Exhibition dates: 20th May – 12th September 2010
Yves Klein (French, 1928-1962)
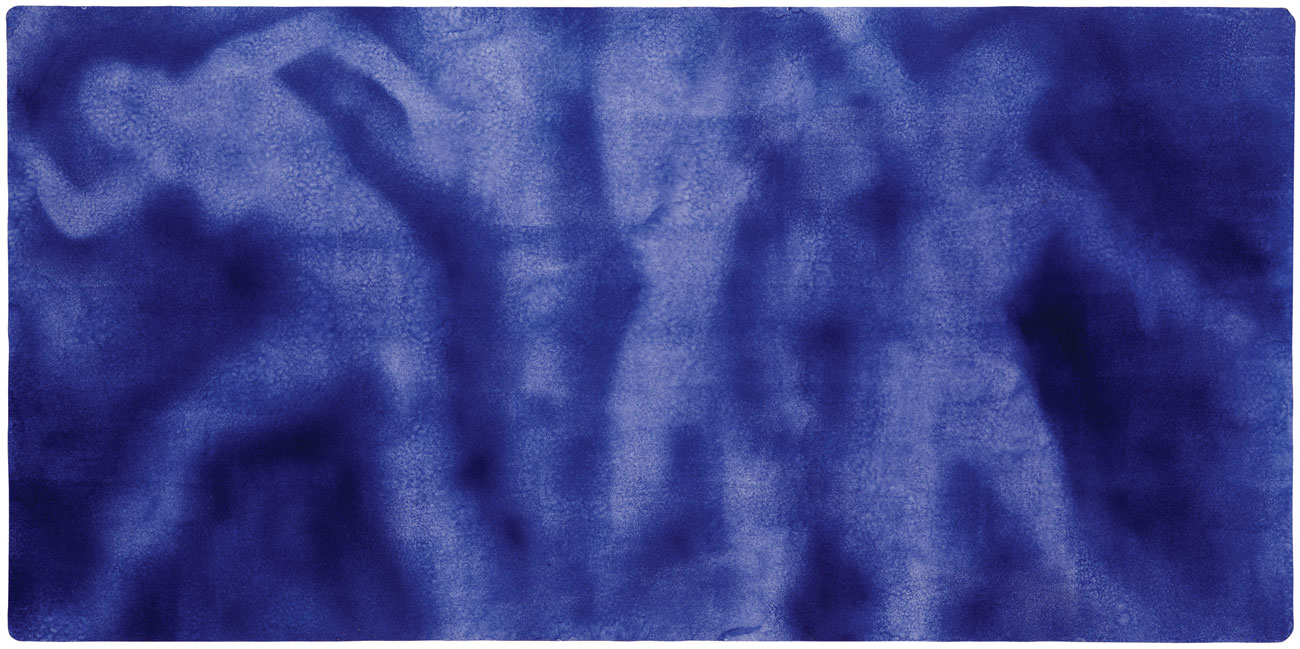
Hiroshima
c. 1961
Dry pigment and synthetic resin on paper mounted on canvas
© The Estate of Yves Klein c/o ADAGP, Paris
Space [ ] the final frontier … where silence is golden !
Many thankx to the Hirshhorn Museum and Sculpture Garden for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image. See all the Hirshhorn Flicker photosets of Yves Klein.
“I am the painter of space. I am not an abstract painter but, on the contrary, a figurative artist, and a realist. Let us be honest, to paint space, I must be in position. I must be in space.”
Yves Klein

Yves Klein (French, 1928-1962)
Untitled Yellow and Pink Monochrome
1955
Dry pigment and binder on canvas
22 x 13 1/2 inch
© The Estate of Yves Klein c/o ADAGP, Paris

Yves Klein (French, 1928-1962)
La Vent du voyage (The Wind of the Journey)
c. 1961
Dry pigment and synthetic resin on canvas
37 x 29 1/2 inch
© The Estate of Yves Klein c/o ADAGP, Paris

Yves Klein (French, 1928-1962)
Le Saut dans le Vide (Leap into the Void)
1960
Gelatin silver print

Yves Klein (French, 1928-1962)
Untitled Green Monochrome
c. 1954
Pure pigment and binder on paper
© The Estate of Yves Klein c/o ADAGP, Paris

Yves Klein (French, 1928-1962)
Architecture de l’air (Air Architecture)
1961
Dry pigment and synthetic resin on paper mounted on canvas
103 x 84 inch
© The Estate of Yves Klein c/o ADAGP, Paris
One of the 20th century’s most influential artists, Yves Klein (French, b. Nice, 1928; d. Paris, 1962), took the European art scene by storm in a prolific but brief career that lasted only from 1954 to 1962. Yves Klein: With the Void, Full Powers, on view at the Hirshhorn May 20 through Sept. 12, is the first major retrospective of the artist’s work in the United States since 1982. Co-curated by the Hirshhorn’s deputy director and chief curator Kerry Brougher and Dia Art Foundation director, former chief curator and deputy director at the Walker Art Center in Minneapolis, the exhibition is co-organised by the Hirshhorn and the Walker and developed in full collaboration with the Yves Klein Archives in Paris.
Presenting approximately 200 works, Yves Klein: With the Void, Full Powers explores the full range of the artist’s body of work and offers an essential overview and examination of a career that marked a key transition in 20th-century art. His work embodied an understanding of art beyond a western conception of modernity, beyond the object and beyond traditional notions of what art can be.
“Klein’s short but intense career is a pivotal moment in contemporary art history,” said Brougher. “His work questioned what art and even society could be in the future, and it provided new pathways leading to pop art, minimalism, conceptual art, installation and performance.”
The exhibition features examples from all of Klein’s major series, from his iconic blue monochromes and Anthropometries to sponge reliefs, Fire Paintings, “air architecture” projects, Cosmogonies and planetary reliefs as well as many works that have rarely been on view. The installation provides insight into the artist’s process and conceptual endeavours through an array of ephemera, including sketches, photographs, letters and writings. Several films, including performances and documentaries, further demonstrate Klein’s creative practice.
“I would like that when people leave the exhibition they leap into a void, leaving behind traditional notions of art and representation, but even more importantly, questioning the notion of materiality and materialism in art as well as in their lives,” said Vergne. “Ultimately, Klein’s lesson is about a different way of being together.”
Numerous objects are on loan directly from the Yves Klein Archives, with additional loans from the Musée National d’Art Moderne, Centre Pompidou in Paris, Kunstmuseen Krefeld in Krefeld, Germany, The Menil Collection in Houston, the Museum of Contemporary Art in Tokyo, the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art and a host of international private collections, including a rare loan from the Monastery of Saint Rita in Cascia, Italy.
Klein was an innovator and visionary whose goal was no less than to radically reinvent what art could be in the postwar world. Through a diverse practice, which included painting, sculpture, performance, photography, music, architecture and writing as well as plans for projects in theatre, dance and cinema, he shifted the focus of art from the material to “immaterial sensibility”; he levitated art above the weariness induced by the Second World War, resurrecting its avant-garde tendencies, injecting a new sense of spirituality and opening doors for much that followed in the 1960s and beyond.
Self-identified as “the painter of space,” Klein sought to achieve immaterial sensibility through pure colour, primarily an ultramarine blue of his own invention – International Klein Blue. This exhibition begins by examining Klein’s early explorations of colour with works in pastels, watercolours and more than 15 coloured monochromes created during the mid-to-late 1950s. Several significant blue monochromes, dating from as early as 1955 up through 1961, are on view. Klein further pushed boundaries in his engagement with colour and form by using pure pigment in tandem with unconventional materials, such as natural sponges. The sponge, which Klein incorporated into his practice in the late 1950s, became a metaphor, as its porous surface completely absorbed his signature colour, giving a material presence to the immaterial.
Among Klein’s best-known works are the Anthropometries, begun in 1958. Under the artist’s direction, nude female models were smeared with International Klein Blue paint and used as “living brushes” to make body prints on prepared sheets of paper. Klein wanted to record the body’s physical energy, and the resulting images represent the model’s temporary physical presence. More than an expression of the inner psyche of the artist, these paintings offer one method of giving visual presence to a cosmic, spiritual body, which neither photography nor film can fully capture. Seven works from this series are on view, including People Begin to Fly (1961) from The Menil Collection and Untitled Anthropometry (1960) from the Hirshhorn’s collection, which features the bodies of Klein and his future wife Rotraut Uecker.
In the late 1950s, but most notably in 1961, Klein began to use fire, which he considered “the universal principle of expression,” as part of his creative process. His Fire Paintings, such as Untitled Fire Painting (1961), in which fire either replaced or was combined with paint, embody concepts of process, transformation, creation, destruction, dissolution and elemental cosmology that were so essential throughout his career. The final galleries of the exhibition include examples from Klein’s “air architecture” projects, including drawings, plans and models for architectural spaces, such as fountains and walls, constructed out of natural elements like air, water and fire – elements that were not traditionally associated with architecture.
Klein created what he considered his first artwork when he signed the blue sky above Nice in 1947, making his first attempt to capture the immaterial. In his celebrated 1958 exhibition Specialization of Sensibility in the Raw Material State of Stabilized Pictorial Sensibility, better known as The Void, at Galerie Iris Clert in Paris, Klein went further by emptying the gallery of all artworks and painting the walls white. Among those who attended the renowned exhibition was Albert Camus, who reacted with a notable entry into the visitors’ album: “with the void, full powers.” In his famous Leap into the Void (1960) image by Harry Shunk and Janos Kender, which was published Nov. 27, 1960, in the faux newspaper Dimanche, which he created for the second Avant-Garde Art Festival, Klein is actually depicted leaping into space himself; the accompanying text asserts: “… to paint space, I must be in position. I must be in space.”
Defying the common understanding and definitions of art – from his experiments with architecture made of air to his leap into the void – Klein aimed to rethink the world in spiritual and aesthetic terms. His philosophy was revolutionary and demonstrated his acute grasp of the contemporary moment, from the horror of the Second World War to the promise of space travel. This presentation of his full oeuvre is essential to discern the shift from modern to contemporary practice and to reveal the extent of the artist’s influence.
Press release from the Hirshhorn website [Online] Cited 04/09/2010 no longer available online

Yves Klein (French, 1928-1962)
Lune II (Moon II)
1961
Pure pigment and undetermined binder on plaster
© The Estate of Yves Klein c/o ADAGP, Paris

Yves Klein (French, 1928-1962)
Untitled Blue Monochrome
1959
© The Estate of Yves Klein c/o ADAGP, Paris
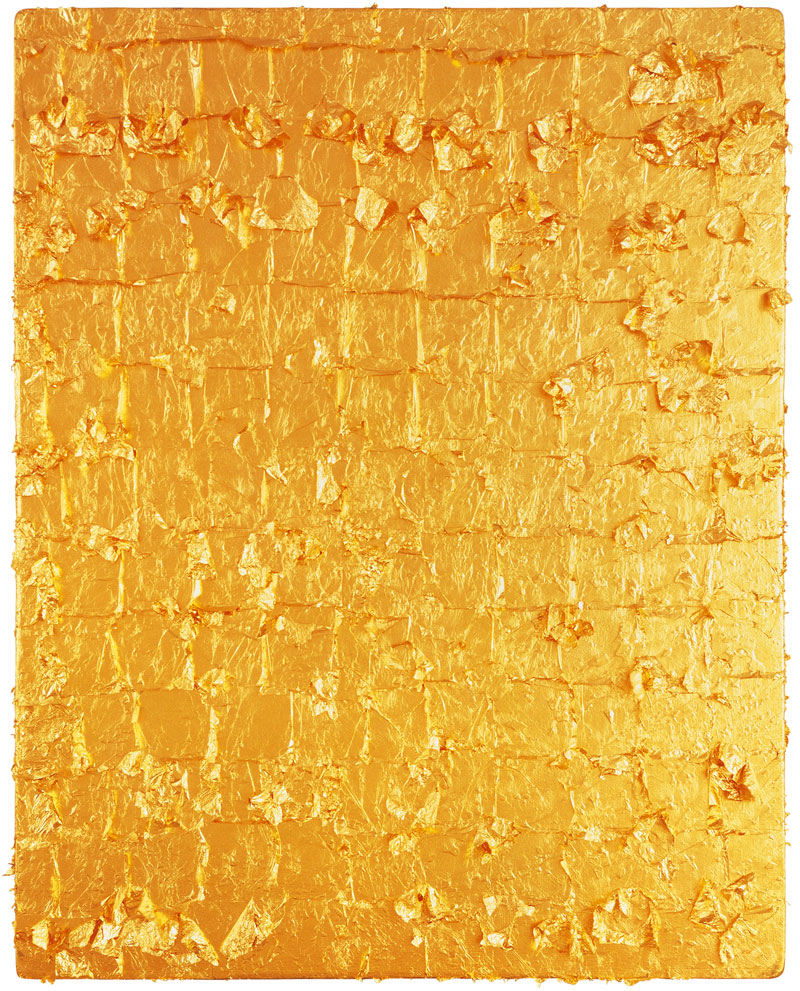

Yves Klein (French, 1928-1962)
Untitled Gold Monochrome
1962
Gold leaf on wood
© Yves Klein, ADAGP, Paris / SAVA

Yves Klein (French, 1928-1962)
La Rêve du Feu (The Dream of Fire)
c. 1961
Yves Klein, ADAGP, Paris / DACS
Harry Shunk and János Kender, photograph of Yves Klein, The Dream of Fire, c. 1961. Artistic action by Yves Klein.

Yves Klein (French, 1928-1962)
Le Silence est d’or (Silence is Golden)
1960
Gold leaf on wood
© Yves Klein, ADAGP, Paris / SAVA
Hirshhorn Museum and Sculpture Garden
The Hirshhorn is located on the National Mall at the corner of 7th Street and Independence Avenue SW, Washington, D.C.
Opening hours:
Open daily except December 25
10am – 5.30pm






You must be logged in to post a comment.