November 2023
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
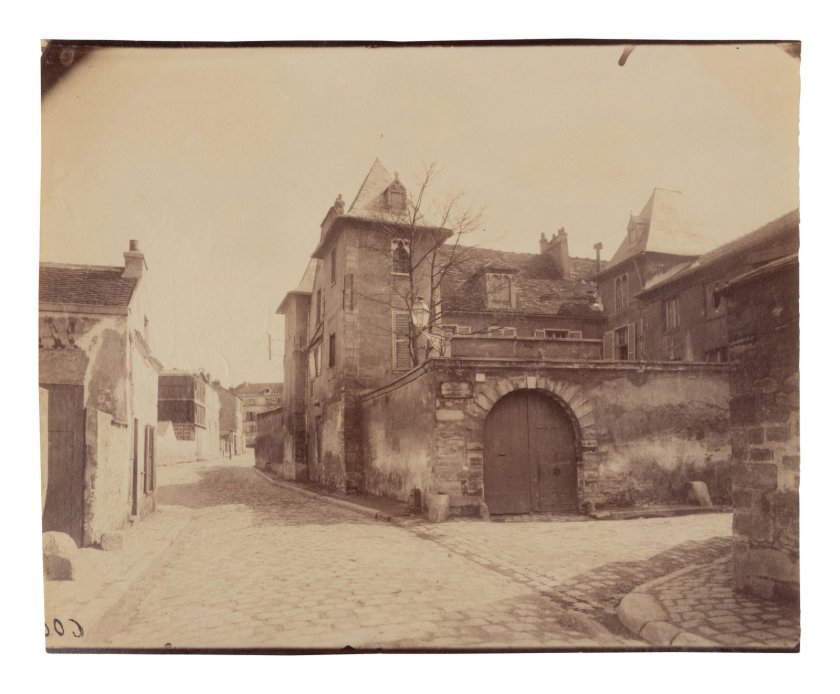
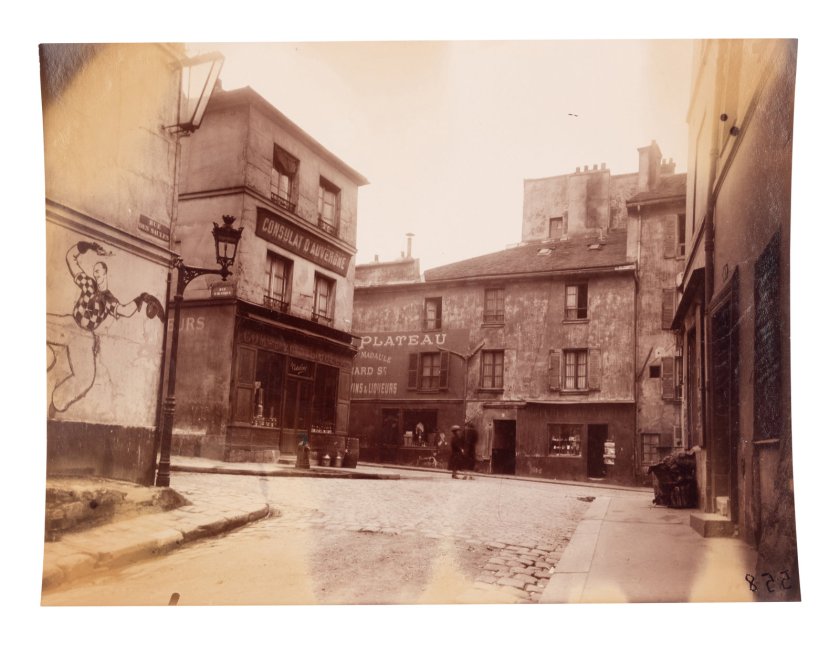
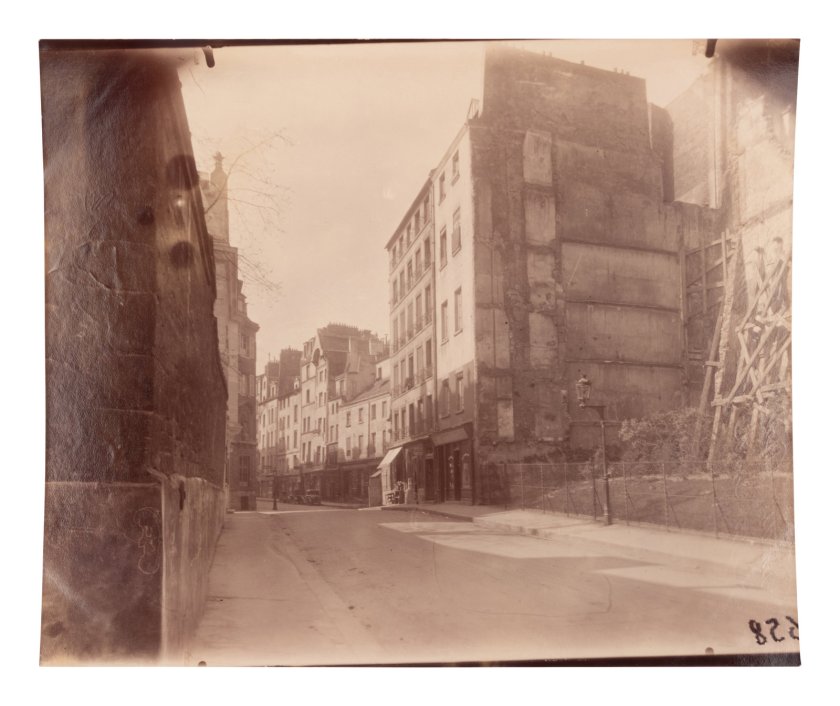
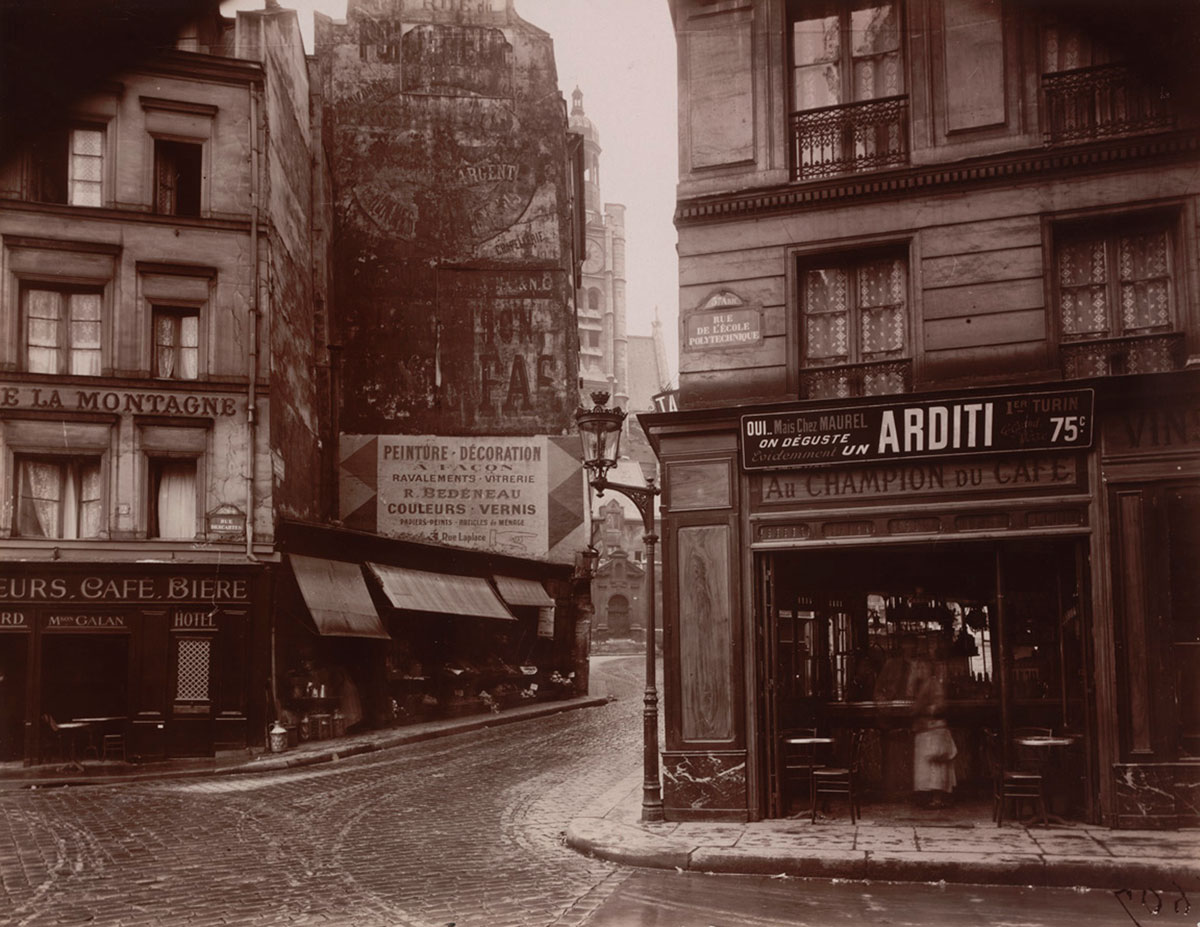
Rue Saint-Médard, 5e arrondissement
1899-1900
Albumen print
I am devastated at news of the loss of my very close friend and photographer Ian Lobb today.
An intelligent, compassionate, creative and spiritual man who was a guiding light during the last 33 years of my life.
He said of Atget, “You always have a sense of feeling self surprised at where his camera is.”
Atget was always an inspiration to us both.
Bless him for his wise counsel all these years.
A tribute will appear at a later time.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Again
Why are the waves,
Coming straight at me?
Fold upon fold
Waves in wind –
And why is the wind
Becoming my breath,
And my breath, the wind?
So now you
Beautiful friend
Breathe my friend
Jump the wave,
Jump up, laughing
The sun right above you,
Here on the coast
Among waves and trees.
Enter your home
Like a nest
Beautiful friend,
Dear friend,
Read till you sleep –
Your breath on the pages
That tell of the road and
On that road where you meet
Those twilight lit:
One, two,
Then three again.
Ian Lobb
“His prints are direct and emotionally clean records of a rare and subtle perception, and represent perhaps the earliest expression of true photographic art.”
Ansel Adams
“There is nothing I could ask for better than to roll myself between sheets of Atgets, each new one I find (and there are thousands) is a revelation.”
Julien Levy
“In looking at the work of Eugène Atget, a new world is opened up in the world of creative expression.”
Berenice Abbott
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Soleil
c. 1896
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Fontaine Jarente – impasse Jarente (Fountain Jarente – Jarente dead end)
1898
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Fontaine Minerve, Institut (Minerva Fountain, Institute)
1899
Albumen print
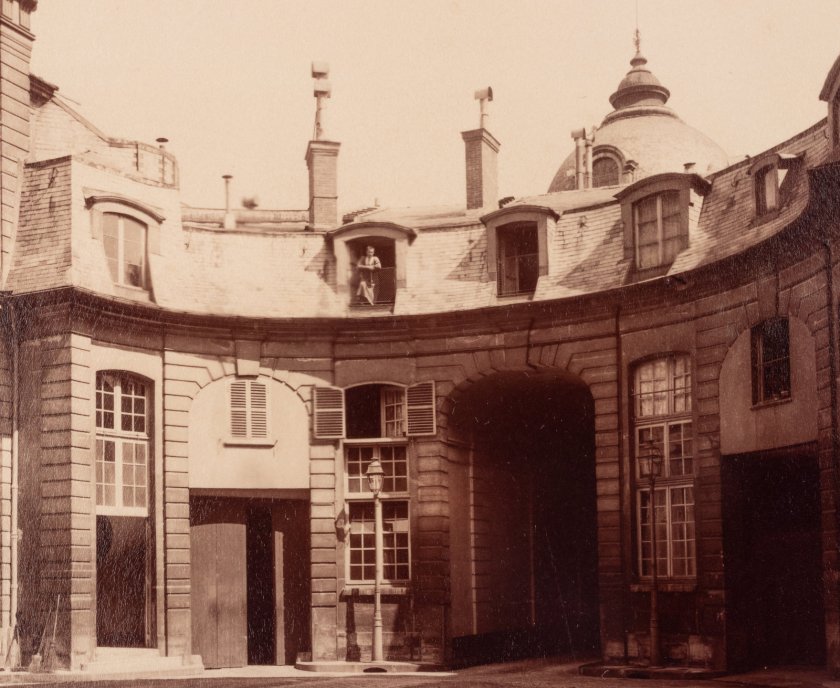
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
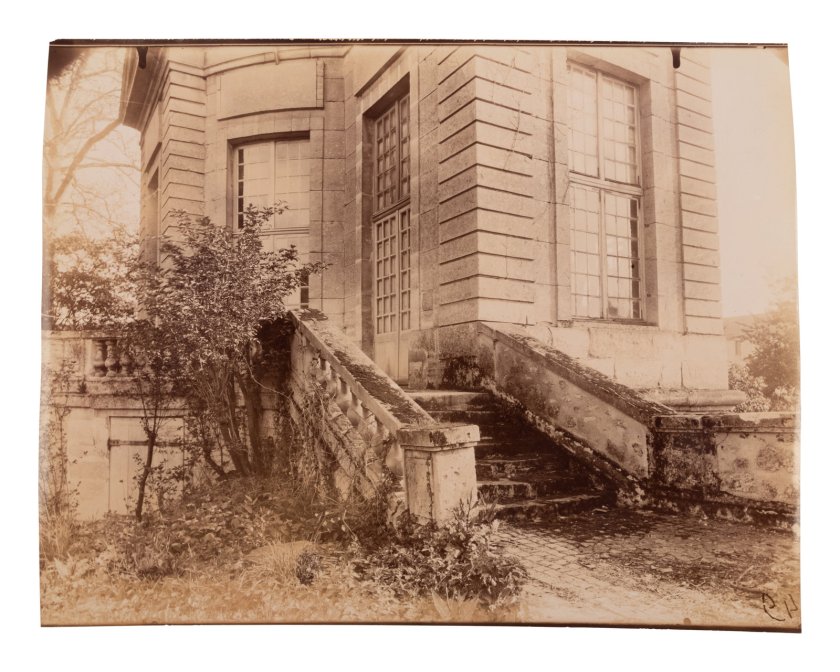
Hôtel de la Comtess de Verrue, rue du Regard
1899
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Avenue de l’Observatoire
1899-1900
Albumen print
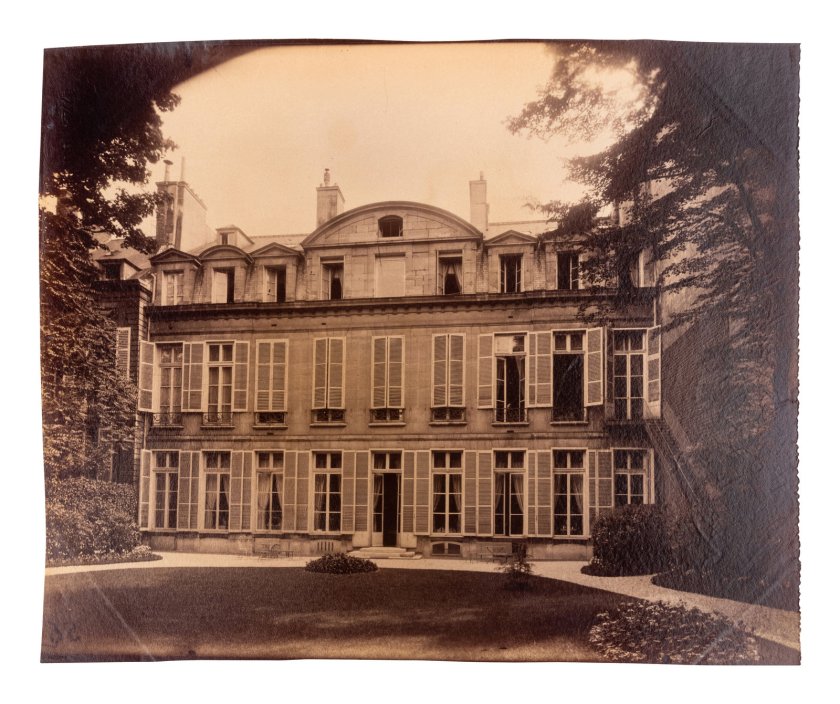
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Hôtel de Gouffier, rue de Varenne 56
1899-1900
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Cactus [Nice]
Before 1900
Albumen print
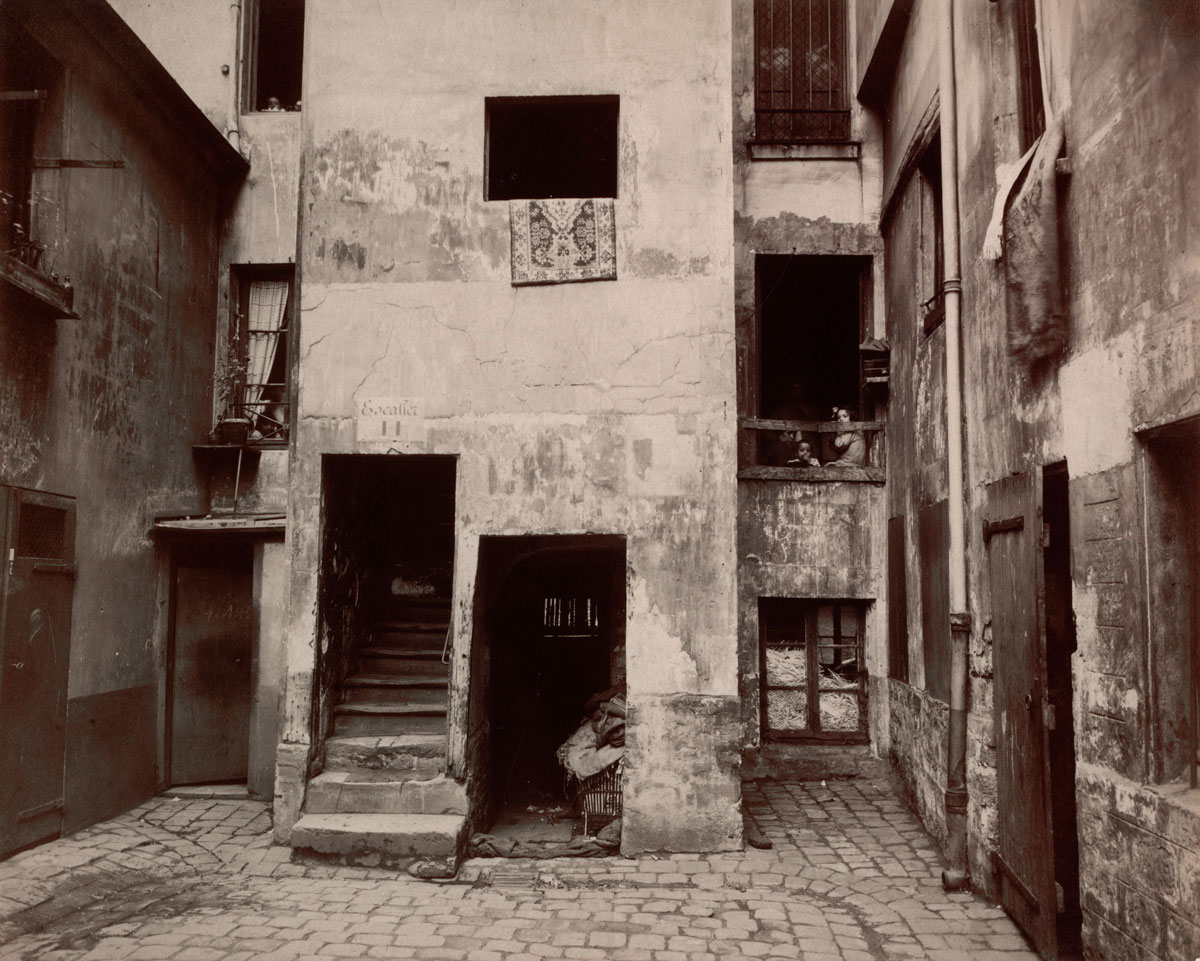
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
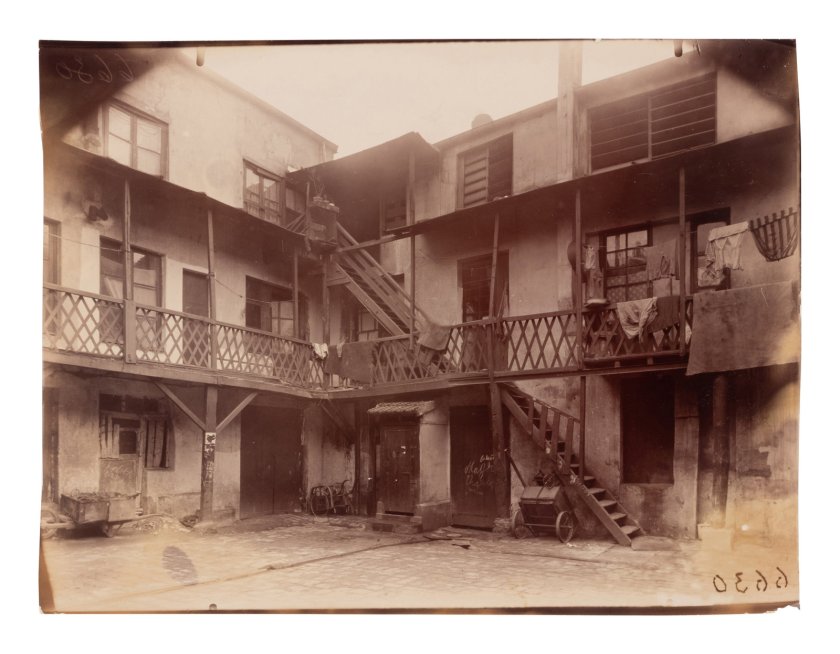
Cour, rue Saint-Jacques 346, disparu, 5e arrondissement (Court, rue Saint-Jacques 346)
1900
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Hôtel d’Argouges de Lyon, rue Séguier 16
1900
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Presbytère de Saint-Sulpice, rue de Vaugirard 50 (Presbytery of Saint-Sulpice)
1900
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
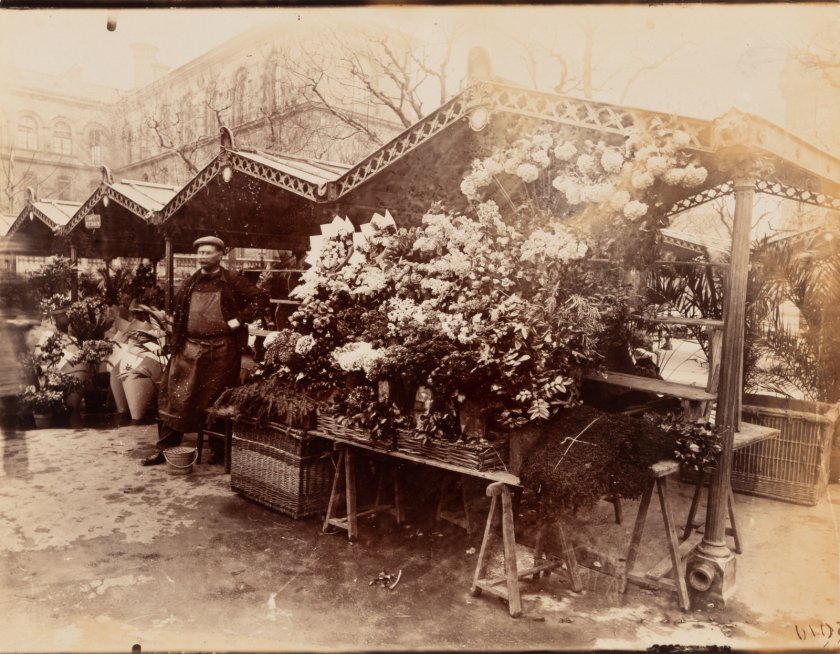
Marché aux fleurs (Flower market)
c. 1900s
Albumen print
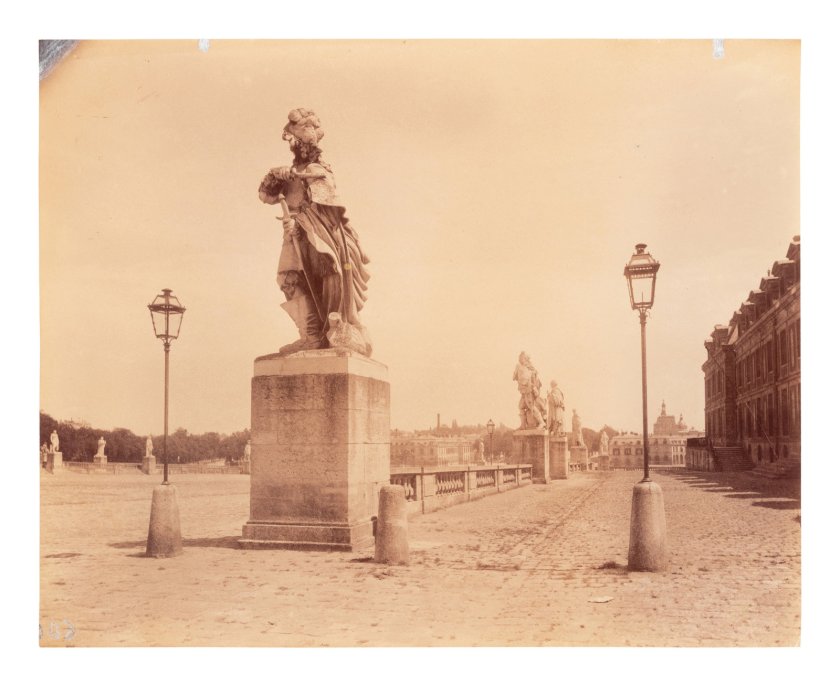
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
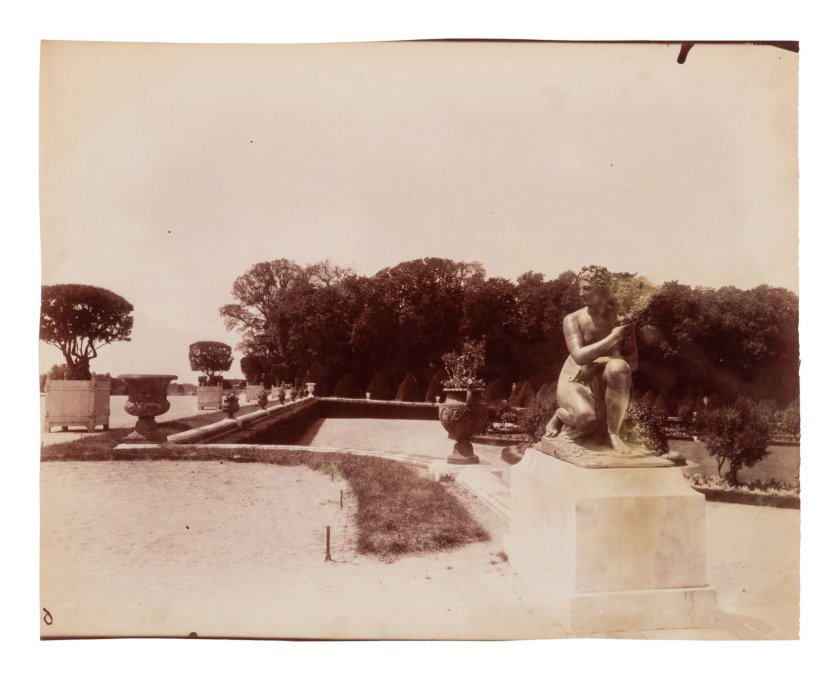
Cours d’Honneur, Versailles (Gentilly – old castle, Versailles)
1901
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Gentilly – ancien château
1901
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Hôtel Beauffremont, rue de Grenelle 87
1901
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Hôtel du Maréchal de Tallard, rue des Archives 78
1901-1902
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Grand Trianon Le Buffet
1902
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
La Vénus accroupie, par Coysevox (Versailles) (The Crouching Venus, by Coysevox, (Versailles))
1902
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
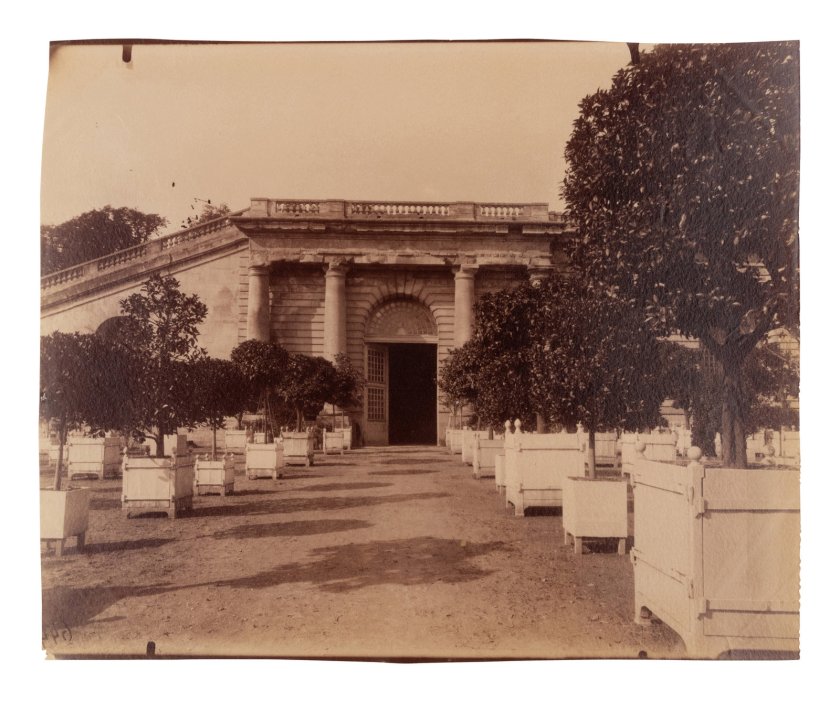
Versailles – l’Orangerie
1903
Albumen print
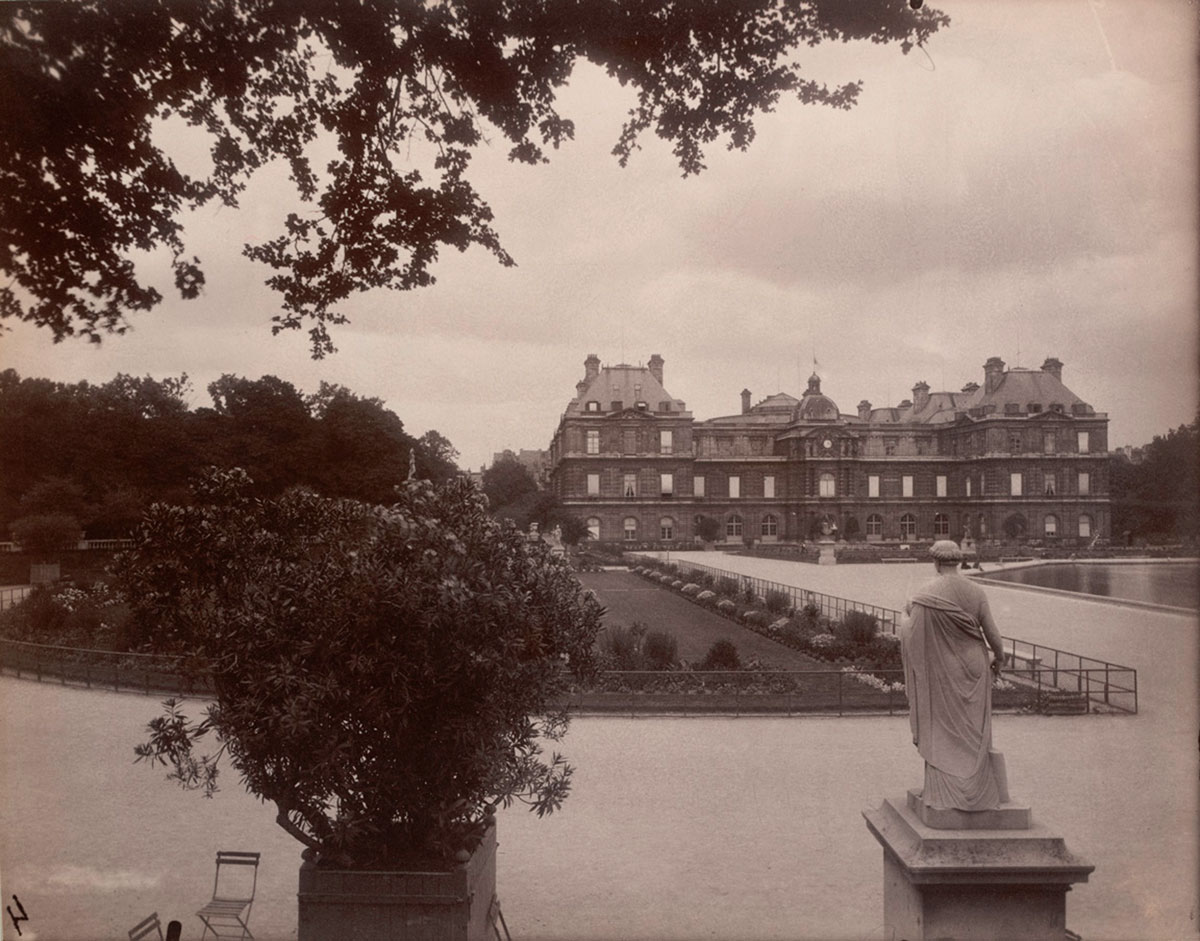
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Oratoire Marie de Médicis, Petit Luxembourg (Marie de Medici Oratory)
1903
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
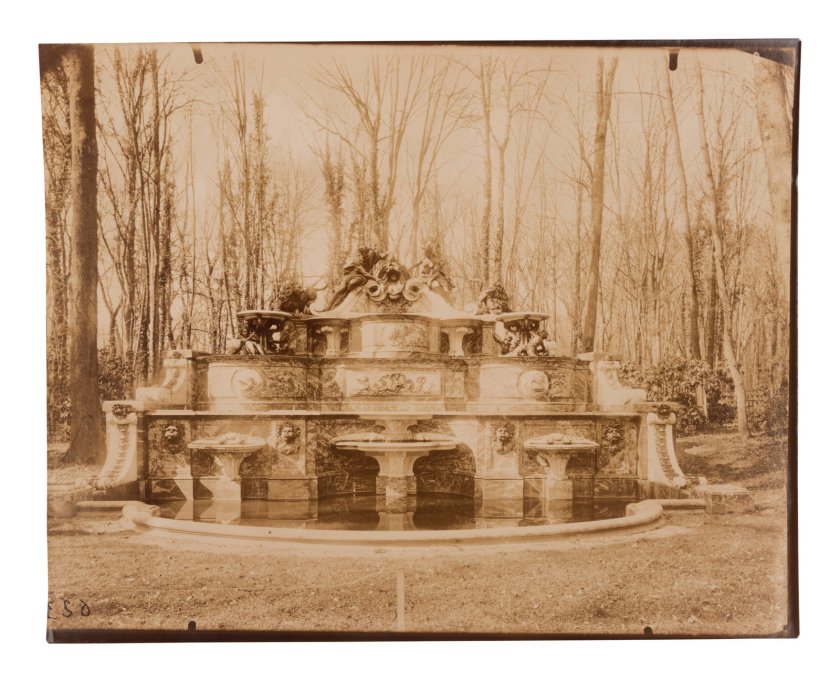
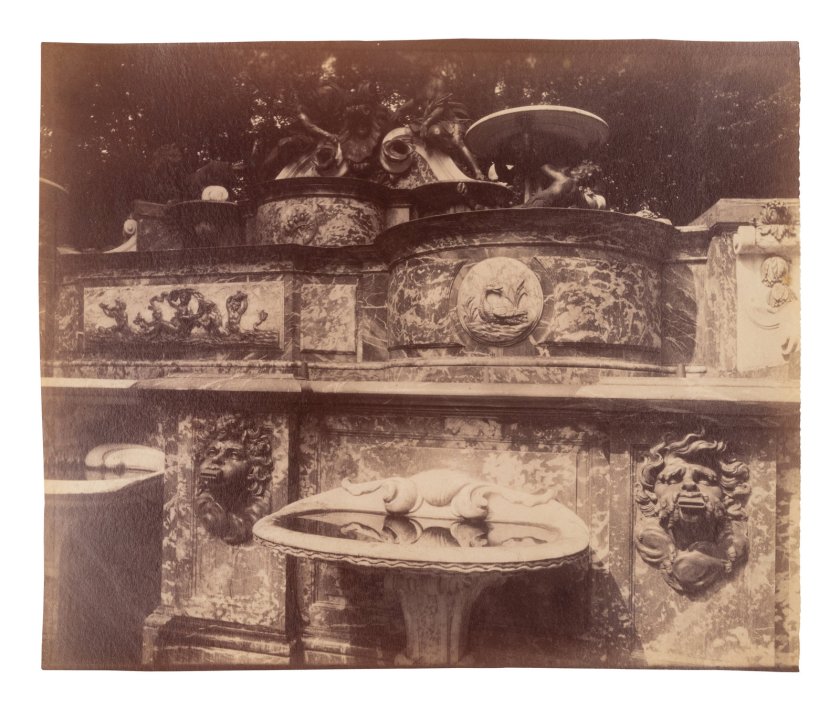
Fontaine du Marché Saint-Honoré (Saint-Honoré Market Fountain)
1903
Albumen print
Atget used a view camera with a bellows placed on a tripod, typical of the second half of the 19th century. He worked with 18 × 24 cm negative glass plates, oriented to obtain either a vertical or horizontal photograph. A tilt-shift technique was used to make perspective corrections. This resulted in vignetting (a circular shadow around the edges of the image), a phenomenon seen in a number of Atget’s photographs.
Atget always used gelatin-silver negative glass plates, 1.5mm thick. The plate was held in the camera in a wooden frame by clips that left characteristic marks on many of the prints. A long exposure time resulted in numerous blurs caused by the presence of moving people or objects. Atget developed the negatives himself and wrote the negative number directly onto the gelatin with a pointed stiletto.
Atget made all of his own photographic prints using a technique in which light-sensitive paper, in contact with the glass negative, was printed-out in natural light (never developed). The printing-out process proceeded until Atget determined that the image had the proper density. The photograph was then washed, gold toned, fixed and washed again. Atget’s prints are never black-and-white; their tone varies from deep sepia to violet-brown. Atget was capable of producing high-quality prints but there is great variation in these today depending on his printing and toning techniques and the way his photographs were preserved and exhibited. He never enlarged his photographs.
Atget’s paper
Atget used three types of paper:
Albumen
The light-sensitive emulsion was formed by silver chloride introduced into an albumen binder (beaten egg whites). The majority of Atget’s prints were on albumen paper. He turned to other processes after the First World War, when such paper could no longer be found on the market.
Matt albumen
After the war Atget used another kind of industrially produced printing-out paper with a matt surface.
Aristotype
Atget chose a commercially manufactured printing-out paper made with gelatin. Aesthetically similar to albumen prints, although thicker and with a glossier surface, the process was the same for toning and printing. Some of these prints have yellow stains from sulphuration due to poor processing of the image (such as the use of an exhausted fixing bath or insufficient washing).
Anonymous. “Atget’s technique,” on the Art Gallery of New South Wales website Nd [Online] Cited 03/10/2023
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Fontaine, rue Geoffrey Saint-Hilaire
1905
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Grand Trianon (escalier) (Grand Trianon (staircase))
1905
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Saint-Severin – rue Saint Séverin
1905-1906
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Grand Trianon – le Buffet
1906
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Maison, rue Saint-Romain [Rouen]
1907
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Nantes – fontaine et Mairie (Nantes – fountain and town hall)
1907
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Tuileries – Coureuse par Coustou (Tuileries – Runner by Coustou)
1907
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Hôtel d’Imbercourt, 15 rue de l’Universite
1909
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Folie Thoinard, 9 rue Coq-Héron
1909
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Façade Saint-Lazare, faubourg Saint-Denis 107
1909
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Hôtel de Vendôme, rue Béranger 3
1909
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Pommiers [et blés] (Apple trees [and wheat])
1910 or earlier
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Sapin ([Petit] Trianon)
1910 or earlier
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Colonne Moris (Place Saint Sulpice) (Morris Column (Place Saint Sulpice))
1910
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Hôtel de Canhillac, place des Vosges 14
1911-1912
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Fontaine, faubourg Saint-Martin (Fountain, Saint-Martin suburb)
1912
Albumen print
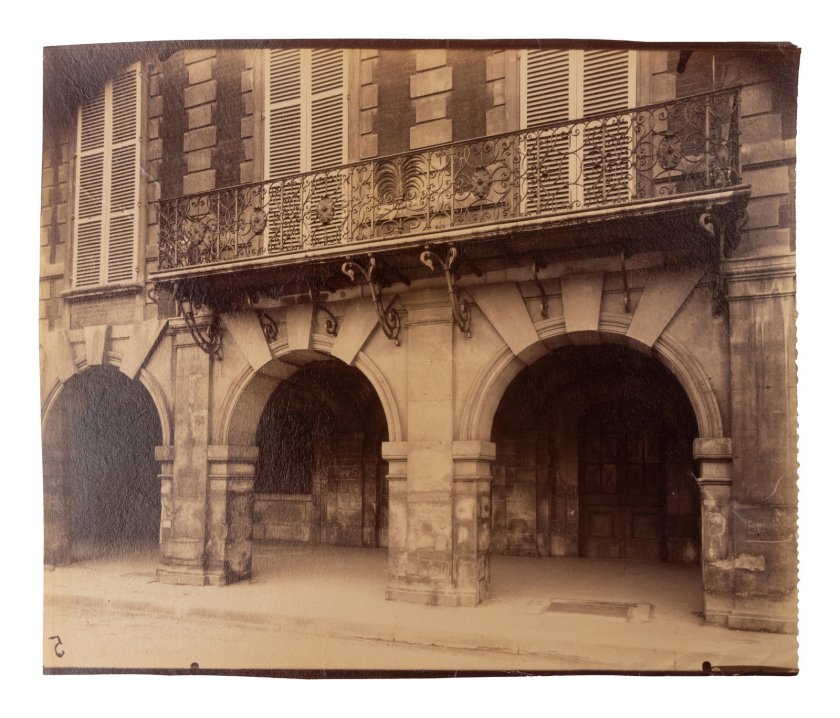
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Balcon, [15] rue du Petit Pont
1913
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Pavilion du Hanovre, boulevard des Capucines 33
1913
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Fête du Trône
1914
Albumen print
“My excitement at seeing these few photographs would not let me rest. Who was this man? I learned that Atget lived up the street from where I worked – at 17 bis rue Campagne Premiere, and that his prints were for sale. Perhaps I could own some. I wanted to see more, and lost no time in seeking him out. I mounted the four flights to his fifth floor apartment. On the door was a modest handmade sign, “Documents pour Artistes”. He ushered me into a room approximately fifteen feet long, the ordinary room of a small apartment, sparsely and simply furnished. Atget, slightly stooped, impressed me as being tired, sad, remote, appealing. He was not talkative. He did not try to “sell” anything. He showed me some albums, which he had made himself, and I selected as many prints as I could afford to pay for from my meager wages as a photographer’s assistant. I returned many times, and we became more friendly.” Several years passed and Berenice Abbott became a portrait photographer. “By that time I had become a portrait photographer on my own, and I persuaded Atget to come to my studio at 44 rue du Bac to sit for his portrait. To my surprise he arrived in a handsome overcoat. I had always seen him in his patched work clothes. It would have been desirable to photograph him in these too, since they were exquisitely photogenic, but time is a fickle unpredictable master and did not permit another sitting. After developing the portraits she took the images to show Atget. Abbott missed the sign and made one more flight of stairs to find the concierge.” She asked about Atget and was shocked to hear that he had died. “Youth is little equipped to accept or even anticipate the fact of death. And I had just finished his portraits.” Inquiring about his collection of photographs, she found that they had been left to Andre Calmette. It took months of correspondence and convincing, but she eventually acquired Atget’s entire collection. Abbott also wrote a book about Atget and published many of his prints. Many critics have attacked Atget’s work, saying Atget was merely a disappointed painter or actor, and a little ashamed of his medium. Claims have been made that Atget did not really know what he was doing, that reflections in his shop front windows were accidents which he did not even see. Berenice Abbott fiercely defended Atget and his work. Goethe had said, “there is no variety of Art that should be looked upon lightly. Each has delights which great talent can bring to fulfillment.” If Atget had not had this talent he would have been just another record producer of the travel guide variety – tourist fare. I believe the photographer’s eye develops to a more intense awareness than other people’s, as a dancer develops his muscles and limbs, and a musician his ear. The photographer’s act is to see the outside world precisely, with intelligence as well as sensuous insight. This act of seeing sharpens the eye to an unprecedented acuteness. He often sees swiftly an entire scene that most people would pass unnoticed. Capturing the city of Paris and its people was the photographic art of Atget. How one becomes a photographer, well-schooled or self-taught, does not matter. Ultimately, it is the test of time. As with many of the world’s great photographer’s, their images are timeless and still have the appeal as when first developed. Not only did Atget document a city; he also captured its essence.
Lori Oden. “Eugène Atget,” on the International Photography Hall of Fame and Museum website Nd [Online] Cited 03/10/2023
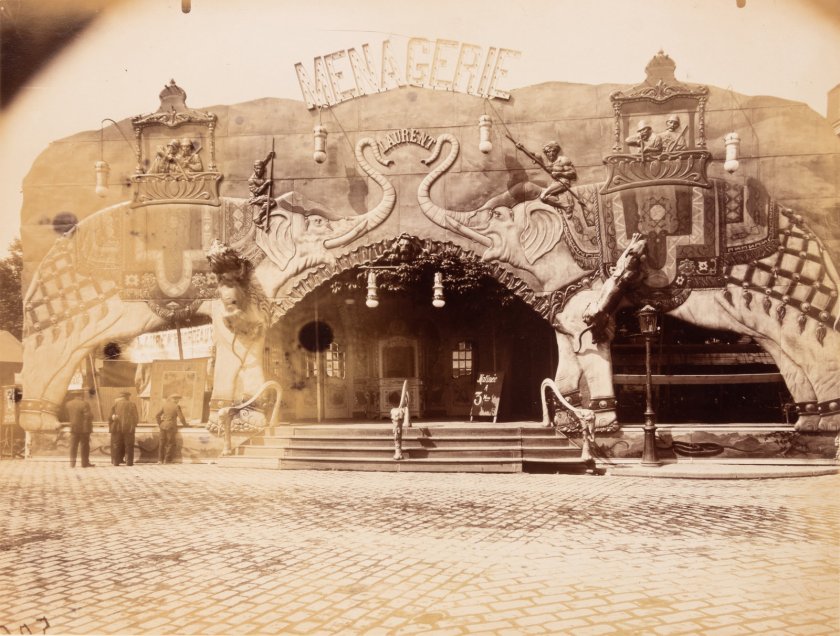
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Plessis Piquet [Entrée pittoresque, Châtillon]
1921
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Porte, avenue de Paris (Versailles)
1922
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Fontaine Jarente, rue Jarente
1922
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Coin, rue Norvins et des Saules (Corner, rue Norvins et des Saules)
1925
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
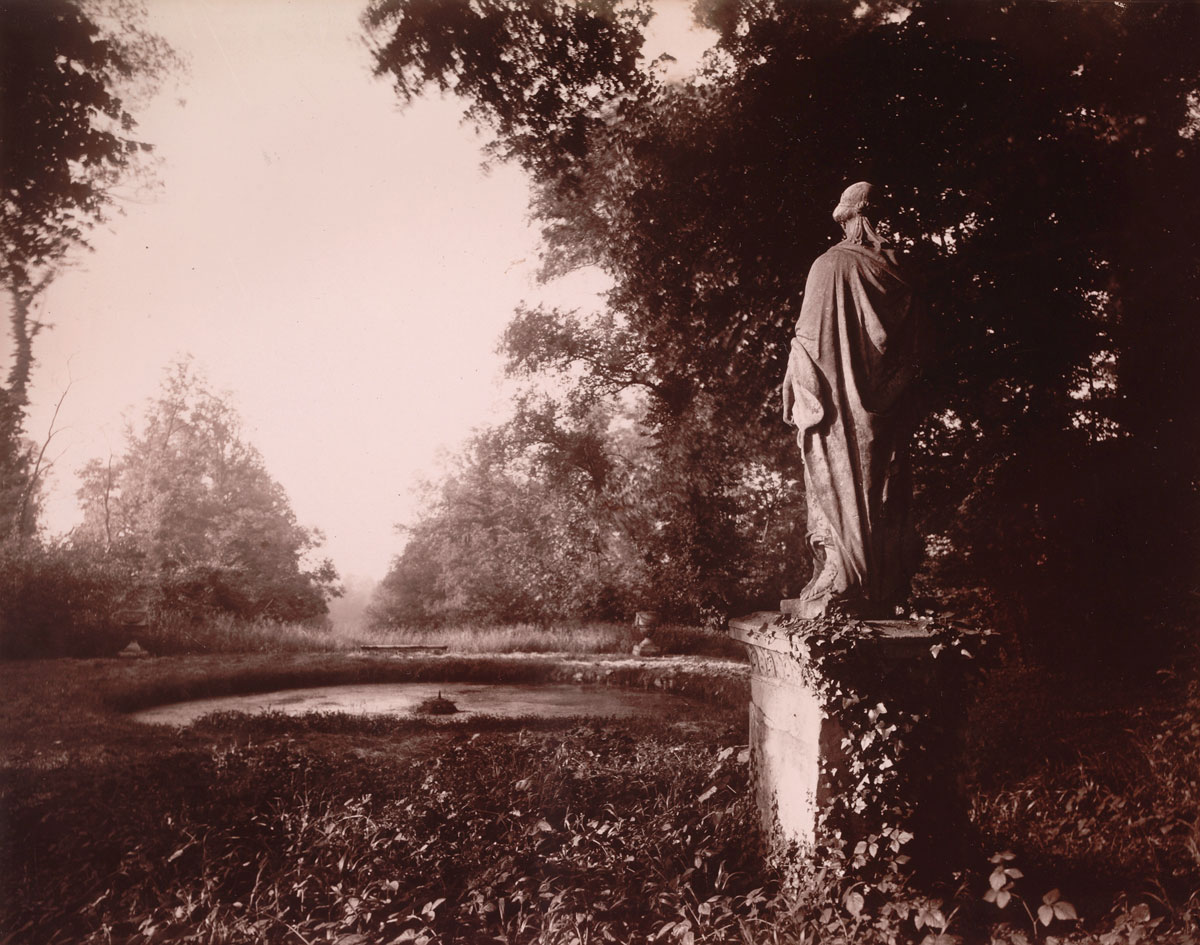
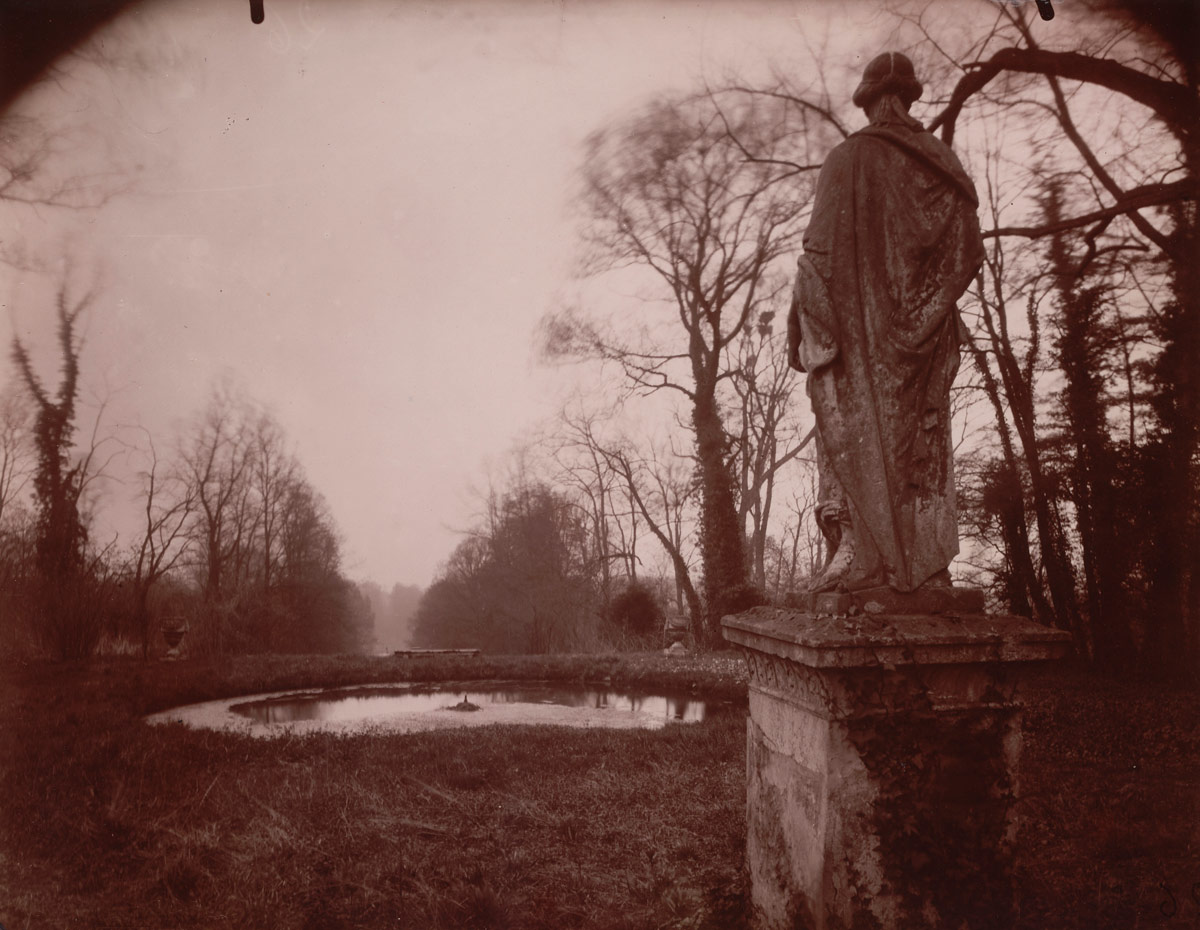
Parc de Sceaux
1925
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Moulin Rouge [86 boulevard de Clichy]
1926
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
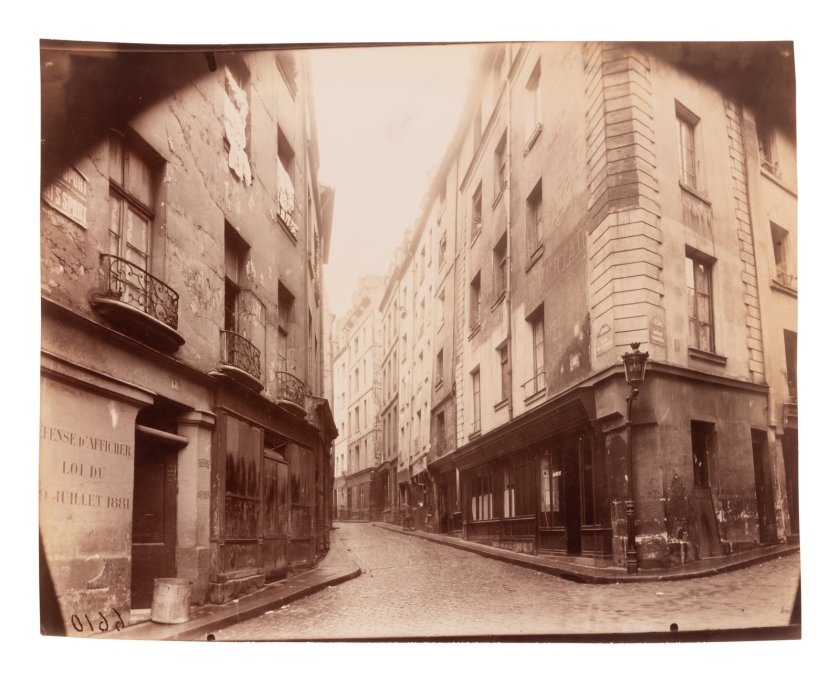
Rue Lanneau
1925
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Passage Moret, ruelle des Gobelins
1926
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
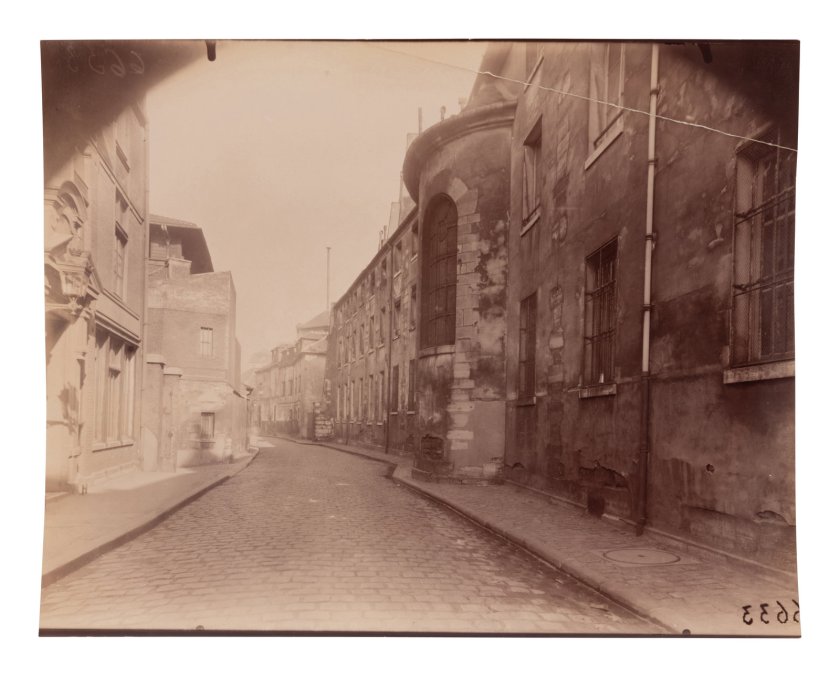
Rue des Gobelins
1926
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Rue des Prêtres Saint-Séverin, au fond rue Boutebrie
1926
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Saint-Médard
1926
Albumen print
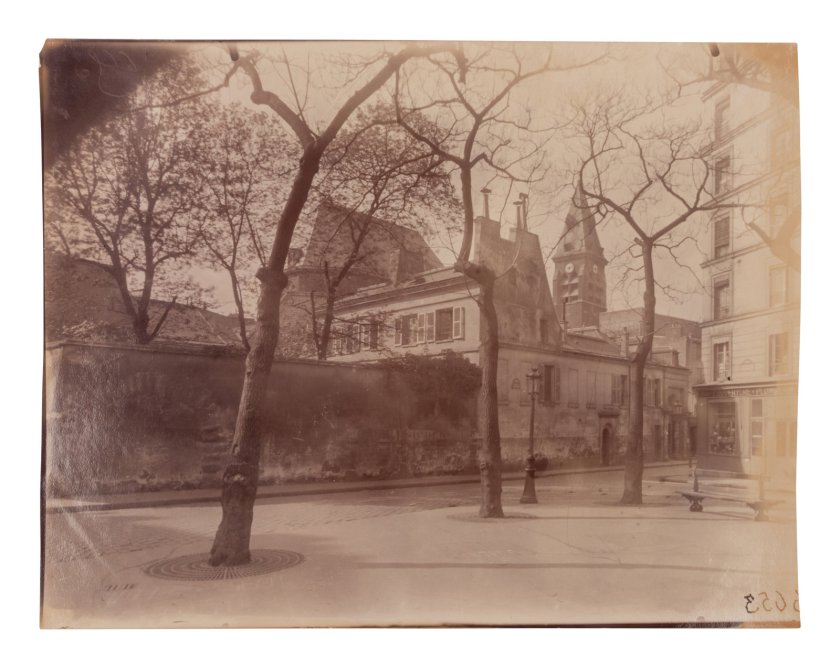
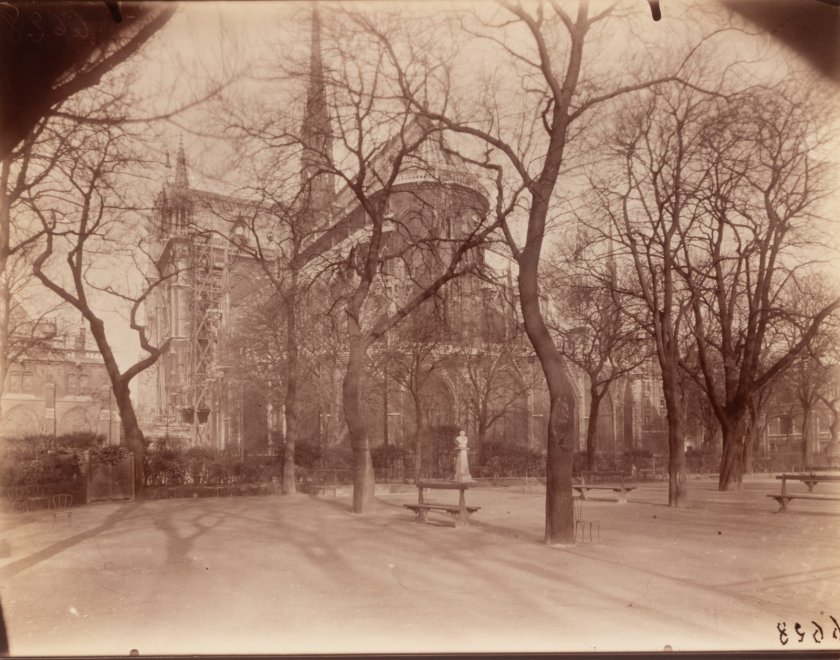
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Square Notre-Dame
1926
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Ruelle des Reculettes, Gobelins
1926
Albumen print
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Saint-Cloud [19h matin, mars 1926]
1926
Albumen print








![Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Cactus [Nice]' before 1900 Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Cactus [Nice]' before 1900](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/atget-cactus-nice-before-1900.jpg?w=840)

















![Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Maison, rue Saint-Romain [Rouen]' 1907 Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Maison, rue Saint-Romain [Rouen]' 1907](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/atget-maison-rue-saint-romain-rouen-1907.jpg?w=650&h=723)






![Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Pommiers [et blés]' 1910 or earlier Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Pommiers [et blés]' 1910 or earlier](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/atget-pommiers-et-bles-1910-or-earlier.jpg?w=650&h=776)
![Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Sapin ([Petit] Trianon)' 1910 or earlier Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Sapin ([Petit] Trianon)' 1910 or earlier](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/atget-sapin-petit-trianon-1910-or-earlier.jpg?w=840)



![Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Balcon, [15] rue du Petit Pont' 1913 Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Balcon, [15] rue du Petit Pont' 1913](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/atget-balcon-15-rue-du-petit-pont-1913.jpg?w=650&h=781)


![Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Plessis Piquet [Entrée pittoresque, Châtillon]' 1921 Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Plessis Piquet [Entrée pittoresque, Châtillon]' 1921](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/atget-plessis-piquet-entree-pittoresque-chatillon-1921.jpg?w=650&h=788)




![Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Moulin Rouge [86 boulevard de Clichy]' 1926 Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Moulin Rouge [86 boulevard de Clichy]' 1926](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/atget-moulin-rouge-86-boulevard-de-clichy-1926.jpg?w=840)







![Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Saint-Cloud [19h matin, mars 1926]' 1926 Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) 'Saint-Cloud [19h matin, mars 1926]' 1926](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/atget-saint-cloud-19h-matin-mars-1926-1926.jpg?w=650&h=787)















You must be logged in to post a comment.