, has become, in the last half-century, above all, one of the most watched and controlled landscapes of the entire planet. It has also become one of the most vulnerable: millions of Mexicans, Central Americans, and many other nationalities have crossed – or tried to cross – the border.
Picturing the Border, a photographic exhibition curated by Nadiah Rivera Fellah[2] and open to the public from July 21, 2024, to January 5, 2025, at the Cleveland Museum of Art, shows other aspects of those living there. The exhibition gathers images taken between the 1970s and the present by North American and Mexican artists such as Louis Carlos Bernal, Graciela Iturbide, Laura Aguilar, Ada Trillo, Guadalupe Rosales, and Miguel Fernández de Castro. The photographs present alternative proposals for understanding and reading the border by placing the people who inhabit it in the spotlight, thus challenging fixed and stereotypical conceptions of identity and culture.
In this exhibition, as in real life, the border stands as a third space, in the same sense proposed by Homi Bhabha: that intermediate space of cultural encounters and dis-encounters from which a new site of enunciation emerges and in which the binary is deconstructed[3]. Edward Soja, in an approach similar to Bhabha’s, regarding the ‘hybridity’ of the spaces of encounters of cultures, defines the thirdspace as the place where “everything comes together… subjectivity and objectivity, the abstract and the concrete, the real and the imagined, the knowable and the unimaginable, the repetitive and the differential, structure, and agency, mind and body, consciousness and the unconscious, the disciplined and the transdisciplinary, everyday life and unending history.”[4] According to Gloria Anzaldúa, “the convergence [of Mexico and the United States] has created a shock culture, a border culture, a third country, a closed country”[5].
But, what do the exhibited photos tell us about this ‘third space,’ this ‘third hybrid country’ that exists between the United States and Mexico? That third country is occupied not only by illegal migration and drug trafficking – the primary approach from the media – but also by symbols deeply rooted in Mexican and border life, such as the Virgin of Guadalupe, the Cholo culture, the use and appropriation of iconic North American products (such as cars) by Mexican Americans, the Day of the Dead celebrations. These photos open a window for us to look, with respect and wonder, at the life that goes on in private and public spaces, often in a very different way than that imagined by those of us who are not directly associated with that geography. It also reminds us of the student and labor protests and strikes that have taken place in that region.
Damaris Puñales-Alpízar. “The Border That Unites: Picturing the Border, at the Cleveland Museum of Art,” on the CANJournal website October 29, 2024 [Online] Cited 01/11/2024
[3] See: Bhabha, Homi. The Location of Culture. Routledge, New York, 1994.
[4] See: Soja, Edward W. Thirdspace. Malden (Mass.): Blackwell, 1996, p. 57.
[5] This phrase presides over the exhibition.
Laura Aguilar (American, 1959–2018)
Yrenia Cervantes
1990
Gelatin silver print
Image: 22.9 x 30.5cm (9 x 12 in.)
Paper: 27.9 x 35.6cm (11 x 14 in.)
The Cleveland Museum of Art
Karl B. Goldfield Trust
© Laura Aguilar Trust
Far from being a flash in the proverbial pan, the border has long incarnated questions about the arbitrary nature of insider and outsider dynamics, legality, and citizenship.
Among the works exploring these themes is the late photographer Laura Aguilar’s black-and-white portrait “Yrenia Cervantes” (1990), in which the titular Chicana muralist and artist stares at her reflection in her dresser mirror. Her bedroom is decorated in the elaborate style of an altar: It includes photos, iconography, and handmade objects. Cervantes is simultaneously of the border and beyond it – the viewer can’t easily determine to which side she belongs.
Kayla Aletha Welch. “Photography Show Aims to Upend Xenophobic Border Narratives,” on the Hyperallergic website July 18, 2024 [Online] Cited 01/11/2024

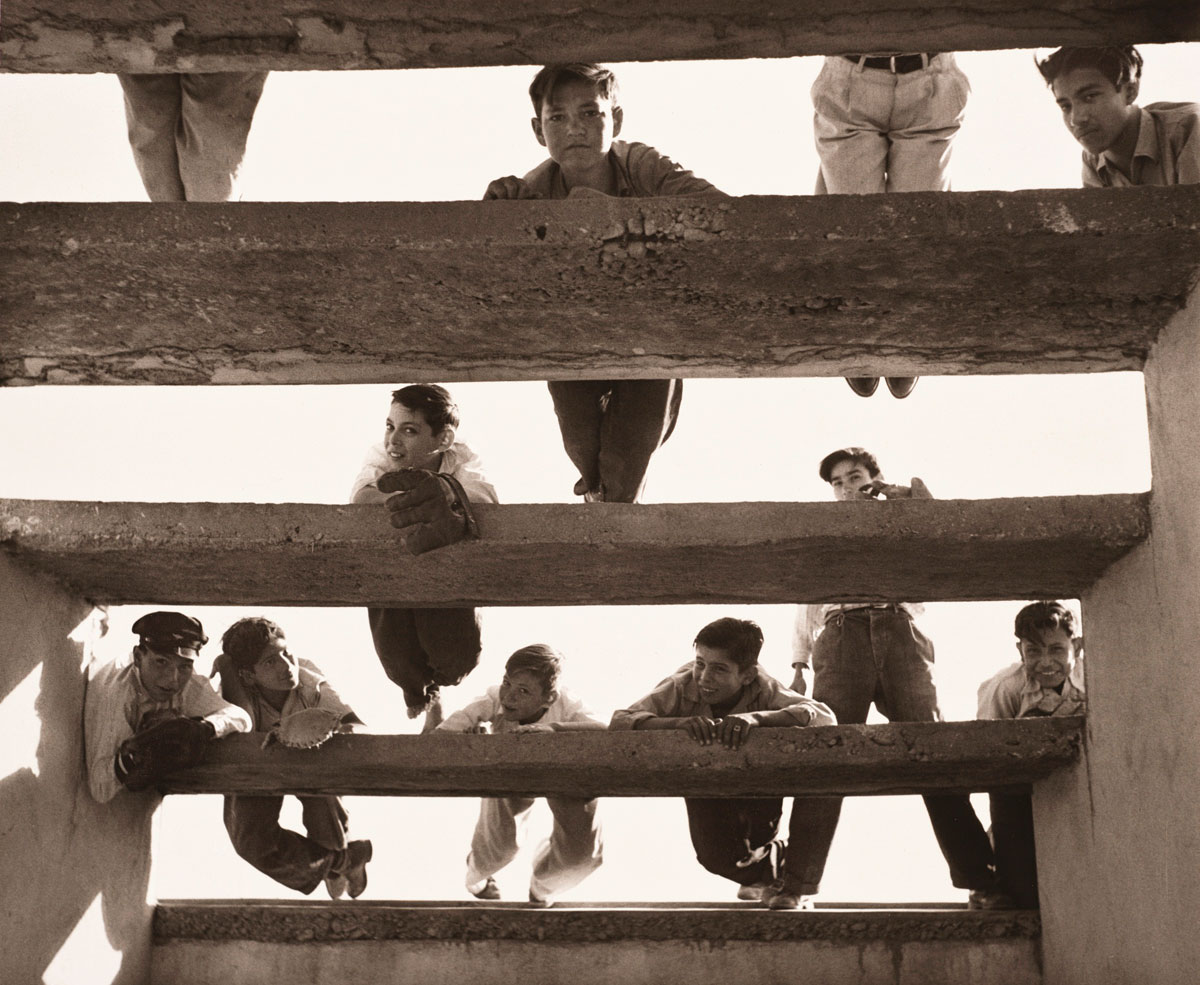
Louis Carlos Bernal (American, 1941-1993)
Albert and Lynn Morales, Silver City, New Mexico
1978

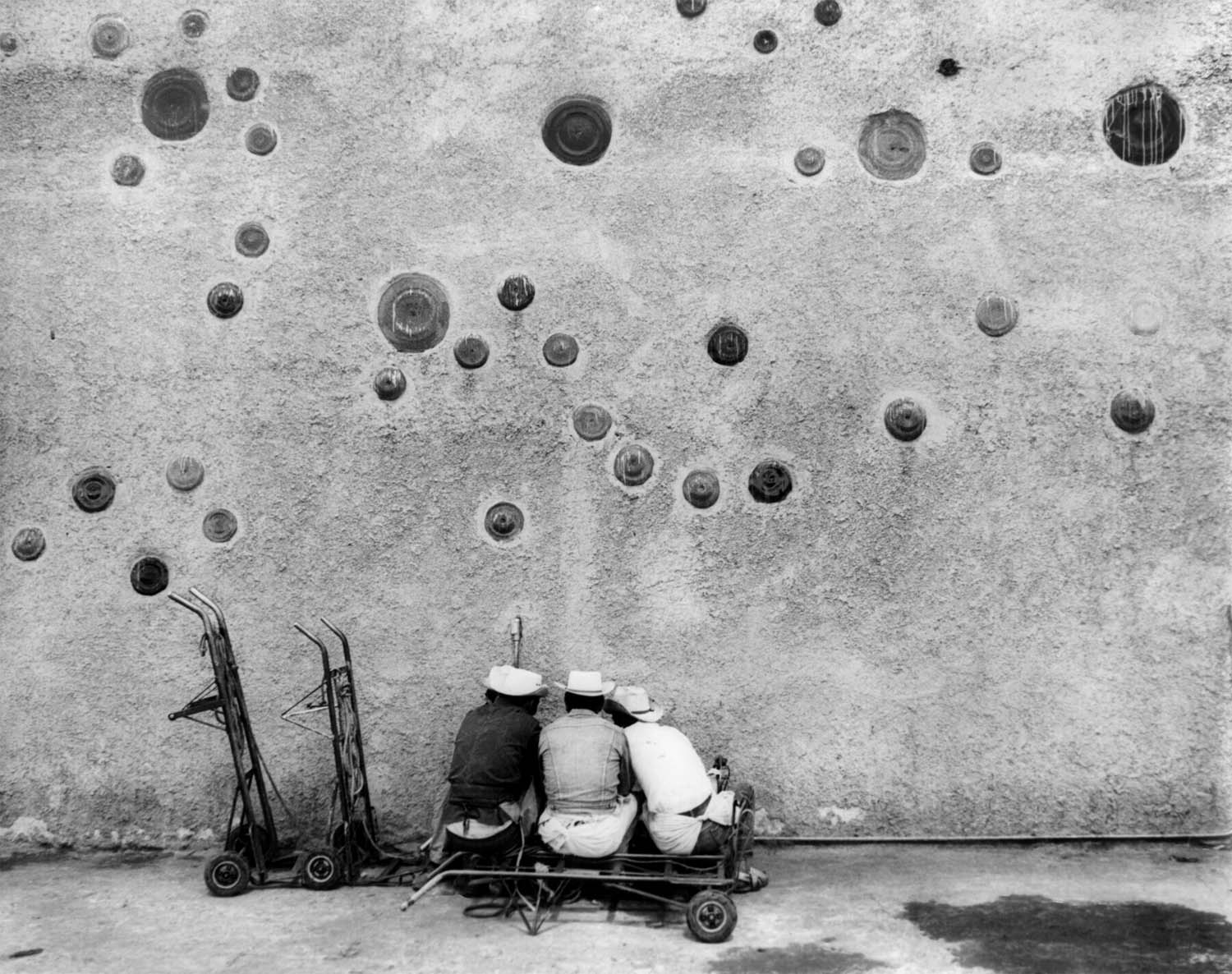
Louis Carlos Bernal (American, 1941-1993)
La Reina de mi Vida (The Queen of my life)
1983
Gelatin silver print
![Louis Carlos Bernal (American, 1941-1993) 'Untitled [Undocumented worker holding Huelga flag at United Farm Workers Demonstration, El Mirage, Arizona]' Negative 1978, printed 2016 Louis Carlos Bernal (American, 1941-1993) 'Untitled [Undocumented worker holding Huelga flag at United Farm Workers Demonstration, El Mirage, Arizona]' Negative 1978, printed 2016](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/ask-58_ccp_bernal_ag182-20230302-110020.jpg)
Louis Carlos Bernal (American, 1941–1993)
Untitled [Undocumented worker holding Huelga flag at United Farm Workers Demonstration, El Mirage, Arizona]
Negative 1978, printed 2016
Digital inkjet print
40.6 x 40.6cm (16 x 16 in.)
Collection of the Center for Creative Photography, University of Arizona, Louis Carlos Bernal Archive, Courtesy of Lisa Bernal Brethour and Katrina Bernal
© Lisa Bernal Brethour and Katrina Bernal
Ricardo Valverde (American/Chicano, 1946-1998)
Whittier Blvd
1979
Gelatin silver print

Exhibition catalogue showing on the cover a photograph by Ricardo Valverde titled La Reina (The Queen) 16th September 1976
Cleveland Museum of Art
11150 East Boulevard
Cleveland, Ohio 44106
Opening hours:
Tuesdays, Thursdays, Saturdays, Sundays 10.00am – 5.00pm
Wednesdays, Fridays 10.00am – 9.00pm
Closed Mondays


























You must be logged in to post a comment.